Using the Evam SDK¶
The Evam SDK is offered as a NPM package@evam-life/sdk, it contains:
A set of APIs to interact with the Evam platform inEvamApi, including getting the currently active case, and application settings.
A set of UI components that help you kickstart your development and make it easier to follow the EvamDesign guidelines, including a App bar component.
Install the SDK¶
Note
This is not necessary if you use the Evam React template, seeGetting started.
To install the Evam SDK, add it topackage.json dependencies:
{ // ... "@evam-life/sdk": "~2.10.0" // Note: Make sure to check the SDK release notes for an up-to-date version // ...}and runnpmi.
SDK versioning¶
Evam adheres toSemantic versioning.
Setup your app metadata¶
Some metadata about your application should be set such as its ID within the Evam platform, its name, logo, settings, etc.
All of this can be set in the Evam manifest located underpublic/evam.json, here is an example content:
{"applicationId":"com.example.application","applicationName":"Demo application","settings":[{"id":"debug","name":"Debug mode","description":"Enable debug mode by displaying logs on screen","value":{"type":"bool","default":false}}],"logo":"logo.png","apiVersion":{"target":"2","minimum":"2"},"permissions":["ACTIVE_OPERATION_READ","DISPLAY_MODE_READ"],"version":"0.0.1","versionCode":1}
Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Unique ID of your application. |
| Application name as it will appear to the end user. |
| Array of entries describing the available settings for this application. The value of those settings will be typically set by the end user to tune their experience. The settings format that will be made available to the application during runtime will be a direct mapping |
| Path to the application logo as it will appear in the bottom bar. The path is relative to the root of the built package. |
| Reserved for future extension. |
| List of permissions required for the application to run. Refer to each function’s documentation to know the required permissions. This is not required in development environment (i.e. in a web browser), as all permissions are granted by default in this case. |
| The app version. |
| A positive integer used as an internal version number. This number helps determine whether one version is more recent than another, with higher numbers indicating more recent versions. |
Use the built-in UI components¶
Currently an App bar component is available, alongside its associated widgets.
App bar component¶
The base App bar component is an efficient framework to start your application without having to setup a navigation system from scratch.
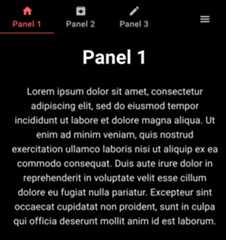
Here is the code associated to the visuals above:
functionApp(){// Define colorsconstAPP_COLORS={day:{black0:"#000000",black0_5:"#17181B",black1:"#202124",black2:"#282A2D",black3:"#2E3134",black4:"#3C4043",orange_primary:"#FF5F5E",orange_secondary:"#FF7B52",orange_tertiary:"#FFBCA9",blue1:"#0857C3",blue2:"#5C88DA",red1:"#E10600"},night:{black0:"#000000",black0_5:"#0E1013",black1:"#17181B",black2:"#202124",black3:"#282A2D",black4:"#2E3134",orange_primary:"#FF5F5E",orange_secondary:"#FF7B52",orange_tertiary:"#FFBCA9",blue1:"#0857C3",blue2:"#5C88DA",red1:"#E10600"}}// Define themeconsttheme=createTheme({transitions:{duration:{shortest:150,shorter:200,short:250,// most basic recommended timingstandard:300,// this is to be used in complex animationscomplex:375,// recommended when something is entering screenenteringScreen:225,// recommended when something is leaving screenleavingScreen:195,},},palette:{background:{default:palette.black0,paper:palette.black4},text:{primary:"#FFFFFF",secondary:"#BBBBBB",disabled:"#999999"},primary:{main:palette.orange_primary,},secondary:{main:palette.orange_secondary,},},components:{MuiButtonBase:{defaultProps:{disableRipple:false,centerRipple:true,}}},typography:{body1:{fontSize:"28px"},h4:{marginBottom:"12px"},h2:{marginBottom:"20px"},h1:{marginBottom:"28px"}},})return(<divclassName="App"><Router><ThemeProvidertheme={theme}><CssBaseline/><EvamAppBarLayouttabs={<EvamTabs><EvamTablabel={"Panel 