WO2022264240A1 - Vehicle management ledger system - Google Patents
Vehicle management ledger systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2022264240A1 WO2022264240A1PCT/JP2021/022597JP2021022597WWO2022264240A1WO 2022264240 A1WO2022264240 A1WO 2022264240A1JP 2021022597 WJP2021022597 WJP 2021022597WWO 2022264240 A1WO2022264240 A1WO 2022264240A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- vehicle
- information
- terminal
- vehicle information
- ledger
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q30/00—Commerce
- G06Q30/06—Buying, selling or leasing transactions
Definitions
- the present inventionrelates to a vehicle management ledger system that manages vehicle information using blockchain.
- the unique attribute information of the vehicle itselffor example, manufacturer, model, chassis number, engine displacement, mileage, etc.
- the vehicle inspection certificateis often destroyed at that time, and there are many vehicles that cannot accurately identify the vehicle usage condition (such as mileage, etc.). exist.
- the value of a vehicle whose vehicle inspection certificate has been destroyedis often evaluated solely based on its appearance and mileage. If there is no information that can accurately identify such usage conditions, even if the odometer has been rewound (tampered with the mileage) by the seller, such a fact cannot be detected, resulting in an unexpected accident or malfunction. is induced.
- blockchainhas been used for a long time now.
- a block chainis a system in which blocks containing a collection of additional data are additionally generated at regular intervals, and these blocks are verified by computers, and the correct records are connected and stored like a chain.
- Blockchainmakes it extremely difficult to prevent tampering with information, so asset transactions can be conducted in a highly reliable system environment.
- a representative example of the introduction of blockchainis the issuance and distribution of virtual currency.
- JP 2021-068339A Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2020-149320 JP 2020-086634 A
- Patent Document 1for different information items related to a vehicle (for example, vehicle type information and area information), a block chain for each information item (for example, vehicle type information block chain and area information block chain) is provided individually. , manages information about the vehicle (Patent Document 1, paragraph 17).
- a plurality of blocks related to the same individual vehiclefor example, a vehicle type information block and a region information block related to a specific vehicle
- Patent Document 1 paragraph 20a plurality of blocks related to the same individual vehicle (for example, a vehicle type information block and a region information block related to a specific vehicle) are associated.
- Patent Literature 1increases the safety against falsification of information, it is necessary to prepare and manage a blockchain for each information item related to the vehicle, which complicates information management.
- information related to the vehicleowner/seller
- locationstorage location/use location
- Patent Document 3when cars are distributed in various places, hash information is generated based on the state of the car when it was transferred and the latest hash information (Patent Document 3, paragraph 38 ). Hash information and corresponding asset information (vehicle type, mileage, owner, repair history, etc.) are associated and stored in a database (Ref. 3, paragraph 39). Hash information remains on the blockchain as traceable information and cannot be tampered with, ensuring the safety and robustness of the information (Ref. 3, paragraph 43).
- vehicle informationincludes (1) information items (vehicle history information) that change along with the history of the vehicle, such as transfer, use, and repair, and (2) permanent information unique to each vehicle.
- information itemsvehicle basic information
- vehicle history informationthat change with the transfer, use, or repair of a vehicle include the date of registration renewal, the name and address of the vehicle owner, the base location of use, the expiration date of the validity period, and the driving at the time of registration. distance, repair history, and the like.
- examples of "vehicle basic information” that does not change even if the vehicle is transferred or usedinclude the vehicle registration number, registration date or issuance date, first registration date, vehicle type, purpose, private use or By business, body shape, vehicle name, passenger capacity, maximum load, vehicle weight, gross vehicle weight, chassis number given by the manufacturer, vehicle length, width, height, front front axle weight, front and rear axle weight These include weight, model, prime mover model, total displacement or rated power, and type of fuel. Therefore, when managing vehicle information in the form of a blockchain, while basic vehicle information that is not affected by the transfer or use of the vehicle is registered for the first time, various information items may change as a result of transfer, use, or repair. In that case, it is thought that it can be efficiently managed by generating changed vehicle history information and adding it to the blockchain. However, in the technique of Patent Document 3, attention is paid to such detailed information items, and no consideration is given to the point of efficiently managing information.
- the present inventionhas been made in view of the above problems, and when managing vehicle information in the form of a blockchain, it is possible to improve the management efficiency of vehicle information and to refer to all vehicle information accumulated from the time of initial registration. for the purpose.
- the vehicle management ledger systemincludes: A vehicle management ledger system that manages vehicle information in a distributed manner by having each of a plurality of ledger management terminals interconnected peer-to-peer hold a vehicle information block chain in which individual vehicle information blocks are linked by hash values.
- a reference terminalwhich is a terminal possessed by each individual user and which requests the ledger management terminal to refer to the vehicle information stored in the vehicle information block; a writing terminal which is owned by each vehicle seller and requests the ledger management terminal to add new vehicle information;
- Each individual reference terminalis reference request means for transmitting a vehicle information reference request to a ledger management terminal when an instruction for a vehicle information reference request from a user of the reference terminal is received; an output unit that displays the vehicle information on a screen when the vehicle information is provided from the ledger management terminal in response to the vehicle information reference request; has Each individual writing terminal an information addition requesting means for requesting the ledger management terminal to write vehicle information when an instruction to request vehicle information writing from a vehicle seller is received;
- the ledger management terminalIn response to a vehicle information write request from the write terminal, vehicle basic information, which is permanent specification information unique to the vehicle, is generated only at the time of initial registration, and the vehicle is transferred, used, repaired, etc. after the initial registration.
- information generating meansfor continuously additionally generating vehicle history information indicating the history of Hash generation means for generating a hash value of the latest vehicle history information by applying a hash function to the latest vehicle history information generated by the information generation means;
- the basic vehicle information generated at the time of initial registration, all vehicle history information after the initial registration including the latest vehicle history information, and the hash value of the latest vehicle history informationare collectively stored in the latest vehicle information block.
- writing block adding meanshas When the latest vehicle information block is written in one of the ledger management terminals among the plurality of ledger management terminals, All the ledger management terminals other than the ledger management terminal that added the vehicle information write the vehicle information in their own storage unit when determining that the latest vehicle information block is qualified, If the reference terminal requests to refer to vehicle information, The vehicle information stored in the vehicle information block is specified, and the specified vehicle information is provided to the reference terminal.
- vehicle informationis configured in a block chain format (a data structure in which vehicle information blocks are linked by hash values).
- a vehicle information block chain 221(vehicle information in block chain form) is held in each of the plurality of ledger management terminals 2 (see FIG. 4). Therefore, even if information managed by paper media such as automobile inspection certificates is lost, vehicle information can be stored in a safe environment where falsification is extremely difficult. If one vehicle information block BL incorporated in the vehicle information block chain 221 shown in FIG. This is because it can only be tampered with by rewriting the all-vehicle information block (BL) distributedly managed by the ledger management terminals 2 that are scattered about.
- the ledger terminals 2-1 to 2-3have the same functions and are connected in a peer-to-peer manner for direct mutual communication.
- the vehicle informationincludes (1) "vehicle history information” that changes with the transfer and use of the vehicle, and (2) “vehicle basic information” that is specification information unique to the vehicle itself. ” in advance. Then, as the vehicle is transferred or used, the vehicle history information HSI (FIG. 8) that changes with the transfer, use (including an increase in mileage), or repair is updated, and the vehicle to which the updated contents are added. An information block BL is generated and added to the vehicle information block chain 221 (Fig. 5). As a result, in the vehicle information block chain 221, vehicle information can be cumulatively stored for each vehicle.
- a vehicle management ledger systemis a vehicle management ledger system according to the first invention,
- the reference terminalcomprises a camera for imaging any subject,
- the vehicle information reference requestis transmitted to the ledger management terminal by reading a predetermined code with the camera.
- a user who wishes to refer to vehicle informationreads a QR code (registered trademark) or other predetermined code CD (FIG. 3) with the camera 16 mounted on the reference terminal 1 used by the user.
- a vehicle ledger reference requestis transmitted to the ledger management terminal 2 .
- the vehicle information provided from the ledger management terminal 2 in response to the vehicle ledger reference requestis displayed on the screen.
- the vehicle management ledger system 100 of the present applicationcan be "operated on a public blockchain", an unspecified number of arbitrary users can freely refer to vehicle information in the vehicle management ledger system 100. It's like Therefore, by disclosing highly reliable vehicle information to the public, it is possible to gain trust in the quality of actual vehicles, and to safely disclose vehicle information to the public without fear of falsification. can.
- a vehicle management ledger systemis a vehicle management ledger system according to the second invention, A code display member having the predetermined code stamped thereon is attached to a predetermined location of an actual vehicle to be referenced for vehicle information, The reference terminal is A vehicle ledger reference request is transmitted to a ledger management terminal by reading a predetermined code stamped on the code display member with a camera.
- the predetermined code CD(QR code (registered trademark), etc.) for designating the reference destination of the vehicle information (the ledger management terminal 2 in which the vehicle information is held) is made of a metal material or the like. It is three-dimensionally engraved on the code display member DSP (Fig. 3). This code display member DSP is physically attached to an actual vehicle (not shown) corresponding to the vehicle information.
- a sticker on which a predetermined code CD such as a QR code (registered trademark) is printedis attached to the vehicle inspection certificate, and the code display member DSP with the code CD engraved is placed anywhere on the vehicle body (for example, the back of the hood, engine, etc.) By physically firmly attaching it to the inside of the room door, etc., access to vehicle information about this vehicle is guaranteed, and vehicle evidence is secured.
- a method for attaching the code display member DSPriveting, welding, or the like can be employed.
- the user of the reference terminal 1When referring to vehicle information about the vehicle, the user of the reference terminal 1 holds the terminal 1 equipped with a camera function and images a predetermined code CD on the code display member DSP attached to the vehicle. By this imaging operation, a vehicle information reference request is transmitted from the reference terminal 1 to the ledger management terminal 2 , and vehicle information is displayed on the reference terminal 1 .
- a vehicle management ledger systemis a vehicle management ledger system according to the first to third inventions
- the vehicle related to the vehicle informationis A mileage transmission mechanism that transmits the mileage of the vehicle at a predetermined timing to the ledger management terminal by wireless communication
- the information generating means of the ledger management terminalis When the mileage of the vehicle transmitted from the vehicle is received at a predetermined timing, the latest vehicle history information describing the mileage is automatically generated.
- the vehicle VCL corresponding to the vehicle informationis equipped with the mileage transmission mechanism DS, and at a predetermined timing (regularly or each time the mileage reaches a predetermined distance), the vehicle VCL is transmitted.
- the distance traveledis transmitted to the ledger management terminal 2 by wireless communication (see FIG. 16).
- the latest vehicle history information HSI in which the transmitted mileage is describedis generated, and the latest vehicle information block BL containing this vehicle history information is added.
- the history of travel distancecan be left as a record without waiting for an opportunity to transfer (sales contract) the vehicle VCL. Therefore, even if a third party physically tampered with the display of the odometer of the vehicle, the fact of tampering can be detected by collating it with the vehicle history information in the vehicle information block BL. Robustness can be improved.
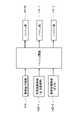
- FIG. 1is a block diagram showing the overall configuration of a vehicle management ledger system according to an embodiment
- FIG. 3is a block diagram showing the electrical configuration of a reference terminal
- FIG. 4is a schematic diagram showing an example of a code display member on which a predetermined code is engraved
- 3is a block diagram showing an electrical configuration of a ledger management terminal
- FIG. Itis a figure which shows an example of the data structure of a vehicle information block chain.
- FIG. 4is a schematic diagram showing an operation of generating a hash value; It is a figure which shows an example of the data structure of vehicle basic information.
- FIG. 4is a schematic diagram showing an operation of generating a hash value
- FIG. 3is a diagram showing the data structure of vehicle history information, in which (a) is an example of vehicle history information created at the time of initial registration, and (b) is an example of vehicle history information created after the initial registration.
- 3is a block diagram showing an electrical configuration of a writing terminal;
- FIG.It is a figure which shows an example of the vehicle basic information input screen in a writing terminal. It is a figure which shows an example of the vehicle history information input screen in a writing terminal. It is a figure which shows an example of the vehicle basic information display screen in a reference terminal. It is a figure which shows an example of the vehicle history information display screen in a reference terminal.
- FIG. 4is a sequence diagram showing the operation of each component in the writing process of vehicle information by the writing terminal;
- FIG. 4is a sequence diagram showing the operation of each component in vehicle information reference processing by a reference terminal;
- Itis a block diagram which shows a modified example of the whole structure of a vehicle management ledger system.
- Embodiment 1 of the present inventiondisperses vehicle information by having a plurality of peer-to-peer interconnected ledger management terminals 2 each hold a vehicle information block chain 221 in which individual vehicle information blocks BL are linked by hash values.
- Thisis an example of configuring a vehicle management ledger system 100 that systematically manages.
- one "vehicle information block" described abovehas information corresponding to one vehicle inspection certificate, and should be called a digital vehicle inspection certificate.
- FIG. 1is a block diagram showing the overall configuration of a vehicle management ledger system 100 according to an embodiment.
- the vehicle management ledger system 100 of this exampleincludes, as shown in FIG. 1, a reference terminal 1 (1-1 and 1-2 in the example of FIG. 1 to 2-3) and the management terminal 3 (3-1 and 3-2 in the example of FIG. 1) are connected in a communicable state via a public communication line 200 such as the Internet or a mobile communication network.
- a public communication line 200such as the Internet or a mobile communication network.
- the numbers of reference terminals 1, ledger management terminals 2, and management terminals 3may be arbitrary. In FIG. 1, for the sake of convenience, only three ledger management terminals 2-1 to 2-3 are shown as the ledger management terminals 2, but the actual ledger management terminals 2 that constitute the system 100 are worldwide. They are scattered, and the number of them reaches tens of thousands. These extremely large numbers of ledger management terminals 2 mutually approve (determine whether or not addition of the vehicle information block BL is appropriate), synchronize, and store all the generated vehicle information blocks BL.
- the reference terminal 1is a terminal possessed by each individual user (referrer of vehicle information).
- the terminal 1requests the ledger management terminal 2 to refer to the vehicle information.
- the ledger management terminal 2is a terminal capable of communicating with individual reference terminals 1 via the public communication line 200 . These ledger terminals 2 are interconnected peer-to-peer. Each ledger management terminal 2 holds a vehicle information block chain 221 in which individual vehicle information blocks BL are associated with each other by hash values.
- This vehicle information block chain 221is not actually generated so as to correspond to each vehicle on a one-to-one basis. By doing so, a group of vehicle information block chains 221 is constructed.
- the vehicle information block BL in this examplestores vehicle information (vehicle basic information FVI and vehicle history information HSI), a hash value HV generated by encrypting the vehicle information with a hash function, and a nonce NC. (Fig. 5).
- vehicle information FVIvehicle basic information
- vehicle history information HSIvehicle history information
- the hash value HVis always added when the vehicle basic information FVI or vehicle history information HSI is added (that is, when these information FVI/HSI are uploaded onto the vehicle information block chain 221). be done.
- a hash value HV-Bis issued by applying a hash function to the information HVI.
- This hash value HV-Bis stored in the vehicle information block BL-1 as shown in FIG.
- a hash value obtained by applying a hash function to the registered or added HSIis issued, and thereafter, a hash is issued each time information is added.
- a hash value HV-1 obtained by applying a hash function to the information HSI-1is issued.
- the hash value HV-1is also stored in the vehicle information block BL-1 as shown in FIG. Thereafter, when the secondary vehicle history information HSI-2 is registered, a hash function is applied to the information HSI-2, and a hash value HV-2 is issued.
- vehicle basic informationis information including information items relating to "unique permanent specifications" for each individual vehicle.
- the vehicle basic information FVI(Fig. 7) contains only information that is not affected by the transfer, use, repair, etc. of the vehicle, so if it is generated only at the time of initial registration, the original registration content will be maintained without modification thereafter. do. Further, once the vehicle basic information FVI is created for a specific vehicle, the vehicle basic information FVI is continuously incorporated into the vehicle information block for the vehicle.
- the basic vehicle information FVIincludes the following information.
