Third-generation rabies viral vectors allow nontoxic retrograde targeting of projection neurons with greatly increased efficiency
- PMID:37989085
- PMCID: PMC10694603
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100644
Third-generation rabies viral vectors allow nontoxic retrograde targeting of projection neurons with greatly increased efficiency
Abstract
Rabies viral vectors have become important components of the systems neuroscience toolkit, allowing both direct retrograde targeting of projection neurons and monosynaptic tracing of inputs to defined postsynaptic populations, but the rapid cytotoxicity of first-generation (ΔG) vectors limits their use to short-term experiments. We recently introduced second-generation, double-deletion-mutant (ΔGL) rabies viral vectors, showing that they efficiently retrogradely infect projection neurons and express recombinases effectively but with little to no detectable toxicity; more recently, we have shown that ΔGL viruses can be used for monosynaptic tracing with far lower cytotoxicity than the first-generation system. Here, we introduce third-generation (ΔL) rabies viral vectors, which appear to be as nontoxic as second-generation ones but have the major advantage of growing to much higher titers, resulting in significantly increased numbers of retrogradely labeled neurons in vivo.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests I.R.W. is a consultant for Monosynaptix, LLC, advising on the design of neuroscientific experiments.
Figures

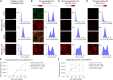
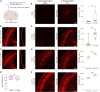
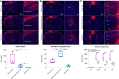

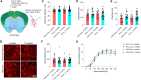
Comment in
- Third-generation rabies viral vectors have low toxicity and improved efficiency as retrograde labeling tools.Schwarz LA.Schwarz LA.Cell Rep Methods. 2023 Nov 20;3(11):100646. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100646.Cell Rep Methods. 2023.PMID:37989082Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- Rabies virus-based barcoded neuroanatomy resolved by single-cell RNA and in situ sequencing.Zhang A, Jin L, Yao S, Matsuyama M, van Velthoven CTJ, Sullivan HA, Sun N, Kellis M, Tasic B, Wickersham I, Chen X.Zhang A, et al.Elife. 2024 Feb 6;12:RP87866. doi: 10.7554/eLife.87866.Elife. 2024.PMID:38319699Free PMC article.
- Nontoxic, double-deletion-mutant rabies viral vectors for retrograde targeting of projection neurons.Chatterjee S, Sullivan HA, MacLennan BJ, Xu R, Hou Y, Lavin TK, Lea NE, Michalski JE, Babcock KR, Dietrich S, Matthews GA, Beyeler A, Calhoon GG, Glober G, Whitesell JD, Yao S, Cetin A, Harris JA, Zeng H, Tye KM, Reid RC, Wickersham IR.Chatterjee S, et al.Nat Neurosci. 2018 Apr;21(4):638-646. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0091-7. Epub 2018 Mar 5.Nat Neurosci. 2018.PMID:29507411Free PMC article.
- A rabies virus-based toolkit for efficient retrograde labeling and monosynaptic tracing.Lin KZ, Li L, Ma WY, Yang X, Han ZP, Luo NS, Wang J, Xu FQ.Lin KZ, et al.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Aug;18(8):1827-1833. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.358618.Neural Regen Res. 2023.PMID:36751812Free PMC article.
- Organization of dopamine and serotonin system: Anatomical and functional mapping of monosynaptic inputs using rabies virus.Ogawa SK, Watabe-Uchida M.Ogawa SK, et al.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2018 Nov;174:9-22. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2017.05.001. Epub 2017 May 2.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2018.PMID:28476484Review.
- G gene-deficient single-round rabies viruses for neuronal circuit analysis.Ghanem A, Conzelmann KK.Ghanem A, et al.Virus Res. 2016 May 2;216:41-54. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.05.023. Epub 2015 Jun 8.Virus Res. 2016.PMID:26065596Review.
Cited by
- Long-term labeling and imaging of synaptically connected neuronal networks in vivo using double-deletion-mutant rabies viruses.Jin L, Sullivan HA, Zhu M, Lavin TK, Matsuyama M, Fu X, Lea NE, Xu R, Hou Y, Rutigliani L, Pruner M, Babcock KR, Ip JPK, Hu M, Daigle TL, Zeng H, Sur M, Feng G, Wickersham IR.Jin L, et al.Nat Neurosci. 2024 Feb;27(2):373-383. doi: 10.1038/s41593-023-01545-8. Epub 2024 Jan 11.Nat Neurosci. 2024.PMID:38212587Free PMC article.
- Rabies virus-based barcoded neuroanatomy resolved by single-cell RNA andin situ sequencing.Zhang A, Jin L, Yao S, Matsuyama M, van Velthoven C, Sullivan H, Sun N, Kellis M, Tasic B, Wickersham IR, Chen X.Zhang A, et al.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 10:2023.03.16.532873. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.16.532873.bioRxiv. 2023.Update in:Elife. 2024 Feb 06;12:RP87866. doi: 10.7554/eLife.87866.PMID:36993334Free PMC article.Updated.Preprint.
- Third-generation rabies viral vectors have low toxicity and improved efficiency as retrograde labeling tools.Schwarz LA.Schwarz LA.Cell Rep Methods. 2023 Nov 20;3(11):100646. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100646.Cell Rep Methods. 2023.PMID:37989082Free PMC article.
- Rabies virus-based barcoded neuroanatomy resolved by single-cell RNA and in situ sequencing.Zhang A, Jin L, Yao S, Matsuyama M, van Velthoven CTJ, Sullivan HA, Sun N, Kellis M, Tasic B, Wickersham I, Chen X.Zhang A, et al.Elife. 2024 Feb 6;12:RP87866. doi: 10.7554/eLife.87866.Elife. 2024.PMID:38319699Free PMC article.
References
- Jin L., Sullivan H.A., Zhu M., Lavin T.K., Matsuyama M., Lea N.E., Xu R., Hou Y., Rutigliani L., Pruner M., et al. Long-term labeling and imaging of synaptically-connected neuronal networks <em>in vivo</em> using nontoxic, double-deletion-mutant rabies viruses. bioRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.12.04.471186. Preprint at. - DOI
- Chatterjee S., Sullivan H.A., MacLennan B.J., Xu R., Hou Y., Lavin T.K., Lea N.E., Michalski J.E., Babcock K.R., Dietrich S., et al. Nontoxic, double-deletion-mutant rabies viral vectors for retrograde targeting of projection neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2018;21:638–646. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0091-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Related information
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
