Interstitial lung diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by theinflammationInflammationInflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function.Inflammation andfibrosisFibrosisAny pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury.Bronchiolitis Obliterans of lung parenchyma, especially the pulmonaryconnective tissueConnective tissueConnective tissues originate from embryonic mesenchyme and are present throughout the body except inside the brain and spinal cord. The main function of connective tissues is to provide structural support to organs. Connective tissues consist of cells and an extracellular matrix.Connective Tissue: Histology in the alveolar walls. It may beidiopathicIdiopathicDermatomyositis (e.g.,idiopathicIdiopathicDermatomyositis pulmonaryfibrosisFibrosisAny pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury.Bronchiolitis Obliterans) or secondary toconnective tissueConnective tissueConnective tissues originate from embryonic mesenchyme and are present throughout the body except inside the brain and spinal cord. The main function of connective tissues is to provide structural support to organs. Connective tissues consist of cells and an extracellular matrix.Connective Tissue: Histology diseases, medications, malignancies, occupational exposure, or allergens. Interstitial lung diseases commonly present with progressive exertionaldyspneaDyspneaDyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary).Dyspnea anddry coughDry CoughStrongyloidiasis.Pulmonary function testingPulmonary Function TestingPulmonary Function Tests shows a restrictive lung disease pattern. Lung high-resolution computed tomography andbiopsyBiopsyRemoval and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body.Ewing Sarcoma usually establish the diagnosis. Treatment includessteroidsSteroidsA group of polycyclic compounds closely related biochemically to terpenes. They include cholesterol, numerous hormones, precursors of certain vitamins, bile acids, alcohols (sterols), and certain natural drugs and poisons. Steroids have a common nucleus, a fused, reduced 17-carbon atom ring system, cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene. Most steroids also have two methyl groups and an aliphatic side-chain attached to the nucleus.Benign Liver Tumors and immunosuppressives.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
IdiopathicIdiopathicDermatomyositis pulmonaryfibrosisFibrosisAny pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury.Bronchiolitis Obliterans,sarcoidosisSarcoidosisSarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease that causes noncaseating granulomas. The exact etiology is unknown. Sarcoidosis usually affects the lungs and thoracic lymph nodes, but it can also affect almost every system in the body, including the skin, heart, and eyes, most commonly.Sarcoidosis, and ILD associated withconnective tissueConnective tissueConnective tissues originate from embryonic mesenchyme and are present throughout the body except inside the brain and spinal cord. The main function of connective tissues is to provide structural support to organs. Connective tissues consist of cells and an extracellular matrix.Connective Tissue: Histology diseases are the most common types of ILD.
It is useful to categorize ILDs into those with and without a known cause.
| Cause unknown | Cause known |
|---|---|
IdiopathicIdiopathicDermatomyositis interstitial pneumonias (IIP):
| Systemic diseases
|
| Age |
|
|---|---|
| SexSexThe totality of characteristics of reproductive structure, functions, phenotype, and genotype, differentiating the male from the female organism.Gender Dysphoria |
|
| Clinical presentation |
|
| Symptoms |
|
| Past medical historyPast Medical HistoryAdult Health Maintenance |
|
| Drug history | MethotrexateMethotrexateAn antineoplastic antimetabolite with immunosuppressant properties. It is an inhibitor of tetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase and prevents the formation of tetrahydrofolate, necessary for synthesis of thymidylate, an essential component of DNA.Antimetabolite Chemotherapy,azathioprineAzathioprineAn immunosuppressive agent used in combination with cyclophosphamide and hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. According to the fourth annual report on carcinogens, this substance has been listed as a known carcinogen.Immunosuppressants,rituximabRituximabA murine-derived monoclonal antibody and antineoplastic agent that binds specifically to the cd20 antigen and is used in the treatment of leukemia; lymphoma and rheumatoid arthritis.Immunosuppressants, tumor-necrosis factor blockers,amiodaroneAmiodaroneAn antianginal and class III antiarrhythmic drug. It increases the duration of ventricular and atrial muscle action by inhibiting potassium channels and voltage-gated sodium channels. There is a resulting decrease in heart rate and in vascular resistance.Pulmonary Fibrosis, nitrofurantoin, chemotherapeutics |
| Family historyFamily HistoryAdult Health Maintenance | Having a close relative with IIP is a strong risk factor for ILD, especially IPF. |
| Social historySocial HistoryAdult Health Maintenance |
|
Autoantibody detection may help with the diagnosis of some CTDs.