- Vehicle registration numberA number that serves as the basis for license plate issuance
- Date of registration/Date of issuanceIn the case of ordinary vehicles, the date of change of the vehicle owner (date of new registration or transfer registration). In the case of ordinary cars, it is renewed only when there is a transfer of ownership.
- JapanIn the case of Japan, it consists of a combination of the "vehicle exhaust emission control and low-emission vehicle certification identification symbol" stipulated by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism and the "symbol specified by the automobile manufacturer.”
- Motor typeThe type of the engine (motor in the case of an electric vehicle) mounted on the vehicle. In the case of a hybrid vehicle, both the engine type and the motor type are indicated.
- Total Displacement or Rated PowerFor internal combustion engines, engine displacement in liters. For electric vehicles, rated power (in kilowatts)
- Type of fuelFuel mainly used by the engine, such as gasoline, light oil, LPG, ANG, and electricity. In the case of a new car, since it is sold by a dealer who is an authorized dealer who has concluded a special agent contract with an automobile manufacturer, the issuing manager in the vehicle basic information FVI is usually "dealer name".
- vehicle history informationis information that includes information items that change "associated with the history” such as transfer, use, and repair of the vehicle.
- vehicle history information HSIat the time of initial registration, the contents related to transfer, use, and repair at the time of new vehicle registration are described (see FIG. 8(a)). Note that the mileage described in the vehicle history information HSI-1 at the time of initial registration is very small (for example, about several kilometers).
- the vehicle history information HSIwill have information when the vehicle is distributed and traded as a used vehicle (see FIG. 8(b)).
- Specific examples of the vehicle history information HSI at the time of distribution in the used car marketinclude details about the new owner (purchaser), indicators indicating the state of use (mileage, appearance/interior quality evaluation, etc.), repair history, etc. mentioned. It should be noted that the vehicle history information HSI is not limited to being generated when a vehicle is bought and sold, and may be generated for each periodic vehicle inspection registration (so-called vehicle inspection) in Japan.
- the vehicle history information HSIincludes the following information.
- Registration update dateDate of renewal of automobile registration
- Owner nameName of the current owner of the vehicle
- Owner addressAddress of the current owner of the vehicle
- Location of base of useLocation of the owner (user) of the vehicle. For individuals, where they actually reside. In the case of corporations, places where there are actual activities such as business offices and sales offices.
- Mileage at the time of registrationMileage of the vehicle from the initial (new car) registration to the new car registration update
- Repair historyFrom the previous car registration update to the new car this time The fact that repairs were made in the period up to registration renewal.
- the second and subsequent vehicle history information HSI after the initial registration is completedas the travel distance, the travel distance at the time of the sales contract as a used car is described.
- the ledger management terminal 2generates the vehicle basic information FVI in response to the vehicle information write request from the writing terminal 3 only at the time of initial registration.
- the ledger management terminal 2also generates vehicle history information HSI at the time of initial registration (see FIG. 8A). Furthermore, every time the writing terminal 3 requests the writing of vehicle information, the ledger management terminal 2 continuously additionally generates the vehicle history information after the initial registration (FIG. 8(b)). reference). That is, the successive vehicle information blocks BL generated in this example always include the vehicle basic information generated at the time of initial registration, and in addition to the vehicle history information generated at the time of initial registration, cumulatively added thereafter. All history information of each successive vehicle that has been acquired is stored (Fig. 5). The dashed lines in FIG. 5 indicate that individual vehicle information blocks BL are associated with each other by hash values HV.
- the ledger management terminal 2provides vehicle information to the reference terminal 1 in response to a vehicle information reference request from the reference terminal 1 .
- reference terminals 1 (1-1 and 1-2 in the example of FIG. 1), ledger management terminals 2 (2-1 to 2-3 in the example of FIG. 1), and writing terminals 3 (in the example of FIG. 1 3-1 and 3-2)will be described in order.
- Any of the components 1, 2, and 3, as shown in FIG. 1,includes an output section including a liquid crystal display, a printer (not shown), etc., a main body for executing various arithmetic processing, a keyboard, a touch panel, and a mouse ( (not shown).
- the main body of the devicehas a control function centered on a CPU that executes arithmetic processing, a storage function that uses a hard disk drive (HDD), ROM, RAM, etc., and a communication function that transmits and receives various signals or information. .
- FIG. 2is a block diagram showing the electrical configuration of the reference terminal 1 according to this embodiment.
- the reference terminal 1includes an input unit 14 and an output unit 15, as shown in FIG.
- ithas a storage unit 12 including a hard disk drive (HDD), ROM, RAM, etc., and a communication unit 13 including a communication port (not shown) forming an input/output path for various signals or information.
- the communication unit 13is connected to a public communication line 200 such as the Internet or a mobile communication network, and performs various communications with other devices.
- a network interface/modem or the likeis used as the communication unit 13 .
- the control unit 11has a CPU (Central Processing Unit), ROM (Read Only Memory), RAM (Random Access Memory), etc., and loads application programs stored in the ROM/storage unit 12 into the RAM. and execute it, thereby realizing various logical means.
- the reference terminal 1implements code recognition means 111 and reference request means 112 .
- the code recognition means 111is means for recognizing information indicated by a predetermined code CD (FIG. 3) when the camera 16 captures the image of the code CD.
- a QR coderegistered trademark
- the predetermined code CDindicates destination information of the ledger management terminal 2 (such as a URL specifying the same terminal 2).
- the reference request means 112 in FIG. 2transmits a vehicle information reference request to the ledger management terminal 2 when a vehicle information reference request is instructed by the user of the reference terminal 1 .
- the reference request means 112issues a vehicle information reference request to the ledger management terminal 2 specified by the URL. Send.
- the reference request means 112manages the ledger designated by this URL. A vehicle information reference request is sent to the terminal 2 .
- the output unit 15displays the vehicle information on the screen when the vehicle information is provided from the ledger management terminal 2 in response to the vehicle information reference request. More specifically, the output unit 15 displays various screens including a vehicle basic information display screen (FIG. 12) and a vehicle history information display screen (FIG. 13).
- Camera 16images an arbitrary subject.
- the camera 16is used to capture a predetermined code such as a QR code (registered trademark) when requesting the ledger management terminal 2 to refer to vehicle information.
- a QR coderegistered trademark
- the predetermined code CDis engraved on the code display member DSP made of a strong metal material (FIG. 3).
- This code display member DSPis physically rigidly attached to the actual vehicle corresponding to the vehicle information.
- the user of the reference terminal 1refers to the vehicle information about the vehicle, the user holds the camera 16 over the vehicle and takes an image of the predetermined code CD on the code display member attached to the vehicle.
- the code display member DSP made of a circular thin plateis shown, but the code display member DSP may adopt any shape as long as a predetermined code CD stamping surface is secured. is possible.
- the reference terminal 1is a stationary PC (Personal Computer) or the like and it is difficult to directly read the predetermined code CD displayed on the actual vehicle, it is written in the vehicle information block chain 221. It is possible to display the information by specifying the URL of an explorer (browsing website) for checking the vehicle information stored in the vehicle.
- Etherscanis a specific example of an explorer that can check the contents of blockchain records as described above.
- FIG. 4is a block diagram showing the electrical configuration of the ledger management terminal 2 according to this embodiment.
- the ledger management terminal 2includes an input section 24 and an output section 25 .
- the terminal 2includes a control unit 21 including a CPU (central processing unit) that executes arbitrary arithmetic processing, and a storage unit 22 including a hard disk drive (HDD), ROM, RAM, etc. , and a communication unit 23 including a communication port (not shown) forming an input/output path for various signals or information.
- the communication unit 23is connected to a public communication line 200 such as the Internet or a mobile communication network, and performs various communications with other devices.
- the control unit 21has a CPU (Central Processing Unit), ROM (Read Only Memory), RAM (Random Access Memory), etc., and loads application programs stored in the ROM/storage unit 22 into the RAM. and execute it, thereby realizing various logical means.
- CPUCentral Processing Unit
- ROMRead Only Memory
- RAMRandom Access Memory
- the login authentication means 211is means for authenticating the user of the writing terminal 3 who wishes to write (add) vehicle information to the vehicle information block chain 221 (FIG. 5).
- the login authentication means 211registers the user ID (e.g., e-mail address) and password transmitted from the writing terminal 3 as a user.
- User registrationhere means that the login authentication means 211 associates the user ID and password received from each writing terminal 3 and writes them in the user information 222 (FIG. 4).
- the user information 222is information specifying a correspondence relationship between identification information (user ID) unique to each user and an attribute (for example, password) related to the user.
- the information generating means 212is means for generating vehicle information (vehicle basic information FVI and vehicle history information HSI). Vehicle information is stored in vehicle information blocks BL (BL-1 to BL-3 in the example of FIG. 5) belonging to the vehicle information block chain 221.
- FIG. The "vehicle information"is information indicating attributes of each vehicle.
- the information generating means 212generates "vehicle basic information" which is specification information unique to each individual vehicle and whose content does not change even if the vehicle is transferred, used, or repaired.
- This basic vehicle information FVIis information positioned as a ledger.
- a unique "chassis number”is assigned to each vehicle manufactured by an automobile manufacturer. Registration of "vehicle basic information” is executed only once at the time of initial registration. will be done.
- the information generating means 212additionally generates variable vehicle history information HSI that changes according to the transfer/use of the vehicle, based on the contents input from the outside. Note that the information generating means 212 permits writing of vehicle information only to the writing terminal 3 that has succeeded in login authentication.
- the nonce calculation means 213calculates a nonce (Number used once) to be incorporated into the latest vehicle information block BL when adding a new vehicle information block BL.
- the nonce calculation means 213calculates a nonce NC such that the relationship between the latest vehicle information to be added at present and the vehicle information block generated immediately before obtains a hash value HV corresponding to a predetermined calculation result.
- the nonce NCis a sequence of consecutive numbers that is used only once (disposable) when generating the hash value HV.
- a predetermined number of high-order digitsfor example, high-order 3 digits
- the number of upper digits of the hash value HV described abovecan be set to any number of digits.
- the hash generation means 214applies a hash function to the latest generation vehicle information additionally generated by the information generation means 212 . As a result, as shown in FIG. 6, the hash generation means 214 generates a hash value HV of the latest vehicle information to be newly added.
- the means 214stores vehicle information stored in the vehicle information block BL-2 (specifically, vehicle basic information FVI, vehicle history information HSI-1 at the time of initial registration, secondary A hash function is applied to the combination of vehicle history information HSI-2). As a result, the hash value HV-2 stored in the vehicle information block BL-2 shown in FIG. 5 is generated.
- the means 214stores individual vehicle information (a combination of basic vehicle information FVI, vehicle history information HSI-1 at the time of initial registration, and secondary vehicle history information HSI-2) stored in the vehicle information block BL-2.
- a hash functionmay be applied.
- the hash generating means 214when the basic vehicle information FVI is generated, the hash generating means 214 generates a hash value HV-B corresponding to the information FVI on a one-to-one basis.
- the vehicle history information HSI-1 at the time of initial registrationis generated, the means 214 generates a hash value HV-1 corresponding to the information HSI-1 on a one-to-one basis.
- the secondary vehicle history information HSI-2is generated, the means 214 generates a hash value HV-2 corresponding to the information HSI-2 on a one-to-one basis.
- the hash generation means 214generates data connecting the latest vehicle information additionally generated by the information generation means 212, the nonce NC calculated by the nonce calculation means 213, and the vehicle information block generated immediately before the latest.
- a hash functionmay be applied to .
- a hash value(an irregular character string with a fixed number of characters) is generated by arithmetic operation (encryption) of a hash function on arbitrary data.
- a character string (hash value HV) encrypted by a hash functionis irreversible in that the original data before encryption cannot be restored no matter how much the hash value HV is referred to.
- the hash functionplays a role in ensuring the prevention of falsification of vehicle information.
- the block addition means 215collectively includes the vehicle basic information FVI generated at the time of initial registration, all vehicle history information after initial registration including the latest vehicle history information HSI, and the hash value of the latest vehicle history information. and write it to the latest vehicle information block BL.
- the latest vehicle history information HSIwhen the latest vehicle history information HSI is added, the latest vehicle information block BL containing this latest vehicle history information is replaced with the vehicle information (vehicle basic information) stored in the immediately preceding vehicle information block.
- vehicle informationvehicle basic information
- the latest vehicle history informationis added.
- the tertiary vehicle history information HSI-3when the tertiary vehicle history information HSI-3 is generated and the vehicle information block BL-3 including the vehicle history information HSI-3 is added to the vehicle information block chain 221, the block BL In -3, in addition to the vehicle information (FVI, HSI-1, HSI-2) contained in the previous vehicle information block BL-2, the latest third vehicle history information HSI-3 is added.
- the hash value HV and the nonce NCare different values in the vehicle information blocks BL-2 and BL-3.
- the block suitability determination means 216determines whether or not the vehicle information block BL added by another ledger management terminal 2 satisfies the agreement rules in the vehicle management ledger system 100 .
- the ledger management terminal 2-1adds a new vehicle information block BL
- all the remaining ledger management terminals 2determines whether or not the vehicle information block BL added by the ledger management terminal 2-1 conforms to the agreement rule. Any agreement rule may be used for verifying the suitability of the vehicle information block BL.
- the information providing means 217provides vehicle information to the reference terminal 1 that has transmitted the vehicle information reference request.
- Vehicle Basic Information FVI(Fig. 7)
- All historical vehicle history information about vehicles(FIGS. 8(a) and 8(b))
- the latest vehicle information block BLstores the basic vehicle information FVI and all the vehicle history information HSI after the initial registration including the latest vehicle history information.
- FIG. 9is a block diagram showing the electrical configuration of the writing terminal 3 according to this embodiment.
- the configuration of the writing terminal 3is basically the same as those of the terminals 1 and 2 described above, except for the logical means implemented in the control unit 31.
- the login request means 311is means for requesting login authentication to the ledger management terminal 2 in order to log in to the ledger management terminal 2 when writing (adding) vehicle information to the vehicle information block chain 221 .
- the user of the writing terminal 3completes user registration (registration of a user ID and password) with respect to the ledger management terminal 2 in advance.
- the passworduses a character string composed of alphanumeric characters and symbols with a predetermined number of digits or more.
- the user IDmay be an arbitrary character string selected by the user, or an e-mail address used by the user may be substituted for the user ID.
- the login request means 311accepts input of a user ID and password via a login screen (not shown), and transmits a login authentication request to the ledger management terminal 2 together with the user ID and password. Note that when the login authentication is successful, addition of vehicle information by the writing terminal 3 is permitted. In this case, the screen transitions to the vehicle basic information input screen (FIG. 10).
- the vehicle informationserves as evidence of vehicle specifications and history (transfer, use, repair), it must be highly reliable and official. Therefore, it is assumed that users of the writing terminal 3 are dealers who have contracted as a special agent with an automobile manufacturer, and second-hand car dealers. That is, in the vehicle management ledger system 100, individuals cannot add vehicle information. It should be noted that these dealers and used car dealers are not limited to those in Japan, and they may be outside Japan. When a company outside Japan writes vehicle information, the vehicle basic information FVI and vehicle history information HSI can be written in the language of the country where the company is located.
- the information writing means 312requests writing of vehicle information (vehicle basic information FVI or vehicle history information HSI).
- the writing terminal 3displays a login screen (not shown) in response to an input specifying the URL of the ledger management terminal 2 by the user.
- the terminal 3transmits a login authentication request to the ledger management terminal 2 together with the user ID and password input by the user through the login screen.
- the case where the writing terminal 3 accesses the ledger management terminal 2-1 and requests login authenticationis taken as an example.
- the ledger management terminal 2-1compares the user ID and password transmitted from the same terminal 3 with the user information 222 (FIG. 4) to perform login authentication. If the login authentication succeeds, the ledger management terminal 2-1 permits the writing terminal 3 to write the vehicle information in step S12 of FIG.
- step S12when vehicle information is registered for the first time, when writing of vehicle information is permitted (step S12), the writing terminal 3 displays the vehicle basic information input screen (FIG. 10). transitions. Also, when the vehicle information is registered for the first time, in order to input the vehicle history information HSI-1 (Fig. 8(a)) for the initial registration, click the button arranged in the vehicle basic information input screen (Fig. 10). By pressing the button, the display is switched to the vehicle history information input screen (FIG. 11).
