WO2021246770A1 - Method and system for automatically reading x-ray image in real time on basis of artificial intelligence - Google Patents
Method and system for automatically reading x-ray image in real time on basis of artificial intelligenceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2021246770A1 WO2021246770A1PCT/KR2021/006852KR2021006852WWO2021246770A1WO 2021246770 A1WO2021246770 A1WO 2021246770A1KR 2021006852 WKR2021006852 WKR 2021006852WWO 2021246770 A1WO2021246770 A1WO 2021246770A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- image
- tag information
- reading
- ray
- file
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B6/00—Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis; Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis combined with radiation therapy equipment
- A61B6/52—Devices using data or image processing specially adapted for radiation diagnosis
- A61B6/5211—Devices using data or image processing specially adapted for radiation diagnosis involving processing of medical diagnostic data
- A61B6/5217—Devices using data or image processing specially adapted for radiation diagnosis involving processing of medical diagnostic data extracting a diagnostic or physiological parameter from medical diagnostic data
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B6/00—Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis; Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis combined with radiation therapy equipment
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B6/00—Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis; Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis combined with radiation therapy equipment
- A61B6/46—Arrangements for interfacing with the operator or the patient
- A61B6/461—Displaying means of special interest
- A61B6/465—Displaying means of special interest adapted to display user selection data, e.g. graphical user interface, icons or menus
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B6/00—Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis; Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis combined with radiation therapy equipment
- A61B6/46—Arrangements for interfacing with the operator or the patient
- A61B6/467—Arrangements for interfacing with the operator or the patient characterised by special input means
- A61B6/468—Arrangements for interfacing with the operator or the patient characterised by special input means allowing annotation or message recording
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B6/00—Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis; Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis combined with radiation therapy equipment
- A61B6/52—Devices using data or image processing specially adapted for radiation diagnosis
- A61B6/5205—Devices using data or image processing specially adapted for radiation diagnosis involving processing of raw data to produce diagnostic data
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H30/00—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images
- G16H30/20—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images for handling medical images, e.g. DICOM, HL7 or PACS
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H30/00—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images
- G16H30/40—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images for processing medical images, e.g. editing
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H50/00—ICT specially adapted for medical diagnosis, medical simulation or medical data mining; ICT specially adapted for detecting, monitoring or modelling epidemics or pandemics
- G16H50/20—ICT specially adapted for medical diagnosis, medical simulation or medical data mining; ICT specially adapted for detecting, monitoring or modelling epidemics or pandemics for computer-aided diagnosis, e.g. based on medical expert systems
Definitions
- the present inventionrelates to a method and system for reading an X-ray image based on artificial intelligence, and more particularly, to a digital X-ray image in real time in a medical field, by applying an artificial intelligence-based automatic X-ray image solution to read it, and an image classification result that is the reading result And the image detection result is created and stored as tag information (Private tag) of an image file in a preset format such as a DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) file, and the reading result stored in the tag information of the image file is analyzed
- the present inventionrelates to an apparatus and method for displaying a reading result with an image console viewer.
- radiographic image of a patientis widely used to primarily diagnose a patient because the examination cost is low and a quick diagnosis is possible.
- the prior art Korean Patent No. 10-1628276discloses a technology for a cloud-based pathology analysis system and method.
- there is a problem in that it takes a lot of time for diagnosis in a place where the Internet infrastructure is not well-equippedso there is a limitation.
- there is a problem with the Internet or the Internet speed is slowed downthere is a problem that the doctor's work can be greatly hindered.
- the present inventionhas been devised to solve the above problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide results to medical staff in real time immediately after obtaining an X-ray image of a patient using an artificial intelligence automatic X-ray reading solution in a medical field. It is to provide a method and system for real-time automatic X-ray image reading based on artificial intelligence.
- Another object of the present inventionis to generate tag information based on the AI-based automatic X-ray image reading result in accordance with the Daicom standard, convert it into an optimal data format according to the data format of the reading result to be stored in the tag, and store the stored tag
- tag informationbased on the AI-based automatic X-ray image reading result in accordance with the Daicom standard, convert it into an optimal data format according to the data format of the reading result to be stored in the tag, and store the stored tag
- Another object of the present inventionis to provide a detailed tag specification for an artificial intelligence-based automatic X-ray reading result and a tag information interpretation and display method, and when a third party develops a solution that displays the reading result using it, the third It is to provide an artificial intelligence-based real-time automatic X-ray image reading method and system that can be universally applied to the user's image console viewer program (image console viewer unit).
- a real-time automatic X-ray image reading systemincludes: an X-ray image acquisition unit for acquiring an X-ray image of a patient; an image console viewer unit that converts the X-ray image received from the image acquisition unit into an image file of a preset format by performing a pre-processing process; an image reading unit that reads an image based on artificial intelligence by inputting an image file received from the image console viewer unit, generates tag information including an image reading result, and adds it to the image file; an image management unit that stores an image file to which tag information is added; and an image viewer unit that receives the image file to which tag information stored in the image management unit is added, and displays the image file on the screen.
- the image reading unitreads the image file received from the image console viewer unit by using the image learning model learned to detect diseases and lesions in the X-ray image using the X-ray image as learning data, and detects each disease and lesion.
- Tag informationincluding Screening Score, outline map information, or heat map information can be added to the image file.
- the image reading unitwhen the image reading result is displayed together with the image file, the image reading unit generates tag information based on the image reading result implemented as images, letters, and numbers in the tag information and location information about the display position of the image reading result can do.
- the image viewer unitwhen displaying the image file on the screen, decodes the tag information added to the image file, so that the image, letters or numbers included in the tag information are displayed together with the image file,
- the display positionmay be individually determined in the image file based on the respective position information.
- the VRValue Representation
- the detection scoreis applied to the DS (Decimal String) to be included in the tag information
- the tag informationincludes Control Maps and Heat Maps. Maps) or image shape (Tuple), list (List) and array (Array) to be included, control map (Control Maps), heat map (Heat Maps) or image shape (Image Shape) After converting information about tuple, list, and array of Byte String) to be included in tag information.
- the image viewer unitwhen the image viewer unit reads image file and tag information, it converts contour maps and heat maps stored as bytes into an array according to each array shape, and then lists ( List) and tuple to create transformed information-based contour maps and heat maps, and when tag information is included in the image file, the image reading result included in the tag information
- the displayed icon and menuare activated so that the image file is displayed together on the displayed screen, and when the display of the image reading result is requested using the displayed icon and menu, the image reading result can be displayed together with the image file have.