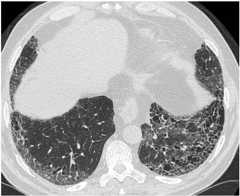
Typical HRCT pattern of UIP. The image shows subpleural and basal predominance of reticular opacities associated with traction bronchiectasis and honeycomb change (clustered cystic airspaces with well-defined thick walls and diameter of 0.3–1.0 cm)
Image: “(HRCT) pattern” by Interstitial Lung Disease Unit, Royal Brompton and Harefield NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK. License:CC BY 4.0
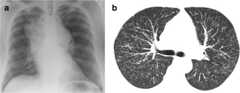
Posterior-anterior chest radiograph of a 67-year-old man with progressive dyspnea revealing bilateral reticular infiltrates with lower lobe predominance
Image: “PA chest radiograph of a 67-year old man” by Department of Medicine, Division of Pulmonary, Allergy and Critical Care, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27710, USA. License:CC BY 2.0
Photomicrograph of biopsy from a 63-year-old man with a multi-disciplinary diagnosis of IPF. The patient shows the typical histopathological features of usual interstitial pneumonia characterized by spatial heterogeneity with areas of subpleural and paraseptal fibrosis and honeycombing changes (cystic airspaces lined by bronchiolar epithelium) alternating with areas of relatively spared lung parenchyma, temporal heterogeneity with admixed areas of active fibrosis with fibroblast foci, extracellular matrix deposition (mainly collagen), and relatively mild or absence of inflammatory cell infiltrate together with regions of histologically normal lung tissue.
Image: “Photomicrograph of biopsy from a 63-year-old man with a multi-disciplinary diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis” by Interstitial Lung Disease Unit, Royal Brompton and Harefield NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK. License:CC BY 4.0
Drug-induced lung disease with am NSIP pattern. The patient has undergone chemotherapy for bladder cancer. Chest CT at the level of the right pulmonary artery at lung window. Diffuse bilateral peripheral reticular pattern, ground glass, and some consolidation.
Image: “Drug-induced lung disease” by Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Marien Hospital, Academic Teaching Hospital, Rochusstr. 2, D- 40479, Düsseldorf, Germany. License:CC BY 4.0
Non-specific interstitial pneumonia. A mesh-like fibrosis of the alveolar septa is seen. Fibroblastic foci are not found. Aggregates of lymphocytes are sometimes found (HE, original magnification 40x).
Image: “Non specific interstitial pneumonia” by Institute of Pathology and Neuropathology, University Hospital Essen, University of Duisburg-Essen, Hufelandstrasse 55, Essen 45147, Germany. License:CC BY 2.0
A 59-year-old woman with a history of left breast cancer and radical mastectomy. The patient was diagnosed with radiotherapy- induced cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (formerly known as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia). Computed tomography shows patchy areas in the left lung and in the middle lobe of the right lung.
Image: “Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia” by Dept of Pulmonary Diseases, Sint Franciscus Gasthuis, Rotterdam, The Netherlands. License:CC BY 2.0
Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia: In alveolar ducts and bronchioles, buds of granulation tissue are detected (HE, original magnification 100x).
