Ester Reactions Summary and Practice Problems
This article summarizes themain reactions of esters with associatedpractice problems. We covered themechanism and other details about each reaction so, if you need to go over them,click on the corresponding links.
Let’s start with thehydrolysis of esters.
Esters can behydrolyzed to carboxylic acid by acid base catalysis. The base-catalyzed hydrolysis, also called saponification, has the advantage of being irreversible.

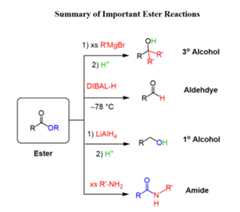
Esters can be converted into primary, secondary and tertiary amidesby anaminolysis reaction with ammonia, primary amine and a secondary amine respectively:

Esters can bereduced to alcohols or aldehydes usingLiAlH4 andDIBAL respectively:

Reacting esters with excessGrignard reagent produces tertiary alcohols:

Below is thesummary of ester reactions that you can use to work on the practice problems:
Practice
Predict the major product(s) for each of the following reactions:

This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Draw a plausible mechanism for the following synthetic transformation:

This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Propose a mechanism for the following synthetic transformation:
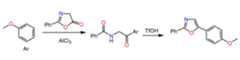
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Friedel-Crafts acylation of carboxylic acids is not very common as the carbonyl group is not so electrophilic. One of the ways to activate the acid is the use of TFAA (Trifluoroacetic anhydride). Propose a mechanism for the following Friedel-Crafts acylation and explain the role of TFAA:

This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Propose a mechanism for the following Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction.

Note: H3O+ with heat is used for hydrolyzing the ester into a carboxylic acid.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Chemiluminescence is used for many applications including glow sticks. The principle behind this process is the excitation of fluorescent dyes such as rhodamines, perylenes, anthracenes, and many more using a chemical reaction. In other words, the source of energy for the excitation of the dye is a chemical reaction. Most often the energy is generated as a result of spontaneously decomposing carbon dioxide dimer which, in turn, is produced via the oxidation of diaryl oxalate diesters with hydrogen peroxide:

Draw a curved arrow mechanism for the formation of the carbon dioxide dimer and explain why perylene is aromatic despite having 20 π electrons.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Check Also
- Preparation of Carboxylic Acids
- Naming Carboxylic Acids
- Naming Nitriles
- Naming Esters
- Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives – Practice Problems
- Fischer Esterification
- Ester Hydrolysis by Acid and Base-Catalyzed Hydrolysis
- What is Transesterification?
- Esters Reaction with Amines – The Aminolysis Mechanism
- Preparation of Acyl (Acid) Chlorides (ROCl)
- Reactions of Acid Chlorides (ROCl) with Nucleophiles
- R2CuLi Organocuprates – Gilman Reagent
- Reaction of Acyl Chlorides with Grignard and Gilman (Organocuprate) Reagents
- Reduction of Acyl Chlorides by LiAlH4, NaBH4, and LiAl(OtBu)3H
- Preparation and Reaction Mechanism of Carboxylic Anhydrides
- Amides – Structure and Reactivity
- Naming Amides
- Amides Hydrolysis: Acid and Base-Catalyzed Mechanism
- Amide Dehydration Mechanism by SOCl2, POCl3, and P2O5
- Amide Reduction Mechanism by LiAlH4
- Reduction of Amides to Amines and Aldehydes
- Amides Preparation and Reactions Summary
- Amides from Carboxylic Acids-DCC and EDC Coupling
- The Mechanism of Nitrile Hydrolysis To Carboxylic Acid
- Nitrile Reduction Mechanism with LiAlH4 and DIBAL to Amine or Aldehyde
- The Mechanism of Grignard and Organolithium Reactions with Nitriles
- The Reactions of Nitriles
- Converting Nitriles to Amides
- Carboxylic Acids to Ketones
- Esters to Ketones
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Practice Problems
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Quiz

