Loss-of-function mutation in PRMT9 causes abnormal synapse development by dysregulation of RNA alternative splicing
- PMID:38561334
- PMCID: PMC10984984
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47107-9
Loss-of-function mutation in PRMT9 causes abnormal synapse development by dysregulation of RNA alternative splicing
Abstract
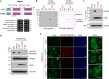
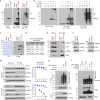
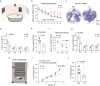
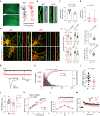
Protein arginine methyltransferase 9 (PRMT9) is a recently identified member of the PRMT family, yet its biological function remains largely unknown. Here, by characterizing an intellectual disability associated PRMT9 mutation (G189R) and establishing a Prmt9 conditional knockout (cKO) mouse model, we uncover an important function of PRMT9 in neuronal development. The G189R mutation abolishes PRMT9 methyltransferase activity and reduces its protein stability. Knockout of Prmt9 in hippocampal neurons causes alternative splicing of ~1900 genes, which likely accounts for the aberrant synapse development and impaired learning and memory in the Prmt9 cKO mice. Mechanistically, we discover a methylation-sensitive protein-RNA interaction between the arginine 508 (R508) of the splicing factor 3B subunit 2 (SF3B2), the site that is exclusively methylated by PRMT9, and the pre-mRNA anchoring site, a cis-regulatory element that is critical for RNA splicing. Additionally, using human and mouse cell lines, as well as an SF3B2 arginine methylation-deficient mouse model, we provide strong evidence that SF3B2 is the primary methylation substrate of PRMT9, thus highlighting the conserved function of the PRMT9/SF3B2 axis in regulating pre-mRNA splicing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Y.X. is a scientific cofounder of Panorama Medicine. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
- Unique Features of Human Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 9 (PRMT9) and Its Substrate RNA Splicing Factor SF3B2.Hadjikyriacou A, Yang Y, Espejo A, Bedford MT, Clarke SG.Hadjikyriacou A, et al.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jul 3;290(27):16723-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.659433. Epub 2015 May 15.J Biol Chem. 2015.PMID:25979344Free PMC article.
- PRMT9 is a type II methyltransferase that methylates the splicing factor SAP145.Yang Y, Hadjikyriacou A, Xia Z, Gayatri S, Kim D, Zurita-Lopez C, Kelly R, Guo A, Li W, Clarke SG, Bedford MT.Yang Y, et al.Nat Commun. 2015 Mar 4;6:6428. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7428.Nat Commun. 2015.PMID:25737013Free PMC article.
- Arginine methylation mediated by the Arabidopsis homolog of PRMT5 is essential for proper pre-mRNA splicing.Deng X, Gu L, Liu C, Lu T, Lu F, Lu Z, Cui P, Pei Y, Wang B, Hu S, Cao X.Deng X, et al.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Nov 2;107(44):19114-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009669107. Epub 2010 Oct 18.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010.PMID:20956294Free PMC article.
- Noncanonical functions of the serine-arginine-rich splicing factor (SR) family of proteins in development and disease.Wagner RE, Frye M.Wagner RE, et al.Bioessays. 2021 Apr;43(4):e2000242. doi: 10.1002/bies.202000242. Epub 2021 Feb 8.Bioessays. 2021.PMID:33554347Review.
- Non-Histone Arginine Methylation by Protein Arginine Methyltransferases.Al-Hamashi AA, Diaz K, Huang R.Al-Hamashi AA, et al.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020;21(7):699-712. doi: 10.2174/1389203721666200507091952.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020.PMID:32379587Free PMC article.Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Related information
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
