WO2023035756A1 - Scheduling method and apparatus for movable device, and electronic device and storage medium - Google Patents
Scheduling method and apparatus for movable device, and electronic device and storage mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2023035756A1 WO2023035756A1PCT/CN2022/104395CN2022104395WWO2023035756A1WO 2023035756 A1WO2023035756 A1WO 2023035756A1CN 2022104395 WCN2022104395 WCN 2022104395WWO 2023035756 A1WO2023035756 A1WO 2023035756A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- navigation
- driving
- mobile device
- devices
- movable
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/29—Geographical information databases
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/04—Forecasting or optimisation specially adapted for administrative or management purposes, e.g. linear programming or "cutting stock problem"
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/04—Forecasting or optimisation specially adapted for administrative or management purposes, e.g. linear programming or "cutting stock problem"
- G06Q10/047—Optimisation of routes or paths, e.g. travelling salesman problem
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/06—Resources, workflows, human or project management; Enterprise or organisation planning; Enterprise or organisation modelling
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/06—Resources, workflows, human or project management; Enterprise or organisation planning; Enterprise or organisation modelling
- G06Q10/063—Operations research, analysis or management
- G06Q10/0631—Resource planning, allocation, distributing or scheduling for enterprises or organisations
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/08—Logistics, e.g. warehousing, loading or distribution; Inventory or stock management
- G06Q10/083—Shipping
- G06Q10/0835—Relationships between shipper or supplier and carriers
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P90/00—Enabling technologies with a potential contribution to greenhouse gas [GHG] emissions mitigation
- Y02P90/02—Total factory control, e.g. smart factories, flexible manufacturing systems [FMS] or integrated manufacturing systems [IMS]
Definitions
- the present inventionrelates to the field of logistics technology, and in particular to a scheduling method, scheduling device, electronic equipment and storage medium of movable equipment.
- the mobile devicepre-stores map data of its environment, and then navigates in the environment based on the map data.
- map dataFor example, smart warehousing, logistics sorting and other scenarios.
- each mobile deviceneeds to perform obstacle detection independently to trigger its own obstacle avoidance function in time to avoid hitting temporary obstacles (such as other mobile devices that appear due to crossing navigation routes).
- each obstacle detectionneeds to consume a lot of computing resources of the mobile device itself, and it takes a lot of computing time, resulting in a delay in the triggering of the obstacle avoidance operation, which reduces the single-machine obstacle avoidance ability of the mobile device and affects the operation of the device.
- Safety
- the inventionprovides a scheduling method, a scheduling device, electronic equipment and a storage medium of a movable device, which are used to realize the switching of navigation states of the movable device, improve the obstacle avoidance ability of the movable device, and ensure the safe operation of the device.
- the present inventionprovides a method for scheduling a mobile device, the method comprising:
- a navigation stop instructionis sent to the mobile device in the at least two mobile devices, so that the mobile device that receives the navigation stop instruction is based on the navigation stop instruction. Stop navigating for a set duration.
- the present inventionprovides a mobile device scheduling device, including:
- An acquisition moduleconfigured to acquire respective navigation information of multiple mobile devices
- a generating moduleconfigured to generate dynamic safety areas for multiple mobile devices based on the navigation information, where the dynamic safety areas are used to represent the safe driving range of the mobile devices in the driving environment;
- a dispatching moduleconfigured to send a navigation stop instruction to the mobile device among the at least two mobile devices if the dynamic security areas of at least two mobile devices overlap each other, so that the mobile device that receives the navigation stop instruction is based on The navigation stop command stops navigation within a preset duration.
- the present inventionprovides an electronic device, which includes a processor and a memory, wherein executable code is stored in the memory, and when the executable code is executed by the processor, the processor At least the scheduling method in the first aspect can be implemented.
- the present inventionprovides a non-transitory machine-readable storage medium, where executable code is stored on the non-transitory machine-readable storage medium, and when the executable code is executed by a processor of an electronic device , so that the processor can at least implement the scheduling method in the first aspect.
- dynamic safety areas of the plurality of mobile devicesare generated respectively, and the dynamic safety areas are used to indicate the safe driving range of the mobile devices in the driving environment. Furthermore, if there are at least two movable devices whose dynamic safety areas overlap with each other, it means that these movable devices have a high risk of collision.
- a navigation messagecan be sent to any one of the at least two movable devices A stop instruction, so that any one of the movable devices stops navigation within a preset time period based on the navigation stop instruction.
- the respective dynamic security areasare dynamically set through the navigation information of multiple mobile devices, and the respective navigation states of the multiple mobile devices are controlled based on the dynamic security areas, so as to avoid mobile devices with overlapping dynamic security areas.
- the collision risk caused by continuing to drivegreatly reduces the collision accident rate of mobile equipment, improves the obstacle avoidance ability of mobile equipment, and ensures the safety of equipment operation.
- Fig. 1is a schematic flow chart diagram of a scheduling method provided by the present invention
- FIG. 2is a schematic diagram of a scheduling scenario provided by the present invention.
- Fig. 3is a schematic diagram of a dynamic security area provided by the present invention.
- FIG. 4is a schematic diagram of a positional relationship of a mobile device provided by the present invention.
- Fig. 5is a schematic structural diagram of a scheduling device provided by the present invention.
- FIG. 6is a schematic structural diagram of an electronic device provided by the present invention.
- the words “if”, “if” as used hereinmay be interpreted as “at” or “when” or “in response to determining” or “in response to detecting”.
- the phrases “if determined” or “if detected (the stated condition or event)”could be interpreted as “when determined” or “in response to the determination” or “when detected (the stated condition or event) )” or “in response to detection of (a stated condition or event)”.
- the mobile devicewill pre-store the map data of the environment, and then navigate in the environment based on the map data. For example, in scenarios such as smart warehousing and logistics sorting, there are often multiple mobile devices in the same environment, and these mobile devices all need to rely on the same map data for mixed operations.
- each mobile deviceneeds to perform obstacle detection independently to trigger its own obstacle avoidance function in time to avoid hitting temporary obstacles (such as other mobile devices that appear due to crossing navigation routes).
- each obstacle detectionneeds to consume a lot of computing resources of the mobile device itself, and it takes a lot of computing time, resulting in a delay in the triggering of the obstacle avoidance operation, which reduces the single-machine obstacle avoidance ability of the mobile device and affects the operation of the device.
- SafetyIn particular, as the driving speed of the mobile device increases and the environment becomes more complex (such as more corners, obstacles, etc.), the requirements for obstacle avoidance capabilities are further enhanced.
- the core idea of the scheduling scheme provided by the embodiment of the present inventionis:
- the respective navigation information of the multiple mobile devicesis acquired, so that the respective dynamic security areas of the multiple mobile devices can be dynamically generated according to the respective navigation information of the multiple mobile devices.
- the dynamic safety areais used to represent the safe driving range of the mobile device in the driving environment.
- a navigation stop instructioncan be sent to any one of the at least two movable devices , so that any mobile device stops navigation within a preset time period based on the navigation stop instruction. Therefore, by controlling the respective navigation states of multiple mobile devices, it is possible to avoid the collision risk caused by the continuous driving of the mobile devices whose dynamic safety areas overlap with each other, greatly reducing the collision accident rate of the mobile devices and improving the safety of the mobile devices. failure capability to ensure the safe operation of the equipment.
- Fig. 1is a flowchart of a scheduling method provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in Fig. 1, the method includes the following steps:
- the mobile devicemay be an autonomous mobile robot (Automated Mobile Robot, AMR), a cargo vehicle, and the like.
- AMRAutomated Mobile Robot
- an autonomous mobile robotrefers to a device capable of highly autonomous spatial movement in a working environment. For example, warehousing collaborative robots, picking robots or handling robots.
- the autonomous mobile robotis provided with a semantic map corresponding to its environment, and the semantic map refers to an environment map including semantic information of multiple objects in the environment.
- the semantic information of an objectrefers to the information that can understand and explain what the object is or its category with the help of natural language, for example, it may include but not limited to the name, shape, location, etc. of the object.
- the semantic mapincludes the location, type, and size of each shelf in the warehouse, as well as the location, type, and size of various obstacles (such as railings, steps, thresholds, etc.) in the warehouse.
- the method provided by the embodiment of the present inventioncan be implemented by a scheduling system and coordinated by multiple mobile devices.
- the dispatching systemmay be set in a cloud service center, or in a mobile device, or in other forms of computing devices, which is not limited by the present invention.
- the method provided by the embodiments of the present inventioncan be applied to various scenarios, for example, it can be applied to warehousing scenarios, logistics sorting scenarios, material distribution scenarios, port freight scenarios, and the like.
- the specific implementation manner of the embodiment of the present inventionis introduced below by taking a storage scenario as an example. Other scenarios may be implemented with reference to the implementation manner of a storage scenario, and details are not repeated here.
- a warehousecan be equipped with multiple mobile devices, so that before unloading or during the delivery of one of the mobile devices, other mobile devices can meet the delivery needs of other goods.
- the driving environment mapsthat is, the map data of the warehouse environment, are pre-registered in multiple mobile devices. Assume that multiple mobile devices are loaded in the loading area and then transported to their respective target unloading points. It is assumed that multiple movable devices are managed by a dispatch system.
- multiple mobile devicescan generate navigation information according to the map data of the driving environment and their own target unloading points, including the driving route, driving speed, driving direction, location, etc.
- the multiple mobile devicesreport their own navigation information to the dispatching system, and the dispatching system receives and enters the respective navigation information of the multiple mobile devices.
- the dispatch systemgenerates respective dynamic safety areas for the plurality of movable devices based on the navigation information.
- the dynamic safety areais used to indicate the safe driving range of the mobile device in the driving environment. If an obstacle appears in the dynamic safety area, or other movable equipment enters the dynamic safety area, the collision can be avoided immediately by reducing the driving speed of the mobile equipment or triggering the braking state of the mobile equipment.
- the range of the dynamic safe areais determined by any one or more factors in the safe braking distance of the mobile device, running stability, safety requirements, and actual running scenarios.
- the range of a part of the dynamic safety area located in the forward direction of the movable deviceis calculated according to the safe braking distance of the movable device.
- the scope of other parts of the dynamic safety area in the non-advancing directionis determined according to the running stability of the mobile equipment, cargo carrying capacity and/or safety requirements.
- the overall range of the dynamic safety area or the range of a part of the dynamic safety area in the non-advancing directioncan also be adjusted according to the road conditions in the actual running scene.
- the scope of the dynamic safety areais expanded according to the actual road conditions.
- the scope of the dynamic safety areacan be reduced according to the actual road conditions, so as to reduce the probability of the mobile device being controlled by traffic.
- the dynamic safety areais a coordinate area dynamically set in the warehouse environment map following the driving trajectory of the mobile device.
- the dispatching systemcan determine whether there is a collision risk on the driving route of the corresponding movable equipment through the dynamic safety area.
- the dispatching systemdetects that there are obstacles (including other movable equipment) in the dynamic safety area, or the dynamic safety area overlaps with the dynamic safety area of other mobile equipment, it means that the corresponding movable
- the devicemay collide with the aforementioned obstacles or other movable devices. In this case, it is necessary to control the navigation state of the mobile device in time to avoid collisions.
- the dispatching systemsends a navigation stop instruction to any one of the at least two movable devices, so that any one of the movable devices can Stop navigating for a preset duration.
- the respective dynamic security areascan be dynamically set according to the navigation information of multiple mobile devices, and the navigation status of multiple mobile devices in the storage scene can be scheduled based on the dynamic security areas, so as to avoid the possibility that the dynamic security areas overlap with each other.
- the collision risk caused by the continuous driving of the mobile equipmentgreatly reduces the collision accident rate of the mobile equipment, improves the obstacle avoidance ability of the mobile equipment, and ensures the safe operation of the equipment.
- the process of obtaining the respective navigation information of multiple mobile devices by the dispatching system in step 101may be implemented as: receiving navigation information reported by multiple mobile devices according to a preset period.
- the navigation information of the mobile deviceincludes, but is not limited to: any one or combination of driving speed, driving direction, location of the mobile device, and device attribute information.
- the equipment attribute informationincludes equipment model, equipment size, maximum driving speed, and braking performance.
- multiple mobile devicesreport navigation information to the dispatching system according to a preset period, so that the dispatching system receives the respective navigation information of multiple mobile devices and updates the Self-stored navigation information library.
- the navigation information periodically reported by the mobile deviceis mainly real-time information about the driving state, such as the location, speed, direction, and trajectory of the mobile device.
- the device attribute information of the movable devicesuch as device model, device size, maximum driving speed, and braking performance
- the navigation information databaseis entered in the navigation information database. Therefore, the amount of data transmission reported by the mobile device to the dispatching system is reduced, the efficiency of navigation information transmission is improved, and the real-time performance of navigation information is guaranteed.
- the preset period for reporting navigation informationmay be formulated according to the driving environment where the mobile device is located. For example, if the driving environment is small and there are many obstacles, it means that the probability of collision accidents is high. In this case, the preset cycle for reporting navigation information can be shortened, for example, it is set to report navigation information every 2s. If the driving environment is large and there are few obstacles, it means that the probability of collision accidents is low. In this case, the preset period for reporting navigation information can be extended, for example, it is set to 10s to report navigation information once.
- the above periodsare examples, and are not limited in the present invention.
- the preset period for reporting the navigation informationmay also be set in other ways.
- the preset period for reporting navigation informationis set according to the driving state of the mobile device. For example, the driving speed of the mobile device is faster, indicating that the probability of a collision accident is higher. In this case, the period for reporting the navigation information can also be shortened. Set period.
- step 102the process of the dispatching system generating the respective dynamic security areas of the plurality of mobile devices based on the respective navigation information of the plurality of mobile devices may be implemented as follows: For the navigation information of the device, a virtual area matching each mobile device is set in the preset driving environment map as the dynamic safety area of each mobile device.
