Sequencing the unsequenceable: expanded CGG-repeat alleles of the fragile X gene
- PMID:23064752
- PMCID: PMC3530672
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.141705.112
Sequencing the unsequenceable: expanded CGG-repeat alleles of the fragile X gene
Abstract
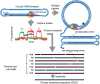
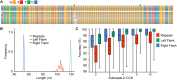
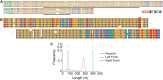
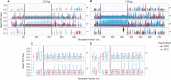
The human fragile X mental retardation 1 (FMR1) gene contains a (CGG)(n) trinucleotide repeat in its 5' untranslated region (5'UTR). Expansions of this repeat result in a number of clinical disorders with distinct molecular pathologies, including fragile X syndrome (FXS; full mutation range, greater than 200 CGG repeats) and fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS; premutation range, 55-200 repeats). Study of these diseases has been limited by an inability to sequence expanded CGG repeats, particularly in the full mutation range, with existing DNA sequencing technologies. Single-molecule, real-time (SMRT) sequencing provides an approach to sequencing that is fundamentally different from other "next-generation" sequencing platforms, and is well suited for long, repetitive DNA sequences. We report the first sequence data for expanded CGG-repeat FMR1 alleles in the full mutation range that reveal the confounding effects of CGG-repeat tracts on both cloning and PCR. A unique feature of SMRT sequencing is its ability to yield real-time information on the rates of nucleoside addition by the tethered DNA polymerase; for the CGG-repeat alleles, we find a strand-specific effect of CGG-repeat DNA on the interpulse distance. This kinetic signature reveals a novel aspect of the repeat element; namely, that the particular G bias within the CGG/CCG-repeat element influences polymerase activity in a manner that extends beyond simple nearest-neighbor effects. These observations provide a baseline for future kinetic studies of repeat elements, as well as for studies of epigenetic and other chemical modifications thereof.
Figures


Similar articles
- FMR1 CGG repeat lengths mediate different regulation of reporter gene expression in comparative transient and locus specific integration assays.Sølvsten C, Nielsen AL.Sølvsten C, et al.Gene. 2011 Oct 15;486(1-2):15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2011.06.034. Epub 2011 Jul 13.Gene. 2011.PMID:21767618
- Transcription-associated R-loop formation across the human FMR1 CGG-repeat region.Loomis EW, Sanz LA, Chédin F, Hagerman PJ.Loomis EW, et al.PLoS Genet. 2014 Apr 17;10(4):e1004294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004294. eCollection 2014 Apr.PLoS Genet. 2014.PMID:24743386Free PMC article.
- CGG-repeat dynamics andFMR1 gene silencing in fragile X syndrome stem cells and stem cell-derived neurons.Zhou Y, Kumari D, Sciascia N, Usdin K.Zhou Y, et al.Mol Autism. 2016 Oct 6;7:42. doi: 10.1186/s13229-016-0105-9. eCollection 2016.Mol Autism. 2016.PMID:27713816Free PMC article.
- [FMR1 PREMUTATION CARRIERS - ARE THEY REALLY ASYMPTOMATIC?].Elizur S, Berkenstadt M, Ries-Levavi L, Gruber N, Pinhas-Hamiel O, Hassin-Baer S, Raas-Rothschild A, Raanani H, Cukierman-Yaffe T, Orvieto R, Cohen Y, Gabis L.Elizur S, et al.Harefuah. 2018 Apr;157(4):241-244.Harefuah. 2018.PMID:29688643Review.Hebrew.
- Fragile X syndrome: the FMR1 CGG repeat distribution among world populations.Peprah E.Peprah E.Ann Hum Genet. 2012 Mar;76(2):178-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.2011.00694.x. Epub 2011 Dec 21.Ann Hum Genet. 2012.PMID:22188182Free PMC article.Review.
Cited by
- Nonhybrid, finished microbial genome assemblies from long-read SMRT sequencing data.Chin CS, Alexander DH, Marks P, Klammer AA, Drake J, Heiner C, Clum A, Copeland A, Huddleston J, Eichler EE, Turner SW, Korlach J.Chin CS, et al.Nat Methods. 2013 Jun;10(6):563-9. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2474. Epub 2013 May 5.Nat Methods. 2013.PMID:23644548
- Identifying the causes and consequences of assembly gaps using a multiplatform genome assembly of a bird-of-paradise.Peona V, Blom MPK, Xu L, Burri R, Sullivan S, Bunikis I, Liachko I, Haryoko T, Jønsson KA, Zhou Q, Irestedt M, Suh A.Peona V, et al.Mol Ecol Resour. 2021 Jan;21(1):263-286. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13252. Epub 2020 Oct 10.Mol Ecol Resour. 2021.PMID:32937018Free PMC article.
- Novel probes for label-free detection of neurodegenerative GGGGCC repeats associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Taki M, Rohilla KJ, Barton M, Funneman M, Benzabeh N, Naphade S, Ellerby LM, Gagnon KT, Shamsi MH.Taki M, et al.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019 Oct;411(26):6995-7003. doi: 10.1007/s00216-019-02075-8. Epub 2019 Aug 21.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019.PMID:31435686Free PMC article.
- Xdrop: Targeted sequencing of long DNA molecules from low input samples using droplet sorting.Madsen EB, Höijer I, Kvist T, Ameur A, Mikkelsen MJ.Madsen EB, et al.Hum Mutat. 2020 Sep;41(9):1671-1679. doi: 10.1002/humu.24063. Epub 2020 Jun 29.Hum Mutat. 2020.PMID:32516842Free PMC article.
- NGS Technologies as a Turning Point in Rare Disease Research , Diagnosis and Treatment.Fernandez-Marmiesse A, Gouveia S, Couce ML.Fernandez-Marmiesse A, et al.Curr Med Chem. 2018 Jan 30;25(3):404-432. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170718101946.Curr Med Chem. 2018.PMID:28721829Free PMC article.Review.
References
- Braida C, Stefanatos RK, Adam B, Mahajan N, Smeets HJ, Niel F, Goizet C, Arveiler B, Koenig M, Lagier-Tourenne C, et al. 2010. Variant CCG and GGC repeats within the CTG expansion dramatically modify mutational dynamics and likely contribute toward unusual symptoms in some myotonic dystrophy type 1 patients. Hum Mol Genet 19: 1399–1412 - PubMed
- Chen LS, Tassone F, Sahota P, Hagerman PJ 2003. The (CGG)n repeat element within the 5′ untranslated region of the FMR1 message provides both positive and negative cis effects on in vivo translation of a downstream reporter. Hum Mol Genet 12: 3067–3074 - PubMed
- Chen L, Hadd A, Sah S, Filipovic-Sadic S, Krosting J, Sekinger E, Pan R, Hagerman PJ, Stenzel TT, Tassone F, et al. 2010. An information-rich CGG repeat primed PCR that detects the full range of fragile X expanded alleles and minimizes the need for southern blot analysis. J Mol Diagn 12: 589–600 - PMC - PubMed
- Chen L, Hadd AG, Sah S, Houghton JF, Filipovic-Sadic S, Zhang W, Hagerman PJ, Tassone F, Latham GJ 2011. High-resolution methylation polymerase chain reaction for fragile X analysis: Evidence for novel FMR1 methylation patterns undetected in Southern blot analyses. Genet Med 13: 528–538 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Related information
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources