Implication of proprotein convertases in the processing and spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
- PMID:15596135
- PMCID: PMC7092861
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.11.063
Implication of proprotein convertases in the processing and spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
Abstract
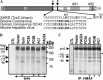
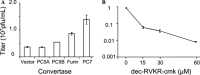
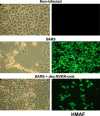
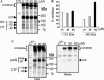
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) is the etiological agent of SARS. Analysis of SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein (S) using recombinant plasmid and virus infections demonstrated that the S-precursor (proS) exists as a approximately 190 kDa endoplasmic reticulum form and a approximately 210 kDa Golgi-modified form. ProS is subsequently processed into two C-terminal proteins of approximately 110 and approximately 80 kDa. The membrane-bound proprotein convertases (PCs) furin, PC7 or PC5B enhanced the production of the approximately 80 kDa protein. In agreement, proS processing, cytopathic effects, and viral titers were enhanced in recombinant Vero E6 cells overexpressing furin, PC7 or PC5B. The convertase inhibitor dec-RVKR-cmk significantly reduced proS cleavage and viral titers of SARS-CoV infected cells. In addition, inhibition of processing by dec-RVKR-cmk completely abrogated the virus-induced cellular cytopathicity. A fluorogenically quenched synthetic peptide encompassing Arg(761) of the spike glycoprotein was efficiently cleaved by furin and the cleavage was inhibited by EDTA and dec-RVKR-cmk. Taken together, our data indicate that furin or PC-mediated processing plays a critical role in SARS-CoV spread and cytopathicity, and inhibitors of the PCs represent potential therapeutic anti-SARS-CoV agents.
Figures

Similar articles
- Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Spike Protein Is Not Activated Directly by Cellular Furin during Viral Entry into Target Cells.Matsuyama S, Shirato K, Kawase M, Terada Y, Kawachi K, Fukushi S, Kamitani W.Matsuyama S, et al.J Virol. 2018 Sep 12;92(19):e00683-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00683-18. Print 2018 Oct 1.J Virol. 2018.PMID:30021905Free PMC article.
- Neuroinflammation-Induced Interactions between Protease-Activated Receptor 1 and Proprotein Convertases in HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder.Kim W, Zekas E, Lodge R, Susan-Resiga D, Marcinkiewicz E, Essalmani R, Mihara K, Ramachandran R, Asahchop E, Gelman B, Cohen ÉA, Power C, Hollenberg MD, Seidah NG.Kim W, et al.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Nov;35(21):3684-700. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00764-15. Epub 2015 Aug 17.Mol Cell Biol. 2015.PMID:26283733Free PMC article.
- The regulated cell surface zymogen activation of the proprotein convertase PC5A directs the processing of its secretory substrates.Mayer G, Hamelin J, Asselin MC, Pasquato A, Marcinkiewicz E, Tang M, Tabibzadeh S, Seidah NG.Mayer G, et al.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jan 25;283(4):2373-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708763200. Epub 2007 Nov 26.J Biol Chem. 2008.PMID:18039650
- How Do Enveloped Viruses Exploit the Secretory Proprotein Convertases to Regulate Infectivity and Spread?Seidah NG, Pasquato A, Andréo U.Seidah NG, et al.Viruses. 2021 Jun 25;13(7):1229. doi: 10.3390/v13071229.Viruses. 2021.PMID:34202098Free PMC article.Review.
- Knock-out mouse models of proprotein convertases: unique functions or redundancy?Creemers JW, Khatib AM.Creemers JW, et al.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:4960-71. doi: 10.2741/3055.Front Biosci. 2008.PMID:18508561Review.
Cited by
- Design of Three Residues Peptides against SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Zannella C, Chianese A, Greco G, Santella B, Squillaci G, Monti A, Doti N, Sanna G, Manzin A, Morana A, De Filippis A, D'Angelo G, Palmieri F, Franci G, Galdiero M.Zannella C, et al.Viruses. 2022 Sep 22;14(10):2103. doi: 10.3390/v14102103.Viruses. 2022.PMID:36298659Free PMC article.