- the image reading unitis an essential item for the image reading result, and the reading result (Positive, Negative), the detection (Screening) result, the detection score (Screening Scores), the contour map information for each disease and lesion (Contour Map Information) and Heat map information may be included.
- the image readerdivides the threshold score, which is the reading standard, into lower Sensitivity (0.3), low Sensitivity (0.4), Default Sensitivity (0.5), High Specificity (0.6), and Higher Specificity (0.7), and tags each
- the image viewer unitgenerates information, and when a threshold score as a reading standard is determined according to a user's input, details of the image reading result displayed on the screen according to the determined threshold score as a reading standard Allow items and details to be determined.
- a real-time automatic X-ray image reading methodincludes: acquiring, by a real-time automatic X-ray image reading system, an X-ray image of a patient; A real-time automatic X-ray image reading system, performing a pre-processing process on the X-ray image to convert it into an image file of a preset format; A real-time automatic X-ray image reading system, inputting an image file, performing artificial intelligence-based image reading, generating tag information including the image reading result, and adding it to the image file; A real-time automatic X-ray image reading system comprising: storing an image file to which tag information is added; and displaying, by the real-time automatic X-ray image reading system, the image file to which the stored tag information is added on the screen.
- an artificial intelligence-based automatic X-ray image reading resultis displayed in real time using a remote Image Console Viewer (AXIR).
- the reading resultthat is, information such as Screening Score, bounding box, Contour Map, and Heatmap, can be generated as reading aids and provided to medical staff.
- the medical staffcan efficiently and effectively read the digital video image based on the above-described reading assistance information.
- the reading result of the image reading unitis stored in the DICOM tag
- the version and meta information for the deep convolutional neural network used for readingare included and stored in the detailed specification, so that the DICOM tag of the present invention is detailed.
- Useful informationcan be provided to companies and individuals developing general image viewers using specifications and contents, and their opinions can be collected and reflected.
- medical workflowis streamlined by providing necessary information to doctors and medical personnel in real time in the process from the patient's X-ray imaging to calculating the diagnosis result,
- efficiency and optimizationit is possible to increase the patient treatment rate in medical institutions, thereby reducing costs.
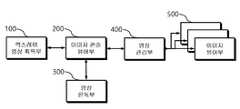
- FIG. 1is a view provided for the explanation of an artificial intelligence-based real-time automatic X-ray image reading system according to an embodiment of the present invention
- FIG. 2is a view provided for explanation of an image console viewer unit according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 3is a view provided for explanation of an image reading unit according to an embodiment of the present invention.
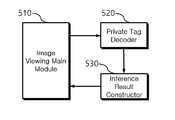
- FIG. 4is a view provided for explanation of an image viewer unit according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 5 to 6are diagrams illustrating an address, VR, VM, Description, and Keyword of a daicom tag for storing a reading result and meta information through an image reading unit according to an embodiment of the present invention
- 21is a view provided for explanation of operation characteristics of an image console viewer unit according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 22 to 23are views provided for explanation of operating characteristics of an image reading unit according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 24 to 25are diagrams provided to explain the operation characteristics of the image viewer unit according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 1is a diagram provided for explanation of an artificial intelligence-based real-time automatic X-ray image reading system (hereinafter, collectively referred to as 'real-time automatic X-ray image reading system') according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 'real-time automatic X-ray image reading system'an artificial intelligence-based real-time automatic X-ray image reading system
- the real-time automatic X-ray image reading systemcan provide real-time results to medical staff immediately after acquiring an X-ray image of a patient using an artificial intelligence automatic X-ray reading solution in a medical field, and artificial intelligence-based automatic X-ray image Creates tag information (Private tag) according to the Daicom standard, converts the read result to the optimal data format according to the data format of the read result to be stored in the tag, and stores it. It can be converted to data format to display the reading result.
- tag informationPrincipal tag
- the real-time automatic X-ray image reading systemincludes an X-ray image acquisition unit 100 , an image console viewer 200 , an image reading unit 300 , an image management unit 400 , and an image viewer unit 500 .
- the X-ray image acquisition unit 100is provided to acquire an X-ray image of a patient.
- the X-ray image acquisition unit 100is composed of an X-ray generator for acquiring an X-ray image from a patient, a digital flat panel X-ray detector, and a control panel, and communicates with the image console viewer 200 and the main function is the patient
- a raw file with a file extension of RAWcan be generated by acquiring an X-ray image of
- the image console viewer 200may be implemented as a computer device, and may be converted into an image file of a preset format by performing a pre-processing process on an X-ray image received from the image acquisition unit.
- the image console viewer 200communicates with the X-ray image acquisition unit 100 and corrects the characteristics of a digital flat panel X-ray detector, and the patient selects the X-ray image to acquire the X-ray image. It is possible to control the acquisition unit 100, receive the acquired X-ray image file, perform various image processing, and register and record information about the patient.
- the image console viewer 200may exchange information with the image reader 300 , and may transmit/receive a medical image of a Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) standard with the image management unit 400 .
- DICOMDigital Imaging and Communications in Medicine
- the image reading unit 300receives an image file received from the image console viewer 200 as input, performs artificial intelligence-based image reading, generates tag information including the image reading result, and adds it to the image file So, it can be encoded.
- the image reading unit 300is implemented as an Automatic X-ray Image Reader (AXIR), and an artificial intelligence-based deep convolution that has been previously learned by inputting the medical image transmitted by the image console viewer 200 as an input.
- AXIRAutomatic X-ray Image Reader
- AXIRAutomatic X-ray Image Reader
- the image reading unit 300uses the image learning model learned to detect diseases and lesions in the X-ray image using the X-ray image as learning data, and the image file received from the image console viewer unit 200 .
- tag informationincluding a Screening Score, contour map information, or heat map information for each disease and lesion can be added to the image file.
- the image reading unit 300is an essential item for the image reading result.
