Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease Severity with fMRI Images Using Robust Multitask Feature Extraction Method and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
- PMID:34007305
- PMCID: PMC8100410
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5514839
Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease Severity with fMRI Images Using Robust Multitask Feature Extraction Method and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
Abstract
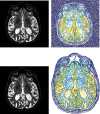
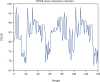
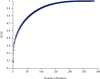
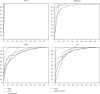
The automatic diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease plays an important role in human health, especially in its early stage. Because it is a neurodegenerative condition, Alzheimer's disease seems to have a long incubation period. Therefore, it is essential to analyze Alzheimer's symptoms at different stages. In this paper, the classification is done with several methods of machine learning consisting ofK-nearest neighbor (KNN), support vector machine (SVM), decision tree (DT), linear discrimination analysis (LDA), and random forest (RF). Moreover, novel convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture is presented to diagnose Alzheimer's severity. The relationship between Alzheimer's patients' functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) images and their scores on the MMSE is investigated to achieve the aim. The feature extraction is performed based on the robust multitask feature learning algorithm. The severity is also calculated based on the Mini-Mental State Examination score, including low, mild, moderate, and severe categories. Results show that the accuracy of the KNN, SVM, DT, LDA, RF, and presented CNN method is 77.5%, 85.8%, 91.7%, 79.5%, 85.1%, and 96.7%, respectively. Moreover, for the presented CNN architecture, the sensitivity of low, mild, moderate, and severe status of Alzheimer patients is 98.1%, 95.2%,89.0%, and 87.5%, respectively. Based on the findings, the presented CNN architecture classifier outperforms other methods and can diagnose the severity and stages of Alzheimer's disease with maximum accuracy.
Copyright © 2021 Morteza Amini et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no financial or other conflicts of interest in this research and its publication.
Figures



Similar articles
- 3D-Deep Learning Based Automatic Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease with Joint MMSE Prediction Using Resting-State fMRI.Duc NT, Ryu S, Qureshi MNI, Choi M, Lee KH, Lee B.Duc NT, et al.Neuroinformatics. 2020 Jan;18(1):71-86. doi: 10.1007/s12021-019-09419-w.Neuroinformatics. 2020.PMID:31093956
- A deeply supervised adaptable neural network for diagnosis and classification of Alzheimer's severity using multitask feature extraction.Ahmadi M, Javaheri D, Khajavi M, Danesh K, Hur J.Ahmadi M, et al.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 26;19(3):e0297996. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297996. eCollection 2024.PLoS One. 2024.PMID:38530836Free PMC article.
- Automated MRI-Based Deep Learning Model for Detection of Alzheimer's Disease Process.Feng W, Halm-Lutterodt NV, Tang H, Mecum A, Mesregah MK, Ma Y, Li H, Zhang F, Wu Z, Yao E, Guo X.Feng W, et al.Int J Neural Syst. 2020 Jun;30(6):2050032. doi: 10.1142/S012906572050032X.Int J Neural Syst. 2020.PMID:32498641
- Comparison review of image classification techniques for early diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy.Wangweera C, Zanini P.Wangweera C, et al.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024 Sep 5;10(6). doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/ad7267.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024.PMID:39173657Review.
- Conventional machine learning and deep learning in Alzheimer's disease diagnosis using neuroimaging: A review.Zhao Z, Chuah JH, Lai KW, Chow CO, Gochoo M, Dhanalakshmi S, Wang N, Bao W, Wu X.Zhao Z, et al.Front Comput Neurosci. 2023 Feb 6;17:1038636. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2023.1038636. eCollection 2023.Front Comput Neurosci. 2023.PMID:36814932Free PMC article.Review.
Cited by
- Dual Semi-Supervised Learning for Classification of Alzheimer's Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment Based on Neuropsychological Data.Wang Y, Gu X, Hou W, Zhao M, Sun L, Guo C.Wang Y, et al.Brain Sci. 2023 Feb 10;13(2):306. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13020306.Brain Sci. 2023.PMID:36831850Free PMC article.
- Single and Combined Neuroimaging Techniques for Alzheimer's Disease Detection.Amini M, Pedram MM, Moradi A, Jamshidi M, Ouchani M.Amini M, et al.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021 Jul 13;2021:9523039. doi: 10.1155/2021/9523039. eCollection 2021.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021.PMID:34335726Free PMC article.Review.
- Connectome-based biophysics models of Alzheimer's disease diagnosis and prognosis.Torok J, Anand C, Verma P, Raj A.Torok J, et al.Transl Res. 2023 Apr;254:13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2022.08.008. Epub 2022 Aug 27.Transl Res. 2023.PMID:36031051Free PMC article.Review.
- Deep Learning-Based Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease.Saleem TJ, Zahra SR, Wu F, Alwakeel A, Alwakeel M, Jeribi F, Hijji M.Saleem TJ, et al.J Pers Med. 2022 May 18;12(5):815. doi: 10.3390/jpm12050815.J Pers Med. 2022.PMID:35629237Free PMC article.Review.
- Differential diagnosis of frontotemporal dementia subtypes with explainable deep learning on structural MRI.Ma D, Stocks J, Rosen H, Kantarci K, Lockhart SN, Bateman JR, Craft S, Gurcan MN, Popuri K, Beg MF, Wang L; ALLFTD consortium.Ma D, et al.Front Neurosci. 2024 Feb 7;18:1331677. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1331677. eCollection 2024.Front Neurosci. 2024.PMID:38384484Free PMC article.
References
- Gardini S., Venneri A., Sambataro F., et al. Increased functional connectivity in the default mode network in mild cognitive impairment: a maladaptive compensatory mechanism associated with poor semantic memory performance. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2015;45(2):457–470. doi: 10.3233/JAD-142547. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Related information
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
