WO2024214253A1 - Blood test aid - Google Patents
Blood test aidDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2024214253A1 WO2024214253A1PCT/JP2023/015055JP2023015055WWO2024214253A1WO 2024214253 A1WO2024214253 A1WO 2024214253A1JP 2023015055 WJP2023015055 WJP 2023015055WWO 2024214253 A1WO2024214253 A1WO 2024214253A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- blood
- substrate
- base material
- pool
- blood test
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/48—Biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Haemocytometers
- G01N33/50—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing
- G01N33/52—Use of compounds or compositions for colorimetric, spectrophotometric or fluorometric investigation, e.g. use of reagent paper and including single- and multilayer analytical elements
Definitions
- the present inventionrelates to a blood test aid used in blood tests to measure the presence or concentration of a specific substance in blood.
- Blood tests that analyze the presence or concentration of specific substances in bloodare widely used to diagnose a subject's health condition. For example, by analyzing the content of various components in the plasma in the blood, it is possible to diagnose the subject's organ function, etc.
- the blood sampleis separated into liquid components, such as plasma or serum, and solid components, such as cells, using a centrifuge or suction/pressurization pump.
- a centrifuge or suction/pressurization pumpNormally, a certain amount of blood (e.g., 5 mL or more) is required to run the blood through a centrifuge, so a doctor, nurse, or clinical laboratory technician must draw blood from the subject.
- typical blood testscan only be performed at medical institutions or specialized testing institutions that are equipped with expensive analytical equipment such as centrifuges and the power supplies to operate them.
- the burden on medical professionals who draw the bloodis also great. In other words, typical blood tests are a heavy burden not only on the subject but also on medical institutions, and are expensive.
- Patent document 1discloses a reagent strip that includes a test pad formed from an anisotropic membrane that contains a color-developing reagent system specific to the analyte and has a side with relatively small holes that define a test surface and an opposite side with relatively large holes that define a sample receiving surface, and a porous sample transport medium attached to the sample receiving surface of the test pad, the transport medium being capable of receiving a whole blood sample and transporting a detectable portion of the sample to the sample receiving surface.
- the amount of plasmais too much, the plasma will overflow from the reagent phase and wrap around the surface from the sides of the reagent phase, resulting in an uneven reaction.
- an appropriate amount of bloodneeds to be added to the testing device.
- the present inventionwas made in consideration of the above, and aims to provide a blood testing aid that allows an appropriate amount of blood to be added to a blood testing device with simple operations.
- the blood test auxiliary tool of one aspect of the present inventionis a blood test auxiliary tool that assists in tests using a blood test device
- the blood test devicehas a first substrate on which a blood addition section, which is an opening through which blood is added, is formed, a second substrate on which an observation window, which is an opening for observing a color reaction, is formed, and a plasma separation membrane and a dry reagent phase are arranged by being laminated between the first and second substrates, and is provided with a first base material on which a pool in which blood is placed is formed, and a second substrate that can be superimposed on the first substrate, and is provided with a guide on the side facing the pool that indicates the position where the blood test device is fixed to the second substrate, and is provided with an opening that exposes the observation window when the blood test device is fixed in accordance with the guide.
- At least one of the first and second substratesmay be provided with a support portion that ensures a gap of a predetermined height between the pool side surface of the pool and the fixing surface of the blood test device on the second substrate when the first substrate and the second substrate are superimposed.
- a protrusion that protrudes beyond the pool side surfacemay be formed on the first base material near the pool.
- the first substrate and the second substratemay be formed from a continuous sheet-like member, and the first substrate and the second substrate may be overlapped by folding the first substrate and the second substrate at the boundary line between them.
- one of the first and second base materialsmay be provided with a convex portion with a protrusion formed on a wall surface
- the other of the first and second base materialsmay be provided with a concave space into which the convex portion can fit
- a depressionmay be formed in the wall surface of the space at a position corresponding to the protrusion, and by fitting the convex portion into the space, the protrusion may fit into the depression, and the first base material and the second base material may be fixed in a superimposed state.
- the present inventionby fixing a blood testing device to a blood testing auxiliary tool and placing blood in a pool, it is possible to add an appropriate amount of blood to the blood testing device with a simple operation.
- FIG. 1is a plan view showing the inner surface side (unfolded state) of a blood test auxiliary device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2is an end view taken along lines AA to FF shown in FIG. 1.
- FIG. 2is a perspective view showing the inner surface side (unfolded state) of the blood test auxiliary device according to the embodiment of the present invention.
- 1is a perspective view showing the outer surface side (in an unfolded state) of a blood test auxiliary device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. FIG. 1is a perspective view showing a blood test auxiliary device (in a folded state) according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2is an enlarged perspective view (blood application part side) illustrating a blood test device used in an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2is an enlarged perspective view (observation window side) illustrating a blood test device used in an embodiment of the present invention.
- 1is an enlarged exploded perspective view illustrating a blood testing device used in an embodiment of the present invention.
- 1A to 1Care schematic diagrams illustrating a method of using the blood test auxiliary device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 1A to 1Care schematic diagrams illustrating a method of using the blood test auxiliary device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 1A to 1Care schematic diagrams illustrating a method of using the blood test auxiliary device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 1A to 1Care schematic diagrams illustrating a method of using the blood test auxiliary device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 1is a graph showing the colorimetric sensitivity of blood glucose in an example.
- 1is a graph showing the colorimetric sensitivity of neutral fats in an example.
- 1is a graph showing the colorimetric sensitivity of total cholesterol in an example.
- 14is a graph showing blood glucose concentrations corresponding to the colorimetric sensitivities shown in FIG. 13.
- 15is a graph showing the concentration of neutral fats corresponding to the colorimetric sensitivities shown in FIG. 14 .
- FIG. 16is a graph showing the concentration of total cholesterol corresponding to the colorimetric sensitivity shown in FIG. 15.
- FIG. 1is a plan view showing the inner side (unfolded state) of the blood test auxiliary according to the embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2is an end view of each of the lines A-A to F-F shown in FIG. 1.
- FIG. 2(a)shows the A-A end face of FIG. 1
- FIG. 2(b)shows the B-B end face of FIG. 1
- FIG. 2(c)shows the C-C end face of FIG. 1
- FIG. 2(d)shows the D-D end face of FIG. 1
- FIG. 2(e)shows the E1-E2-E3-E4 end face of FIG. 1
- FIG. 2(f)shows the F-F end face of FIG. 1.
- FIG. 2(a)shows the A-A end face of FIG. 1
- FIG. 2(b)shows the B-B end face of FIG. 1
- FIG. 2(c)shows the C-C end face of FIG. 1
- FIG. 2(d)shows the D-D end face of
- FIG. 3is a perspective view showing the inner side (unfolded state) of the blood test auxiliary.
- FIG. 4is a perspective view showing the outer side (unfolded state) of the blood test auxiliary.
- FIG. 5is a perspective view showing the blood test auxiliary (folded state).
- the blood test auxiliary device (hereinafter also simply referred to as the auxiliary device) 1is an instrument that assists in testing blood that has been self-drawn by a subject.
- the auxiliary device 1comprises a lower substrate (first substrate) 11 and an upper substrate (second substrate) 12 that can be stacked on top of each other.
- first substratefirst substrate
- second substrateupper substrate
- the side that becomes the outside when the lower substrate 11 and the upper substrate 13 are stacked on top of each other when the auxiliary device 1 is in use (see Figure 5)is referred to as the outer side, and the side that becomes the inside is referred to as the inner side.
- the detailed configuration of the auxiliary device 1will be described later.
- Fig. 6is a perspective view (blood addition part side) illustrating a blood test device used in an embodiment of the present invention.
- Fig. 7is a perspective view (observation window side) of the same blood test device.
- Fig. 8is an exploded perspective view of the same blood test device.
- the blood testing device 2 shown in Figures 6 to 8is intended to measure the presence or concentration of a specific substance contained in plasma based on a color reaction that occurs in a dry reagent phase by contacting the plasma separated from blood with a dry reagent phase impregnated with a reagent.
- Measurable test itemsare not particularly limited as long as they are components contained in plasma and show a color reaction with a specific reagent.
- Specific examples of test itemsinclude AST, ALT, ⁇ -GT, neutral fats, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, total cholesterol, blood glucose, HbA1c, etc., as well as minerals such as zinc and magnesium.
- the testing device 2comprises a first substrate 21 and a second substrate 22 arranged opposite each other, and a diffusion layer 23, a plasma separation section 24, and reagent phases 25a-25c arranged and stacked between the first substrate 21 and the second substrate 22.
- the number of testable itemsmay be one or two, or four or more.
- the first substrate 21 and the second substrate 22are formed from a thin sheet material.
- the material for the first substrate 21 and the second substrate 22may be a resin material such as PET (polyethylene terephthalate) or cardboard with a water-repellent finish, as long as it can maintain the shape of the testing device 2 and is not permeated by the blood or plasma sample or reacts with these liquids.
- the first substrate 21is formed with a blood addition section 21a, which is an opening through which the blood sample is added.
- the shape of the blood addition section 21ais rectangular, but this shape is not particularly limited, and various shapes such as an elliptical or oval shape can be used as long as the shape allows for the addition of blood.
- the second substrate 22has observation windows 22a-22c, which are openings for observing the color reactions of the reagent phases 25a-25c, respectively.
- the number of these observation windows 22a-22cis set according to the number of test items (i.e., the number of reagent phases 25a-25c).
- the shape of each observation window 22a-22cis square, but this shape is not particularly limited and may be circular, elliptical, or the like.
- alignment openings 27may be formed in corresponding locations on the first substrate 21 and the second substrate 22, respectively.
- the first substrate 21 and the second substrate 22may be formed from two plates separated from each other as shown in FIG. 8, or may be formed by bending a single elongated plate.
- a spacer 26may be placed between the first substrate 21 and the second substrate 22 to form a space 20a of a height sufficient to accommodate the diffusion layer 23, the plasma separation section 24, and the reagent phases 25a to 25c.
