Allylic Bromination by NBS with Practice Problems
In allylic bromination, the Br atom appears on the carbon next to the double bond:

This reaction goes through a radical mechanism, and it is interesting to notice the difference with theaniti-Markovnikov radical bromination:
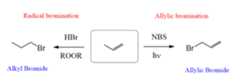
We will discuss why these reactions form different products later. For now, let’s understand how the allylic bromination happens.
First, it is important to mention thatallylic radicals are “very stable”. They are even more stable than the tertiary radicals because of resonance stabilization:

This is the driving force of the allylic bromination.
The Mechanism of Allylic Bromination
Step 1: The first step of allylic bromination is the homolytic cleavage of the N-Br bond (initiation) of theN-bromosuccinimide (NBS):

Notice that the imide group canstabilize the radical by two additional resonance structures, which help to initiate the homolysis of the N-Br bond:

Step 2: After this, the Br radical abstracts an allylic H, forming the corresponding allylic radical:

Step 3:The HBr produced in this step then reacts with NBS, producing Br2 in low concentration.

Step 4: In the next step, the Br2is then quickly captured by the allylic radical, thus keeping the concentration of HBr and Br2 at a minimum, suppressing the competing electrophilic addition to the double bond.

The process repeats until the termination and consumption of the reactant(s).
Looking at the last step, there is one question we didn’t address here:where is the Br2 coming from?
The source of Br2 is theNBS, which, besides producing the Br radical, generates a low concentration of Br2.
Allylic Bromination vs Addition to the Double Bond
Now, let’s go back and figure out this question:why does the Br radical generated by NBSnot add to the double bond like in theanti-Markovnikov bromination?

The answer is it does! However, because the concentration of HBr is low (remember, HBr is needed to supply the hydrogen and convert the radical into alkyl bromide), the addition reaction reverses and proceeds by allylic bromination:

The regiochemistry of Allylic Bromination
The example we discussed above was based on the simplest alkene with an allylic position (propene). As a result,only one product could be obtained since the tworesonance structures are superimposable mirror images:

However, if theradical stabilization does not result in identical allylic radicals,a mixture of allylic bromides is obtained:
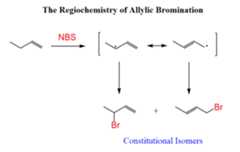
Notice that bothallylic resonance structures contribute to the formation of the twoconstitutional isomers. So,whenever you are asked to determine the products of allylic bromination, draw both resonance forms and place the Br atoms accordingly.
For example, predict the products of allylic bromination of the following alkene:

Step 1: Draw the allylic radical:

Step 2: Draw the resonance structures of the radical:
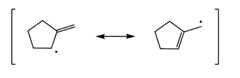
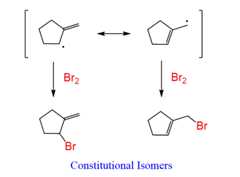
Step 3: Add the Br to the allylic radical of eachresonance structure:
Stereochemistry of Allylic Bromination
There is no stereochemical control on the allylic bromination. Just like any radical (or carbocation) reaction, whenever possible, bothRand Sconfigurations of the radical carbon are formed.
For example,1-butene, which we discussed earlier, formsthree products in total:

One of the radicals forms a mixture ofenantiomers, while the other one can only form one product. This product is aconstitutional isomer of the two enantiomers.
Practice
Predict the products when each of the following compounds is treated with NBS under UV light:


This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Check Also
- Free-Radical Addition of HBr: Anti-Markovnikov Addition
- Initiation, Propagation, and Termination in Radical Reactions
- Selectivity in Radical Halogenation
- Stability of Radicals
- Resonance Structures of Radicals
- Stereochemistry of Radical Halogenation
- Allylic Bromination
- Reactions at the Benzylic Position
- Benzylic Bromination
- Radical Halogenation in Organic Synthesis