1"}index={0}icon={<HomefontSize={"large"}/>}/><EvamTablabel={"Panel 2"}index={1}icon={<ArchiveIconfontSize={"large"}/>}/><EvamTablabel={"Panel 3"}index={2}icon={<EditIconfontSize={"large"}/>}/></EvamTabs>}>// Note: for clarity, this content will put in a separate// React Fragment named "MainView" after this example<BoxpaddingLeft={1}paddingRight={1}><EvamTabPanelindex={0}><h1>Panel1</h1><p>Loremipsumdolorsitamet,consecteturadipiscingelit,seddoeiusmodtemporincididuntutlaboreetdoloremagnaaliqua.Utenimadminimveniam,quisnostrudexercitationullamcolaborisnisiutaliquipexeacommodoconsequat.Duisauteiruredolorinreprehenderitinvoluptatevelitessecillumdoloreeufugiatnullapariatur.Excepteursintoccaecatcupidatatnonproident,suntinculpaquiofficiadeseruntmollitanimidestlaborum.</p></EvamTabPanel><EvamTabPanelindex={1}><h1>Panel2</h1><p>Sedutperspiciatisundeomnisistenatuserrorsitvoluptatemaccusantiumdoloremquelaudantium,totamremaperiam,eaqueipsaquaeabilloinventoreveritatisetquasiarchitectobeataevitaedictasuntexplicabo.</p></EvamTabPanel><EvamTabPanelindex={2}><h1>Panel3</h1><p>Atveroeosetaccusamusetiustoodiodignissimosducimusquiblanditiispraesentiumvoluptatumdelenitiatquecorruptiquosdoloresetquasmolestiasexcepturisintoccaecaticupiditatenonprovident,similiquesuntinculpaquiofficiadeseruntmollitiaanimi,idestlaborumetdolorumfuga.Etharumquidemrerumfacilisestetexpeditadistinctio.</p></EvamTabPanel></Box></EvamAppBarLayout></ThemeProvider></Router></div>)}
With added Search functionality¶
Adding a Search functionality at the top right of the App bar component can be done by setting theextraFunction property ofEvamAppBarLayout:
<divclassName="App"><Router><ThemeProvidertheme={theme}><CssBaseline/><EvamAppBarLayouttabs={<EvamTabs><EvamTablabel={"Panel 1"}index={0}icon={<HomefontSize={"large"}/>}/><EvamTablabel={"Panel 2"}index={1}icon={<ArchiveIconfontSize={"large"}/>}/><EvamTablabel={"Panel 3"}index={2}icon={<EditIconfontSize={"large"}/>}/></EvamTabs>}extraFunction={<EvamTabSearch/>}><Routes><Routepath={"/"}element={<MainView/>}></Route><Routepath={"/search"}element={<SearchView/>}></Route></Routes></EvamAppBarLayout></ThemeProvider></Router></div>
And here is theSearchView definition:
import{useSearchParams}from"react-router-dom";interfaceSearchViewProps{}exportfunctionSearchView(props:SearchViewProps){const{...other}=propsconst[params]=useSearchParams()return(<div{...other}><h1>Noresultfor"{params.get("searchText")}"</h1><p>Wecouldnotfindanything,pleasereviewyourquery.</p></div>)}
Note that we have added a Router and Routes objects fromreact-router-dom to this example as we have now 2 different views we must keep track of:
The
MainViewwith the 3 tabsThe
SearchViewwith the search bar and search results.
In this example, we have deciced to implement the search functionality as an independent view, but we could have kept it on the Main View by simply routing “/search” routes to the Main View.
This is the result:


Note: the second screenshot above is after searching for “hello world”.
TheEvamTabSearch component, once clicked, will automatically navigate to “/search”. And whenever the search query is updated in the input box, the path will update to “/search?searchText=<ENCODED_SEARCH_QUERY>”. For instance, when searching for “hello world”, the path will be “/search?searchText=hello%20world”.
This allows for a flexible implementation of the Search function.
Additionally, it is possible to further customize the look of the top bar when in search mode with 2 properties ofEvamAppBarLayout:
searchHint: text shown when the search input is empty, defaults to “Search”showSearchCancel: set to false to hide the cancel button in the top bar.