- the diffusion layer 23is formed from a material made of hydrophilic fibers woven into a sheet, and is arranged so that a portion of it is exposed from the blood addition section 21a provided on the first substrate 21.
- the diffusion layer 23quickly guides the blood added to the blood addition section 21a over a wide range in the planar direction by capillary action, and acts to uniformly soak into one side of the plasma separation section 24.
- the diffusion layer 23can be, for example, a plain woven hydrophilic polyester material.
- the plasma separation section 24is formed from a porous sheet material, trapping cellular components from the blood that has soaked into one side and separating the plasma by allowing liquid components to pass through in the thickness direction of the membrane.
- a porous polymer membranesuch as a polysulfone (PS) membrane or an asymmetric PS membrane can be used as the plasma separation section 24.
- the reagent phases 25a-25care dry reagent phases in which filter paper (such as chromatography paper) is impregnated with a reagent corresponding to the test item and dried, and are arranged so that a portion of them is exposed from each of the observation windows 22a-22c.
- the reagent phases 25a-25creact with a specific substance contained in the plasma that has passed through the plasma separation section 24 and become colored. This color reaction can be visually observed from the observation window 22a-22c side as the plasma has sufficiently permeated the reagent phases 25a-25c.
- the diffusion layer 23, the plasma separation section 24, and the reagent phases 25a to 25care attached to the first substrate 21 or the second substrate 22 using double-sided tape or the like.
- the first substrate 21 and the second substrate 22are also attached to each other using double-sided tape or the like, or to each other via the spacer 26.
- the lower base material 11 and the upper base material 13 of the support tool 1are formed by vacuum molding using a resin material such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene (PE).
- PETpolyethylene terephthalate
- PEpolyethylene
- the method and material for forming the lower base material 11 and the upper base material 13are not limited to this.
- a composite material of pulp and resin, or a material obtained by subjecting cardboard to a water-repellent treatmentmay be used, or the lower base material 11 and the upper base material 13 may be formed using a press process or a pulp molding technique.
- the auxiliary device 1is configured such that the lower base material 11 and the upper base material 13 are integrally formed and are folded at the boundary line 15 between the lower base material 11 and the upper base material 13 so that the two are superimposed.
- the lower base material 11 and the upper base material 13may also be formed separately from each other.
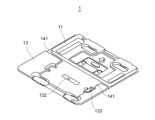
- a pool 111 in which blood is placedis formed on the inner surface side of the lower substrate 11.
- the capacity of the pool 111is determined based on the appropriate amount of blood to be added to the testing device 2 (for example, 30 ⁇ L to 40 ⁇ L) so that when the pool 111 is filled with blood such that the blood rises slightly above the upper surface of the pool 111 (i.e., the pool side surface 112) due to surface tension, it will be approximately the appropriate amount.
- the size of the opening surface of the pool 111is preferably the same as or slightly smaller than the blood addition section 21a of the testing device 2. Even if the opening surface of the pool 111 is smaller than the blood addition section 21a, the blood can be widely diffused over the entire surface of the plasma separation section 24 by the diffusion layer 23 by bringing the blood into contact with a part of the blood addition section 21a.
- the shape of the opening surface of the pool 111may be the same as or different from that of the blood addition section 21a. In this embodiment, the blood addition section 21a is rectangular, whereas the opening surface of the pool 111 is elliptical.
- a protrusion 113is formed near the pool 111, protruding further inward than the pool side surface 112.
- This protrusion 113functions as a support that ensures a gap G (see FIG. 2C) of a predetermined height between the pool side surface 112 and the fixing surface 13a of the test device 2 on the upper substrate 12 when the lower substrate 11 and the upper substrate 12 are overlapped.
- the height of this gap Gis preferably set to be approximately the same as the thickness of the test device 2 or slightly smaller than the test device 2.
- the blood addition portion 21a of the test device 2can be brought into contact with the blood placed in the pool 111 without the user applying external force to the holder 1, and the test device 2 can be maintained in a moderately compressed state without being strongly crushed.
- the protrusion 113can also be used as a guide for the user to check the amount of blood to be added when adding it to the pool 111. Furthermore, a mark (e.g., an arrow) 114 indicating the position of the pool 111 may be placed near the pool 111.
- a marke.g., an arrow
- a guide 131is provided on the inner surface of the upper base material 13 (i.e., the side facing the pool 111) to indicate the position where the test device 2 is fixed to the upper base material 13.
- the guide 131is provided so as to protrude toward the inner surface side beyond the fixing surface 13a of the test device 2.
- the test device 2can be attached to the blood test device 2 in the appropriate position by abutting the end side of the test device 2 against the inner wall of the guide 131.
- the guide 131may simply be a printed mark indicating the attachment position of the test device 2.
- the upper base material 13has an opening 132 that exposes the observation windows 22a to 25c when the inspection device 2 is fixed in place in accordance with the guide 131.
- the upper base material 13may also have an alignment opening 133 formed therein that corresponds to the alignment opening 27 of the inspection device 2.
- the lower substrate 11is formed with support portions 115 and 116 that protrude from the floor surface of the lower substrate 11 to the inner side.
- the top surface of the support portion 115abuts against the floor surface 134 of the upper substrate 13, and the top surface of the support portion 116 abuts against the floor surface 135 of the upper substrate.
- these support portions 115 and 116can also function as a means for ensuring a gap G of a predetermined height between the pool side surface 112 of the pool 111 provided on the lower substrate 11 and the fixing surface 13a of the testing device 2 on the upper substrate 13.
- both the lower base material 11 and the upper base material 13may be provided with support parts that protrude to the inner side and abut against each other at the top surface.
- the protrusion part 113may be omitted, and either or both of the support parts 115 and 116 may be provided. In short, it is sufficient that a gap G is secured between the pool side surface 112 and the fixing surface 13a when the upper base material 13 is superimposed on the lower base material 11.
- the upper substrate 13has two convex portions 136 that protrude from the floor surface toward the inner side. Protrusions 137 are formed on the outer wall surfaces of these convex portions 136. Meanwhile, the lower substrate 11 has two convex portions 121 that protrude from the floor surface. The spaces between these convex portions 121 and the outer periphery 120 form spaces 122 into which the two convex portions 136 can each fit. In the inner wall surface of the outer periphery 120 and the outer wall surface of the convex portions 121 that form each space 122, depressions 123, 124 are formed at positions that correspond to the protrusions 137 of the upper substrate 13.
- the protrusions 137 on the convex portion 136 sidefit into the recesses 123 and 124 on the space 122 side, and the lower substrate 11 and the upper substrate 13 can be fixed in a closed state.
- a convex portion with a protrusion on the outer wall surfacemay be provided on the lower base material 11, and a space with a recess formed on the wall surface may be provided on the upper base material 13.
- a guide 141may be formed on the outer surface of the upper substrate 13, protruding toward the surface on which the opening 132 is formed.
- the guide 141can be used to align the opening 132 with a card-shaped color sample (color comparison card) used when observing the color reaction of the reagent phases 25a to 25c.
- the test items corresponding to the reagent phases 25a to 25c exposed from the opening 132may be displayed around the opening 132 on the outer surface of the upper substrate 13 by printing or stickers.
- FIG. 12are schematic diagrams for explaining a method of using the blood test auxiliary device according to this embodiment.
- TCHDtotal cholesterol
- TGtriglycerides
- GLUblood glucose
- the test device 2is attached to the inner surface of the upper base material 13 of the auxiliary tool 1.
- the alignment opening 27 of the test device 2is aligned with the alignment opening 133 of the upper base material 13, the blood addition section 21a is faced to the inner surface, and the test device 2 is placed inside the guide 131.
- the means for attaching the test device 2and for example, double-sided tape can be used.
- the subjectplaces blood collected by puncturing his/her fingertip or the like in the pool 111.
- the bloodcan be transferred to the pool 111 by directly contacting the blood pool formed on the fingertip or the like with the pool 111.
- the amount of bloodis such that the surface of the blood 3 rises above the pool side surface 112 due to surface tension.
- the subjectcan check whether the amount of blood 3 is sufficient by using the protrusion 113 as a guide.
- FIG. 10(b)if the surface of the blood 3 is lower than the pool side surface 112, the blood 3 cannot come into contact with the diffusion layer 23 inside the blood addition section 21a, and the amount of blood may be insufficient.
- FIG. 10(c)even if the surface of the blood 3 is higher than the pool side surface 112, if the entire pool 111 is not filled with blood, the amount of blood may still be insufficient.
- the upper base material 13is folded at the boundary line 15 and overlapped with the lower base material 11.
- the convex portion 136 of the upper base material 13is fitted into the space 122 of the lower base material 11. This allows the assistive device 1 to be kept closed without the subject having to hold it down.
- the height of the gap G between the pool side surface 112 of the lower substrate 11 and the fixing surface 13a of the upper substrate 13is approximately the same as the thickness of the test device 2. Therefore, by closing the auxiliary tool 1, the first substrate 21 of the test device 2 is brought into almost contact with the pool side surface 112. As a result, the surface of the blood 3 filling the pool 111 comes into contact with the diffusion layer 23 inside the blood addition section 21a. As a result, almost all of the blood 3 in the pool 111 is sucked in by capillary action and added to the test device 2.
- the auxiliary tool 1when the auxiliary tool 1 is closed, it is acceptable for there to be a small gap between the test device 2 and the pool side surface 112.
- the blood 3fills the pool 111 in a raised state due to surface tension (see FIG. 10(a)), so if a portion of the surface of the blood 3 can come into contact with the diffusion layer 23, the blood will be sucked in from that point.
- the blood that has spread over the entire surface of the diffusion layer 23soaks into the plasma separation section 24.
- the plasma separated by the plasma separation section 24then soaks into the reagent phases 25a-25c.
- the color of the reagent phases 25a-25c in which a color reaction has occurredis compared with a reference color to estimate the concentration of the test item.
