AMD Instinct™ MI250 microarchitecture
Contents
AMD Instinct™ MI250 microarchitecture#
2025-10-20
7 min read time
The microarchitecture of the AMD Instinct MI250 GPU is based on theAMD CDNA 2 architecture that targets compute applications such as HPC,artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) and that run oneverything from individual servers to the world’s largest exascalesupercomputers. The overall system architecture is designed for extremescalability and compute performance.
The following image shows the components of a single Graphics Compute Die (GCD) of the CDNA 2 architecture. On the top and the bottom are AMD Infinity Fabric™interfaces and their physical links that are used to connect the GPU die to theother system-level components of the node (see also Section 2.2). Bothinterfaces can drive four AMD Infinity Fabric links. One of the AMD InfinityFabric links of the controller at the bottom can be configured as a PCIe link.Each of the AMD Infinity Fabric links between GPUs can run at up to 25 GT/sec,which correlates to a peak transfer bandwidth of 50 GB/sec for a 16-wide link (two bytes per transaction). Section 2.2 has more details on the number of AMDInfinity Fabric links and the resulting transfer rates between the system-levelcomponents.
To the left and the right are memory controllers that attach the High BandwidthMemory (HBM) modules to the GCD. AMD Instinct MI250 GPUs use HBM2e, which offersa peak memory bandwidth of 1.6 TB/sec per GCD.
The execution units of the GPU are depicted in the following image as ComputeUnits (CU). The MI250 GCD has 104 active CUs. Each compute unit is furthersubdivided into four SIMD units that process SIMD instructions of 16 dataelements per instruction (for the FP64 data type). This enables the CU toprocess 64 work items (a so-called “wavefront”) at a peak clock frequency of 1.7GHz. Therefore, the theoretical maximum FP64 peak performance per GCD is 22.6TFLOPS for vector instructions. This equates to 45.3 TFLOPS for vector instructions for both GCDs together. The MI250 compute units also provide specializedexecution units (also called matrix cores), which are geared toward executingmatrix operations like matrix-matrix multiplications. For FP64, the peakperformance of these units amounts to 90.5 TFLOPS.

Computation and Data Type | FLOPS/CLOCK/CU | Peak TFLOPS |
|---|---|---|
Matrix FP64 | 256 | 90.5 |
Vector FP64 | 128 | 45.3 |
Matrix FP32 | 256 | 90.5 |
Packed FP32 | 256 | 90.5 |
Vector FP32 | 128 | 45.3 |
Matrix FP16 | 1024 | 362.1 |
Matrix BF16 | 1024 | 362.1 |
Matrix INT8 | 1024 | 362.1 |
The above table summarizes the aggregated peak performance of the AMD Instinct MI250 Open Compute Platform (OCP) Open Accelerator Modules (OAMs) and its two GCDs for different data types and execution units. The middle column lists the peak performance (number of data elements processed in a single instruction) of a single compute unit if a SIMD (or matrix) instruction is being retired in each clock cycle. The third column lists the theoretical peak performance of the OAM module. The theoretical aggregated peak memory bandwidth of the GPU is 3.2 TB/sec (1.6 TB/sec per GCD).

The following image shows the block diagram of an OAM package that consistsof two GCDs, each of which constitutes one GPU device in the system. The twoGCDs in the package are connected via four AMD Infinity Fabric links running ata theoretical peak rate of 25 GT/sec, giving 200 GB/sec peak transfer bandwidthbetween the two GCDs of an OAM, or a bidirectional peak transfer bandwidth of400 GB/sec for the same.
Node-level architecture#
The following image shows the node-level architecture of a system that isbased on the AMD Instinct MI250 GPU. The MI250 OAMs attach to the hostsystem via PCIe Gen 4 x16 links (yellow lines). Each GCD maintains its own PCIex16 link to the host part of the system. Depending on the server platform, theGCD can attach to the AMD EPYC processor directly or via an optional PCIe switch. Note that some platforms may offer an x8 interface to the GCDs, which reducesthe available host-to-GPU bandwidth.
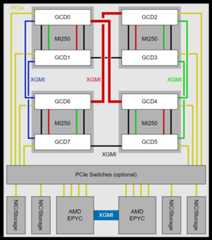
The preceding image shows the node-level architecture of a system with AMDEPYC processors in a dual-socket configuration and four AMD Instinct MI250GPUs. The MI250 OAMs attach to the host processors system via PCIe Gen 4x16 links (yellow lines). Depending on the system design, a PCIe switch mayexist to make more PCIe lanes available for additional components like networkinterfaces and/or storage devices. Each GCD maintains its own PCIe x16 link tothe host part of the system or to the PCIe switch. Please note, some platformsmay offer an x8 interface to the GCDs, which will reduce the availablehost-to-GPU bandwidth.
Between the OAMs and their respective GCDs, a peer-to-peer (P2P) network allowsfor direct data exchange between the GPU dies via AMD Infinity Fabric links (black, green, and red lines). Each of these 16-wide links connects to one of thetwo GPU dies in the MI250 OAM and operates at 25 GT/sec, which corresponds to atheoretical peak transfer rate of 50 GB/sec per link (or 100 GB/secbidirectional peak transfer bandwidth). The GCD pairs 2 and 6 as well as GCDs 0and 4 connect via two XGMI links, which is indicated by the thicker red line inthe preceding image.