- the reading resultPanitive, Negative
- the detectionScreening
- the detection scoreScreening Scores
- the contour map informationContour Map Information
- the image reading unit 300when the image reading result is displayed together with the image file, based on the image reading result implemented as an image, letters, and numbers in the tag information and location information about the display position of the image reading result You can create tag information with
- the image reading unit 300lower Sensitivity (0.3), low Sensitivity (0.4), Default Sensitivity (0.5), High Specificity (0.6), Higher Specificity (0.7), the threshold score (Threshold Score) as a reading standard
- Each tag informationcan be created by dividing by .
- the image reading unit 300records, in a lookup table, information on detailed items and details included in tag information according to a threshold score serving as a reading standard, in a lookup table, and Upon reading, based on the lookup table, detailed items and details of essential items to be included in the tag information are determined, and tag information can be generated based on this.
- the threshold scorewhich is the reading standard
- the Default Sensitivity0.5
- the detailed items and detailsare briefly displayed, so that the specificity is increased.
- itis displayed in a direction in which the sensitivity decreases, and the lower the value of 0.5, the more detailed it is.
- the image viewer unit 500when a threshold score as a reading standard is determined according to a user's input, the image reading result displayed on the screen according to the determined threshold score (Threshold Score) as a reading reference You can let the details and details be decided.
- the image management unit 400may store an image file to which tag information is added.
- the image manager 400may be implemented as a Picture Achieve and Communication System (PACS) for storing and transmitting medical images, and may store and transmit medical images processed by the real-time automatic X-ray image reading system. .
- PACSPicture Achieve and Communication System
- the image viewer unit 500may receive, decode (decode) the image file to which the tag information stored in the image management unit 400 is added, and display (display) the decryption result on the screen.
- the image viewer unit 500is implemented as a computing device or program for an interface that accesses the medical image stored in the image management unit 400 and displays it on a monitor screen, and the image reading unit 300 reads it.
- the tag information added to the medical image converted into an image filecan be decoded, and the reading result can be converted into an image or letters and numbers, superimposed on an existing medical image image, and generated to be provided to the medical staff.
- the medical staffcan more easily and accurately read the presence or absence of abnormalities and lesions in the medical image with reference to various reading results.
- the image viewer unit 500when displaying the image file on the screen, decodes the tag information added to the image file, so that the image, letters or numbers included in the tag information are displayed together with the image file, , the display positions of letters or numbers may be individually determined in the image file based on the respective position information.
- the image viewer unit 500when reading the image file and tag information, converts contour maps and heat maps stored as bytes into an array (Array Shape) according to each array shape. Array) and then converted to List and Tuple to create transformed information-based Contour Maps and Heat Maps, and if tag information is included in the image file, tag The icon and menu for displaying the image reading result included in the information are activated so that the image file is displayed together on the screen, and when a display of the image reading result is requested using the displayed icon and menu, the image reading result is displayed It can be displayed together with the image file.
- Array Shapean array
- ArrayList and Tuple to create transformed information-based Contour Maps and Heat Maps
- tag informationis included in the image file
- tag The icon and menu for displaying the image reading result included in the informationare activated so that the image file is displayed together on the screen, and when a display of the image reading result is requested using the displayed icon and menu, the image reading result is displayed It can be displayed together with the image file.
- FIG. 2is a diagram provided to explain the image console viewer 200 according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- the image console viewer 200performs a pre-processing process on an X-ray image received from the image acquisition unit to convert it into an image file of a preset format
- an image processor 210, X-ray Controller 220, Image Console Main Module 230, and DICOM Handler & Private tag Decoder 240may include
- the image processor 210receives a raw file having a raw file extension from the X-ray image acquisition unit 100 and performs noise cancellation, gamma correction, and brightness optimization ( Brightness Optimization, Adaptive Histogram Equalization (AHE), Global Contrast Adjustment, Local Contrast Enhancement, Image Sharpness & Smoothness Enhancing, Multi-frequency Processing ), etc., by performing image processing for image enhancement, the medical image on which image processing has been completed is converted into an image file, and thus a medical image in the form of a dicom file can be generated.
- the X-ray controller 220is provided for controlling and calibrating the X-ray image acquisition unit 100 .
- the image console main module 230may perform all functions of the image console viewer 200 and provide an interface to medical staff.
- the image console main module (Image Console Main Module) 230acquires an X-ray image by a medical staff registering patient information or controlling the X-ray image acquisition unit 100 , and provides a medical image to the image management unit 400 . It may perform a function of transmitting or receiving.
- the DICOM Handler & Private tag Decoder 240transmits the medical image in the form of a DICOM file generated through the image processor 210 to the image reader 300 and , when a medical image is read through the image reading unit 300 , a medical image to which tag information including a reading result is added is received, transmitted to the image management unit 400 , and tag information for the reading result is decoded. Reading results can be generated.
- 3is a diagram provided to explain the image reading unit 300 according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- the image reading unit 300receives an image file received from the image console viewer 200 as input, performs artificial intelligence-based image reading, and generates tag information including the image reading result.
- Image Pre-processing 310Image Classification Model 320, Object Detection Model 330, and Daicom Tag Generator (Inference Result DICOM Tag Adder) 340 may be included.
- the image pre-processing 310when a medical image in the form of a dicom file is received from the image console viewer 200 , the image pixel array of the received medical image is read, In order to match the size of the input tensor of the convolutional neural network, down-sampling may be performed, and image normalization and standardization may be performed.
- An Image Classification Model 320 and an Object Detection Model 330use a deep convolutional neural network based on pre-learned artificial intelligence to read a medical image in the form of a dicom file and , a detection score, a heatmap, a contour map, and a bounding box for each lesion can be generated as a result of the reading.
- the image classification model 320 and the object detection model 330include a string for the disease and lesion name in the tag information
- the stringWhen VR (Value Representation) of VR (Value Representation) is applied to LO (long String) to be included in tag information, and integer and floating-point Screening Scores are included in tag information, the detection score is set to DS (Decimal String) to be included in the tag information by applying to the tag information, and the tuple, list, and array of control maps, heat maps, or image shapes are included in tag information
- DSDecimal String
- 16 A byte for bitis applied to OW (Other Word String) and a byte for 8 bit is applied to OB (Other Byte String) to be included in tag information.
- the DICOM tag generator (Inference Result DICOM Tag Adder) 340generates tag information to store the lesion classification and detection result of the medical image, converts the data type according to the data type stored in the tag information, and encodes it , the encoding result can be saved.
