Power Analysis and Sample Size Planning in ANCOVA Designs
- PMID:31823115
- PMCID: PMC8225521
- DOI: 10.1007/s11336-019-09692-3
Power Analysis and Sample Size Planning in ANCOVA Designs
Erratum in
- Erratum to: Power Analysis and Sample Size Planning in Ancova Designs.Shieh G.Shieh G.Psychometrika. 2021 Sep;86(3):841. doi: 10.1007/s11336-021-09780-3.Psychometrika. 2021.PMID:34165692Free PMC article.No abstract available.
Abstract
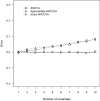
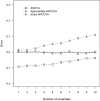
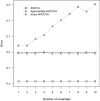
The analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) has notably proven to be an effective tool in a broad range of scientific applications. Despite the well-documented literature about its principal uses and statistical properties, the corresponding power analysis for the general linear hypothesis tests of treatment differences remains a less discussed issue. The frequently recommended procedure is a direct application of the ANOVA formula in combination with a reduced degrees of freedom and a correlation-adjusted variance. This article aims to explicate the conceptual problems and practical limitations of the common method. An exact approach is proposed for power and sample size calculations in ANCOVA with random assignment and multinormal covariates. Both theoretical examination and numerical simulation are presented to justify the advantages of the suggested technique over the current formula. The improved solution is illustrated with an example regarding the comparative effectiveness of interventions. In order to facilitate the application of the described power and sample size calculations, accompanying computer programs are also presented.
Keywords: general linear hypothesis; omnibus test; power; sample size.
Figures
References
- Bratcher TL, Moran MA, Zimmer WJ. Tables of sample sizes in the analysis of variance. Journal of Quality Technology. 1970;2:156–164. doi: 10.1080/00224065.1970.11980429. - DOI
- Cochran WG. Analysis of covariance: Its nature and uses. Biometrics. 1957;13:261–281. doi: 10.2307/2527916. - DOI
- Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum; 1988.
- Elashoff JD. Analysis of covariance: A delicate instrument. American Educational Research Journal. 1969;6:381–401. doi: 10.2307/2527916. - DOI
- Fisher RA. Statistical methods for research workers. 4. Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd; 1932.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources