Synaptotagmin-IV modulates synaptic function and long-term potentiation by regulating BDNF release
- PMID:19448629
- PMCID: PMC2846764
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2315
Synaptotagmin-IV modulates synaptic function and long-term potentiation by regulating BDNF release
Abstract
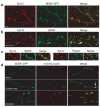
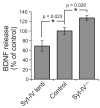
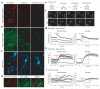
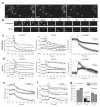
Synaptotagmin-IV (syt-IV) is a membrane trafficking protein that influences learning and memory, but its localization and role in synaptic function remain unclear. We found that syt-IV localized to brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-containing vesicles in hippocampal neurons. Syt-IV/BDNF-harboring vesicles underwent exocytosis in both axons and dendrites, and syt-IV inhibited BDNF release at both sites. Knockout of syt-IV increased, and overexpression decreased, the rate of synaptic vesicle exocytosis from presynaptic terminals indirectly via changes in postsynaptic release of BDNF. Thus, postsynaptic syt-IV regulates the trans-synaptic action of BDNF to control presynaptic vesicle dynamics. Furthermore, selective loss of presynaptic syt-IV increased spontaneous quantal release, whereas a loss of postsynaptic syt-IV increased quantal amplitude. Finally, syt-IV knockout mice showed enhanced long-term potentiation (LTP), which depended entirely on disinhibition of BDNF release. Thus, regulation of BDNF secretion by syt-IV emerges as a mechanism for maintaining synaptic strength in a useful range during LTP.
Figures


Similar articles
- Distinct subsets of Syt-IV/BDNF vesicles are sorted to axons versus dendrites and recruited to synapses by activity.Dean C, Liu H, Staudt T, Stahlberg MA, Vingill S, Bückers J, Kamin D, Engelhardt J, Jackson MB, Hell SW, Chapman ER.Dean C, et al.J Neurosci. 2012 Apr 18;32(16):5398-413. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4515-11.2012.J Neurosci. 2012.PMID:22514304Free PMC article.
- Loss of synaptotagmin IV results in a reduction in synaptic vesicles and a distortion of the Golgi structure in cultured hippocampal neurons.Arthur CP, Dean C, Pagratis M, Chapman ER, Stowell MH.Arthur CP, et al.Neuroscience. 2010 Apr 28;167(1):135-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.01.056. Epub 2010 Feb 4.Neuroscience. 2010.PMID:20138128Free PMC article.
- Altered hippocampal short-term plasticity and associative memory in synaptotagmin IV (-/-) mice.Ferguson GD, Wang H, Herschman HR, Storm DR.Ferguson GD, et al.Hippocampus. 2004;14(8):964-74. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20013.Hippocampus. 2004.PMID:15390175
- Function of Drosophila Synaptotagmins in membrane trafficking at synapses.Quiñones-Frías MC, Littleton JT.Quiñones-Frías MC, et al.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 May;78(9):4335-4364. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03788-9. Epub 2021 Feb 22.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021.PMID:33619613Free PMC article.Review.
- Modulation of hippocampal synaptic transmission and plasticity by neurotrophins.Lu B, Gottschalk W.Lu B, et al.Prog Brain Res. 2000;128:231-41. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(00)28020-5.Prog Brain Res. 2000.PMID:11105682Review.No abstract available.
Cited by
- Neuromodulator release in neurons requires two functionally redundant calcium sensors.van Westen R, Poppinga J, Díez Arazola R, Toonen RF, Verhage M.van Westen R, et al.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 May 4;118(18):e2012137118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2012137118.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021.PMID:33903230Free PMC article.
- Rat and Drosophila synaptotagmin 4 have opposite effects during SNARE-catalyzed membrane fusion.Wang Z, Chapman ER.Wang Z, et al.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 1;285(40):30759-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.137745. Epub 2010 Aug 5.J Biol Chem. 2010.PMID:20688915Free PMC article.
- AMPA receptor incorporation into synapses during LTP: the role of lateral movement and exocytosis.Makino H, Malinow R.Makino H, et al.Neuron. 2009 Nov 12;64(3):381-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.08.035.Neuron. 2009.PMID:19914186Free PMC article.
- Alterations of transcriptome signatures in head trauma-related neurodegenerative disorders.Cho H, Hyeon SJ, Shin JY, Alvarez VE, Stein TD, Lee J, Kowall NW, McKee AC, Ryu H, Seo JS.Cho H, et al.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 1;10(1):8811. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65916-y.Sci Rep. 2020.PMID:32483284Free PMC article.
- High abundance of BDNF within glutamatergic presynapses of cultured hippocampal neurons.Andreska T, Aufmkolk S, Sauer M, Blum R.Andreska T, et al.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Apr 11;8:107. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00107. eCollection 2014.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014.PMID:24782711Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Related information
Grants and funding
- NS44057/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS049748/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS049748/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH61876/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- GM 56827/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS044057/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS30016/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS030016/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM056827/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061876/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 NS030016/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS049748-01A1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