- the virtual area matched with each mobile devicechanges along with the traveling track of each mobile device.
- the shape of the virtual areais set according to the shape of the movable device.
- the external dimensions of the mobile deviceare determined according to the device model of the mobile device, and the matching virtual area shape is preset according to the external dimensions.
- the coordinates of the geometric center of the virtual area in the driving environment mapcoincide with the coordinates of the location of the mobile device.
- the shape of the virtual areais a rectangle
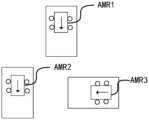
- the mobile devicesinclude AMR1, AMR2, and AMR3.
- the dispatching systemreceives the navigation information of the three AMRs, according to the navigation information of the three AMRs, a rectangular virtual area matching each AMR is respectively set in the preset driving environment map as the dynamic map of each AMR. safe area.
- a larger safety area spacecan also be set in front of the driving direction.
- the space occupied by the movable device in front of the driving directionmay be larger than the space occupied by the rear of the driving direction.
- the safe braking distancecan be understood as the maximum distance that needs to be met when a collision can be avoided by reducing the vehicle speed or entering the braking state.
- the arrow in Figure 3indicates the driving direction of the AMR.
- the space occupied by the front of the driving direction in the three AMR dynamic safety areasis larger than the space occupied by the rear of the driving direction.
- the range of the dynamic safety areacan be further adjusted according to other factors such as running stability, safety requirements, and actual operating scenarios.
- the shape of the virtual areamay also be a triangle, a circle, or other figures, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present invention.
- the shapeit needs to meet the safety braking distance set for the movable equipment in advance, so that the final dynamic safety area can be used as the basis for evaluating whether the movable equipment will collide.
- the navigation information of each mobile deviceincludes the traveling speed, traveling direction, location, and device type of each mobile device.
- the process of setting a virtual area matching each mobile device in the preset driving environment mapcan be realized as follows: according to each mobile device According to the driving speed, driving direction, location and matching safe braking distance of each mobile device, determine the matching safe braking distance of each mobile device; in the driving environment map Dynamically update the virtual area matched by each mobile device.
- the mobile device areports initial navigation information to the dispatching system. It is further assumed that the initial navigation information includes the device type, device identifier and location of the mobile device a. Based on this, after receiving the initial navigation information, the dispatching system creates an initial virtual area matching the mobile device a in the driving environment map.
- the navigation information periodically reported by the mobile device a to the dispatching systemincludes the travel speed, travel direction, and location of the mobile device a. Based on this, the dispatching system determines the matching safe braking distance of the movable device a at the current driving speed according to the traveling speed of the movable device a and the type of the device. Furthermore, the dispatching system dynamically updates the virtual area matched by the mobile device a in the driving environment map according to the driving speed, driving direction, location and matching safe braking distance of the mobile device a.
- the dynamic safety area corresponding to the movable deviceis dynamically adjusted. For example, if it is detected that the traveling speed of the mobile device increases, in this case, the range of the dynamic safety area corresponding to the mobile device may be expanded to avoid safety risks caused by the high-speed driving of the mobile device.
- the corresponding dynamic The safe areaif it is detected that the cargo loaded on the mobile device changes, for example, the newly loaded cargo is a fragile item, or the weight changes due to cargo loading and unloading operations, the corresponding dynamic The safe area, so as to ensure that the revised dynamic safe area conforms to the current driving state of the mobile device. For example, fragile objects cannot be decelerated or braked suddenly, so the dynamic safety range needs to be extended. As another example, changes in the weight of the cargo may affect the braking speed, so the dynamic safety range also needs to be adjusted.
- the coreis to dynamically plan a dynamic safety area that meets the safe braking distance in the driving environment map according to the driving state of the mobile device reflected in the navigation information, to assist in evaluating the collision risk of the mobile device .
- the dispatching systemneeds to judge whether there is a collision risk for all the movable devices under control based on the dynamic safety area.
- the scheduling systemmay determine whether the dynamic security areas of at least two movable devices among the plurality of movable devices overlap with each other according to a preset frequency.
- the dispatching systemneeds to check the navigation status of some of the movable devices Take control.
- the process of the dispatching system sending a navigation stop instruction to any one of the at least two movable devicesmay be implemented as: determining the driving priorities of the at least two movable devices; Among the mobile devices, the mobile device whose driving priority is in the preset sequence sends a navigation stop command. After the mobile device receives the navigation stop instruction, it will stop the navigation within a preset time period based on the navigation stop instruction, so as to avoid collision between at least two movable devices.
- the navigation stop instructionis used to instruct the mobile device to stop the preset duration of navigation. For example, instruct the mobile device to stop navigating for N seconds.
- the navigation stop commandcan be implemented as a brake trigger command, a deceleration command, and the like.
- the preset durations indicated in the navigation stop instructions issued to multiple mobile devicesmay be the same or different.
- the dynamic security areas of mobile devices a and bboth overlap with the dynamic security area of mobile device c. If the dynamic safety areas of mobile devices a and b do not overlap, it means that there is no risk of collision between mobile devices a and b. Therefore, the navigation stop instructions issued to mobile devices a and b indicate that The preset durations may be the same. If the dynamic safety areas of mobile devices a and b overlap each other, it means that there is also a risk of collision between mobile devices a and b. Therefore, the preset duration indicated by the navigation stop instructions issued to mobile devices a and b should be different. In this way, by controlling the mobile devices a and b to resume navigation at different times, collisions between the mobile devices a and b are avoided.
- the preset sequencemay be set according to an actual application scenario. For example, assuming that the movable device card with the highest driving priority is ranked first, then the preset order can be set to all other orders other than the first order. Based on this, the dispatching system sends a navigation stop command to all the mobile devices with the highest driving priority among the at least two mobile devices, and within the preset time period, the one with the highest driving priority among the at least two mobile devices can The mobile device continues to navigate. Therefore, the navigation state of the mobile device lower than the highest driving priority can be controlled so that it stops navigating, and the mobile device with the highest driving priority can be kept in the original driving state. Traffic control for mobile devices.
- the process of sending a navigation stop instruction to the mobile device whose driving priority is in the preset order among at least two mobile devicescan be realized as follows: according to the driving priority of multiple target mobile devices level, and the matching relationship between driving priority and stop navigation duration, determine the corresponding stop navigation duration of multiple target mobile devices; among them, the higher the driving priority, the shorter the stop navigation duration; based on the respective A corresponding navigation stop instruction is generated for the matching stop navigation duration; and the corresponding navigation stop instruction is sent to multiple target mobile devices.
- the matching relationship between driving priority and stop navigation durationcan be preset in the dispatching system according to the actual application scenario.
- the above-mentioned matching relationshipcan be set according to the warehouse area, shelf spacing, loading and unloading speed, etc., and entered into the dispatching system in advance.
- different navigation stop durationsare respectively configured for the multiple target mobile devices in the preset order, so as to further avoid the risk of collision caused by multiple mobile devices returning to the navigation state at the same time.
- different navigation stop durationscan also be set for these mobile devices, so that these mobile devices resume the navigation state at different times, In this way, the risk of collision caused by multiple mobile devices with the same driving priority recovering the navigation state at the same time is further avoided.
- the navigation stop duration of movable devices a, b, and ccan be set to N seconds, N+ S seconds, N+2S seconds.
- the unit navigation stop duration Smay be set according to actual conditions.
- Embodiments of the present inventionprovide the following manners for determining driving priorities of at least two mobile devices whose dynamic safety areas overlap with each other.
- the process of determining the driving priorities of the at least two mobile devicesincludes: according to the navigation information of the at least two mobile devices, determining The driving directions and positions of at least two movable devices; for at least two movable devices in the same driving direction, the driving priority is determined based on the sequence of positions, wherein the closer the position is, the higher the driving priority is.
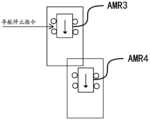
- the dynamic security areas of the mobile devices AMR3 and AMR4overlap each other.
- the positional relationship between AMR3 and AMR4is shown in Figure 4.
- the direction of the arrowidentifies the traveling direction of the mobile device. It can be seen that AMR3 and AMR4 are in the same driving direction, and the position of AMR4 in this driving direction is more forward, so the driving priority of AMR4 is higher than that of AMR3.
- the dispatching systemissues a navigation stop instruction to AMR3 based on the driving priorities of AMR3 and AMR4.
- the navigation information of at least two movable devicesincludes the location of the navigation target point and the location of the movable device.
- the positional relationship between the at least two mobile devices and their respective navigation target pointsis determined, specifically, the relationship between the positions of the at least two mobile devices and their respective navigation target points is calculated. distance.
- the driving priorities of at least two movable devicesare determined according to the positional relationship. Among them, the closer the distance between the location of the mobile device and the navigation target point, the higher the driving priority. In this way, through the positional relationship between the mobile device and the navigation target point, the mobile device that can reach the navigation target point faster can be selected, so that it can reach the navigation target point first to complete the navigation task, and further improve the work efficiency of the mobile device.
- the process of determining the driving priorities of the at least two mobile devicesincludes: acquiring the number of navigation stop times of the at least two mobile devices; The driving priorities of the at least two mobile devices are determined according to the number of navigation stops; the higher the number of navigation stops, the higher the driving priority.
- AMR5 and AMR6mobile devices in the warehouse. It is assumed that the dynamic safe regions of AMR5 and AMR6 overlap each other. Assume that AMR5 and AMR6 stop navigation for 3 times and 0 times respectively during this handling process.
- the dispatching systemobtains the number of navigation stops of AMR5 and AMR6 during this transportation process. Since the number of navigation stops of AMR5 is higher than that of AMR6, the dispatching system can set the driving priorities of AMR5 and AMR6 respectively according to the number of navigation stops, wherein the driving priority of AMR5 is higher than that of AMR6. In practical applications, it can be set that each time the number of stop navigation is increased, the preset weight value will be added to the original driving priority.
- the dispatching systemupdates the number of navigation stop times of the mobile device according to the number of times the navigation stop instruction is issued to the mobile device. For example, each time a navigation stop command is sent to the mobile device, the number of times the mobile device stops navigation is increased by 1. In practical applications, optionally, if the number of navigation stop times is temporarily stored in the temporary storage space, each time the mobile device reaches the navigation target point, it means that the navigation task is completed. At this time, the number of navigation stop times in the temporary storage space can be cleared. Zero to save storage space.
- the number of navigation stops of the mobile deviceis bound to the navigation task, and according to the route passed by the navigation task and the number of navigation stops, popular routes or popular locations in the current driving environment are selected. Therefore, popular routes or popular locations can be avoided during subsequent route planning, which can not only improve the transport efficiency of mobile equipment, but also further avoid collisions of mobile equipment during mixed operations and reduce the collision accident rate.
- the process of determining the driving priority of the at least two mobile devicesincludes: acquiring order information corresponding to the at least two mobile devices; The driving priority of at least two movable devices is determined according to the order information.
- the order information corresponding to the mobile deviceincludes a picking list or an order assigned to the mobile device.
- the picking list corresponding to the mobile deviceincludes a cargo identification for indicating the goods to be picked, and the location of the goods to be picked.
- a picking listmay correspond to one order, or may correspond to multiple orders, or may be generated after rearrangement of multiple orders.
- multiple orderscan be rearranged according to the type and/or location of the goods to be picked, so that the mobile device can plan a better route based on the rearranged picking list.
- the order informationalso includes the order priority. Specifically, when creating an order or picking list, set the corresponding order priority for the order or picking list based on the actual order requirements (such as order timeliness, order type, quantity of goods, etc.), so as to meet the orders of various users need.
- the higher the order priority in the order informationthe higher the driving priority of the mobile device.
- the scheduling systemobtains the orders bound to AMR7, AMR8, and AMR9 and the corresponding order information.
- the higher the order timeliness requirements in the order informationthe higher the order priority.
- urgent shipmentshave the highest requirement on timeliness, so the order priority corresponding to AMR7 is the highest, and the driving priority of AMR7 is the highest.
- the driving priorities of the above three mobile devices from high to loware: AMR7, AMR9/AMR8. Among them, AMR9/AMR8 are in the same driving priority.
- the driving priority of the mobile equipmentcan be further divided in combination with the loading situation of the goods, so as to improve the picking efficiency. Considering that some situations may occur during the picking process (such as temporary out of stock, etc.) to reduce the picking efficiency, optionally, in order to ensure the picking efficiency, the picked goods can be delivered first, that is, the goods that are already loaded
- the driving priority of the mobile equipment in the stateis higher than the driving priority of the mobile equipment in the state of not carrying cargo.
- AMR7 and AMR9are in the state of carrying cargo, and AMR8 is in the state of not carrying cargo.
- the dispatching systemcan set the driving priority of AMR7, AMR8, and AMR9 according to the cargo loading situation.
- the above three The driving priority of movable equipmentis adjusted from high to low: AMR7, AMR9, AMR8.
- the driving priority of the mobile devicecan be further divided in combination with the type of goods in the order information.
- fragile itemshave higher requirements on driving speed and safe braking distance. If the driving speed is too high or the braking distance is short, fragile items may be damaged. Therefore, compared with ordinary Cargo and fragile parts have a higher driving priority to avoid the risk of cargo damage caused by temporarily adjusting the driving state.
- the mapping relationship between cargo types and driving prioritiesis preset.
- the driving priority of the mobile devicecan be adjusted according to the order information corresponding to the mobile device, so as to ensure the safe operation of the mobile device and improve the delivery efficiency of the mobile device.
- the respective dynamic safety areasare dynamically set through the navigation information of multiple mobile devices, and then the respective navigation states of the multiple mobile devices are controlled based on the dynamic safety areas, so as to avoid possible overlapping of dynamic safety areas.