- step S12 of FIG. 11When entering the second and subsequent vehicle history information HSI, if the writing of vehicle information is permitted, the screen directly transitions to the vehicle history information input screen (FIG. 11).
- step S13 of FIG. 14the writing terminal 3 requests the ledger management terminal 2 to write vehicle information (vehicle basic information FVI or vehicle history information HSI).
- vehicle basic information FVIis input by the user via the vehicle basic information input screen (FIG. 10)
- vehicle history information HSIis input by the user via the vehicle history information input screen (FIG. 11).
- the person who inputs the basic vehicle information FVI and the vehicle history information HSIis a dealer or a used car dealer.
- step S14 of FIG. 14the ledger management terminal 2 generates basic vehicle information FVI or vehicle history information HSI based on the information input at the writing terminal 3.
- FIG. 14the ledger management terminal 2 generates basic vehicle information FVI or vehicle history information HSI based on the information input at the writing terminal 3.
- step S15the terminal 2 calculates a nonce NC.
- the ledger management terminal 2determines that the hash value HV generated from the latest vehicle information to be added and the vehicle information block BL immediately before the latest has a predetermined upper digit number (for example, upper 3 digits). Calculate a nonce NC that is all "0".
- the ledger management terminal 2When the nonce NC that satisfies the above calculation result is calculated, the ledger management terminal 2 generates a hash value (step S16). Furthermore, the ledger management terminal 2 includes (1) basic vehicle information FVI generated at the time of initial registration, (2) all vehicle history information HSI after the initial registration including the latest vehicle history information HSI, and (3) relevant vehicle history information HSI. Hash values HV of the latest vehicle history information are collectively additionally written in the latest vehicle information block BL (step S17). The latest vehicle information block BL added is associated with the existing vehicle information block chain 221 via the hash value HV.
- step S18when it is determined that the new vehicle information block BL is appropriate, all the ledger management terminals 2-2 to 2-3 except for the terminal 2-1 store the vehicle information block BL in their own memory. It is added to the vehicle information block chain 221 stored in the part 2 (step S19). Thus, a series of operations when the writing terminal 3 writes the vehicle information is completed.
- the user of the reference terminal 1holds up the camera 16 mounted on the terminal 1 and picks up an image of a predetermined code CD on the code display member DSP attached to the vehicle. Then, the reference terminal 1 reads the URL indicated by the predetermined code CD photographed by the camera 16, and transmits a vehicle information reference request to the ledger management terminal 2 specified by the URL (FIG. 15, step S21).
- the reference terminal 1is a stationary PC or the like, and the predetermined code CD attached to the actual vehicle cannot be imaged by the camera. Therefore, in this example, even when the URL of an explorer (browsing website) for checking vehicle information is input by the user through the input unit 14, the reference terminal 1 manages the ledger designated by the URL. It is configured to be able to transmit a vehicle information reference request to the terminal 2 .
- the ledger management terminal 2provides vehicle information (vehicle basic information FVI or vehicle history information HSI) to the reference terminal 1 that has transmitted the vehicle information reference request (step S22).
- vehicle informationvehicle basic information FVI or vehicle history information HSI
- the reference terminal 1displays a vehicle basic information display screen (FIG. 12)/vehicle history information display screen (FIG. 13) on the output unit 15 (liquid crystal display or the like) (step S23).
- the vehicle basic information display screen (FIG. 12) and the vehicle history information display screen (FIG. 13)are respectively provided with buttons for switching between the display screens. can display the screen.
- all vehicle information(vehicle basic information FVI and , cumulative all-vehicle history information HSI from the time of initial registration (FIG. 5). Therefore, when the user refers to the vehicle information by using the reference terminal 1, the user can access all the vehicle information (basic vehicle information FVI and cumulative all vehicle history information HSI from the time of initial registration) related to a specific vehicle. can refer to. Therefore, even if you do not have a vehicle inspection certificate at hand, or if the vehicle is distributed in a country without a vehicle inspection system, you can refer to the vehicle information (mileage without falsification, transfer history, etc.) related to the desired vehicle. becomes.
- the users of the writing terminal 3 for writing vehicle informationare limited to dealers and used car dealers, and writing by individuals is prohibited. Therefore, the vehicle information is guaranteed to be highly reliable and authentic as evidence of vehicle specifications and history (transfer, use, repair).
- the code display member DSPwhich is made of a robust metal material and stamped with a predetermined code CD, is attached to the actual vehicle corresponding to the vehicle information by riveting, welding, or the like. It is firmly attached physically by the method. Therefore, it is difficult to remove the code CD from the actual vehicle in order to access the vehicle information, and the traceability of the vehicle information regarding the vehicle is guaranteed even in the actual vehicle.
- the reference terminal 1not only stationary/notebook PCs but also portable multifunctional electronic devices such as smart phones, tablet terminals, and wristwatch terminals can be adopted. Displaying vehicle information puts a considerable processing load on the CPU, but the processing performance of smartphones and tablet terminals is improving rapidly, and when executing vehicle information display processing A comfortable operating speed can also be secured.
- the camera 16is used to read a predetermined code CD (for example, a QR code) from a code display member DSP attached to an actual vehicle. ), and while directly checking the actual vehicle, you can refer to the vehicle's specifications and past history.
- a predetermined code CDfor example, a QR code
- a travel distance transmission mechanism DSis installed in the vehicle VCL related to vehicle information.
- the mileage transmission mechanism DSis configured to be able to transmit and receive data to and from the ledger management terminal 2 by wireless communication via the public communication line 200 . Further, the transmission mechanism DS transmits the travel distance of the vehicle to the ledger management terminal 2 by wireless communication at a predetermined timing.
- a specific example of the predetermined timingmay be every month or every year, or every time the running distance increases by a predetermined distance (for example, 1000 km).
- the information generation means 212 (FIG. 4) of the ledger management terminal 2receives the mileage of the vehicle transmitted from the vehicle VCL at a predetermined timing, it automatically generates the latest vehicle history information HSI describing the mileage. do. Then, in the ledger management terminal 2, the latest vehicle information block BL including this vehicle history information HSI is added.
- the mileage of the vehicle VCLis sent to the ledger management terminal 2 at a predetermined timing, and the terminal 2 generates the latest vehicle history information HSI in which the mileage is described.
- the terminal 2By doing so, it is possible to record the history of travel distances without waiting for an opportunity to transfer (sales contract) the vehicle VCL. Therefore, even if a third party physically tampered with the display of the odometer of the vehicle VCL, the fact of tampering can be detected by comparing with the vehicle history information HSI in the vehicle information block BL, and the odometer can be illegally operated. It is possible to increase the robustness against
Landscapes
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Accounting & Taxation (AREA)
- Finance (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、ブロックチェーンにより車両情報を管理する車両管理台帳システムに関する。The present invention relates to a vehicle management ledger system that manages vehicle information using blockchain.
近年、日本から海外むけに中古車の輸出が盛んに行われている。
中古車輸出業協同組合の統計によれば、2018年の中古車の輸出台数は132万6579台となっている。
とりわけ、アフリカ諸国むけの中古車輸出台数は、2016年~2018年の実績として、1年ごとに5万台~6万台程度増加している。In recent years, the export of used cars from Japan to overseas markets has been flourishing.
According to statistics from the used car exporters cooperative, the number of used cars exported in 2018 was 1,326,579.
In particular, the number of used cars exported to African countries increased by 50,000 to 60,000 units per year from 2016 to 2018.
ところで、日本国内では、自動車検査登録(いわゆる車検)が義務づけられている。
車検制度では、自動車や自動二輪車(排気量250cc超過のもの)について、保安基準の適否を確認すべく所定期間ごとに国土交通省が検査を行い、また自動車の所有権を公証するための情報が登録される。
このような車検制度を設けている国は、世界的に見ると圧倒的に少数派であり、日本・ドイツ・イギリス・イタリア・韓国・台湾など数えるほどしかないのが実情である。By the way, in Japan, automobile inspection registration (so-called vehicle inspection) is obligatory.
Under the vehicle inspection system, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism inspects automobiles and motorcycles (with an engine displacement of over 250cc) at regular intervals to confirm whether they comply with safety standards. be registered.
Countries that have such a vehicle inspection system are overwhelmingly minority in the world, and the reality is that there are only a few such as Japan, Germany, England, Italy, South Korea, and Taiwan.
日本国内にとどまっている間は、車検制度のもと、車検証の記載を基に、車両それ自体の固有の属性情報(例えば、メーカ・型式・車台番号・排気量・走行距離など)を特定することが可能である。
しかしながら、日本国内の中古車がいざ海外に輸出されてしまうと、その際に車検証が破棄されてしまうことも多く、車両の使用状態(たとえば、走行距離など)を正確に特定できない車両も多々存在する。
車検証が破棄された車両の価値は、その外観と走行距離のみを頼りに評価されることが多い。
このような使用状態を正確に特定できる情報がない場合、販売者により走行距離計の巻戻し(走行距離の改ざん)がなされていても、そのような事実を検出できず、思いがけない事故や不具合を誘発している。While staying in Japan, under the vehicle inspection system, based on the description on the vehicle inspection certificate, the unique attribute information of the vehicle itself (for example, manufacturer, model, chassis number, engine displacement, mileage, etc.) is specified. It is possible to
However, when a used car made in Japan is exported overseas, the vehicle inspection certificate is often destroyed at that time, and there are many vehicles that cannot accurately identify the vehicle usage condition (such as mileage, etc.). exist.
The value of a vehicle whose vehicle inspection certificate has been destroyed is often evaluated solely based on its appearance and mileage.
If there is no information that can accurately identify such usage conditions, even if the odometer has been rewound (tampered with the mileage) by the seller, such a fact cannot be detected, resulting in an unexpected accident or malfunction. is induced.
ところで、昨今では「ブロックチェーン」という言葉が使われはじめて久しい。
ブロックチェーンとは、追加データの集合体を含んでなるブロックを一定時間ごとに追加生成し、これらのブロックをコンピュータ同士で検証し合いながら正しい記録をチェーン(鎖)のように連結して保管する分散型データベースのことをいう。
ブロックチェーンを使用すると情報の改ざん防止が極めて困難であるため、非常に信頼性の高いシステム環境下で資産取引を行うことができる。
ブロックチェーンの代表的な導入例としては、仮想通貨の発行・流通が挙げられる。By the way, the term “blockchain” has been used for a long time now.
A block chain is a system in which blocks containing a collection of additional data are additionally generated at regular intervals, and these blocks are verified by computers, and the correct records are connected and stored like a chain. A distributed database.
Blockchain makes it extremely difficult to prevent tampering with information, so asset transactions can be conducted in a highly reliable system environment.
A representative example of the introduction of blockchain is the issuance and distribution of virtual currency.
このように、改ざんを防ぎつつ、資産的価値を有する取引対象の情報を安全に保持できるブロックチェーンの性質に着目し、ブロックチェーンを用いて車両に関する情報を保持する技術が提案されている(例えば、特許文献1~3参照)。In this way, focusing on the properties of blockchains that can safely store information on transaction objects that have asset value while preventing tampering, technology has been proposed that uses blockchains to store information about vehicles (for example, , see
特許文献1の技術によれば、車両にまつわる異なる情報項目(たとえば、車種情報と地域情報)について、各情報項目ごとのブロックチェーン(たとえば、車種情報ブロックチェーンと地域情報ブロックチェーン)を個々に設けて、車両に関する情報を管理する(特許文献1・第17段落)。
なお、同文献1の技術では、同一個体の車両にまつわる複数のブロック(たとえば、ある固有の車両に関する、車種情報ブロックと地域情報ブロック)は対応付けされている(特許文献1・第20段落)。According to the technology of
In the technique of
一般に、自動車は、中古車市場において流通する売買機会の多い動産である。
このように売買が行われた場合、車両自体に関する情報(例えば、メーカ・型式・車台番号・排気量・走行距離など)は変わらないものの、車両に関わる関係者(たとえば、所有者名)や場所(保管場所・使用場所)などの情報は変更される。In general, automobiles are personal properties that are often traded in the used car market.
When a sale is made in this way, information about the vehicle itself (such as the manufacturer, model, chassis number, engine displacement, mileage, etc.) does not change, but the people involved in the vehicle (such as the name of the owner) and the location of the vehicle do not change. Information such as (storage location/usage location) is changed.
特許文献1の技術では、情報の改ざんに対する安全性は高まるものの、車両にまつわる1つ1つの情報項目についてそれぞれブロックチェーンを用意して管理する必要があり、情報管理が複雑となってしまう。
とりわけ、車両が売買された場合、車両に関わる関係者(所有者・販売業者)や場所(保管場所・使用場所)などの情報が変更されるため、同文献1の技術により、譲渡に関連する情報項目1つ1つを個々のブロックチェーンにより管理すると、管理作業の負担が増大してしまうという問題がある。Although the technology of
In particular, when a vehicle is bought and sold, information related to the vehicle (owner/seller) and location (storage location/use location) are changed. If each information item is managed by an individual block chain, there is a problem that the burden of management work increases.
特許文献3の技術によれば、自動車が点々と流通した場合、譲渡された際の自動車の状態と、最新のハッシュ情報とに基づいて、ハッシュ情報が生成される(特許文献3・第38段落)。
ハッシュ情報と、それに対応する資産情報(車種・走行距離・オーナー・修復歴など)は、関連付けてデータベースに保存される(同文献3・第39段落)。
ハッシュ情報は、トレース可能な情報としてブロックチェーン上に残り続けることにより、改ざんできないため、情報の安全性や堅牢性が担保される(同文献3・第43段落)。According to the technique of
Hash information and corresponding asset information (vehicle type, mileage, owner, repair history, etc.) are associated and stored in a database (Ref. 3, paragraph 39).
Hash information remains on the blockchain as traceable information and cannot be tampered with, ensuring the safety and robustness of the information (Ref. 3, paragraph 43).
なお、一般的に、車両情報には、(1)車両の譲渡・使用・修理といった経歴に付随して変わっていく情報項目(車両経歴情報)と、(2)個々の車両ごとに固有の永続的な仕様に関する情報項目(車両基本情報)の2種類がある。
車両の譲渡・使用・修理に伴って変化する「車両経歴情報」の例としては、登録更新日、車両所有者の氏名・住所、使用の本拠位置、有効期間の満了する日、登録時の走行距離、修理履歴などが挙げられる。In general, vehicle information includes (1) information items (vehicle history information) that change along with the history of the vehicle, such as transfer, use, and repair, and (2) permanent information unique to each vehicle. There are two types of information items (vehicle basic information) related to specific specifications.
Examples of "vehicle history information" that change with the transfer, use, or repair of a vehicle include the date of registration renewal, the name and address of the vehicle owner, the base location of use, the expiration date of the validity period, and the driving at the time of registration. distance, repair history, and the like.
一方、車両の譲渡・使用がなされても変化しない「車両基本情報」の例としては、自動車登録番号、登録年月日や交付年月日、初度登録年月、自動車の種類、用途、自家用又は事業の別、車体の形状、車名、乗車定員、最大積載量、車両重量、車両総重量、メーカにより付与される車台番号、車両の長さ・幅・高さ、前前軸重・前後軸重、型式、原動機の型式、総排気量又は定格出力、燃料の種類といったものがある。
したがって、車両情報をブロックチェーン形態で管理する場合、車両の譲渡・使用に左右されない車両基本情報は初回登録しておく一方、その後、譲渡・使用・修理に伴って様々な情報項目に変更があった場合、変更された車両経歴情報を生成し、ブロックチェーンに追加してやると効率的に管理できると考えられる。
しかしながら、特許文献3の技術では、このような子細な情報項目に着目して、効率的に情報を管理するところまでは検討がなされていない。On the other hand, examples of "vehicle basic information" that does not change even if the vehicle is transferred or used include the vehicle registration number, registration date or issuance date, first registration date, vehicle type, purpose, private use or By business, body shape, vehicle name, passenger capacity, maximum load, vehicle weight, gross vehicle weight, chassis number given by the manufacturer, vehicle length, width, height, front front axle weight, front and rear axle weight These include weight, model, prime mover model, total displacement or rated power, and type of fuel.
