WO2023221370A1 - Batch task processing method and apparatus, and electronic device - Google Patents
Batch task processing method and apparatus, and electronic deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2023221370A1 WO2023221370A1PCT/CN2022/123597CN2022123597WWO2023221370A1WO 2023221370 A1WO2023221370 A1WO 2023221370A1CN 2022123597 WCN2022123597 WCN 2022123597WWO 2023221370 A1WO2023221370 A1WO 2023221370A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- completed
- tasks
- task
- results
- sub
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/48—Program initiating; Program switching, e.g. by interrupt
- G06F9/4806—Task transfer initiation or dispatching
- G06F9/4843—Task transfer initiation or dispatching by program, e.g. task dispatcher, supervisor, operating system
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F12/00—Accessing, addressing or allocating within memory systems or architectures
- G06F12/02—Addressing or allocation; Relocation
- G06F12/08—Addressing or allocation; Relocation in hierarchically structured memory systems, e.g. virtual memory systems
- G06F12/0802—Addressing of a memory level in which the access to the desired data or data block requires associative addressing means, e.g. caches
- G06F12/0877—Cache access modes
Definitions
- the present disclosurerelates to the field of artificial intelligence technology, specifically to the field of cloud computing, and more specifically to a batch task processing method, device and electronic equipment.
- Embodiments of the present disclosureprovide a method, device and electronic device for batch task processing.
- a batch task processing methodincluding:
- the tasks to be completedare scheduled according to the completion progress of the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks.
- the methodfurther includes:
- the batch taskis input into the first buffer.
- scheduling the tasks to be completed according to the completion progress of the tasks to be completed in the batch tasksincludes:
- executing the tasks to be completed in the batch tasksincludes:
- obtaining the completed tasks in the first buffer and inputting them into the second bufferincludes:
- Completed tasksare determined based on the number of sub-results and the threshold number of sub-results.
- determining the completed task based on the number of sub-results and the threshold number of sub-resultsincludes:
- the task to be completedis determined to be the completed task.
- the methodfurther includes:
- the task to be completedIn response to the task to be completed including the completion identifier, it is determined that the task to be completed is a completed task.
- the methodfurther includes:
- the sub-results corresponding to the completed tasksare arranged in the order of generation to generate the task results.
- the methodfurther includes:
- a device for batch task processingincluding:
- Batch task generation moduleused to generate batch tasks based on tasks to be completed
- a task execution moduleused to execute the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks
- a task scheduling moduleconfigured to schedule the tasks to be completed according to the completion progress of the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks.
- the devicefurther includes:
- An input moduleis used to input the batch tasks into the first buffer.
- the task scheduling moduleincludes:
- Scheduling sub-moduleused to obtain completed tasks in the first buffer and input them into the second buffer, where the completed tasks are tasks to be completed that have been executed;
- the output submoduleis used to output the task results of the completed tasks and delete the completed tasks in the second buffer.
- the task execution moduleincludes:
- the operation sub-moduleis used to perform inference operations based on the tasks to be completed to generate sub-results.
- the scheduling submoduleincludes:
- a threshold acquisition moduleused to obtain the threshold number of sub-results of the task to be completed
- the first task identification unitis used to determine the completed task according to the number of sub-results and the threshold value of the number of sub-results.
- the task identification unitincludes:
- the task identification subunitdetermines that the task to be completed is the completed task if the number of sub-results is equal to the threshold of the number of sub-results.
- the devicefurther includes:
- the second task identification unitis configured to determine that the task to be completed is a completed task in response to the task to be completed including a completion identifier.
- the devicefurther includes:
- the result acquisition subunitis used to arrange the sub-results corresponding to the completed tasks in the order of generation to generate the task results.
- the devicefurther includes:
- a task adding moduleis used to add new to-be-completed tasks to the batch tasks in response to a new task request.
- an electronic deviceincluding:
- the memorystores instructions executable by the at least one processor, and the instructions are executed by the at least one processor, so that the at least one processor can perform as described in any one of the above first aspects. Methods.
- a non-transitory computer-readable storage mediumstoring computer instructions, wherein the computer instructions are used to cause the computer to execute as described in any one of the above-mentioned first aspects. method described.
- a computer program productincluding a computer program that, when executed by a processor, implements the method described in any one of the above first aspects.
- a computer programis provided, wherein the computer program includes computer program code, and when the computer program code is run on a computer, it causes the computer to perform any one of the above first aspects. method described in the item.
- Schedulingis performed according to the completion progress of the tasks to be completed, and the processing of the completed tasks is ended, so as to avoid wasting computing resources on the completed tasks to be completed, reduce the delay of task completion, and improve the efficiency of task processing.
- Figure 1is a schematic diagram of a batch task processing method provided according to an embodiment of the present disclosure
- Figure 2is a schematic diagram of a batch task processing method provided according to an embodiment of the present disclosure
- Figure 3is a schematic diagram of a batch task processing method provided according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
- Figure 4is a schematic structural diagram of a batch task processing device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
- Figure 5is a schematic structural diagram of a batch task processing device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 6is a block diagram of an electronic device used to implement a batch task processing method according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
- various neural network modelsare applied in various fields such as life and health, retail, and industry.
- the successful application of deep learning models in the commercial fieldrelies on multiple links.
- the trained modelusually also needs to be optimized and deployed according to the usage scenario. The user inputs data to the deployed model, and after the input data undergoes model inference operations, the user obtains the corresponding output result.
- the main goal in model trainingis to improve the performance of training tasks and pursue high throughput.
- more attentionis paid to latency, that is, to shorten the time from when the user makes a request to receiving a reply as much as possible.
- the upper-layer scheduling mechanismwill combine the requests into a large batch (Batch) according to the number of user requests at the current moment, and then uniformly input the trained model for calculation.
- Common reasoning tasks in the field of natural languageare generation tasks, which refer to tasks such as machine translation and article generation.
- generation tasksrefer to tasks such as machine translation and article generation.
- the usermakes a request to generate an article, and the user request is input into the trained model to perform inference operations to generate the article.
- the userinputs a piece of text and instructs the text to be translated into a specified language, then the text is input into the model for loop operation. Due to the characteristics of the model, the model will only generate one word in each loop operation. Generate a translated word corresponding to a word. If there are n words in the translated text that needs to be generated, n loop operations need to be performed in the model to complete the translation of the text and obtain the corresponding translated text.
- tasks with different word number requirementsare assembled into a Batch.
- Tasks with a small number of wordswill require fewer calculation rounds than tasks with a large number of words.
- the generated resultsare uniformly returned to the user, but the model is still operating during the waiting period, that is, the model for tasks with a small number of generated words has been idling many times.
- the average delay of all tasks in the batchis equal to the task with the largest number of generated words, to a certain extent.
- the latency for generating tasks with a smaller number of wordshas been increased. For example, the number of words that need to be generated is proportional to the amount of calculations that cycle through the model.
- the task of generating 20 wordswill be in the next 80 rounds.
- the generation processis in an idling state, which not only wastes computing resources to a certain extent, but also increases the delay of tasks in the entire batch and reduces task processing efficiency.
- FIG. 1is a schematic diagram of a batch task processing method provided according to an embodiment of the present disclosure. As shown in Figure 1, the method includes Following steps: 101-103.
- Step 101Generate batch tasks based on tasks to be completed.
- the methodis aimed at inference tasks in deep learning, and the method is mainly executed by an upper-layer scheduling module.
- the usersends a request according to the demand, and the request contains the tasks to be completed, and the tasks to be completed are combined into a batch task, that is, a Batch.
- a batch taskThrough batch tasks, multiple tasks are executed at the same time each time, which improves the efficiency of task execution.
- Step 102Execute the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks.
- the batch tasksare input into a pre-trained model, and the model performs calculations according to the goals of the tasks to be completed to complete the tasks to be completed.
- the modelis a recurrent neural network model.
- the task to be completedis a text translation task or a text generation task.
- the text translation taskis a task of translating the text to be translated into a text in a specified language.
- the text generation taskis based on the input initial text. The task of generating subsequent text.
- Step 103Schedule the tasks to be completed according to the completion progress of the tasks to be completed in the batch task.
- the task resultsare obtained by the model through at least one inference operation, and one inference operation is performed in each cycle. All tasks to be completed in the batch tasks are parallel Perform inference operations. Since the number of inference operations required to complete different tasks to be completed is different, in order to efficiently output the task results, after the end of each cycle, the tasks to be completed are scheduled according to the completion progress of the tasks to be completed, and the completed tasks to be completed are removed.
- the batch tasksreduce the delay of tasks to be completed.
- Embodiments of the present disclosureschedule according to the completion progress of the to-be-completed tasks, end the processing of completed tasks, avoid wasting computing resources on completed to-be-completed tasks, reduce task completion delays, and improve task processing efficiency.
- the methodfurther includes:
- the batch taskis input into the first buffer.
- a first cache areais set up in the cache space to store the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks.
- the tasks to be completed in the first cache areaare tasks that have not yet been completed, that is, a model needs to be input for execution.
- For inference operation tasksafter generating the batch tasks, the batch tasks are input into the first cache area.
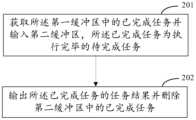
- FIG 2is a schematic diagram of a batch task processing method provided according to an embodiment of the present disclosure. As shown in Figure 2, step 103 in Figure 1 includes the following steps: 201-202.
- Step 201Obtain the completed tasks in the first buffer and input them into the second buffer.
- the completed tasksare the tasks to be completed that have been executed;
- a second cache areais set up in the cache space to store completed tasks.
- the upper-layer scheduling modulescans the first buffer area after each cycle, it is recognized that there are completed tasks in the first buffer area. After the task is completed, the completed task is transferred to the second cache area.