- the collision risk caused by the continuous driving of the mobile equipmentgreatly reduces the collision accident rate of the mobile equipment, improves the obstacle avoidance ability of the mobile equipment, and ensures the safe operation of the equipment.
- scheduling deviceof one or more embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below. Those skilled in the art can understand that these scheduling devices can be configured by using commercially available hardware components through the steps taught in this solution.
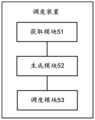
- FIG. 5is a schematic structural diagram of a scheduling device provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 5, the device includes:
- An acquisition module 51configured to acquire respective navigation information of the plurality of mobile devices
- a generation module 52configured to generate dynamic safety areas for each of the plurality of mobile devices based on the navigation information, where the dynamic safety areas are used to represent the safe driving range of the mobile device in the driving environment;
- the scheduling module 53is configured to send a navigation stop instruction to any one of the at least two movable devices if the dynamic security areas of at least two movable devices overlap each other, so that any one of the movable devices can move
- the devicestops navigation within a preset time period based on the navigation stop instruction.
- the scheduling module 53is configured to:
- the scheduling module 53is also used for:
- the scheduling module 53sends the When navigating stop commands, use to:
- the driving priority of multiple target mobile devicesdetermines the corresponding stop navigation duration of multiple target mobile devices; wherein, the higher the travel priority, the longer the stop navigation duration. short;
- Corresponding navigation stop instructionsare sent to a plurality of target movable devices.
- the scheduling module 53determines the driving priorities of the at least two movable devices, it is used to:
- the driving priorityis determined based on the sequence of positions, wherein the closer the position is, the higher the driving priority is.
- the scheduling module 53determines the driving priorities of the at least two movable devices, it is used to:
- the driving priority of the at least two mobile devicesis determined according to the number of times of stopping navigation; wherein, the more times of stopping navigation, the higher the driving priority.
- the scheduling module 53determines the driving priorities of the at least two movable devices, it is used to:
- the driving priority of the at least two movable devicesis determined according to the order information; wherein, the higher the order priority in the order information, the higher the driving priority.
- the obtaining module 51obtains the respective navigation information of multiple mobile devices, it is used to:
- the navigation informationincludes: any one or a combination of driving speed, driving direction, location of the mobile device, and device attribute information.
- the generation module 52when the generation module 52 generates the respective dynamic security areas of the plurality of mobile devices based on the navigation information, it is used to:
- each mobile deviceAccording to the navigation information of each mobile device, set a virtual area matching each mobile device in the preset driving environment map as the dynamic safety area of each mobile device;
- the virtual area matched with each mobile devicechanges along with the traveling track of each mobile device.
- the navigation information of each mobile deviceincludes the travel speed, travel direction, location, and device type of each mobile device;
- the generation module 52is used for:
- each movable equipmentdetermines the matching safe braking distance of each movable equipment
- the virtual area matched by each mobile deviceis dynamically updated in the driving environment map.
- the device shown in FIG. 5can execute the scheduling method provided in the embodiments shown in FIGS. 1 to 4.
- the structure of the scheduling apparatus shown in FIG. 5may be implemented as an electronic device.
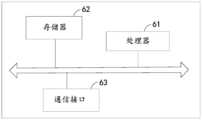
- the electronic devicemay include: a processor 61 and a memory 62 .
- executable codesare stored on the memory 62, and when the executable codes are executed by the processor 61, the processor 61 can at least realize the functions provided in the embodiments shown in FIGS. 1 to 4 above. scheduling method.
- the electronic devicemay also include a communication interface 63 for communicating with other devices.
- an embodiment of the present inventionprovides a non-transitory machine-readable storage medium, the non-transitory machine-readable storage medium stores executable code, and when the executable code is executed by the processor of the electronic device , so that the processor can at least implement the scheduling method provided in the embodiment shown in FIGS. 1 to 4 .
- the scheduling method provided by the embodiment of the present inventioncan be executed by a certain program/software, which can be provided by the network side, and the electronic device mentioned in the foregoing embodiments can download the program/software to a local non-volatile In the permanent storage medium, and when it needs to execute the aforementioned scheduling method, the program/software is read into the memory by the CPU, and then the program/software is executed by the CPU to realize the scheduling method provided in the aforementioned embodiment, and the execution process Refer to the schematic diagrams in FIGS. 1 to 4 above.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Operations Research (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Game Theory and Decision Science (AREA)
- Educational Administration (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese本发明涉及物流技术领域,尤其涉及一种可移动设备的调度方法、调度装置、电子设备和存储介质。The present invention relates to the field of logistics technology, and in particular to a scheduling method, scheduling device, electronic equipment and storage medium of movable equipment.
相关技术中,可移动设备会预先存储所处环境的地图数据,然后基于该地图数据在所处环境中进行导航。在一些应用场景中,往往会出现多个可移动设备处于同一环境中,这些可移动设备都需要依赖于相同地图数据进行混合作业。例如智能仓储、物流分拣等场景。In related technologies, the mobile device pre-stores map data of its environment, and then navigates in the environment based on the map data. In some application scenarios, there are often multiple mobile devices in the same environment, and these mobile devices all need to rely on the same map data for mixed operations. For example, smart warehousing, logistics sorting and other scenarios.
在混合作业过程中,每一可移动设备都需要单独进行障碍物检测,以及时触发自身的避障功能,避免撞到临时出现的障碍物(比如因导航路线交叉出现的其他可移动设备)。但是,每次障碍物检测都需要消耗可移动设备自身较多的计算资源,花费较多计算时间,造成避障操作的触发存在延时,降低了可移动设备的单机避障能力,影响设备运行安全。During mixed operations, each mobile device needs to perform obstacle detection independently to trigger its own obstacle avoidance function in time to avoid hitting temporary obstacles (such as other mobile devices that appear due to crossing navigation routes). However, each obstacle detection needs to consume a lot of computing resources of the mobile device itself, and it takes a lot of computing time, resulting in a delay in the triggering of the obstacle avoidance operation, which reduces the single-machine obstacle avoidance ability of the mobile device and affects the operation of the device. Safety.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明提供一种可移动设备的调度方法、调度装置、电子设备和存储介质,用以实现可移动设备的导航状态切换,提高可移动设备的避障能力,保证设备运行安全。The invention provides a scheduling method, a scheduling device, electronic equipment and a storage medium of a movable device, which are used to realize the switching of navigation states of the movable device, improve the obstacle avoidance ability of the movable device, and ensure the safe operation of the device.
第一方面,本发明提供一种可移动设备的调度方法,该方法包括:In a first aspect, the present invention provides a method for scheduling a mobile device, the method comprising:
获取多个可移动设备各自的导航信息;Obtain respective navigation information of multiple mobile devices;
基于导航信息生成多个可移动设备各自的动态安全区域,该动态安全区域用于表示可移动设备在行驶环境中的安全行驶范围;Generate respective dynamic safety areas of multiple mobile devices based on the navigation information, where the dynamic safety areas are used to represent the safe driving range of the mobile devices in the driving environment;
若存在至少两个可移动设备的动态安全区域相互重叠,则向至少两个可 移动设备中的可移动设备发送导航停止指令,以使接收到导航停止指令的可移动设备基于导航停止指令在预设时长内停止导航。If the dynamic security areas of at least two mobile devices overlap with each other, a navigation stop instruction is sent to the mobile device in the at least two mobile devices, so that the mobile device that receives the navigation stop instruction is based on the navigation stop instruction. Stop navigating for a set duration.
第二方面,本发明提供一种可移动设备的调度装置,包括:In a second aspect, the present invention provides a mobile device scheduling device, including:
获取模块,用于获取多个可移动设备各自的导航信息;An acquisition module, configured to acquire respective navigation information of multiple mobile devices;
生成模块,用于基于导航信息生成多个可移动设备各自的动态安全区域,该动态安全区域用于表示可移动设备在行驶环境中的安全行驶范围;A generating module, configured to generate dynamic safety areas for multiple mobile devices based on the navigation information, where the dynamic safety areas are used to represent the safe driving range of the mobile devices in the driving environment;
调度模块,用于若存在至少两个可移动设备的动态安全区域相互重叠,则向至少两个可移动设备中的可移动设备发送导航停止指令,以使接收到导航停止指令的可移动设备基于导航停止指令在预设时长内停止导航。A dispatching module, configured to send a navigation stop instruction to the mobile device among the at least two mobile devices if the dynamic security areas of at least two mobile devices overlap each other, so that the mobile device that receives the navigation stop instruction is based on The navigation stop command stops navigation within a preset duration.
第三方面,本发明提供一种电子设备,其中包括处理器和存储器,其中,所述存储器上存储有可执行代码,当所述可执行代码被所述处理器执行时,使所述处理器至少可以实现第一方面中的调度方法。In a third aspect, the present invention provides an electronic device, which includes a processor and a memory, wherein executable code is stored in the memory, and when the executable code is executed by the processor, the processor At least the scheduling method in the first aspect can be implemented.
第四方面,本发明提供了一种非暂时性机器可读存储介质,所述非暂时性机器可读存储介质上存储有可执行代码,当所述可执行代码被电子设备的处理器执行时,使所述处理器至少可以实现第一方面中的调度方法。In a fourth aspect, the present invention provides a non-transitory machine-readable storage medium, where executable code is stored on the non-transitory machine-readable storage medium, and when the executable code is executed by a processor of an electronic device , so that the processor can at least implement the scheduling method in the first aspect.
在本发明实施例中,首先根据多个可移动设备各自的导航信息,生成多个可移动设备各自的动态安全区域,该动态安全区域用于表示可移动设备在行驶环境中的安全行驶范围。进而,若存在至少两个可移动设备的动态安全区域相互重叠,则说明这些可移动设备具有较高的碰撞风险,此情况下,可以向至少两个可移动设备中任意一个可移动设备发送导航停止指令,以使该任意一个可移动设备基于导航停止指令在预设时长内停止导航。In the embodiment of the present invention, firstly, according to the respective navigation information of the plurality of mobile devices, dynamic safety areas of the plurality of mobile devices are generated respectively, and the dynamic safety areas are used to indicate the safe driving range of the mobile devices in the driving environment. Furthermore, if there are at least two movable devices whose dynamic safety areas overlap with each other, it means that these movable devices have a high risk of collision. In this case, a navigation message can be sent to any one of the at least two movable devices A stop instruction, so that any one of the movable devices stops navigation within a preset time period based on the navigation stop instruction.
本发明实施例中,通过多个可移动设备的导航信息动态设置各自的动态安全区域,并基于动态安全区域控制多个可移动设备各自的导航状态,以避免动态安全区域相互重叠的可移动设备继续行驶带来的碰撞风险,大大降低了可移动设备的碰撞事故率,提高可移动设备的避障能力,保证设备运行安全。In the embodiment of the present invention, the respective dynamic security areas are dynamically set through the navigation information of multiple mobile devices, and the respective navigation states of the multiple mobile devices are controlled based on the dynamic security areas, so as to avoid mobile devices with overlapping dynamic security areas. The collision risk caused by continuing to drive greatly reduces the collision accident rate of mobile equipment, improves the obstacle avoidance ability of mobile equipment, and ensures the safety of equipment operation.
为了更清楚地说明本发明中的技术方案,下面将对本发明描述中所需要使用的附图作一简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图是本发明的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to illustrate the technical solution in the present invention more clearly, the accompanying drawings that need to be used in the description of the present invention will be briefly introduced below. Obviously, the accompanying drawings in the following description are some embodiments of the present invention. Ordinary technicians can also obtain other drawings based on these drawings on the premise of not paying creative work.
图1为本发明提供的一种调度方法的流程图示意图;Fig. 1 is a schematic flow chart diagram of a scheduling method provided by the present invention;
图2为本发明提供的一种调度场景的原理示意图;FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of a scheduling scenario provided by the present invention;
图3为本发明提供的一种动态安全区域的示意图;Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of a dynamic security area provided by the present invention;
图4为本发明提供的一种可移动设备的位置关系示意图;FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram of a positional relationship of a mobile device provided by the present invention;
图5为本发明提供的一种调度装置的结构示意图;Fig. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of a scheduling device provided by the present invention;
图6为本发明提供的一种电子设备的结构示意图。FIG. 6 is a schematic structural diagram of an electronic device provided by the present invention.
为使本发明实施例的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有作出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。In order to make the purpose, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments It is a part of embodiments of the present invention, but not all embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
在本发明实施例中使用的术语是仅仅出于描述特定实施例的目的,而非旨在限制本发明。在本发明实施例和所附权利要求书中所使用的单数形式的“一种”、“所述”和“该”也旨在包括多数形式,除非上下文清楚地表示其他含义,“多种”一般包含至少两种。Terms used in the embodiments of the present invention are only for the purpose of describing specific embodiments, and are not intended to limit the present invention. The singular forms "a", "said" and "the" used in the embodiments of the present invention and the appended claims are also intended to include plural forms, unless the context clearly indicates otherwise, "multiple" Generally contain at least two.
取决于语境,如在此所使用的词语“如果”、“若”可以被解释成为“在……时”或“当……时”或“响应于确定”或“响应于检测”。类似地,取决于语境,短语“如果确定”或“如果检测(陈述的条件或事件)”可以被解释成为“当确定时”或“响应于确定”或“当检测(陈述的条件或事件)时”或“响应于检测(陈述的条件或事件)”。Depending on the context, the words "if", "if" as used herein may be interpreted as "at" or "when" or "in response to determining" or "in response to detecting". Similarly, depending on the context, the phrases "if determined" or "if detected (the stated condition or event)" could be interpreted as "when determined" or "in response to the determination" or "when detected (the stated condition or event) )" or "in response to detection of (a stated condition or event)".