- the DICOM tag generator (Inference Result DICOM Tag Adder) 340stores as it is if the read result is a string or a number (Number, integer or floating point), and the read result is a tuple or list If it is (List), it can be converted into an array (Array), and the converted array can be converted into bytes and stored.
- the image viewer unit 500may accurately decode and process tag information for the reading result, and store meta information necessary to generate the reading result together.
- the meta informationincludes version information on the Image Classification Model 320 and the Object Detection Model 330, and includes the type and size of data for the reading result. ), a shape, and the number of data bytes.
- the image reading unit 300receives the medical image in the form of a daicom file from the image console viewer unit 200, and the result of reading the received medical image and the image viewer unit 500 are stored in the daicom tag.
- the medical image in which meta information for accurately decoding the included reading result and generating the reading result is storedmay be transmitted to the image console viewer 200 .
- FIG. 4is a diagram provided to explain the image viewer unit 500 according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- the image viewer unit 500receives, decodes (decodes) an image file to which tag information stored in the image management unit 400 is added, and displays the decryption result on the screen, the image viewing main It may include a module (Image Viewing Main Module) 510, a tag information decoder (Private tag Decoder) 520 and a reader (Inference Result Constructor) 530 .
- a moduleImage Viewing Main Module
- tag information decoderPrimaryvate tag Decoder
- readerInference Result Constructor
- the image viewing main module 510reads the received medical image in the form of a dicom file, and decodes tag information added to the medical image through a private tag decoder 520 .
- the reading result and meta information included in the decrypted tag informationcan be superimposed on the medical image and displayed together on the screen.
- the tag information decoder (Private tag Decoder) 520decodes the tag information, converts the bytes for the read result into an array based on the decoding result, and converts meta information such as the decoded image shape and the number of data bytes.
- a read resultcan be generated by resizing an array or converting an array into a list and a tuple.
- the reader (Inference Result Constructor) 530superimposes the reading results of the detection score, bounding box, contour map, heat map, etc. generated on the medical image on the medical image to provide the medical team with a role to help the reading of the lesion can be performed.
- 5 to 6are diagrams illustrating an address, VR, VM, Description, and Keyword of a Daicom tag for storing a reading result and meta information through the image reading unit 300 according to an embodiment of the present invention. to be.
- 0x1001is assigned to the group number of the tag information, the element number is assigned from 0x1001 to 0x100F, and the file name, image type, lesion name, and It is a tag list that can store detection probability, bounding box, number of contour maps, shape of each contour coordinate, coordinate values of each contour map, heat map, and the like.
- the VR (value representation) of each tagindicates the data type stored in the tag.
- "LO”stands for long String
- "OW”stands for Other Word String
- “DS”stands for Decimal String
- "OB”stands for Other Byte String.
- OBis used to store a heat map.
- a heatmapstores a single channel having a value between 0 and 1
- the data typeis Float32 and "OW" VR can be applied.
- the image viewer unit 500 that implements the heatmap by decoding the DYCOM tagneeds to generate a color heatmap.
- a color heat mapmay be generated and stored.
- FIG. 6is a diagram illustrating meta information for accurately decoding tag information in the image viewer unit 500 or the image console viewer unit 200 .
- a software engineer who develops and maintains the image viewer software using meta informationcan accurately decode the information of the daicom tag information, generate the reading result of the medical image, and provide the image to the medical staff.
- the 7 to 20are images of reading the DYCOM file before and after storing the tag information (Private tag) for the reading result and meta information through the image reading unit 300 according to an embodiment of the present invention with the DYCOM file viewer.
- the fileis an exemplified drawing.
- FIG. 7 and 13show the medical image in the form of a daicom file generated by the image console viewer 200 using a general DYCOM viewer. 300) indicates that there is no tag information for the read result.
- FIG 8 and 14show a medical image in the form of a daicom file in which tag information is added to the result of reading the medical image generated by the image console viewer 200 by the image reading unit 300 in the form of a general daicom file. This is shown using the viewer.
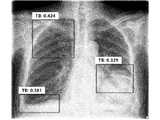
- FIG. 8shows that tag information on the reading result of the image reading unit 300 for the medical image of FIG. 7 is stored in the bounding box as shown.
- FIGS. 9 and 15are a reading result of a medical image, showing a bounding box superimposed on an image, FIGS. 10 and 16 are showing a contour map superimposed on an image, and FIGS. 9 and 17 are hits
- a map(Heat Map) is shown by superimposing it on an image, and FIGS. 12 and 18 show a detection score (Screening Score) with an image.
- FIG. 19shows an example of a result of the image reading unit 300 reading a plurality of lesions in a medical image, which indicates that tag information can be additionally generated as many as the number of lesions and stored in the private dicot tag. it has been shown
- FIG. 20is an example showing a plurality of detection results of the image reading unit 300 for a medical image by superimposing a plurality of bounding boxes on an image. This also indicates that the coordinates of the bounding box, the lesion name, and the detection probability can be additionally stored in the tag information as much as the number of bounding boxes.
- 21is a diagram provided to explain the operating characteristics of the image console viewer 200 according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- the image console viewer 200when the X-ray image acquisition unit 100 acquires an X-ray image from a patient, the image console viewer 200 generates a raw image from the X-ray image acquisition unit is received, the image is processed to be converted into an image file of a preset format such as a DYCOM file, and the medical image converted into the image file is transmitted to the image reading unit 300 .
- a preset formatsuch as a DYCOM file
- the image console viewer 200controls the X-ray image acquisition unit 100 to acquire an X-ray image, and changes the image acquisition condition of the X-ray image acquisition unit 100 or a calibration function of the X-ray detector. , patient settings, patient scheduling and monitoring, user settings, and image enhancement processing.
- the image management unit 400may perform various functions such as communication and storing, searching, and delivering medical images.
- the image console viewer 200maintains a state of waiting for a request from a user after completion of the normal system initialization operation (S2010) (S2020), and when a user's request occurs, processing is performed according to the request content It can be done (S2040).
- the image console viewer 200reads a raw file of a raw type from the X-ray image acquisition unit 100 and performs image processing for image enhancement It can be done (S2050).
- the image console viewer 200may generate a medical image as a DYCOM file by adding information on a standard DYCOM tag in accordance with a medical digital communication and image standard (S2060).