- Step 201Output the task results of the completed tasks and delete the completed tasks in the second buffer.
- the upper-layer scheduling modulescans the second buffer after each cycle. If it recognizes that the completed task exists, it immediately generates a task result corresponding to the completed task and outputs the task result. Then the second buffer is cleared, and then the next cycle is performed.
- the embodiment of the present disclosureuses the second buffer to transfer completed tasks to be completed from batch tasks in a timely manner after completion, thereby avoiding waste of computing resources and improving the efficiency of obtaining task results.
- executing the tasks to be completed in the batch tasksincludes:
- the modelis used to perform an inference operation on the task to be completed, and one inference operation performed in each cycle can generate a sub-result corresponding to the task to be completed.
- the task to be completedis a text translation task.
- the modelperforms inference operations based on the text of the task to be completed to obtain a corresponding translation word, which is the sub-result.
- obtaining the completed tasks in the first buffer and inputting them into the second bufferincludes:
- Completed tasksare determined based on the number of sub-results and the threshold number of sub-results.
- the modelcan obtain in advance the maximum number of sub-results in the to-be-completed results, that is, the sub-result number threshold.
- the upper-layer scheduling moduleobtains the sub-result quantity threshold from the model to determine whether there are completed tasks in the first buffer.
- determining the completed task based on the number of sub-results and the threshold of the number of sub-resultsincludes:
- the task to be completedis determined to be the completed task.
- the upper-layer scheduling moduledetects the first buffer to obtain the number of sub-results of the task to be completed. For a task to be completed, if the number of sub-results is equal to the threshold number of sub-results, it means that the corresponding inference operation has been completely executed in the task to be completed, and the task can be determined to be completed. If the number of sub-results is less than the threshold of the number of sub-results, it means that the task to be completed has not fully executed the corresponding inference operation, and the model needs to be continued to be input for inference operation in the next cycle.
- the methodfurther includes:
- the sub-results corresponding to the completed tasksare arranged in the order of generation to generate the task results.
- the operationwhen the model performs the inference operation, the operation is performed according to the grammatical and logical order of the words to generate each sub-result. Therefore, after the completed task is input into the second buffer, it is necessary to calculate the sub-result according to the The generation sequence arranges the corresponding sub-results to generate the task results.
- the task to be completedis a translation task
- the sub-result number thresholdis 4, which means that the maximum length of a translated sentence is 4 words, that is, 4 sub-results need to be generated.
- the number of sub-resultsequals the threshold number of sub-results, and the model can complete the inference operation of the task to be completed.
- the upper-layer scheduling moduledetermines that it is a completed task and inputs it into the second buffer. District. After arranging the 4 sub-results (4 translation results) in the order of generation, the task result, that is, the translation result can be generated.
- the methodfurther includes:
- the task to be completedIn response to the task to be completed including the completion identifier, it is determined that the task to be completed is a completed task.
- the completed taskcan be determined based on the completion identification. After the model completes the corresponding inference operation, a completion identification will be generated. The upper-layer scheduling module detects the task to be completed after each cycle. If it contains all If the completion identifier is specified, the task to be completed is determined to be a completed task.
- the completion indicatoris a sentence terminator.
- the methodfurther includes:
- tasks with a smaller number of sub-resultsare transferred out of the first buffer after completion, leaving sufficient computing resources in the system to support the model.
- the usercan send the new task request, and the upper-layer scheduling module can add the new to-be-completed task to the batch task according to the new task request after the to-be-completed task is completed, that is, input
- the first bufferis used to perform inference operations on the newly added tasks to be completed according to the model.
- FIG. 3is a schematic diagram of a batch task processing method according to an embodiment of the present disclosure. As shown in Figure 3, the method includes the following steps:
- the upper-layer scheduling modulecombines the tasks to be completed into a Batch of size N according to the number of user requests at the current moment, and inputs the Batch into the trained word generation model.
- each of the N tasks to be completedneeds to generate 1 to N words, that is, sub-results.
- the number of generated wordsis the same as the number of inference operations performed through the model loop.
- a "calculation” buffer and a “completion” bufferare allocated.
- the “calculation” bufferis the first buffer, and the “completion” buffer is the second buffer.
- the “calculation” buffercontains all the tasks to be completed in the current batch, and the “completion” buffer is empty.
- the scheduling modulewill input the tasks to be completed in the "calculation” buffer into the model for inference operation, and after the model performs an inference operation, check whether the tasks to be completed in the "calculation” buffer are Completed. If the generation is completed, the task to be completed is determined to be a completed task and the completed task is transferred from the "calculation" buffer to the "completion” buffer. Once the upper-layer scheduling module finds that there are tasks in the "completion” buffer, it will immediately return the generated results to the user, clear the “completion” buffer, and the cycle ends.
- the delay for each word generatedis t, and the inference delay of all previous tasks in the entire batch is Nt
- using the early exit scheduling method proposed by the embodiment of the present disclosurecan reduce the average delay by at least 50%.
- the average The time delayis (1+N)t/2.
- the execution time of the kernel layerwill also be reduced, and subsequent inference will be faster and faster.
- FIG. 4is a schematic structural diagram of a batch task processing device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure. As shown in Figure 4, the device includes the following modules:
- Batch task generation module 410used to generate batch tasks based on tasks to be completed
- Task execution module 420used to execute the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks
- the task scheduling module 430is used to schedule the tasks to be completed according to the completion progress of the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks;
- the devicefurther includes:
- An input moduleis used to input the batch tasks into the first buffer.
- FIG. 5is a schematic structural diagram of a batch task processing device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
- the task scheduling moduleincludes the following modules:
- Scheduling sub-module 510is used to obtain completed tasks in the first buffer and input them into the second buffer, where the completed tasks are tasks to be completed that have been executed;
- the output sub-module 520is used to output the task results of the completed tasks and delete the completed tasks in the second buffer.
- the task execution moduleincludes:
- the operation sub-moduleis used to perform inference operations based on the tasks to be completed to generate sub-results.
- the scheduling submoduleincludes:
- a threshold acquisition moduleused to obtain the threshold number of sub-results of the task to be completed
- the first task identification unitis used to determine the completed task according to the number of sub-results and the threshold value of the number of sub-results.
- the task identification unitincludes:
- the task identification subunitdetermines that the task to be completed is the completed task if the number of sub-results is equal to the threshold of the number of sub-results.
- the devicefurther includes:
- the second task identification unitis configured to determine that the task to be completed is a completed task in response to the task to be completed including a completion identifier.
- the devicefurther includes:
- the result acquisition subunitis used to arrange the sub-results corresponding to the completed tasks in the order of generation to generate the task results.
- the devicefurther includes:
- a task adding moduleis used to add new to-be-completed tasks to the batch tasks in response to a new task request.
- Embodiments of the present disclosurealso provide an electronic device, a readable storage medium, a computer program product, and a computer program.
- FIG. 6shows a schematic block diagram of an example electronic device 600 that may be used to implement embodiments of the present disclosure.
- Electronic devicesare intended to refer to various forms of digital computers, such as laptop computers, desktop computers, workstations, personal digital assistants, servers, blade servers, mainframe computers, and other suitable computers.
- Electronic devicesmay also represent various forms of mobile devices, such as personal digital assistants, cellular phones, smart phones, wearable devices, and other similar computing devices.
- the components shown herein, their connections and relationships, and their functionsare examples only and are not intended to limit implementations of the disclosure described and/or claimed herein.
- the device 600includes a computing unit 601 that can execute according to a computer program stored in a read-only memory (ROM) 602 or loaded from a storage unit 608 into a random access memory (RAM) 603 Various appropriate actions and treatments. In the RAM 603, various programs and data required for the operation of the device 600 can also be stored.
- Computing unit 601, ROM 602 and RAM 603are connected to each other via bus 604.
- An input/output (I/O) interface 605is also connected to bus 604.
- I/O interface 605Multiple components in device 600 are connected to I/O interface 605, including: input unit 606, such as keyboard, mouse, etc.; output unit 607, such as various types of displays, speakers, etc.; storage unit 608, such as magnetic disk, optical disk, etc. ; and communication unit 609, such as a network card, modem, wireless communication transceiver, etc.
- the communication unit 609allows the device 600 to exchange information/data with other devices through computer networks such as the Internet and/or various telecommunications networks.
- Computing unit 601may be a variety of general and/or special purpose processing components having processing and computing capabilities. Some examples of the computing unit 601 include, but are not limited to, a central processing unit (CPU), a graphics processing unit (GPU), various dedicated artificial intelligence (AI) computing chips, various computing units that run machine learning model algorithms, digital signal processing processor (DSP), and any appropriate processor, controller, microcontroller, etc.
- the computing unit 601performs various methods and processes described above, such as the batch task processing method.
- the batch task processing methodmay be implemented as a computer software program, which is tangibly included in a machine-readable medium, such as the storage unit 608.
- part or all of the computer programmay be loaded and/or installed onto device 600 via ROM 602 and/or communication unit 609.
- the computer programWhen the computer program is loaded into the RAM 603 and executed by the computing unit 601, one or more steps of the batch task processing method described above may be performed.
- the computing unit 601may be configured to perform the batch task processing method in any other suitable manner (eg, by means of firmware).
- Various implementations of the systems and techniques described abovemay be implemented in digital electronic circuit systems, integrated circuit systems, field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), application specific integrated circuits (ASICs), application specific standard products (ASSPs), systems on a chip implemented in a system (SOC), load programmable logic device (CPLD), computer hardware, firmware, software, and/or a combination thereof.
- FPGAsfield programmable gate arrays
- ASICsapplication specific integrated circuits
- ASSPsapplication specific standard products
- SOCsystem
- CPLDload programmable logic device
- computer hardwarefirmware, software, and/or a combination thereof.