另外,下述各方法实施例中的步骤时序仅为一种举例,而非严格限定。In addition, the sequence of steps in the following method embodiments is only an example, rather than a strict limitation.
相关技术中,可移动设备会预先存储所处环境的地图数据,然后基于该 地图数据在所处环境中进行导航。例如,在智能仓储、物流分拣等场景中,往往会出现多个可移动设备处于同一环境中,这些可移动设备都需要依赖于相同地图数据进行混合作业。In related technologies, the mobile device will pre-store the map data of the environment, and then navigate in the environment based on the map data. For example, in scenarios such as smart warehousing and logistics sorting, there are often multiple mobile devices in the same environment, and these mobile devices all need to rely on the same map data for mixed operations.
在混合作业过程中,每一可移动设备都需要单独进行障碍物检测,以及时触发自身的避障功能,避免撞到临时出现的障碍物(比如因导航路线交叉出现的其他可移动设备)。但是,每次障碍物检测都需要消耗可移动设备自身较多的计算资源,花费较多计算时间,造成避障操作的触发存在延时,降低了可移动设备的单机避障能力,影响设备运行安全。尤其是,随着可移动设备的行驶速度提高,所处环境的复杂化(比如出现更多拐角、障碍物等),对避障能力要求进一步提升。During mixed operations, each mobile device needs to perform obstacle detection independently to trigger its own obstacle avoidance function in time to avoid hitting temporary obstacles (such as other mobile devices that appear due to crossing navigation routes). However, each obstacle detection needs to consume a lot of computing resources of the mobile device itself, and it takes a lot of computing time, resulting in a delay in the triggering of the obstacle avoidance operation, which reduces the single-machine obstacle avoidance ability of the mobile device and affects the operation of the device. Safety. In particular, as the driving speed of the mobile device increases and the environment becomes more complex (such as more corners, obstacles, etc.), the requirements for obstacle avoidance capabilities are further enhanced.
因此,亟待提出一种解决方案,用以降低混合作业过程中可移动设备的碰撞事故率,提高可移动设备的避障能力,保证设备运行安全。Therefore, it is urgent to propose a solution to reduce the collision accident rate of mobile equipment in the mixed operation process, improve the obstacle avoidance ability of mobile equipment, and ensure the safety of equipment operation.
为了解决上述问题,本发明实施例提供的调度方案的核心思想是:In order to solve the above problems, the core idea of the scheduling scheme provided by the embodiment of the present invention is:
首先,获取多个可移动设备各自的导航信息,这样根据多个可移动设备各自的导航信息,能够动态生成多个可移动设备各自的动态安全区域。该动态安全区域用于表示可移动设备在行驶环境中的安全行驶范围。Firstly, the respective navigation information of the multiple mobile devices is acquired, so that the respective dynamic security areas of the multiple mobile devices can be dynamically generated according to the respective navigation information of the multiple mobile devices. The dynamic safety area is used to represent the safe driving range of the mobile device in the driving environment.
进而,若存在至少两个可移动设备的动态安全区域相互重叠,则说明这些可移动设备具有较高的碰撞风险,因此,可以向至少两个可移动设备中任意一个可移动设备发送导航停止指令,以使该任意一个可移动设备基于导航停止指令在预设时长内停止导航。从而,通过控制多个可移动设备各自的导航状态,能够避免动态安全区域相互重叠的可移动设备继续行驶带来的碰撞风险,大大降低了可移动设备的碰撞事故率,提高可移动设备的避障能力,保证设备运行安全。Furthermore, if there are at least two movable devices whose dynamic safety areas overlap with each other, it means that these movable devices have a higher risk of collision, therefore, a navigation stop instruction can be sent to any one of the at least two movable devices , so that any mobile device stops navigation within a preset time period based on the navigation stop instruction. Therefore, by controlling the respective navigation states of multiple mobile devices, it is possible to avoid the collision risk caused by the continuous driving of the mobile devices whose dynamic safety areas overlap with each other, greatly reducing the collision accident rate of the mobile devices and improving the safety of the mobile devices. failure capability to ensure the safe operation of the equipment.
在介绍了调度方案的核心思路之后,下面具体介绍本发明的各种非限制性实施例。After introducing the core idea of the scheduling scheme, various non-limiting embodiments of the present invention are specifically introduced below.
图1为本发明实施例提供的一种调度方法的流程图,如图1所示,该方法包括如下步骤:Fig. 1 is a flowchart of a scheduling method provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in Fig. 1, the method includes the following steps:
101、获取多个可移动设备各自的导航信息。101. Acquire respective navigation information of multiple mobile devices.
102、基于导航信息生成多个可移动设备各自的动态安全区域。102. Generate respective dynamic security areas of multiple mobile devices based on the navigation information.
103、若存在至少两个可移动设备的动态安全区域相互重叠,则向至少两个可移动设备中任意一个可移动设备发送导航停止指令,以使任意一个可移动设备基于导航停止指令在预设时长内停止导航。103. If the dynamic safety areas of at least two movable devices overlap with each other, send a navigation stop instruction to any one of the at least two movable devices, so that any one of the movable devices will be within a preset time based on the navigation stop instruction. Stop navigating for a period of time.
在本发明实施例中,可移动设备可以是自主移动机器人(Automated Mobile Robot,AMR)、载货车辆等。具体来说,自主移动机器人是指在工作环境中能够高度自主地进行空间移动的设备。例如,仓储协作机器人、拣货机器人或者搬运机器人等。In the embodiment of the present invention, the mobile device may be an autonomous mobile robot (Automated Mobile Robot, AMR), a cargo vehicle, and the like. Specifically, an autonomous mobile robot refers to a device capable of highly autonomous spatial movement in a working environment. For example, warehousing collaborative robots, picking robots or handling robots.
以自主移动机器人为例,自主移动机器人中设置有所处环境对应有语义地图,该语义地图指的是包含所处环境中多个对象的语义信息的环境地图。对象的语义信息是指能够借助自然语言去领会和解释对象是什么或所属种类等信息,例如可以包含但不限于对象的名称、形状、位置等。例如,在仓储环境中,语义地图包括仓库中各个货架的位置、类型、尺寸,以及仓库中各种障碍物(如栏杆、台阶、门槛等)的位置、类型、尺寸。Taking the autonomous mobile robot as an example, the autonomous mobile robot is provided with a semantic map corresponding to its environment, and the semantic map refers to an environment map including semantic information of multiple objects in the environment. The semantic information of an object refers to the information that can understand and explain what the object is or its category with the help of natural language, for example, it may include but not limited to the name, shape, location, etc. of the object. For example, in a warehouse environment, the semantic map includes the location, type, and size of each shelf in the warehouse, as well as the location, type, and size of various obstacles (such as railings, steps, thresholds, etc.) in the warehouse.
本发明实施例提供的方法可以由调度系统实现,并由多个可移动设备相配合。实际应用中,调度系统可以设置在云端服务中心,也可以是设置在可移动设备中,还可以设置在其他形式的计算设备中,本发明并不限定。The method provided by the embodiment of the present invention can be implemented by a scheduling system and coordinated by multiple mobile devices. In practical applications, the dispatching system may be set in a cloud service center, or in a mobile device, or in other forms of computing devices, which is not limited by the present invention.
在实际应用中,本发明实施例提供的方法可以应用于多种场景中,例如可以应用于仓储场景、物流分拣场景、物料配送场景、港口货运场景等。下面以仓储场景为例介绍本发明实施例的具体实施方式,其他场景可以参照仓储场景的实施方式实施,在此不再赘述。In practical applications, the method provided by the embodiments of the present invention can be applied to various scenarios, for example, it can be applied to warehousing scenarios, logistics sorting scenarios, material distribution scenarios, port freight scenarios, and the like. The specific implementation manner of the embodiment of the present invention is introduced below by taking a storage scenario as an example. Other scenarios may be implemented with reference to the implementation manner of a storage scenario, and details are not repeated here.
在仓储场景中,可以给一个货仓配备多个可移动设备,这样在其中一个可移动设备上卸货之前或运货的过程中,其他可移动设备可以满足其他货物的运送需求。假设多个可移动设备中预先录入行驶环境地图,也就是货仓环境的地图数据。假设多个可移动设备分别到装货区域上货后运送到各自的目标卸货点。假设多个可移动设备均由调度系统进行管控。In the warehousing scenario, a warehouse can be equipped with multiple mobile devices, so that before unloading or during the delivery of one of the mobile devices, other mobile devices can meet the delivery needs of other goods. It is assumed that the driving environment maps, that is, the map data of the warehouse environment, are pre-registered in multiple mobile devices. Assume that multiple mobile devices are loaded in the loading area and then transported to their respective target unloading points. It is assumed that multiple movable devices are managed by a dispatch system.
基于上述假设,多个可移动设备可根据行驶环境地图数据以及自身的目标卸货点产生导航信息,包括从装货区域到目标卸货点的行驶过程中各个可移动设备的行驶路线、行驶速度、行驶方向、所处位置等。在多个可移动设备混合作业的过程中,多个可移动设备分别将自身的导航信息上报到调度系统中,由调度系统接收并录入多个可移动设备各自的导航信息。Based on the above assumptions, multiple mobile devices can generate navigation information according to the map data of the driving environment and their own target unloading points, including the driving route, driving speed, driving direction, location, etc. During the mixed operation of multiple mobile devices, the multiple mobile devices report their own navigation information to the dispatching system, and the dispatching system receives and enters the respective navigation information of the multiple mobile devices.
进而,调度系统基于导航信息生成多个可移动设备各自的动态安全区域。本发明实施例中,动态安全区域用于表示可移动设备在行驶环境中的安全行驶范围。如果动态安全区域中出现障碍物,或其他可移动设备进入动态安全区域,即可立即通过降低可移动设备的行驶速度或者触发可移动设备进入制动状态来避免发生碰撞。Furthermore, the dispatch system generates respective dynamic safety areas for the plurality of movable devices based on the navigation information. In the embodiment of the present invention, the dynamic safety area is used to indicate the safe driving range of the mobile device in the driving environment. If an obstacle appears in the dynamic safety area, or other movable equipment enters the dynamic safety area, the collision can be avoided immediately by reducing the driving speed of the mobile equipment or triggering the braking state of the mobile equipment.
实际应用中,可选地,该动态安全区域的范围是由可移动设备的安全制动距离、运行平稳性、安全要求以及实际运行场景中的任意一种或多种因素决定的。例如,在可移动设备的动态安全区域中,根据可移动设备的安全制动距离计算位于可移动设备前进方向上的部分动态安全区域的范围。例如,根据可移动设备的运行平稳性、货品承载能力和/或安全要求确定非前进方向上的其他部分动态安全区域的范围。进一步地,还可根据实际运行场景中的路况调整动态安全区域的整体范围或非前进方向上的部分动态安全区域的范围。例如,在路况较为复杂的运行场景中,根据实际路况扩大动态安全区域的范围。相对地,在路况较为简单的运行场景中,为提高运行效率,可以根据实际路况缩小动态安全区域的范围,以降低可移动设备被交通管制的概率。In practical applications, optionally, the range of the dynamic safe area is determined by any one or more factors in the safe braking distance of the mobile device, running stability, safety requirements, and actual running scenarios. For example, in the dynamic safety area of the movable device, the range of a part of the dynamic safety area located in the forward direction of the movable device is calculated according to the safe braking distance of the movable device. For example, the scope of other parts of the dynamic safety area in the non-advancing direction is determined according to the running stability of the mobile equipment, cargo carrying capacity and/or safety requirements. Further, the overall range of the dynamic safety area or the range of a part of the dynamic safety area in the non-advancing direction can also be adjusted according to the road conditions in the actual running scene. For example, in an operating scenario with complex road conditions, the scope of the dynamic safety area is expanded according to the actual road conditions. In contrast, in the operation scenario with relatively simple road conditions, in order to improve the operation efficiency, the scope of the dynamic safety area can be reduced according to the actual road conditions, so as to reduce the probability of the mobile device being controlled by traffic.
在仓储场景中,动态安全区域是在货仓环境地图中跟随可移动设备的行驶轨迹动态设置的坐标区域。调度系统通过动态安全区域可以确定对应可移动设备的行驶路线上是否出现碰撞风险。简单来说,如果调度系统监测到在动态安全区域中存在障碍物(包括其他可移动设备),或者该动态安全区域与其他可移动设备的动态安全区域相互重叠,即表示该区域对应的可移动设备可能会与上述障碍物或其他可移动设备发生碰撞。此情况下,需要及时对可移动设备的导航状态进行控制,避免发生碰撞。具体地,若存在至少两个可移动设备的动态 安全区域相互重叠,则调度系统向至少两个可移动设备中任意一个可移动设备发送导航停止指令,以使任意一个可移动设备基于导航停止指令在预设时长内停止导航。In the warehouse scene, the dynamic safety area is a coordinate area dynamically set in the warehouse environment map following the driving trajectory of the mobile device. The dispatching system can determine whether there is a collision risk on the driving route of the corresponding movable equipment through the dynamic safety area. In simple terms, if the dispatching system detects that there are obstacles (including other movable equipment) in the dynamic safety area, or the dynamic safety area overlaps with the dynamic safety area of other mobile equipment, it means that the corresponding movable The device may collide with the aforementioned obstacles or other movable devices. In this case, it is necessary to control the navigation state of the mobile device in time to avoid collisions. Specifically, if the dynamic security areas of at least two movable devices overlap each other, the dispatching system sends a navigation stop instruction to any one of the at least two movable devices, so that any one of the movable devices can Stop navigating for a preset duration.