- the image console viewer 200may transmit the medical image in the form of a diacom file to the image reader 300 without directly transmitting the medical image in the form of a diacom file to the image management unit 400 after generating it ( S2070).
- the image reading unit 300generates tag information based on the reading result of the medical image in the form of a dicom file, adds it to the medical image in the form of a dicom file, and displays the medical image to which the tag information is added to the image console It can be transmitted to the viewer unit 200 .
- the image console viewer 200transmits a medical image having tag information storing the reading result of the medical image to the image management unit 400 .
- the image reading unit 300 solution of the present inventionis applied to immediately read it, and the operation of storing the reading result in the DIACOM standard medical image is performed.
- 22 to 23are diagrams provided to explain the operating characteristics of the image reading unit 300 according to an embodiment of the present invention.
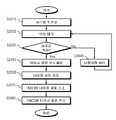
- FIG. 22is a flowchart of the image reading unit 300 reading the medical image and storing the reading result in the DICOM tag information, updating the DICOM file format medical image, and then transferring it back to the image console viewer 200 .
- the image reading unit 300classifies and detects the lesion of the medical image using a pre-learned artificial intelligence-based deep convolutional neural network, reads it, and includes the reading result tag information is generated, added to the medical image, and the medical image to which the tag information is added is transmitted to the image console viewer 200 .
- the image reading unit 300resides in the memory for a deep convolutional neural model for reading a medical image during system initialization and performs various operations and functions so that it can be read. In this state, it may be confirmed whether the medical image is transmitted from the image console viewer 200 ( S2120 ).
- the image reading unit 300reads the presence and/or location of the lesion on the medical image using the deep convolutional neural network (S2130), and outputs the read result to the DYCOM In order to store the tag information in an optimal state, the reading result may be classified and converted (S2140).
- the image reading unit 300may generate tag information for each reading result to be stored (S2150), and store the reading result and meta information of the image reading unit 300 in each tag (S2160, S2160, S2170).
- the image reading unit 300updates the medical image in the form of a daicom file by adding tag information to the existing DICOM medical image (S2180), and delivers the medical image in the form of a DICOM file to the image console viewer 200 It can be (S2190).
- the reading resultmay be displayed in various forms as illustrated in FIGS. 7 to 20 .
- Detection probability or scorecoordinate information of bounding box, class name and classification probability, coordinate information of outline map and number of outline maps, class name, heat map pixel array size information and pixel value are displayed.
- the various reading results described abovecan be classified into character strings, numbers, tuples, lists, arrays, etc. according to data classes and data attributes, and also whether the data are integers or real numbers, and the number of bytes required to represent the numbers in each case It can be classified according to the standard, and in order to transmit it according to the Daicom standard, it must be converted into a one-dimensional data form and transmitted.
- 23is an operation flowchart for explaining a read result classification and conversion method for storing a read result in tag information according to the present invention.
- the image reading unit 300reads a medical image and classifies data classes and data types (properties) of the reading results to generate tag information based on the reading results ( S2210 ).
- the image reading unit 300determines whether the tuple value is a real number or an integer number and whether the tuple value is a real number or an integer if the data class is a tuple, such as an image form expressed in a two-dimensional array or an image form of a contour map (S2215-Yes). Based on the conversion to an array (S2220), and again converted into a one-dimensional byte (S2225), tag information may be generated and added to the medical image.
- the image reading unit 300converts it into an array based on whether the value of the list is a real number or an integer and the number of bytes required (S2235) ), by converting it back to a one-dimensional byte ( S2240 ), it is possible to generate tag information and add it to the medical image.
- the image reading unit 300converts it into a one-dimensional byte (S2250) to generate tag information and add it to the medical image. .
- the image reading unit 300may process a data class such as a class name and a detection probability corresponding to a lesion as a result of the reading as character strings and numbers (S2260) to generate tag information and add it to the medical image.
- a data classsuch as a class name and a detection probability corresponding to a lesion as a result of the reading as character strings and numbers (S2260) to generate tag information and add it to the medical image.
- the image reading unit 300efficiently and effectively decodes the private DICOM tag in the image viewer unit 500 while conforming to the DICOM standard and restores the data classes and types (attributes) of various reading results to generate the reading results. This allows it to be displayed overlaid with the image.
- 24 to 25are diagrams provided to explain the operating characteristics of the image viewer unit 500 according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- a typical image vieweris a high-performance multi-monitor viewer for workstations, laptops, and tablets, has a variety of tool sets through image manipulation, layout and markup, and has a report writer, CD/media writing and hanging protocol, etc. It can be used to read, explain, and input a diagnosis result while a medical image is displayed during treatment.
- the tag informationis decoded to help the doctor make a diagnosis, and the reading result is reproduced to obtain the original detection score (Screening Score), An operation of generating a bounding box, a contour map, and a heat map will be described.
- the image console viewer 200transmits and stores the medical image in which the tag information received from the image reading unit 300 is stored to the image management unit 400 so that the medical staff can view the medical image using the image viewer 500 . reading, it is possible to see and read the reading result of the medical image.
- the image viewer unit 500may perform all necessary operations for system initialization (S2310), wait for a request from the user, and maintain the request standby state (S2320), and the user's request When generated, processing may be performed according to the request content (S2340).
- the image viewer unit 500decodes the tag information (S2350), and decodes the data class and type (attribute) (S2360) ), the reading result is generated in the form of a Screening Score, a Bounding Box, a Contour Map and a Heat Map (S2370), and displayed (displayed) on the screen, so that the medical staff It helps to read medical images.
- 25is a flowchart illustrating an operation of the image viewer unit 500 to accurately restore tag information information.
- the image viewer unit 500must decode in the exact reverse order to the order in which it was stored to normally decode the Screening Score, Bounding Box, Contour Map, and Heat Map. can do.
- the image viewer unit 500classifies the data class and data type (property) of the read result (S2410), converts the one-dimensional byte code into an array, converts it into a tuple, a list, and an array, and converts it into a heat map and a contour map Resizing can be done for creation.
- the image viewer unit 500restores (decoding) as it is, and if it is a byte (S2415-Yes), converts it to a character string or number (S2420), and a tuple If it is a byte corresponding to (S2425-Yes), it is converted into an array (S2430), converted into a tuple (S2435), and a byte corresponding to a list by applying the same real number or integer division as when saving and the required number of bytes exactly.
