NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Entrez Sequences Help [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-.

Entrez Sequences Help [Internet].
Show detailsEntrez Sequences Quick Start
Peter Cooper,Melissa Landrum,Ilene Mizrachi, andJane Weisemann.
Author Information and AffiliationsCreated:June 29, 2010; Last Update:July 5, 2024.
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
This is a quick start guide for the Entrez Protein, and Nucleotide databases. The instructions here should allow you to quickly begin searching and using the features of the Entrez sequence databases.
•How do I use a simple query, such as a word or a phrase?
•How can I make my search more specific with Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT)?
•How can I change the format, number, or sorting order of records displayed?
•How do I download sequence records to a file on my computer?
•How can I change the information that is shown such as optional biological features or sequence?
•How do I analyze the sequence data directly or find additional related data?
•How can I search for a sub-sequence, or pattern in a protein or nucleotide sequence?
•How can I locate and highlight a biological feature in a protein or nucleotide sequence?
How do I use a simple query, such as a word or a phrase?
You can use a protein name, gene name, or gene symbol directly. Searching with a submitter or author name in the following format will produce the best results.
Smith JR (last name followed by initials, no punctuation)
Database identifiers such as accession numbers or gi numbers will directly retrieve the full sequence record.
CAA79696
NP_778203
263191547
BC043443
NM_002020
To find a match to an exact phrase, enclose it in quotation marks.
"contactin associated protein"
"duchenne muscular dystrophy"
How can I make my search more specific with Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT)?
Use the Boolean operator AND to find records that contain every one of your search terms, the intersection of search results.
contactin AND neurofascinProteinNucleotide
Use the Boolean operator OR to find records that include one of several search terms, the union of search results.
contactin OR neurofascinProteinNucleotide
Use the Boolean operator NOT to exclude records matching a search term
contactin NOT neurofascinProteinNucleotide
How do I restrict my search to specific subsets of records such as those from a specific organism, molecule type or source database?
You can use theFacets on the left-hand side of the page to show only certain kinds of records. Follow these links to jump to the Facet of interest:organism,molecule type,source database.
Facets
Use the facets on the left-hand side of any of the Protein, Nucleotide results pages to restrict the types of records shown.
Organism
To get records from a specific organism or group of organisms click the appropriate Species filter. You can use the Customize option to add a filter for a particular organism or group or organisms. You use the common or scientific name of a species, strain, or higher taxon as a Filter term. Examples: human,Mus musculus,Drosophila similis, green plants, bacteria.





You can also use the linked numbers in the Top Organisms list in the right-hand column of search results to filter select records from specific organisms from your results.

Molecule type
In the Nucleotide database you can use the Molecule types facet to limit results to a particular molecule type.

Source database
The Source databases facet allows you to limit to results from a particular database.

The source databases for NCBI nucleotide and protein sequences are listed below.
•Protein: SwissProt andPIR components ofUniProt; Protein Research Foundation (PRF); protein chain sequences from the Protein Data Bank (PDB); and translations of coding regions on sequences in EntrezNucleotide (RefSeq,International Sequence Database Collaboration –DDBJ /ENA-EMBL /GenBank, Third Party Annotation (TPA).
•Nucleotide:International Sequence Database Collaboration (DDBJ /ENA-EMBL /GenBank); NCBI Reference Sequences (RefSeq); Nucleotide sequences fromPDB; Third Party Annotation (TPA).
How do I change the format, number, or sorting order of records displayed?
The menus at the upper left of the results page headed bySummary,20 per page andSort by Default Order allow you to change the format displayed, the number of records and the sorting order respectively. Click any of these and select the desired format, items per page, or sorting order from the listed radio buttons. The new settings will apply automatically.

How can I download sequence records to a file on my computer?
Click theSend to menu that appears at the upper right of document summaries or record views and select the file radio button. Then choose the desired format from the pull-down list. Click theCreate File button to save the records.

How do I change the information that is shown such as optional biological features or sequence?
Open theCustomize View dialog that appears in the right-hand column of a record display. You can change the kinds of biological features shown and toggle the sequence on or off using the radio buttons and check boxes. Click theUpdate View button to activate the changes.


How can I display a portion of the sequence?
Open theChange region shown dialog that appears in the right-hand column of a record display. You can change the kinds of biological features shown and toggle the sequence on or off using the radio buttons and check boxes. Click theUpdate View button to activate the changes.

How do I analyze the sequence data directly or find additional related data?
There are direct links to analysis tools including BLAST, Primer-BLAST (Nucleotide), and Conserved Domain Database Search (Protein) in the right-hand column of displayed records.