- the colorimetric card 4 shown in FIG. 12can be used to estimate the concentration.
- the colorimetric card 4displays scales 41-43 consisting of color samples that the reagent phases 25a-25c can show for each test item (for example, total cholesterol (TCHO), triglycerides (TG), blood glucose (GLU)).
- the scales 41-43display numerical values indicating the concentration of the component corresponding to each color (or the stage corresponding to the concentration).
- openings 44-46 corresponding to the positions of the reagent phases 25a-25c appearing in the opening 132 of the auxiliary tool 1are formed within the area of each scale 41-43.
- the values displayed on each scale 41 to 43indicate the concentration (mg/dL) range that can be detected by a simple test in stages. Specifically, the concentration of total cholesterol is shown in seven stages, the concentration of triglycerides is shown in five stages, and the concentration of blood glucose is shown in seven stages.
- the reagent phases 25a to 25cappear in sequence in the openings 44 to 46.
- the subjectcan visually determine the test results (concentration of each component) by comparing the colors of the reagent phases 25a to 25c that appear in the openings 44 to 46, respectively, with the color samples in the scales 41 to 43.
- the auxiliary tool 1can be disposed of without opening it. This prevents contamination by the tested blood.
- the test device 2is fixed to the auxiliary tool 1, blood is placed in the pool 111 of the auxiliary tool 1, and the auxiliary tool 1 is closed to perform the test, making it possible to add an appropriate amount of blood to the blood test device with simple operations.
- a protrusion 113 that protrudes from the pool side surface 112is provided near the pool 111, so that the subject can use it as a guide for the amount of blood when placing blood in the pool 111.
- the inspection device 2is attached to the auxiliary tool 1 and inspection is performed, making it easy to handle the inspection device 2.
- the reaction in test device 2begins by closing auxiliary tool 1, making it easy to control the test time.
- the waiting time from when blood is added to test device 2 until sufficient reaction is observed in reagent phases 25a to 25ccan be accurately counted.
- the test device 2by attaching the test device 2 to the auxiliary tool 1 in accordance with the guide 131, the color reaction of the reagent phases 25a to 25c can be observed from the outer surface of the auxiliary tool 1.
- the support portions 115 and 116are provided to ensure a gap G of a predetermined height between the pool side surface 112 and the fixing surface 13a, so that the testing device 2 can be held without being crushed.
- the upper substrate 13can be fixed to the lower substrate 11 and maintained in a closed state by fitting the convex portion 136 with the protrusion 137 formed on the wall surface into the space 122 with the recesses 123, 124 formed on the wall surface. Therefore, contamination of the surroundings by blood can be prevented during the waiting time for the color reaction, during observation using the color comparison card 4, and even at the time of disposal.
- the outer peripheral shape and size of the lower substrate 11 and the upper substrate 13are the same (see FIG. 5), but the outer peripheral shape or size of the two may be different.
- a notchmay be provided in a part of the upper substrate 13.
- the auxiliary tool 1is placed on a desk, blood is placed in the pool 111, and then the part of the lower substrate 11 corresponding to the notch is pressed to keep the lower substrate 11 horizontal, and the upper substrate 13 is placed over the lower substrate 11. This makes it easier to handle the auxiliary tool 1.
- a tongue protruding outwardmay be formed on either the lower substrate 11 or the upper substrate 13.
- the tonguecan be pressed down to place the upper substrate 13 over the lower substrate 11.
- the tonguecan be pinched and placed over the lower substrate 11.
- tonguesmay be formed on both the lower substrate 11 and the upper substrate 13 at different positions.
- test device 2An experimental test device having a similar configuration to test device 2 was created, and an experiment was carried out as follows in which the amount of blood placed in auxiliary tool 1 was changed and the colorimetric sensitivity in the reagent phase was measured.
- Reagent phase MaterialTest paper impregnated with glucose concentration measuring reagents (ingredients: piperazine-1,4-bis(2-ethanesulfonic acid) (PIPES), N-ethyl-N-(2-hydroxy-3-sulfopropyl)-3,5-dimethoxyaniline sodium (DAOS), 4-aminoantipyrine (4-AA), mutarotase, peroxidase (POD), glucose oxidase) and dried.
- PPESglucose concentration measuring reagents
- Plasma separation section MaterialAsymmetric polysulfone Size: 5 mm (short side of the device) x 10 mm (longitudinal direction of the device), thickness 0.33 mm
- Diffusion layer Materialhydrophilic polyester plain weave sheet Size: 5 mm (short side of device) x 10 mm (longitudinal direction of device), thickness 0.12 mm
- Experimental method(1) A blood test device was attached to a specified location on the support tool. (2) Experimental blood (whole blood) was dropped into the pool of the support tool. Three different amounts of blood were used: 30 ⁇ L, 35 ⁇ L, and 40 ⁇ L. In all cases, the surface of the blood was raised above the side of the pool due to surface tension. (3) Five minutes after the auxiliary tool was closed, the reagent phase exposed in the observation window was photographed with an optical camera, and the colorimetric sensitivity of each reagent phase was estimated based on the image. Furthermore, the CV value of the colorimetric sensitivity was calculated. (4) Based on the colorimetric sensitivity, the concentration (mg/dL) of each component was calculated.
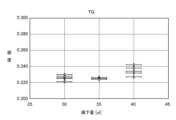
- FIG. 13is a graph showing the colorimetric sensitivity of blood glucose in the example.
- FIG. 14is a graph showing the colorimetric sensitivity of triglycerides in the example.
- FIG. 15is a graph showing the colorimetric sensitivity of total cholesterol in the example.
- FIG. 16is a graph showing the blood glucose concentration corresponding to the colorimetric sensitivity shown in FIG. 13.
- FIG. 17is a graph showing the triglyceride concentration corresponding to the colorimetric sensitivity shown in FIG. 14.
- FIG. 18is a graph showing the total cholesterol concentration corresponding to the colorimetric sensitivity shown in FIG. 15.
- the horizontal axisshows the amount of blood dropped into the pool
- the vertical axisshows the colorimetric sensitivity.
- the horizontal axisshows the colorimetric sensitivity
- the vertical axisshows the concentration of each component (mg/dL).
- the CV values of colorimetric sensitivitywere 1.61% for blood glucose, 2.42% for triglycerides, and 2.44% for total cholesterol.
- the blood volumes set in the experimentwere 30 ⁇ L, 35 ⁇ L (approximately 17% increase), and 40 ⁇ L (approximately 14% increase).
- the colorimetric sensitivitywas generally within the range of ⁇ 0.02 regardless of the amount of blood dripped.
- the CV value of the colorimetric sensitivitywas within 3% for all components. Therefore, it can be said that the variation in colorimetric sensitivity due to the amount of blood dripped is small.
- the variation in colorimetric sensitivity shown in Figures 13 to 15does not have a significant effect on the concentration of each component.
- the same level for blood glucoseis approximately 80 mg or more and less than 120 mg per dL
- the same level for triglyceridesis approximately 70 mg or more and less than 100 mg
- the same level for total cholesterolis approximately 180 mg or more and less than 220 mg.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Investigating Or Analysing Biological Materials (AREA)
- Measurement Of The Respiration, Hearing Ability, Form, And Blood Characteristics Of Living Organisms (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、血液中の特定の物質の有無又は濃度を測定するための血液検査に使用される血液検査用補助具に関する。The present invention relates to a blood test aid used in blood tests to measure the presence or concentration of a specific substance in blood.
被検者の健康状態を診断するため、血液に含まれる特定の物質の有無又は濃度を分析する血液検査が広く行われている。例えば、血液中の血漿に含まれる各種成分の含有量を分析することにより、被検者の臓器機能等を診断することができる。Blood tests that analyze the presence or concentration of specific substances in blood are widely used to diagnose a subject's health condition. For example, by analyzing the content of various components in the plasma in the blood, it is possible to diagnose the subject's organ function, etc.
一般的な血液検査において、検体である血液は、遠心分離器や吸引・加圧ポンプ等を用いて、液体成分である血漿又は血清と固体成分である細胞等とに分離される。通常、遠心分離機にかけるためには、ある程度の量(例えば5mL以上)の血液が必要になるため、医師、看護師、又は臨床検査技師が被検者から採血しなければならない。そのため、一般的な血液検査は、遠心分離機等の高価な分析機器や、それを作動させるための電源設備が整った医療機関又は専門の検査機関においてしか行うことができない。また、採血する医療従事者の負担も大きい。つまり、一般的な血液検査においては、被検者のみならず、医療機関の負担も大きく、コストも高い。In a typical blood test, the blood sample is separated into liquid components, such as plasma or serum, and solid components, such as cells, using a centrifuge or suction/pressurization pump. Normally, a certain amount of blood (e.g., 5 mL or more) is required to run the blood through a centrifuge, so a doctor, nurse, or clinical laboratory technician must draw blood from the subject. For this reason, typical blood tests can only be performed at medical institutions or specialized testing institutions that are equipped with expensive analytical equipment such as centrifuges and the power supplies to operate them. In addition, the burden on medical professionals who draw the blood is also great. In other words, typical blood tests are a heavy burden not only on the subject but also on medical institutions, and are expensive.
一方、予防医学や健康寿命の延伸といった観点から、自分自身で健康を管理するという意識が社会に広まっている。それに伴い、迅速に検査することができ、目視により結果を判定することができる簡易な検査デバイスへのニーズが高まっている。On the other hand, from the perspective of preventive medicine and extending healthy lifespan, awareness of managing one's own health is spreading throughout society. Accordingly, there is a growing need for simple testing devices that can perform tests quickly and allow results to be determined visually.
