
- Python - Home
- Python - Overview
- Python - History
- Python - Features
- Python vs C++
- Python - Hello World Program
- Python - Application Areas
- Python - Interpreter
- Python - Environment Setup
- Python - Virtual Environment
- Python - Basic Syntax
- Python - Variables
- Python - Private Variables
- Python - Data Types
- Python - Type Casting
- Python - Unicode System
- Python - Literals
- Python - Operators
- Python - Arithmetic Operators
- Python - Comparison Operators
- Python - Assignment Operators
- Python - Logical Operators
- Python - Bitwise Operators
- Python - Membership Operators
- Python - Identity Operators
- Python - Walrus Operator
- Python - Operator Precedence
- Python - Comments
- Python - User Input
- Python - Numbers
- Python - Booleans
- Python - Floating Points
- Python - Control Flow
- Python - Decision Making
- Python - If Statement
- Python - If else
- Python - Nested If
- Python - Conditional User Inputs
- Python - Match-Case Statement
- Python - Loops
- Python - for Loops
- Python - for-else Loops
- Python - While Loops
- Python - break Statement
- Python - continue Statement
- Python - pass Statement
- Python - Nested Loops
- Python Functions & Modules
- Python - Functions
- Python - Default Arguments
- Python - Keyword Arguments
- Python - Keyword-Only Arguments
- Python - Positional Arguments
- Python - Positional-Only Arguments
- Python - Arbitrary Arguments
- Python - Variables Scope
- Python - Function Annotations
- Python - Modules
- Python - Packing and Unpacking
- Python - Built in Functions
- Python Strings
- Python - Strings
- Python - Slicing Strings
- Python - Modify Strings
- Python - String Concatenation
- Python - String Formatting
- Python - Escape Characters
- Python - String Methods
- Python - String Exercises
- Python Lists
- Python - Lists
- Python - Access List Items
- Python - Change List Items
- Python - Add List Items
- Python - Remove List Items
- Python - Loop Lists
- Python - List Comprehension
- Python - Sort Lists
- Python - Copy Lists
- Python - Join Lists
- Python - List Methods
- Python - List Exercises
- Python Tuples
- Python - Tuples
- Python - Access Tuple Items
- Python - Update Tuples
- Python - Unpack Tuples
- Python - Loop Tuples
- Python - Join Tuples
- Python - Tuple Methods
- Python - Namedtuple
- Python - Tuple Exercises
- Python Sets
- Python - Sets
- Python - Access Set Items
- Python - Add Set Items
- Python - Remove Set Items
- Python - Loop Sets
- Python - Join Sets
- Python - Copy Sets
- Python - Set Operators
- Python - Set Methods
- Python - Set Exercises
- Python Dictionaries
- Python - Dictionaries
- Python - Access Dictionary Items
- Python - Change Dictionary Items
- Python - Add Dictionary Items
- Python - Remove Dictionary Items
- Python - Dictionary View Objects
- Python - Loop Dictionaries
- Python - Copy Dictionaries
- Python - Nested Dictionaries
- Python - Dictionary Methods
- Python - Dictionary Exercises
- Python Arrays
- Python - Arrays
- Python - Access Array Items
- Python - Add Array Items
- Python - Remove Array Items
- Python - Loop Arrays
- Python - Copy Arrays
- Python - Reverse Arrays
- Python - Sort Arrays
- Python - Join Arrays
- Python - Array Methods
- Python - Array Exercises
- Python File Handling
- Python - File Handling
- Python - Write to File
- Python - Read Files
- Python - Renaming and Deleting Files
- Python - Directories
- Python - File Methods
- Python - OS File/Directory Methods
- Python - OS Path Methods
- Object Oriented Programming
- Python - OOPs Concepts
- Python - Classes & Objects
- Python - Class Attributes
- Python - Class Methods
- Python - Static Methods
- Python - Constructors
- Python - Access Modifiers
- Python - Inheritance
- Python - Multiple Inheritance
- Python - Multilevel Inheritance
- Python - Polymorphism
- Python - Method Overriding
- Python - Method Overloading
- Python - Dynamic Binding
- Python - Dynamic Typing
- Python - Abstraction
- Python - Encapsulation
- Python - Interfaces
- Python - Packages
- Python - Inner Classes
- Python - Anonymous Class and Objects
- Python - Singleton Class
- Python - Wrapper Classes
- Python - Enums
- Python - Reflection
- Python - Data Classes
- Python Errors & Exceptions
- Python - Syntax Errors
- Python - Exceptions
- Python - try-except Block
- Python - try-finally Block
- Python - Raising Exceptions
- Python - Exception Chaining
- Python - Nested try Block
- Python - User-defined Exception
- Python - Logging
- Python - Assertions
- Python - Warnings
- Python - Built-in Exceptions
- Python - Debugger (PDB)
- Python Multithreading
- Python - Multithreading
- Python - Thread Life Cycle
- Python - Creating a Thread
- Python - Starting a Thread
- Python - Joining Threads
- Python - Naming Thread
- Python - Thread Scheduling
- Python - Thread Pools
- Python - Main Thread
- Python - Thread Priority
- Python - Daemon Threads
- Python - Synchronizing Threads
- Python Synchronization
- Python - Inter-thread Communication
- Python - Thread Deadlock
- Python - Interrupting a Thread
- Python Networking
- Python - Networking
- Python - Socket Programming
- Python - URL Processing
- Python - Generics
- Python Libraries
- NumPy Tutorial
- Pandas Tutorial
- SciPy Tutorial
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- Django Tutorial