There are also links to related data in the right-hand column that may provide additional information and pre-computed analyses for the displayed records.
How can I search for a sub-sequence, or pattern in a protein or nucleotide sequence?
You can access theFind-in-sequence feature in the Analysis tools in the right-hand column of single and multiple-record displays. This tool can find sub-sequences or patterns in displayed nucleotide or protein sequences. Clicking theFind-in-this-Sequence orFind-in-these sequences link opens a search box bar at the bottom of the page.
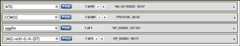
Find-in-sequence works with single and multiple sequence displays with any format that shows the sequence (GenBank, GenPept, FASTA). The tool can find sub-sequences and patterns typed in the box and works with standard (IUPAC) nucleotide and protein single letter and ambiguity codes as well asProsite patterns that match motifs and domain signatures in protein sequences. Valid single letter codes are given below.
| Nucleotide Codes | |||
| A | adenosine | Y | T or C |
| C | cytidine | M | A or C |
| G | guanine | W | A or T |
| T | thymidine | R | G or A |
| N | A, G, C, or T | B | G, T, or C |
| U | uridine (matches T) | D | G, A, or T |
| K | G or T | H | A, C, or T |
| S | G or C | V | G, C, or A |
| Amino Acid Codes | |||
| A | alanine | N | asparagine |
| B | aspartate/asparagine | P | proline |
| C | cysteine | Q | glutamine |
| D | aspartate | R | arginine |
| E | glutamate | S | serine |
| F | phenylalanine | T | threonine |
| G | glycine | V | valine |
| H | histidine | W | tryptophan |
| I | isoleucine | Y | tyrosine |
| K | lysine | Z | glutamate/glutamine |
| L | leucine | X | any |
| M | methionine | ||
Find matches by clicking the find button. The first 500 matches are highlighted for each displayed sequence. The first or current match is highlighted in white text on a dark background in the sequence, and its position is shown in the search bar. The other matches are highlighted with a light blue background. The tool ignores spaces and line breaks in the formatted sequence. Clicking the arrow keys jumps to the next or previous match.
How can I locate and highlight a biological feature in a protein or nucleotide sequence?
You can highlight a feature by clicking on linked feature in the FEATURES table of a displayed nucleotide or protein sequence. A portion of a FEATURES table is shown below for a nucleotide sequence (NG_008957).

Clicking the feature activates the feature search bar that appears at the bottom of the display and highlights the corresponding residues in the display as shown below for an exon feature in the RefSeq gene record for the MAOA gene (NG_008957).

The “Details” box that shows the annotation from the FEATURES table for the highlighted location can be collapsed if desired by clicking the link. Clicking the “Details” link again re-opens the box.
Discontigous features that have multiple segments such as mRNA alignments on genomic DNA can also be highlighted. In all cases the number of segments is shown at the right of the sequence accession. Opposite strand features are indicated with the notation “minus strand” to the right of the number of segments of the bar. The image below shows mRNA minus strand feature for the PON2 gene from an annotated BAC clone sequence (AC005021).

Navigating Using the Feature Highlight Bar
If there is more than one feature of the same type, as in the first example shown above, the navigational arrows on the bar allow jumping to the next, previous, first, and last instances of that feature. The Feature pull-down list at the right-hand side of the bar allows selecting other available feature types. The highlight moves to the next available instance of the selected feature type. The “Feature” link returns the display to the corresponding position in the FEATURES table of the record.
Displaying Highlighted Regions as Separate Sequences
The FASTA and GenBank links on the right-hand side of the bar present the highlighted sub-sequence in the these formats in the Nucleotide or Protein Entrez system and provide a simple means to display and download the corresponding sequence or to forward it to the analysis available analysis tools: BLAST, Primer-BLAST, Find in this Sequence, and Identify Conserved Domains (protein only).
- PubReader
- Print View
- Cite this PageCooper P, Landrum M, Mizrachi I, et al. Entrez Sequences Quick Start. 2010 Jun 29 [Updated 2024 Jul 5]. In: Entrez Sequences Help [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-.
- PDF version of this page (1.0M)
- PDF version of this title (2.0M)
- How do I use a simple query, such as a word or a phrase?
- How can I make my search more specific with Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT)?
- How do I restrict my search to specific subsets of records such as those from a specific organism, molecule type or source database?
- How do I analyze the sequence data directly or find additional related data?
- How can I search for a sub-sequence, or pattern in a protein or nucleotide sequence?
- How can I locate and highlight a biological feature in a protein or nucleotide sequence?
- Entrez Sequences Quick Start - Entrez Sequences HelpEntrez Sequences Quick Start - Entrez Sequences Help
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...