高価な分析機器や電源を使用せずとも、血液から血漿又は血清を分離することができ、さらに、分離された血漿又は血清に含まれる特定の物質の有無又は濃度を精度良く検査できる簡易な検査デバイスがあれば、設備の整った医療機関や検査機関でなくても、また、専門の技術を持たない一般の人であっても、自分自身で簡便に、且つ安価に、自己採血した微量の血液を用いて検査することができる。それにより、一般の人の日常的な健康管理にはもちろん、外出が困難な在宅者の健康管理にも役立てることができる。また、医療体制が脆弱な国や地域、或いは、被災地など電源の確保が困難な地域であっても、検査が可能となる。従って、使い易く精度の良い検査デバイスの開発に対する社会的要請は大きい。 If there was a simple testing device that could separate plasma or serum from blood without using expensive analytical equipment or power sources, and that could accurately test for the presence or concentration of specific substances contained in the separated plasma or serum, then even those not at a well-equipped medical institution or testing facility, and even ordinary people without specialized skills, could easily and inexpensively test themselves using a small amount of self-drawn blood. This would be useful not only for everyday health management for the general public, but also for health management for people at home who find it difficult to go out. Furthermore, testing would be possible even in countries and regions with weak medical systems, or in areas where it is difficult to secure power sources, such as disaster areas. Therefore, there is a great social demand for the development of an easy-to-use and highly accurate testing device.
特許文献1には、解析物に特定の発色試薬系を含みかつ試験面を定める比較的小さな孔のある側と試料受容面を定める比較的大きな孔のある反対側とを有する異方性膜より形成された試験用パッド、及び試験用パッドの試料受容面に取り付けられた多孔性の試料移送媒体であって、全血試料を受け入れることができかつ試料の検知可能な部分を試料受容面に移送することができる前記移送媒体を備えた試薬ストリップが開示されている。
血液から分離された血漿を試薬相に染み込ませることにより生じる呈色反応を観察する簡易式の血液検査デバイスにおいては、次のような問題がある。即ち、信頼性及び再現性の良い検査結果を得るためには、試薬相の全面に対し、必要且つ十分な量の血漿を接触させなければならない。血漿の量が不足している場合、血漿と試薬相との接触により得られる呈色反応の感度が低くなり、反応を観測できなくなってしまうおそれがあるからである。或いは、血漿の量が不足している場合には、試薬相において反応のムラが生じ、検査の再現性が低下してしまうという問題もある。他方、血漿の量が多すぎる場合、血漿が試薬相から溢れてしまい、試薬相の側方から表面に血漿が回り込むなどして、不均一な反応となってしまう。つまり、試薬相に対して適切な量の血漿を染み込ませることが重要であり、そうすることで、血液に含まれる特定の物質の濃度に応じた正確な呈色反応を得ることができ、再現性も良好となる。そして、そのためには、検査デバイスに対し、適量の血液を添加する必要がある。In a simple blood testing device that observes the color reaction caused by soaking the reagent phase with plasma separated from blood, there are the following problems. That is, in order to obtain reliable and reproducible test results, a necessary and sufficient amount of plasma must be brought into contact with the entire surface of the reagent phase. If the amount of plasma is insufficient, the sensitivity of the color reaction obtained by contact between the plasma and the reagent phase will be low, and there is a risk that the reaction will not be observed. Alternatively, if the amount of plasma is insufficient, there is a problem that the reaction will be uneven in the reagent phase, and the reproducibility of the test will decrease. On the other hand, if the amount of plasma is too much, the plasma will overflow from the reagent phase and wrap around the surface from the sides of the reagent phase, resulting in an uneven reaction. In other words, it is important to soak the reagent phase with an appropriate amount of plasma, and by doing so, an accurate color reaction according to the concentration of a specific substance contained in the blood can be obtained, and reproducibility will also be good. And for that, an appropriate amount of blood needs to be added to the testing device.
しかしながら、一般の被験者が自身で検査することができる検査デバイスにおいて、被験者に、自己採血した血液をピペットや毛細管等の器具を用いて計量させることは現実的ではない。However, when it comes to testing devices that allow general subjects to test themselves, it is not realistic to require subjects to measure the amount of self-collected blood using instruments such as pipettes or capillary tubes.
本発明は上記に鑑みてなされたものであって、簡便な操作で血液検査デバイスに適量の血液を添加することができる血液検査用補助具を提供することを目的とする。The present invention was made in consideration of the above, and aims to provide a blood testing aid that allows an appropriate amount of blood to be added to a blood testing device with simple operations.
上記課題を解決するために、本発明の一態様である血液検査用補助具は、血液検査デバイスを用いた検査を補助する血液検査用補助具であって、前記血液検査デバイスは、血液が添加される開口である血液添加部が形成された第1の基板と、呈色反応を観察するための開口である観察窓が形成された第2の基板と、該第1及び第2の基板の間に積層されて配置された血漿分離膜及び乾式試薬相とを有し、血液が配置されるプールが形成された第1の基材と、前記第1の基材と重ね合わせが可能な第2の基材であって、前記プールと対向する側に、該第2の基材に対して前記血液検査デバイスが固定される位置を示すガイドが設けられると共に、該ガイドに合わせて前記血液検査デバイスを固定した場合に前記観察窓を露出させる開口が形成された第2の基材と、を備える。In order to solve the above problems, the blood test auxiliary tool of one aspect of the present invention is a blood test auxiliary tool that assists in tests using a blood test device, and the blood test device has a first substrate on which a blood addition section, which is an opening through which blood is added, is formed, a second substrate on which an observation window, which is an opening for observing a color reaction, is formed, and a plasma separation membrane and a dry reagent phase are arranged by being laminated between the first and second substrates, and is provided with a first base material on which a pool in which blood is placed is formed, and a second substrate that can be superimposed on the first substrate, and is provided with a guide on the side facing the pool that indicates the position where the blood test device is fixed to the second substrate, and is provided with an opening that exposes the observation window when the blood test device is fixed in accordance with the guide.
上記血液検査用補助具において、前記第1の基材と前記第2の基材とを重ね合わせた場合に、前記プールのプールサイド面と前記第2の基材における前記血液検査デバイスの固定面との間に所定の高さのギャップを確保する支持部が、前記第1及び第2の基材の少なくともいずれか一方に設けられていても良い。In the above blood test auxiliary device, at least one of the first and second substrates may be provided with a support portion that ensures a gap of a predetermined height between the pool side surface of the pool and the fixing surface of the blood test device on the second substrate when the first substrate and the second substrate are superimposed.
上記血液検査用補助具において、前記第1の基材の前記プールの近傍に、前記プールサイド面よりも突出する突起部が形成されていても良い。In the blood test auxiliary device, a protrusion that protrudes beyond the pool side surface may be formed on the first base material near the pool.
上記血液検査用補助具において、前記第1の基材と前記第2の基材とは、互いに連続するシート状部材により形成され、前記第1の基材と前記第2の基材との境界線において折り畳むことにより、前記第1の基材と前記第2の基材とが重ね合わせられるようにしても良い。In the above blood test auxiliary device, the first substrate and the second substrate may be formed from a continuous sheet-like member, and the first substrate and the second substrate may be overlapped by folding the first substrate and the second substrate at the boundary line between them.
上記血液検査用補助具において、前記第1及び第2の基材の一方に、壁面に突起が形成された凸部が設けられ、前記第1及び第2の記載の他方に、前記凸部が嵌合可能な凹状のスペースが設けられ、前記スペースの壁面のうち前記突起に対応する位置に窪みが形成され、前記凸部を前記スペースに嵌合させることにより、前記突起が窪みに嵌り込み、前記第1の基材と前記第2の基材とが重ね合わせられた状態で固定されるようにしても良い。In the above blood test auxiliary device, one of the first and second base materials may be provided with a convex portion with a protrusion formed on a wall surface, the other of the first and second base materials may be provided with a concave space into which the convex portion can fit, and a depression may be formed in the wall surface of the space at a position corresponding to the protrusion, and by fitting the convex portion into the space, the protrusion may fit into the depression, and the first base material and the second base material may be fixed in a superimposed state.
本発明によれば、血液検査用補助具に血液検査デバイスを固定し、プールに血液を配置することにより、簡便な操作で血液検査デバイスに適量の血液を添加することが可能となる。According to the present invention, by fixing a blood testing device to a blood testing auxiliary tool and placing blood in a pool, it is possible to add an appropriate amount of blood to the blood testing device with a simple operation.
以下、本発明の実施の形態に係る血液検査用補助具について、図面を参照しながら説明する。なお、これらの実施の形態によって本発明が限定されるものではない。また、各図面の記載において、同一部分には同一の符号を付して示している。Below, blood test auxiliary devices according to embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Note that the present invention is not limited to these embodiments. In addition, in the descriptions of the drawings, the same parts are denoted by the same reference numerals.
以下の説明において参照する図面は、本発明の内容を理解し得る程度に形状、大きさ、及び位置関係を概略的に示しているに過ぎない。即ち、本発明は各図で例示された形状、大きさ、及び位置関係のみに限定されるものではない。また、図面の相互間においても、互いの寸法の関係や比率が異なる部分が含まれている場合がある。
ここで、本明細書において微量とは、数μL~数十μL程度のことをいう。The drawings referred to in the following description merely show the shape, size, and positional relationship in a schematic manner to the extent that the contents of the present invention can be understood. In other words, the present invention is not limited to the shape, size, and positional relationship exemplified in each drawing. In addition, there may be cases where the dimensional relationship and ratio of each part differs between the drawings.
In this specification, a small amount refers to a few μL to several tens of μL.
