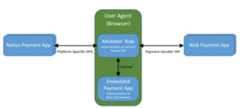
Overview
In this document we envision the following flow:
- An origin requests permission from the user to handle payment requests for a set of supported payment methods. For example, a user visiting a retail or bank site may be prompted to register a payment handler from that origin. The origin establishes the scope of the permission but the origin's capabilities may evolve without requiring additional user consent.
- Payment handlers are defined inservice worker code.
- When the merchant (or otherpayee) calls the [[payment-request]] methodcanMakePayment() orshow() (e.g., when the user -- thepayer -- pushes a button on a checkout page), the user agent computes a list of candidate payment handlers, comparing the payment methods accepted by the merchant with those known to the user agent through any number of mechanisms, including, but not limited to:
- Those previously registered through this API.
- Those that may be registered through this API during the course of the transaction, e.g., identified through apayment method manifest.
- Those registered through other mechanisms, e.g., the operating system.
- The user agent displays a set of choices to the user: the candidate payment handlers. The user agent displays these choices using information (labels and icons) provided at registration or otherwise available from the Web app.
- When thepayer user selects a payment handler, the user agent fires a {{PaymentRequestEvent}} (cf. theuser interaction task source) in theservice worker for the selected payment handler. The {{PaymentRequestEvent}} includes some information from the PaymentRequest (defined in [[!payment-request]]) as well as additional information (e.g., payee's origin).
- Once activated, the payment handler performs whatever steps are necessary tohandle the payment request, and return an appropriate payment response to thepayee. If interaction with the user is necessary, thepayment handler can open a window for that purpose.
- The user agent receives a response asynchronously once the payment handler has finished handling the request. The response becomes thePaymentResponse (of [[!payment-request]]).
An origin may implement a payment app with more than one service worker and therefore multiplepayment handlers may be registered per origin. The handler that is invoked is determined by the selection made by the user.
Handling a Payment Request
Apayment handler is a Web application that can handle a request for payment on behalf of the user.
The logic of a payment handler is driven by the payment methods that it supports. Some payment methods expect little to no processing by the payment handler which simply returns payment card details in the response. It is then the job of the payee website to process the payment using the returned data as input.
In contrast, some payment methods, such as a crypto-currency payments or bank originated credit transfers, require that the payment handler initiate processing of the payment. In such cases the payment handler will return a payment reference, endpoint URL or some other data that the payee website can use to determine the outcome of the payment (as opposed to processing the payment itself).
Handling a payment request may include numerous interactions: with the user through a new window or other APIs (such as [[[WebCryptoAPI]]]) or with other services and origins through web requests or other means.
This specification does not address these activities that occur between the payment handler accepting the {{PaymentRequestEvent}} and the payment handler returning a response. All of these activities which may be required to configure the payment handler and handle the payment request, are left to the implementation of the payment handler, including:
- how the user establishes an account with an origin that provides payment services.
- how an origin authenticates a user.
- how communication takes place between the payee server and the payee Web application, or between a payment app origin and other parties.
Thus, an origin will rely on many other Web technologies defined elsewhere for lifecycle management, security, user authentication, user interaction, and so on.
Relation to Other Types of Payment Apps
This specification does not address how third-party mobile payment apps interact (through proprietary mechanisms) with user agents, or how user agents themselves provide simple payment app functionality.