


This is a common ESP8266 Arduino shield with the following markings:
WiFi 2.4 GHz802.11 b/g/nDesigned inBeijingP.R.ChinaMoer info $ techsupport Please goto elecshop.mlArduino ESP8266 WiFiShield Version 1.0by WangTongzeThe voltage switching circuitry on this shield doesn't work properly as itarrives, so you'll have to modify it slightly if you intend it to work asa shield (withSW1 andSW2 set toON).
The DIP switches are:
| Switch | Function |
|---|---|
| SW1 | Connect ESP8266 TX to pin D0 |
| SW2 | Connect ESP8266 RX to pin D1 |
| SW3 | Enable bootloader mode |
| SW4 | Use DFU LED to show serial activity (?) |
Power is drawn from the5v pin (notVin) so if connecting toPixl.jsensure thatVin and5V are shorted on the solder jumperunless you plan to power the shield separately.
SW1 andSW2 areOFFTXD pin onDebug Port toD0 on the Arduino headerRXD pin onDebug Port toD1 on the Arduino header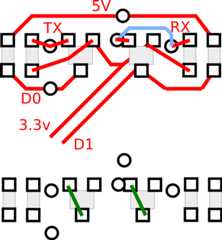

SW1 andSW2 areONTXD andRXD should now be available onD0 andD1 at 3.3v levelsIf connecting to Pixl.js you should be aware that when if Pixl.jsdetects aconnection onD0 at boot, it'll start usingSerial1as a console device rather than the LCD.
To avoid this you'll need to explicitly set the console back to the LCD at boottime:
function onInit() { Terminal.setConsole();}To connect to a WiFi access point.
var WIFI_NAME = "WiFi_Name";var WIFI_PASS = "WPA2_Key";var wifi;function getPage() { require("http").get("http://www.pur3.co.uk/hello.txt", function(res) { console.log("Response: ",res); res.on('data', function(d) { console.log("--->"+d); }); });}function go() { Serial1.setup(115200,{rx:D0,tx:D1}); wifi = require("ESP8266WiFi_0v25").connect(Serial1, function(err) { if (err) throw err; console.log("Connecting to WiFi"); wifi.connect(WIFI_NAME, WIFI_PASS, function(err) { if (err) throw err; console.log("Connected"); // Now you can do something, like an HTTP request getPage(); }); });}To set up as an access point calledESP123 with passwordHelloWorldthat serves up a webpage on address192.168.4.1:
var wifi;function pageHandler(req, res) { res.writeHead(200); res.end("Hello World");}function go() { Serial1.setup(115200,{rx:D0,tx:D1}); wifi = require("ESP8266WiFi_0v25").connect(Serial1, function(err) { if (err) throw err; console.log("Connecting to WiFi"); wifi.createAP("ESP123","HelloWorld",5,"wpa2_psk", function(err) { if (err) throw err; console.log("Connected!"); require("http").createServer(pageHandler).listen(80); }); });}Seethe ESP8266 page for more information on how touse the ESP8266, and theInternet page for more examplesof things you can do on Espruino with an Internet connection.
This page is auto-generated fromGitHub. If you see any mistakes or have suggestions, pleaselet us know.