pygad.gacnn Module¶
This section of the PyGAD’s library documentation discusses thepygad.gacnn module.
Thepygad.gacnn module trains convolutional neural networks usingthe genetic algorithm. It makes use of the 2 modulespygad andpygad.cnn.
pygad.gacnn.GACNN Class¶
Thepygad.gacnn module has a class namedpygad.gacnn.GACNN fortraining convolutional neural networks (CNNs) using the geneticalgorithm. The constructor, methods, function, and attributes within theclass are discussed in this section.
__init__()¶
In order to train a CNN using the genetic algorithm, the first thing todo is to create an instance of thepygad.gacnn.GACNN class.
Thepygad.gacnn.GACNN class constructor accepts the followingparameters:
model: model: An instance of the pygad.cnn.Model classrepresenting the architecture of all solutions in the population.num_solutions: Number of CNNs (i.e. solutions) in the population.Based on the value passed to this parameter, a number of identicalCNNs are created where their parameters are optimized using thegenetic algorithm.
Instance Attributes¶
All the parameters in thepygad.gacnn.GACNN class constructor areused as instance attributes. Besides such attributes, there is an extraattribute added to the instances from thepygad.gacnn.GACNN classwhich is:
population_networks: A list holding references to all thesolutions (i.e. CNNs) used in the population.
Methods in the GACNN Class¶
This section discusses the methods available for instances of thepygad.gacnn.GACNN class.
create_population()¶
Thecreate_population() method creates the initial population of thegenetic algorithm as a list of CNNs (i.e. solutions). All the networksare copied from the CNN model passed to constructor of the GACNN class.
The list of networks is assigned to thepopulation_networksattribute of the instance.
update_population_trained_weights()¶
Theupdate_population_trained_weights() method updates thetrained_weights attribute of the layers of each network (check thedocumentation of thepygad.cnn module) for more information)according to the weights passed in thepopulation_trained_weightsparameter.
Accepts the following parameters:
population_trained_weights: A list holding the trained weights ofall networks as matrices. Such matrices are to be assigned to thetrained_weightsattribute of all layers of all networks.
Functions in thepygad.gacnn Module¶
This section discusses the functions in thepygad.gacnn module.
pygad.gacnn.population_as_vectors()¶
Accepts the population as a list of references to thepygad.cnn.Model class and returns a list holding all weights of thelayers of each solution (i.e. network) in the population as a vector.
For example, if the population has 6 solutions (i.e. networks), thisfunction accepts references to such networks and returns a list with 6vectors, one for each network (i.e. solution). Each vector holds theweights for all layers for a single network.
Accepts the following parameters:
population_networks: A list holding references to thepygad.cnn.Modelclass of the networks used in the population.
Returns a list holding the weights vectors for all solutions (i.e.networks).
pygad.gacnn.population_as_matrices()¶
Accepts the population as both networks and weights vectors and returnsthe weights of all layers of each solution (i.e. network) in thepopulation as a matrix.
For example, if the population has 6 solutions (i.e. networks), thisfunction returns a list with 6 matrices, one for each network holdingits weights for all layers.
Accepts the following parameters:
population_networks: A list holding references to thepygad.cnn.Modelclass of the networks used in the population.population_vectors: A list holding the weights of all networks asvectors. Such vectors are to be converted into matrices.
Returns a list holding the weights matrices for all solutions (i.e.networks).
Steps to Build and Train CNN using Genetic Algorithm¶
The steps to use this project for building and training a neural networkusing the genetic algorithm are as follows:
Prepare the training data.
Create an instance of the
pygad.gacnn.GACNNclass.Fetch the population weights as vectors.
Prepare the fitness function.
Prepare the generation callback function.
Create an instance of the
pygad.GAclass.Run the created instance of the
pygad.GAclass.Plot the Fitness Values
Information about the best solution.
Making predictions using the trained weights.
Calculating some statistics.
Let’s start covering all of these steps.
Prepare the Training Data¶
Before building and training neural networks, the training data (inputand output) is to be prepared. The inputs and the outputs of thetraining data are NumPy arrays.
The data used in this example is available as 2 files:
dataset_inputs.npy:Data inputs.https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NumPyCNN/blob/master/dataset_inputs.npy
dataset_outputs.npy:Class labels.https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NumPyCNN/blob/master/dataset_outputs.npy
The data consists of 4 classes of images. The image shape is(100,100,3) and there are 20 images per class. For moreinformation about the dataset, check theReading the Data section ofthepygad.cnn module.
Simply download these 2 files and read them according to the next code.
importnumpytrain_inputs=numpy.load("dataset_inputs.npy")train_outputs=numpy.load("dataset_outputs.npy")
For the output array, each element must be a single number representingthe class label of the sample. The class labels must start at0. So,if there are 80 samples, then the shape of the output array is(80).If there are 5 classes in the data, then the values of all the 200elements in the output array must range from 0 to 4 inclusive.Generally, the class labels start from0 toN-1 whereN isthe number of classes.
Note that the project only supports that each sample is assigned to onlyone class.
Building the Network Architecture¶
Here is an example for a CNN architecture.
importpygad.cnninput_layer=pygad.cnn.Input2D(input_shape=(80,80,3))conv_layer=pygad.cnn.Conv2D(num_filters=2,kernel_size=3,previous_layer=input_layer,activation_function="relu")average_pooling_layer=pygad.cnn.AveragePooling2D(pool_size=5,previous_layer=conv_layer,stride=3)flatten_layer=pygad.cnn.Flatten(previous_layer=average_pooling_layer)dense_layer=pygad.cnn.Dense(num_neurons=4,previous_layer=flatten_layer,activation_function="softmax")
After the network architecture is prepared, the next step is to create aCNN model.
Building Model¶
The CNN model is created as an instance of thepygad.cnn.Modelclass. Here is an example.
model=pygad.cnn.Model(last_layer=dense_layer,epochs=5,learning_rate=0.01)
After the model is created, a summary of the model architecture can beprinted.
Model Summary¶
Thesummary() method in thepygad.cnn.Model class prints asummary of the CNN model.
model.summary()
----------NetworkArchitecture----------<class'cnn.Conv2D'><class'cnn.AveragePooling2D'><class'cnn.Flatten'><class'cnn.Dense'>----------------------------------------
The next step is to create an instance of thepygad.gacnn.GACNNclass.
Create an Instance of thepygad.gacnn.GACNN Class¶
After preparing the input data and building the CNN model, an instanceof thepygad.gacnn.GACNN class is created by passing the appropriateparameters.
Here is an example where thenum_solutions parameter is set to 4which means the genetic algorithm population will have 6 solutions (i.e.networks). All of these 6 CNNs will have the same architectures asspecified by themodel parameter.
importpygad.gacnnGACNN_instance=pygad.gacnn.GACNN(model=model,num_solutions=4)
After creating the instance of thepygad.gacnn.GACNN class, next isto fetch the weights of the population as a list of vectors.
Fetch the Population Weights as Vectors¶
For the genetic algorithm, the parameters (i.e. genes) of each solutionare represented as a single vector.
For this task, the weights of each CNN must be available as a singlevector. In other words, the weights of all layers of a CNN must begrouped into a vector.
To create a list holding the population weights as vectors, one for eachnetwork, thepygad.gacnn.population_as_vectors() function is used.
population_vectors=gacnn.population_as_vectors(population_networks=GACNN_instance.population_networks)
Such population of vectors is used as the initial population.
initial_population=population_vectors.copy()
After preparing the population weights as a set of vectors, next is toprepare 2 functions which are:
Fitness function.
Callback function after each generation.
Prepare the Fitness Function¶
The PyGAD library works by allowing the users to customize the geneticalgorithm for their own problems. Because the problems differ in how thefitness values are calculated, then PyGAD allows the user to use acustom function as a maximization fitness function. This function mustaccept 2 positional parameters representing the following:
The solution.
The solution index in the population.
The fitness function must return a single number representing thefitness. The higher the fitness value, the better the solution.
Here is the implementation of the fitness function for training a CNN.
It uses thepygad.cnn.predict() function to predict the class labelsbased on the current solution’s weights. Thepygad.cnn.predict()function uses the trained weights available in thetrained_weightsattribute of each layer of the network for making predictions.
Based on such predictions, the classification accuracy is calculated.This accuracy is used as the fitness value of the solution. Finally, thefitness value is returned.
deffitness_func(ga_instance,solution,sol_idx):globalGACNN_instance,data_inputs,data_outputspredictions=GACNN_instance.population_networks[sol_idx].predict(data_inputs=data_inputs)correct_predictions=numpy.where(predictions==data_outputs)[0].sizesolution_fitness=(correct_predictions/data_outputs.size)*100returnsolution_fitness
Prepare the Generation Callback Function¶
After each generation of the genetic algorithm, the fitness functionwill be called to calculate the fitness value of each solution. Withinthe fitness function, thepygad.cnn.predict() function is used forpredicting the outputs based on the current solution’strained_weights attribute. Thus, it is required that such anattribute is updated by weights evolved by the genetic algorithm aftereach generation.