- the image viewer unit 500In order to process the medical image reading result of the present invention by the image viewer unit 500, it is possible to accurately generate the reading result from the tag information by utilizing the information necessary for restoration as described above, and also to the DYCOM meta information. Since it is possible to obtain accurate information necessary for generating a reading result by deciphering the tag, a software engineer developing the general image viewer unit 500 can generate the result read by the image reading unit 300 .
- the technical idea of the present inventioncan also be applied to a computer-readable recording medium containing a computer program for performing the functions of the apparatus and method according to the present embodiment.
- the technical ideas according to various embodiments of the present inventionmay be implemented in the form of computer-readable codes recorded on a computer-readable recording medium.
- the computer-readable recording mediummay be any data storage device readable by the computer and capable of storing data.
- the computer-readable recording mediummay be a ROM, RAM, CD-ROM, magnetic tape, floppy disk, optical disk, hard disk drive, or the like.
- the computer-readable code or program stored in the computer-readable recording mediummay be transmitted through a network connected between computers.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- High Energy & Nuclear Physics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Medical Treatment And Welfare Office Work (AREA)
- Apparatus For Radiation Diagnosis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 인공지능 기반의 엑스레이 영상 판독 방법 및 시스템에 관한 것으로, 더욱 상세하게는 의료현장에서 실시간으로 디지털 엑스레이 영상에 대해서 인공지능 기반 자동 엑스레이 영상 솔루션을 적용하여 판독하고 그 판독 결과인 이미지 분류 결과 및 이미지 검출 결과를 다이콤(DICOM, Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) 파일과 같은 기설정된 포맷의 이미지 파일의 태그 정보(Private tag)를 생성하여 저장하고, 이미지 파일의 태그 정보에 저장된 판독 결과를 해석하여 이미지 콘솔 뷰어로 판독 결과를 표시하는 장치 및 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a method and system for reading an X-ray image based on artificial intelligence, and more particularly, to a digital X-ray image in real time in a medical field, by applying an artificial intelligence-based automatic X-ray image solution to read it, and an image classification result that is the reading result And the image detection result is created and stored as tag information (Private tag) of an image file in a preset format such as a DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) file, and the reading result stored in the tag information of the image file is analyzed The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for displaying a reading result with an image console viewer.
일반적으로, 의료 영상은 현대 의학에서 환자의 진단 및 치료를 위한 중요한 도구 중의 하나이다. 특히, 환자의 방사선 촬영이미지는 검사 비용이 저렴하고 빠른 진단이 가능하기 때문에 일차적으로 환자를 진단하기 위해 많이 활용되고 있다.In general, medical imaging is one of the important tools for diagnosis and treatment of patients in modern medicine. In particular, the radiographic image of a patient is widely used to primarily diagnose a patient because the examination cost is low and a quick diagnosis is possible.
그러나, 숙련된 방사선 전문의라고 하더라도 환자의 방사선 촬영 이미지에서 정확하게 병변(lesion)의 위치를 파악하고 상기 병변을 야기한 질병을 진단하는 것은 매우 어려운 문제이다. 이는 3차원의 인체 내부 구조를 2차원의 방사선 촬영 이미지로 변환하는 과정에서 발생하는 정보의 유실과 사람의 지각 능력의 한계 등 복합적인 요인으로 인해 발생한다.However, it is very difficult for even an experienced radiologist to accurately locate a lesion in a radiographic image of a patient and diagnose a disease causing the lesion. This occurs due to complex factors such as loss of information that occurs in the process of converting a three-dimensional internal structure of the human body into a two-dimensional radiographic image and limitations in human perception.
상술한 문제를 해결하기 위해 인공지능 기반 지도 학습(supervised learning) 방식의 다양한 기계 학습(machine learning) 알고리즘을 적용하여 컴퓨터 보조 진단(Computer-Aided Diagnosis; CAD)을 수행하는 연구가 진행되고 있다.In order to solve the above-mentioned problem, research on performing computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) by applying various machine learning algorithms of an artificial intelligence-based supervised learning method is being conducted.
예를 들면, 종래기술인 한국등록특허 제10-1628276호에는 클라우드 기반 병리 분석 시스템 및 방법에 대한 기술이 개시되어 있으나, 클라우드 서버에 접속하여 결핵 등과 같은 병리 진단을 하는 경우에, 대학병원, 대형병원에서와 같이 인터넷 인프라가 잘 갖추어진 곳에서는 자동 진단을 하는데 큰 문제가 없지만, 인터넷 인프라가 잘 갖추어지지 않은 곳에서는 진단에 많은 시간이 소요된다는 문제점이 있어 그 한계가 존재한다. 더불어, 인터넷에 문제가 발생하거나 인터넷 속도가 저하되는 경우에는 의사의 업무에 막대한 지장을 줄 수 있다는 문제가 있다.For example, the prior art Korean Patent No. 10-1628276 discloses a technology for a cloud-based pathology analysis system and method. There is no big problem in auto-diagnosis in a place where the Internet infrastructure is well-equipped, as shown in Figure 1. However, there is a problem in that it takes a lot of time for diagnosis in a place where the Internet infrastructure is not well-equipped, so there is a limitation. In addition, if there is a problem with the Internet or the Internet speed is slowed down, there is a problem that the doctor's work can be greatly hindered.
따라서 본 발명에서는 이러한 문제점을 해결하여 의료현장에서 의료인이 실시간으로 보다 효과적이고 효율적으로 엑스레이 영상의 판독 결과를 획득하고, 관리할 수 있는 방안의 모색이 요구된다.Therefore, in the present invention, it is required to find a way to solve these problems and to enable medical personnel to more effectively and efficiently obtain and manage X-ray image reading results in real time in a medical field.
본 발명은 상기와 같은 문제점을 해결하기 위하여 안출된 것으로서, 본 발명의 목적은, 의료현장에서 인공지능 자동 엑스레이 판독 솔루션을 이용하여 환자의 엑스레이 영상을 취득한 후 바로 의료진에게 실시간으로 결과를 제공할 수 있는 인공지능 기반 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 방법 및 시스템을 제공함에 있다.The present invention has been devised to solve the above problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide results to medical staff in real time immediately after obtaining an X-ray image of a patient using an artificial intelligence automatic X-ray reading solution in a medical field. It is to provide a method and system for real-time automatic X-ray image reading based on artificial intelligence.