Therefore, when managing vehicle information in the form of a blockchain, while basic vehicle information that is not affected by the transfer or use of the vehicle is registered for the first time, various information items may change as a result of transfer, use, or repair. In that case, it is thought that it can be efficiently managed by generating changed vehicle history information and adding it to the blockchain.
However, in the technique of
本発明は上記の問題に鑑みてなされたものであり、車両情報をブロックチェーン形態で管理する際、車両情報の管理効率を向上させるとともに初回登録時から累積された全車両情報を参照可能にすることを目的とする。The present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and when managing vehicle information in the form of a blockchain, it is possible to improve the management efficiency of vehicle information and to refer to all vehicle information accumulated from the time of initial registration. for the purpose.
〔第1発明〕
そこで、上記の課題を解決するために、本願の第1発明に係る車両管理台帳システムは、
個々の車両情報ブロックがハッシュ値により連関された車両情報ブロックチェーンを、ピアツーピア相互接続された複数の台帳管理端末が各々保持することで、車両情報を分散的に管理する車両管理台帳システムであって、
個々のユーザが各々所持する端末であって、前記車両情報ブロックに格納されている車両情報の参照を前記台帳管理端末に要求する参照端末と、
車両の販売者が各々所持する端末であって、車両情報の新規追加を前記台帳管理端末に要求する書込端末と、
公衆通信回線を介して参照端末および書込端末と通信可能な端末であって、書込端末からの要求に応じて車両情報を書込むとともに、参照端末からの要求に応じて車両情報を提供する前記台帳管理端末と、
を具備してなり、
個々の参照端末は各々、
当該参照端末のユーザによる車両情報参照要求の指示を受付けると、車両情報参照要求を台帳管理端末に送信する参照要求手段と、
前記車両情報参照要求に応じて車両情報が台帳管理端末から提供されたときに、同車両情報を画面表示する出力部と、
を有し、
個々の書込端末は各々、
車両の販売者による車両情報書込要求の指示を受付けると、前記台帳管理端末に対し、車両情報の書込を要求する情報追加要求手段、を有し、
前記台帳管理端末は、
前記書込端末からの車両情報書込要求に応じて、車両に固有の永続的な仕様情報である車両基本情報を初回登録時にのみ生成するとともに、初回登録以後の車両の譲渡・使用・修理その他の経歴を示す車両経歴情報を継続的に追加生成する情報生成手段と、
前記情報生成手段が生成した最新の車両経歴情報にハッシュ関数を適用することで、当該最新の車両経歴情報のハッシュ値を生成するハッシュ生成手段と、
初回登録時に生成された車両基本情報と、最新の車両経歴情報を含む初回登録以後のすべての車両経歴情報と、当該最新の車両経歴情報のハッシュ値とを一括して、最新の車両情報ブロックに書込むブロック追加手段と、
を有し、
複数の台帳管理端末の内いずれか1台の台帳管理端末において、最新の車両情報ブロックが書込まれたときに、
当該車両情報を追加した台帳管理端末以外のすべての台帳管理端末は、最新の車両情報ブロックが適格であると判定したときに、自己の記憶部に、当該車両情報を書込み、
参照端末から車両情報の参照が要求された場合、
車両情報ブロックに格納されている車両情報を特定して、当該参照端末に同特定した車両情報を提供する構成とした。[First invention]
Therefore, in order to solve the above problems, the vehicle management ledger system according to the first invention of the present application includes:
A vehicle management ledger system that manages vehicle information in a distributed manner by having each of a plurality of ledger management terminals interconnected peer-to-peer hold a vehicle information block chain in which individual vehicle information blocks are linked by hash values. ,
a reference terminal, which is a terminal possessed by each individual user and which requests the ledger management terminal to refer to the vehicle information stored in the vehicle information block;
a writing terminal which is owned by each vehicle seller and requests the ledger management terminal to add new vehicle information;
A terminal that can communicate with a reference terminal and a writing terminal via a public communication line, writes vehicle information in response to a request from the writing terminal, and provides vehicle information in response to a request from the reference terminal. the ledger management terminal;
and
Each individual reference terminal is
reference request means for transmitting a vehicle information reference request to a ledger management terminal when an instruction for a vehicle information reference request from a user of the reference terminal is received;
an output unit that displays the vehicle information on a screen when the vehicle information is provided from the ledger management terminal in response to the vehicle information reference request;
has
Each individual writing terminal
an information addition requesting means for requesting the ledger management terminal to write vehicle information when an instruction to request vehicle information writing from a vehicle seller is received;
The ledger management terminal
In response to a vehicle information write request from the write terminal, vehicle basic information, which is permanent specification information unique to the vehicle, is generated only at the time of initial registration, and the vehicle is transferred, used, repaired, etc. after the initial registration. information generating means for continuously additionally generating vehicle history information indicating the history of
Hash generation means for generating a hash value of the latest vehicle history information by applying a hash function to the latest vehicle history information generated by the information generation means;
The basic vehicle information generated at the time of initial registration, all vehicle history information after the initial registration including the latest vehicle history information, and the hash value of the latest vehicle history information are collectively stored in the latest vehicle information block. writing block adding means;
has
When the latest vehicle information block is written in one of the ledger management terminals among the plurality of ledger management terminals,
All the ledger management terminals other than the ledger management terminal that added the vehicle information write the vehicle information in their own storage unit when determining that the latest vehicle information block is qualified,
If the reference terminal requests to refer to vehicle information,
The vehicle information stored in the vehicle information block is specified, and the specified vehicle information is provided to the reference terminal.
第1発明に係る車両管理台帳システムによれば、車両情報がブロックチェーン形態(車両情報ブロックがハッシュ値により連関されたデータ構造)で構成されている。
そして、車両情報ブロックチェーン221(ブロックチェーン形態の車両情報)が、複数台の台帳管理端末2にそれぞれ保持されている(図4参照)。
そのため、車検証などの紙媒体で管理されている情報が失われてしまった場合でも、車両情報を、改ざんが非常に困難で安全な環境に保管しておくことができる。
図5に示す車両情報ブロックチェーン221に組込まれている、ある1つの車両情報ブロックBLを改ざんする場合、この生成された車両情報ブロックBL以後に追加生成されるすべての車両情報ブロックBL(世界各国に点在する台帳管理端末2に分散管理されている全車両情報ブロックBL)を書換えることでしか改ざんできないからである。
なお、車両管理台帳システム100(図1)においては、各台帳管理端末2-1~2-3は、互いに同一機能を有するとともに相互に直接通信を行うピアツーピア方式で通信接続されている。According to the vehicle management ledger system according to the first invention, vehicle information is configured in a block chain format (a data structure in which vehicle information blocks are linked by hash values).
A vehicle information block chain 221 (vehicle information in block chain form) is held in each of the plurality of ledger management terminals 2 (see FIG. 4).
Therefore, even if information managed by paper media such as automobile inspection certificates is lost, vehicle information can be stored in a safe environment where falsification is extremely difficult.
If one vehicle information block BL incorporated in the vehicle
In the vehicle management ledger system 100 (FIG. 1), the ledger terminals 2-1 to 2-3 have the same functions and are connected in a peer-to-peer manner for direct mutual communication.
また、第1発明によれば、車両情報を、(1)車両の譲渡・使用に伴って変化する「車両経歴情報」と、(2)車両それ自体に固有の仕様情報である「車両基本情報」にあらかじめ分別しておく。
そして、車両の譲渡や使用がなされるに従って、これら譲渡・使用(走行距離の増大を含む)・修理に伴って変化する車両経歴情報HSI(図8)を更新し、その更新内容を追加した車両情報ブロックBLを生成して、車両情報ブロックチェーン221に追加してやる(図5)。
これにより、車両情報ブロックチェーン221において、各車両1台1台について、累積的に車両情報を蓄えていくことができる。In addition, according to the first invention, the vehicle information includes (1) "vehicle history information" that changes with the transfer and use of the vehicle, and (2) "vehicle basic information" that is specification information unique to the vehicle itself. ” in advance.
Then, as the vehicle is transferred or used, the vehicle history information HSI (FIG. 8) that changes with the transfer, use (including an increase in mileage), or repair is updated, and the vehicle to which the updated contents are added. An information block BL is generated and added to the vehicle information block chain 221 (Fig. 5).
As a result, in the vehicle
一般に、通常のブロックチェーンでは、データのまとまりであるブロックを生成する際、追加が必要となったデータ(例えば、取引データなど)のみが追加される。
しかしながら、本願発明においては、1台1台の各車両別に生成される車両情報ブロックBL内に、常に、すべての車両情報(車両基本情報FVIと、初回登録時から記録された累積的な全車両経歴情報HSI)が納められている(図5参照)。
そのため、参照端末1によりユーザが車両情報を参照した際、当該ユーザは、ある特定の車両にまつわるすべての車両情報(車両基本情報FVIと、初回登録時からの累積的な全車両経歴情報HSI)を参照できる。
このような車両情報提供機能があれば、車検制度を持たない多くの国々においても、日本国内の車検証に相当する情報管理スキームを確立できる。Generally, in a normal blockchain, only data that needs to be added (for example, transaction data) is added when a block that is a collection of data is generated.
However, in the present invention, in the vehicle information block BL generated for each vehicle, all vehicle information (vehicle basic information FVI and cumulative all vehicle information recorded from the time of initial registration) history information HSI) is stored (see FIG. 5).
Therefore, when the user refers to the vehicle information by using the
With such a vehicle information provision function, even in many countries that do not have vehicle inspection systems, it is possible to establish an information management scheme equivalent to the vehicle inspection system in Japan.
〔第2発明〕
本願の第2発明に係る車両管理台帳システムは、第1発明に係る車両管理台帳システムであって、
前記参照端末は、任意の被写体を撮像するカメラを備え、
車両情報の参照を前記台帳管理端末に要求する際、前記カメラにより所定のコードを読取ることにより、車両情報参照要求を台帳管理端末に送信する構成とした。[Second Invention]
A vehicle management ledger system according to a second invention of the present application is a vehicle management ledger system according to the first invention,
The reference terminal comprises a camera for imaging any subject,
When requesting the ledger management terminal to refer to the vehicle information, the vehicle information reference request is transmitted to the ledger management terminal by reading a predetermined code with the camera.
昨今では、携帯電話・スマートフォン・タブレット端末などの携帯型電子装置の普及が著しく進んでいる。
このような携帯型電子装置の多くは、QR(Quick Response)コード(登録商標)などを認識可能なカメラ機能を備えている。
第2発明によれば、車両情報の参照を希望するユーザは、自己が使用する参照端末1に搭載されたカメラ16により、QRコード(登録商標)その他の所定のコードCD(図3)を読取ることで、車両台帳参照要求を台帳管理端末2あてに送信する。
そして、車両台帳参照要求に応じて台帳管理端末2から提供された車両情報を、画面表示する。
なお、本願の車両管理台帳システム100は「パブリックブロックチェーンで稼働」させることが可能であるため、広くあまねく、不特定多数の任意のユーザが自由に、車両管理台帳システム100における車両情報を参照できるようになっている。
そのため、信頼性の高い車両情報を社会公開することで、実車両の品質に対する信頼を獲得することができ、また、情報の改ざんを恐れることなく世間に対して車両情報を安全に公開することもできる。Recently, the spread of portable electronic devices such as mobile phones, smart phones, and tablet terminals has progressed remarkably.
Many of such portable electronic devices have a camera function capable of recognizing a QR (Quick Response) code (registered trademark) or the like.
According to the second invention, a user who wishes to refer to vehicle information reads a QR code (registered trademark) or other predetermined code CD (FIG. 3) with the
Then, the vehicle information provided from the
In addition, since the vehicle
Therefore, by disclosing highly reliable vehicle information to the public, it is possible to gain trust in the quality of actual vehicles, and to safely disclose vehicle information to the public without fear of falsification. can.
〔第3発明〕
本願の第3発明に係る車両管理台帳システムは、第2発明に係る車両管理台帳システムであって、
車両情報の参照対象となる実際の車両の所定箇所に、前記所定のコードが刻印されたコード表示部材が装着されており、
前記参照端末は、
前記コード表示部材に刻印されている所定のコードを、カメラで読取ることにより、車両台帳参照要求を台帳管理端末に送信する構成とした。[Third Invention]
A vehicle management ledger system according to a third invention of the present application is a vehicle management ledger system according to the second invention,
A code display member having the predetermined code stamped thereon is attached to a predetermined location of an actual vehicle to be referenced for vehicle information,
The reference terminal is
A vehicle ledger reference request is transmitted to a ledger management terminal by reading a predetermined code stamped on the code display member with a camera.
第3発明によれば、車両情報の参照先(車両情報が保持されている台帳管理端末2)を指定するための所定のコードCD(QRコード(登録商標)など)が、金属材料などからなるコード表示部材DSPに立体的に刻印されている(図3)。
そして、このコード表示部材DSPが、車両情報に対応する実際の車両(図示略)に物理的に取付けられている。
QRコード(登録商標)等からなる所定のコードCDが印刷されたシールを車検証に貼付するとともに、当該コードCDが刻印されたコード表示部材DSPを車体の任意の箇所(例えば、ボンネット裏面・エンジンルーム・ドアの内側など)に物理的に強固に取付けておくことで、この車両に関する車両情報へのアクセスが保証され、ひいては車両のエビデンス確保も図られる。
なお、コード表示部材DSPの取付方法としては、リベット止めや溶接などを採用できる。According to the third invention, the predetermined code CD (QR code (registered trademark), etc.) for designating the reference destination of the vehicle information (the
This code display member DSP is physically attached to an actual vehicle (not shown) corresponding to the vehicle information.
A sticker on which a predetermined code CD such as a QR code (registered trademark) is printed is attached to the vehicle inspection certificate, and the code display member DSP with the code CD engraved is placed anywhere on the vehicle body (for example, the back of the hood, engine, etc.) By physically firmly attaching it to the inside of the room door, etc., access to vehicle information about this vehicle is guaranteed, and vehicle evidence is secured.
As a method for attaching the code display member DSP, riveting, welding, or the like can be employed.
なお、参照端末1のユーザは、当該車両に関する車両情報を参照する場合、カメラ機能を備える同端末1をかざして、同車両に取付けられたコード表示部材DSP上の所定のコードCDを撮像する。
この撮像動作により、車両情報参照要求が参照端末1から台帳管理端末2あてに送信され、ひいては参照端末1上に車両情報が表示される。When referring to vehicle information about the vehicle, the user of the
By this imaging operation, a vehicle information reference request is transmitted from the
〔第4発明〕
また、上記の課題を解決するために、本願の第4発明に係る車両管理台帳システムは、第1~第3発明に係る車両管理台帳システムであって、
前記車両情報に係る車両は、
前記台帳管理端末に対して、無線通信により、所定のタイミングで車両の走行距離を送信する走行距離送信機構、を備え、
前記台帳管理端末の情報生成手段は、
所定のタイミングにおいて前記車両から送信された当該車両の走行距離を受信すると、同走行距離を記載した最新の車両経歴情報を自動生成する構成とした。[Fourth invention]
In order to solve the above problems, a vehicle management ledger system according to a fourth invention of the present application is a vehicle management ledger system according to the first to third inventions,
The vehicle related to the vehicle information is
A mileage transmission mechanism that transmits the mileage of the vehicle at a predetermined timing to the ledger management terminal by wireless communication,
The information generating means of the ledger management terminal is
When the mileage of the vehicle transmitted from the vehicle is received at a predetermined timing, the latest vehicle history information describing the mileage is automatically generated.
第4発明によれば、車両情報に対応する車両VCLに走行距離送信機構DSを搭載しておき、所定のタイミング(定期的、または、走行距離が所定距離に到達するごと)で当該車両VCLの走行距離を、無線通信により台帳管理端末2あてに送信する(図16参照)。
そして、台帳管理端末2において、当該送られた走行距離が記載された最新の車両経歴情報HSIを生成し、この車両経歴情報を含んだ最新の車両情報ブロックBLを追加する。
このようにすることにより、車両VCLの譲渡(売買契約)の機会を待たずとも、走行距離の履歴を記録として残すことができる。
そのため、たとえ第三者が車両の走行距離計の表示を物理的に改ざんしたとしても、車両情報ブロックBLの車両経歴情報と照合することにより改ざん事実の検出でき、走行距離計の物理的改ざんに対する堅牢性を高めることができる。
According to the fourth invention, the vehicle VCL corresponding to the vehicle information is equipped with the mileage transmission mechanism DS, and at a predetermined timing (regularly or each time the mileage reaches a predetermined distance), the vehicle VCL is transmitted. The distance traveled is transmitted to the
Then, in the
By doing so, the history of travel distance can be left as a record without waiting for an opportunity to transfer (sales contract) the vehicle VCL.