- These various embodimentsmay include implementation in one or more computer programs executable and/or interpreted on a programmable system including at least one programmable processor, the programmable processor
- the processorwhich may be a special purpose or general purpose programmable processor, may receive data and instructions from a storage system, at least one input device, and at least one output device, and transmit data and instructions to the storage system, the at least one input device, and the at least one output device.
- An output devicemay be a special purpose or general purpose programmable processor, may receive data and instructions from a storage system, at least one input device, and at least one output device, and transmit data and instructions to the storage system, the at least one input device, and the at least one output device.
- An output devicemay be a special purpose or general purpose programmable processor, may receive data and instructions from a storage system, at least one input device, and at least one output device, and transmit data and instructions to the storage system, the at least one input device, and the at least one output device.
- Program code for implementing the methods of the present disclosuremay be written in any combination of one or more programming languages. These program codes may be provided to a processor or controller of a general-purpose computer, special-purpose computer, or other programmable data processing device, such that the program codes, when executed by the processor or controller, cause the functions specified in the flowcharts and/or block diagrams/ The operation is implemented.
- the program codemay execute entirely on the machine, partly on the machine, as a stand-alone software package, partly on the machine and partly on a remote machine or entirely on the remote machine or server.
- a machine-readable mediummay be a tangible medium that may contain or store a program for use by or in connection with an instruction execution system, apparatus, or device.
- the machine-readable mediummay be a machine-readable signal medium or a machine-readable storage medium.
- Machine-readable mediamay include, but are not limited to, electronic, magnetic, optical, electromagnetic, infrared, or semiconductor systems, devices or devices, or any suitable combination of the foregoing.
- machine-readable storage mediawould include one or more wire-based electrical connections, laptop disks, hard drives, random access memory (RAM), read only memory (ROM), erasable programmable read only memory (EPROM or flash memory), optical fiber, portable compact disk read-only memory (CD-ROM), optical storage device, magnetic storage device, or any suitable combination of the above.
- RAMrandom access memory
- ROMread only memory
- EPROM or flash memoryerasable programmable read only memory
- CD-ROMportable compact disk read-only memory
- magnetic storage deviceor any suitable combination of the above.
- the systems and techniques described hereinmay be implemented on a computer having a display device (eg, a CRT (cathode ray tube) or LCD (liquid crystal display) monitor) for displaying information to the user ); and a keyboard and pointing device (eg, a mouse or a trackball) through which a user can provide input to the computer.
- a display deviceeg, a CRT (cathode ray tube) or LCD (liquid crystal display) monitor
- a keyboard and pointing deviceeg, a mouse or a trackball
- Other kinds of devicesmay also be used to provide interaction with the user; for example, the feedback provided to the user may be any form of sensory feedback (e.g., visual feedback, auditory feedback, or tactile feedback); and may be provided in any form, including Acoustic input, voice input or tactile input) to receive input from the user.
- the systems and techniques described hereinmay be implemented in a computing system that includes back-end components (e.g., as a data server), or a computing system that includes middleware components (e.g., an application server), or a computing system that includes front-end components (e.g., A user's computer having a graphical user interface or web browser through which the user can interact with implementations of the systems and technologies described herein), or including such backend components, middleware components, or any combination of front-end components in a computing system.
- the components of the systemmay be interconnected by any form or medium of digital data communication (eg, a communications network). Examples of communication networks include: local area network (LAN), wide area network (WAN), the Internet, and blockchain networks.
- Computer systemsmay include clients and servers. Clients and servers are generally remote from each other and typically interact over a communications network. The relationship of client and server is created by computer programs running on corresponding computers and having a client-server relationship with each other.
- the servercan be a cloud server, also known as cloud computing server or cloud host. It is a host product in the cloud computing service system to solve the problem of traditional physical host and VPS service ("Virtual Private Server", or "VPS" for short) Among them, there are defects such as difficult management and weak business scalability.
- the servercan also be a distributed system server or a server combined with a blockchain.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese相关申请的交叉引用Cross-references to related applications
本申请基于申请号为2022105474564、申请日为2022年5月19日的中国专利申请提出,并要求该中国专利申请的优先权,该中国专利申请的全部内容在此引入本申请作为参考。This application is filed based on a Chinese patent application with application number 2022105474564 and a filing date of May 19, 2022, and claims the priority of the Chinese patent application. The entire content of the Chinese patent application is hereby incorporated by reference into this application.
本公开涉及人工智能技术领域,具体涉及云计算领域,更具体地涉及一种批量任务处理的方法、装置及电子设备。The present disclosure relates to the field of artificial intelligence technology, specifically to the field of cloud computing, and more specifically to a batch task processing method, device and electronic equipment.
近年来,随着大模型在自然语言处理等领域的卓越表现,使得它们在越来越多的实际场景中发挥作用,在实际场景中,通常会对训练好的模型进行推理部署,在接收到任务请求后,通过模型进行计算,并将最终计算得到的结果返回到请求方。In recent years, with the outstanding performance of large models in fields such as natural language processing, they have played a role in more and more practical scenarios. In practical scenarios, the trained models are usually deployed for inference and after receiving After the task is requested, the calculation is performed through the model and the final calculated result is returned to the requester.
但是目前的任务处理技术对任务的计算效率较低,由此导致了计算资源的浪费。However, current task processing technology has low computational efficiency for tasks, resulting in a waste of computing resources.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本公开的实施方式中提供了一种用于批量任务处理的方法、装置及电子设备。Embodiments of the present disclosure provide a method, device and electronic device for batch task processing.
根据本公开的第一方面实施方式,提供了一种批量任务处理的方法,包括:According to the first embodiment of the present disclosure, a batch task processing method is provided, including:
根据待完成任务生成批量任务;Generate batch tasks based on tasks to be completed;
执行所述批量任务中的待完成任务;Execute the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks;
根据所述批量任务中待完成任务的完成进度调度所述待完成任务。The tasks to be completed are scheduled according to the completion progress of the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks.
在一些实施方式中,所述根据待完成任务生成批量任务后,还包括:In some implementations, after generating batch tasks according to the tasks to be completed, the method further includes:
将所述批量任务输入第一缓冲区。The batch task is input into the first buffer.
在一些实施方式中,所述根据所述批量任务中待完成任务的完成进度调度所述待完成任务,包括:In some embodiments, scheduling the tasks to be completed according to the completion progress of the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks includes:
获取所述第一缓冲区中的已完成任务并输入第二缓冲区,所述已完成任务为执行完毕的待完成任务;Obtain the completed tasks in the first buffer and input them into the second buffer, where the completed tasks are the tasks to be completed that have been executed;
输出所述已完成任务的任务结果并删除第二缓冲区中的已完成任务。Output the task results of said completed tasks and delete the completed tasks in the second buffer.
在一些实施方式中,所述执行所述批量任务中的待完成任务,包括:In some embodiments, executing the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks includes:
根据所述待完成任务进行推理运算,以生成子结果。Perform inference operations based on the tasks to be completed to generate sub-results.
在一些实施方式中,所述获取所述第一缓冲区中的已完成任务并输入第二缓冲区,包括:In some implementations, obtaining the completed tasks in the first buffer and inputting them into the second buffer includes:
获取所述待完成任务的子结果数量阈值;Obtain the threshold number of sub-results for the task to be completed;
根据子结果数量和所述子结果数量阈值确定已完成任务。Completed tasks are determined based on the number of sub-results and the threshold number of sub-results.
在一些实施方式中,所述根据子结果数量和所述子结果数量阈值确定已完成任务,包括:In some embodiments, determining the completed task based on the number of sub-results and the threshold number of sub-results includes:
如果所述子结果数量与所述子结果数量阈值相等,则确定所述待完成任务为所述已完成任务。If the number of sub-results is equal to the threshold of the number of sub-results, the task to be completed is determined to be the completed task.
在一些实施方式中,所述方法还包括:In some embodiments, the method further includes:
响应于所述待完成任务中包括完成标识,确定所述待完成任务为已完成任务。In response to the task to be completed including the completion identifier, it is determined that the task to be completed is a completed task.
在一些实施方式中,所述方法还包括:In some embodiments, the method further includes:
将所述已完成任务对应的子结果按生成顺序排列以生成所述任务结果。The sub-results corresponding to the completed tasks are arranged in the order of generation to generate the task results.
在一些实施方式中,所述方法还包括:In some embodiments, the method further includes:
响应于新增任务请求,将新增待完成任务加入所述批量任务中。In response to the new task request, add the new to-be-completed task to the batch task.
根据本公开的第二方面实施方式,提供了一种批量任务处理的装置,包括:According to a second embodiment of the present disclosure, a device for batch task processing is provided, including:
批量任务生成模块,用于根据待完成任务生成批量任务;Batch task generation module, used to generate batch tasks based on tasks to be completed;
任务执行模块,用于执行所述批量任务中的待完成任务;A task execution module, used to execute the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks;
任务调度模块,用于根据所述批量任务中待完成任务的完成进度调度所述待完成任务。A task scheduling module, configured to schedule the tasks to be completed according to the completion progress of the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks.
在一些实施方式中,所述装置还包括:In some embodiments, the device further includes:
输入模块,用于将所述批量任务输入第一缓冲区。An input module is used to input the batch tasks into the first buffer.
在一些实施方式中,所述任务调度模块包括:In some implementations, the task scheduling module includes:
调度子模块,用于获取所述第一缓冲区中的已完成任务并输入第二缓冲区,所述已完成任务为执行完毕的待完成任务;Scheduling sub-module, used to obtain completed tasks in the first buffer and input them into the second buffer, where the completed tasks are tasks to be completed that have been executed;
输出子模块,用于输出所述已完成任务的任务结果并删除第二缓冲区中的已完成任务。The output submodule is used to output the task results of the completed tasks and delete the completed tasks in the second buffer.
