Parallel molecular evolution in an herbivore community
- PMID:23019645
- PMCID: PMC3770729
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1226630
Parallel molecular evolution in an herbivore community
Abstract
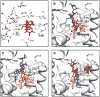
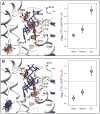
Numerous insects have independently evolved the ability to feed on plants that produce toxic secondary compounds called cardenolides and can sequester these compounds for use in their defense. We surveyed the protein target for cardenolides, the alpha subunit of the sodium pump, Na(+),K(+)-ATPase (ATPα), in 14 species that feed on cardenolide-producing plants and 15 outgroups spanning three insect orders. Despite the large number of potential targets for modulating cardenolide sensitivity, amino acid substitutions associated with host-plant specialization are highly clustered, with many parallel substitutions. Additionally, we document four independent duplications of ATPα with convergent tissue-specific expression patterns. We find that unique substitutions are disproportionately associated with recent duplications relative to parallel substitutions. Together, these findings support the hypothesis that adaptation tends to take evolutionary paths that minimize negative pleiotropy.
Figures

Similar articles
- Community-wide convergent evolution in insect adaptation to toxic cardenolides by substitutions in the Na,K-ATPase.Dobler S, Dalla S, Wagschal V, Agrawal AA.Dobler S, et al.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Aug 7;109(32):13040-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1202111109. Epub 2012 Jul 23.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012.PMID:22826239Free PMC article.
- Predictability in the evolution of Orthopteran cardenolide insensitivity.Yang L, Ravikanthachari N, Mariño-Pérez R, Deshmukh R, Wu M, Rosenstein A, Kunte K, Song H, Andolfatto P.Yang L, et al.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019 Jul 22;374(1777):20180246. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0246. Epub 2019 Jun 3.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019.PMID:31154978Free PMC article.
- Gene duplications circumvent trade-offs in enzyme function: Insect adaptation to toxic host plants.Dalla S, Dobler S.Dalla S, et al.Evolution. 2016 Dec;70(12):2767-2777. doi: 10.1111/evo.13077. Epub 2016 Oct 19.Evolution. 2016.PMID:27683239
- Toxic cardenolides: chemical ecology and coevolution of specialized plant-herbivore interactions.Agrawal AA, Petschenka G, Bingham RA, Weber MG, Rasmann S.Agrawal AA, et al.New Phytol. 2012 Apr;194(1):28-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.04049.x. Epub 2012 Jan 31.New Phytol. 2012.PMID:22292897Review.
- Coping with toxic plant compounds--the insect's perspective on iridoid glycosides and cardenolides.Dobler S, Petschenka G, Pankoke H.Dobler S, et al.Phytochemistry. 2011 Sep;72(13):1593-604. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.04.015. Epub 2011 May 26.Phytochemistry. 2011.PMID:21620425Review.
Cited by
- Identification of the NA+/K+-ATPase α-Isoforms in Six Species of Poison Dart Frogs and their Sensitivity to Cardiotonic Steroids.Medina-Ortiz K, Navia F, Mosquera-Gil C, Sánchez A, Sterling G, Fierro L, Castaño S.Medina-Ortiz K, et al.J Chem Ecol. 2023 Apr;49(3-4):116-132. doi: 10.1007/s10886-023-01404-7. Epub 2023 Mar 6.J Chem Ecol. 2023.PMID:36877397Free PMC article.
- Constraints on the evolution of toxin-resistant Na,K-ATPases have limited dependence on sequence divergence.Mohammadi S, Herrera-Álvarez S, Yang L, Rodríguez-Ordoñez MDP, Zhang K, Storz JF, Dobler S, Crawford AJ, Andolfatto P.Mohammadi S, et al.PLoS Genet. 2022 Aug 16;18(8):e1010323. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010323. eCollection 2022 Aug.PLoS Genet. 2022.PMID:35972957Free PMC article.
- Dramatic dietary shift maintains sequestered toxins in chemically defended snakes.Yoshida T, Ujiie R, Savitzky AH, Jono T, Inoue T, Yoshinaga N, Aburaya S, Aoki W, Takeuchi H, Ding L, Chen Q, Cao C, Tsai TS, Silva A, Mahaulpatha D, Nguyen TT, Tang Y, Mori N, Mori A.Yoshida T, et al.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Mar 17;117(11):5964-5969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1919065117. Epub 2020 Feb 24.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020.PMID:32094167Free PMC article.
- The genetic causes of convergent evolution.Stern DL.Stern DL.Nat Rev Genet. 2013 Nov;14(11):751-64. doi: 10.1038/nrg3483. Epub 2013 Oct 9.Nat Rev Genet. 2013.PMID:24105273Review.
- Phylogenetic incongruence and the evolutionary origins of cardenolide-resistant forms of Na(+) ,K(+) -ATPase in Danaus butterflies.Aardema ML, Andolfatto P.Aardema ML, et al.Evolution. 2016 Aug;70(8):1913-21. doi: 10.1111/evo.12999. Epub 2016 Jul 27.Evolution. 2016.PMID:27405795Free PMC article.
References
- Crow JF. Annu Rev Genet. 2008;42:1. - PubMed
- Kimura M. The Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution. Cambridge Univ. Press; Cambridge: 1983.
- Carroll SB. Cell. 2008;134:25. - PubMed
- Stern DL. Evolution, Development, and the Predictable Genome. Roberts and Company Publishers; Greenwood Village, CO: 2011.
- Wright S. Evolution and the Genetics of Populations. Univ. of Chicago Press; Chicago: 1968. pp. 1–4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Related information
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