PyGAD has a parameter accepted by thepygad.GA class constructornamedon_generation. It could be assigned to a function that iscalled after each generation. The function must accept a singleparameter representing the instance of thepygad.GA class.
This callback function can be used to update thetrained_weightsattribute of layers of each network in the population.
Here is the implementation for a function that updates thetrained_weights attribute of the layers of the population networks.
It works by converting the current population from the vector form tothe matric form using thepygad.gacnn.population_as_matrices()function. It accepts the population as vectors and returns it asmatrices.
The population matrices are then passed to theupdate_population_trained_weights() method in thepygad.gacnnmodule to update thetrained_weights attribute of all layers for allsolutions within the population.
defcallback_generation(ga_instance):globalGACNN_instance,last_fitnesspopulation_matrices=gacnn.population_as_matrices(population_networks=GACNN_instance.population_networks,population_vectors=ga_instance.population)GACNN_instance.update_population_trained_weights(population_trained_weights=population_matrices)print(f"Generation ={ga_instance.generations_completed}")
After preparing the fitness and callback function, next is to create aninstance of thepygad.GA class.
Create an Instance of thepygad.GA Class¶
Once the parameters of the genetic algorithm are prepared, an instanceof thepygad.GA class can be created. Here is an example where thenumber of generations is 10.
importpygadnum_parents_mating=4num_generations=10mutation_percent_genes=5ga_instance=pygad.GA(num_generations=num_generations,num_parents_mating=num_parents_mating,initial_population=initial_population,fitness_func=fitness_func,mutation_percent_genes=mutation_percent_genes,on_generation=callback_generation)
The last step for training the neural networks using the geneticalgorithm is calling therun() method.
Run the Created Instance of thepygad.GA Class¶
By calling therun() method from thepygad.GA instance, thegenetic algorithm will iterate through the number of generationsspecified in itsnum_generations parameter.
ga_instance.run()
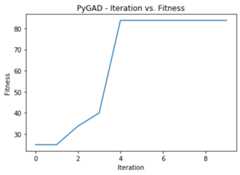
Plot the Fitness Values¶
After therun() method completes, theplot_fitness() method canbe called to show how the fitness values evolve by generation.
ga_instance.plot_fitness()
Information about the Best Solution¶
The following information about the best solution in the last populationis returned using thebest_solution() method in thepygad.GAclass.
Solution
Fitness value of the solution
Index of the solution within the population
Here is how such information is returned.
solution,solution_fitness,solution_idx=ga_instance.best_solution()print(f"Parameters of the best solution :{solution}")print(f"Fitness value of the best solution ={solution_fitness}")print(f"Index of the best solution :{solution_idx}")
...Fitnessvalueofthebestsolution=83.75Indexofthebestsolution:0Bestfitnessvaluereachedafter4generations.
Making Predictions using the Trained Weights¶
Thepygad.cnn.predict() function can be used to make predictionsusing the trained network. As printed, the network is able to predictthe labels correctly.
predictions=pygad.cnn.predict(last_layer=GANN_instance.population_networks[solution_idx],data_inputs=data_inputs)print(f"Predictions of the trained network :{predictions}")
Calculating Some Statistics¶
Based on the predictions the network made, some statistics can becalculated such as the number of correct and wrong predictions inaddition to the classification accuracy.
num_wrong=numpy.where(predictions!=data_outputs)[0]num_correct=data_outputs.size-num_wrong.sizeaccuracy=100*(num_correct/data_outputs.size)print(f"Number of correct classifications :{num_correct}.")print(f"Number of wrong classifications :{num_wrong.size}.")print(f"Classification accuracy :{accuracy}.")
Numberofcorrectclassifications:67.Numberofwrongclassifications:13.Classificationaccuracy:83.75.
Examples¶
This section gives the complete code of some examples that build andtrain neural networks using the genetic algorithm. Each subsectionbuilds a different network.