在一些实施方式中,所述任务执行模块包括:In some implementations, the task execution module includes:
运算子模块,用于根据所述待完成任务进行推理运算,以生成子结果。The operation sub-module is used to perform inference operations based on the tasks to be completed to generate sub-results.
在一些实施方式中,所述调度子模块包括:In some implementations, the scheduling submodule includes:
阈值获取模块,用于获取所述待完成任务的子结果数量阈值;A threshold acquisition module, used to obtain the threshold number of sub-results of the task to be completed;
第一任务识别单元,用于根据子结果数量和所述子结果数量阈值确定已完成任务。The first task identification unit is used to determine the completed task according to the number of sub-results and the threshold value of the number of sub-results.
在一些实施方式中,所述任务识别单元,包括:In some implementations, the task identification unit includes:
任务识别子单元,如果所述子结果数量与所述子结果数量阈值相等,则确定所述待完成任务为所述已完成任务。The task identification subunit determines that the task to be completed is the completed task if the number of sub-results is equal to the threshold of the number of sub-results.
在一些实施方式中,所述装置还包括:In some embodiments, the device further includes:
第二任务识别单元,用于响应于所述待完成任务中包括完成标识,确定所述待完成任务为已完成任务。The second task identification unit is configured to determine that the task to be completed is a completed task in response to the task to be completed including a completion identifier.
在一些实施方式中,所述装置还包括:In some embodiments, the device further includes:
结果获取子单元,用于将所述已完成任务对应的子结果按生成顺序排列以生成所述任务结果。The result acquisition subunit is used to arrange the sub-results corresponding to the completed tasks in the order of generation to generate the task results.
在一些实施方式中,所述装置还包括:In some embodiments, the device further includes:
任务添加模块,用于响应于新增任务请求,将新增待完成任务加入所述批量任务中。A task adding module is used to add new to-be-completed tasks to the batch tasks in response to a new task request.
根据本公开的第三方面实施方式,提供了一种电子设备,包括:According to a third aspect implementation of the present disclosure, an electronic device is provided, including:
至少一个处理器;以及at least one processor; and
与所述至少一个处理器通信连接的存储器;其中,a memory communicatively connected to the at least one processor; wherein,
所述存储器存储有可被所述至少一个处理器执行的指令,所述指令被所述至少一个处理器执行,以使所述至少一个处理器能够执行如上述第一方面中任一项所述的方法。The memory stores instructions executable by the at least one processor, and the instructions are executed by the at least one processor, so that the at least one processor can perform as described in any one of the above first aspects. Methods.
根据本公开的第四方面实施方式,提供了一种存储有计算机指令的非瞬时计算机可读存储介质,其中,所述计算机指令用于使所述计算机执行如上述第一方面中任一项所述的方法。According to a fourth aspect of the present disclosure, there is provided a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium storing computer instructions, wherein the computer instructions are used to cause the computer to execute as described in any one of the above-mentioned first aspects. method described.
根据本公开的第五方面实施方式,提供了一种计算机程序产品,包括计算机程序,所述计算机程序在被处理器执行时实现如上述第一方面中任一项所述的方法。According to an embodiment of a fifth aspect of the present disclosure, a computer program product is provided, including a computer program that, when executed by a processor, implements the method described in any one of the above first aspects.
根据本公开的第六方面实施方式,提供了一种计算机程序,其中所述计算机程序包括计算机程序代码,当所述计算机程序代码在计算机上运行时,使得计算机执行如上述第一方面中任一项所述的方法。According to an embodiment of a sixth aspect of the present disclosure, a computer program is provided, wherein the computer program includes computer program code, and when the computer program code is run on a computer, it causes the computer to perform any one of the above first aspects. method described in the item.
本公开至少具备以下有益效果:This disclosure has at least the following beneficial effects:
根据所述待完成任务的完成进度进行调度,结束对已完成任务的处理,避免计算资源浪费在已经完成的待完成任务上,降低任务完成的时延,提升任务处理效率。Scheduling is performed according to the completion progress of the tasks to be completed, and the processing of the completed tasks is ended, so as to avoid wasting computing resources on the completed tasks to be completed, reduce the delay of task completion, and improve the efficiency of task processing.
应当理解,本部分所描述的内容并非旨在标识本公开的实施例的关键或重要特征,也不用于限制本公开的范围。本公开的其它特征将通过以下的说明书而变得容易理解。It should be understood that what is described in this section is not intended to identify key or important features of the embodiments of the disclosure, nor is it intended to limit the scope of the disclosure. Other features of the present disclosure will become readily understood from the following description.
附图用于更好地理解本方案,不构成对本公开的限定。其中:The accompanying drawings are used to better understand the present solution and do not constitute a limitation of the present disclosure. in:
图1是根据本公开实施例提供的一种批量任务处理方法的示意图;Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of a batch task processing method provided according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图2是根据本公开实施例提供的一种批量任务处理方法的示意图;Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of a batch task processing method provided according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图3是根据本公开实施例提供的一种批量任务处理方法的示意图;Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of a batch task processing method provided according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图4是根据本公开实施例提供的一种批量任务处理装置的结构示意图;Figure 4 is a schematic structural diagram of a batch task processing device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图5是根据本公开实施例提供的一种批量任务处理装置的结构示意图;Figure 5 is a schematic structural diagram of a batch task processing device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图6是用来实现本公开实施例的批量任务处理的方法的电子设备的框图。FIG. 6 is a block diagram of an electronic device used to implement a batch task processing method according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
以下结合附图对本公开的示范性实施例做出说明,其中包括本公开实施例的各种细节以助于理解,应当将它们认为仅仅是示范性的。因此,本领域普通技术人员应当认识到,可以对这里描述的实施例做出各种改变和修改,而不会背离本公开的范围和精神。同样,为了清楚和简明,以下的描述中省略了对公知功能和结构的描述。Exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure are described below with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which various details of the embodiments of the present disclosure are included to facilitate understanding and should be considered to be exemplary only. Accordingly, those of ordinary skill in the art will recognize that various changes and modifications can be made to the embodiments described herein without departing from the scope and spirit of the disclosure. Also, descriptions of well-known functions and constructions are omitted from the following description for clarity and conciseness.
随着计算机硬件的提升与深度学习领域的快速发展,各种神经网络模型被应用与生命健康,零售,工业等各个领域。深度学习模型的成功应用于商业领域依赖于多个环节,除了模型训练之外,通常还需要将训练好的模型针对使用场景进行优化和部署。用户向部署好的模型传入数据,在输入数据经过模型推理运算后,用户得到对应的输出结果。With the improvement of computer hardware and the rapid development of the field of deep learning, various neural network models are applied in various fields such as life and health, retail, and industry. The successful application of deep learning models in the commercial field relies on multiple links. In addition to model training, the trained model usually also needs to be optimized and deployed according to the usage scenario. The user inputs data to the deployed model, and after the input data undergoes model inference operations, the user obtains the corresponding output result.
在模型训练中的主要目标是提升训练任务性能追求的高吞吐,在使用模型进行推理任务时更多的关注的是时延性,即尽可能的缩短用户从发出请求到收到回复的时间。在真实场景中,为了充分利用计算资源,上层调度机制会根据当前时刻用户请求的数量,将所述请求组合成一个大的批量(Batch),再统一输入训练好的模型进行运算。The main goal in model training is to improve the performance of training tasks and pursue high throughput. When using the model for inference tasks, more attention is paid to latency, that is, to shorten the time from when the user makes a request to receiving a reply as much as possible. In real scenarios, in order to make full use of computing resources, the upper-layer scheduling mechanism will combine the requests into a large batch (Batch) according to the number of user requests at the current moment, and then uniformly input the trained model for calculation.
在自然语言领域常见的推理任务为生成任务,所述生成任务指机器翻译、文章生成这类任务。例如,用户发出请求要求生成一篇文章,将用户请求输入训练好的模型 进行推理运算以生成文章。例如,用户输入一段文本并指示将文本翻译为指定语言,那就把这段文本输入模型进行循环运算,由于模型的特性为每次循环运算中模型只会生成一个词,每次循环运算中模型生成一个词对应的翻译词,如果需要生成的翻译文本中有n个词,则需要在模型中进行n次循环运算才能将文本翻译完毕,得到对应翻译的文本。Common reasoning tasks in the field of natural language are generation tasks, which refer to tasks such as machine translation and article generation. For example, the user makes a request to generate an article, and the user request is input into the trained model to perform inference operations to generate the article. For example, if the user inputs a piece of text and instructs the text to be translated into a specified language, then the text is input into the model for loop operation. Due to the characteristics of the model, the model will only generate one word in each loop operation. Generate a translated word corresponding to a word. If there are n words in the translated text that needs to be generated, n loop operations need to be performed in the model to complete the translation of the text and obtain the corresponding translated text.
相关技术中,把有不同生成词数需求的任务组装成一个Batch,生成词数少的任务会比生成词数多的任务需要的计算轮次少,在完成后需要等待生成词数多的任务完成后统一返回生成结果给用户,但是在等待期间模型仍然在运算,即生成词数少的任务模型空转了多次,Batch中所有任务的平均时延和生成词数最多的任务相等,一定程度上增加了生成字数较少任务的时延。例如,需要生成的词数与循环通过模型的计算量成正比,比如将生成20个词的任务和生成100个词的任务放入同一个Batch,会导致生成20个词的任务在后80轮生成过程中处于空转的状态,这样不仅在一定程度上浪费了计算资源外,还导致整个Batch中任务的时延增加,降低了任务处理效率。In related technology, tasks with different word number requirements are assembled into a Batch. Tasks with a small number of words will require fewer calculation rounds than tasks with a large number of words. After completion, you need to wait for tasks with a large number of words to be generated. After completion, the generated results are uniformly returned to the user, but the model is still operating during the waiting period, that is, the model for tasks with a small number of generated words has been idling many times. The average delay of all tasks in the batch is equal to the task with the largest number of generated words, to a certain extent. The latency for generating tasks with a smaller number of words has been increased. For example, the number of words that need to be generated is proportional to the amount of calculations that cycle through the model. For example, if a task of generating 20 words and a task of generating 100 words are put into the same Batch, the task of generating 20 words will be in the next 80 rounds. The generation process is in an idling state, which not only wastes computing resources to a certain extent, but also increases the delay of tasks in the entire batch and reduces task processing efficiency.
