Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Energy Education - Acid rain
- American Association for the Advancement of Science - Science - Is Acid Rain a Thing of the Past?
- University of Minnesota Libraries - Environmental Biology - Acid Rain
- Asia Center for Air Pollution Research - Acid rain
- New York State - Department of Environmental Conservation - Acid Rain
- LiveScience - Acid Rain: Causes, Effects and Solutions
- Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies - Acid Rain
- USGS - Water Science School - Acid Rain and Water
- Chemistry LibreTexts - The Chemistry of Acid Rain
- WebMD - What is Acid Rain?
- National Center for Biotechnology Information - PubMed Central - Acid rain and air pollution: 50 years of progress in environmental science and policy
- United States Environment Protection Agency - What is Acid Rain?
- International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology - A Study on Acid Rain: Effects and Control Measures (PDF)
acid rain
- What is acid rain and how is it formed?
- What chemicals are responsible for acid rain?
- How does acid rain affect the environment?
- What are the sources of the pollutants that cause acid rain?
- How does acid rain impact aquatic life and ecosystems?
- What are the effects of acid rain on human-made structures?
- How can acid rain affect human health?
- What regions of the world are most affected by acid rain?
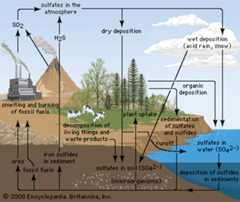
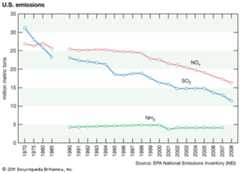
acid rain,precipitation possessing apH of about 5.2 or below primarily produced from the emission ofsulfur dioxide (SO2) andnitrogen oxides (NOx; the combination of NO and NO2) from human activities, mostly thecombustion offossil fuels. In acid-sensitive landscapes,aciddeposition can reduce the pH of surfacewaters and lowerbiodiversity. It weakenstrees and increases their susceptibility to damage from other stressors, such asdrought, extreme cold, andpests. In acid-sensitive areas, acid rain also depletessoil of important plantnutrients and buffers, such ascalcium andmagnesium, and can releasealuminum, bound to soil particles androck, in its toxic dissolved form. Acid rain contributes to thecorrosion of surfaces exposed to airpollution and is responsible for the deterioration oflimestone andmarble buildings and monuments.
- Also called:
- acid precipitation or acid deposition
The phraseacid rain was first used in 1852 by Scottish chemistRobert Angus Smith during his investigation of rainwaterchemistry near industrial cities inEngland andScotland. The phenomenon became an important part of his bookAir and Rain: The Beginnings of a Chemical Climatology (1872). It was not until the late 1960s and early 1970s, however, that acid rain was recognized as a regional environmental issue affecting large areas of westernEurope and easternNorth America. Acid rain also occurs inAsia and parts ofAfrica,South America, andAustralia. As a global environmental issue, it is frequently overshadowed byclimate change. Although the problem of acid rain has been significantly reduced in some areas, it remains an important environmental issue within and downwind from major industrial and industrial agricultural regionsworldwide.