Therefore, even if a third party physically tampered with the display of the odometer of the vehicle, the fact of tampering can be detected by collating it with the vehicle history information in the vehicle information block BL. Robustness can be improved.
以下、図1乃至図16を参照して、本発明の車両管理台帳システムについて説明する。
[実施形態]
本発明の実施形態1は、個々の車両情報ブロックBLがハッシュ値により連関された車両情報ブロックチェーン221を、ピアツーピア相互接続された複数の台帳管理端末2が各々保持することで、車両情報を分散的に管理する車両管理台帳システム100を構成した例である。
なお、本説明例では、上述した「車両情報ブロック」1つは、車検証1枚あたりに相当する情報を有しており、デジタル車検証ともいうべきものである。A vehicle management ledger system according to the present invention will be described below with reference to FIGS. 1 to 16. FIG.
[Embodiment]
In this example of explanation, one "vehicle information block" described above has information corresponding to one vehicle inspection certificate, and should be called a digital vehicle inspection certificate.
図1は、実施形態に係る車両管理台帳システム100の全体構成を示すブロック図である。
本例の車両管理台帳システム100は、図1に示すように、参照端末1(同図1の例では1-1・1-2)と、台帳管理端末2(同図1の例では2-1~2-3)と、管理端末3(同図1の例では3-1・3-2)とを、インターネットや移動体通信網等の公衆通信回線200を介して通信可能な状態で接続したシステムである。FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the overall configuration of a vehicle
The vehicle
参照端末1・台帳管理端末2・管理端末3の各台数は、任意でよい。
なお、図1においては、便宜上、台帳管理端末2として台帳管理端末2-1~2-3の3台のみを示しているが、本システム100を構成する実際の台帳管理端末2は世界規模で点在しており、その台数は数万台にも及ぶものである。
そして、これら非常に多数の台帳管理端末2が、生成された車両情報ブロックBLすべてについて、相互に承認(車両情報ブロックBL追加の適否判定)・同期・保存を行っている。The numbers of
In FIG. 1, for the sake of convenience, only three ledger management terminals 2-1 to 2-3 are shown as the
These extremely large numbers of
参照端末1は、個々のユーザ(車両情報の参照者)が各々所持する端末である。
同端末1は、車両情報の参照を台帳管理端末2に要求する。The
The terminal 1 requests the
台帳管理端末2は、公衆通信回線200を介して、個々の参照端末1と通信可能な端末である。
これらの台帳管理端末2は、ピアツーピア相互接続されている。
台帳管理端末2は各々、個々の車両情報ブロックBLがハッシュ値により相互に連関された車両情報ブロックチェーン221を保持している。The
These
Each
この車両情報ブロックチェーン221は、実際上、個々の車両1台に対して1対1で対応するように生成されるわけではなく、非常に多数の車両についてそれぞれ作成された車両情報ブロックBLが連関されることにより、ひとまとまりの車両情報ブロックチェーン221を構成している。This vehicle
本例における車両情報ブロックBLには、車両情報(車両基本情報FVIおよび車両経歴情報HSI)と、車両情報をハッシュ関数により暗号化することで生成されるハッシュ値HVと、ナンスNCとが格納されている(図5)。
なお、車両基本情報FVI(図7)ならびに車両経歴情報HSI(図8(a)・図8(b)参照)は、文字情報だけに限定されるものでなく、車両や当該車両に関連する物品(例えば、車検証)の画像を含むものでもよい。
本例においては、ハッシュ値HVは、車両基本情報FVIないしは車両経歴情報HSIが追加されたとき(つまり、これらの情報FVI・HSIが車両情報ブロックチェーン221上にアップロードされたとき)に、常時追加される。
図6の例では「車両基本情報HVIが登録」された時点で、当該情報HVIにハッシュ関数を適用することでハッシュ値HV-Bが発行される。
このハッシュ値HV-Bは、図5のように、車両情報ブロックBL-1に格納される。
また「車両経歴情報HSIが登録または追加」された時点で、登録ないしは追加されたHSIにハッシュ関数を適用したハッシュ値が発行され、その後、情報が追加されるごとにハッシュは発行される。
同図6の例では、初回登録時の車両経歴情報HSI-1が登録(車両情報ブロックチェーン221上へのアップロード)された際、同情報HSI-1にハッシュ関数を適用したハッシュ値HV-1が発行される。
当該ハッシュ値HV-1についても、図5のように、車両情報ブロックBL-1に格納される。
その後、第2次の車両経歴情報HSI-2が登録された際に、同情報HSI-2にハッシュ関数が適用され、ハッシュ値HV-2が発行される。The vehicle information block BL in this example stores vehicle information (vehicle basic information FVI and vehicle history information HSI), a hash value HV generated by encrypting the vehicle information with a hash function, and a nonce NC. (Fig. 5).
The basic vehicle information FVI (Fig. 7) and the vehicle history information HSI (see Figs. 8(a) and 8(b)) are not limited to character information, and include information about the vehicle and articles related to the vehicle. (for example, a vehicle inspection certificate) may be included.
In this example, the hash value HV is always added when the vehicle basic information FVI or vehicle history information HSI is added (that is, when these information FVI/HSI are uploaded onto the vehicle information block chain 221). be done.
In the example of FIG. 6, when "vehicle basic information HVI is registered", a hash value HV-B is issued by applying a hash function to the information HVI.
This hash value HV-B is stored in the vehicle information block BL-1 as shown in FIG.
Also, when "vehicle history information HSI is registered or added", a hash value obtained by applying a hash function to the registered or added HSI is issued, and thereafter, a hash is issued each time information is added.
In the example of FIG. 6, when the vehicle history information HSI-1 at the time of initial registration is registered (uploaded onto the vehicle information block chain 221), a hash value HV-1 obtained by applying a hash function to the information HSI-1 is is issued.
The hash value HV-1 is also stored in the vehicle information block BL-1 as shown in FIG.
Thereafter, when the secondary vehicle history information HSI-2 is registered, a hash function is applied to the information HSI-2, and a hash value HV-2 is issued.
上記の「車両基本情報」は、個々の車両ごとに「固有の永続的な仕様」に関する情報項目を含んでなる情報である。
車両基本情報FVI(図7)は、車両の譲渡・使用・修理などに左右されない情報のみを含むものであるため、初回登録時にのみ生成されると、その後、修正されることなく当初の登録内容を維持する。
また、ある特定の1台の車両について車両基本情報FVIが作成されると、それ以後、その車両基本情報FVIは、当該車両に関する車両情報ブロックに継続的に組込まれる。The above-mentioned "vehicle basic information" is information including information items relating to "unique permanent specifications" for each individual vehicle.
The vehicle basic information FVI (Fig. 7) contains only information that is not affected by the transfer, use, repair, etc. of the vehicle, so if it is generated only at the time of initial registration, the original registration content will be maintained without modification thereafter. do.
Further, once the vehicle basic information FVI is created for a specific vehicle, the vehicle basic information FVI is continuously incorporated into the vehicle information block for the vehicle.
本実施形態では、図7のように、車両基本情報FVIは、以下の情報を含んでいる。
(1)自動車登録番号:ナンバープレート交付の根拠となる番号
(2)登録年月日/交付年月日:普通車の場合、車両の所有者の異動日(新規登録または移転登録の日)。普通車の場合、所有権の移転があった場合にのみ更新される。
(3)初度登録年月:車両が最初に登録(ナンバープレート交付)された年月
(4)自動車の種類:軽自動車・普通・小型・大型特殊のいずれか
(5)用途:乗用・貨物のいずれか
(6)自家用又は事業用の別:自家用・事業用のいずれか
(7)車体の形状:自動車メーカが独自に定めた車両の形状(箱型・ステーションワゴンなど)および車体の形状コードを示す数字
(8)車名:メーカ名およびメーカが付与した車名コード
(9)乗車定員:車両に搭乗可能な最大人数
(10)最大積載量:運搬可能な貨物重量の上限値、または、定員乗車時の最大積載量と前席のみ乗車時の最大積載量
(11)車両重量:車両の空車重量
(12)車両総重量:フル乗車・フル積載した場合の総重量
(13)車台番号:車両の製造メーカにより付与される、車両ごとに固有の識別番号
(14)車両の長さ・幅・高さ:車両の寸法(ミリ単位以下は切捨)
(15)前前軸重・前後軸重:車両重量測定時の前後タイヤにかかる重量
(16)型式:車両の構造・仕様などを分類するための文字列。日本国内の場合、国土交通省が規定した「自動車排出ガス規制及び低排出ガス車認定の識別記号」と「自動車メーカが定めた記号」の組合せからなる。
(17)原動機の型式:車両に搭載されたエンジン(電気自動車の場合、モータ)の型式。ハイブリッド車の場合、エンジン型式とモータ型式を併記する。
(18)総排気量又は定格出力:内燃機関の場合はエンジンの排気量(リットル単位)。電気自動車の場合、定格出力(キロワット単位)
(19)燃料の種類:ガソリン・軽油・LPG・ANG・電気など、エンジンが主として使用する燃料
(20)発行管理者情報:車両基本情報FVIを登録した管理者に関する情報。なお、新車の場合、自動車メーカと特約店契約を結んだ正規販売業者であるディーラーにより販売されるため、通常、車両基本情報FVIにおける発行管理者は「ディーラー名」となる。In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 7, the basic vehicle information FVI includes the following information.
(1) Vehicle registration number: A number that serves as the basis for license plate issuance (2) Date of registration/Date of issuance: In the case of ordinary vehicles, the date of change of the vehicle owner (date of new registration or transfer registration). In the case of ordinary cars, it is renewed only when there is a transfer of ownership.
(3) Date of initial registration: The date the vehicle was first registered (issued license plate) (4) Vehicle type: Light vehicle, ordinary vehicle, small vehicle, or large special vehicle (5) Use: passenger or cargo Either (6) Private use or business use: Either private use or business use (7) Body shape: Vehicle shape (box type, station wagon, etc.) independently determined by the automobile manufacturer and the body shape code (8) Vehicle name: manufacturer name and vehicle name code assigned by the manufacturer (9) Passenger capacity: maximum number of people who can ride in the vehicle (10) Maximum load capacity: upper limit of transportable cargo weight or capacity Maximum load capacity when boarding and maximum load capacity when only the front seats are boarded (11) Vehicle weight: Empty vehicle weight (12) Gross vehicle weight: Total weight when fully loaded and fully loaded (13) Chassis number: Vehicle Unique identification number for each vehicle, given by the manufacturer (14) Vehicle length, width, height: vehicle dimensions (rounded down to millimeters)
(15) Front front axle weight/front rear axle weight: weight applied to front and rear tires when vehicle weight is measured (16) Model: character string for classifying vehicle structure, specifications, and the like. In the case of Japan, it consists of a combination of the "vehicle exhaust emission control and low-emission vehicle certification identification symbol" stipulated by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism and the "symbol specified by the automobile manufacturer."
(17) Motor type: The type of the engine (motor in the case of an electric vehicle) mounted on the vehicle. In the case of a hybrid vehicle, both the engine type and the motor type are indicated.
(18) Total Displacement or Rated Power: For internal combustion engines, engine displacement in liters. For electric vehicles, rated power (in kilowatts)
(19) Type of fuel: Fuel mainly used by the engine, such as gasoline, light oil, LPG, ANG, and electricity. In the case of a new car, since it is sold by a dealer who is an authorized dealer who has concluded a special agent contract with an automobile manufacturer, the issuing manager in the vehicle basic information FVI is usually "dealer name".
また、上述した「車両経歴情報」とは、車両の譲渡・使用・修理といった「経歴に付随」して変わっていく情報項目を含んでなる情報である。
車両経歴情報HSIは、初回登録時においては、新車登録されたときの譲渡・使用・修理に関する内容が記載される(図8(a)参照)。
なお、初回登録時の車両経歴情報HSI-1に記載される走行距離は、非常に僅少である(例えば、数キロメートル程度)。The above-mentioned "vehicle history information" is information that includes information items that change "associated with the history" such as transfer, use, and repair of the vehicle.
In the vehicle history information HSI, at the time of initial registration, the contents related to transfer, use, and repair at the time of new vehicle registration are described (see FIG. 8(a)).
Note that the mileage described in the vehicle history information HSI-1 at the time of initial registration is very small (for example, about several kilometers).
また、初回登録が済んだあとの次回(第2次)以降は、車両経歴情報HSIは、中古車として流通して売買された際の情報を持つことになる(図8(b)参照)。
中古車市場流通時の車両経歴情報HSIの具体例としては、新たな所有者(購入者)に関する内容、使用状態を示す指標(走行距離、外観・内観の良好性評価など)、修理履歴などが挙げられる。
なお、車両経歴情報HSIは、車両が売買された際に生成するに限らず、日本国内においては定期的な自動車検査登録(いわゆる車検)ごとに生成してもよい。Also, from the next time (secondary) onwards after the initial registration is completed, the vehicle history information HSI will have information when the vehicle is distributed and traded as a used vehicle (see FIG. 8(b)).
Specific examples of the vehicle history information HSI at the time of distribution in the used car market include details about the new owner (purchaser), indicators indicating the state of use (mileage, appearance/interior quality evaluation, etc.), repair history, etc. mentioned.
It should be noted that the vehicle history information HSI is not limited to being generated when a vehicle is bought and sold, and may be generated for each periodic vehicle inspection registration (so-called vehicle inspection) in Japan.
本実施形態では、図8(a)・図8(b)のように、車両経歴情報HSIは、以下の情報を含んでいる。
(1)登録更新日:自動車登録を更新した日
(2)所有者名:車両の現所有者の氏名
(3)所有者住所:車両の現所有者の住所
(4)使用の本拠の位置:自動車の保有者(使用者)の拠点。個人の場合、実際に居住しているところ。法人の場合、事業所・営業所など活動の実態があるところ。
(5)登録時の走行距離:初回(新車)登録時から、今回新たに行う自動車登録更新までの間の車両の走行距離
(6)修理履歴:前回の自動車登録更新から、今回新たに行う自動車登録更新までの間においてなされた修理の事実。
なお、初回登録が済んだあとの第2次以降の車両経歴情報HSIにおいて、走行距離としては、中古車としての売買契約時における走行距離が記載される。In this embodiment, as shown in FIGS. 8A and 8B, the vehicle history information HSI includes the following information.
(1) Registration update date: Date of renewal of automobile registration (2) Owner name: Name of the current owner of the vehicle (3) Owner address: Address of the current owner of the vehicle (4) Location of base of use: Location of the owner (user) of the vehicle. For individuals, where they actually reside. In the case of corporations, places where there are actual activities such as business offices and sales offices.
(5) Mileage at the time of registration: Mileage of the vehicle from the initial (new car) registration to the new car registration update (6) Repair history: From the previous car registration update to the new car this time The fact that repairs were made in the period up to registration renewal.
In the second and subsequent vehicle history information HSI after the initial registration is completed, as the travel distance, the travel distance at the time of the sales contract as a used car is described.
台帳管理端末2は、書込端末3からの車両情報書込要求に応じて、車両基本情報FVIを初回登録時にのみ生成する。
また、台帳管理端末2は、初回登録時、車両経歴情報HSIについても生成する(図8(a)参照)。
さらに、台帳管理端末2は、書込端末3から車両情報書込要求がされる都度、初回登録が済んだあとの次回以降の車両経歴情報についても継続的に追加生成する(図8(b)参照)。
すなわち、本例において生成される歴代の車両情報ブロックBLには、初回登録時に生成された車両基本情報が常に含まれるとともに、初回登録時に生成された車両経歴情報に加え、そののち累積的に追加されていった歴代の各車両経歴情報すべてが格納されている(図5)。
なお、図5中の破線は、個々の車両情報ブロックBLが、ハッシュ値HVによって相互に連関していることを示している。The
The
Furthermore, every time the writing terminal 3 requests the writing of vehicle information, the
That is, the successive vehicle information blocks BL generated in this example always include the vehicle basic information generated at the time of initial registration, and in addition to the vehicle history information generated at the time of initial registration, cumulatively added thereafter. All history information of each successive vehicle that has been acquired is stored (Fig. 5).
