Biochemical characterization of a novel oxidatively stable, halotolerant, and high-alkaline subtilisin from Alkalihalobacillus okhensis Kh10-101T
- PMID:35727859
- PMCID: PMC9527586
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.13457
Biochemical characterization of a novel oxidatively stable, halotolerant, and high-alkaline subtilisin from Alkalihalobacillus okhensis Kh10-101T
Abstract
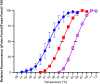
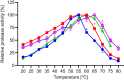
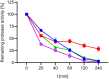
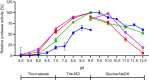
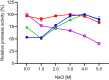
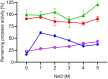
Halophilic and halotolerant microorganisms represent a promising source of salt-tolerant enzymes suitable for various biotechnological applications where high salt concentrations would otherwise limit enzymatic activity. Considering the current growing enzyme market and the need for more efficient and new biocatalysts, the present study aimed at the characterization of a high-alkaline subtilisin from Alkalihalobacillus okhensis Kh10-101T . The protease gene was cloned and expressed in Bacillus subtilis DB104. The recombinant protease SPAO with 269 amino acids belongs to the subfamily of high-alkaline subtilisins. The biochemical characteristics of purified SPAO were analyzed in comparison with subtilisin Carlsberg, Savinase, and BPN'. SPAO, a monomer with a molecular mass of 27.1 kDa, was active over a wide range of pH 6.0-12.0 and temperature 20-80 °C, optimally at pH 9.0-9.5 and 55 °C. The protease is highly oxidatively stable to hydrogen peroxide and retained 58% of residual activity when incubated at 10 °C with 5% (v/v) H2 O2 for 1 h while stimulated at 1% (v/v) H2 O2 . Furthermore, SPAO was very stable and active at NaCl concentrations up to 5.0 m. This study demonstrates the potential of SPAO for biotechnological applications in the future.
Keywords: Alkalihalobacillus okhensis; detergent protease; halotolerant protease; high-alkaline subtilisin; oxidative stable protease.
© 2022 The Authors. FEBS Open Bio published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
- New robust subtilisins from halotolerant and halophilic Bacillaceae.Falkenberg F, Voß L, Bott M, Bongaerts J, Siegert P.Falkenberg F, et al.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Jun;107(12):3939-3954. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12553-w. Epub 2023 May 9.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023.PMID:37160606Free PMC article.
- Biochemical characterisation of a novel broad pH spectrum subtilisin from Fictibacillus arsenicus DSM 15822T.Falkenberg F, Kohn S, Bott M, Bongaerts J, Siegert P.Falkenberg F, et al.FEBS Open Bio. 2023 Nov;13(11):2035-2046. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13701. Epub 2023 Sep 7.FEBS Open Bio. 2023.PMID:37649135Free PMC article.
- Biochemical and molecular characterization of a detergent-stable serine alkaline protease from Bacillus pumilus CBS with high catalytic efficiency.Jaouadi B, Ellouz-Chaabouni S, Rhimi M, Bejar S.Jaouadi B, et al.Biochimie. 2008 Sep;90(9):1291-305. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2008.03.004. Epub 2008 Mar 20.Biochimie. 2008.PMID:18397761
- Bacterial alkaline proteases: molecular approaches and industrial applications.Gupta R, Beg QK, Lorenz P.Gupta R, et al.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002 Jun;59(1):15-32. doi: 10.1007/s00253-002-0975-y. Epub 2002 Apr 20.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002.PMID:12073127Review.
- Operative utility of salt-stable proteases of halophilic and halotolerant bacteria in the biotechnology sector.Mokashe N, Chaudhari B, Patil U.Mokashe N, et al.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Oct 1;117:493-522. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.217. Epub 2018 May 30.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018.PMID:29857102Review.
Cited by
- In silico and experimental characterization of a new polyextremophilic subtilisin-like protease fromMicrobacterium metallidurans and its application as a laundry detergent additive.Gorrab A, Ouertani R, Hammami K, Souii A, Kallel F, Masmoudi AS, Cherif A, Neifar M.Gorrab A, et al.3 Biotech. 2024 Sep;14(9):200. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-04043-1. Epub 2024 Aug 12.3 Biotech. 2024.PMID:39144069
- Novel recombinant aminoacylase from Paraburkholderia monticola capable of N-acyl-amino acid synthesis.Haeger G, Jolmes T, Oyen S, Jaeger KE, Bongaerts J, Schörken U, Siegert P.Haeger G, et al.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec;108(1):93. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12868-8. Epub 2024 Jan 10.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024.PMID:38204129Free PMC article.
- Phylogenetic survey of the subtilase family and a data-mining-based search for new subtilisins fromBacillaceae.Falkenberg F, Bott M, Bongaerts J, Siegert P.Falkenberg F, et al.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 26;13:1017978. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1017978. eCollection 2022.Front Microbiol. 2022.PMID:36225363Free PMC article.
- New robust subtilisins from halotolerant and halophilic Bacillaceae.Falkenberg F, Voß L, Bott M, Bongaerts J, Siegert P.Falkenberg F, et al.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Jun;107(12):3939-3954. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12553-w. Epub 2023 May 9.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023.PMID:37160606Free PMC article.
- Biochemical characterization of immobilized recombinant subtilisin and synthesis and functional characterization of recombinant subtilisin capped silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles.Shettar SS, Bagewadi ZK, Yunus Khan TM, Mohamed Shamsudeen S, Kolvekar HN.Shettar SS, et al.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2024 Jul;31(7):104009. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2024.104009. Epub 2024 May 4.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2024.PMID:38766505Free PMC article.
References
- Gupta R, Beg QK, Lorenz P. Bacterial alkaline proteases: molecular approaches and industrial applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002;59:15–32. - PubMed
- Naveed M, Nadeem F, Mehmood T, Bilal M, Anwar Z, Amjad F. Protease—a versatile and ecofriendly biocatalyst with multi‐industrial applications: an updated review. Catal Lett. 2021;151:307–23.
- Saeki K, Magallones MV, Takimura Y, Hatada Y, Kobayashi T, Kawai S, et al. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of a new subtilisin from an alkaliphilic Bacillus isolate. Curr Microbiol. 2003;47:337–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Related information
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