- A fluorogenic peptide containing the processing site of human SARS corona virus S-protein: kinetic evaluation and NMR structure elucidation.Basak A, Mitra A, Basak S, Pasko C, Chrétien M, Seaton P.Basak A, et al.Chembiochem. 2007 Jun 18;8(9):1029-37. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200700007.Chembiochem. 2007.PMID:17471479Free PMC article.
- Deletion of the gene encoding proprotein convertase 5/6 causes early embryonic lethality in the mouse.Essalmani R, Hamelin J, Marcinkiewicz J, Chamberland A, Mbikay M, Chrétien M, Seidah NG, Prat A.Essalmani R, et al.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jan;26(1):354-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.1.354-361.2006.Mol Cell Biol. 2006.PMID:16354705Free PMC article.
- Host cell proteases: Critical determinants of coronavirus tropism and pathogenesis.Millet JK, Whittaker GR.Millet JK, et al.Virus Res. 2015 Apr 16;202:120-34. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.11.021. Epub 2014 Nov 22.Virus Res. 2015.PMID:25445340Free PMC article.Review.
- Chloroquine is a potent inhibitor of SARS coronavirus infection and spread.Vincent MJ, Bergeron E, Benjannet S, Erickson BR, Rollin PE, Ksiazek TG, Seidah NG, Nichol ST.Vincent MJ, et al.Virol J. 2005 Aug 22;2:69. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-2-69.Virol J. 2005.PMID:16115318Free PMC article.
References
- Ksiazek T.G., Erdman D., Goldsmith C.S., Zaki S.R., Peret T., Emery S., Tong S., Urbani C., Comer J.A., Lim W., Rollin P.E, Dowell S.F., Ling A.E., Humphrey C.D., Shieh W.J., Guarner J., Paddock C.D., Rota P., Fields B., DeRisi J., Yang J.Y., Cox N., Hughes J.M., LeDuc J.W., Bellini W.J., Anderson L.J. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1953–1966. - PubMed
- Marra M.A., Jones S.J., Astell C.R., Holt R.A., Brooks-Wilson A., Butterfield Y.S., Khattra J., Asano J.K., Barber S.A., Chan S.Y., Cloutier A., Coughlin S.M., Freeman D., Girn N., Griffith O.L., Leach S.R., Mayo M., McDonald H., Montgomery S.B., Pandoh P.K., Petrescu A.S., Robertson A.G., Schein J.E., Siddiqui A., Smailus D.E., Stott J.M., Yang G.S., Plummer F., Andonov A., Artsob H., Bastien N., Bernard K., Booth T.F., Bowness D., Czub M., Drebot M., Fernando L., Flick R., Garbutt M., Gray M., Grolla A., Jones S., Feldmann H., Meyers A., Kabani A., Li Y., Normand S., Stroher U., Tipples G.A., Tyler S., Vogrig R., Ward D., Watson B., Brunham R.C., Krajden M., Petric M., Skowronski D.M., Upton C., Roper R.L. Science. 2003;300:1399–1404. - PubMed
- Rota P.A., Oberste M.S., Monroe S.S., Nix W.A., Campagnoli R., Icenogle J.P., Penaranda S., Bankamp B., Maher K., Chen M.H., Tong S., Tamin A., Lowe L., Frace M., DeRisi J.L., Chen Q., Wang D., Erdman D.D., Peret T.C., Burns C., Ksiazek T.G., Rollin P.E., Sanchez A., Liffick S., Holloway B., Limor J., McCaustland K., Olsen-Rasmussen M., Fouchier R., Gunther S., Osterhaus A.D., Drosten C., Pallansch M.A., Anderson L.J., Bellini W.J. Science. 2003;300:1394–1399. - PubMed
- Ng M.L., Tan S.H., See E.E., Ooi E.E., Ling A.E. J. Gen. Virol. 2003;84:3291–3303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Related information
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
