infinite loop (endless loop)
What is an infinite loop?
An infiniteloop -- sometimes called anendless loop -- is a piece ofcode that lacks a functional exit so that it repeats indefinitely. In computer programming, a loop is a sequence ofinstructions that is continually repeated until a certain condition is reached.
Infinite loops can be used intentionally or can occur as the result of a programming error or abug. A pseudo-infinite loop is one that looks as if it will be infinite but stops at some point.
The term infinite loop is sometimes used to describe an endless iteration situation inDevOps feedback loops and software development processes.
What is a loop in programming?
A loop in computer programming is created when a sequence of instructions repeats until a certain terminating condition is reached. Typically, a definedprocess is completed -- such as getting an item of data and changing it -- and then a condition is checked, such as whether a counter has reached a prescribed number. Once the prescribed number is reached the loop ends.
Loops are used to execute the same code multiple times. For example, code that checks the attendance status of each student in a classroom could return a Y for present and an N for absent. The program would need to run through the class roster of 26 students and do this for each member of the class. The program's stopping condition would occur after 26 students had been checked.
There are different types of loops, anddifferent programming languages have different loop syntaxes. Some types of loops include the following:
- Afor loop repeats a block of code a known number of times. It iterates through a list and runs code once for each item in the list.
- Awhile loop will continue to repeat as long as a specified condition is met. It checks for the condition before running the loop code.
- Ado loop runs code, then checks for the condition afterward.
- Ado-while loopis like a while loop but puts the condition at the end, so that the loop runs at least one time if the condition is not met. A while loop will not run if the condition is not met.
No matter the loop type or language syntax, most loops have an exit condition that tells the loop when to end.
How do infinite loops work?
Infinite loops continue as long as theexit condition doesn't occur. A loop without an exit condition happens when one of the following conditions exists:
- The loop has no terminating condition.
- The loop has a terminating condition that cannot be met.
- The loop has a condition that instructs it to start over.
In the attendance checking program example, the 26 students are listed in alphabetical order and labeled numerically, with the first student on the list being number one and the last student being number 26. In this case, the loop would normally be set to terminate after the loop runs 26 times. However, the following criteria could turn it into an infinite loop:
- No terminating condition is set, and the loop returns to student one and checks through the entire list over and over again.
- The terminating condition is set to a number that does not fall into the list of 26 students, such as -1 or 316.
- The loop contains instructions to return to student one sometime before 26 is reached or a break statement is written that causes an intentional interruption in the loop.
In all cases, if the presence of the specified condition cannot be ascertained, the next instruction in the sequence tells the program to return to the first instruction and repeat the sequence. This typically continues until the program terminates automatically after a certain amount of time, or the operating system (OS) terminates the program with an error.
Why are infinite loops used?
An infinite loop often results from a programming error. For example, the conditions for exit are incorrectly written.
However, there are instances when an infinite loop is used intentionally, enabling a program to run continuously. Some examples include the following:
- Embedded systems. A cartridge-based video game is anembedded system that uses an infinite loop. The game runs an infinite loop until the console is powered off because there is no underlying OS to return to.
- Operating systems. OSes are infinite loops that continually check for user input and respond accordingly. The loop continues until the device is turned off or reset.
- Web servers.Web servers are designed to take a request, return a webpage and then wait indefinitely for the next request.
- Viruses.Malware can use infinite loops to overwhelm a computer's processing power and cause it to crash. This technique is used to carry out adistributed denial-of-service attack, which occupies a computer or network's resources so that legitimate users can't access them.
The following joke captures the spirit of infinite loops such as malware:
- Q: Why did the programmer die in the shower?
- A: Because the bottle said "lather, rinse, repeat."
The programmer, thinking like a computer, presumably lathered and rinsed repeatedly until they died of exhaustion, starvation or drowned.