図1は、本発明の実施形態に係る血液検査用補助具の内面側(展開した状態)を示す平面図である。図2は、図1に示すA-A~F-Fの各ラインにおける端面図である。詳細には、図2の(a)は図1のA-A端面を示し、図2の(b)は図1のB-B端面を示し、図2の(c)は図1のC-C端面を示し、図2の(d)は図1のD-D端面を示し、図2の(e)は図1のE1-E2-E3-E4端面を示し、図2の(f)は図1のF-F端面を示す。図3は、同血液検査用補助具の内面側(展開した状態)を示す斜視図である。図4は、同血液検査用補助具の外面側(展開した状態)を示す斜視図である。図5は、同血液検査用補助具(折り畳んだ状態)を示す斜視図である。1 is a plan view showing the inner side (unfolded state) of the blood test auxiliary according to the embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 is an end view of each of the lines A-A to F-F shown in FIG. 1. In detail, FIG. 2(a) shows the A-A end face of FIG. 1, FIG. 2(b) shows the B-B end face of FIG. 1, FIG. 2(c) shows the C-C end face of FIG. 1, FIG. 2(d) shows the D-D end face of FIG. 1, FIG. 2(e) shows the E1-E2-E3-E4 end face of FIG. 1, and FIG. 2(f) shows the F-F end face of FIG. 1. FIG. 3 is a perspective view showing the inner side (unfolded state) of the blood test auxiliary. FIG. 4 is a perspective view showing the outer side (unfolded state) of the blood test auxiliary. FIG. 5 is a perspective view showing the blood test auxiliary (folded state).
本実施形態に係る血液検査用補助具(以下、単に補助具とも記す)1は、被験者が自己採血した血液の検査を補助する器具である。図1~図5に示すように、補助具1は、互いに重ね合わせることが可能な下側基材(第1の基材)11及び上側基材(第2の基材)12を備える。本明細書においては、補助具1の使用時に下側基材11と上側基材13とを重ね合わせた際に外側となる側(図5参照)を外面側、内側となる側を内面側と記す。補助具1の詳細は構成については後述する。The blood test auxiliary device (hereinafter also simply referred to as the auxiliary device) 1 according to this embodiment is an instrument that assists in testing blood that has been self-drawn by a subject. As shown in Figures 1 to 5, the
(検査デバイスの構成)
図6は、本発明の実施形態において用いられる血液検査デバイスを例示する斜視図(血液添加部側)である。図7は、同血液検査デバイスの斜視図(観察窓側)である。図8は、同血液検査デバイスの分解斜視図である。(Testing device configuration)
Fig. 6 is a perspective view (blood addition part side) illustrating a blood test device used in an embodiment of the present invention. Fig. 7 is a perspective view (observation window side) of the same blood test device. Fig. 8 is an exploded perspective view of the same blood test device.
図6~図8に例示する血液検査デバイス(以下、単に検査デバイスとも記す)2は、血液から分離された血漿を、試薬を含侵させた乾式試薬相に接触させることにより、該乾式試薬相に生じる呈色反応に基づいて、血漿に含まれる特定の物質の有無又は濃度を測定するためのものである。測定可能な検査項目は、血漿に含まれる成分であり、且つ、所定の試薬に対して呈色反応を示す成分であれば特に限定されない。検査項目の具体例としては、AST、ALT、γ-GT、中性脂肪、HDLコレステロール、LDLコレステロール、総コレステロール、血糖、HbA1c等の他、亜鉛やマグネシウム等のミネラルが挙げられる。The blood testing device (hereinafter also referred to simply as the testing device) 2 shown in Figures 6 to 8 is intended to measure the presence or concentration of a specific substance contained in plasma based on a color reaction that occurs in a dry reagent phase by contacting the plasma separated from blood with a dry reagent phase impregnated with a reagent. Measurable test items are not particularly limited as long as they are components contained in plasma and show a color reaction with a specific reagent. Specific examples of test items include AST, ALT, γ-GT, neutral fats, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, total cholesterol, blood glucose, HbA1c, etc., as well as minerals such as zinc and magnesium.
検査デバイス2は、互いに対向して配置された第1基板21及び第2基板22と、これら第1基板21と第2基板22との間に積層されて配置された拡散層23、血漿分離部24、及び試薬相25a~25cとを備える。検査デバイス2において同時に検査可能な項目数は特に限定されない。本実施形態においては、3つの試薬相25a~25cを設けることにより、3つの検査項目(例えば、総コレステロール、中性脂肪、血糖)を同時に検査可能としているが、検査可能な項目の数(試薬相の数)は1つ又は2つ、或いは4つ以上であっても良い。The
第1基板21及び第2基板22は、薄手のシート材により形成されている。第1基板21及び第2基板22の材料は、PET(ポリエチレンテレフタレート)などの樹脂材料や、撥水加工が施された厚紙など、検査デバイス2の形状を維持することができ、且つ、試料である血液や血漿が浸み込んだり、これらの液体と反応したりしないような材料であれば良い。The
第1基板21には、試料である血液が添加される開口である血液添加部21aが形成されている。なお、本実施形態においては、血液添加部21aの形状を矩形状としているが、この形状は特に限定されず、血液の添加が可能な形状であれば、楕円形状や長円形など、様々な形状を採用することができる。The
第2基板22には、試薬相25a~25cの呈色反応をそれぞれ観察するための開口である観察窓22a~22cが形成されている。これらの観察窓22a~22cの数も、検査項目の数(即ち、試薬相25a~25cの数)に応じて設定される。なお、本実施形態においては、各観察窓22a~22cの形状を正方形としているが、この形状は特に限定されず、円形や楕円形等であっても良い。また、第1基板21及び第2基板22の対応する箇所に、位置合わせ用開口27をそれぞれ形成しても良い。The
これらの第1基板21と第2基板22との間に、拡散層23、血漿分離部24、及び試薬相25a~25cが、この順に積層されて配置されている。なお、第1基板21及び第2基板22は、図8に示すように、互いに分離された2枚の板材によって形成しても良いし、1枚の細長い板材を折り曲げることによって形成しても良い。また、第1基板21と第2基板22との間に、拡散層23、血漿分離部24、及び試薬相25a~25cを配置可能な高さの空間20aを形成するためのスペーサ26を配置しても良い。Between the
拡散層23は、親水性を有する繊維をシート状に織った部材により形成され、第1基板21に設けられた血液添加部21aから一部が露出するように配置されている。拡散層23は、血液添加部21aに添加された血液を、毛管現象により面方向の広範囲に素早く誘導し、血漿分離部24の一方の面に均一に染み込ませるように作用する。拡散層23としては、例えば親水性ポリエステルを平織にした部材を用いることができる。The
血漿分離部24は、多孔質のシート材により形成され、一方の面に染み込んだ血液のうち細胞成分をトラップし、液体成分を膜厚方向に通過させることにより血漿を分離する。血漿分離部24としては、ポリスルホン(PS)膜や非対称PS膜等の多孔質性高分子膜を用いることができる。The
試薬相25a~25cは、検査項目に応じた試薬を濾紙(クロマト紙等)に含侵させて乾燥させた乾式試薬相であり、観察窓22a~22cのそれぞれから一部が露出するように配置されている。試薬相25a~25cは、血漿分離部24を透過した血漿に含まれる所定の物質と反応して呈色する。この呈色反応は、血漿が試薬相25a~25cに十分染み渡ることにより、観察窓22a~22cの側から目視観察することができる。The reagent phases 25a-25c are dry reagent phases in which filter paper (such as chromatography paper) is impregnated with a reagent corresponding to the test item and dried, and are arranged so that a portion of them is exposed from each of the
これらの拡散層23、血漿分離部24、及び試薬相25a~25cは、両面テープ等を用いて第1基板21又は第2基板22に接着されている。また、第1基板21と第2基板22も、両面テープ等を用いて互いに、或いは、スペーサ26を介して接着されている。The
(血液検査用補助具の構成)
再び図1~図5を参照すると、補助具1の下側基材11及び上側基材13は、例えば、ポリエチレンテレフタレート(PET)やポリエチレン(PE)等の樹脂材料を用いて真空成形することにより形成されている。もっとも、下側基材11及び上側基材13の形成方法及び材料はこれには限定されない。例えば、パルプと樹脂の複合材料や、ボール紙に撥水加工を施した材料を用いても良いし、プレス加工やパルプ成形技術を用いて下側基材11及び上側基材13を成形しても良い。(Configuration of blood test auxiliary equipment)
1 to 5 again, the
また、本実施形態において、補助具1は、下側基材11及び上側基材13を一体的に形成し、下側基材11と上側基材13との境界線15において折り畳むことにより、両者が重ね合わせられるように構成されている。しかしながら、下側基材11及び上側基材13を互いに分離して形成しても良い。In addition, in this embodiment, the
図1~図3に示すように、下側基材11の内面側には、血液が配置されるプール111が形成されている。プール111の容量は、検査デバイス2において適量とされる血液の添加量(一例として、30μL~40μL)をもとに、血液が表面張力によりプール111の上面(即ち、プールサイド面112)よりも若干盛り上がるように血液でプール111を満たした場合に、概ね適量となるように決定されている。As shown in Figures 1 to 3, a
プール111の開口面のサイズは、プール111に検査デバイス2の血液添加部21aと同程度か同程度よりも若干小さくすることが好ましい。プール111の開口面が血液添加部21aよりも小さい場合であっても、血液添加部21aの一部に血液を接触させることで、拡散層23により血漿分離部24の全面に血液を広く拡散させることができる。また、プール111の開口面の形状は、血液添加部21aと同じであっても良いし異なっていても良い。本実施形態においては、血液添加部21aが矩形であるのに対し、プール111の開口面を楕円形としている。The size of the opening surface of the
プール111の近傍には、プールサイド面112よりも内面側に突出する突起部113が形成されている。この突起部113は、下側基材11と上側基材12とを重ね合わせた場合に、プールサイド面112と上側基材12における検査デバイス2の固定面13aとの間に所定の高さのギャップG(図2の(c)参照)を確保する支持部として機能する。このギャップGの高さは、好ましくは、検査デバイス2の厚さと概ね同程度か、検査デバイス2よりも若干小さくとなるように設定される。ギャップGを適切に設定することで、下側基材11と上側基材12とを重ね合わせた際に、ユーザが保持具1に外から力を加えることなく、検査デバイス2の血液添加部21aをプール111に配置された血液に接触させることができると共に、検査デバイス2を強く押し潰すことなく、適度に圧迫した状態を維持することができる。A
また、突起部113を、ユーザがプール111に血液を添加する際の添加量を確認するためのガイドとして使用することもできる。さらに、プール111の近傍に、プール111の位置を示すマーク(例えば矢印)114を配置しても良い。The
上側基材13の内面側(即ち、プール111と対向する側)には、上側基材13に対して検査デバイス2が固定される位置を示すガイド131が設けられている。本実施形態において、ガイド131は、検査デバイス2の固定面13aよりも内面側に突出するように設けられている。ガイド131の内壁に検査デバイス2の端部側面を突き当てることにより、検査デバイス2を血液検査デバイス2の適正な位置に取り付けることができる。なお、ガイド131は、単に検査デバイス2の取付位置を示す印刷されたマークであっても良い。A
上側基材13には、ガイド131に合わせて検査デバイス2を固定した場合に、観察窓22a~25cを露出させる開口132が形成されている。また、上側基材13に、検査デバイス2の位置合わせ用開口27に対応する位置合わせ用開口133を形成しても良い。The
下側基材11には、下側基材11の床面から内面側に突出する支持部115,116が形成されている。下側基材11に上側基材13を重ね合わせたとき、支持部115の天面は、上側基材13の床面134に当接し、支持部116の天面は、上側基材の床面135に当接する。これらの支持部115,116も、下側基材11に上側基材13を重ね合わせた場合に、下側基材11に設けられたプール111のプールサイド面112と上側基材13における検査デバイス2の固定面13aとの間に所定の高さのギャップGを確保する手段として機能させることができる。The
なお、支持部115と支持部116とは、いずれか一方のみを設けることとしても良い。また、上側基材13の側に内面側に突出する支持部を設け、その天面を下側基材11の床面に当接させるようにしても良い。或いは、下側基材11と上側基材13の双方に、内面側に突出し、天面において互いに当接する支持部を設けても良い。さらに、突起部113が設けられている場合には、支持部115,116を設けることは必須ではない。反対に、突起部113を省略して、支持部115,116のいずれか又は両方を設けることとしても良い。要は、下側基材11に上側基材13を重ね合わせた場合に、プールサイド面112と固定面13aとの間にギャップGが確保されれば良い。It is also possible to provide only one of the
上側基材13には、床面から内面側に突出する2つの凸部136が設けられている。これらの凸部136の外壁面には、突起137が形成されている。一方、下側基材11には、床面から突出する2つの凸部121が形成されている。これらの凸部121と外周部120との間のスペースが、2つの凸部136がそれぞれ嵌合可能なスペース122となっている。各スペース122を形成する外周部120の内壁面及び凸部121の外壁面のうち、上側基材13の突起137に対応する位置には、窪み123,124が形成されている。下側基材11に上側基材13を重ね合わせ、上側基材13の凸部136を下側基材11のスペース122に嵌合させることで、凸部136側の突起137がスペース122側の窪み123,124に嵌り込み、下側基材11と上側基材13とを閉じた状態で固定することができる。The
なお、下側基材11と上側基材13とを閉じた状態で固定する構成として、外壁面に突起が設けられた凸部を下側基材11に設け、壁面に窪みが形成されたスペースを上側基材13に設けても良い。In addition, as a configuration for fixing the
図4及び図5に示すように、上側基材13の外面側に、開口132が形成されている面に対して突出するガイド141を形成しても良い。ガイド141は、試薬相25a~25cの呈色反応を観察する際に使用されるカード状の色見本(比色カード)と開口132との位置合わせに使用することができる。また、上側基材13の外面側の開口132の周囲に、開口132から露出する試薬相25a~25cに対応する検査項目を、印刷やシールにより表示しても良い。As shown in Figures 4 and 5, a
(血液検査用補助具の使用方法)
図9~図12は、本実施形態に係る血液検査用補助具の使用方法を説明するための模式図である。なお、図12においては、上側基材13の外面側の開口132の周囲に、開口132から露出する試薬相25a~25cに対応する検査項目の例として、「TCHD(総コレステロール)」、「TG(中性脂肪)」、「GLU(血糖)が表示されている。(How to use blood test aids)
9 to 12 are schematic diagrams for explaining a method of using the blood test auxiliary device according to this embodiment. In Fig. 12, "TCHD (total cholesterol)", "TG (triglycerides)", and "GLU (blood glucose)" are displayed around opening 132 on the outer surface of
まず、図9に示すように、補助具1の上側基材13の内面側に、検査デバイス2を貼り付ける。この際、検査デバイス2の位置合わせ用開口27を上側基材13の位置合わせ用開口133に合わせ、血液添加部21aを内面側に向け、ガイド131の内側に検査デバイス2を配置する。検査デバイス2の貼り付け手段は特に限定されず、例えば、両面テープを用いることができる。First, as shown in FIG. 9, the
次に、被験者が自身で指先等を穿刺することにより採取した血液を、プール111に配置する。この際、指先等に形成された血溜まりを直接プール111に接触させることで、血液をプール111に移送することができる。血液の量は、図10の(a)に示すように、表面張力により血液3の表面がプールサイド面112から盛り上がる程度とすることが好ましい。この際、被験者は、突起部113を目安に、血液3の量が十分であるかどうかを確認することができる。図10の(b)に示すように、血液3の表面がプールサイド面112よりも下がっている場合、血液3が血液添加部21a内側の拡散層23に接触できず、また、血液量も不十分となるおそれがある。また、図10の(c)に示すように、血液3の表面がプールサイド面112よりも盛り上がっている場合であっても、プール111全体が血液で満たされていない場合には、やはり血液量が不十分となるおそれがある。Next, the subject places blood collected by puncturing his/her fingertip or the like in the
その後、図11に示すように、境界線15において上側基材13を折り曲げ、下側基材11に重ね合わせる。この際、上側基材13の凸部136を下側基材11のスペース122に嵌合させる。これにより、被験者が特に押さえておくことなく、補助具1が閉じられた状態を維持することができる。Then, as shown in FIG. 11, the
ここで、上述したように、下側基材11のプールサイド面112と上側基材13の固定面13aとの間にギャップGの高さは、検査デバイス2の厚さと同程度となっている。そのため、補助具1を閉じることで、検査デバイス2の第1基板21がプールサイド面112にほぼ接触した状態となる。それにより、プール111に満たされた血液3の表面が、血液添加部21a内側の拡散層23に接触する。これにより、プール111内のほぼ全ての血液3が毛細管現象により吸引され、検査デバイス2に添加される。As described above, the height of the gap G between the
ここで、補助具1を閉じた際に、検査デバイス2とプールサイド面112との間に僅かな隙間がある状態でも構わない。血液3は、表面張力により盛り上がっている状態でプール111に満たされているため(図10の(a)参照)、血液3の表面の一部が拡散層23に接触することができれば、そこを起点に血液が吸引されるからである。Here, when the
また、検査デバイス2における適量を超えて、血液3がプール111に溜まっている場合でも問題はない。補助具1を閉じる際に、余分な血液3がプールサイド面112を通じて逃げるため、結局のところ、プール111の容量を僅かに超える量しか検査デバイス2に添加されないからである。なお、プールサイド面112を通じて逃げた血液も、補助具1内に留まるため、血液の漏れに起因する周囲の汚染を防ぐことができる。Also, there is no problem if
拡散層23の全面に広がった血液は、血漿分離部24に染み込む。そして、血漿分離部24により分離された血漿が試薬相25a~25cに染み渡る。補助具1を閉じてから所定時間経過後、呈色反応が生じた試薬相25a~25cの色を基準色と比較することにより、検査項目の濃度を推定する。The blood that has spread over the entire surface of the
濃度の推定には、例えば、図12に示す比色カード4を用いることができる。比色カード4には、検査項目(例えば、総コレステロール(TCHO)、中性脂肪(TG)、血糖(GLU))ごとに、試薬相25a~25cが示し得る色見本からなるスケール41~43が表示されている。スケール41~43には、各色に応じた成分の濃度(又は濃度に応じたステージ)を示す数値が表示されている。また、各スケール41~43の領域内に、補助具1の開口132に現れる試薬相25a~25cの位置に対応する開口44~46が形成されている。For example, the colorimetric card 4 shown in FIG. 12 can be used to estimate the concentration. The colorimetric card 4 displays scales 41-43 consisting of color samples that the reagent phases 25a-25c can show for each test item (for example, total cholesterol (TCHO), triglycerides (TG), blood glucose (GLU)). The scales 41-43 display numerical values indicating the concentration of the component corresponding to each color (or the stage corresponding to the concentration). In addition, openings 44-46 corresponding to the positions of the reagent phases 25a-25c appearing in the
図12において、各スケール41~43に表示された数値は、簡易検査で検出可能な範囲の濃度(mg/dL)を段階的に示している。具体的には、総コレステロールについては濃度が7段階で示され、中性脂肪については濃度が5段階で示され、血糖については濃度が7段階で示されている。In Figure 12, the values displayed on each scale 41 to 43 indicate the concentration (mg/dL) range that can be detected by a simple test in stages. Specifically, the concentration of total cholesterol is shown in seven stages, the concentration of triglycerides is shown in five stages, and the concentration of blood glucose is shown in seven stages.