- OpenCV Tutorial
- Python Miscellenous
- Python - Date & Time
- Python - Maths
- Python - Iterators
- Python - Generators
- Python - Generator Expressions
- Python - Lambda Expressions
- Python - Closures
- Python - Decorators
- Python - Recursion
- Python - Reg Expressions
- Python - PIP
- Python - Database Access
- Python - Weak References
- Python - Serialization
- Python - Templating
- Python - Output Formatting
- Python - Performance Measurement
- Python - Data Compression
- Python - CGI Programming
- Python - XML Processing
- Python - GUI Programming
- Python - Command-Line Arguments
- Python - Docstrings
- Python - JSON
- Python - Sending Email
- Python - Further Extensions
- Python - Tools/Utilities
- Python - Odds and Ends
- Python - GUIs
- Python Advanced Concepts
- Python - Abstract Base Classes
- Python - Custom Exceptions
- Python - Higher Order Functions
- Python - Object Internals
- Python - Memory Management
- Python - Metaclasses
- Python - Metaprogramming with Metaclasses
- Python - Mocking and Stubbing
- Python - Monkey Patching
- Python - Signal Handling
- Python - Type Hints
- Python - Automation Tutorial
- Python - Humanize Package
- Python - Context Managers
- Python - Coroutines
- Python - Descriptors
- Python - Diagnosing and Fixing Memory Leaks
- Python - Immutable Data Structures
- Python - Domain Specific Language (DSL)
- Python - Data Model
- Python Useful Resources
- Python - Questions & Answers
- Python - Interview Questions & Answers
- Python - Online Quiz
- Python - Quick Guide
- Python - Reference
- Python - Cheatsheet
- Python - Projects
- Python - Useful Resources
- Python - Discussion
- Python Compiler
- NumPy Compiler
- Matplotlib Compiler
- SciPy Compiler
Python for-else Loops
Python - For Else Loop
Python supports an optionalelse block to be associated with afor loop. If aelse block is used with afor loop, it is executed only when the for loop terminates normally.
The for loop terminates normally when it completes all its iterations without encountering abreak statement, which allows us to exit the loop when a certain condition is met.
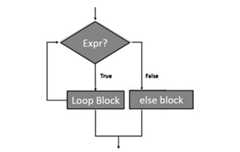
Flowchart of For Else Loop
The following flowchart illustrates use offor-else loop −
Syntax of For Else Loop
Following is the syntax of for loop with optional else block −
for variable_name in iterable: #stmts in the loop . . .else: #stmts in else clause . .
Example of For Else Loop
The following example illustrates the combination of an else statement with a for statement inPython. Till the count is less than 5, the iteration count is printed. As it becomes 5, the print statement in else block is executed, before the control is passed to the next statement in the main program.
for count in range(6): print ("Iteration no. {}".format(count))else: print ("for loop over. Now in else block")print ("End of for loop")On executing, this code will produce the followingoutput −
Iteration no. 1Iteration no. 2Iteration no. 3Iteration no. 4Iteration no. 5for loop over. Now in else blockEnd of for loop
For-Else Construct without break statement
As mentioned earlier in this tutorial, the else block executes only when the loop terminates normally i.e. without using break statement.
Example
In the following program, we use the for-else loop without break statement.
for i in ['T','P']: print(i)else: # Loop else statement # there is no break statement in for loop, hence else part gets executed directly print("ForLoop-else statement successfully executed")On executing, the above program will generate the following output
TPForLoop-else statement successfully executed
For-Else Construct with break statement
In case of forceful termination (by using break statement) of the loop, else statement is overlooked by the interpreter and hence its execution is skipped.
Example
The following program shows how else conditions work in case of a break statement.
for i in ['T','P']: print(i) breakelse: # Loop else statement # terminated after 1st iteration due to break statement in for loop print("Loop-else statement successfully executed")On executing, the above program will generate the following output
T
For-Else with break statement and if conditions
If we usefor-else construct withbreak statement andif condition, thefor loop will iterate over the iterators and within this loop, you can use anif block to check for a specific condition. If the loop completes without encountering abreak statement, the code in the else block is executed.
Example
The following program shows how else conditions works in case of break statement andconditional statements.
# creating a function to check whether the list item is a positive# or a negative numberdef positive_or_negative(): # traversing in a list for i in [5,6,7]: # checking whether the list element is greater than 0 if i>=0: # printing positive number if it is greater than or equal to 0 print ("Positive number") else: # Else printing Negative number and breaking the loop print ("Negative number") break # Else statement of the for loop else: # Statement inside the else block print ("Loop-else Executed")# Calling the above-created functionpositive_or_negative()On executing, the above program will generate the following output
Positive numberPositive numberPositive numberLoop-else Executed