Programmable deletion, replacement, integration and inversion of large DNA sequences with twin prime editing
- PMID:34887556
- PMCID: PMC9117393
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-021-01133-w
Programmable deletion, replacement, integration and inversion of large DNA sequences with twin prime editing
Abstract
The targeted deletion, replacement, integration or inversion of genomic sequences could be used to study or treat human genetic diseases, but existing methods typically require double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs) that lead to undesired consequences, including uncontrolled indel mixtures and chromosomal abnormalities. Here we describe twin prime editing (twinPE), a DSB-independent method that uses a prime editor protein and two prime editing guide RNAs (pegRNAs) for the programmable replacement or excision of DNA sequences at endogenous human genomic sites. The two pegRNAs template the synthesis of complementary DNA flaps on opposing strands of genomic DNA, which replace the endogenous DNA sequence between the prime-editor-induced nick sites. When combined with a site-specific serine recombinase, twinPE enabled targeted integration of gene-sized DNA plasmids (>5,000 bp) and targeted sequence inversions of 40 kb in human cells. TwinPE expands the capabilities of precision gene editing and might synergize with other tools for the correction or complementation of large or complex human pathogenic alleles.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
D.R.L. is a consultant and equity holder of Beam Therapeutics, Prime Medicine, Pairwise Plants, and Chroma Medicine, companies that use genome editing or genome engineering technologies. A.V.A., C.J.P., and J.M.L. are currently employees at Prime Medicine. A.V.A., X.D.G., C.J.P., and D.R. L. have filed patent applications on twinPE and prime editing through the Broad Institute.
Figures
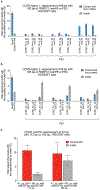



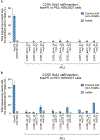
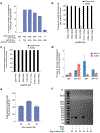








Similar articles
- Deletion and replacement of long genomic sequences using prime editing.Jiang T, Zhang XO, Weng Z, Xue W.Jiang T, et al.Nat Biotechnol. 2022 Feb;40(2):227-234. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01026-y. Epub 2021 Oct 14.Nat Biotechnol. 2022.PMID:34650270Free PMC article.
- Twin prime editor: seamless repair without damage.Awan MJA, Ali Z, Amin I, Mansoor S.Awan MJA, et al.Trends Biotechnol. 2022 Apr;40(4):374-376. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2022.01.013. Epub 2022 Feb 10.Trends Biotechnol. 2022.PMID:35153078
- Precise genomic deletions using paired prime editing.Choi J, Chen W, Suiter CC, Lee C, Chardon FM, Yang W, Leith A, Daza RM, Martin B, Shendure J.Choi J, et al.Nat Biotechnol. 2022 Feb;40(2):218-226. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01025-z. Epub 2021 Oct 14.Nat Biotechnol. 2022.PMID:34650269Free PMC article.
- In vivo somatic cell base editing and prime editing.Newby GA, Liu DR.Newby GA, et al.Mol Ther. 2021 Nov 3;29(11):3107-3124. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.09.002. Epub 2021 Sep 10.Mol Ther. 2021.PMID:34509669Free PMC article.Review.
- The Development, Optimization and Future of Prime Editing.Petrova IO, Smirnikhina SA.Petrova IO, et al.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 1;24(23):17045. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317045.Int J Mol Sci. 2023.PMID:38069367Free PMC article.Review.
Cited by
- Mammalian Antigen Display for Pandemic Countermeasures.Quezada A, Annapareddy A, Javanmardi K, Cooper J, Finkelstein IJ.Quezada A, et al.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2762:191-216. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3666-4_12.Methods Mol Biol. 2024.PMID:38315367
- Roles of Skeletal Muscle in Development: A Bioinformatics and Systems Biology Overview.Milanese JS, Marcotte R, Costain WJ, Kablar B, Drouin S.Milanese JS, et al.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2023;236:21-55. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-38215-4_2.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2023.PMID:37955770
- Targeted genomic translocations and inversions generated using a paired prime editing strategy.Kweon J, Hwang HY, Ryu H, Jang AH, Kim D, Kim Y.Kweon J, et al.Mol Ther. 2023 Jan 4;31(1):249-259. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.09.008. Epub 2022 Sep 15.Mol Ther. 2023.PMID:36114670Free PMC article.
- Efficient Genome Editing with Chimeric Oligonucleotide-Directed Editing.Nguyen LT, Rakestraw NR, Pizzano BLM, Young CB, Huang Y, Beerensson KT, Fang A, Antal SG, Anamisis KV, Peggs CMD, Yan J, Jing Y, Burdine RD, Adamson B, Toettcher JE, Myhrvold C, Jain PK.Nguyen LT, et al.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 10:2024.07.09.602710. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.09.602710.bioRxiv. 2024.PMID:39026836Free PMC article.Preprint.
- Rare immune diseases paving the road for genome editing-based precision medicine.Pavel-Dinu M, Borna S, Bacchetta R.Pavel-Dinu M, et al.Front Genome Ed. 2023 Feb 8;5:1114996. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2023.1114996. eCollection 2023.Front Genome Ed. 2023.PMID:36846437Free PMC article.Review.
References
Methods References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Related information
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