또한, 본 발명의 다른 목적은, 인공지능 기반 자동 엑스레이 영상의 판독 결과를 다이콤 표준에 맞추어 태그 정보를 생성하여 태그에 저장할 판독 결과의 데이터 형식에 따라 최적의 데이터 형식으로 변환 저장하여, 저장된 태그를 최적의 데이터 형식에 기반하여 해독하여 원 데이터 형식으로 변환하여 판독 결과를 표시할 수 있는 인공지능 기반 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 방법 및 시스템을 제공함에 있다.In addition, another object of the present invention is to generate tag information based on the AI-based automatic X-ray image reading result in accordance with the Daicom standard, convert it into an optimal data format according to the data format of the reading result to be stored in the tag, and store the stored tag To provide a real-time automatic X-ray image reading method and system based on artificial intelligence that can decode and display the reading result by converting it into the original data format based on the optimal data format.
그리고 본 발명의 또 다른 목적은, 인공지능 기반 자동 엑스레이 판독 결과에 대한 태그 상세 규격 및 태그 정보 해석 및 표시방법을 제공하여 제3자가 이를 이용하여 판독 결과를 표시하는 솔루션을 개발하는 경우, 제3자의 이미지 콘솔 뷰어 프로그램(이미지 콘솔 뷰어부)에 범용적으로 적용할 수 있는 인공지능 기반 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 방법 및 시스템을 제공함에 있다.And another object of the present invention is to provide a detailed tag specification for an artificial intelligence-based automatic X-ray reading result and a tag information interpretation and display method, and when a third party develops a solution that displays the reading result using it, the third It is to provide an artificial intelligence-based real-time automatic X-ray image reading method and system that can be universally applied to the user's image console viewer program (image console viewer unit).
상기 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른, 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 시스템은, 환자의 엑스레이 영상을 획득하는 엑스레이 영상 획득부; 영상 획득부로부터 수신되는 엑스레이 영상을 대상으로 전처리 과정을 수행하여 기설정된 포맷의 이미지 파일로 변환하도록 하는 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부; 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부로부터 수신되는 이미지 파일을 입력으로, 인공지능 기반의 영상 판독을 수행하고, 영상 판독 결과가 포함된 태그 정보를 생성하여, 이미지 파일에 부가하는 영상 판독부; 태그 정보가 부가된 이미지 파일을 저장하는 영상 관리부; 및 영상 관리부에 저장된 태그 정보가 부가된 이미지 파일을 수신하여, 화면에 표시하는 이미지 뷰어부;를 포함한다.According to an embodiment of the present invention for achieving the above object, a real-time automatic X-ray image reading system includes: an X-ray image acquisition unit for acquiring an X-ray image of a patient; an image console viewer unit that converts the X-ray image received from the image acquisition unit into an image file of a preset format by performing a pre-processing process; an image reading unit that reads an image based on artificial intelligence by inputting an image file received from the image console viewer unit, generates tag information including an image reading result, and adds it to the image file; an image management unit that stores an image file to which tag information is added; and an image viewer unit that receives the image file to which tag information stored in the image management unit is added, and displays the image file on the screen.
그리고 영상 판독부는, 엑스레이 영상을 학습 데이터로 엑스레이 영상 내 질환 및 병변의 검출을 위해 학습된 이미지 학습 모델을 이용하여, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부로부터 수신되는 이미지 파일을 판독하고, 각 질환 및 병변에 대해 검출 점수(Screening Score), 윤곽선 맵 정보 또는 히트 맵 정보가 포함된 태그 정보를 이미지 파일에 부가할 수 있다.In addition, the image reading unit reads the image file received from the image console viewer unit by using the image learning model learned to detect diseases and lesions in the X-ray image using the X-ray image as learning data, and detects each disease and lesion. Tag information including Screening Score, outline map information, or heat map information can be added to the image file.
또한, 영상 판독부는, 영상 판독 결과가 이미지 파일과 함께 표시되는 경우, 태그 정보에 이미지, 문자 및 숫자로 구현되는 영상 판독 결과와 영상 판독 결과의 표시 위치에 대한 위치 정보를 기반으로 태그 정보를 생성할 수 있다.In addition, when the image reading result is displayed together with the image file, the image reading unit generates tag information based on the image reading result implemented as images, letters, and numbers in the tag information and location information about the display position of the image reading result can do.
그리고 이미지 뷰어부는, 이미지 파일을 화면에 표시하는 경우, 이미지 파일에 부가된 태그 정보를 해독하여, 태그 정보에 포함된 이미지, 문자 또는 숫자가 이미지 파일과 함께 표시되도록 하되, 이미지, 문자 또는 숫자의 표시 위치가, 각각의 위치 정보를 기반으로 이미지 파일 내에서 개별적으로 결정되도록 할 수 있다.And the image viewer unit, when displaying the image file on the screen, decodes the tag information added to the image file, so that the image, letters or numbers included in the tag information are displayed together with the image file, The display position may be individually determined in the image file based on the respective position information.
또한, 영상 판독부는, 태그 정보에 질환 및 병변 명에 대한 문자열(String)이 포함되도록 하는 경우, 문자열의 VR(Value Representation)을 LO(long String)에 적용하여 태그 정보에 포함되도록 하고, 태그 정보에 정수 및 부동소수점인 검출 점수(Screening Scores)가 포함되도록 하는 경우, 검출 점수를 DS(Decimal String)에 적용하여 태그 정보에 포함되도록 하고, 태그 정보에 컨트롤 맵(Control Maps), 히트 맵(Heat Maps) 또는 이미지형태(Image Shape)의 튜플(Tuple), 리스트(List) 및 어레이(Array)가 포함되도록 하는 경우, 컨트롤 맵(Control Maps), 히트 맵(Heat Maps) 또는 이미지형태(Image Shape)의 튜플(Tuple), 리스트(List) 및 어레이(Array)에 대한 정보를 바이트로 변환시킨 후, 16비트에 대한 바이트를 OW(Other Word String)에 적용하고, 8비트에 대한 바이트를 OB(Other Byte String)에 적용하여 태그 정보에 포함되도록 할 수 있다.In addition, when the image reading unit includes a string for the disease and lesion name in the tag information, the VR (Value Representation) of the string is applied to the LO (long String) to be included in the tag information, and the tag information In the case of including integer and floating-point Screening Scores, the detection score is applied to the DS (Decimal String) to be included in the tag information, and the tag information includes Control Maps and Heat Maps. Maps) or image shape (Tuple), list (List) and array (Array) to be included, control map (Control Maps), heat map (Heat Maps) or image shape (Image Shape) After converting information about tuple, list, and array of Byte String) to be included in tag information.