The dashed lines in FIG. 5 indicate that individual vehicle information blocks BL are associated with each other by hash values HV.
また、台帳管理端末2は、参照端末1からの車両情報参照要求に応じて、同端末1に車両情報を提供する。
Also, the
つぎに、参照端末1(図1の例では1-1・1-2)・台帳管理端末2(図1の例では2-1~2-3)・書込端末3(図1の例では3-1・3-2)の各電気的構成について順次説明する。Next, reference terminals 1 (1-1 and 1-2 in the example of FIG. 1), ledger management terminals 2 (2-1 to 2-3 in the example of FIG. 1), and writing terminals 3 (in the example of FIG. 1 3-1 and 3-2) will be described in order.
これら端末1・2・3は、計算処理能力や記憶容量等の規模に相違があるものの装置構成は似通っている。いずれの構成要素1・2・3も、図1に示したごとく、液晶ディスプレイやプリンタ(図示略)等を含む出力部と、各種の演算処理を実行する装置本体と、キーボード・タッチパネル及びマウス(図示略)を含む入力部と、を備えている。
また装置本体は、演算処理を実行するCPUを中心とした制御機能、ハードディスクドライブ(HDD)、ROM、RAM等を利用する記憶機能、及び各種信号あるいは情報を送受信する通信機能等を有している。These
The main body of the device has a control function centered on a CPU that executes arithmetic processing, a storage function that uses a hard disk drive (HDD), ROM, RAM, etc., and a communication function that transmits and receives various signals or information. .
図2は、本実施形態に係る参照端末1の電気的構成を示すブロック図である。
参照端末1は、図2に示すように、入力部14と、出力部15とを備えている
また、参照端末1は、任意の演算処理を実行するCPU(中央処理装置)を含む制御部11のほか、ハードディスクドライブ(HDD)・ROM・RAM等を含む記憶部12、及び、各種信号あるいは情報の入出力経路をなす通信ポート(図示略)を含む通信部13を備えている。
通信部13は、インターネットや移動体通信網等の公衆通信回線200に接続され、他装置との間で各種の通信を行う。通信部13としてはネットワークインターフェース・モデム等が使用される。FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing the electrical configuration of the
The
The
制御部11は、CPU(Central Processing Unit:中央処理装置)・ROM(Read Only Memory)・RAM(Random Access Memory)等を有し、ROM・記憶部12に記憶されているアプリケーションプログラムをRAMにロードして実行し、それにより各種の論理的手段を実現する。
参照端末1では、コード認識手段111および参照要求手段112が実現される。The
The
コード認識手段111は、所定のコードCD(図3)がカメラ16により撮像された際に、当該コードCDが示している情報を認識する手段である。
ここで、上述した所定のコードCDとしては、マトリクス型2次元コードであるQRコード(登録商標)などが該当する。
本例において、所定のコードCDは、台帳管理端末2の宛先情報(同端末2を指定するURLなど)を示している。The code recognition means 111 is means for recognizing information indicated by a predetermined code CD (FIG. 3) when the
Here, a QR code (registered trademark), which is a matrix-type two-dimensional code, or the like corresponds to the predetermined code CD described above.
In this example, the predetermined code CD indicates destination information of the ledger management terminal 2 (such as a URL specifying the same terminal 2).
図2の参照要求手段112は、当該参照端末1のユーザによる車両情報参照要求の指示がされると、車両情報参照要求を台帳管理端末2に送信する。
本例では、カメラ16で写した所定のコードCDの示すURLがコード認識手段111により認識された場合、参照要求手段112が、当該URLで特定される台帳管理端末2あてに車両情報参照要求を送信する。
また、本例では、車両情報を確認するためのエクスプローラ(閲覧用ウェブサイト)のURLが入力部14を介してユーザ入力された場合にも、参照要求手段112は、このURLが指定する台帳管理端末2あてに車両情報参照要求を送信する。The reference request means 112 in FIG. 2 transmits a vehicle information reference request to the
In this example, when the URL indicated by the predetermined code CD photographed by the
Further, in this example, even when the URL of an explorer (browsing website) for checking vehicle information is input by the user through the
なお、出力部15は、車両情報参照要求に応じて車両情報が台帳管理端末2から提供されたときに、同車両情報を画面表示する。
より詳細には、出力部15は、車両基本情報表示画面(図12)・車両経歴情報表示画面(図13)をはじめとする各種画面を表示する。The
More specifically, the
カメラ16は、任意の被写体を撮像する。
なお、本例において、カメラ16は、車両情報の参照を台帳管理端末2に要求する際、QRコード(登録商標)などの所定のコードを撮像するために使用される。
In this example, the
本願発明では、上記の所定のコードCDは、頑強な金属材料などからなるコード表示部材DSPに刻印されている(図3)。
このコード表示部材DSPは、車両情報に対応する実際の車両に物理的に強固に取付けられる。
参照端末1のユーザは、当該車両に関する車両情報を参照する場合、カメラ16をかざして、同車両に取付けられたコード表示部材上の所定のコードCDを撮像する。
なお、図3の例では、円形状の薄板からなるコード表示部材DSPを示しているが、コード表示部材DSPは所定のコードCDの刻印面が確保されている限り、任意の形状を採用することが可能である。In the present invention, the predetermined code CD is engraved on the code display member DSP made of a strong metal material (FIG. 3).
This code display member DSP is physically rigidly attached to the actual vehicle corresponding to the vehicle information.
When the user of the
In the example of FIG. 3, the code display member DSP made of a circular thin plate is shown, but the code display member DSP may adopt any shape as long as a predetermined code CD stamping surface is secured. is possible.
また、参照端末1が据置型のPC(Personal Computer)などであって、実際の車両に表示されている所定のコードCDを直接的に読取ることが難しい場合、車両情報ブロックチェーン221に書込まれている車両情報を確認するためのエクスプローラ(閲覧用ウェブサイト)をURL指定してアクセスすることで、表示させることが可能である。
なお、仮想通貨の分野の例となるものの、上記のようなブロックチェーンの記録内容を確認可能なエクスプローラの一具体例としてはEtherscanが挙げられる。In addition, when the
Although it is an example in the field of virtual currency, Etherscan is a specific example of an explorer that can check the contents of blockchain records as described above.
つぎに、台帳管理端末2の電気的構成について説明する。
図4は、本実施形態に係る台帳管理端末2の電気的構成を示すブロック図である。
台帳管理端末2は、入力部24と、出力部25とを備えている。
また、図4に示すように、同端末2は、任意の演算処理を実行するCPU(中央処理装置)を含む制御部21のほか、ハードディスクドライブ(HDD)・ROM・RAM等を含む記憶部22、及び、各種信号あるいは情報の入出力経路をなす通信ポート(図示略)を含む通信部23を備えている。
通信部23は、インターネットや移動体通信網等の公衆通信回線200に接続され、他装置との間で各種の通信を行う。Next, the electrical configuration of the
FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing the electrical configuration of the
The
As shown in FIG. 4, the
The
制御部21は、CPU(Central Processing Unit:中央処理装置)・ROM(Read Only Memory)・RAM(Random Access Memory)等を有し、ROM・記憶部22に記憶されているアプリケーションプログラムをRAMにロードして実行し、それにより各種の論理的手段を実現する。
台帳管理端末2では、ログイン認証手段211と、情報生成手段212と、ナンス算出手段213と、ハッシュ生成手段214と、ブロック追加手段215と、ブロック適否判定手段216および情報提供手段217が実現される。The
In the
ログイン認証手段211は、車両情報ブロックチェーン221(図5)に対する車両情報の書込(追加)を所望する書込端末3のユーザを認証する手段である。
ログイン認証手段211は、書込端末3から送信されたユーザID(例えば、メールアドレス)とパスワードをユーザ登録する。
ここでいうユーザ登録とは、ログイン認証手段211が各書込端末3から受信したユーザIDとパスワードを対応付けてユーザ情報222(図4)に書込むことをいう。
ユーザ情報222は、各ユーザに固有の識別情報(ユーザID)と、そのユーザに関する属性(例えば、パスワード)との対応関係を指定する情報である。The login authentication means 211 is means for authenticating the user of the writing
The login authentication means 211 registers the user ID (e.g., e-mail address) and password transmitted from the writing
User registration here means that the login authentication means 211 associates the user ID and password received from each writing
The
情報生成手段212は、車両情報(車両基本情報FVIおよび車両経歴情報HSI)を生成する手段である。
車両情報は、車両情報ブロックチェーン221に帰属する車両情報ブロックBL(図5の例では、BL-1~BL-3)内に格納される。
当該「車両情報」は、個々の車両に関する属性を示す情報である。The information generating means 212 is means for generating vehicle information (vehicle basic information FVI and vehicle history information HSI).
Vehicle information is stored in vehicle information blocks BL (BL-1 to BL-3 in the example of FIG. 5) belonging to the vehicle
The "vehicle information" is information indicating attributes of each vehicle.
情報生成手段212は、車両の個体ごとに固有の仕様情報であって車両の譲渡・使用・修理がなされても内容が変わらない「車両基本情報」を生成する。
この車両基本情報FVIは、元台帳として位置付けられる情報である。The information generating means 212 generates "vehicle basic information" which is specification information unique to each individual vehicle and whose content does not change even if the vehicle is transferred, used, or repaired.
This basic vehicle information FVI is information positioned as a ledger.
なお、自動車メーカにより製造された各車両には、それぞれ固有の「車台番号」が付与されている。
「車両基本情報」の登録は、初回登録時の1回のみ実行されるが、この車両基本情報の登録動作により「車両固有の識別情報である車台番号と、車両情報ブロックチェーン221の紐付け」がなされることになる。A unique "chassis number" is assigned to each vehicle manufactured by an automobile manufacturer.
Registration of "vehicle basic information" is executed only once at the time of initial registration. will be done.
また、情報生成手段212は、外部から入力された内容を基に、車両の譲渡・使用に伴って変化する変動的な車両経歴情報HSIを追加的に生成する。
なお、情報生成手段212は、ログイン認証に成功した書込端末3に対してのみ、車両情報の書込を許可する。In addition, the information generating means 212 additionally generates variable vehicle history information HSI that changes according to the transfer/use of the vehicle, based on the contents input from the outside.
Note that the information generating means 212 permits writing of vehicle information only to the writing
ナンス算出手段213は、車両情報ブロックBLを新規に追加する際、この最新の車両情報ブロックBLに組込むナンス(Number used once)を算出する。
同ナンス算出手段213は、現在追加しようとしている最新の車両情報および直前に生成された車両情報ブロックの関係が、所定の演算結果に該当するハッシュ値HVが得られるようなナンスNCを算出する。
なお、ナンスNCは、ハッシュ値HVを生成される際に1回限り(使い捨て)で用いられる、連続した数字の列である。The nonce calculation means 213 calculates a nonce (Number used once) to be incorporated into the latest vehicle information block BL when adding a new vehicle information block BL.
The nonce calculation means 213 calculates a nonce NC such that the relationship between the latest vehicle information to be added at present and the vehicle information block generated immediately before obtains a hash value HV corresponding to a predetermined calculation result.
The nonce NC is a sequence of consecutive numbers that is used only once (disposable) when generating the hash value HV.
本例においては「所定の演算結果」として、生成されたハッシュ値HVにおける上位の所定桁数(例えば、上位3桁)がすべて「0」になることが課せられる。
上述したハッシュ値HVの上位桁数は、任意の桁数に設定することが可能である。In this example, as the "predetermined calculation result", it is imposed that a predetermined number of high-order digits (for example, high-
The number of upper digits of the hash value HV described above can be set to any number of digits.
ハッシュ生成手段214は、情報生成手段212が追加的に生成した最新世代の車両情報に対して、ハッシュ関数を適用する。
これにより、図6のように、ハッシュ生成手段214は、新たに追加しようとしている最新の車両情報のハッシュ値HVを生成する。
同図6の例では、同手段214は、車両情報ブロックBL-2に格納される車両情報(具体的には、車両基本情報FVI・初回登録時の車両経歴情報HSI-1・第2次の車両経歴情報HSI-2の組合せ)に対して、ハッシュ関数を適用する。
これにより、図5に示した車両情報ブロックBL-2に格納されるハッシュ値HV-2が生成される。
同手段214は、車両情報ブロックBL-2に格納される個々の車両情報(車両基本情報FVI・初回登録時の車両経歴情報HSI-1・第2次の車両経歴情報HSI-2の組合せ)に対して、ハッシュ関数を適用するものでもよい。
このような構成下では、ハッシュ生成手段214は、車両基本情報FVIが生成されたときに、同情報FVIに1対1で対応するハッシュ値HV-Bを生成する。
また、同手段214は、初回登録時の車両経歴情報HSI-1が生成されたときに、同情報HSI-1に1対1で対応するハッシュ値HV-1を生成する。
さらに、同手段214は、第2次の車両経歴情報HSI-2が生成されたときに、同情報HSI-2に1対1で対応するハッシュ値HV-2を生成する。The hash generation means 214 applies a hash function to the latest generation vehicle information additionally generated by the information generation means 212 .
As a result, as shown in FIG. 6, the hash generation means 214 generates a hash value HV of the latest vehicle information to be newly added.
In the example of FIG. 6, the
As a result, the hash value HV-2 stored in the vehicle information block BL-2 shown in FIG. 5 is generated.
The means 214 stores individual vehicle information (a combination of basic vehicle information FVI, vehicle history information HSI-1 at the time of initial registration, and secondary vehicle history information HSI-2) stored in the vehicle information block BL-2. Alternatively, a hash function may be applied.
Under such a configuration, when the basic vehicle information FVI is generated, the hash generating means 214 generates a hash value HV-B corresponding to the information FVI on a one-to-one basis.
Further, when the vehicle history information HSI-1 at the time of initial registration is generated, the
Further, when the secondary vehicle history information HSI-2 is generated, the
なお、ハッシュ生成手段214は、情報生成手段212が追加的に生成した最新の車両情報と、ナンス算出手段213が算出したナンスNCと、最新の直前に生成された車両情報ブロックとを接続したデータに対し、ハッシュ関数を適用するものでもよい。Note that the hash generation means 214 generates data connecting the latest vehicle information additionally generated by the information generation means 212, the nonce NC calculated by the nonce calculation means 213, and the vehicle information block generated immediately before the latest. A hash function may be applied to .
本例において、ハッシュ値(一定文字数の不規則な文字列)は、任意のデータに対するハッシュ関数の演算操作(暗号化)により生成される。
ハッシュ関数により暗号化された文字列(ハッシュ値HV)は、いくらハッシュ値HVを参照しても暗号化前の元のデータを復元することができないという不可逆性がある。
このようにハッシュ関数は、車両情報のデータ改ざん防止を担保する役割を果たす。In this example, a hash value (an irregular character string with a fixed number of characters) is generated by arithmetic operation (encryption) of a hash function on arbitrary data.
A character string (hash value HV) encrypted by a hash function is irreversible in that the original data before encryption cannot be restored no matter how much the hash value HV is referred to.
In this way, the hash function plays a role in ensuring the prevention of falsification of vehicle information.
ブロック追加手段215は、初回登録時に生成された車両基本情報FVIと、最新の車両経歴情報HSIを含む初回登録以後のすべての車両経歴情報と、当該最新の車両経歴情報のハッシュ値とを一括して、最新の車両情報ブロックBLに書込む。The block addition means 215 collectively includes the vehicle basic information FVI generated at the time of initial registration, all vehicle history information after initial registration including the latest vehicle history information HSI, and the hash value of the latest vehicle history information. and write it to the latest vehicle information block BL.