Infinite loop examples
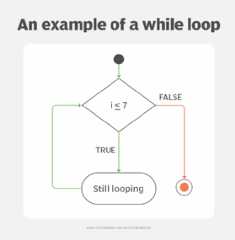
The following is an example of infinite loop code inPython:
i=1while i <= 7print ("still looping")In this loop, the program checks the value of i, then says that if i is less than or equal to 7, the program will print the phrase "still looping." The exit condition is if i is greater than 7. Since there is nothing changing the value of i, this exit condition cannot be fulfilled. The program will print the phrase "still looping" indefinitely until the computer is shut off or crashes.
Infinite loops can appear in a variety of computing contexts and are used in a variety of programming languages. In some contexts, loop conditions can cause a cybersecurity breach. Cybersecurity professionals shouldlearn these 5 essential programming languages to be able to stop these threats and others effectively.
Continue Reading About infinite loop (endless loop)
Related Terms
- What is an entity relationship diagram (ERD)?
- An entity relationship diagram (ERD), also known as an entity relationship model, is a graphical representation that depicts ... See complete definition
- What is data analytics (DA)?
- Data analytics (DA) is the process of examining data sets to find trends and draw conclusions about the information they contain. See complete definition
- What is natural language processing (NLP)?
- Natural language processing (NLP) is the ability of a computer program to understand human language as it's spoken and written --... See complete definition
New & Updated Definitions
- What is 6G? Overview of 6G networks & technology
6G (sixth-generation wireless) is the successor to 5G cellular technology and is expected to be globally available by around 2030. See More.
- phase-locked loop (PLL)
- What is identity and access management? Guide to IAM
- What are AI agents? Types and examples
- What is time-sensitive networking (TSN) via 5G?
- What is millimeter wave (mmWave)?
- What are eMBB, URLLC and mMTC in 5G? Use cases explained
- What is Open RAN (ORAN)? Benefits and use cases
- Agentic process automation: The enterprise guide to autonomous AI workflows
- What is 6G? Overview of 6G networks & technology
6G (sixth-generation wireless) is the successor to 5G cellular technology and is expected to be globally available by around 2030.
- phase-locked loop (PLL)
A phase-locked loop (PLL) is an electronic circuit with a voltage or voltage-driven oscillator that constantly adjusts to match ...
- What is time-sensitive networking (TSN) via 5G?
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) is a set of IEEE 802.1 standards that transform traditional Ethernet into a deterministic, ...
- What is identity and access management? Guide to IAM
No longer just a good idea, IAM is a crucial piece of the cybersecurity puzzle. It's how an organization regulates access to ...
- What is data masking?
Data masking is a security technique that modifies sensitive data in a data set so it can be used safely in a non-production ...
- What is antivirus software?
Antivirus software (antivirus program) is a security program designed to prevent, detect, search and remove viruses and other ...
- What is a chief data officer (CDO)?
A chief data officer (CDO) in many organizations is a C-level executive whose position has evolved into a range of strategic data...
- What is user-generated content?
User-generated content (UGC) is published information that an unpaid contributor provides to a website.
- What is business process outsourcing (BPO)?
Business process outsourcing (BPO) is a business practice in which an organization contracts with an external service provider to...
- What is compensation management?
Compensation management is the discipline and process for determining employees' appropriate pay, incentives, rewards, bonuses ...
- What is HR technology (human resources tech)?
HR technology (human resources tech) refers to the hardware and software that support an organization's human resource management...
- What is core HR (core human resources)?
Core HR (core human resources) is an umbrella term that refers to the essential, mandatory and fundamental tasks and functions of...
- What are virtual agents and how are they being used?
A virtual agent is an AI-powered software application or service that interacts with humans or other digital systems in a ...
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC): How to calculate and reduce it
Customer acquisition cost (CAC) is the cost associated with convincing a consumer to buy your product or service, including ...
- What is direct marketing?
Direct marketing is a type of advertising campaign that seeks to elicit an action (such as an order, a visit to a store or ...
