Stochastic noise in splicing machinery
- PMID:19546110
- PMCID: PMC2724286
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp471
Stochastic noise in splicing machinery
Abstract
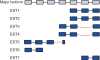
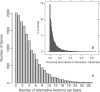
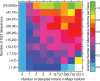
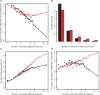
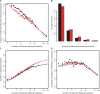
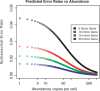
The number of known alternative human isoforms has been increasing steadily with the amount of available transcription data. To date, over 100 000 isoforms have been detected in EST libraries, and at least 75% of human genes have at least one alternative isoform. In this paper, we propose that most alternative splicing events are the result of noise in the splicing process. We show that the number of isoforms and their abundance can be predicted by a simple stochastic noise model that takes into account two factors: the number of introns in a gene and the expression level of a gene. The results strongly support the hypothesis that most alternative splicing is a consequence of stochastic noise in the splicing machinery, and has no functional significance. The results are also consistent with error rates tuned to ensure that an adequate level of functional product is produced and to reduce the toxic effect of accumulation of misfolding proteins. Based on simulation of sampling of virtual cDNA libraries, we estimate that error rates range from 1 to 10% depending on the number of introns and the expression level of a gene.
Figures




Similar articles
- Quantification of stochastic noise of splicing and polyadenylation in Entamoeba histolytica.Hon CC, Weber C, Sismeiro O, Proux C, Koutero M, Deloger M, Das S, Agrahari M, Dillies MA, Jagla B, Coppee JY, Bhattacharya A, Guillen N.Hon CC, et al.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Feb 1;41(3):1936-52. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1271. Epub 2012 Dec 20.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013.PMID:23258700Free PMC article.
- Human gene MOB: structure specification and aspects of transcriptional activity.Vladychenskaya IP, Dergunova LV, Dmitrieva VG, Limborska SA.Vladychenskaya IP, et al.Gene. 2004 Sep 1;338(2):257-65. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2004.06.003.Gene. 2004.PMID:15315829
- Strengths and weaknesses of EST-based prediction of tissue-specific alternative splicing.Gupta S, Zink D, Korn B, Vingron M, Haas SA.Gupta S, et al.BMC Genomics. 2004 Sep 28;5:72. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-5-72.BMC Genomics. 2004.PMID:15453915Free PMC article.
- Evolution of alternative splicing: deletions, insertions and origin of functional parts of proteins from intron sequences.Kondrashov FA, Koonin EV.Kondrashov FA, et al.Trends Genet. 2003 Mar;19(3):115-9. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(02)00029-X.Trends Genet. 2003.PMID:12615001Review.
- How prevalent is functional alternative splicing in the human genome?Sorek R, Shamir R, Ast G.Sorek R, et al.Trends Genet. 2004 Feb;20(2):68-71. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2003.12.004.Trends Genet. 2004.PMID:14746986Review.
Cited by
- Discovery and mass spectrometric analysis of novel splice-junction peptides using RNA-Seq.Sheynkman GM, Shortreed MR, Frey BL, Smith LM.Sheynkman GM, et al.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Aug;12(8):2341-53. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O113.028142. Epub 2013 Apr 29.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013.PMID:23629695Free PMC article.
- Extensive RNA editing and splicing increase immune self-representation diversity in medullary thymic epithelial cells.Danan-Gotthold M, Guyon C, Giraud M, Levanon EY, Abramson J.Danan-Gotthold M, et al.Genome Biol. 2016 Oct 24;17(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-1079-9.Genome Biol. 2016.PMID:27776542Free PMC article.
- Expression dynamics of the Medicago truncatula transcriptome during the symbiotic interaction with Sinorhizobium meliloti: which role for nitric oxide?Boscari A, Del Giudice J, Ferrarini A, Venturini L, Zaffini AL, Delledonne M, Puppo A.Boscari A, et al.Plant Physiol. 2013 Jan;161(1):425-39. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.208538. Epub 2012 Nov 7.Plant Physiol. 2013.PMID:23136381Free PMC article.
- Comparative proteomics reveals a significant bias toward alternative protein isoforms with conserved structure and function.Ezkurdia I, del Pozo A, Frankish A, Rodriguez JM, Harrow J, Ashman K, Valencia A, Tress ML.Ezkurdia I, et al.Mol Biol Evol. 2012 Sep;29(9):2265-83. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss100. Epub 2012 Mar 22.Mol Biol Evol. 2012.PMID:22446687Free PMC article.
- DeepIsoFun: a deep domain adaptation approach to predict isoform functions.Shaw D, Chen H, Jiang T.Shaw D, et al.Bioinformatics. 2019 Aug 1;35(15):2535-2544. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty1017.Bioinformatics. 2019.PMID:30535380Free PMC article.
References
- Modrek B, Lee C. A genomic view of alternative splicing. Nat. Genet. 2002;30:13. - PubMed
- Pan Q, Shai O, Lee LJ, Frey BJ, Blencowe BJ. Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2008;40:1413. - PubMed
- Kriventseva EV, Koch I, Apweiler R, Vingron M, Bork P, Gelfand MS, Sunyaev S. Increase of functional diversity by alternative splicing. Trends Genet. 2003;19:124. - PubMed
- Sorek R, Shamir R, Ast G. How prevalent is functional alternative splicing in the human genome? Trends Genet. 2004;20:68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Related information
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