換言すれば、最新の車両経歴情報HSIを追加する場合、この最新の車両経歴情報を含む最新の車両情報ブロックBLは、その直前に生成された車両情報ブロックに格納されている車両情報(車両基本情報FVIおよび車両経歴情報HSI)に加えて、当該最新の車両経歴情報が追加されたものとなっている。
図5の例では、第3次の車両経歴情報HSI-3を生成して、当該車両経歴情報HSI-3を含む車両情報ブロックBL-3を車両情報ブロックチェーン221に追加する場合、当該ブロックBL-3内には、直前の車両情報ブロックBL-2に含まれる車両情報(FVI・HSI-1・HSI-2)に加えて、最新である第3次の車両経歴情報HSI-3が追加される。
なお、車両情報ブロックBL-2とBL-3において、ハッシュ値HVおよびナンスNCは相互に異なった値となっている。In other words, when the latest vehicle history information HSI is added, the latest vehicle information block BL containing this latest vehicle history information is replaced with the vehicle information (vehicle basic information) stored in the immediately preceding vehicle information block. In addition to the information FVI and vehicle history information HSI), the latest vehicle history information is added.
In the example of FIG. 5, when the tertiary vehicle history information HSI-3 is generated and the vehicle information block BL-3 including the vehicle history information HSI-3 is added to the vehicle
Note that the hash value HV and the nonce NC are different values in the vehicle information blocks BL-2 and BL-3.
ブロック適否判定手段216は、他の台帳管理端末2により追加された車両情報ブロックBLが、車両管理台帳システム100における合意規則を充足しているかどうかを判定する。
図1において、台帳管理端末2-1が新規の車両情報ブロックBLを追加した場合、当該端末2-1を除く残りすべての台帳管理端末2(図1の例では、2-2~2-3)が、台帳管理端末2-1により追加された車両情報ブロックBLが合意規則に則しているか否かの適否を判定することになる。
なお、車両情報ブロックBLの適否を照合するための合意規則は、任意であり、例えば、POW(Proof of Work)・PBFT(Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance)などを採用可能である。The block suitability determination means 216 determines whether or not the vehicle information block BL added by another
In FIG. 1, when the ledger management terminal 2-1 adds a new vehicle information block BL, all the remaining ledger management terminals 2 (in the example of FIG. 1, 2-2 to 2-3 ) determines whether or not the vehicle information block BL added by the ledger management terminal 2-1 conforms to the agreement rule.
Any agreement rule may be used for verifying the suitability of the vehicle information block BL.
情報提供手段217は、車両情報参照要求を送信してきた参照端末1に対し、車両情報を提供する。
(1)車両の車両基本情報FVI(図7)
(2)車両についての歴代のすべての車両経歴情報(図8(a)・図8(b))
なお、上述したように、最新の車両情報ブロックBLには、車両基本情報FVIと、最新の車両経歴情報を含む初回登録以後のすべての車両経歴情報HSIとが格納されている。
The
(1) Vehicle Basic Information FVI (Fig. 7)
(2) All historical vehicle history information about vehicles (FIGS. 8(a) and 8(b))
As described above, the latest vehicle information block BL stores the basic vehicle information FVI and all the vehicle history information HSI after the initial registration including the latest vehicle history information.
つぎに、書込端末3の電気的構成について説明する。
図9は、本実施形態に係る書込端末3の電気的構成を示すブロック図である。
書込端末3の構成は、制御部31において実現される論理的手段を除けば、上述した各端末1・2と基本的構成は同一である。
書込端末3の制御部31では、ログイン要求手段311および情報書込手段312が実現される。Next, the electrical configuration of the writing
FIG. 9 is a block diagram showing the electrical configuration of the writing
The configuration of the writing
In the
ログイン要求手段311は、車両情報ブロックチェーン221に対する車両情報の書込(追加)を行う際、台帳管理端末2にログインするために、同端末2に対してログイン認証を要求する手段である。
なお、書込端末3のユーザは、あらかじめ台帳管理端末2に対するユーザ登録(ユーザIDとパスワードの登録)を済ませておく。
本例において、パスワードは、所定桁数以上の英数字・記号で構成された文字列を使用する。
また、ユーザIDとしては、ユーザが選択した任意の文字列でもよく、またユーザが使用している電子メールアドレスなどをユーザIDとして代用してもよい。The login request means 311 is means for requesting login authentication to the
Note that the user of the writing
In this example, the password uses a character string composed of alphanumeric characters and symbols with a predetermined number of digits or more.
The user ID may be an arbitrary character string selected by the user, or an e-mail address used by the user may be substituted for the user ID.
本例において、ログイン要求手段311は、ログイン画面(図示略)を介してユーザIDとパスワードの入力を受付け、これらユーザIDおよびパスワードとともにログイン認証要求を台帳管理端末2へ送信する。
なお、ログイン認証に成功した場合、書込端末3による車両情報の追加が許可される。この場合、車両基本情報入力画面(図10)に画面遷移する。In this example, the login request means 311 accepts input of a user ID and password via a login screen (not shown), and transmits a login authentication request to the
Note that when the login authentication is successful, addition of vehicle information by the writing
なお、車両情報は、車両に関する仕様や経歴(譲渡・使用・修理)のエビデンスとしての役割を担うものであるため、信頼性の高い正規のものである必要がある。
そのため、書込端末3のユーザとしては、自動車メーカと特約店契約したディーラーや、中古車販売業者を想定している。
すなわち、本車両管理台帳システム100においては、個人は車両情報の追加ができないようになっている。
なお、これらのディーラーや中古車販売業者は、日本国内の業者であるに限らず、日本国外の業者であってもよい。
日本国外の業者が車両情報を書込む場合、車両基本情報FVIおよび車両経歴情報HSIは、当該業者が所在している国の言語で記載することが可能である。Since the vehicle information serves as evidence of vehicle specifications and history (transfer, use, repair), it must be highly reliable and official.
Therefore, it is assumed that users of the writing
That is, in the vehicle
It should be noted that these dealers and used car dealers are not limited to those in Japan, and they may be outside Japan.
When a company outside Japan writes vehicle information, the vehicle basic information FVI and vehicle history information HSI can be written in the language of the country where the company is located.
情報書込手段312は、車両情報(車両基本情報FVIまたは車両経歴情報HSI)の書込を要求する。
The information writing means 312 requests writing of vehicle information (vehicle basic information FVI or vehicle history information HSI).
つぎに、本実施形態に係る車両管理台帳システム100の動作について説明する。
まず、書込端末3の利用者の操作によりユーザIDとパスワードを入力し、台帳管理端末2へのユーザ登録が完了した後、書込端末3が車両情報を書込むときの動作について説明する。Next, the operation of the vehicle
First, the operation when the user of the writing
書込端末3は、ユーザによる台帳管理端末2のURLを指定した入力に応じてログイン画面(図示略)を表示する。
つぎに、図14・ステップS11において、同端末3は、ログイン画面を介してユーザ入力されたユーザID・パスワードとともにログイン認証要求を台帳管理端末2に送信する。
なお、同図14では、書込端末3が台帳管理端末2-1にアクセスしてログイン認証を要求した場合を例に挙げている。The writing
Next, in step S11 of FIG. 14, the
In FIG. 14, the case where the writing
台帳管理端末2-1は、同端末3から送信されたユーザIDとパスワードをユーザ情報222(図4)と照合して、ログイン認証を行う。
ログイン認証に成功した場合、図14・ステップS12において、台帳管理端末2-1は、車両情報の書込を書込端末3に許可する。The ledger management terminal 2-1 compares the user ID and password transmitted from the
If the login authentication succeeds, the ledger management terminal 2-1 permits the writing
本例では、車両情報の初回登録が行われる際には、車両情報の書込が許可されると(ステップS12)、書込端末3において、車両基本情報入力画面(図10)へと表示画面が遷移する。
また、車両情報の初回登録を行う際、初回登録分の車両経歴情報HSI-1(図8(a))を入力するには、車両基本情報入力画面(図10)内に配置されたボタンの押下により、車両経歴情報入力画面(図11)に表示を切替える。In this example, when vehicle information is registered for the first time, when writing of vehicle information is permitted (step S12), the writing
Also, when the vehicle information is registered for the first time, in order to input the vehicle history information HSI-1 (Fig. 8(a)) for the initial registration, click the button arranged in the vehicle basic information input screen (Fig. 10). By pressing the button, the display is switched to the vehicle history information input screen (FIG. 11).
なお、車両基本情報FVI・車両経歴情報HSI-1の初回登録が完了されている場合、いったん入力がなされた車両基本情報FVIの内容は、それ以後、書換えられることはない。
そのため、初回登録完了後の次回(第2次)以降については、図14・ステップS12において車両情報の書込が許可された際、車両基本情報入力画面(図10)への画面遷移は不要である。
第2次以降の車両経歴情報HSI入力の際は、車両情報の書込が許可されると、車両経歴情報入力画面(図11)に直接遷移する。If the initial registration of the basic vehicle information FVI/vehicle history information HSI-1 has been completed, the content of the basic vehicle information FVI once entered will not be rewritten thereafter.
Therefore, from the next time (secondary) onwards after the completion of the initial registration, when writing of vehicle information is permitted in step S12 of FIG. be.
When entering the second and subsequent vehicle history information HSI, if the writing of vehicle information is permitted, the screen directly transitions to the vehicle history information input screen (FIG. 11).
続いて、図14・ステップS13において、書込端末3は、台帳管理端末2に対し、車両情報(車両基本情報FVIまたは車両経歴情報HSI)の書込を要求する。
車両基本情報FVIは、車両基本情報入力画面(図10)を介してユーザ入力され、車両経歴情報HSIは、車両経歴情報入力画面(図11)を介してユーザ入力される。
なお、これら車両基本情報FVIや車両経歴情報HSIの入力者は、ディーラーや中古車販売業者である。Subsequently, in step S13 of FIG. 14, the writing terminal 3 requests the
The vehicle basic information FVI is input by the user via the vehicle basic information input screen (FIG. 10), and the vehicle history information HSI is input by the user via the vehicle history information input screen (FIG. 11).
The person who inputs the basic vehicle information FVI and the vehicle history information HSI is a dealer or a used car dealer.
図14・ステップS14において、台帳管理端末2は、書込端末3において入力された情報を基に、車両基本情報FVIまたは車両経歴情報HSIを生成する。In step S14 of FIG. 14, the
続いて、ステップS15において、同端末2は、ナンスNCを算出する。
本例では、台帳管理端末2は、現在追加しようとしている最新の車両情報および最新の直前の車両情報ブロックBLから生成されたハッシュ値HVにおいて、上位の所定桁数(例えば、上位3桁)がすべて「0」になるようなナンスNCを算出する。Subsequently, in step S15, the
In this example, the
上記の演算結果を充たすようなナンスNCが算出されると、台帳管理端末2は、ハッシュ値を生成する(ステップS16)。
さらに、台帳管理端末2は、(1)初回登録時に生成された車両基本情報FVIと、(2)最新の車両経歴情報HSIを含む初回登録以後のすべての車両経歴情報HSIと、(3)当該最新の車両経歴情報のハッシュ値HVを一括して、最新の車両情報ブロックBLに追加的に書込む(ステップS17)。
なお、追加された最新の車両情報ブロックBLは、ハッシュ値HVを介して、既存の車両情報ブロックチェーン221と連関されている。When the nonce NC that satisfies the above calculation result is calculated, the
Furthermore, the
The latest vehicle information block BL added is associated with the existing vehicle
なお、本車両管理台帳システム100では、いずれかの台帳管理端末2において新規の車両情報ブロックBLが追加された場合、当該端末2を除く残りすべての台帳管理端末2により、この車両情報ブロックの適否が判定される。
そのため、図14の例では、台帳管理端末2-1が新規の車両情報ブロックBLを追加した場合、当該端末2-1を除く残りすべての台帳管理端末2-2~2-3が、この追加された車両情報ブロックBLが合意規則に則しているか否かの適否を判定する(ステップS18)。
そして、新規の車両情報ブロックBLが適正であるとの判定がなされると、当該端末2-1を除く全台帳管理端末2-2~2-3は、当該車両情報ブロックBLを、自己の記憶部2に記憶されている車両情報ブロックチェーン221に追加する(ステップS19)。
以上で、書込端末3が車両情報を書込むときの一連の動作が終了する。In the vehicle
Therefore, in the example of FIG. 14, when the ledger management terminal 2-1 adds a new vehicle information block BL, all the remaining ledger management terminals 2-2 to 2-3 except for the terminal 2-1 add the new vehicle information block BL. It is determined whether the vehicle information block BL conforms to the agreement rule (step S18).
Then, when it is determined that the new vehicle information block BL is appropriate, all the ledger management terminals 2-2 to 2-3 except for the terminal 2-1 store the vehicle information block BL in their own memory. It is added to the vehicle
Thus, a series of operations when the writing
つぎに、参照端末1により、台帳管理端末2上に保持されている車両情報を閲覧するときの動作について説明する。Next, the operation of browsing the vehicle information held on the
まず、参照端末1のユーザは、同端末1に搭載されたカメラ16をかざして、車両に取付けられたコード表示部材DSP上の所定のコードCDを撮像する。
すると、参照端末1は、カメラ16で写した所定のコードCDの示すURLを読取り、当該URLで特定される台帳管理端末2あてに車両情報参照要求を送信する(図15・ステップS21)。First, the user of the
Then, the
なお、参照端末1が据置型のPCなどであって、実際の車両に取付けられている所定のコードCDをカメラで撮像できないケースも起こりうる。
そのため、本例では、車両情報を確認するためのエクスプローラ(閲覧用ウェブサイト)のURLが入力部14を介してユーザ入力された場合にも、参照端末1が、当該URLにより指定された台帳管理端末2あてに車両情報参照要求を送信できるよう構成されている。It should be noted that there may be a case where the
Therefore, in this example, even when the URL of an explorer (browsing website) for checking vehicle information is input by the user through the
台帳管理端末2は、車両情報参照要求を送信してきた参照端末1に対し、車両情報(車両基本情報FVIまたは車両経歴情報HSI)を提供する(ステップS22)。The
すると、参照端末1は、出力部15(液晶ディスプレイ等)上に、車両基本情報表示画面(図12)・車両経歴情報表示画面(図13)を表示する(ステップS23)。
なお、車両基本情報表示画面(図12)・車両経歴情報表示画面(図13)には各々、表示画面を相互に切替えるためのボタンが配設されており、参照端末1のユーザは、所望の画面を表示できる。
以上で、参照端末1が車両情報を参照するときの一連の動作が終了するThen, the
The vehicle basic information display screen (FIG. 12) and the vehicle history information display screen (FIG. 13) are respectively provided with buttons for switching between the display screens. can display the screen.
Thus, a series of operations when the
以上説明したように、本実施形態に係る車両管理台帳システム100によれば、1台1台の各車両別に生成される車両情報ブロックBL内に、常に、すべての車両情報(車両基本情報FVIと、初回登録時からの累積的な全車両経歴情報HSI)が納められている(図5)。
そのため、参照端末1によりユーザが車両情報を参照した際、当該ユーザは、ある特定の車両にまつわるすべての車両情報(車両基本情報FVIと、初回登録時からの累積的な全車両経歴情報HSI)を参照できる。
そのため、車検証が手元にない場合や、また車検制度のない国において車両が流通している場合であっても、所望する車両にまつわる車両情報(改ざんのない走行距離や譲渡歴など)を参照可能となる。As described above, according to the vehicle
Therefore, when the user refers to the vehicle information by using the
Therefore, even if you do not have a vehicle inspection certificate at hand, or if the vehicle is distributed in a country without a vehicle inspection system, you can refer to the vehicle information (mileage without falsification, transfer history, etc.) related to the desired vehicle. becomes.
また、本車両管理台帳システム100においては、車両情報を書込む書込端末3のユーザが、ディーラーや中古車販売業者に限定されており、個人による書込は禁止されている。
そのため、車両情報は、車両に関する仕様や経歴(譲渡・使用・修理)のエビデンスとして、信頼性の高い正規のものであることが担保される。In the vehicle
Therefore, the vehicle information is guaranteed to be highly reliable and authentic as evidence of vehicle specifications and history (transfer, use, repair).
なお、本願の車両管理台帳システム100においては、車両情報に対応する実際の車両に対し、頑強な金属材料などからなる所定のコードCDの刻印されたコード表示部材DSPが、リベット止めや溶接などの手法により物理的に強固に固着される。
そのため、車両情報にアクセスするためコードCDを実車から除去することが困難となっており、実車においてもその車両に関する車両情報のトレーサビリティ(追跡可能性)が保証される。In the vehicle
Therefore, it is difficult to remove the code CD from the actual vehicle in order to access the vehicle information, and the traceability of the vehicle information regarding the vehicle is guaranteed even in the actual vehicle.
