Acetals as Protecting Groups for Aldehydes and Ketones
Acetals are the protecting groups for aldehydes and ketones. They can be used, for example, when aselective reduction of an ester is needed in the presence of an aldehyde or a ketone:

Remember,aldehydes are more reactive than esters and when mixed with, for example LiAlH4,they will react first before the ester is reduced and that is when the aldehyde is mostly gone:

So, theproblem, and the objective, hereis to temporarily protect the aldehyde,reduce the ester, and thenremove the protecting group to bring the aldehyde back in the normal form:

Acetals are suitable for this purpose because;
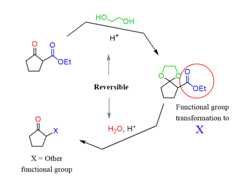
1)they are stable under basic conditions, 2) theformation of acetals is a reversible process which means they can be put on and off as needed:
This is what we have seen earlier withsilyl ethers which are used asprotecting groups for alcohols when strong a base is present in the reaction mixture.
So, what we do is first react the molecule with a diol forming a cyclic acetal, thenreduce the ester with LiAlH4 to an alcohol, and lastly, remove the protecting acetal by acid catalysis:

Notice that the ester does not react with the diol as it requires more forcing conditions, and this allows to selectively protect the aldehyde in the next reaction.
In the following practice problems, we will se how acetals are used as protecting groups for aldehydes an ketones in reductions with LiAlH4, in theGrignard reaction andalkylation reaction of alkynes.
Practice
What is the reason the following Grignard reagent cannot be prepared and stored as shown below?
Explain by showing the corresponding chemical reaction.

The Grignard reagent is very reactive towards ketones and these two groups are incompatible to be present in the same molecule.
Both intermolecular and intramolecular reactions are possible:

Explain why the following synthetic transformation cannot be achieved with good efficiency:

This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
How can the following synthetic transformations be achieved using acetal or other protecting groups?


This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to theanswers and solutions for all the Practice Problems, including over 40 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, Reaction Maps,and the powerful set ofOrganic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Check Also
- Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones
- How to Name a Compound with Multiple Functional Groups
- Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones
- Nucleophilic Addition to Carbonyl Groups
- Reduction of Carbonyl Compounds by Hydride Ion
- Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones with Water
- Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones with Alcohols: Acetals and Hemiacetals
- Formation and Reactions of Imines and Enamines
- Reductive Amination
- Acetal Hydrolysis Mechanism
- Imine and Enamine Hydrolysis Mechanism
- Hydrolysis of Acetals, Imines, and Enamines-Practice Problems
- Reaction of Aldehydes and Ketones with CN, Cyanohydrin Formation
- Grignard Reaction with Practice Problems
- Grignard Reaction in Organic Synthesis with Practice Problems
- The Wittig Reaction: Examples and Mechanism
- The Wittig Reaction: Practice Problems
- Aldehydes and Ketones to Carboxylic Acids
- Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones – Practice Problems
- Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Practice Quiz
- Reactions Map of Aldehydes
- Reactions Map of Ketones
2 thoughts on “Acetals as Protecting Groups for Aldehydes and Ketones”
how can I isolate a compound from a plant or an animal?
ReplyAlthough the principle is the same, I will leave the isolation from animals to biologists and doctors. A typical example in organic chemistry labs is the isolation of caffeine from common products such as tea leaves, coffee, and soft drinks like Pepsi or Cola. The caffeine is extracted using a solvent based on its solubility, separated from other compounds, and then purified, often by recrystallization. At the core of this process is the difference in solubility due to the polarity of the components. Other examples of isolating compounds in organic chemistry labs include essential oils from plants, chlorophyll from spinach, carotenoids from carrots or tomatoes, alkaloids from plant material, etc.
Reply

