NaIO4 Oxidative Cleavage of Diols
Sodium periodate (NaIO4) is astrong oxidizing agent mainly used for theoxidative cleavage of 1,2-diols (vicinal diols),forming aldehydesand ketones depending on the structure of the alcohol.

So, there are two things happening here: 1) the OH group is oxidized to a carbonyl, and 2) the C-C bond with the oxygens is cleaved. And the pattern is that a primary OH group gives formaldehyde, secondary OH groups produce a ketone, while a tertiary alcohol results in a ketone.
The Mechanism of NaIO4 Oxidative Cleavage
The reaction starts with a nucleophilic addition of the OH groups to the iodine, forming a cyclic iodate ether, which eventually, after proton transfer steps, is cleaved into two carbonyl groups:

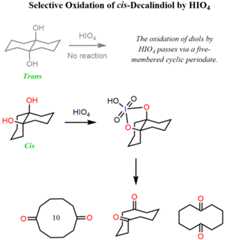
An indirect confirmation of the mechanism going via a five-membered intermediate is the selective oxidation of thecis-decalindiol. Thetrans isomer is not oxidized by HIO4 because the opposite orientation of the OH groups does not allow for the formation of a five-membered cyclic periodate:
Although the mechanisms are not entirely identical, this is somewhat similar to the oxidative cleavage of alkenes withpotassium permanganate (KMnO4) orozonolysis followed by treatment with hydrogen peroxide.
However, the difference is that KMnO4 oxidizes the resulting aldehydes and/or ketones further to carboxylic acids:

There is a name reaction called The Lemieux–Johnson or Malaprade–Lemieux–Johnsonoxidation,which consists of two steps of syn dihydroxylation of alkenes, followed by oxidative cleavage of the diol with NaIO4:

Remember, in thesyn dihydroxylation of alkenes with OsO4,NMO (N-methylmorpholine N-oxide) is often added to the reaction, and it deoxidizes the Os6+ species back into OsO4, which can perform another oxidation of the alkene:

Check this66-question,Multiple-ChoiceQuiz with a 2-hour Video Solutionon the naming, preparation, and reactions of Alcohols.
Check Also
- Ozonolysis of Alkenes with Practice Problems
- Syn Dihydroxylation of Alkenes with KMnO4 and OsO4
- Anti-Dihydroxylation of Alkenes with MCPBA and Other Peroxides with Practice Problems
Reactions of Alcohols
- Nomenclature of Alcohols: Naming Alcohols based on IUPAC Rules with Practice Problems
- Preparation of Alcohols via Substitution or Addition Reactions
- Reaction of Alcohols with HCl, HBr, and HI Acids
- Mesylates and Tosylates as Good Leaving Groups
- SOCl2 and PBr3 for Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl Halides
- Alcohols in Substitution Reactions Practice Problems
- POCl3 for Dehydration of Alcohols
- Dehydration of Alcohols by E1 and E2 Elimination
- The Oxidation States of Organic Compounds
- LiAlH4 and NaBH4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism
- Alcohols from Carbonyl Reductions – Practice Problems
- Grignard Reaction in Preparing Alcohols with Practice Problems
- Grignard Reaction in Organic Synthesis with Practice Problems
- Protecting Groups For Alcohols in Organic Synthesis
- Oxidation of Alcohols: PCC, PDC, CrO3, DMP, Swern, and All of That
- Diols: Nomenclature, Preparation, and Reactions
- The Pinacol Rearrangement
- The Williamson Ether Synthesis
- Alcohol Reactions Practice Problems
- Naming Thiols and Sulfides
- Reactions of Thiols
- Alcohols Quiz – Naming, Preparation, and Reactions
- Reactions Map of Alcohols
4 thoughts on “NaIO4 Oxidative Cleavage of Diols”
Is thenPotassium permanganate equal to NAIO4
Reply
In cleavage of Diols ?Potassium permanganate can oxidize a double bond to a diol in basic media and at lower temperatures. In acidic conditions and elevated temperatures, it cleaves the C-C bond and further oxidizes the C-O bonds to a ketone and carboxylic acid.
Reply
NaIO4 doesn’t usually oxidize a double bond, at least in undergraduate textbooks. It is gentler with diols too as it stops their oxidation at an aldehyde and a ketone.
Hi, nice demo drawings!
Reply
Stil I have to point out that the writing doesn’t show clearly that IO4(-) turns into IO3(-).
Cleaning C-C an oxydise 2 OH into C=O (ketons and/or aldehydes means oxydation and concomitant reduction hidden by (NaO-)I(-OH)2=O because discretly = NaOI(=O)2 +H2O (NaIO3)


