PDZ binding of TARPγ-8 controls synaptic transmission but not synaptic plasticity
- PMID:22002768
- PMCID: PMC3206644
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2952
PDZ binding of TARPγ-8 controls synaptic transmission but not synaptic plasticity
Abstract
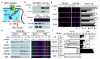
The reduction in synaptic transmission and plasticity in mice lacking the hippocampus-enriched AMPA receptor (AMPAR) auxiliary subunit TARPγ-8 could be a result of a reduction in AMPAR expression or of the direct action of γ-8. We generated TARPγ-8Δ4 knock-in mice lacking the C-terminal PDZ ligand. We found that synaptic transmission and AMPARs were reduced in the mutant mice, but extrasynaptic AMPAR expression and long-term potentiation (LTP) were unaltered. Our findings suggest that there are distinct TARP-dependent mechanisms for synaptic transmission and LTP.
Figures

References
- Rouach N, et al. TARP gamma-8 controls hippocampal AMPA receptor number, distribution and synaptic plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:1525–1533. - PubMed
- Fukaya M, et al. Abundant distribution of TARP gamma-8 in synaptic and extrasynaptic surface of hippocampal neurons and its major role in AMPA receptor expression on spines and dendrites. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;24:2177–2190. - PubMed
- Zamanillo D, et al. Importance of AMPA receptors for hippocampal synaptic plasticity but not for spatial learning. Science. 1999;284:1805–1811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