为了解决相关技术中的问题,本公开实施例提出了一种批量任务处理方法,图1是根据本公开实施例提供的一种批量任务处理方法的示意图,如图1所示,所述方法包括以下步骤:101-103。In order to solve the problems in related technologies, an embodiment of the present disclosure proposes a batch task processing method. Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of a batch task processing method provided according to an embodiment of the present disclosure. As shown in Figure 1, the method includes Following steps: 101-103.
步骤101:根据待完成任务生成批量任务。Step 101: Generate batch tasks based on tasks to be completed.
本公开实施例中,所述方法针对深度学习中的推理任务,所述方法主要由具备上层调度模块执行。用户根据需求发送请求,所述请求中包含所述待完成任务,将所述待完成任务组合成为一个批量任务,即Batch。通过批量任务,每次将多个任务同时执行,提高了任务执行的效率。In the embodiment of the present disclosure, the method is aimed at inference tasks in deep learning, and the method is mainly executed by an upper-layer scheduling module. The user sends a request according to the demand, and the request contains the tasks to be completed, and the tasks to be completed are combined into a batch task, that is, a Batch. Through batch tasks, multiple tasks are executed at the same time each time, which improves the efficiency of task execution.
步骤102:执行所述批量任务中的待完成任务。Step 102: Execute the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks.
本公开实施例中,将所述批量任务输入预先训练好的模型,所述模型根据待完成任务的目标进行运算以完成所述待完成任务。In the embodiment of the present disclosure, the batch tasks are input into a pre-trained model, and the model performs calculations according to the goals of the tasks to be completed to complete the tasks to be completed.
在一些实施例中,所述模型为循环神经网络模型。In some embodiments, the model is a recurrent neural network model.
在一些实施例中,所述待完成任务为文本翻译任务或文本生成任务,所述文本翻译任务为将待翻译文本翻译为指定语言的文本的任务,所述文本生成任务为根据输入的初始文本生成后续文本的任务。In some embodiments, the task to be completed is a text translation task or a text generation task. The text translation task is a task of translating the text to be translated into a text in a specified language. The text generation task is based on the input initial text. The task of generating subsequent text.
步骤103:根据所述批量任务中待完成任务的完成进度调度所述待完成任务。Step 103: Schedule the tasks to be completed according to the completion progress of the tasks to be completed in the batch task.
本公开实施例中,所述批量任务中待完成任务在执行时,由模型经过至少一次推理运算获取任务结果,每次循环中进行一次推理运算,所述批量任务中的所有待完成任务为并行进行推理运算。由于完成不同的待完成任务所需要的推理运算次数不同,为了高效地输出任务结果,在每个循环结束后根据待完成任务的完成进度调度所述待完成任务,将已经完成的待完成任务移出所述批量任务,降低了待完成任务的时延。In the embodiment of the present disclosure, when the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks are executed, the task results are obtained by the model through at least one inference operation, and one inference operation is performed in each cycle. All tasks to be completed in the batch tasks are parallel Perform inference operations. Since the number of inference operations required to complete different tasks to be completed is different, in order to efficiently output the task results, after the end of each cycle, the tasks to be completed are scheduled according to the completion progress of the tasks to be completed, and the completed tasks to be completed are removed. The batch tasks reduce the delay of tasks to be completed.
本公开实施例根据所述待完成任务的完成进度进行调度,结束对已完成任务的处理,避免计算资源浪费在已经完成的待完成任务上,降低任务完成的时延,提升任务处理效率。Embodiments of the present disclosure schedule according to the completion progress of the to-be-completed tasks, end the processing of completed tasks, avoid wasting computing resources on completed to-be-completed tasks, reduce task completion delays, and improve task processing efficiency.
在一些实施例中,所述根据待完成任务生成批量任务后,还包括:In some embodiments, after generating batch tasks according to the tasks to be completed, the method further includes:
将所述批量任务输入第一缓冲区。The batch task is input into the first buffer.
本公开实施例中,在缓存空间中设置第一缓存区以存储所述批量任务中的待完成任务,所述第一缓存区中的待完成任务为还未完成的任务,即需要输入模型进行推理运算的任务,在生成所述批量任务后将所述批量任务输入所述第一缓存区。In the embodiment of the present disclosure, a first cache area is set up in the cache space to store the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks. The tasks to be completed in the first cache area are tasks that have not yet been completed, that is, a model needs to be input for execution. For inference operation tasks, after generating the batch tasks, the batch tasks are input into the first cache area.
图2是根据本公开实施例提供的一种批量任务处理方法的示意图,如图2所示,图1中的步骤103中包括以下步骤:201-202。Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of a batch task processing method provided according to an embodiment of the present disclosure. As shown in Figure 2,
步骤201:获取所述第一缓冲区中的已完成任务并输入第二缓冲区,所述已完成任务为执行完毕的待完成任务;Step 201: Obtain the completed tasks in the first buffer and input them into the second buffer. The completed tasks are the tasks to be completed that have been executed;
本公开实施例中,在缓存空间中设置第二缓存区以存储已完成任务,当上层调度模块在每次循环后扫描所述第一缓冲区,识别到所述第一缓冲区中存在已完成任务后,将所述已完成任务转入所述第二缓存区。In the embodiment of the present disclosure, a second cache area is set up in the cache space to store completed tasks. When the upper-layer scheduling module scans the first buffer area after each cycle, it is recognized that there are completed tasks in the first buffer area. After the task is completed, the completed task is transferred to the second cache area.
步骤201:输出所述已完成任务的任务结果并删除所述第二缓冲区中的已完成任务。Step 201: Output the task results of the completed tasks and delete the completed tasks in the second buffer.
本公开实施例中,上层调度模块在每次循环后扫描所述第二缓冲区,如果识别到存在所述已完成任务,则立即生成所述已完成任务对应的任务结果,输出所述任务结果后清空所述第二缓冲区,之后再进行下一轮循环。In the embodiment of the present disclosure, the upper-layer scheduling module scans the second buffer after each cycle. If it recognizes that the completed task exists, it immediately generates a task result corresponding to the completed task and outputs the task result. Then the second buffer is cleared, and then the next cycle is performed.
本公开实施例通过所述第二缓冲区将已经完成的待完成任务在完成后及时从批量任务中转移出来,避免计算资源浪费,提高了获取任务结果的效率。The embodiment of the present disclosure uses the second buffer to transfer completed tasks to be completed from batch tasks in a timely manner after completion, thereby avoiding waste of computing resources and improving the efficiency of obtaining task results.
在一些实施例中,所述执行所述批量任务中的待完成任务,包括:In some embodiments, executing the tasks to be completed in the batch tasks includes:
根据所述待完成任务进行推理运算,以生成子结果。Perform inference operations based on the tasks to be completed to generate sub-results.
本公开实施例中,通过所述模型对所述待完成任务进行推理运算,每次循环进行的一次推理运算可以并生成所述待完成任务对应的一个子结果。In the embodiment of the present disclosure, the model is used to perform an inference operation on the task to be completed, and one inference operation performed in each cycle can generate a sub-result corresponding to the task to be completed.
在一些实施例中,所述待完成任务为文本翻译任务。每次循环中,将所述待完成任务输入模型后,模型根据待完成任务的文本进行推理运算,以获取对应的一个翻译词,也即所述子结果。In some embodiments, the task to be completed is a text translation task. In each cycle, after the task to be completed is input into the model, the model performs inference operations based on the text of the task to be completed to obtain a corresponding translation word, which is the sub-result.
在一些实施例中,所述获取所述第一缓冲区中的已完成任务并输入第二缓冲区,包括:In some embodiments, obtaining the completed tasks in the first buffer and inputting them into the second buffer includes:
获取所述待完成任务的子结果数量阈值;Obtain the threshold number of sub-results for the task to be completed;
根据子结果数量和所述子结果数量阈值确定已完成任务。Completed tasks are determined based on the number of sub-results and the threshold number of sub-results.
本公开实施例中,所述模型可以预先得到所述待完成结果中子结果的最大数量,即所述子结果数量阈值。上层调度模块从模型中获取所述子结果数量阈值以判断第一缓冲区中是否存在已完成任务。In this embodiment of the present disclosure, the model can obtain in advance the maximum number of sub-results in the to-be-completed results, that is, the sub-result number threshold. The upper-layer scheduling module obtains the sub-result quantity threshold from the model to determine whether there are completed tasks in the first buffer.
在一些实施例中,所述根据子结果数量和所述子结果数量阈值确定已完成任务,包括:In some embodiments, determining the completed task based on the number of sub-results and the threshold of the number of sub-results includes:
如果所述子结果数量与所述子结果数量阈值相等,则确定所述待完成任务为所述已完成任务。If the number of sub-results is equal to the threshold of the number of sub-results, the task to be completed is determined to be the completed task.