なお、参照端末1としては、据置型・ノート型のPCはもちろん、スマートフォン・タブレット端末・腕時計型端末などの携帯型の多機能電子装置も採用可能である。
車両情報を表示する際は、CPUに対しかなりの処理負担がかかるものの、スマートフォンやタブレット端末であれば処理性能が日進月歩の勢いで飛躍的に向上しており、車両情報の表示処理を実行する際にも快適な動作速度を担保できる。
また携帯型の多機能電子装置であれば、携行性というメリットを備えるがゆえに、カメラ16を使用して、実際の車両に取付けられているコード表示部材DSPから所定のコードCD(例えば、QRコード)を直接読取り、車両の実物を直に確認しながら、その車両の仕様や過去の経歴を参照できる。
As the
Displaying vehicle information puts a considerable processing load on the CPU, but the processing performance of smartphones and tablet terminals is improving rapidly, and when executing vehicle information display processing A comfortable operating speed can also be secured.
In addition, since a portable multifunctional electronic device has the advantage of portability, the
[変形例:ブロックチェーンに対する、走行距離の定期的な書込]
上記実施形態では、車両情報にかかる車両の譲渡(売買契約)がなされた際に、車両経歴情報HSIを生成することを想定している。
そのため、車両経歴情報HSIに記載される走行距離の情報更新についても、車両の譲渡(売買契約)がなされる機会まで待つ必要がある。
しかしながら、車両の譲渡機会を待つことなく、車両の走行距離を所定のタイミング(定期的、または、所定距離だけ走行距離が増加する毎)で車両情報ブロックチェーン221に記録するようにすれば、走行距離計の物理的な改ざん(メータの巻戻し)がされたとしても、同ブロックチェーン221上の正規の車両情報と照らし合わせることにより、このような不正行為を検出できるものと想定される。[Modification: Periodic writing of mileage to blockchain]
In the above-described embodiment, it is assumed that the vehicle history information HSI is generated when the vehicle related to the vehicle information is transferred (sales contract).
Therefore, it is necessary to wait until the vehicle is transferred (sales contract) for the update of the mileage recorded in the vehicle history information HSI.
However, if the mileage of the vehicle is recorded in the vehicle
このような動作を実現するために、本システム100Aにおいては、図16に示すように、車両情報に係る車両VCLに走行距離送信機構DSを搭載する。
走行距離送信機構DSは、公衆通信回線200を介した無線通信により、台帳管理端末2とデータの送受が可能に構成されている。
また、同送信機構DSは、台帳管理端末2に対し、無線通信により、所定のタイミングで車両の走行距離を送信する。
所定のタイミングの具体例としては、月次毎や年次毎でもよく、また、走行距離が所定距離(たとえば、1000km)だけ増加する毎などでもよい。In order to realize such an operation, in the
The mileage transmission mechanism DS is configured to be able to transmit and receive data to and from the
Further, the transmission mechanism DS transmits the travel distance of the vehicle to the
A specific example of the predetermined timing may be every month or every year, or every time the running distance increases by a predetermined distance (for example, 1000 km).
台帳管理端末2の情報生成手段212(図4)は、所定のタイミングにおいて車両VCLから送信されてきた当該車両の走行距離を受信すると、同走行距離を記載した最新の車両経歴情報HSIを自動生成する。
そして、台帳管理端末2において、この車両経歴情報HSIを含んだ最新の車両情報ブロックBLを追加する。When the information generation means 212 (FIG. 4) of the
Then, in the
この変形例によれば、所定のタイミングで、車両VCLの走行距離を台帳管理端末2あてに送り、同端末2にて、この走行距離が記載された最新の車両経歴情報HSIを生成する。
このようにすることで、車両VCLの譲渡(売買契約)の機会を待つことなく、走行距離の履歴を記録として残すことができるようになる。
そのため、第三者が車両VCLの走行距離計の表示を物理的に改ざんしたとしても、車両情報ブロックBLにおける車両経歴情報HSIと照合することにより改ざんの事実が検出でき、走行距離計の不正操作に対する堅牢性を高めることができる。According to this modification, the mileage of the vehicle VCL is sent to the
By doing so, it is possible to record the history of travel distances without waiting for an opportunity to transfer (sales contract) the vehicle VCL.
Therefore, even if a third party physically tampered with the display of the odometer of the vehicle VCL, the fact of tampering can be detected by comparing with the vehicle history information HSI in the vehicle information block BL, and the odometer can be illegally operated. It is possible to increase the robustness against
以上、実施形態を参照して本発明を説明したが、本発明は上記実施形態に限定されるものではない。本発明の構成や詳細には、本発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲で当業者が理解し得る各種の変形が可能である。Although the present invention has been described with reference to the embodiments, the present invention is not limited to the above embodiments. Various modifications that can be understood by those skilled in the art can be made to the configuration and details of the present invention without departing from the gist of the present invention.
1 参照端末
2 台帳管理端末
3 書込端末
100 車両管理台帳システム
200 公衆通信回線1
Claims (4)
Translated fromJapanese個々のユーザが各々所持する端末であって、前記車両情報ブロックに格納されている車両情報の参照を前記台帳管理端末に要求する参照端末と、
車両の販売者が各々所持する端末であって、車両情報の新規追加を前記台帳管理端末に要求する書込端末と、
公衆通信回線を介して参照端末および書込端末と通信可能な端末であって、書込端末からの要求に応じて車両情報を書込むとともに、参照端末からの要求に応じて車両情報を提供する前記台帳管理端末と、
を具備してなり、
個々の参照端末は各々、
当該参照端末のユーザによる車両情報参照要求の指示を受付けると、車両情報参照要求を台帳管理端末に送信する参照要求手段と、
前記車両情報参照要求に応じて車両情報が台帳管理端末から提供されたときに、同車両情報を画面表示する出力部と、
を有し、
個々の書込端末は各々、
車両の販売者による車両情報書込要求の指示を受付けると、前記台帳管理端末に対し、車両情報の書込を要求する情報追加要求手段、を有し、
前記台帳管理端末は、
前記書込端末からの車両情報書込要求に応じて、車両に固有の永続的な仕様情報である車両基本情報を初回登録時にのみ生成するとともに、初回登録以後の車両の譲渡・使用・修理その他の経歴を示す車両経歴情報を継続的に追加生成する情報生成手段と、
前記情報生成手段が生成した最新の車両経歴情報にハッシュ関数を適用することで、当該最新の車両経歴情報のハッシュ値を生成するハッシュ生成手段と、
初回登録時に生成された車両基本情報と、最新の車両経歴情報を含む初回登録以後のすべての車両経歴情報と、当該最新の車両経歴情報のハッシュ値とを一括して、最新の車両情報ブロックに書込むブロック情報管理手段と、
を有し、
複数の台帳管理端末の内いずれか1台の台帳管理端末において、最新の車両情報ブロックが書込まれたときに、
当該車両情報を追加した台帳管理端末以外のすべての台帳管理端末は、最新の車両情報ブロックが適格であると判定したときに、自己の記憶部に、当該車両情報を書込み、
参照端末から車両情報の参照が要求された場合、
車両情報ブロックに格納されている車両情報を特定して、当該参照端末に同特定した車両情報を提供する
ように構成されたことを特徴とする、車両管理台帳システム。
A vehicle management ledger system that manages vehicle information in a distributed manner by having each of a plurality of ledger management terminals interconnected peer-to-peer hold a vehicle information block chain in which individual vehicle information blocks are linked by hash values. ,
a reference terminal, which is a terminal possessed by each individual user and which requests the ledger management terminal to refer to the vehicle information stored in the vehicle information block;
a writing terminal which is owned by each vehicle seller and requests the ledger management terminal to add new vehicle information;
A terminal that can communicate with a reference terminal and a writing terminal via a public communication line, writes vehicle information in response to a request from the writing terminal, and provides vehicle information in response to a request from the reference terminal. the ledger management terminal;
and
Each individual reference terminal is
reference request means for transmitting a vehicle information reference request to a ledger management terminal when an instruction for a vehicle information reference request from a user of the reference terminal is received;
an output unit that displays the vehicle information on a screen when the vehicle information is provided from the ledger management terminal in response to the vehicle information reference request;
has
Each individual writing terminal
an information addition requesting means for requesting the ledger management terminal to write vehicle information when an instruction to request vehicle information writing from a vehicle seller is received;
The ledger management terminal
In response to a vehicle information write request from the write terminal, vehicle basic information, which is permanent specification information unique to the vehicle, is generated only at the time of initial registration, and the vehicle is transferred, used, repaired, etc. after the initial registration. information generating means for continuously additionally generating vehicle history information indicating the history of
Hash generation means for generating a hash value of the latest vehicle history information by applying a hash function to the latest vehicle history information generated by the information generation means;
The basic vehicle information generated at the time of initial registration, all vehicle history information after the initial registration including the latest vehicle history information, and the hash value of the latest vehicle history information are collectively stored in the latest vehicle information block. a writing block information management means;
has
When the latest vehicle information block is written in one of the ledger management terminals among the plurality of ledger management terminals,
All the ledger management terminals other than the ledger management terminal that added the vehicle information write the vehicle information in their own storage units when determining that the latest vehicle information block is eligible,
If the reference terminal requests to refer to vehicle information,
A vehicle management ledger system characterized by being configured to identify vehicle information stored in a vehicle information block and provide the identified vehicle information to the reference terminal.
前記参照端末は、任意の被写体を撮像するカメラを備え、
車両情報の参照を前記台帳管理端末に要求する際、前記カメラにより所定のコードを読取ることにより、車両台帳参照要求を台帳管理端末に送信する
ように構成されたことを特徴とする、車両管理台帳システム。
The vehicle management ledger system according to claim 1,
The reference terminal comprises a camera for imaging any subject,
A vehicle management ledger characterized in that, when requesting the ledger management terminal to refer to vehicle information, a vehicle ledger reference request is transmitted to the ledger management terminal by reading a predetermined code with the camera. system.
車両情報の参照対象となる実際の車両の所定箇所に、前記所定のコードが刻印されたコード表示部材が装着されており、
前記参照端末は、
前記コード表示部材に刻印されている所定のコードを、カメラで読取ることにより、車両台帳参照要求を台帳管理端末に送信する
ように構成されたことを特徴とする、車両管理台帳システム。
The vehicle management ledger system according to claim 2,
A code display member having the predetermined code stamped thereon is attached to a predetermined location of an actual vehicle to be referenced for vehicle information,
The reference terminal is
A vehicle management ledger system, wherein a vehicle ledger reference request is transmitted to a ledger management terminal by reading a predetermined code stamped on the code display member with a camera.
前記車両情報に係る車両は、
前記台帳管理端末に対して、無線通信により、所定のタイミングで車両の走行距離を送信する走行距離送信機構、を備え、
前記台帳管理端末の情報生成手段は、
所定のタイミングにおいて前記車両から送信された当該車両の走行距離を受信すると、同走行距離を記載した最新の車両経歴情報を自動生成する
ように構成されたことを特徴とする、車両管理台帳システム。The vehicle management ledger system according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
The vehicle related to the vehicle information is
A mileage transmission mechanism that transmits the mileage of the vehicle at a predetermined timing to the ledger management terminal by wireless communication,
The information generating means of the ledger management terminal is
A vehicle management ledger system characterized by being configured to automatically generate the latest vehicle history information describing the mileage when receiving the mileage of the vehicle transmitted from the vehicle at a predetermined timing.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/022597WO2022264240A1 (en) | 2021-06-15 | 2021-06-15 | Vehicle management ledger system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/022597WO2022264240A1 (en) | 2021-06-15 | 2021-06-15 | Vehicle management ledger system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2022264240A1true WO2022264240A1 (en) | 2022-12-22 |
Family
ID=84526857
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/022597CeasedWO2022264240A1 (en) | 2021-06-15 | 2021-06-15 | Vehicle management ledger system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2022264240A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024122044A1 (en)* | 2022-12-09 | 2024-06-13 | 日本電気株式会社 | Vehicle log verification system, vehicle log verification method, and program |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20180018723A1 (en)* | 2016-07-18 | 2018-01-18 | Royal Bank Of Canada | Distributed ledger platform for vehicle records |
| JP2020030548A (en)* | 2018-08-21 | 2020-02-27 | 7s HOLDING株式会社 | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program |
| JP2020086634A (en)* | 2018-11-19 | 2020-06-04 | 株式会社A.L.I.Technologies | Asset information registration method |
| JP2020149320A (en)* | 2019-03-13 | 2020-09-17 | 株式会社デンソー | Ledger management system, and ledger management node |
| JP2021068339A (en)* | 2019-10-28 | 2021-04-30 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Vehicle information management system |
- 2021
- 2021-06-15WOPCT/JP2021/022597patent/WO2022264240A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20180018723A1 (en)* | 2016-07-18 | 2018-01-18 | Royal Bank Of Canada | Distributed ledger platform for vehicle records |
| JP2020030548A (en)* | 2018-08-21 | 2020-02-27 | 7s HOLDING株式会社 | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program |
| JP2020086634A (en)* | 2018-11-19 | 2020-06-04 | 株式会社A.L.I.Technologies | Asset information registration method |
| JP2020149320A (en)* | 2019-03-13 | 2020-09-17 | 株式会社デンソー | Ledger management system, and ledger management node |
| JP2021068339A (en)* | 2019-10-28 | 2021-04-30 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Vehicle information management system |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024122044A1 (en)* | 2022-12-09 | 2024-06-13 | 日本電気株式会社 | Vehicle log verification system, vehicle log verification method, and program |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110599276B (en) | Bill reimbursement method, device and equipment and computer storage medium | |
| US20200118094A1 (en) | Secure real-time product ownership tracking using distributed electronic ledgers | |
| CN111936995B (en) | Distributed storage of customs clearance data | |
| CA3183038A1 (en) | Systems and methods for building blockchains for verifying assets for smart contracts | |
| US20240249355A1 (en) | Tokenized carbon credit trading platform | |
| US20120084135A1 (en) | System and method for tracking transaction records in a network | |
| CN109684375A (en) | Method, accounting node and medium for querying transaction information in blockchain network | |
| CN105378774A (en) | Secure transaction system and method | |
| CN105096134A (en) | Security scheme for authenticating digital entities and aggregate object origins | |
| Menges et al. | DEALER: decentralized incentives for threat intelligence reporting and exchange | |
| CN114124428B (en) | Block chain-based access method and device for Internet of things equipment | |
| Chen et al. | BCVehis: A blockchain-based service prototype of vehicle history tracking for used-car trades in China | |
| CN110599273B (en) | Data processing method, data processing device, node equipment and storage medium | |
| US20250028790A1 (en) | Systems and Methods for Token Use and Protection Using Blockchain | |
| Butera et al. | Blockchain and nfts-based trades of second-hand vehicles | |
| WO2022264240A1 (en) | Vehicle management ledger system | |
| JP5042606B2 (en) | Electronic receipt authentication device and electronic receipt system | |
| US20240104641A1 (en) | System and method of providing access to one or more technologies via a rental platform | |
| JP7274198B2 (en) | Asset information registration method | |
| WO2024180430A1 (en) | Server device, information processing method, and non-transitory storage medium | |
| CN112150089A (en) | Second-hand vehicle cloud checking and evaluating system | |
| CN111709838B (en) | Transaction method based on intellectual property standardized digital asset and related equipment | |
| Barreto et al. | Blockchain-based system to ensure the integrity of used vehicle purchase transactions: under researchers’ perspective | |
| Joseph et al. | Development of a Blockchain-Based Vehicle History System | |
| JP7575021B1 (en) | Registration System |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | Ref document number:21945920 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 | |
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase | Ref country code:DE | |
| 32PN | Ep: public notification in the ep bulletin as address of the adressee cannot be established | Free format text:NOTING OF LOSS OF RIGHTS PURSUANT TO RULE 112(1) EPC (EPO FORM 1205A DATED 08.03.2024) | |
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase | Ref country code:JP | |
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase | Ref country code:JP | |
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase | Ref document number:21945920 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 |