Development of Anti-Virulence Therapeutics against Mono-ADP-Ribosyltransferase Toxins
- PMID:33375750
- PMCID: PMC7824265
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins13010016
Development of Anti-Virulence Therapeutics against Mono-ADP-Ribosyltransferase Toxins
Abstract
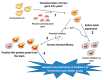
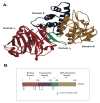
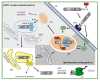
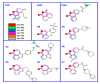
Mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase toxins are often key virulence factors produced by pathogenic bacteria as tools to compromise the target host cell. These toxins are enzymes that use host cellular NAD+ as the substrate to modify a critical macromolecule target in the host cell machinery. This post-translational modification of the target macromolecule (usually protein or DNA) acts like a switch to turn the target activity on or off resulting in impairment of a critical process or pathway in the host. One approach to stymie bacterial pathogens is to curtail the toxic action of these factors by designing small molecules that bind tightly to the enzyme active site and prevent catalytic function. The inactivation of these toxins/enzymes is targeted for the site of action within the host cell and small molecule therapeutics can function as anti-virulence agents by disarming the pathogen. This represents an alternative strategy to antibiotic therapy with the potential as a paradigm shift that may circumvent multi-drug resistance in the offending microbe. In this review, work that has been accomplished during the past two decades on this approach to develop anti-virulence compounds against mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase toxins will be discussed.
Keywords: anti-virulence agents; bacterial toxins; drug discovery; mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase toxins; protein crystallography; virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
- A Structural Approach to Anti-Virulence: A Discovery Pipeline.McCarthy M, Goncalves M, Powell H, Morey B, Turner M, Merrill AR.McCarthy M, et al.Microorganisms. 2021 Dec 4;9(12):2514. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9122514.Microorganisms. 2021.PMID:34946116Free PMC article.
- Newly discovered and characterized antivirulence compounds inhibit bacterial mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase toxins.Turgeon Z, Jørgensen R, Visschedyk D, Edwards PR, Legree S, McGregor C, Fieldhouse RJ, Mangroo D, Schapira M, Merrill AR.Turgeon Z, et al.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Mar;55(3):983-91. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01164-10. Epub 2010 Dec 6.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011.PMID:21135177Free PMC article.
- Molecular mechanisms of the cytotoxicity of ADP-ribosylating toxins.Deng Q, Barbieri JT.Deng Q, et al.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2008;62:271-88. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.62.081307.162848.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2008.PMID:18785839Review.
- Several New Putative Bacterial ADP-Ribosyltransferase Toxins Are Revealed from In Silico Data Mining, Including the Novel Toxin Vorin, Encoded by the Fire Blight PathogenErwinia amylovora.Tremblay O, Thow Z, Merrill AR.Tremblay O, et al.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Dec 11;12(12):792. doi: 10.3390/toxins12120792.Toxins (Basel). 2020.PMID:33322547Free PMC article.
- A role of intracellular mono-ADP-ribosylation in cancer biology.Scarpa ES, Fabrizio G, Di Girolamo M.Scarpa ES, et al.FEBS J. 2013 Aug;280(15):3551-62. doi: 10.1111/febs.12290. Epub 2013 May 10.FEBS J. 2013.PMID:23590234Review.
Cited by
- Synthesis of an Anti-CD7 Recombinant Immunotoxin Based on PE24 in CHO andE. coli Cell-Free Systems.Krebs SK, Stech M, Jorde F, Rakotoarinoro N, Ramm F, Marinoff S, Bahrke S, Danielczyk A, Wüstenhagen DA, Kubick S.Krebs SK, et al.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 8;23(22):13697. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213697.Int J Mol Sci. 2022.PMID:36430170Free PMC article.
- The DarT/DarG Toxin-Antitoxin ADP-Ribosylation System as a Novel Target for a Rational Design of Innovative Antimicrobial Strategies.Catara G, Caggiano R, Palazzo L.Catara G, et al.Pathogens. 2023 Feb 2;12(2):240. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12020240.Pathogens. 2023.PMID:36839512Free PMC article.
- A Structural Approach to Anti-Virulence: A Discovery Pipeline.McCarthy M, Goncalves M, Powell H, Morey B, Turner M, Merrill AR.McCarthy M, et al.Microorganisms. 2021 Dec 4;9(12):2514. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9122514.Microorganisms. 2021.PMID:34946116Free PMC article.
- Anti-Virulence Strategy against the Honey Bee Pathogenic BacteriumPaenibacillus larvae via Small Molecule Inhibitors of the Bacterial Toxin Plx2A.Ebeling J, Pieper F, Göbel J, Knispel H, McCarthy M, Goncalves M, Turner M, Merrill AR, Genersch E.Ebeling J, et al.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Aug 29;13(9):607. doi: 10.3390/toxins13090607.Toxins (Basel). 2021.PMID:34564612Free PMC article.
References
- Habboush Y., Guzman N. Antibiotic Resistance. StatPearls; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2020.
- Talbot G.H., Bradley J., Edwards J.E., Jr., Gilbert D., Scheld M., Bartlett J.G. Bad bugs need drugs: An update on the development pipeline from the Antimicrobial Availability Task Force of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006;42:657–668. doi: 10.1086/499819. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Related information
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
