Naming Alcohols with Practice Problems
Naming alcohols follows the same rules we discussed earlier for the IUPACnomenclature rules for alkanes.
This is the brief summary of steps:
Step 1. Identify the parent chain.
Step 2. Identify the substituents.
Step 3. Number the parent chain giving the OH group the lowest locant
Step 4. Put everything together having the substituents in alphabetical order.
There are, of course, some deviations since we now have a new functional group – the hydroxyl group.
These are the changes you need to take into consideration.
1) The presence of a hydroxyl is identified bychanging the parent suffix from “e” to “ol”:

2) Choose theparent chain such that it is thelongest carbon chain containingthe carbon atom connected to the OH group:

3) Thehydroxyl group has a higher priority than alkyl substituents or π bonds. Therefore, you need to number the parent chain such that theOH gets the lowest number possible:

The locant indicating the position of the hydroxyl group can be placed before the parent or before the suffix “ol.” Both names are acceptable according to the IUPAC recommendations:

If theOH group is connected to a chiral center, you will also need to include theabsolute configuration at the beginning of the name. Also, if there is a double, theE and Z configuration should be addressed when applicable:

When naming acyclic alcohol, start numbering the ringbeginning with the carbon connected to the OH group. This rule always puts the OH group at C1, therefore, the “1” is usually omitted from the name:

When other groups are present on the ring, it is numbered clockwise or counterclockwisedepending on which direction gives the next substituent the lower number:
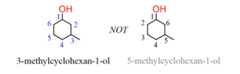
Alcohols can also be identified by their common names:

Practice
Provide an IUPAC name for each of the following alcohols:
Indicate the stereochemistry where needed.


This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Check Also
- Preparation of Alcohols via Substitution or Addition Reactions
- Reaction of Alcohols with HCl, HBr, and HI Acids
- Mesylates and Tosylates as Good Leaving Groups
- SOCl2 and PBr3 for Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl Halides
- Alcohols in Substitution Reactions Practice Problems
- POCl3 for Dehydration of Alcohols
- Dehydration of Alcohols by E1 and E2 Elimination
- The Oxidation States of Organic Compounds
- LiAlH4 and NaBH4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism
- Alcohols from Carbonyl Reductions – Practice Problems
- The Grignard Reaction
- Grignard Reaction in Organic Synthesis with Practice Problems
- Protecting Groups For Alcohols in Organic Synthesis
- Oxidation of Alcohols: PCC, PDC, CrO3, DMP, Swern, and All of That
- Jones Oxidation
- Diols: Nomenclature, Preparation, and Reactions
- NaIO4 Oxidative Cleavage of Diols
- The Pinacol Rearrangement
- The Williamson Ether Synthesis
- Alcohol Reactions Practice Problems
- Naming Thiols and Sulfides
- Reactions of Thiols
- Alcohols Quiz – Naming, Preparation, and Reactions
- Reactions Map of Alcohols
- Preparation of Epoxides
- Ring-Opening Reactions of Epoxides
- Reactions of Epoxides under Acidic and Basic Conditions
- Reactions of Epoxides Practice Problems
- The Grignard Reaction of Epoxides
- Naming Ethers
- The Williamson Ether Synthesis
- Reactions of Ethers-Ether Cleavage
5 thoughts on “Naming Alcohols with Practice Problems”
Well explained thanks
ReplyThis q. Good for our practice.
ReplyI think your answer for problem … is wrong.
on carbon 2 there is a 1-methylpropyl group
should the correct answer be…4-ethyl-7,8-dimethyl-2-(1-methylpropyl)-1-nonanol
Reply1-methylpropyl is the systematic name ofsec-butyl, and yes, according to the new IUPAC rules, 1-methylpropyl is the correct way of naming it.Sec-butyl is still widely acceptable in most textbooks thus by many professors. I have a paragraph “IUPAC Moments” about this in thenomenclature postwhich you can findhere.
Reply
G) will the answer be 7,8-dimethyl-4-ethyl-2-(1-methylpropyl) nonanol ?
Reply

