Tipping points induced by parameter drift in an excitable ocean model
- PMID:34045519
- PMCID: PMC8159979
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-90138-1
Tipping points induced by parameter drift in an excitable ocean model
Erratum in
- Author Correction: Tipping points induced by parameter drift in an excitable ocean model.Pierini S, Ghil M.Pierini S, et al.Sci Rep. 2022 May 18;12(1):8303. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12470-4.Sci Rep. 2022.PMID:35585180Free PMC article.No abstract available.
Abstract
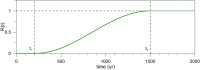
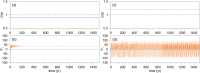
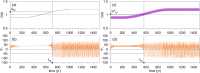
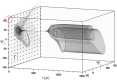
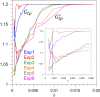
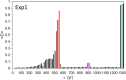
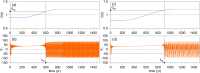
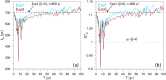
Numerous systems in the climate sciences and elsewhere are excitable, exhibiting coexistence of and transitions between a basic and an excited state. We examine the role of tipping between two such states in an excitable low-order ocean model. Ensemble simulations are used to obtain the model's pullback attractor (PBA) and its properties, as a function of a forcing parameter [Formula: see text] and of the steepness [Formula: see text] of a climatological drift in the forcing. The tipping time [Formula: see text] is defined as the time at which the transition to relaxation oscillations (ROs) arises: at constant forcing this occurs at [Formula: see text]. As the steepness [Formula: see text] decreases, [Formula: see text] is delayed and the corresponding forcing amplitude decreases, while remaining always above [Formula: see text]. With periodic perturbations, that amplitude depends solely on [Formula: see text] over a significant range of parameters: this provides an example of rate-induced tipping in an excitable system. Nonlinear resonance occurs for periods comparable to the RO time scale. Coexisting PBAs and total independence from initial states are found for subsets of parameter space. In the broader context of climate dynamics, the parameter drift herein stands for the role of anthropogenic forcing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
- Future precipitation increase constrained by climatological pattern of cloud effect.Zhou W, Leung LR, Siler N, Lu J.Zhou W, et al.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 11;14(1):6363. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42181-x.Nat Commun. 2023.PMID:37821452Free PMC article.
- Quantifying stochastic uncertainty in detection time of human-caused climate signals.Santer BD, Fyfe JC, Solomon S, Painter JF, Bonfils C, Pallotta G, Zelinka MD.Santer BD, et al.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Oct 1;116(40):19821-19827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1904586116. Epub 2019 Sep 16.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019.PMID:31527233Free PMC article.
- Global reconstruction reduces the uncertainty of oceanic nitrous oxide emissions and reveals a vigorous seasonal cycle.Yang S, Chang BX, Warner MJ, Weber TS, Bourbonnais AM, Santoro AE, Kock A, Sonnerup RE, Bullister JL, Wilson ST, Bianchi D.Yang S, et al.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jun 2;117(22):11954-11960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1921914117. Epub 2020 May 18.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020.PMID:32424089Free PMC article.
- Modes of Pangean lake level cyclicity driven by astronomical climate pacing modulated by continental position andpCO[Formula: see text].Landwehrs J, Feulner G, Willeit M, Petri S, Sames B, Wagreich M, Whiteside JH, Olsen PE.Landwehrs J, et al.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Nov 16;119(46):e2203818119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2203818119. Epub 2022 Nov 7.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022.PMID:36343239Free PMC article.
- The Global S[Formula: see text] Tide in Earth's Nutation.Schindelegger M, Einšpigel D, Salstein D, Böhm J.Schindelegger M, et al.Surv Geophys. 2016;37:643-680. doi: 10.1007/s10712-016-9365-3. Epub 2016 Feb 15.Surv Geophys. 2016.PMID:27471334Free PMC article.Review.
References
- Hide R. Some experiments on thermal convection in a rotating liquid. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1953;79:161.
- Stommel H. Thermohaline convection with two stable regimes of flow. Tellus. 1961;2:244–230.
- Lorenz EN. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963;20:130–141.
- Veronis G. An analysis of the wind-driven ocean circulation with a limited number of Fourier components. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963;20:577–593.
- Ghil M, Read P, Smith L. Geophysical flows as dynamical systems: the influence of Hide’s experiments. Astron. Geophys. 2010;51:4–28.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