通过上述步骤能够根据多个可移动设备的导航信息动态设置各自的动态安全区域,并基于动态安全区域对仓储场景中多个可移动设备的导航状态进行调度,从而避免动态安全区域相互重叠的可移动设备继续行驶带来的碰撞风险,大大降低了可移动设备的碰撞事故率,提高可移动设备的避障能力,保证设备运行安全。Through the above steps, the respective dynamic security areas can be dynamically set according to the navigation information of multiple mobile devices, and the navigation status of multiple mobile devices in the storage scene can be scheduled based on the dynamic security areas, so as to avoid the possibility that the dynamic security areas overlap with each other. The collision risk caused by the continuous driving of the mobile equipment greatly reduces the collision accident rate of the mobile equipment, improves the obstacle avoidance ability of the mobile equipment, and ensures the safe operation of the equipment.
下面结合附图介绍图1示出的各个步骤的具体实现方式。The specific implementation of each step shown in FIG. 1 will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
假设具体应用场景中设置有多个可移动设备。假设多个可移动设备由调度系统进行管控。It is assumed that multiple mobile devices are set in a specific application scenario. Assume that multiple mobile devices are managed by a dispatch system.
基于此,可选地,101中调度系统获取多个可移动设备各自的导航信息的过程可以实现为:接收多个可移动设备按照预设周期上报的导航信息。Based on this, optionally, the process of obtaining the respective navigation information of multiple mobile devices by the dispatching system in
本发明实施例中,可移动设备的导航信息包括但不限于:行驶速度、行驶方向、可移动设备所处位置、设备属性信息中的任意一种或组合。其中,设备属性信息包括设备型号、设备尺寸、最大行驶速度、制动性能。In the embodiment of the present invention, the navigation information of the mobile device includes, but is not limited to: any one or combination of driving speed, driving direction, location of the mobile device, and device attribute information. Wherein, the equipment attribute information includes equipment model, equipment size, maximum driving speed, and braking performance.
具体地,如图2所示,在一可选实施例中,多个可移动设备按照预设周期向调度系统上报导航信息,从而,调度系统接收多个可移动设备各自的导航信息,并更新自身存储的导航信息库。可以理解的是,可移动设备周期性上报的导航信息主要是关于行驶状态的实时信息,例如可移动设备所处位置、行驶速度、行驶方向、行驶轨迹等。Specifically, as shown in FIG. 2, in an optional embodiment, multiple mobile devices report navigation information to the dispatching system according to a preset period, so that the dispatching system receives the respective navigation information of multiple mobile devices and updates the Self-stored navigation information library. It can be understood that the navigation information periodically reported by the mobile device is mainly real-time information about the driving state, such as the location, speed, direction, and trajectory of the mobile device.
可选地,在新增可移动设备时,在导航信息库中录入可移动设备的设备属性信息,如设备型号、设备尺寸、最大行驶速度、制动性能。从而,减少可移动设备向调度系统上报的数据传输量,提高导航信息传输效率,保证导航信息的实时性。Optionally, when adding a new movable device, the device attribute information of the movable device, such as device model, device size, maximum driving speed, and braking performance, is entered in the navigation information database. Therefore, the amount of data transmission reported by the mobile device to the dispatching system is reduced, the efficiency of navigation information transmission is improved, and the real-time performance of navigation information is guaranteed.
实际应用中,上报导航信息的预设周期可以是根据可移动设备所处的行驶环境制定。例如,如果行驶环境场地较小且障碍物较多,说明碰撞事故发生的 概率较高,此情况下,可缩短上报导航信息的预设周期,如设置为每2s上报一次导航信息。如果行驶环境场地较大且障碍物较少,说明碰撞事故发生的概率较低,此情况下,可延长上报导航信息的预设周期,如设置为10s上报一次导航信息。以上周期均为示例,本发明中并不限定。In practical applications, the preset period for reporting navigation information may be formulated according to the driving environment where the mobile device is located. For example, if the driving environment is small and there are many obstacles, it means that the probability of collision accidents is high. In this case, the preset cycle for reporting navigation information can be shortened, for example, it is set to report navigation information every 2s. If the driving environment is large and there are few obstacles, it means that the probability of collision accidents is low. In this case, the preset period for reporting navigation information can be extended, for example, it is set to 10s to report navigation information once. The above periods are examples, and are not limited in the present invention.
除此之外,本发明实施例中还可通过其他方式设置上报导航信息的预设周期。例如,根据可移动设备的行驶状态设置上报导航信息的预设周期,例如,可移动设备的行驶速度较快,说明碰撞事故发生的概率较高,此情况下,也可缩短上报导航信息的预设周期。In addition, in the embodiment of the present invention, the preset period for reporting the navigation information may also be set in other ways. For example, the preset period for reporting navigation information is set according to the driving state of the mobile device. For example, the driving speed of the mobile device is faster, indicating that the probability of a collision accident is higher. In this case, the period for reporting the navigation information can also be shortened. Set period.
进而,可选地,102中,调度系统基于多个可移动设备各自的导航信息生成多个可移动设备各自的动态安全区域的过程,可以实现为:根据多个可移动设备中每一可移动设备的导航信息,在预设的行驶环境地图中设置与每一可移动设备匹配的虚拟区域,作为每一可移动设备的动态安全区域。Furthermore, optionally, in
其中,与每一可移动设备匹配的虚拟区域随每一可移动设备的行驶轨迹变化。可选地,根据可移动设备的形状设置虚拟区域的形状。例如,根据可移动设备的设备型号确定可移动设备的外形尺寸,并根据外形尺寸预先设置匹配的虚拟区域形状。进一步可选地,虚拟区域的几何中心在行驶环境地图中的坐标与可移动设备所处位置的坐标重合。Wherein, the virtual area matched with each mobile device changes along with the traveling track of each mobile device. Optionally, the shape of the virtual area is set according to the shape of the movable device. For example, the external dimensions of the mobile device are determined according to the device model of the mobile device, and the matching virtual area shape is preset according to the external dimensions. Further optionally, the coordinates of the geometric center of the virtual area in the driving environment map coincide with the coordinates of the location of the mobile device.
具体地,如图3所示,在一可选实施例中,假设虚拟区域形状为矩形,假设可移动设备包括AMR1、AMR2、AMR3。基于此,调度系统接收到3个AMR各自的导航信息之后,根据3个AMR的导航信息,在预设的行驶环境地图中分别设置与每一AMR匹配的矩形虚拟区域,作为每一AMR的动态安全区域。Specifically, as shown in FIG. 3 , in an optional embodiment, it is assumed that the shape of the virtual area is a rectangle, and it is assumed that the mobile devices include AMR1, AMR2, and AMR3. Based on this, after the dispatching system receives the navigation information of the three AMRs, according to the navigation information of the three AMRs, a rectangular virtual area matching each AMR is respectively set in the preset driving environment map as the dynamic map of each AMR. safe area.
为了保证留给可移动设备充足的安全制动距离,可选地,还可在行驶方向前方设置更大的安全区域空间。具体地,可以在动态安全区域中将可移动设备在行驶方向前方所占空间大于行驶方向后方所占空间。其中,安全制动距离可以理解为,能够通过降低车速或进入制动状态来避免发生碰撞时所需满足的最大距离。例如,图3中箭头表示AMR的行驶方向,显然,3个AMR动态安全区域中行驶方向前方所占空间大于行驶方向后方所占空间。实际应用中,还可 根据运行平稳性、安全要求以及实际运行场景等其他因素进一步调整动态安全区域的范围。In order to ensure a sufficient safety braking distance for the movable equipment, optionally, a larger safety area space can also be set in front of the driving direction. Specifically, in the dynamic safety area, the space occupied by the movable device in front of the driving direction may be larger than the space occupied by the rear of the driving direction. Among them, the safe braking distance can be understood as the maximum distance that needs to be met when a collision can be avoided by reducing the vehicle speed or entering the braking state. For example, the arrow in Figure 3 indicates the driving direction of the AMR. Obviously, the space occupied by the front of the driving direction in the three AMR dynamic safety areas is larger than the space occupied by the rear of the driving direction. In practical applications, the range of the dynamic safety area can be further adjusted according to other factors such as running stability, safety requirements, and actual operating scenarios.
实际上,虚拟区域的形状还可以是三角形、圆形、或其他图形,本发明实施例并不限定。但无论何种形状均需满足预先为可移动设备设置的安全制动距离,使最终得到的动态安全区域能够作为评估可移动设备是否会发生碰撞的依据。In fact, the shape of the virtual area may also be a triangle, a circle, or other figures, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present invention. However, no matter what the shape is, it needs to meet the safety braking distance set for the movable equipment in advance, so that the final dynamic safety area can be used as the basis for evaluating whether the movable equipment will collide.
实际应用中,导航信息的类型不同,动态安全区域的设置方式也不同。In practical applications, the types of navigation information are different, and the way of setting the dynamic security area is also different.
在一可选设置方式中,假设每一可移动设备的导航信息包括每一可移动设备的行驶速度、行驶方向、所处位置、设备类型。In an optional setting manner, it is assumed that the navigation information of each mobile device includes the traveling speed, traveling direction, location, and device type of each mobile device.
基于此,上述实施例中,根据每一可移动设备的导航信息,在预设的行驶环境地图中设置与每一可移动设备匹配的虚拟区域的过程,可以实现为:根据每一可移动设备的行驶速度以及设备类型,确定每一可移动设备匹配的安全制动距离;根据每一可移动设备的行驶速度、行驶方向、所处位置以及匹配的安全制动距离,在所述行驶环境地图中动态更新每一可移动设备匹配的虚拟区域。Based on this, in the above-mentioned embodiment, according to the navigation information of each mobile device, the process of setting a virtual area matching each mobile device in the preset driving environment map can be realized as follows: according to each mobile device According to the driving speed, driving direction, location and matching safe braking distance of each mobile device, determine the matching safe braking distance of each mobile device; in the driving environment map Dynamically update the virtual area matched by each mobile device.
具体而言,假设新增一个可移动设备a。基于此,在可移动设备a进入行驶环境后,可移动设备a向调度系统上报初始导航信息。进一步假设初始导航信息包括可移动设备a的设备类型、设备标识以及所处位置。基于此,调度系统接收初始导航信息之后,在行驶环境地图中创建可移动设备a匹配的初始虚拟区域。Specifically, it is assumed that a new removable device a is newly added. Based on this, after the mobile device a enters the driving environment, the mobile device a reports initial navigation information to the dispatching system. It is further assumed that the initial navigation information includes the device type, device identifier and location of the mobile device a. Based on this, after receiving the initial navigation information, the dispatching system creates an initial virtual area matching the mobile device a in the driving environment map.
进而,假设可移动设备a向调度系统周期性上报的导航信息,包括可移动设备a的行驶速度、行驶方向、所处位置。基于此,调度系统根据可移动设备a的行驶速度以及设备类型,确定可移动设备a在当前行驶速度下匹配的安全制动距离。进而,调度系统根据可移动设备a的行驶速度、行驶方向、所处位置以及匹配的安全制动距离,在行驶环境地图中动态更新可移动设备a匹配的虚拟区域。Furthermore, it is assumed that the navigation information periodically reported by the mobile device a to the dispatching system includes the travel speed, travel direction, and location of the mobile device a. Based on this, the dispatching system determines the matching safe braking distance of the movable device a at the current driving speed according to the traveling speed of the movable device a and the type of the device. Furthermore, the dispatching system dynamically updates the virtual area matched by the mobile device a in the driving environment map according to the driving speed, driving direction, location and matching safe braking distance of the mobile device a.
相关技术中,高速行驶会给可移动设备的混合作业带来更高的安全风险,需要可移动设备具有更强的避障能力。因此,另一可选实施例中,若检测到 可移动设备的行驶速度发生变化,则动态调整可移动设备对应的动态安全区域。比如,若检测到可移动设备的行驶速度提高,此情况下,可扩大可移动设备对应的动态安全区域的范围,以避免可移动设备因高速行驶带来的安全风险。In related technologies, high-speed driving will bring higher safety risks to the mixed operation of mobile equipment, which requires the mobile equipment to have stronger obstacle avoidance capabilities. Therefore, in another optional embodiment, if it is detected that the traveling speed of the movable device changes, the dynamic safety area corresponding to the movable device is dynamically adjusted. For example, if it is detected that the traveling speed of the mobile device increases, in this case, the range of the dynamic safety area corresponding to the mobile device may be expanded to avoid safety risks caused by the high-speed driving of the mobile device.
再一可选实施例中,若检测到可移动设备所载货物发生变化,比如新装载的货物为易碎物品,或者因货物装卸操作使得重量发生变化,均可动态调整可移动设备对应的动态安全区域,以保证修正后的动态安全区域符合可移动设备当前的行驶状态。比如,易碎物品不可突然减速或制动,因此需要扩大动态安全范围。又比如,货物重量变化可能会影响制动速度,因此也需要调整动态安全范围。In yet another optional embodiment, if it is detected that the cargo loaded on the mobile device changes, for example, the newly loaded cargo is a fragile item, or the weight changes due to cargo loading and unloading operations, the corresponding dynamic The safe area, so as to ensure that the revised dynamic safe area conforms to the current driving state of the mobile device. For example, fragile objects cannot be decelerated or braked suddenly, so the dynamic safety range needs to be extended. As another example, changes in the weight of the cargo may affect the braking speed, so the dynamic safety range also needs to be adjusted.
当然,除了上述示例的动态安全区域设置方式外,还可采用其他方式设置可移动设备的动态安全区域,此处不再展开。无论何种方式,其核心均是根据导航信息所反映的可移动设备的行驶状态,在行驶环境地图中动态规划出满足安全制动距离的动态安全区域,用以辅助评估可移动设备的碰撞风险。Of course, in addition to the dynamic security area setting method in the above example, other methods can also be used to set the dynamic security area of the mobile device, which will not be expanded here. Regardless of the method, the core is to dynamically plan a dynamic safety area that meets the safe braking distance in the driving environment map according to the driving state of the mobile device reflected in the navigation information, to assist in evaluating the collision risk of the mobile device .