Image Classification¶
This example is discussed in theSteps to Build and Train CNN usingGenetic Algorithm section that builds the an image classifier. Itscomplete code is listed below.
importnumpyimportpygad.cnnimportpygad.gacnnimportpygad"""Convolutional neural network implementation using NumPyA tutorial that helps to get started (Building Convolutional Neural Network using NumPy from Scratch) available in these links: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/building-convolutional-neural-network-using-numpy-from-ahmed-gad https://towardsdatascience.com/building-convolutional-neural-network-using-numpy-from-scratch-b30aac50e50a https://www.kdnuggets.com/2018/04/building-convolutional-neural-network-numpy-scratch.htmlIt is also translated into Chinese: http://m.aliyun.com/yunqi/articles/585741"""deffitness_func(ga_instance,solution,sol_idx):globalGACNN_instance,data_inputs,data_outputspredictions=GACNN_instance.population_networks[sol_idx].predict(data_inputs=data_inputs)correct_predictions=numpy.where(predictions==data_outputs)[0].sizesolution_fitness=(correct_predictions/data_outputs.size)*100returnsolution_fitnessdefcallback_generation(ga_instance):globalGACNN_instance,last_fitnesspopulation_matrices=pygad.gacnn.population_as_matrices(population_networks=GACNN_instance.population_networks,population_vectors=ga_instance.population)GACNN_instance.update_population_trained_weights(population_trained_weights=population_matrices)print(f"Generation ={ga_instance.generations_completed}")print(f"Fitness ={ga_instance.best_solutions_fitness}")data_inputs=numpy.load("dataset_inputs.npy")data_outputs=numpy.load("dataset_outputs.npy")sample_shape=data_inputs.shape[1:]num_classes=4data_inputs=data_inputsdata_outputs=data_outputsinput_layer=pygad.cnn.Input2D(input_shape=sample_shape)conv_layer1=pygad.cnn.Conv2D(num_filters=2,kernel_size=3,previous_layer=input_layer,activation_function="relu")average_pooling_layer=pygad.cnn.AveragePooling2D(pool_size=5,previous_layer=conv_layer1,stride=3)flatten_layer=pygad.cnn.Flatten(previous_layer=average_pooling_layer)dense_layer2=pygad.cnn.Dense(num_neurons=num_classes,previous_layer=flatten_layer,activation_function="softmax")model=pygad.cnn.Model(last_layer=dense_layer2,epochs=1,learning_rate=0.01)model.summary()GACNN_instance=pygad.gacnn.GACNN(model=model,num_solutions=4)# GACNN_instance.update_population_trained_weights(population_trained_weights=population_matrices)# population does not hold the numerical weights of the network instead it holds a list of references to each last layer of each network (i.e. solution) in the population. A solution or a network can be used interchangeably.# If there is a population with 3 solutions (i.e. networks), then the population is a list with 3 elements. Each element is a reference to the last layer of each network. Using such a reference, all details of the network can be accessed.population_vectors=pygad.gacnn.population_as_vectors(population_networks=GACNN_instance.population_networks)# To prepare the initial population, there are 2 ways:# 1) Prepare it yourself and pass it to the initial_population parameter. This way is useful when the user wants to start the genetic algorithm with a custom initial population.# 2) Assign valid integer values to the sol_per_pop and num_genes parameters. If the initial_population parameter exists, then the sol_per_pop and num_genes parameters are useless.initial_population=population_vectors.copy()num_parents_mating=2# Number of solutions to be selected as parents in the mating pool.num_generations=10# Number of generations.mutation_percent_genes=0.1# Percentage of genes to mutate. This parameter has no action if the parameter mutation_num_genes exists.ga_instance=pygad.GA(num_generations=num_generations,num_parents_mating=num_parents_mating,initial_population=initial_population,fitness_func=fitness_func,mutation_percent_genes=mutation_percent_genes,on_generation=callback_generation)ga_instance.run()# After the generations complete, some plots are showed that summarize how the outputs/fitness values evolve over generations.ga_instance.plot_fitness()# Returning the details of the best solution.solution,solution_fitness,solution_idx=ga_instance.best_solution()print(f"Parameters of the best solution :{solution}")print(f"Fitness value of the best solution ={solution_fitness}")print(f"Index of the best solution :{solution_idx}")ifga_instance.best_solution_generation!=-1:print(f"Best fitness value reached after{ga_instance.best_solution_generation} generations.")# Predicting the outputs of the data using the best solution.predictions=GACNN_instance.population_networks[solution_idx].predict(data_inputs=data_inputs)print(f"Predictions of the trained network :{predictions}")# Calculating some statisticsnum_wrong=numpy.where(predictions!=data_outputs)[0]num_correct=data_outputs.size-num_wrong.sizeaccuracy=100*(num_correct/data_outputs.size)print(f"Number of correct classifications :{num_correct}.")print(f"Number of wrong classifications :{num_wrong.size}.")print(f"Classification accuracy :{accuracy}.")