See example below:
<divclassName="App"><Router><ThemeProvidertheme={theme}><CssBaseline/><EvamAppBarLayoutsearchHint={"Sök"}showSearchCancel={true}tabs={<EvamTabs><EvamTablabel={"Panel 1"}index={0}icon={<HomefontSize={"large"}/>}/><EvamTablabel={"Panel 2"}index={1}icon={<ArchiveIconfontSize={"large"}/>}/><EvamTablabel={"Panel 3"}index={2}icon={<EditIconfontSize={"large"}/>}/></EvamTabs>}extraFunction={<EvamTabSearch/>}><Routes><Routepath={"/"}element={<MainView/>}></Route><Routepath={"/search"}element={<SearchView/>}></Route></Routes></EvamAppBarLayout></ThemeProvider></Router></div>
With added Menu¶
If your application requires extra navigation options, adding a hamburger menu is a good way to provide them without cluttering the visuals. It can be done with theextraFunction property just like for Search:
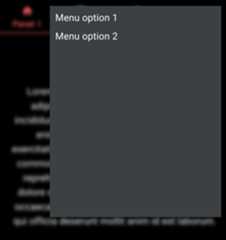
<divclassName="App"><Router><ThemeProvidertheme={theme}><CssBaseline/><EvamAppBarLayouttabs={<EvamTabs><EvamTablabel={"Panel 1"}index={0}icon={<HomefontSize={"large"}/>}/><EvamTablabel={"Panel 2"}index={1}icon={<ArchiveIconfontSize={"large"}/>}/><EvamTablabel={"Panel 3"}index={2}icon={<EditIconfontSize={"large"}/>}/></EvamTabs>}extraFunction={// Simple hamburger menu layout with 2 options<EvamHamburgerMenusx={{backdropFilter:"blur(5px)"}}><Boxheight={600}width={500}><EvamMenuItemid={"Menu option 1"}>Menuoption1</EvamMenuItem><EvamMenuItemid={"Menu option 2"}>Menuoption2</EvamMenuItem></Box></EvamHamburgerMenu>}><Routes><Routepath={"/"}element={<MainView/>}></Route><Routepath={formatRoutePathByMenuId("Menu option 1")}element={<h1>Option1</h1>}/><Routepath={formatRoutePathByMenuId("Menu option 2")}element={<h1>Option2</h1>}/></Routes></EvamAppBarLayout></ThemeProvider></Router></div>
This is the result:
Main View | After touching menu button | After selecting option 1 |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Similarly to theEvamTabSearch component,EvamHamburgerMenu also uses navigation to propagate user actions to the app:
Selecting an
EvamMenuItemnavigates to “/hmenu/<ENCODED_ID>”, for instance for a menu id “Menu option 1”, the path will be “/hmenu/Menu%20option%201”. To make it easy with routing, the functionformatRoutePathByMenuIdis available to compute the final path from a menu id.Touching the “Back arrow” goes back to “/”.
Use the Evam API¶
Interacting with the Evam platform is made possible through the Evam API.
It contains a set of functions to access the platform data and simulate specific events in a development environment.
The guiding principles behind the API functions are:
They should be safe to use, this means that it should not be possible to negatively affect (e.g. crash) the platform by using them
They should not require extensive tooling to be used - the Evam API is a singleton and using it in several places in your app does not require a dependency injection system (even though it will be compatible with it)
They should be reactive - this means that your application does not have to implement busy-waiting on the Evam data as it will be fed to your app when updated through callbacks
The API is entirely written in Typescript, making it type-safe (to the extent permitted by Typescript) and Javascript-compatible.
