Alpha-synuclein is a DNA binding protein that modulates DNA repair with implications for Lewy body disorders
- PMID:31358782
- PMCID: PMC6662836
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-47227-z
Alpha-synuclein is a DNA binding protein that modulates DNA repair with implications for Lewy body disorders
Abstract
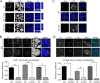
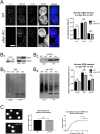
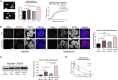
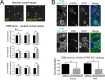
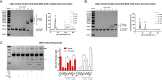
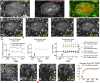
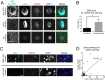
Alpha-synuclein is a presynaptic protein that forms abnormal cytoplasmic aggregates in Lewy body disorders. Although nuclear alpha-synuclein localization has been described, its function in the nucleus is not well understood. We demonstrate that alpha-synuclein modulates DNA repair. First, alpha-synuclein colocalizes with DNA damage response components within discrete foci in human cells and mouse brain. Removal of alpha-synuclein in human cells leads to increased DNA double-strand break (DSB) levels after bleomycin treatment and a reduced ability to repair these DSBs. Similarly, alpha-synuclein knock-out mice show increased neuronal DSBs that can be rescued by transgenic reintroduction of human alpha-synuclein. Alpha-synuclein binds double-stranded DNA and helps to facilitate the non-homologous end-joining reaction. Using a new, in vivo imaging approach that we developed, we find that serine-129-phosphorylated alpha-synuclein is rapidly recruited to DNA damage sites in living mouse cortex. We find that Lewy inclusion-containing neurons in both mouse model and human-derived patient tissue demonstrate increased DSB levels. Based on these data, we propose a model whereby cytoplasmic aggregation of alpha-synuclein reduces its nuclear levels, increases DSBs, and may contribute to programmed cell death via nuclear loss-of-function. This model could inform development of new treatments for Lewy body disorders by targeting alpha-synuclein-mediated DNA repair mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
- Transgenic mice overexpressing tyrosine-to-cysteine mutant human alpha-synuclein: a progressive neurodegenerative model of diffuse Lewy body disease.Zhou W, Milder JB, Freed CR.Zhou W, et al.J Biol Chem. 2008 Apr 11;283(15):9863-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M710232200. Epub 2008 Jan 30.J Biol Chem. 2008.PMID:18238775
- Alpha-synuclein modulates the repair of genomic DNA double-strand breaks in a DNA-PKcs-regulated manner.Rose EP, Osterberg VR, Gorbunova V, Unni VK.Rose EP, et al.Neurobiol Dis. 2024 Oct 15;201:106675. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106675. Epub 2024 Sep 19.Neurobiol Dis. 2024.PMID:39306014Free PMC article.
- 14-3-3 Proteins Reduce Cell-to-Cell Transfer and Propagation of Pathogenic α-Synuclein.Wang B, Underwood R, Kamath A, Britain C, McFerrin MB, McLean PJ, Volpicelli-Daley LA, Whitaker RH, Placzek WJ, Becker K, Ma J, Yacoubian TA.Wang B, et al.J Neurosci. 2018 Sep 19;38(38):8211-8232. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1134-18.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 9.J Neurosci. 2018.PMID:30093536Free PMC article.
- Pathological roles of α-synuclein in neurological disorders.Vekrellis K, Xilouri M, Emmanouilidou E, Rideout HJ, Stefanis L.Vekrellis K, et al.Lancet Neurol. 2011 Nov;10(11):1015-25. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70213-7.Lancet Neurol. 2011.PMID:22014436Review.
- Propagation of alpha-synuclein pathology: hypotheses, discoveries, and yet unresolved questions from experimental and human brain studies.Uchihara T, Giasson BI.Uchihara T, et al.Acta Neuropathol. 2016 Jan;131(1):49-73. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1485-1. Epub 2015 Oct 7.Acta Neuropathol. 2016.PMID:26446103Free PMC article.Review.
Cited by
- Neurotrophic factors for disease-modifying treatments of Parkinson's disease: gaps between basic science and clinical studies.Chmielarz P, Saarma M.Chmielarz P, et al.Pharmacol Rep. 2020 Oct;72(5):1195-1217. doi: 10.1007/s43440-020-00120-3. Epub 2020 Jul 22.Pharmacol Rep. 2020.PMID:32700249Free PMC article.Review.
- Nuclear alpha-synuclein accelerates cell senescence and neurodegeneration.Du T, Li G, Zong Q, Luo H, Pan Y, Ma K.Du T, et al.Immun Ageing. 2024 Jul 12;21(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12979-024-00429-0.Immun Ageing. 2024.PMID:38997709Free PMC article.
- Aggregated Alpha-Synuclein Inclusions within the Nucleus Predict Impending Neuronal Cell Death in a Mouse Model of Parkinsonism.Weston LJ, Bowman AM, Osterberg VR, Meshul CK, Woltjer RL, Unni VK.Weston LJ, et al.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 4;23(23):15294. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315294.Int J Mol Sci. 2022.PMID:36499619Free PMC article.
- Common cancer treatments targeting DNA double strand breaks affect long-term memory and relate to immediate early gene expression in a sex-dependent manner.Boutros SW, Krenik D, Holden S, Unni VK, Raber J.Boutros SW, et al.Oncotarget. 2022 Jan 24;13:198-213. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28180. eCollection 2022.Oncotarget. 2022.PMID:35106123Free PMC article.
- Inhibitory activities of grape bioactive compounds against enzymes linked with human diseases.Dwibedi V, Jain S, Singhal D, Mittal A, Rath SK, Saxena S.Dwibedi V, et al.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Feb;106(4):1399-1417. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-11801-9. Epub 2022 Feb 2.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022.PMID:35106636Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Related information
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