本公开实施例中,在每次循环结束后,上层调度模块检测第一缓冲区,以获取待完成任务所述子结果的数量。对于一个待完成任务,如果子结果数量与所述子结果数量阈值相等,说明该待完成任务中已经完全执行了对应的推理运算,可以确定为已完成任务。如果所述子结果数量小于所述子结果数量阈值,说明该待完成任务还未完全执行对应的推理运算,需要在下一次循环中继续输入模型进行推理运算。In the embodiment of the present disclosure, after each cycle ends, the upper-layer scheduling module detects the first buffer to obtain the number of sub-results of the task to be completed. For a task to be completed, if the number of sub-results is equal to the threshold number of sub-results, it means that the corresponding inference operation has been completely executed in the task to be completed, and the task can be determined to be completed. If the number of sub-results is less than the threshold of the number of sub-results, it means that the task to be completed has not fully executed the corresponding inference operation, and the model needs to be continued to be input for inference operation in the next cycle.
在一些实施例中,所述方法还包括:In some embodiments, the method further includes:
将所述已完成任务对应的子结果按生成顺序排列以生成所述任务结果。The sub-results corresponding to the completed tasks are arranged in the order of generation to generate the task results.
本公开实施例中,所述模型在执行推理运算时,按照词的语法逻辑顺序进行运算以生成各个子结果,所以将所述已完成任务输入第二缓冲区后,需要根据所述子结果的生成顺序将对应的子结果排列,生成所述任务结果。In the embodiment of the present disclosure, when the model performs the inference operation, the operation is performed according to the grammatical and logical order of the words to generate each sub-result. Therefore, after the completed task is input into the second buffer, it is necessary to calculate the sub-result according to the The generation sequence arranges the corresponding sub-results to generate the task results.
在一些实施例中,所述待完成任务为翻译任务,所述子结果数量阈值为4,说明翻译后句子的最大长度为4个词,即需要生成4个子结果。在第4次循环后所述子结果数量等于所述子结果数量阈值,所述模型即可完成所述待完成任务的推理运算,则 上层调度模块确定其为已完成任务,并输入第二缓冲区中。将4个子结果(4个翻译结果)按照生成的顺序排列后即可生成所述任务结果,即翻译结果。In some embodiments, the task to be completed is a translation task, and the sub-result number threshold is 4, which means that the maximum length of a translated sentence is 4 words, that is, 4 sub-results need to be generated. After the 4th cycle, the number of sub-results equals the threshold number of sub-results, and the model can complete the inference operation of the task to be completed. Then the upper-layer scheduling module determines that it is a completed task and inputs it into the second buffer. District. After arranging the 4 sub-results (4 translation results) in the order of generation, the task result, that is, the translation result can be generated.
在一些实施例中,所述方法还包括:In some embodiments, the method further includes:
响应于所述待完成任务中包括完成标识,确定所述待完成任务为已完成任务。In response to the task to be completed including the completion identifier, it is determined that the task to be completed is a completed task.
本公开实施例中,可以根据完成标识确定已完成任务,模型对所述待完全执行对应的推理运算后,会生成完成标识,上层调度模块在每次循环后对待完成任务进行检测,如果包含所述完成标识,则确定所述待完成任务为已完成任务。In the embodiment of the present disclosure, the completed task can be determined based on the completion identification. After the model completes the corresponding inference operation, a completion identification will be generated. The upper-layer scheduling module detects the task to be completed after each cycle. If it contains all If the completion identifier is specified, the task to be completed is determined to be a completed task.
在一些实施例中,所述完成标识为句子结束符。In some embodiments, the completion indicator is a sentence terminator.
在一些实施例中,所述方法还包括:In some embodiments, the method further includes:
响应于新增任务请求,将新增待完成任务加入所述批量任务中。In response to the new task request, add the new to-be-completed task to the batch task.
本公开实施例中,由于不同待完成任务完成所需要的循环次数不同,子结果数量较少的任务在完成后被转出所述第一缓冲区,系统中就空缺出足够的计算资源支持模型进行推理运算,为了有效地利用计算资源。用户在发出初始的请求后,可以发送所述新增任务请求,上层调度模块可以在所述待完成任务完成后,根据新增任务请求将新增待完成任务加入所述批量任务中,即输入所述第一缓冲区以根据所述模型对所述新增待完成任务进行推理运算。In the embodiment of the present disclosure, due to the different number of cycles required to complete different tasks to be completed, tasks with a smaller number of sub-results are transferred out of the first buffer after completion, leaving sufficient computing resources in the system to support the model. Perform inference operations in order to efficiently utilize computing resources. After the user issues the initial request, the user can send the new task request, and the upper-layer scheduling module can add the new to-be-completed task to the batch task according to the new task request after the to-be-completed task is completed, that is, input The first buffer is used to perform inference operations on the newly added tasks to be completed according to the model.
图3是根据本公开实施例提供的一种批量任务处理方法的示意图,如图3所示,所述方法包括以下步骤:Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of a batch task processing method according to an embodiment of the present disclosure. As shown in Figure 3, the method includes the following steps:
首先,上层调度模块根据当前时刻用户请求的数量,将待完成任务组合成一个大小为N的Batch,并将该Batch输入训练好的词生成模型中。在一些实施例中,这N个待完成任务分别需要生成1~N个词,即子结果,在待完成任务中,生成词的数量和通过模型循环进行推理运算的次数相同。First, the upper-layer scheduling module combines the tasks to be completed into a Batch of size N according to the number of user requests at the current moment, and inputs the Batch into the trained word generation model. In some embodiments, each of the N tasks to be completed needs to generate 1 to N words, that is, sub-results. In the tasks to be completed, the number of generated words is the same as the number of inference operations performed through the model loop.
其次,分配“计算”缓冲区和“完成”缓冲区,所述“计算”缓冲区即第一缓冲区,所述“完成”缓冲区即第二缓冲区。系统开始运行时,“计算”缓冲区中有当前Batch中所有的待完成任务,“完成”缓冲区为空。Secondly, a "calculation" buffer and a "completion" buffer are allocated. The "calculation" buffer is the first buffer, and the "completion" buffer is the second buffer. When the system starts running, the "calculation" buffer contains all the tasks to be completed in the current batch, and the "completion" buffer is empty.
每一轮循环开始时,调度模块会将“计算”缓冲区中的待完成任务一起输入模型中进行推理运算,并在模型进行一次推理运算后,检查“计算”缓冲区中的待完成任务是否完成,若完成生成,则确定该待完成任务为已完成任务并将已完成任务从“计算”缓冲区转入“完成”缓冲区。一旦上层调度模块发现“完成”缓冲区中有任务,则会立即将 生成结果返回给用户,并清空“完成”缓冲区,循环结束。At the beginning of each cycle, the scheduling module will input the tasks to be completed in the "calculation" buffer into the model for inference operation, and after the model performs an inference operation, check whether the tasks to be completed in the "calculation" buffer are Completed. If the generation is completed, the task to be completed is determined to be a completed task and the completed task is transferred from the "calculation" buffer to the "completion" buffer. Once the upper-layer scheduling module finds that there are tasks in the "completion" buffer, it will immediately return the generated results to the user, clear the "completion" buffer, and the cycle ends.
以上面生成1~N个词的Batch为例,在第一次循环时,整个大小为N的Batch都要输入模型进行推理运算,在第一个循环结束后,上层调度模块发现生成1个词的任务结束了,于是将它放入“完成”缓冲区,在第二次循环时,“计算”缓冲区中剩下的N-1个待完成任务继续计算,同时将“完成”缓冲区中生成的任务结果返回给用户,在当前循环结束后,生成2个词的任务也可以放入“完成”缓冲区了,以此类推,直到第N次循环时,只会有生成N个词的任务在计算。Take the above Batch that generates 1 to N words as an example. In the first loop, the entire Batch of size N must be input into the model for inference operation. After the first loop ends, the upper-layer scheduling module finds that 1 word is generated. The task is over, so it is put into the "completion" buffer. In the second cycle, the remaining N-1 tasks to be completed in the "calculation" buffer continue to be calculated, and at the same time, the remaining N-1 tasks in the "completion" buffer are added to the "completion" buffer. The generated task results are returned to the user. After the current cycle ends, the task of generating 2 words can also be put into the "completion" buffer, and so on, until the Nth cycle, only N words will be generated. The task is calculating.
若每生成一个词的时延为t,之前整个Batch中所有任务的推理时延为Nt,使用本公开实施例提出的提前退出的调度方法,最低能将平均时延降低50%,此时平均时延为(1+N)t/2。并且因为还包括Batch中的任务减少,内核Kernel层执行时间也会减少,后面推理会越来越快。If the delay for each word generated is t, and the inference delay of all previous tasks in the entire batch is Nt, using the early exit scheduling method proposed by the embodiment of the present disclosure can reduce the average delay by at least 50%. At this time, the average The time delay is (1+N)t/2. And because there are fewer tasks in the batch, the execution time of the kernel layer will also be reduced, and subsequent inference will be faster and faster.
图4是根据本公开实施例提供的一种批量任务处理装置的结构示意图,如图4所示,所述装置包括以下模块:Figure 4 is a schematic structural diagram of a batch task processing device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure. As shown in Figure 4, the device includes the following modules:
批量任务生成模块410,用于根据待完成任务生成批量任务;Batch
任务执行模块420,用于执行所述批量任务中的待完成任务;
任务调度模块430,用于根据所述批量任务中待完成任务的完成进度调度所述待完成任务;The
在一些实施例中,所述装置还包括:In some embodiments, the device further includes:
输入模块,用于将所述批量任务输入第一缓冲区。An input module is used to input the batch tasks into the first buffer.
