JavaScript Data Types
AJavaScript variable can hold8 types of data.
7 Primitive Data Types and1 Object Data Type.
The Object data type can hold many different object types.
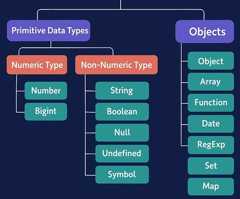
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Number | A number representing a numeric value |
| Bigint | A number representing a large integer |
| String | A text of characters enclosed in quotes |
| Boolean | A data type representing true or false |
| Undefined | A variable with no assigned value |
| Null | A value representing object absence |
| Symbol | A unique primitive identifier |
| Object | A collection of key-value pairs of data |
Examples
let length = 16;
let weight = 7.5;
// BigInt
let x = 1234567890123456789012345n;
let y = BigInt(1234567890123456789012345)
// Strings
let color = "Yellow";
let lastName = "Johnson";
// Boolean
let x = true;
let y = false;
// Undefined
let x;
let y;
// Null
let x = null;
let y = null;
// Symbol
const x = Symbol();
const y = Symbol();
// Object
const person = {firstName:"John", lastName:"Doe"};
// Array Object
const cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"];
// Date Object
const date = new Date("2022-03-25");
The Concept of Data Types
In programming, data types is an important concept.
To be able to operate on variables, it is important to know something about the type.
Without data types, a computer cannot safely solve this:
Does it make any sense to add "Volvo" to sixteen? Will it produce an error or will it produce a result?
JavaScript will treat the example above as:
Note
When adding a number and a string, JavaScript will treat the number as a string.
JavaScript evaluates expressions from left to right. Different sequences can produce different results:
#"tryit.asp?filename=tryjs_datatypes_addstrings_1">Try it Yourself »
#"tryit.asp?filename=tryjs_datatypes_addstrings_2">Try it Yourself »
In the first example, JavaScript treats 16 and 4 as numbers, until it reaches "Volvo".
In the second example, since the first operand is a string, all operands are treated as strings.
JavaScript Types are Dynamic
JavaScript has dynamic types. This means that the same variable can be used to hold different data types:
Example
x = 5; // Now x is a Number
x = "John"; // Now x is a String
Built-In Object Types
A JavaScript object can represent aJavScript object or aUser defined object.
Built-in JavavaScript object types can be:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
| Array | Array of values accessed by a numerical index |
| Map | Array of key-value pairs where the keys can be of any data type |
| Set | Array of values where each value can only appear once |
| WeakMap | A type of Map with weak references to the stored objects. |
| WeakSet | A type of Set with weak references to the stored objects. |
| Math | An object that provides math constants and functions like PI and random() |
| Date | Object for working with dates and times |
| RegExp | Object for working with regular expressions |
| Error | Object represents error conditions during program execution |
| JSON | Object with methods for parsing values between JSON and objects |
| Promise | Object representing the completion or failure of an asynchronous operation |
| Int8Array | Array for storing fixed-size 8-bits integer values |
| Int16Array | Array for storing fixed-size 16-bits integer values |
| Int32Array | Array for storing fixed-size 32-bits integer values |
| Float16Array | Array for storing fixed-size 16-bits floating-point values |
| Float32Array | Array for storing fixed-size 32-bits floating-point values |
| Float64Array | Array for storing fixed-size 64-bits floating-point values |
| BigInt64Array | Array for storing fixed-size 64-bits big integer values |
The typeof Operator
You can use the JavaScripttypeof operator to find the type of a JavaScript variable.
Thetypeof operator returns the type of a variable or an expression:
Example
typeof "John" // Returns "string"
typeof "John Doe" // Returns "string"
Example
typeof 314 // Returns "number"
typeof 3.14 // Returns "number"
typeof (3) // Returns "number"
typeof (3 + 4) // Returns "number"