比色カード4を補助具1のガイド141に合わせて置き、図12に示す矢印の方向にスライドさせることにより、開口44~46に試薬相25a~25cが順次現れる。被験者は、開口44~46にそれぞれ現れる試薬相25a~25cの色と、スケール41~43中の色見本とを比較することにより、検査結果(各成分の濃度)を目視で判定することができる。By placing the color comparison card 4 in line with the
検査終了後には、補助具1を開くことなく、そのまま廃棄することができる。それにより、検査済みの血液による汚染等を防ぐことができる。After the test is completed, the
以上説明したように、本実施形態によれば、補助具1に検査デバイス2を固定し、補助具1のプール111に血液を配置し、補助具1を閉じることに検査を行うので、簡便な操作で血液検査デバイスに適量の血液を添加することが可能となる。As described above, according to this embodiment, the
また、本実施形態によれば、プール111の近傍に、プールサイド面112よりも突出する突起部113を設けるので、被験者が血液をプール111に配置する際に、血液量の目安とすることができる。In addition, according to this embodiment, a
また、本実施形態によれば、補助具1に検査デバイス2を貼り付けて検査を行うので、検査デバイス2の取り扱いが容易になる。Furthermore, according to this embodiment, the
また、本実施形態によれば、プール111に血液3を配置した後、補助具1を閉じることにより検査デバイス2における反応が始まるので、検査時間をコントロールし易い。つまり、検査デバイス2に血液が添加されてから試薬相25a~25cにおいて十分な反応が示されるまでの待機時間を正確にカウントすることができる。Furthermore, according to this embodiment, after placing
また、本実施形態によれば、ガイド131に合わせて検査デバイス2を補助具1に貼り付けることで、試薬相25a~25cの呈色反応を補助具1の外側面から観察することができる。Furthermore, according to this embodiment, by attaching the
また、本実施形態によれば、下側基材11と上側基材13を重ね合わせた場合に、プールサイド面112と固定面13aとの間に所定の高さのギャップGを確保する支持部115,116を設けるので、検査デバイス2を押し潰すことなく検査デバイス2を保持することができる。In addition, according to this embodiment, when the
また、本実施形態によれば、壁面に突起137が形成された凸部136を、壁面に窪123,124が形成されたスペース122に嵌め込むことにより、下側基材11に上側基材13を固定し、閉じた状態を維持することができる。従って、呈色反応の待機時間中や、比色カード4を使用した観察中、廃棄時に至るまで、血液による周囲の汚染を防ぐことができる。Furthermore, according to this embodiment, the
(変形例)
上記実施形態においては、下側基材11と上側基材13の外周形状及びサイズを互いに揃えているが(図5参照)、両者の外周形状又はサイズを異ならせても良い。例えば、上側基材13の一部に切り欠きを入れても良い。この場合、補助具1を机上に置き、プール111に血液を配置した後、切り欠きに対応する下側基材11の部分を押さえて下側基材11を水平に保ったまま、下側基材11に上側基材13を被せることができる。これにより、補助具1の取り扱いを簡単にすることができる。(Modification)
In the above embodiment, the outer peripheral shape and size of the
また、下側基材11及び上側基材13のいずれか一方に、外周側に突出する舌部を形成しても良い。下側基材11に舌部を形成した場合、該舌部を押さえて、下側基材11に上側基材13を被せることができる。反対に、上側基材13に舌部を形成した場合には、舌部をつまんで下側基材11に被せることができる。或いは、下側基材11及び上側基材13の両方に舌部を、互いに異なる位置に形成しても良い。Also, a tongue protruding outward may be formed on either the
(実施例)
検査デバイス2と同様の構成を有する実験用検査デバイスを作成し、補助具1に配置する血液の量を変化させ、試薬相における比色感度を測定する実験を以下のように行った。(Example)
An experimental test device having a similar configuration to test
1.実験用検査デバイスの作成
血液添加部及び観察窓となる開口がそれぞれ形成された2つの基板の間に、次の材料からなる試薬相、血漿分離部、及び拡散層を配置した実験用の検査デバイスを15本作製した。
(1)試薬相
材料:クロマト紙にグルコース濃度測定用の試薬(成分:ピペラジン-1,4-ビス(2-エタンスルホン酸)(PIPES)、N-エチル-N-(2-ヒドロキシ-3-スルホプロピル)-3,5-ジメトキシアニリンナトリウム(DAOS)、4-アミノアンチピリン(4-AA)、ムタロターゼ、ペルオキシダーゼ(POD)、グルコースオキシダーゼ)を含侵させ乾燥させた試験紙
サイズ :5mm(デバイスの短手方向)×2.5mm(デバイスの長手方向)、厚さ0.17mm
(2)血漿分離部
材料:非対称ポリスルホン
サイズ :5mm(デバイスの短手方向)×10mm(デバイスの長手方向)、厚さ0.33mm
(3)拡散層
材料:親水性ポリエステルの平織シート
サイズ:5mm(デバイスの短手報告)×10mm(デバイスの長手方向)、厚さ0.12mm1. Creation of an experimental test device Fifteen experimental test devices were created in which a reagent phase, a plasma separation part, and a diffusion layer made of the following materials were placed between two substrates each having an opening for a blood application part and an observation window.
(1) Reagent phase Material: Test paper impregnated with glucose concentration measuring reagents (ingredients: piperazine-1,4-bis(2-ethanesulfonic acid) (PIPES), N-ethyl-N-(2-hydroxy-3-sulfopropyl)-3,5-dimethoxyaniline sodium (DAOS), 4-aminoantipyrine (4-AA), mutarotase, peroxidase (POD), glucose oxidase) and dried. Size: 5 mm (short side of device) x 2.5 mm (longitudinal side of device), thickness 0.17 mm.
(2) Plasma separation section Material: Asymmetric polysulfone Size: 5 mm (short side of the device) x 10 mm (longitudinal direction of the device), thickness 0.33 mm
(3) Diffusion layer Material: hydrophilic polyester plain weave sheet Size: 5 mm (short side of device) x 10 mm (longitudinal direction of device), thickness 0.12 mm
2.実験方法
(1)補助具の所定箇所に血液検査デバイスを貼り付けた。
(2)補助具のプールに実験用血液(全血)を滴下した。血液の量は、30μL、35μL、40μLの3種類とした。なお、いずれの場合も、血液の表面が、表面張力によりプールサイド面よりも盛り上がっている状態であった。
(3)補助具を閉じてから5分経過後、観察窓に露出した試薬相を光学カメラにより撮影し、画像に基づいて各試薬相における比色感度を推定した。さらに、比色感度のCV値を算出した。
(4)比色感度をもとに、各成分の濃度(mg/dL)を算出した。2. Experimental method (1) A blood test device was attached to a specified location on the support tool.
(2) Experimental blood (whole blood) was dropped into the pool of the support tool. Three different amounts of blood were used: 30 μL, 35 μL, and 40 μL. In all cases, the surface of the blood was raised above the side of the pool due to surface tension.
(3) Five minutes after the auxiliary tool was closed, the reagent phase exposed in the observation window was photographed with an optical camera, and the colorimetric sensitivity of each reagent phase was estimated based on the image. Furthermore, the CV value of the colorimetric sensitivity was calculated.
(4) Based on the colorimetric sensitivity, the concentration (mg/dL) of each component was calculated.
3.実験結果
図13は、実施例における血糖の比色感度を示すグラフである。図14は、同中性脂肪の比色感度を示すグラフである。図15は、同総コレステロールの比色感度を示すグラフである。図16は、図13に示す比色感度に対応する血糖の濃度を示すグラフである。図17は、図14に示す比色感度に対応する中性脂肪の濃度を示すグラフである。図18は、図15に示す比色感度に対応する総コレステロールの濃度を示すグラフである。図13~図15において、横軸はプールに滴下した血液の量、縦軸は比色感度を示す。図16~図18において、横軸は比色感度、縦軸は各成分の濃度(mg/dL)を示す。3. Experimental Results FIG. 13 is a graph showing the colorimetric sensitivity of blood glucose in the example. FIG. 14 is a graph showing the colorimetric sensitivity of triglycerides in the example. FIG. 15 is a graph showing the colorimetric sensitivity of total cholesterol in the example. FIG. 16 is a graph showing the blood glucose concentration corresponding to the colorimetric sensitivity shown in FIG. 13. FIG. 17 is a graph showing the triglyceride concentration corresponding to the colorimetric sensitivity shown in FIG. 14. FIG. 18 is a graph showing the total cholesterol concentration corresponding to the colorimetric sensitivity shown in FIG. 15. In FIGS. 13 to 15, the horizontal axis shows the amount of blood dropped into the pool, and the vertical axis shows the colorimetric sensitivity. In FIGS. 16 to 18, the horizontal axis shows the colorimetric sensitivity, and the vertical axis shows the concentration of each component (mg/dL).
比色感度のCV値は、血糖で1.61%、中性脂肪で2.42%、総コレステロールで2.44%であった。The CV values of colorimetric sensitivity were 1.61% for blood glucose, 2.42% for triglycerides, and 2.44% for total cholesterol.
4.考察
実験において設定した血液量は、30μL、35μL(約17%増)、40μL(約14%増)であった。図13~図15に示すように、成分によって若干のばらつきは見られるものの、滴下した血液の量によらず、比色感度は概ねΔ0.02の範囲に収まっていた。また、いずれの成分においても、比色感度のCV値は3%以内に収まっていた。従って、滴下した血液量に起因する比色感度の変動は小さいと言える。4. Discussion The blood volumes set in the experiment were 30 μL, 35 μL (approximately 17% increase), and 40 μL (approximately 14% increase). As shown in Figures 13 to 15, although there was some variation depending on the component, the colorimetric sensitivity was generally within the range of Δ0.02 regardless of the amount of blood dripped. In addition, the CV value of the colorimetric sensitivity was within 3% for all components. Therefore, it can be said that the variation in colorimetric sensitivity due to the amount of blood dripped is small.
図16~図18を参照すると、図13~図15に示す比色感度のばらつきは、各成分の濃度に大きな影響を及ぼすものではないことがわかる。ここで、図12に示す比色カード4においては、血糖については1dLあたり概ね80mg以上120mg未満が同一の段階、中性脂肪については概ね70mg以上100mg未満が同一の段階、総コレステロールについては180mg以上220mg未満が同一の段階となっている。このように、ユーザが呈色反応を目視判定する簡易検査においては、実施例における程度の比色感度のばらつきがあったとしても、濃度に換算すれば同一の段階に収まる範囲であり、判定結果に影響を及ぼすものではないといえる。Referring to Figures 16 to 18, it can be seen that the variation in colorimetric sensitivity shown in Figures 13 to 15 does not have a significant effect on the concentration of each component. Here, in the colorimetric card 4 shown in Figure 12, the same level for blood glucose is approximately 80 mg or more and less than 120 mg per dL, the same level for triglycerides is approximately 70 mg or more and less than 100 mg, and the same level for total cholesterol is approximately 180 mg or more and less than 220 mg. Thus, in a simple test in which the user visually determines the color reaction, even if there is variation in colorimetric sensitivity to the extent shown in the examples, it falls within the same range when converted to concentration and does not affect the determination result.
