High throughput variant libraries and machine learning yield design rules for retron gene editors
- PMID:39658047
- PMCID: PMC11754653
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1199
High throughput variant libraries and machine learning yield design rules for retron gene editors
Abstract
The bacterial retron reverse transcriptase system has served as an intracellular factory for single-stranded DNA in many biotechnological applications. In these technologies, a natural retron non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is modified to encode a template for the production of custom DNA sequences by reverse transcription. The efficiency of reverse transcription is a major limiting step for retron technologies, but we lack systematic knowledge of how to improve or maintain reverse transcription efficiency while changing the retron sequence for custom DNA production. Here, we test thousands of different modifications to the Retron-Eco1 ncRNA and measure DNA production in pooled variant library experiments, identifying regions of the ncRNA that are tolerant and intolerant to modification. We apply this new information to a specific application: the use of the retron to produce a precise genome editing donor in combination with a CRISPR-Cas9 RNA-guided nuclease (an editron). We use high-throughput libraries in Saccharomyces cerevisiae to additionally define design rules for editrons. We extend our new knowledge of retron DNA production and editron design rules to human genome editing to achieve the highest efficiency Retron-Eco1 editrons to date.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
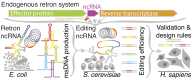

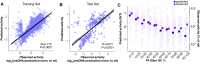
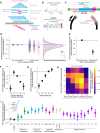
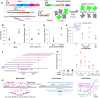
Update of
- High Throughput Variant Libraries and Machine Learning Yield Design Rules for Retron Gene Editors.Crawford KD, Khan AG, Lopez SC, Goodarzi H, Shipman SL.Crawford KD, et al.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 9:2024.07.08.602561. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.08.602561.bioRxiv. 2024.Update in:Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 11;53(2):gkae1199. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1199.PMID:39026735Free PMC article.Updated.Preprint.
Similar articles
- High Throughput Variant Libraries and Machine Learning Yield Design Rules for Retron Gene Editors.Crawford KD, Khan AG, Lopez SC, Goodarzi H, Shipman SL.Crawford KD, et al.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 9:2024.07.08.602561. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.08.602561.bioRxiv. 2024.Update in:Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 11;53(2):gkae1199. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1199.PMID:39026735Free PMC article.Updated.Preprint.
- Precise genome editing across kingdoms of life using retron-derived DNA.Lopez SC, Crawford KD, Lear SK, Bhattarai-Kline S, Shipman SL.Lopez SC, et al.Nat Chem Biol. 2022 Feb;18(2):199-206. doi: 10.1038/s41589-021-00927-y. Epub 2021 Dec 23.Nat Chem Biol. 2022.PMID:34949838Free PMC article.
- Simultaneous multi-site editing of individual genomes using retron arrays.González-Delgado A, Lopez SC, Rojas-Montero M, Fishman CB, Shipman SL.González-Delgado A, et al.Nat Chem Biol. 2024 Nov;20(11):1482-1492. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01665-7. Epub 2024 Jul 9.Nat Chem Biol. 2024.PMID:38982310Free PMC article.
- Retron Library Recombineering: Next Powerful Tool for Genome Editing after CRISPR/Cas.Kaur N, Pati PK.Kaur N, et al.ACS Synth Biol. 2024 Apr 19;13(4):1019-1025. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00667. Epub 2024 Mar 13.ACS Synth Biol. 2024.PMID:38480006Review.
- Off-Target Editing by CRISPR-Guided DNA Base Editors.Park S, Beal PA.Park S, et al.Biochemistry. 2019 Sep 10;58(36):3727-3734. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00573. Epub 2019 Aug 26.Biochemistry. 2019.PMID:31433621Free PMC article.Review.
References
- Millman A., Bernheim A., Stokar-Avihail A., Fedorenko T., Voichek M., Leavitt A., Oppenheimer-Shaanan Y., Sorek R.. Bacterial retrons function in anti-phage defense. Cell. 2020; 183:1551–1561. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Related information
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
