Detection of Stable Elite Haplotypes and Potential Candidate Genes of Boll Weight Across Multiple Environments via GWAS in Upland Cotton
- PMID:35769298
- PMCID: PMC9234699
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.929168
Detection of Stable Elite Haplotypes and Potential Candidate Genes of Boll Weight Across Multiple Environments via GWAS in Upland Cotton
Abstract
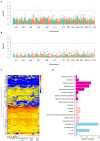
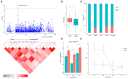
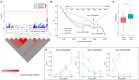
Boll weight (BW) is a key determinant of yield component traits in cotton, and understanding the genetic mechanism of BW could contribute to the progress of cotton fiber yield. Although many yield-related quantitative trait loci (QTLs) responsible for BW have been determined, knowledge of the genes controlling cotton yield remains limited. Here, association mapping based on 25,169 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and 2,315 insertions/deletions (InDels) was conducted to identify high-quality QTLs responsible for BW in a global collection of 290 diverse accessions, and BW was measured in nine different environments. A total of 19 significant markers were detected, and 225 candidate genes within a 400 kb region (± 200 kb surrounding each locus) were predicted. Of them, two major QTLs with highly phenotypic variation explanation on chromosomes A08 and D13 were identified among multiple environments. Furthermore, we found that two novel candidate genes (Ghir_A08G009110 andGhir_D13G023010) were associated with BW and thatGhir_D13G023010 was involved in artificial selection during cotton breeding by population genetic analysis. The transcription level analyses showed that these two genes were significantly differentially expressed between high-BW accession and low-BW accession during the ovule development stage. Thus, these results reveal valuable information for clarifying the genetic basics of the control of BW, which are useful for increasing yield by molecular marker-assisted selection (MAS) breeding in cotton.
Keywords: MAS; SNP; association mapping; boll weight; candidate genes.
Copyright © 2022 Feng, Li, Tang, Liu, Ji, Sun, Liu, Zhao, Huang, Zhang, Zhang and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
- Lint percentage and boll weight QTLs in three excellent upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum): ZR014121, CCRI60, and EZ60.Niu H, Kuang M, Huang L, Shang H, Yuan Y, Ge Q.Niu H, et al.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Apr 5;23(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04147-5.BMC Plant Biol. 2023.PMID:37020180Free PMC article.
- An RTM-GWAS procedure reveals the QTL alleles and candidate genes for three yield-related traits in upland cotton.Su J, Wang C, Ma Q, Zhang A, Shi C, Liu J, Zhang X, Yang D, Ma X.Su J, et al.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Sep 7;20(1):416. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02613-y.BMC Plant Biol. 2020.PMID:32894064Free PMC article.
- High-density linkage map construction and QTL analyses for fiber quality, yield and morphological traits using CottonSNP63K array in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.).Zhang K, Kuraparthy V, Fang H, Zhu L, Sood S, Jones DC.Zhang K, et al.BMC Genomics. 2019 Nov 21;20(1):889. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6214-z.BMC Genomics. 2019.PMID:31771502Free PMC article.
- Genome-wide association study reveals novel quantitative trait loci and candidate genes of lint percentage in upland cotton based on the CottonSNP80K array.Chen Y, Gao Y, Chen P, Zhou J, Zhang C, Song Z, Huo X, Du Z, Gong J, Zhao C, Wang S, Zhang J, Wang F, Zhang J.Chen Y, et al.Theor Appl Genet. 2022 Jul;135(7):2279-2295. doi: 10.1007/s00122-022-04111-1. Epub 2022 May 16.Theor Appl Genet. 2022.PMID:35570221Review.
- Fiber Quality Improvement in Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.): Quantitative Trait Loci Mapping and Marker Assisted Selection Application.Ijaz B, Zhao N, Kong J, Hua J.Ijaz B, et al.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Dec 11;10:1585. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01585. eCollection 2019.Front Plant Sci. 2019.PMID:31921240Free PMC article.Review.
Cited by
- Identification of miRNAs and their target genes associated with improved maize seed vigor induced by gibberellin.Jin Y, Wang B, Tian L, Zhao L, Guo S, Zhang H, Xu L, Han Z.Jin Y, et al.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 13;13:1008872. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1008872. eCollection 2022.Front Plant Sci. 2022.PMID:36176685Free PMC article.
- Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase GhCDPK16 Exerts a Positive Regulatory Role in Enhancing Drought Tolerance in Cotton.Yan M, Chai M, Li L, Dong Z, Jin H, Tan M, Ye Z, Yu S, Feng Z.Yan M, et al.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 30;25(15):8308. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158308.Int J Mol Sci. 2024.PMID:39125876Free PMC article.
- Identification of novel candidate loci and genes for seed vigor-related traits in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) via GWAS.Li L, Hu Y, Wang Y, Zhao S, You Y, Liu R, Wang J, Yan M, Zhao F, Huang J, Yu S, Feng Z.Li L, et al.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Sep 1;14:1254365. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1254365. eCollection 2023.Front Plant Sci. 2023.PMID:37719213Free PMC article.
- Genome-wide association study of fiber yield-related traits uncovers the novel genomic regions and candidate genes in Indian upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.).Joshi B, Singh S, Tiwari GJ, Kumar H, Boopathi NM, Jaiswal S, Adhikari D, Kumar D, Sawant SV, Iquebal MA, Jena SN.Joshi B, et al.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Oct 23;14:1252746. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1252746. eCollection 2023.Front Plant Sci. 2023.PMID:37941674Free PMC article.
- Genome-wide association study reveals novel QTLs and candidate genes for seed vigor in rice.Dai L, Lu X, Shen L, Guo L, Zhang G, Gao Z, Zhu L, Hu J, Dong G, Ren D, Zhang Q, Zeng D, Qian Q, Li Q.Dai L, et al.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 26;13:1005203. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1005203. eCollection 2022.Front Plant Sci. 2022.PMID:36388599Free PMC article.
References
- Bates D., Mächler M., Bolker B., Walker S. (2014). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 67, 1–48. 10.18637/jss.v067.i01 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