Read the Evam platform data¶
There are many objects that can be read from the Evam platform:
TheOperation:
it describes a mission being assigned to an emergency vehicle and is meant to be a wrapper over region-specific data frames such as the SOS profiles in Sweden. Contrary to those, an Operation in the Evam SDK always has the same fields and these fields have the same types. In the SDK v1, the only Operation that can be obtained is the one currently being worked on by the vehicle (“Active operation”). The SDK v2 adds a function to observe all operations received in the Evam platform.TheSettings:
your application can specify a set of parameters in its application manifest (seeSetup your app metadata). Those settings will be set by the end user upon installation of you app, and the Evam platform will feed them to your app at runtime when it starts and when the settings are updated by the end user. The obtainedsettingsobject will have the same format as the settings supplied in the App manifest.TheDevice Role:
this is one of three values ‘SINGLE_DEVICE’, ‘RECEIVING_DEVICE’ or ‘MAIN_DEVICE’. This will be configured within Vehicle Services via the setup.TheLocation:
the vehicles current location, latitude, logitude, and timestamp,TheInternet State:
one of seven possible values where ‘NO_INTERNET’ means no connection whatsoever. Aside from that all other states are named ‘CONNECTED_…’ where ‘…’ can be either ‘2G’, ‘EDGE’, ‘3G’, ‘4G’, ‘5G’ or ‘WIFI’.TheVehicle State:
vehicle state stores various data regarding the logged in vehicle. Such data are vehicle status, active case full id, vehicle location and whatnot.TheTrip Location History:
stores an array of Location objects representing the trip history.TheAvailable Vehicle Status list:
all the possible Vehicle Status values that can be selected by the end user. Those are typically engaged in sequence and describe, among other things, the status of the Operation (accepted, on the way to site, complete, etc).TheBattery state:
details about the Evam device’s battery are provided such as its charge state, or health status.TheDisplay mode: light or dark.
TheRakel state:
various details about the Rakel radio connected to the Evam device.
To use this SDK, instantiateEvamApi() and access its observer functions.
import{EvamApi}from"@evam-life/sdk";constevamApi=newEvamApi();// Register observer for active operationevamApi.onNewOrUpdatedActiveOperation((activeCase)=>{// Handle updated case})// Register observer for device locationevamApi.onNewOrUpdatedLocation((deviceLocation)=>{// Handle updated device location})// Add as many API function calls as required
It is recommended you set up all needed observersonNew... as soon as your applicationstarts. The typical pattern is to handle each update fromEvamApi by passingthe observed data in your preferred application data store, such as Redux.
Check theSDK reference for a comprehensive list of the available API functions.
Simulate events in the in-browser development environment¶
The Operations and Settings will be provided by the Evam platform as shown below, but you may simulate incoming Operations and Settings updates in a development environment (i.e. a web browser such as Chrome or Firefox running on your development computer). This allows you to test those scenarios with proper tooling and without needing an Evam device.
It is compatible with test libraries such asjest.
This is how you may inject such events using the API:
import{EvamApi,Operation}from"@evam-life/sdk";importOperationStatefrom"@evam-life/sdk/sdk/domain/OperationState";constevamApi=newEvamApi();// Get Evam API instanceevamApi.injectOperation(Operation.fromJSON({operationID:"56",patientName:"Test Testkort",operationState:OperationState.ACTIVE,patientUID:"900608-2381",callCenterId:"18",caseFolderId:"1",prio:"PRIO 1",vehicleStatus:{name:"Test status",event:undefined,successorName:undefined,isStartStatus:false,isEndStatus:false,categoryType:"other",categoryName:"test",},destinationSiteLocation:{latitude:59.35393,longitude:17.973795,street:"Vretenvägen 13"},name:"Test operation",sendTime:(newDate()).getTime()/1000,createdTime:(newDate()).getTime()/1000,}))
Please note that those functions will not work when run in the Evam platform (i.e. an Evam device) and will result in Exceptions being thrown.
You can check what environment you are running in in this way:
if(!EvamApi.isRunningInVehicleServices){// Perform event simulations}
Recommended workflow¶
The Evam SDK is built on top of the NodeJS ecosystem and React library, which provides any developer with a rich set of tools to efficiently develop and application out of the box. Developing an app for the Evam platform is very similar to developing a React web application.
Only an IDE such as VS Code and a web browser such as Chrome are needed.
One notable difference is that your application will be run and used in a mobile device (typically a tablet), with limited screen real estate. To ensure your application will look as intended in the Evam Platform, make sure to use the “Device Mode” of your web browser (example for Chrome:Device mode).
You can find out which device dimensions are available in the Evam platform in theLayout documentation in the design guidelines.
Setting your device dimensions to the smallest available ones is a good starting point.
SeeDevelopment environment for more information about this development environment in-browser.