以上より、プールに滴下した血液量を変化させたとしても、血液検査デバイスにおいて、同一の血液サンプルであれば概ね同一の濃度で検出されることがわかった。これは、プールに滴下した血液量によらず、血液検査デバイスには概ね一定量の血液が添加されていたことを示す。従って、本実施形態に係る補助具1を用いることで、検査デバイス2に適量の血液を添加することができたと言える。From the above, it was found that even if the amount of blood dripped into the pool was changed, the same blood sample was detected at roughly the same concentration in the blood testing device. This shows that regardless of the amount of blood dripped into the pool, a roughly constant amount of blood was added to the blood testing device. Therefore, it can be said that by using the assisting
以上説明した本発明は、上記実施形態及び変形例に限定されるものではなく、上記実施形態及び変形例に開示されている複数の構成要素を適宜組み合わせることによって、種々の発明を形成することができる。例えば、上記実施形態及び変形例に示した全構成要素からいくつかの構成要素を除外して形成しても良いし、上記実施形態及び変形例に示した構成要素を適宜組み合わせて形成しても良い。The present invention described above is not limited to the above embodiment and modifications, and various inventions can be formed by appropriately combining multiple components disclosed in the above embodiment and modifications. For example, some components may be removed from all the components shown in the above embodiment and modifications, or the components shown in the above embodiment and modifications may be appropriately combined to form various inventions.
1…血液検査用補助部(補助具)、2…血液検査デバイス(検査デバイス)、3…血液、4…比色カード、11…下側基材、13…上側基材、13a…固定面、15…境界線、20a…空間、21…第1基板、21a…血液添加部、22…第2基板、22a~22c…観察窓、23…拡散層、24…血漿分離部、25a~25c…試薬相、26…スペーサ、27…位置合わせ用開口、41~43…スケール、44~46…開口、111…プール、112…プールサイド面、113…突起部、114…マーク、115,116…支持部、120…外周部、121…凸部、122…スペース、123…窪み、131…ガイド、132…開口、133…位置合わせ用開口、134,135…床面、136…凸部、137…突起、141…ガイド1...blood test auxiliary part (auxiliary tool), 2...blood test device (test device), 3...blood, 4...colorimetric card, 11...lower substrate, 13...upper substrate, 13a...fixing surface, 15...boundary line, 20a...space, 21...first substrate, 21a...blood addition part, 22...second substrate, 22a-22c...observation window, 23...diffusion layer, 24...plasma separation part, 25a-25c...reagent phase, 26...spacer, 27...position Alignment opening, 41-43...scale, 44-46...opening, 111...pool, 112...pool side surface, 113...projection, 114...mark, 115, 116...support, 120...periphery, 121...projection, 122...space, 123...recess, 131...guide, 132...opening, 133...alignment opening, 134, 135...floor surface, 136...projection, 137...projection, 141...guide
Claims (5)
Translated fromJapanese前記血液検査デバイスは、血液が添加される開口である血液添加部が形成された第1の基板と、呈色反応を観察するための開口である観察窓が形成された第2の基板と、該第1及び第2の基板の間に積層されて配置された血漿分離膜及び乾式試薬相とを有し、
血液が配置されるプールが形成された第1の基材と、
前記第1の基材と重ね合わせが可能な第2の基材であって、前記プールと対向する側に、該第2の基材に対して前記血液検査デバイスが固定される位置を示すガイドが設けられると共に、該ガイドに合わせて前記血液検査デバイスを固定した場合に前記観察窓を露出させる開口が形成された第2の基材と、
を備える血液検査用補助具。A blood test auxiliary tool that assists a test using a blood test device,
The blood test device includes a first substrate having a blood application section, which is an opening through which blood is applied, a second substrate having an observation window, which is an opening for observing a color reaction, and a plasma separation membrane and a dry reagent phase, which are laminated and disposed between the first and second substrates;
a first substrate having a pool formed therein in which blood is placed;
a second substrate that can be superimposed on the first substrate, the second substrate having a guide on a side facing the pool that indicates a position where the blood test device is fixed to the second substrate, and an opening that exposes the observation window when the blood test device is fixed in accordance with the guide;
A blood testing aid comprising:
前記第1の基材と前記第2の基材との境界線において折り畳むことにより、前記第1の基材と前記第2の基材とが重ね合わせられる、請求項1~3のいずれか1項に記載の血液検査用補助具。the first base material and the second base material are formed of continuous sheet-like members,
The blood test auxiliary device according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein the first base material and the second base material are overlapped by folding at a boundary line between the first base material and the second base material.
前記第1及び第2の記載の他方に、前記凸部が嵌合可能な凹状のスペースが設けられ、
前記スペースの壁面のうち前記突起に対応する位置に窪みが形成され、
前記凸部を前記スペースに嵌合させることにより、前記突起が窪みに嵌り込み、前記第1の基材と前記第2の基材とが重ね合わせられた状態で固定される、
請求項1~4のいずれか1項に記載の血液検査用補助具。
a protrusion having a wall surface formed with a projection is provided on one of the first and second base materials;
The other of the first and second embodiments is provided with a concave space into which the convex portion can be fitted,
A recess is formed in a wall surface of the space at a position corresponding to the protrusion,
By fitting the convex portion into the space, the protrusion fits into the recess, and the first base material and the second base material are fixed in a superposed state.
The blood test auxiliary device according to any one of claims 1 to 4.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2023/015055WO2024214253A1 (en) | 2023-04-13 | 2023-04-13 | Blood test aid |
| TW113113646ATWI894911B (en) | 2023-04-13 | 2024-04-12 | Adapter for blood test device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2023/015055WO2024214253A1 (en) | 2023-04-13 | 2023-04-13 | Blood test aid |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2024214253A1true WO2024214253A1 (en) | 2024-10-17 |
Family
ID=93059001
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2023/015055PendingWO2024214253A1 (en) | 2023-04-13 | 2023-04-13 | Blood test aid |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2024214253A1 (en) |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04223267A (en)* | 1990-03-26 | 1992-08-13 | Cascade Medical Inc | Nonreturnable reagent unit |
| JP2006058093A (en)* | 2004-08-18 | 2006-03-02 | National Institute For Materials Science | Blood analyzer |
| JP2008082899A (en)* | 2006-09-27 | 2008-04-10 | Terumo Corp | Component measuring chip |
| JP2012524257A (en)* | 2009-04-17 | 2012-10-11 | デジタル オプティクス シーオー エルティーディー | Biosensor for disease diagnosis that enables rapid blood cell separation |
| JP2015501929A (en)* | 2011-11-23 | 2015-01-19 | カルマルク スウェーデン エービー | Test system configuration and test method |
| JP2016519771A (en)* | 2013-04-12 | 2016-07-07 | エリューム・ピーティーワイ・リミテッド | Sampling and testing devices for the human or animal body |
- 2023
- 2023-04-13WOPCT/JP2023/015055patent/WO2024214253A1/enactivePending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04223267A (en)* | 1990-03-26 | 1992-08-13 | Cascade Medical Inc | Nonreturnable reagent unit |
| JP2006058093A (en)* | 2004-08-18 | 2006-03-02 | National Institute For Materials Science | Blood analyzer |
| JP2008082899A (en)* | 2006-09-27 | 2008-04-10 | Terumo Corp | Component measuring chip |
| JP2012524257A (en)* | 2009-04-17 | 2012-10-11 | デジタル オプティクス シーオー エルティーディー | Biosensor for disease diagnosis that enables rapid blood cell separation |
| JP2015501929A (en)* | 2011-11-23 | 2015-01-19 | カルマルク スウェーデン エービー | Test system configuration and test method |
| JP2016519771A (en)* | 2013-04-12 | 2016-07-07 | エリューム・ピーティーワイ・リミテッド | Sampling and testing devices for the human or animal body |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| TW202504549A (en) | 2025-02-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CA2297965C (en) | Analytical cartridge | |
| US6555061B1 (en) | Multi-layer reagent test strip | |
| EP0451981A2 (en) | Disposable reagent unit | |
| US8425859B2 (en) | Test strip card | |
| CN1162359A (en) | Optically readable strip for analyte detection having on-strip orientation index | |
| WO2005028662A2 (en) | Test strip and method for determining ldl cholesterol concentration from whole blood | |
| US8409413B2 (en) | Sampling device for liquid samples | |
| JP2020505606A (en) | Vertical flow assay device for detecting glucose concentration in a fluid sample | |
| JP2004325456A (en) | Test strip with clear base support layer for visually perception of liquid sample during application | |
| US10054603B2 (en) | Systems and methods for reagentless test strips | |
| WO2024214253A1 (en) | Blood test aid | |
| TWI894911B (en) | Adapter for blood test device | |
| EP4261539B1 (en) | Blood testing device | |
| US20250003964A1 (en) | Assay Device and Method for Measuring Sodium Concentration in Blood Using Ion-Cryptand Complex Depletion | |
| US20180355402A1 (en) | Diagnostic strip for determining the amount of sarcosine, creatinine and hydrogen peroxide in a biological or environmental sample | |
| KR20230058320A (en) | Analytical Apparatus and Method for Simultaneous Isolation of Red Blood Cells and Proteins from Blood Fluid Samples | |
| KR20150106520A (en) | Diagnostic apparatus and diagnostic system having the same | |
| EP1540353A2 (en) | Test strip and method for determining ldl cholesterol concentration from whole blood | |
| JP2631900B2 (en) | Clinical test method using dry analytical elements | |
| CN110554205A (en) | Method for measuring high density lipoprotein cholesterol |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | Ref document number:23933029 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 |