图5是根据本公开实施例提供的一种批量任务处理装置的结构示意图,如图5所示,所述任务调度模块包括以下模块:Figure 5 is a schematic structural diagram of a batch task processing device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure. As shown in Figure 5, the task scheduling module includes the following modules:
调度子模块510,用于获取所述第一缓冲区中的已完成任务并输入第二缓冲区,所述已完成任务为执行完毕的待完成任务;
输出子模块520,用于输出所述已完成任务的任务结果并删除所述第二缓冲区中的已完成任务。The
在一些实施例中,所述任务执行模块包括:In some embodiments, the task execution module includes:
运算子模块,用于根据所述待完成任务进行推理运算,以生成子结果。The operation sub-module is used to perform inference operations based on the tasks to be completed to generate sub-results.
在一些实施例中,所述调度子模块包括:In some embodiments, the scheduling submodule includes:
阈值获取模块,用于获取所述待完成任务的子结果数量阈值;A threshold acquisition module, used to obtain the threshold number of sub-results of the task to be completed;
第一任务识别单元,用于根据子结果数量和所述子结果数量阈值确定已完成任务。The first task identification unit is used to determine the completed task according to the number of sub-results and the threshold value of the number of sub-results.
在一些实施例中,所述任务识别单元,包括:In some embodiments, the task identification unit includes:
任务识别子单元,如果所述子结果数量与所述子结果数量阈值相等,则确定所述待完成任务为所述已完成任务。The task identification subunit determines that the task to be completed is the completed task if the number of sub-results is equal to the threshold of the number of sub-results.
在一些实施例中,所述装置还包括:In some embodiments, the device further includes:
第二任务识别单元,用于响应于所述待完成任务中包括完成标识,确定所述待完成任务为已完成任务。The second task identification unit is configured to determine that the task to be completed is a completed task in response to the task to be completed including a completion identifier.
在一些实施例中,所述装置还包括:In some embodiments, the device further includes:
结果获取子单元,用于将所述已完成任务对应的子结果按生成顺序排列以生成所述任务结果。The result acquisition subunit is used to arrange the sub-results corresponding to the completed tasks in the order of generation to generate the task results.
在一些实施例中,所述装置还包括:In some embodiments, the device further includes:
任务添加模块,用于响应于新增任务请求,将新增待完成任务加入所述批量任务中。A task adding module is used to add new to-be-completed tasks to the batch tasks in response to a new task request.
本公开的实施例还提供了一种电子设备、一种可读存储介质、一种计算机程序产品和一种计算机程序。Embodiments of the present disclosure also provide an electronic device, a readable storage medium, a computer program product, and a computer program.
图6示出了可以用来实施本公开的实施例的示例电子设备600的示意性框图。电子设备旨在表示各种形式的数字计算机,诸如,膝上型计算机、台式计算机、工作台、个人数字助理、服务器、刀片式服务器、大型计算机、和其它适合的计算机。电子设备还可以表示各种形式的移动装置,诸如,个人数字处理、蜂窝电话、智能电话、可穿戴设备和其它类似的计算装置。本文所示的部件、它们的连接和关系、以及它们的功能仅仅作为示例,并且不意在限制本文中描述的和/或者要求的本公开的实现。Figure 6 shows a schematic block diagram of an example
如图6所示,设备600包括计算单元601,其可以根据存储在只读存储器(ROM)602中的计算机程序或者从存储单元608加载到随机访问存储器(RAM)603中的计算机程序,来执行各种适当的动作和处理。在RAM 603中,还可存储设备600操作所需的各种程序和数据。计算单元601、ROM 602以及RAM 603通过总线604彼此相连。输入/输出(I/O)接口605也连接至总线604。As shown in FIG. 6 , the
设备600中的多个部件连接至I/O接口605,包括:输入单元606,例如键盘、鼠标等;输出单元607,例如各种类型的显示器、扬声器等;存储单元608,例如磁盘、光盘等;以及通信单元609,例如网卡、调制解调器、无线通信收发机等。通信单元609允许设备600通过诸如因特网的计算机网络和/或各种电信网络与其他设备交换信息/数据。Multiple components in
计算单元601可以是各种具有处理和计算能力的通用和/或专用处理组件。计算单元601的一些示例包括但不限于中央处理单元(CPU)、图形处理单元(GPU)、各种专用的人工智能(AI)计算芯片、各种运行机器学习模型算法的计算单元、数字信号处理器(DSP)、以及任何适当的处理器、控制器、微控制器等。计算单元601执行上文所描述的各个方法和处理,例如所述批量任务处理方法。例如,在一些实施例中,所述批量任务处理方法可被实现为计算机软件程序,其被有形地包含于机器可读介质,例如存储单元608。在一些实施例中,计算机程序的部分或者全部可以经由ROM 602和/或通信单元609而被载入和/或安装到设备600上。当计算机程序加载到RAM 603并由计算单元601执行时,可以执行上文描述的所述批量任务处理方法的一个或多个步骤。备选地,在其他实施例中,计算单元601可以通过其他任何适当的方式(例如,借助于固件)而被配置为执行所述批量任务处理方法。
本文中以上描述的系统和技术的各种实施方式可以在数字电子电路系统、集成电路系统、场可编程门阵列(FPGA)、专用集成电路(ASIC)、专用标准产品(ASSP)、芯片上系统的系统(SOC)、负载可编程逻辑设备(CPLD)、计算机硬件、固件、软件、和/或它们的组合中实现。这些各种实施方式可以包括:实施在一个或者多个计算机程序中,该一个或者多个计算机程序可在包括至少一个可编程处理器的可编程系统上执行和/或解释,该可编程处理器可以是专用或者通用可编程处理器,可以从存储系统、至少一个输入装置、和至少一个输出装置接收数据和指令,并且将数据和指令传输至该存储系统、该至少一个输入装置、和该至少一个输出装置。Various implementations of the systems and techniques described above may be implemented in digital electronic circuit systems, integrated circuit systems, field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), application specific integrated circuits (ASICs), application specific standard products (ASSPs), systems on a chip implemented in a system (SOC), load programmable logic device (CPLD), computer hardware, firmware, software, and/or a combination thereof. These various embodiments may include implementation in one or more computer programs executable and/or interpreted on a programmable system including at least one programmable processor, the programmable processor The processor, which may be a special purpose or general purpose programmable processor, may receive data and instructions from a storage system, at least one input device, and at least one output device, and transmit data and instructions to the storage system, the at least one input device, and the at least one output device. An output device.
用于实施本公开的方法的程序代码可以采用一个或多个编程语言的任何组合来编写。这些程序代码可以提供给通用计算机、专用计算机或其他可编程数据处理装置的处理器或控制器,使得程序代码当由处理器或控制器执行时使流程图和/或框图中所规定的功能/操作被实施。程序代码可以完全在机器上执行、部分地在机器上执行,作为独立软件包部分地在机器上执行且部分地在远程机器上执行或完全在远程机器或服务器上执行。Program code for implementing the methods of the present disclosure may be written in any combination of one or more programming languages. These program codes may be provided to a processor or controller of a general-purpose computer, special-purpose computer, or other programmable data processing device, such that the program codes, when executed by the processor or controller, cause the functions specified in the flowcharts and/or block diagrams/ The operation is implemented. The program code may execute entirely on the machine, partly on the machine, as a stand-alone software package, partly on the machine and partly on a remote machine or entirely on the remote machine or server.
在本公开的上下文中,机器可读介质可以是有形的介质,其可以包含或存储以供指令执行系统、装置或设备使用或与指令执行系统、装置或设备结合地使用的程序。机器可读介质可以是机器可读信号介质或机器可读储存介质。机器可读介质可以包括但不限于电子的、磁性的、光学的、电磁的、红外的、或半导体系统、装置或设备,或者上述内容的任何合适组合。机器可读存储介质的更具体示例会包括基于一个或多 个线的电气连接、便携式计算机盘、硬盘、随机存取存储器(RAM)、只读存储器(ROM)、可擦除可编程只读存储器(EPROM或快闪存储器)、光纤、便捷式紧凑盘只读存储器(CD-ROM)、光学储存设备、磁储存设备、或上述内容的任何合适组合。In the context of this disclosure, a machine-readable medium may be a tangible medium that may contain or store a program for use by or in connection with an instruction execution system, apparatus, or device. The machine-readable medium may be a machine-readable signal medium or a machine-readable storage medium. Machine-readable media may include, but are not limited to, electronic, magnetic, optical, electromagnetic, infrared, or semiconductor systems, devices or devices, or any suitable combination of the foregoing. More specific examples of machine-readable storage media would include one or more wire-based electrical connections, laptop disks, hard drives, random access memory (RAM), read only memory (ROM), erasable programmable read only memory (EPROM or flash memory), optical fiber, portable compact disk read-only memory (CD-ROM), optical storage device, magnetic storage device, or any suitable combination of the above.
为了提供与用户的交互,可以在计算机上实施此处描述的系统和技术,该计算机具有:用于向用户显示信息的显示装置(例如,CRT(阴极射线管)或者LCD(液晶显示器)监视器);以及键盘和指向装置(例如,鼠标或者轨迹球),用户可以通过该键盘和该指向装置来将输入提供给计算机。其它种类的装置还可以用于提供与用户的交互;例如,提供给用户的反馈可以是任何形式的传感反馈(例如,视觉反馈、听觉反馈、或者触觉反馈);并且可以用任何形式(包括声输入、语音输入或者、触觉输入)来接收来自用户的输入。To provide interaction with a user, the systems and techniques described herein may be implemented on a computer having a display device (eg, a CRT (cathode ray tube) or LCD (liquid crystal display) monitor) for displaying information to the user ); and a keyboard and pointing device (eg, a mouse or a trackball) through which a user can provide input to the computer. Other kinds of devices may also be used to provide interaction with the user; for example, the feedback provided to the user may be any form of sensory feedback (e.g., visual feedback, auditory feedback, or tactile feedback); and may be provided in any form, including Acoustic input, voice input or tactile input) to receive input from the user.