进而,获取可移动设备的动态安全区域后,调度系统需要基于动态安全区域判断受管控的所有可移动设备是否存在碰撞风险。可选地,调度系统可按照预设频率判断多个可移动设备中是否存在至少两个可移动设备的动态安全区域相互重叠。Furthermore, after obtaining the dynamic safety area of the mobile device, the dispatching system needs to judge whether there is a collision risk for all the movable devices under control based on the dynamic safety area. Optionally, the scheduling system may determine whether the dynamic security areas of at least two movable devices among the plurality of movable devices overlap with each other according to a preset frequency.
若存在至少两个可移动设备的动态安全区域相互重叠,则说明至少两个可移动设备可能会发生碰撞,此情况下,调度系统需要对至少两个可移动设备中部分可移动设备的导航状态进行控制。其中,可选地,还可以进一步判断至少两个可移动设备的动态安全区域的重叠面积是否大于设定面积阈值。若是,则判定上述至少两个可移动设备存在的碰撞风险较大,此情况下需执行步骤103。若否,则上述至少两个可移动设备存在的碰撞风险较小,此情况下认定为暂不需要处理。从而,避免频繁调度带来的可移动设备运行效率降低。If the dynamic safety areas of at least two movable devices overlap with each other, it means that at least two movable devices may collide. In this case, the dispatching system needs to check the navigation status of some of the movable devices Take control. Wherein, optionally, it may be further judged whether the overlapping area of the dynamic security areas of at least two movable devices is greater than a set area threshold. If yes, it is determined that the collision risk of the at least two movable devices is relatively high, and in this case, step 103 needs to be performed. If not, the risk of collision between the at least two movable devices is relatively small, and in this case, it is determined that no processing is required for the time being. Therefore, the reduction in operating efficiency of the mobile device caused by frequent scheduling is avoided.
进而,103中,可选地,调度系统向至少两个可移动设备中任意一个可移动 设备发送导航停止指令的过程,可以实现为:确定至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级;向至少两个可移动设备中行驶优先级处于预设顺位的可移动设备发送导航停止指令。可移动设备收到导航停止指令后,会基于导航停止指令在预设时长内停止导航,从而避免至少两个可移动设备发生碰撞。其中,导航停止指令用于向可移动设备指示停止导航的预设时长。例如,指示可移动设备停止导航N秒。实际应用中,导航停止指令可以实现为制动触发指令、减速指令等。Furthermore, in 103, optionally, the process of the dispatching system sending a navigation stop instruction to any one of the at least two movable devices may be implemented as: determining the driving priorities of the at least two movable devices; Among the mobile devices, the mobile device whose driving priority is in the preset sequence sends a navigation stop command. After the mobile device receives the navigation stop instruction, it will stop the navigation within a preset time period based on the navigation stop instruction, so as to avoid collision between at least two movable devices. Wherein, the navigation stop instruction is used to instruct the mobile device to stop the preset duration of navigation. For example, instruct the mobile device to stop navigating for N seconds. In practical applications, the navigation stop command can be implemented as a brake trigger command, a deceleration command, and the like.
值得说明的是,实际应用中,下发给多个可移动设备的导航停止指令中指示的预设时长可以是相同的,也可以是不同的。例如,假设可移动设备a和b的动态安全区域均与可移动设备c的动态安全区域重叠。如果可移动设备a和b的动态安全区域之间不重叠,则说明可移动设备a和b之间暂不存在碰撞风险,因此,下发给可移动设备a和b的导航停止指令所指示的预设时长可以是相同的。如果可移动设备a和b的动态安全区域相互重叠,则说明可移动设备a和b之间也存在碰撞风险,因此,下发给可移动设备a和b的导航停止指令所指示的预设时长应当是不同的。这样,通过控制可移动设备a和b在不同时刻恢复导航,避免可移动设备a和b之间发生碰撞。It should be noted that, in practical applications, the preset durations indicated in the navigation stop instructions issued to multiple mobile devices may be the same or different. For example, assume that the dynamic security areas of mobile devices a and b both overlap with the dynamic security area of mobile device c. If the dynamic safety areas of mobile devices a and b do not overlap, it means that there is no risk of collision between mobile devices a and b. Therefore, the navigation stop instructions issued to mobile devices a and b indicate that The preset durations may be the same. If the dynamic safety areas of mobile devices a and b overlap each other, it means that there is also a risk of collision between mobile devices a and b. Therefore, the preset duration indicated by the navigation stop instructions issued to mobile devices a and b should be different. In this way, by controlling the mobile devices a and b to resume navigation at different times, collisions between the mobile devices a and b are avoided.
本实施例中,预设顺位可以是根据实际应用场景设置的。例如,假设行驶优先级最高的可移动设备牌排在第一顺位,那么,预设顺位可以设置为非第一顺位的其他所有顺位。基于此,调度系统向至少两个可移动设备中低于最高行驶优先级的所有可移动设备发送导航停止指令,并在预设时长内为至少两个可移动设备中行驶优先级最高的一个可移动设备继续导航。从而,即可对低于最高行驶优先级的可移动设备的导航状态进行管控以使其停止导航,又可保持行驶优先级最高的可移动设备处于原有的行驶状态,实现了对多个可移动设备的交通管制。In this embodiment, the preset sequence may be set according to an actual application scenario. For example, assuming that the movable device card with the highest driving priority is ranked first, then the preset order can be set to all other orders other than the first order. Based on this, the dispatching system sends a navigation stop command to all the mobile devices with the highest driving priority among the at least two mobile devices, and within the preset time period, the one with the highest driving priority among the at least two mobile devices can The mobile device continues to navigate. Therefore, the navigation state of the mobile device lower than the highest driving priority can be controlled so that it stops navigating, and the mobile device with the highest driving priority can be kept in the original driving state. Traffic control for mobile devices.
实际应用中,还可能会出现一个行驶优先级中出现多个可移动设备的情况。对于此情况,在一可选实施例中,假设处于预设顺位的目标可移动设备有多个。基于此,上文实施例中,向至少两个可移动设备中行驶优先级处于预设顺位的可移动设备发送导航停止指令的过程,可以实现为:根据多个目标可移动设备 的行驶优先级、以及行驶优先级与停止导航时长的匹配关系,确定多个目标可移动设备各自匹配的停止导航时长;其中,行驶优先级越高,停止导航时长越短;基于多个目标可移动设备各自匹配的停止导航时长生成对应的导航停止指令;向多个目标可移动设备发送对应的导航停止指令。In practical applications, there may also be situations where multiple movable devices appear in one driving priority. For this situation, in an optional embodiment, it is assumed that there are multiple target movable devices in a preset order. Based on this, in the above embodiment, the process of sending a navigation stop instruction to the mobile device whose driving priority is in the preset order among at least two mobile devices can be realized as follows: according to the driving priority of multiple target mobile devices level, and the matching relationship between driving priority and stop navigation duration, determine the corresponding stop navigation duration of multiple target mobile devices; among them, the higher the driving priority, the shorter the stop navigation duration; based on the respective A corresponding navigation stop instruction is generated for the matching stop navigation duration; and the corresponding navigation stop instruction is sent to multiple target mobile devices.
其中,行驶优先级与停止导航时长的匹配关系可以是根据实际应用场景预先设置到调度系统中的。例如,仓储场景中可根据仓库面积、货架摆放间距、装卸速度等设置上述匹配关系,并预先录入到调度系统中。Wherein, the matching relationship between driving priority and stop navigation duration can be preset in the dispatching system according to the actual application scenario. For example, in the warehousing scene, the above-mentioned matching relationship can be set according to the warehouse area, shelf spacing, loading and unloading speed, etc., and entered into the dispatching system in advance.
从而,通过上述步骤为处于预设顺位的多个目标可移动设备分别配置不同的导航停止时长,以进一步避免多个可移动设备同时恢复导航状态而产生的碰撞风险。Therefore, through the above steps, different navigation stop durations are respectively configured for the multiple target mobile devices in the preset order, so as to further avoid the risk of collision caused by multiple mobile devices returning to the navigation state at the same time.
进一步可选地,如果处于同一行驶优先级的可移动设备有多个,那么,还可以为这些可移动设备设置不同的导航停止时长,以使处于这些可移动设备分别在不同时刻恢复导航状态,从而进一步避免同一行驶优先级的多个可移动设备同时恢复导航状态带来的碰撞风险。Further optionally, if there are multiple mobile devices with the same driving priority, different navigation stop durations can also be set for these mobile devices, so that these mobile devices resume the navigation state at different times, In this way, the risk of collision caused by multiple mobile devices with the same driving priority recovering the navigation state at the same time is further avoided.
例如,处于同一行驶优先级的可移动设备有3个,分别是可移动设备a、b、c,那么,可以将可移动设备a、b、c的导航停止时长分别设置为N秒、N+S秒、N+2S秒。其中,单位导航停止时长S可根据实际情况设置。For example, there are three movable devices at the same driving priority, namely movable devices a, b, and c. Then, the navigation stop duration of movable devices a, b, and c can be set to N seconds, N+ S seconds, N+2S seconds. Wherein, the unit navigation stop duration S may be set according to actual conditions.
在本发明实施例中提供了以下几种确定动态安全区域相互重叠的至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级的方式。Embodiments of the present invention provide the following manners for determining driving priorities of at least two mobile devices whose dynamic safety areas overlap with each other.
在一可选实施例中,对于动态安全区域相互重叠的至少两个可移动设备,确定至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级的过程,包括:根据至少两个可移动设备的导航信息,确定至少两个可移动设备的行驶方向以及所处位置;对于同一行驶方向上的至少两个可移动设备,基于位置前后顺序确定行驶优先级,其中,位置越靠前,行驶优先级越高。In an optional embodiment, for at least two mobile devices whose dynamic safety areas overlap with each other, the process of determining the driving priorities of the at least two mobile devices includes: according to the navigation information of the at least two mobile devices, determining The driving directions and positions of at least two movable devices; for at least two movable devices in the same driving direction, the driving priority is determined based on the sequence of positions, wherein the closer the position is, the higher the driving priority is.
具体来说,假设可移动设备AMR3和AMR4的动态安全区域相互重叠。假设AMR3和AMR4的位置关系如图4所示。在图4中,箭头方向标识可移动设备的行驶方向。可见,AMR3和AMR4处于同一行驶方向上,并且AMR4在该 行驶方向上的位置更靠前,因此AMR4的行驶优先级高于AMR3的行驶优先级。进而,在图4中,调度系统基于AMR3和AMR4的行驶优先级,向AMR3下发导航停止指令。Specifically, it is assumed that the dynamic security areas of the mobile devices AMR3 and AMR4 overlap each other. Assume that the positional relationship between AMR3 and AMR4 is shown in Figure 4. In FIG. 4 , the direction of the arrow identifies the traveling direction of the mobile device. It can be seen that AMR3 and AMR4 are in the same driving direction, and the position of AMR4 in this driving direction is more forward, so the driving priority of AMR4 is higher than that of AMR3. Furthermore, in FIG. 4 , the dispatching system issues a navigation stop instruction to AMR3 based on the driving priorities of AMR3 and AMR4.
值得说明的是,除了基于位置先后顺序确定行驶优先级之外,实际应用中还可采用其他方式基于导航信息确定至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级,本发明并不限定。It is worth noting that, in addition to determining the driving priority based on the sequence of locations, other methods may also be used to determine the driving priority of at least two mobile devices based on navigation information in practical applications, which is not limited in the present invention.
举例来说,在一可选示例中,假设至少两个可移动设备的导航信息包括导航目标点所处位置以及可移动设备所处位置。基于此,根据至少两个可移动设备的导航信息,确定至少两个可移动设备与各自导航目标点的位置关系,具体地,计算出至少两个可移动设备所处位置与各自导航目标点的距离。进而,根据该位置关系确定至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级。其中,可移动设备所处位置与导航目标点的距离越近,行驶优先级越高。这样,通过可移动设备与导航目标点的位置关系,能够选取出更快到达导航目标点的可移动设备,使其优先到达导航目标点完成导航任务,进一步提高可移动设备的工作效率。For example, in an optional example, it is assumed that the navigation information of at least two movable devices includes the location of the navigation target point and the location of the movable device. Based on this, according to the navigation information of the at least two mobile devices, the positional relationship between the at least two mobile devices and their respective navigation target points is determined, specifically, the relationship between the positions of the at least two mobile devices and their respective navigation target points is calculated. distance. Furthermore, the driving priorities of at least two movable devices are determined according to the positional relationship. Among them, the closer the distance between the location of the mobile device and the navigation target point, the higher the driving priority. In this way, through the positional relationship between the mobile device and the navigation target point, the mobile device that can reach the navigation target point faster can be selected, so that it can reach the navigation target point first to complete the navigation task, and further improve the work efficiency of the mobile device.
另一可选实施例中,对于动态安全区域相互重叠的至少两个可移动设备,确定至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级的过程,包括:获取至少两个可移动设备的停止导航次数;根据停止导航次数确定至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级;其中,停止导航次数越多,行驶优先级越高。In another optional embodiment, for at least two mobile devices whose dynamic safety areas overlap with each other, the process of determining the driving priorities of the at least two mobile devices includes: acquiring the number of navigation stop times of the at least two mobile devices; The driving priorities of the at least two mobile devices are determined according to the number of navigation stops; the higher the number of navigation stops, the higher the driving priority.
以仓储场景为例,假设货仓中设置有2个可移动设备记为AMR5和AMR6。假设AMR5和AMR6的动态安全区域相互重叠。假设AMR5和AMR6在本次搬运过程中的停止导航次数分别为3次和0次。Taking the warehouse scenario as an example, suppose that there are two mobile devices in the warehouse, marked as AMR5 and AMR6. It is assumed that the dynamic safe regions of AMR5 and AMR6 overlap each other. Assume that AMR5 and AMR6 stop navigation for 3 times and 0 times respectively during this handling process.
