Homotopic Enantiotopic Diastereotopic Practice Problems
In the previous post we talked abouthomotopic, enantiotopic, diastereotopic and constitutionally heterotopic protons.
In short, these are all about whether a set of protons is in thesame environment or not, and for theNMR purposes, it helps us determine thenumber of signals we should expect for a given molecule.
Readthis article for more details if you need to and if you are ready,scroll down and work on these problems.
Remember, you have two methods for determining whether the protons are homotopic, enantiotopic, diastereotopic and constitutionally heterotopic;
First, and probably, the easier/faster method is thecheck of symmetry elements according to this flowchart:

Again, for more details check the post mentioned earlier.
The second method is used if you are in doubt about the symmetry or its absence in the molecule. And this is the method ofreplacing the hydrogens with another element.
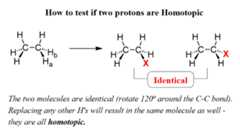
If replacing two protons with a different group (X) gives the same compound, the protons are called Homotopic.
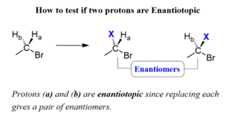
If replacing two protons with a different group (X) gives a pair of enantiomers, the protons are called Enantiotopic.
If replacing two protons with a different group (X) gives a pair of diastereomers, the protons are called Diastereotopic.

And if replacing two protons gives two constitutional isomers, the protons are said to beconstitutionally heterotopic or simply heterotopic protons:

Practice
For each of the following compounds, determine whether the two protons shown in red are homotopic, enantiotopic, or diastereotopic:

The relationship of protons is shown by two methods:
- Thesymmetry elements
- Byreplacement of protons
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Check Also
- NMR spectroscopy – An Easy Introduction
- NMR Chemical Shift
- NMR Chemical Shift Range and Value Table
- NMR Number of Signals and Equivalent Protons
- Homotopic Enantiotopic Diastereotopic and Heterotopic
- Homotopic Enantiotopic Diastereotopic Practice Problems
- Integration in NMR Spectroscopy
- Splitting and Multiplicity (N+1 rule) in NMR Spectroscopy
- NMR Signal Splitting N+1 Rule Multiplicity Practice Problems
- 13C NMR NMR
- DEPT NMR: Signals and Problem Solving
- NMR Spectroscopy-Carbon-Dept-IR Practice Problems