可以将此处描述的系统和技术实施在包括后台部件的计算系统(例如,作为数据服务器)、或者包括中间件部件的计算系统(例如,应用服务器)、或者包括前端部件的计算系统(例如,具有图形用户界面或者网络浏览器的用户计算机,用户可以通过该图形用户界面或者该网络浏览器来与此处描述的系统和技术的实施方式交互)、或者包括这种后台部件、中间件部件、或者前端部件的任何组合的计算系统中。可以通过任何形式或者介质的数字数据通信(例如,通信网络)来将系统的部件相互连接。通信网络的示例包括:局域网(LAN)、广域网(WAN)、互联网和区块链网络。The systems and techniques described herein may be implemented in a computing system that includes back-end components (e.g., as a data server), or a computing system that includes middleware components (e.g., an application server), or a computing system that includes front-end components (e.g., A user's computer having a graphical user interface or web browser through which the user can interact with implementations of the systems and technologies described herein), or including such backend components, middleware components, or any combination of front-end components in a computing system. The components of the system may be interconnected by any form or medium of digital data communication (eg, a communications network). Examples of communication networks include: local area network (LAN), wide area network (WAN), the Internet, and blockchain networks.
计算机系统可以包括客户端和服务器。客户端和服务器一般远离彼此并且通常通过通信网络进行交互。通过在相应的计算机上运行并且彼此具有客户端-服务器关系的计算机程序来产生客户端和服务器的关系。服务器可以是云服务器,又称为云计算服务器或云主机,是云计算服务体系中的一项主机产品,以解决了传统物理主机与VPS服务("Virtual Private Server",或简称"VPS")中,存在的管理难度大,业务扩展性弱的缺陷。服务器也可以为分布式系统的服务器,或者是结合了区块链的服务器。Computer systems may include clients and servers. Clients and servers are generally remote from each other and typically interact over a communications network. The relationship of client and server is created by computer programs running on corresponding computers and having a client-server relationship with each other. The server can be a cloud server, also known as cloud computing server or cloud host. It is a host product in the cloud computing service system to solve the problem of traditional physical host and VPS service ("Virtual Private Server", or "VPS" for short) Among them, there are defects such as difficult management and weak business scalability. The server can also be a distributed system server or a server combined with a blockchain.
需要说明的是,前述对批量任务处理的方法实施例的解释说明也适用于上述实施例中的装置、电子设备、计算机可读存储介质、计算机程序产品和计算机程序,此处不再赘述。It should be noted that the foregoing explanations of the batch task processing method embodiments also apply to the devices, electronic equipment, computer-readable storage media, computer program products and computer programs in the above-mentioned embodiments, and will not be described again here.
应该理解,可以使用上面所示的各种形式的流程,重新排序、增加或删除步骤。例如,本发公开中记载的各步骤可以并行地执行也可以顺序地执行也可以不同的次序执行,只要能够实现本公开公开的技术方案所期望的结果,本文在此不进行限制。It should be understood that various forms of the process shown above may be used, with steps reordered, added or deleted. For example, each step described in the present disclosure can be executed in parallel, sequentially, or in a different order. As long as the desired results of the technical solution disclosed in the present disclosure can be achieved, there is no limitation here.
上述具体实施方式,并不构成对本公开保护范围的限制。本领域技术人员应该明 白的是,根据设计要求和其他因素,可以进行各种修改、组合、子组合和替代。任何在本公开的精神和原则之内所作的修改、等同替换和改进等,均应包含在本公开保护范围之内。The above-mentioned specific embodiments do not constitute a limitation on the scope of the present disclosure. It will be understood by those skilled in the art that various modifications, combinations, sub-combinations and substitutions are possible depending on design requirements and other factors. Any modifications, equivalent substitutions, improvements, etc. made within the spirit and principles of this disclosure shall be included in the protection scope of this disclosure.
Claims (22)
Translated fromChineseApplications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210547456.4ACN114860410A (en) | 2022-05-19 | 2022-05-19 | Batch task processing method and device and electronic equipment |
| CN202210547456.4 | 2022-05-19 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2023221370A1true WO2023221370A1 (en) | 2023-11-23 |
Family
ID=82638927
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2022/123597CeasedWO2023221370A1 (en) | 2022-05-19 | 2022-09-30 | Batch task processing method and apparatus, and electronic device |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114860410A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2023221370A1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US12111825B2 (en) | 2022-11-10 | 2024-10-08 | Bank Of America Corporation | Event-driven batch processing system with granular operational access |
| CN119718583A (en)* | 2024-12-18 | 2025-03-28 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Task scheduling method, device, electronic equipment, storage medium and program product |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114860410A (en)* | 2022-05-19 | 2022-08-05 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Batch task processing method and device and electronic equipment |
| CN116822629B (en)* | 2023-05-19 | 2025-04-22 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Text reasoning task processing method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20160011901A1 (en)* | 2014-07-09 | 2016-01-14 | Google Inc. | Dynamic Shard Allocation Adjustment |
| CN110968420A (en)* | 2018-09-30 | 2020-04-07 | 北京国双科技有限公司 | Scheduling method and device for multi-crawler platform, storage medium and processor |
| US20210134273A1 (en)* | 2019-10-31 | 2021-05-06 | International Business Machines Corporation | Iterative intent building utilizing dynamic scheduling of batch utterance expansion methods |
| CN112948079A (en)* | 2021-02-18 | 2021-06-11 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Task scheduling method, device, equipment and computer storage medium |
| CN114138447A (en)* | 2021-12-08 | 2022-03-04 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Task processing method, apparatus, device and storage medium |
| CN114860410A (en)* | 2022-05-19 | 2022-08-05 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Batch task processing method and device and electronic equipment |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102831012A (en)* | 2011-06-16 | 2012-12-19 | 日立(中国)研究开发有限公司 | Task scheduling device and task scheduling method in multimode distributive system |
| CN113986488A (en)* | 2021-10-20 | 2022-01-28 | 北京爱芯科技有限公司 | Method and device for scheduling calculation tasks, computer equipment and storage medium |
- 2022
- 2022-05-19CNCN202210547456.4Apatent/CN114860410A/enactivePending
- 2022-09-30WOPCT/CN2022/123597patent/WO2023221370A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20160011901A1 (en)* | 2014-07-09 | 2016-01-14 | Google Inc. | Dynamic Shard Allocation Adjustment |
| CN110968420A (en)* | 2018-09-30 | 2020-04-07 | 北京国双科技有限公司 | Scheduling method and device for multi-crawler platform, storage medium and processor |
| US20210134273A1 (en)* | 2019-10-31 | 2021-05-06 | International Business Machines Corporation | Iterative intent building utilizing dynamic scheduling of batch utterance expansion methods |
| CN112948079A (en)* | 2021-02-18 | 2021-06-11 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Task scheduling method, device, equipment and computer storage medium |
| CN114138447A (en)* | 2021-12-08 | 2022-03-04 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Task processing method, apparatus, device and storage medium |
| CN114860410A (en)* | 2022-05-19 | 2022-08-05 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Batch task processing method and device and electronic equipment |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US12111825B2 (en) | 2022-11-10 | 2024-10-08 | Bank Of America Corporation | Event-driven batch processing system with granular operational access |
| CN119718583A (en)* | 2024-12-18 | 2025-03-28 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Task scheduling method, device, electronic equipment, storage medium and program product |
| CN119718583B (en)* | 2024-12-18 | 2025-09-26 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Task scheduling method, device, electronic device, storage medium and program product |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114860410A (en) | 2022-08-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2023221370A1 (en) | Batch task processing method and apparatus, and electronic device | |
| CN112597754B (en) | Text error correction methods, devices, electronic equipment and readable storage media | |
| WO2023201981A1 (en) | Mixture-of-experts model implementation method and system, electronic device, and storage medium | |
| CN112508768B (en) | Single-operator multi-model pipeline reasoning method, system, electronic device and medium | |
| US20220292337A1 (en) | Neural network processing unit, neural network processing method and device | |
| CN114911596B (en) | Scheduling method, device, electronic device and storage medium for model training | |
| US20220391780A1 (en) | Method of federated learning, electronic device, and storage medium | |
| CN114968520B (en) | Task search method and device, server and storage medium | |
| CN114780022B (en) | Additional write operation realization method, device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN113986580A (en) | Task processing method and device | |
| CN118734970A (en) | A method, device, apparatus and medium for speculative decoding in a large language model | |
| CN114937478A (en) | Method for training a model, method and apparatus for generating molecules | |
| WO2025055266A1 (en) | Image processing method and apparatus, device, and medium | |
| CN114297119B (en) | Intelligent contract execution method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN115759260A (en) | Inference method and device of deep learning model, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114547492A (en) | Training method for generating model, method, device, equipment and medium for generating file | |
| CN114416357A (en) | Method and device for creating container group, electronic equipment and medium | |
| CN118656221A (en) | Microservice merging method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN113641404B (en) | Program running method, device, processor chip, electronic device and storage medium | |
| CN115860121A (en) | Text reasoning method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN116541224A (en) | Performance testing method, device, electronic device and readable storage medium | |
| CN114742035A (en) | Text processing method and network model training method based on attention mechanism optimization | |
| CN114841341A (en) | Model training and data processing method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN115936094B (en) | Training method, device, electronic device and storage medium for text processing model | |
| JP7524128B2 (en) | Text prediction method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | Ref document number:22942397 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 | |
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase | Ref country code:DE | |
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase | Ref document number:22942397 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 | |
| 32PN | Ep: public notification in the ep bulletin as address of the adressee cannot be established | Free format text:NOTING OF LOSS OF RIGHTS PURSUANT TO RULE 112(1) EPC (EPO FORM 1205A DATED 30.05.2025) |