Image: “Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia” by Institute of Pathology and Neuropathology, University Hospital Essen, University of Duisburg-Essen, Hufelandstrasse 55, Essen 45147, Germany. License:CC BY 2.0| IPF | SystemicsclerosisSclerosisA pathological process consisting of hardening or fibrosis of an anatomical structure, often a vessel or a nerve.Wilms Tumor–associated ILD | SarcoidosisSarcoidosisSarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease that causes noncaseating granulomas. The exact etiology is unknown. Sarcoidosis usually affects the lungs and thoracic lymph nodes, but it can also affect almost every system in the body, including the skin, heart, and eyes, most commonly.Sarcoidosis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Older adult with gradualshortness of breathShortness of breathDyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary).Dyspnea anddry coughDry CoughStrongyloidiasis | Gradualshortness of breathShortness of breathDyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary).Dyspnea anddry coughDry CoughStrongyloidiasis,fatigueFatigueThe state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli.Fibromyalgia,skinSkinThe skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue.Skin: Structure and Functions tightening, Raynaud’s phenomenon, reflux,dysphagiaDysphagiaDysphagia is the subjective sensation of difficulty swallowing. Symptoms can range from a complete inability to swallow, to the sensation of solids or liquids becoming “stuck.” Dysphagia is classified as either oropharyngeal or esophageal, with esophageal dysphagia having 2 sub-types: functional and mechanical.Dysphagia | Asymptomatic or with gradualshortness of breathShortness of breathDyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary).Dyspnea and cough,fatigueFatigueThe state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli.Fibromyalgia,palpitationsPalpitationsEbstein’s Anomaly, jointpainPainAn unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons.Pain: Types and Pathways, eye andskinSkinThe skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue.Skin: Structure and Functions involvement |
| Signs | Crackles at lungbasesBasesUsually a hydroxide of lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium or cesium, but also the carbonates of these metals, ammonia, and the amines.Acid-Base Balance and digitalclubbingClubbingCardiovascular Examination | Crackles,skinSkinThe skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue.Skin: Structure and Functions thickening and jointswellingSwellingInflammation,telangiectasiasTelangiectasiasAtaxia-telangiectasia | None or crackles,skinSkinThe skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue.Skin: Structure and Functions findings, jointswellingSwellingInflammation,lymphadenopathyLymphadenopathyLymphadenopathy is lymph node enlargement (> 1 cm) and is benign and self-limited in most patients. Etiologies include malignancy, infection, and autoimmune disorders, as well as iatrogenic causes such as the use of certain medications. Generalized lymphadenopathy often indicates underlying systemic disease.Lymphadenopathy |
| Exposures | Tobacco smoke | Mostly unknown | Mostly unknown |
| HRCTHRCTPulmonary Function Tests |
| UIP or NSIP pattern, dilatedesophagusEsophagusThe esophagus is a muscular tube-shaped organ of around 25 centimeters in length that connects the pharynx to the stomach. The organ extends from approximately the 6th cervical vertebra to the 11th thoracic vertebra and can be divided grossly into 3 parts: the cervical part, the thoracic part, and the abdominal part.Esophagus: Anatomy, pulmonary vascular dilation | Mediastinal/hilarlymphadenopathyLymphadenopathyLymphadenopathy is lymph node enlargement (> 1 cm) and is benign and self-limited in most patients. Etiologies include malignancy, infection, and autoimmune disorders, as well as iatrogenic causes such as the use of certain medications. Generalized lymphadenopathy often indicates underlying systemic disease.Lymphadenopathy, reticulonodular peribronchiovascular involvement |
| Histopathology | UIP pattern (fibroblastic foci, honeycombing, spatial heterogeneity) | NSIP pattern with occasional UIP features | Non-caseating granuloma |
| Clinical course | 3–5 year survival: 50% | 10-year survival: 70%–80% | Overall good survival |

Computed tomography scans in a patient with systemic sclerosis:
(A) Interstitial lung disease was observed in lower lobes in a 47-year-old patient.
(B) Squamous cell lung cancer occurred in the area of interstitial lung disease in a 50-year-old patient.
Patient with sarcoidosis: (a). Chest radiograph showing massive hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy; (b) thoracic CT scan showing diffuse nodular infiltration of the lung interstitium. Neither of these patients complained of cough.
Image: “Chest radiograph” by College of Medicine, Swansea University, Swansea, Wales, UK. License:CC BY 2.0USMLE™ is a joint program of the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB®) and National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME®). MCAT is a registered trademark of the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). NCLEX®, NCLEX-RN®, and NCLEX-PN® are registered trademarks of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc (NCSBN®). None of the trademark holders are endorsed by nor affiliated with Lecturio.
Sign up now and get free access to Lecturio with concept pages, medical videos, and questions for your medical education.
Best Week. Best Price. Best Prep! 💸 Get 40% off all plans and certificates now >>
Lecturio Premium gives you full access to all content & features
Verify your email now to get a free trial.
Lecturio Premium gives you full access to all contents and features—including Lecturio’s Qbank with up-to-date board-style questions.