Meso Compounds
In my experience of teaching, I have noticed that conveying the message aboutmeso compounds is a lot easier whenFischer projections are used. So, we will talk about it by drawing the Fischer projections of three isomers of 2,3-dichlrobutane:

Here is how you recognize themeso isomer: it is the one thatcontains a plane of symmetry.
Out of the three, it is only the last one that has a plane of symmetry. It cuts the molecule in two,mirror-reflected halves:

One important clarification before we finalize the statement aboutmeso compounds.
Ameso compoundmust contain chirality centers. This means that not any molecule that has a plane of symmetry is ameso compound. For example:

Let’s get back to 2,3-dichlrobutane for additional details that are very important.
Notice that the first two isomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images. Therefore, they areenantiomers.
And to clarify why they nonsuperimposable, rotate the right isomer 180o to have it look like the left one and you will notice that the positions of Br groups are different, i.e. it does not represent the same molecule:

You can also check this by assigning theR andS configuration. It is inverted from 2R, 3S to 2S, 3R which confirms that they are enantiomers.

Here is the important part about themeso isomer! Unlike the first two, itdoes NOT have an enantiomer!
Why?
To answer this question, go ahead and draw its mirror image since enantiomers are mirror images:

At first, these may look like a pair of enantiomers. However, if you flip any of them, you can see that it represents the same molecule as its mirror image:

In other words, it is superimposable to its mirror image which means the two structures represent the same molecule. Therefore, ameso compound cannot have an enantiomer.
This is consistent with what we discussed in the beginning of stereochemistry-any object has a mirror image, but only chiral objects are nonsuperimposable to their mirror images. And these mirror images are called enantiomers.
Features of Meso Compounds
Let’s emphasize a few important observations:
1) Meso compounds are achiral
- This, in turn, means thatmeso compounds areoptically inactive.
Yes,meso compounds do have chiral centers but they are all inverted. EveryR is inverted toS and everyS is inverted intoR:

It is similar to having a racemic mixture where equal amounts ofR andS configurations of the same carbon are present. They cancel out the rotation of plane-polarized light making the mixtureoptically inactive.
2) Meso compounds cannot have enantiomers
- Like any other molecule that is not chiral, meso compounds cannot have enantiomers since their mirror image represents the same compound:

Wedge and dash in Meso compounds
Sometimes, it is not obvious to spot themeso isomer when it is drawn in bond-line representation. The reason is that it is tempting to assume that themeso isomer is the one with all wedge or all dashed lines since it looks like there is a plane of symmetry.
For example, which of the isomers is a meso compound?

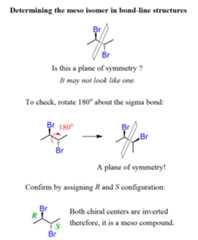
It looks like it is possible to place a plane of symmetry between the two bromines of the first isomer:

However, notice that even though the Br groups are on the same side (both wedge), they are still pointing in opposite directions – up and down. Therefore, they are not reflected through a plane of symmetry:

The second isomer, on the other hand, does have a plane of symmetry! Yes, the Br groups are on opposite sides (wedge and dash), however, if we rotate about the central sigma bond, they both appear right next to each other:
To summarize, if you are asked to draw themeso isomer of a plain bond-line structure, you have two options. One is two draw the carbon chain in a regular zig-zag form and have the identical groups on the chiral carbon on opposite sides (wedge-dash):
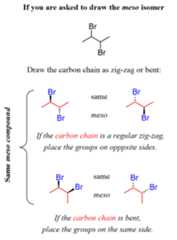
And the other is to draw the carbon chain with these two groups pointing to the same direction having either both wedge or both dash lines (which is the same molecule since it is a meso compound).

Practice
All the molecules shown below areachiralbecause of the presence of a plane of symmetry. Confirm that they are achiral by drawing the corresponding plane of symmetry and determine if they aremeso compounds. Remember that the plane of symmetry can slice atoms in half.

This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Determine whether each of the molecules is chiral or achiral. Explain your answer by showing the appropriate symmetry element:

This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Check Also
- How to Determine the R and S Configuration
- The R and S Configuration Practice Problems
- What is Nonsuperimposable in Organic Chemistry
- Chirality and Enantiomers
- Diastereomers-Introduction and Practice Problems
- Cis and Trans Stereoisomerism in Alkenes
- E and Z Alkene Configuration with Practice Problems
- Enantiomers vs Diastereomers
- Enantiomers Diastereomers the Same or Constitutional Isomers with Practice Problems
- Configurational Isomers
- Optical Activity
- Specific Rotation
- Racemic Mixtures
- Enantiomeric Excess (ee): Percentage of Enantiomers from Specific Rotation with Practice Problems
- Symmetry and Chirality. Meso Compounds
- Fischer Projections with Practice Problems
- R and S Configuration in the Fischer Projection
- R and S configuration on Newman projections
- R and S Configuration of Allenes
- Converting Bond-Line, Newman Projection, and Fischer Projections
- Resolution of Enantiomers: Separate Enantiomers by Converting to Diastereomers
- Stereochemistry Practice Problems Quiz
9 thoughts on “Meso Compounds”
I needed to review this concept and the trick about the wedge and dash notation for the alkyne quiz. Thanks for linking them.
ReplyYou are welcome, Autumn. It’s good to hear this feedback.
ReplySo much information. Thank you, sir!
ReplyHi, why is the c) from exercise 2 chiral?
ReplyHello, the logic applied for meso compound where both the Cl are on the same side, can be applied for the one with Cl on different sides. From that, we get the same compound like meso one, but that would be wrong. Please clarify.
Replywhy 1. a) is meso? I thought it doesn’t have chiral centers. Thank you in advance.
Reply


