Suppression of host gene expression by nsp1 proteins of group 2 bat coronaviruses
- PMID:19264783
- PMCID: PMC2682096
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02485-08
Suppression of host gene expression by nsp1 proteins of group 2 bat coronaviruses
Abstract
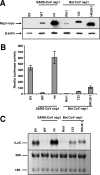
nsp1 protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), a group 2b CoV, suppresses host gene expression by promoting host mRNA degradation and translation inhibition. The present study analyzed the activities of nsp1 proteins from the group 2 bat CoV strains Rm1, 133, and HKU9-1, belonging to groups 2b, 2c, and 2d, respectively. The host mRNA degradation and translational suppression activities of nsp1 of SARS-CoV and Rm1 nsp1 were similar and stronger than the activities of the nsp1 proteins of 133 and HKU9-1. Rm1 nsp1 expression in trans strongly inhibited the induction of type I interferon (IFN-I) and IFN-stimulated genes in cells infected with an IFN-inducing SARS-CoV mutant, while 133 and HKU9-1 nsp1 proteins had relatively moderate IFN-inhibitory activities. The results of our studies suggested a conserved function among nsp1 proteins of SARS-CoV and group 2 bat CoVs.
Figures



References
- Atasoy, U., S. L. Curry, I. López de Silances, A.-B. Shyu, V. Casolaro, M. Gorospe, and C. Stellato. 2003. Regulation of eotaxin gene expression by TNF-α and IL-4 through mRNA stabilization: involvement of the RNA-binding protein HuR. J. Immunol. 1714369-4378. - PubMed
- Condeelis, J., and R. H. Singer. 2005. How and why does β-actin mRNA target? Biol. Cell 9797-110. - PubMed
- Devaraj, S. G., N. Wang, Z. Chen, Z. Chen, M. Tseng, N. Barretto, R. Lin, C. J. Peters, C.-T. K. Tseng, S. C. Bake, and K. Li. 2007. Regulation of IRF-3-dependent innate immunity by the papain-like protease domain of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Biol. Chem. 28232208-32221. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
