Quarantine Vehicle Scheduling for Transferring High-Risk Individuals in Epidemic Areas
- PMID:32230995
- PMCID: PMC7177222
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17072275
Quarantine Vehicle Scheduling for Transferring High-Risk Individuals in Epidemic Areas
Abstract
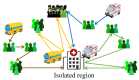
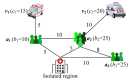
In a large-scale epidemic outbreak, there can be many high-risk individuals to be transferred for medical isolation in epidemic areas. Typically, the individuals are scattered across different locations, and available quarantine vehicles are limited. Therefore, it is challenging to efficiently schedule the vehicles to transfer the individuals to isolated regions to control the spread of the epidemic. In this paper, we formulate such a quarantine vehicle scheduling problem for high-risk individual transfer, which is more difficult than most well-known vehicle routing problems. To efficiently solve this problem, we propose a hybrid algorithm based on the water wave optimization (WWO) metaheuristic and neighborhood search. The metaheuristic uses a small population to rapidly explore the solution space, and the neighborhood search uses a gradual strategy to improve the solution accuracy. Computational results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm significantly outperforms several existing algorithms and obtains high-quality solutions on real-world problem instances for high-risk individual transfer in Hangzhou, China, during the peak period of the novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19).
Keywords: epidemics; medical isolation; optimization; public health emergencies; vehicle scheduling; water wave optimization (WWO).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
- Eksioglu B., Vural A.V., Reisman A. The vehicle routing problem: A taxonomic review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2009;57:1472–1483. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2009.05.009. - DOI
- Hussain K., Mohd Salleh M.N., Cheng S., Shi Y. Metaheuristic research: a comprehensive survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019;52:2191–2233. doi: 10.1007/s10462-017-9605-z. - DOI
- Zheng Y.J. Water wave optimization: A new nature-inspired metaheuristic. Comput. Oper. Res. 2015;55:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2014.10.008. - DOI
- Dantzig G.B., Ramser J.H. The truck dispatching problem. Manag. Sci. 1959;6:80–91. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.6.1.80. - DOI
- Solomon M.M. Algorithms for the vehicle routing and scheduling problems with time window constraints. Oper. Res. 1987;35:254–265. doi: 10.1287/opre.35.2.254. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
