Set up your development environment#
Fork the scikit-learn repository#
First, you need tocreate an account onGitHub (if you do not already have one) and fork theproject repository by clicking on the ‘Fork’button near the top of the page. This creates a copy of the code under youraccount on the GitHub user account. For more details on how to fork arepository seethis guide.
The following steps explain how to set up a local clone of your forked git repositoryand how to locally install scikit-learn according to your operating system.
Set up a local clone of your fork#
Clone your fork of the scikit-learn repo from your GitHub account to yourlocal disk:
git clone https://github.com/YourLogin/scikit-learn.git # add --depth 1 if your connection is slowand change into that directory:
cd scikit-learnNext, add theupstream remote. This saves a reference to the mainscikit-learn repository, which you can use to keep your repositorysynchronized with the latest changes (you’ll need this later in theDevelopment workflow):
git remote add upstream https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn.gitCheck that theupstream andorigin remote aliases are configured correctlyby running:
git remote -vThis should display:
origin https://github.com/YourLogin/scikit-learn.git (fetch)origin https://github.com/YourLogin/scikit-learn.git (push)upstream https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn.git (fetch)upstream https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn.git (push)
Set up a dedicated environment and install dependencies#
Using an isolated environment such asvenv orconda makes it possible toinstall a specific version of scikit-learn with pip or conda and its dependencies,independently of any previously installed Python packages, which will avoid potentialconflicts with other packages.
In addition to the required Python dependencies, you need to have a working C/C++compiler withOpenMP support to build scikit-learncython extensions.The platform-specific instructions below describe how to set up a suitable compiler and installthe required packages.
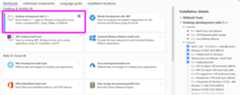
First, you need to install a compiler withOpenMP support.Download theBuild Tools for Visual Studio installerand run the downloadedvs_buildtools.exe file. During the installation you willneed to make sure you select “Desktop development with C++”, similarly to thisscreenshot:
Next, Download and installthe conda-forge installer (Miniforge)for your system. Conda-forge provides a conda-based distribution ofPython and the most popular scientific libraries.Open the downloaded “Miniforge Prompt” and create a new conda environment withthe required python packages:
conda create -n sklearn-dev -c conda-forge ^ python numpy scipy cython meson-python ninja ^ pytest pytest-cov ruff==0.11.2 mypy numpydoc ^ joblib threadpoolctl
Activate the newly created conda environment:
conda activate sklearn-devFirst, you need to install a compiler withOpenMP support.Download theBuild Tools for Visual Studio installerand run the downloadedvs_buildtools.exe file. During the installation you willneed to make sure you select “Desktop development with C++”, similarly to thisscreenshot:

Next, install the 64-bit version of Python (3.11 or later), for instance from theofficial website.
Now create a virtual environment (venv) and install the required python packages:
python -m venv sklearn-devsklearn-dev\Scripts\activate # activatepip install wheel numpy scipy cython meson-python ninja ^ pytest pytest-cov ruff==0.11.2 mypy numpydoc ^ joblib threadpoolctl
The default C compiler on macOS does not directly support OpenMP. To enable theinstallation of thecompilers meta-package from the conda-forge channel,which provides OpenMP-enabled C/C++ compilers based on the LLVM toolchain,you first need to install the macOS command line tools:
xcode-select --installNext, download and installthe conda-forge installer (Miniforge) for your system.Conda-forge provides a conda-based distribution ofPython and the most popular scientific libraries.Create a new conda environment with the required python packages:
conda create -n sklearn-dev -c conda-forge python \ numpy scipy cython meson-python ninja \ pytest pytest-cov ruff==0.11.2 mypy numpydoc \ joblib threadpoolctl compilers llvm-openmp
and activate the newly created conda environment:
conda activate sklearn-devThe default C compiler on macOS does not directly support OpenMP, so you first needto enable OpenMP support.
Install the macOS command line tools:
xcode-select --installNext, install the LLVM OpenMP library withHomebrew:
brew install libompInstall a recent version of Python (3.11 or later) usingHomebrew(brewinstallpython) or by manually installing the package from theofficial website.
Now create a virtual environment (venv) and install the required python packages:
python -m venv sklearn-devsource sklearn-dev/bin/activate # activatepip install wheel numpy scipy cython meson-python ninja \ pytest pytest-cov ruff==0.11.2 mypy numpydoc \ joblib threadpoolctl
Download and installthe conda-forge installer (Miniforge) for your system.Conda-forge provides a conda-based distribution of Python and the mostpopular scientific libraries.Create a new conda environment with the required python packages(includingcompilers for a working C/C++ compiler with OpenMP support):
conda create -n sklearn-dev -c conda-forge python \ numpy scipy cython meson-python ninja \ pytest pytest-cov ruff==0.11.2 mypy numpydoc \ joblib threadpoolctl compilers
and activate the newly created environment:
conda activate sklearn-devTo check your installed Python version, run:
python3 --versionIf you don’t have Python 3.11 or later, please installpython3from your distribution’s package manager.
Next, you need to install the build dependencies, specifically a C/C++compiler with OpenMP support for your system. Here you find the commands forthe most widely used distributions:
On debian-based distributions (e.g., Ubuntu), the compiler is included inthe
build-essentialpackage, and you also need the Python header files:sudo apt-get install build-essential python3-devOn redhat-based distributions (e.g. CentOS), install
gcc`for C and C++,as well as the Python header files:sudo yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ python3-develOn Arche Linux, the Python header files are already included in the pythoninstallation, and
gcc`includes the required compilers for C and C++:sudo pacman -S gcc
Now create a virtual environment (venv) and install the required python packages:
python -m venv sklearn-devsource sklearn-dev/bin/activate # activatepip install wheel numpy scipy cython meson-python ninja \ pytest pytest-cov ruff==0.11.2 mypy numpydoc \ joblib threadpoolctl
Install editable version of scikit-learn#
Make sure you are in thescikit-learn directoryand your venv or condasklearn-dev environment is activated.You can now install an editable version of scikit-learn withpip:
pip install --editable . --verbose --no-build-isolation --config-settings editable-verbose=trueNote on--config-settings#
--config-settingseditable-verbose=true is optional but recommendedto avoid surprises when you importsklearn.meson-python implementseditable installs by rebuildingsklearn when executingimportsklearn.With the recommended setting you will see a message when this happens,rather than potentially waiting without feedback and wonderingwhat is taking so long. Bonus: this means you only have to run thepipinstall command once,sklearn will automatically be rebuilt whenimportingsklearn.
Note that--config-settings is only supported inpip version 23.1 orlater. To upgradepip to a compatible version, runpipinstall-Upip.
To check your installation, make sure that the installed scikit-learn has aversion number ending with.dev0:
python -c "import sklearn; sklearn.show_versions()"You should now have a working installation of scikit-learn and your git repositoryproperly configured.
It can be useful to run the tests now (even though it will take some time)to verify your installation and to be aware of warnings and errors that are notrelated to you contribution:
pytestFor more information on testing, see also thePull request checklistandUseful pytest aliases and flags.