基于此,调度系统获取AMR5和AMR6在本次搬运过程中的停止导航次数。由于AMR5的停止导航次数高于AMR6的停止导航次数,因此,调度系统可将根据停止导航次数分别设置AMR5和AMR6的行驶优先级,其中AMR5的行驶优先级高于AMR6的行驶优先级。实际应用中,可设置每增加一次停止导航次数,即在原行驶优先级的基础上加预设权值。Based on this, the dispatching system obtains the number of navigation stops of AMR5 and AMR6 during this transportation process. Since the number of navigation stops of AMR5 is higher than that of AMR6, the dispatching system can set the driving priorities of AMR5 and AMR6 respectively according to the number of navigation stops, wherein the driving priority of AMR5 is higher than that of AMR6. In practical applications, it can be set that each time the number of stop navigation is increased, the preset weight value will be added to the original driving priority.
通过这一实施例,可筛选出导航状态被暂停较多的可移动设备,并调高这些设备的行驶优先级,以便这些设备能够及时完成行驶任务,提高可移动设备的运送效率。Through this embodiment, it is possible to screen out mobile devices whose navigation states are more suspended, and increase the driving priority of these devices, so that these devices can complete the driving task in time and improve the transport efficiency of the mobile devices.
其中,可选地,调度系统根据向可移动设备下发导航停止指令的次数,更新该可移动设备的停止导航次数。例如,每次向可移动设备下发导航停止指令即将该可移动设备的停止导航次数加1。实际应用中,可选地,如果停止导航次数暂存在临时存储空间中,可移动设备每次到达导航目标点即表示本次导航任务完成,此时,可将临时存储空间中的停止导航次数清零,以节省存储空间。Wherein, optionally, the dispatching system updates the number of navigation stop times of the mobile device according to the number of times the navigation stop instruction is issued to the mobile device. For example, each time a navigation stop command is sent to the mobile device, the number of times the mobile device stops navigation is increased by 1. In practical applications, optionally, if the number of navigation stop times is temporarily stored in the temporary storage space, each time the mobile device reaches the navigation target point, it means that the navigation task is completed. At this time, the number of navigation stop times in the temporary storage space can be cleared. Zero to save storage space.
进一步可选地,将可移动设备的停止导航次数与导航任务绑定,并根据导航任务所经过的路线以及停止导航次数,选取出当前行驶环境中的热门线路或热门地点。从而,在后续路线规划时可以对热门线路或热门地点进行规避,不仅能够提高可移动设备的运送效率,还能够进一步避免可移动设备在混合作业过程中的碰撞,降低碰撞事故率。Further optionally, the number of navigation stops of the mobile device is bound to the navigation task, and according to the route passed by the navigation task and the number of navigation stops, popular routes or popular locations in the current driving environment are selected. Therefore, popular routes or popular locations can be avoided during subsequent route planning, which can not only improve the transport efficiency of mobile equipment, but also further avoid collisions of mobile equipment during mixed operations and reduce the collision accident rate.
再一可选实施例中,对于动态安全区域相互重叠的至少两个可移动设备,确定至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级的过程,包括:获取至少两个可移动设备对应的订单信息;根据订单信息确定至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级。In yet another optional embodiment, for at least two mobile devices whose dynamic security areas overlap with each other, the process of determining the driving priority of the at least two mobile devices includes: acquiring order information corresponding to the at least two mobile devices; The driving priority of at least two movable devices is determined according to the order information.
本发明实施例中,可移动设备对应的订单信息包括分配给可移动设备的拣货单或订单。以拣货单为例,可移动设备对应的拣货单包括用于指示待拣货物的货物标识、以及待拣货物所处货位。拣货单可以是对应于一个订单,也可以对应于多个订单,还可以是由多个订单重排后生成的。可选地,多个订单可以按照待拣货物的货物类型和/或所处位置进行重排,以使可移动设备能够基于重排后的拣货单规划出较佳路线。In the embodiment of the present invention, the order information corresponding to the mobile device includes a picking list or an order assigned to the mobile device. Taking the picking list as an example, the picking list corresponding to the mobile device includes a cargo identification for indicating the goods to be picked, and the location of the goods to be picked. A picking list may correspond to one order, or may correspond to multiple orders, or may be generated after rearrangement of multiple orders. Optionally, multiple orders can be rearranged according to the type and/or location of the goods to be picked, so that the mobile device can plan a better route based on the rearranged picking list.
值得说明的是,订单信息中还包括订单优先级。具体地,在创建订单或拣货单时,基于实际下单需求(如订单时效、订单类型、货物数量等)为订单或拣货单设置对应的订单优先级,以满足各种用户的下单需求。在一可选实施例中,订单信息中的订单优先级越高,可移动设备的行驶优先级越高。It is worth noting that the order information also includes the order priority. Specifically, when creating an order or picking list, set the corresponding order priority for the order or picking list based on the actual order requirements (such as order timeliness, order type, quantity of goods, etc.), so as to meet the orders of various users need. In an optional embodiment, the higher the order priority in the order information, the higher the driving priority of the mobile device.
以仓储场景为例,假设货仓中设置有3个可移动设备记为AMR7、AMR8、 AMR9。假设AMR7、AMR8、AMR9的动态安全区域相互重叠。假设订单信息中AMR7、AMR8、AMR9所对应的订单时效分别为急件、普通时效件、普通时效件。Taking the storage scenario as an example, assume that there are three mobile devices in the warehouse, marked as AMR7, AMR8, and AMR9. It is assumed that the dynamic security areas of AMR7, AMR8, and AMR9 overlap each other. Assume that the order timeliness corresponding to AMR7, AMR8, and AMR9 in the order information are urgent, ordinary timeliness, and ordinary timeliness pieces respectively.
基于此,调度系统获取AMR7、AMR8、AMR9所绑定的订单以及对应的订单信息。其中,订单信息中订单时效的要求越高,订单优先级越高。在本示例中,急件对时效的要求最高,故而AMR7对应的订单优先级最高,AMR7的行驶优先级最高。上述三个可移动设备的行驶优先级从高到低为:AMR7、AMR9/AMR8。其中AMR9/AMR8处于同一行驶优先级。Based on this, the scheduling system obtains the orders bound to AMR7, AMR8, and AMR9 and the corresponding order information. Wherein, the higher the order timeliness requirements in the order information, the higher the order priority. In this example, urgent shipments have the highest requirement on timeliness, so the order priority corresponding to AMR7 is the highest, and the driving priority of AMR7 is the highest. The driving priorities of the above three mobile devices from high to low are: AMR7, AMR9/AMR8. Among them, AMR9/AMR8 are in the same driving priority.
进一步,还可结合货物搭载情况进一步对可移动设备的行驶优先级进行划分,以便提高拣货效率。考虑到拣货过程中可能会发生某些情况(如临时缺货等)降低拣货效率,可选地,为了保证拣货效率,可以优先运送已被拣取的货物,也即处于已搭载货物状态的可移动设备的行驶优先级,高于处于未搭载货物状态的可移动设备的行驶优先级。Furthermore, the driving priority of the mobile equipment can be further divided in combination with the loading situation of the goods, so as to improve the picking efficiency. Considering that some situations may occur during the picking process (such as temporary out of stock, etc.) to reduce the picking efficiency, optionally, in order to ensure the picking efficiency, the picked goods can be delivered first, that is, the goods that are already loaded The driving priority of the mobile equipment in the state is higher than the driving priority of the mobile equipment in the state of not carrying cargo.
基于上文示例,假设AMR7、AMR9处于已搭载货物的状态,AMR8处于未搭载货物的状态,基于此,调度系统可将AMR7、AMR8、AMR9的行驶优先级按照货物搭载情况进行设置,上述三个可移动设备的行驶优先级从高到低调整为:AMR7、AMR9、AMR8。Based on the above example, assume that AMR7 and AMR9 are in the state of carrying cargo, and AMR8 is in the state of not carrying cargo. Based on this, the dispatching system can set the driving priority of AMR7, AMR8, and AMR9 according to the cargo loading situation. The above three The driving priority of movable equipment is adjusted from high to low: AMR7, AMR9, AMR8.
除此之外,还可结合订单信息中的货物类型进一步对可移动设备的行驶优先级进行划分。在一可选实施例中,易碎物品对行驶速度以及安全制动距离的要求更高,如果行驶速度过高或制动距离较短,可能会导致易碎物品发生损坏,因此,相对于普通货物,易碎件的行驶优先级较高,避免临时调整行驶状态带来的货物损坏风险。实际应用中,可选地,预先设置货物类型与行驶优先级之间的映射关系。In addition, the driving priority of the mobile device can be further divided in combination with the type of goods in the order information. In an optional embodiment, fragile items have higher requirements on driving speed and safe braking distance. If the driving speed is too high or the braking distance is short, fragile items may be damaged. Therefore, compared with ordinary Cargo and fragile parts have a higher driving priority to avoid the risk of cargo damage caused by temporarily adjusting the driving state. In practical applications, optionally, the mapping relationship between cargo types and driving priorities is preset.
通过这一实施例,能够针对可移动设备对应的订单信息,调整可移动设备的行驶优先级,从而保证可移动设备的运行安全,提高可移动设备的运送效率。Through this embodiment, the driving priority of the mobile device can be adjusted according to the order information corresponding to the mobile device, so as to ensure the safe operation of the mobile device and improve the delivery efficiency of the mobile device.
无论是上述哪一种行驶优先级的确定方式,其核心均是通过行驶优先级对可移动设备的行驶状态进行区分,从而辅助调度系统评估可移动设备的实际行 驶状态,完成对存在碰撞风险的至少两个可移动设备的交通管制。No matter which of the above-mentioned ways of determining the driving priority, its core is to distinguish the driving state of the movable equipment through the driving priority, so as to assist the dispatching system to evaluate the actual driving state of the movable equipment and complete the collision risk assessment. Traffic control of at least two removable devices.
图1示出的调度方法中,通过多个可移动设备的导航信息动态设置各自的动态安全区域,进而基于动态安全区域控制多个可移动设备各自的导航状态,避免动态安全区域相互重叠的可移动设备继续行驶带来的碰撞风险,大大降低了可移动设备的碰撞事故率,提高可移动设备的避障能力,保证设备运行安全。In the scheduling method shown in FIG. 1 , the respective dynamic safety areas are dynamically set through the navigation information of multiple mobile devices, and then the respective navigation states of the multiple mobile devices are controlled based on the dynamic safety areas, so as to avoid possible overlapping of dynamic safety areas. The collision risk caused by the continuous driving of the mobile equipment greatly reduces the collision accident rate of the mobile equipment, improves the obstacle avoidance ability of the mobile equipment, and ensures the safe operation of the equipment.
以下将详细描述本发明的一个或多个实施例的调度装置。本领域技术人员可以理解,这些调度装置均可使用市售的硬件组件通过本方案所教导的步骤进行配置来构成。The scheduling device of one or more embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below. Those skilled in the art can understand that these scheduling devices can be configured by using commercially available hardware components through the steps taught in this solution.
图5为本发明实施例提供的一种调度装置的结构示意图,如图5所示,该装置包括:FIG. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of a scheduling device provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 5, the device includes:
获取模块51,用于获取所述多个可移动设备各自的导航信息;An acquisition module 51, configured to acquire respective navigation information of the plurality of mobile devices;
生成模块52,用于基于所述导航信息生成所述多个可移动设备各自的动态安全区域,所述动态安全区域用于表示可移动设备在行驶环境中的安全行驶范围;A generation module 52, configured to generate dynamic safety areas for each of the plurality of mobile devices based on the navigation information, where the dynamic safety areas are used to represent the safe driving range of the mobile device in the driving environment;
调度模块53,用于若存在至少两个可移动设备的动态安全区域相互重叠,则向所述至少两个可移动设备中任意一个可移动设备发送导航停止指令,以使所述任意一个可移动设备基于所述导航停止指令在预设时长内停止导航。The scheduling module 53 is configured to send a navigation stop instruction to any one of the at least two movable devices if the dynamic security areas of at least two movable devices overlap each other, so that any one of the movable devices can move The device stops navigation within a preset time period based on the navigation stop instruction.
可选地,所述调度模块53,用于:Optionally, the scheduling module 53 is configured to:
确定所述至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级;determining a travel priority for the at least two movable devices;
向所述至少两个可移动设备中行驶优先级处于预设顺位的可移动设备发送所述导航停止指令。Sending the navigation stop instruction to a mobile device whose driving priority is in a preset sequence among the at least two mobile devices.
可选地,所述调度模块53还用于:Optionally, the scheduling module 53 is also used for:
在预设时长内为所述至少两个可移动设备中行驶优先级最高的可移动设备继续导航。Continue navigation for the mobile device with the highest driving priority among the at least two mobile devices within a preset time period.
可选地,若处于预设顺位的目标可移动设备有多个,则所述调度模块53向所述至少两个可移动设备中行驶优先级处于预设顺位的可移动设备发送所 述导航停止指令时,用于:Optionally, if there are multiple target mobile devices in the preset sequence, the scheduling module 53 sends the When navigating stop commands, use to:
根据多个目标可移动设备的行驶优先级、以及行驶优先级与停止导航时长的匹配关系,确定多个目标可移动设备各自匹配的停止导航时长;其中,行驶优先级越高,停止导航时长越短;According to the driving priority of multiple target mobile devices and the matching relationship between the driving priority and the stop navigation duration, determine the corresponding stop navigation duration of multiple target mobile devices; wherein, the higher the travel priority, the longer the stop navigation duration. short;
基于多个目标可移动设备各自匹配的停止导航时长生成对应的导航停止指令;Generate corresponding navigation stop instructions based on the matching stop navigation durations of multiple target movable devices;
向多个目标可移动设备发送对应的导航停止指令。Corresponding navigation stop instructions are sent to a plurality of target movable devices.
可选地,所述调度模块53确定所述至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级时,用于:Optionally, when the scheduling module 53 determines the driving priorities of the at least two movable devices, it is used to:
根据所述至少两个可移动设备的导航信息,确定所述至少两个可移动设备的行驶方向以及所处位置;Determine the driving directions and locations of the at least two mobile devices according to the navigation information of the at least two mobile devices;
对于同一行驶方向上的至少两个可移动设备,基于位置前后顺序确定行驶优先级,其中,位置越靠前,行驶优先级越高。For at least two movable devices in the same driving direction, the driving priority is determined based on the sequence of positions, wherein the closer the position is, the higher the driving priority is.
可选地,所述调度模块53确定所述至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级时,用于:Optionally, when the scheduling module 53 determines the driving priorities of the at least two movable devices, it is used to:
获取所述至少两个可移动设备的停止导航次数;Acquiring the number of times of stopping navigation of the at least two movable devices;
根据所述停止导航次数确定所述至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级;其中,停止导航次数越多,行驶优先级越高。The driving priority of the at least two mobile devices is determined according to the number of times of stopping navigation; wherein, the more times of stopping navigation, the higher the driving priority.
可选地,所述调度模块53确定所述至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级时,用于:Optionally, when the scheduling module 53 determines the driving priorities of the at least two movable devices, it is used to:
获取所述至少两个可移动设备对应的订单信息;Obtain order information corresponding to the at least two movable devices;
根据所述订单信息确定所述至少两个可移动设备的行驶优先级;其中,所述订单信息中的订单优先级越高,行驶优先级越高。The driving priority of the at least two movable devices is determined according to the order information; wherein, the higher the order priority in the order information, the higher the driving priority.
可选地,所述获取模块51获取多个可移动设备各自的导航信息时,用于:Optionally, when the obtaining module 51 obtains the respective navigation information of multiple mobile devices, it is used to:
接收多个可移动设备按照预设周期上报的导航信息;Receive navigation information reported by multiple mobile devices according to a preset period;
其中,所述导航信息包括:行驶速度、行驶方向、可移动设备所处位置、设备属性信息中的任意一种或组合。Wherein, the navigation information includes: any one or a combination of driving speed, driving direction, location of the mobile device, and device attribute information.
可选地,所述生成模块52基于所述导航信息生成所述多个可移动设备各自的动态安全区域时,用于:Optionally, when the generation module 52 generates the respective dynamic security areas of the plurality of mobile devices based on the navigation information, it is used to:
根据每一可移动设备的导航信息,在预设的行驶环境地图中设置与每一可移动设备匹配的虚拟区域,作为每一可移动设备的动态安全区域;According to the navigation information of each mobile device, set a virtual area matching each mobile device in the preset driving environment map as the dynamic safety area of each mobile device;
其中,与每一可移动设备匹配的虚拟区域随每一可移动设备的行驶轨迹变化。Wherein, the virtual area matched with each mobile device changes along with the traveling track of each mobile device.
可选地,所述每一可移动设备的导航信息包括每一可移动设备的行驶速度、行驶方向、所处位置、设备类型;Optionally, the navigation information of each mobile device includes the travel speed, travel direction, location, and device type of each mobile device;
所述生成模块52根据每一可移动设备的导航信息,在预设的行驶环境地图中设置与每一可移动设备匹配的虚拟区域时,用于:The generation module 52 is used for:
根据每一可移动设备的行驶速度以及设备类型,确定每一可移动设备匹配的安全制动距离;According to the driving speed and equipment type of each movable equipment, determine the matching safe braking distance of each movable equipment;
根据每一可移动设备的行驶速度、行驶方向、所处位置以及匹配的安全制动距离,在所述行驶环境地图中动态更新每一可移动设备匹配的虚拟区域。According to the driving speed, driving direction, location and matching safe braking distance of each mobile device, the virtual area matched by each mobile device is dynamically updated in the driving environment map.
图5所示装置可以执行前述图1至图4所示实施例中提供的调度方法,详细的执行过程和技术效果参见前述实施例中的描述,在此不再赘述。The device shown in FIG. 5 can execute the scheduling method provided in the embodiments shown in FIGS. 1 to 4. For the detailed execution process and technical effects, refer to the descriptions in the foregoing embodiments, and details are not repeated here.
在一个可能的设计中,上述图5所示调度装置的结构可实现为一电子设备,如图6所示,该电子设备可以包括:处理器61、存储器62。其中,所述存储器62上存储有可执行代码,当所述可执行代码被所述处理器61执行时,使所述处理器61至少可以实现如前述图1至图4所示实施例中提供的调度方法。In a possible design, the structure of the scheduling apparatus shown in FIG. 5 may be implemented as an electronic device. As shown in FIG. 6 , the electronic device may include: a
可选地,该电子设备中还可以包括通信接口63,用于与其他设备进行通信。Optionally, the electronic device may also include a
另外,本发明实施例提供了一种非暂时性机器可读存储介质,所述非暂时性机器可读存储介质上存储有可执行代码,当所述可执行代码被电子设备的处理器执行时,使所述处理器至少可以实现如前述图1至图4所示实施例中提供的调度方法。In addition, an embodiment of the present invention provides a non-transitory machine-readable storage medium, the non-transitory machine-readable storage medium stores executable code, and when the executable code is executed by the processor of the electronic device , so that the processor can at least implement the scheduling method provided in the embodiment shown in FIGS. 1 to 4 .
以上所描述的装置实施例仅仅是示意性的,其中所述作为分离部件说明的单元可以是或者也可以不是物理上分开的。可以根据实际的需要选择其中的部 分或者全部模块来实现本实施例方案的目的。本领域普通技术人员在不付出创造性的劳动的情况下,即可以理解并实施。The device embodiments described above are merely illustrative, and the units described as separate components may or may not be physically separate. Part or all of the modules can be selected according to actual needs to realize the purpose of the solution of this embodiment. It can be understood and implemented by those skilled in the art without any creative efforts.
通过以上的实施方式的描述,本领域的技术人员可以清楚地了解到各实施方式可借助加必需的通用硬件平台的方式来实现,当然也可以通过硬件和软件结合的方式来实现。基于这样的理解,上述技术方案本质上或者说对现有技术做出贡献的部分可以以计算机产品的形式体现出来,本发明可采用在一个或多个其中包含有计算机可用程序代码的计算机可用存储介质(包括但不限于磁盘存储器、CD-ROM、光学存储器等)上实施的计算机程序产品的形式。Through the above description of the embodiments, those skilled in the art can clearly understand that each embodiment can be realized by means of a general hardware platform plus necessary, and of course, can also be realized by a combination of hardware and software. Based on such an understanding, the above-mentioned technical solution can be embodied in the form of computer products in essence or in other words, the part that contributes to the prior art, and the present invention can adopt computer-usable media (including but not limited to disk storage, CD-ROM, optical storage, etc.) embodied in the form of a computer program product.
本发明实施例提供的调度方法可以由某种程序/软件来执行,该程序/软件可以由网络侧提供,前述实施例中提及的电子设备可以将该程序/软件下载到本地的非易失性存储介质中,并在其需要执行前述调度方法时,通过CPU将该程序/软件读取到内存中,进而由CPU执行该程序/软件以实现前述实施例中所提供的调度方法,执行过程可以参见前述图1至图4中的示意。The scheduling method provided by the embodiment of the present invention can be executed by a certain program/software, which can be provided by the network side, and the electronic device mentioned in the foregoing embodiments can download the program/software to a local non-volatile In the permanent storage medium, and when it needs to execute the aforementioned scheduling method, the program/software is read into the memory by the CPU, and then the program/software is executed by the CPU to realize the scheduling method provided in the aforementioned embodiment, and the execution process Refer to the schematic diagrams in FIGS. 1 to 4 above.
最后应说明的是:以上实施例仅用以说明本发明的技术方案,而非对其限制;尽管参照前述实施例对本发明进行了详细的说明,本领域的普通技术人员应当理解:其依然可以对前述各实施例所记载的技术方案进行修改,或者对其中部分技术特征进行等同替换;而这些修改或者替换,并不使相应技术方案的本质脱离本发明各实施例技术方案的精神和范围。Finally, it should be noted that: the above embodiments are only used to illustrate the technical solutions of the present invention, rather than to limit them; although the present invention has been described in detail with reference to the foregoing embodiments, those of ordinary skill in the art should understand that: it can still be Modifications are made to the technical solutions described in the foregoing embodiments, or equivalent replacements are made to some of the technical features; and these modifications or replacements do not make the essence of the corresponding technical solutions deviate from the spirit and scope of the technical solutions of the various embodiments of the present invention.
Claims (13)
Translated fromChineseApplications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111057970.1 | 2021-09-09 | ||
| CN202111057970.1ACN115796410A (en) | 2021-09-09 | 2021-09-09 | Scheduling method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2023035756A1true WO2023035756A1 (en) | 2023-03-16 |
Family
ID=85417013
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2022/104395CeasedWO2023035756A1 (en) | 2021-09-09 | 2022-07-07 | Scheduling method and apparatus for movable device, and electronic device and storage medium |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115796410A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2023035756A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN119252076B (en)* | 2024-12-04 | 2025-02-18 | 中建科工集团智慧停车科技有限公司 | AGV type stereo garage anti-collision detection method, system, equipment and medium |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6393362B1 (en)* | 2000-03-07 | 2002-05-21 | Modular Mining Systems, Inc. | Dynamic safety envelope for autonomous-vehicle collision avoidance system |
| US9927252B1 (en)* | 2016-12-14 | 2018-03-27 | Uber Technologies, Inc. | Safe routing for navigation systems |
| CN108225364A (en)* | 2018-01-04 | 2018-06-29 | 吉林大学 | A kind of pilotless automobile driving task decision system and method |
| US20210171063A1 (en)* | 2019-12-10 | 2021-06-10 | Rideflux Inc. | Method, apparatus, and computer program for avoiding collision of autonomous vehicle |
| CN113608528A (en)* | 2021-07-12 | 2021-11-05 | 千里眼(广州)人工智能科技有限公司 | Robot scheduling method, device, robot and storage medium |
- 2021
- 2021-09-09CNCN202111057970.1Apatent/CN115796410A/enactivePending
- 2022
- 2022-07-07WOPCT/CN2022/104395patent/WO2023035756A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6393362B1 (en)* | 2000-03-07 | 2002-05-21 | Modular Mining Systems, Inc. | Dynamic safety envelope for autonomous-vehicle collision avoidance system |
| US9927252B1 (en)* | 2016-12-14 | 2018-03-27 | Uber Technologies, Inc. | Safe routing for navigation systems |
| CN108225364A (en)* | 2018-01-04 | 2018-06-29 | 吉林大学 | A kind of pilotless automobile driving task decision system and method |
| US20210171063A1 (en)* | 2019-12-10 | 2021-06-10 | Rideflux Inc. | Method, apparatus, and computer program for avoiding collision of autonomous vehicle |
| CN113608528A (en)* | 2021-07-12 | 2021-11-05 | 千里眼(广州)人工智能科技有限公司 | Robot scheduling method, device, robot and storage medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115796410A (en) | 2023-03-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11052539B2 (en) | Method, server and storage medium for robot routing | |
| US10421186B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for working-place backflow of robots | |
| US11860621B2 (en) | Travel control device, travel control method, travel control system and computer program | |
| CN110065910B (en) | Method and device for dispatching transportation equipment in warehouse and warehousing system | |
| CN109062202A (en) | Intelligent storage delivery system based on Internet of Things driving | |
| CN118034272A (en) | Multi-AGV path planning method and system based on dynamic obstacle avoidance | |
| US12027051B2 (en) | Mobile object control apparatus, mobile object control method, and computer readable recording medium | |
| CN116612654B (en) | Unmanned vehicle team scheduling method and device and electronic equipment | |
| CN109598459B (en) | Logistics distribution method and device and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN109656224A (en) | A kind of intelligence AGV central dispatch system and method | |
| JP7336529B2 (en) | AGV Abnormal Processing Method, Device, Electronic Device, and Storage Medium | |
| CN110817220A (en) | RGV avoiding method, RGV and RGV avoiding system | |
| CN113138597A (en) | Obstacle avoidance method of intelligent trolley and intelligent trolley | |
| CN111832816A (en) | A medical AGV group logistics control system and method based on scheduling algorithm | |
| CN116166029A (en) | Multi-AGV navigation method and system compatible with local obstacle avoidance function | |
| WO2023035756A1 (en) | Scheduling method and apparatus for movable device, and electronic device and storage medium | |
| JP2024045465A (en) | Travel controller, travel control method and computer program | |
| CN117657216A (en) | Speed planning method, device and equipment for automatic driving vehicle and vehicle | |
| CN118295387A (en) | AGV vehicle scheduling method, system and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN108454640B (en) | Vehicle control method and system | |
| CN115796544A (en) | A dispatching method and device for unmanned horizontal transportation in a port | |
| CN115351803A (en) | Path planning method and device for warehouse logistics robot | |
| CN111746994B (en) | AGV car following method and picking system | |
| CN118396497A (en) | Intelligent transportation method and system based on ULD AGV | |
| CN117416649A (en) | Robot queue scheduling method for warehousing system, warehousing system and its scheduling equipment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | Ref document number:22866231 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 | |
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase | Ref country code:DE | |
| 32PN | Ep: public notification in the ep bulletin as address of the adressee cannot be established | Free format text:NOTING OF LOSS OF RIGHTS PURSUANT TO RULE 112(1) EPC (EPO FORM 1205A DATED 21.06.2024) | |
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase | Ref document number:22866231 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 |