그리고 이미지 뷰어부는, 이미지 파일 및 태그 정보 판독 시, 바이트로 저장된 윤곽선 맵(Contour Maps)과 히트 맵(Heat Maps)을 각각의 어레이 형상(Array Shape)에 따라 어레이(Array)로 변환시킨 후 리스트(List) 및 튜플(Tuple)로 변환하여 변환된 정보 기반 윤곽선 맵(Contour Maps) 및 히트 맵(Heat Maps)를 생성하고, 이미지 파일에 태그 정보가 포함되는 경우, 태그 정보에 포함된 영상 판독 결과를 표시하는 아이콘 및 메뉴가 활성화되어, 이미지 파일이 표시되는 화면에 함께 표시되도록 하고, 표시된 아이콘 및 메뉴를 이용하여 영상 판독 결과의 표시를 요청하는 경우, 영상 판독 결과가 이미지 파일과 함께 표시되도록 할 수 있다.And when the image viewer unit reads image file and tag information, it converts contour maps and heat maps stored as bytes into an array according to each array shape, and then lists ( List) and tuple to create transformed information-based contour maps and heat maps, and when tag information is included in the image file, the image reading result included in the tag information The displayed icon and menu are activated so that the image file is displayed together on the displayed screen, and when the display of the image reading result is requested using the displayed icon and menu, the image reading result can be displayed together with the image file have.
또한, 영상 판독부는, 영상 판독 결과에 대한 필수 항목으로 각 질환 및 병변에 대한 판독결과(Positive, Negative), 검출(Screening) 결과, 검출 점수(Screening Scores), 윤곽선 맵 정보(Contour Map Information) 및 히트 맵 정보(Heat Map information)이 포함되도록 할 수 있다.In addition, the image reading unit is an essential item for the image reading result, and the reading result (Positive, Negative), the detection (Screening) result, the detection score (Screening Scores), the contour map information for each disease and lesion (Contour Map Information) and Heat map information may be included.
그리고 영상 판독부는, 판독 기준이 되는 임계 점수(Threshold Score)를 lower Sensitivity(0.3), low Sensitivity(0.4), Default Sensitivity(0.5), High Specificity(0.6), Higher Specificity(0.7)으로 구분하여 각각 태그 정보를 생성하고, 이미지 뷰어부는, 사용자의 입력에 따라 판독 기준이 되는 임계 점수(Threshold Score)가 결정되면, 결정된 판독 기준이 되는 임계 점수(Threshold Score)에 따라 화면에 표시되는 영상 판독 결과의 세부 항목 및 세부 내용이 결정되도록 할 수 있다.And the image reader divides the threshold score, which is the reading standard, into lower Sensitivity (0.3), low Sensitivity (0.4), Default Sensitivity (0.5), High Specificity (0.6), and Higher Specificity (0.7), and tags each The image viewer unit generates information, and when a threshold score as a reading standard is determined according to a user's input, details of the image reading result displayed on the screen according to the determined threshold score as a reading standard Allow items and details to be determined.
한편, 본 발명의 다른 실시예에 따른, 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 방법은, 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 시스템이, 환자의 엑스레이 영상을 획득하는 단계; 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 시스템이, 엑스레이 영상을 대상으로 전처리 과정을 수행하여 기설정된 포맷의 이미지 파일로 변환하도록 하는 단계; 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 시스템이, 이미지 파일을 입력으로, 인공지능 기반의 영상 판독을 수행하고, 영상 판독 결과가 포함된 태그 정보를 생성하여, 이미지 파일에 부가하는 단계; 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 시스템이, 태그 정보가 부가된 이미지 파일을 저장하는 단계; 및 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 시스템이, 저장된 태그 정보가 부가된 이미지 파일을 화면에 표시하는 단계;를 포함한다.On the other hand, according to another embodiment of the present invention, a real-time automatic X-ray image reading method includes: acquiring, by a real-time automatic X-ray image reading system, an X-ray image of a patient; A real-time automatic X-ray image reading system, performing a pre-processing process on the X-ray image to convert it into an image file of a preset format; A real-time automatic X-ray image reading system, inputting an image file, performing artificial intelligence-based image reading, generating tag information including the image reading result, and adding it to the image file; A real-time automatic X-ray image reading system comprising: storing an image file to which tag information is added; and displaying, by the real-time automatic X-ray image reading system, the image file to which the stored tag information is added on the screen.
이상 설명한 바와 같이, 본 발명의 실시예들에 따르면, 환자의 엑스레이 영상을 획득하자 마자 거의 실시간으로 인공지능 기반 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 결과를 원격의 이미지 콘솔 뷰어(Image Console Viewer)를 활용하여 AXIR(영상 판독부)가 판독한 결과, 즉, 검출 점수(Screening Score), 바운딩 박스(bounding Box), 윤곽선 맵(Contour Map) 및 히트 맵(Heatmap) 등의 정보를 판독 보조 자료로 생성하여 의료진에게 제공할 수 있다. 이를 통해, 의료진은 전술한 판독 보조 정보에 기반하여 디지털 영상 이미지를 효율적이고 효과적으로 판독할 수 있다.As described above, according to the embodiments of the present invention, as soon as an X-ray image of a patient is acquired, an artificial intelligence-based automatic X-ray image reading result is displayed in real time using a remote Image Console Viewer (AXIR). The reading result), that is, information such as Screening Score, bounding box, Contour Map, and Heatmap, can be generated as reading aids and provided to medical staff. can Through this, the medical staff can efficiently and effectively read the digital video image based on the above-described reading assistance information.
또한, 본 발명의 실시예들에 따르면, 디지털 엑스레이 영상을 획득하여 이미지 처리를 한 후 다이콤 파일을 저장하는 시점에서 본 발명의 AXIR(영상 판독부)를 이용하여 추론한 검출 점수(Screening Score), 바운딩 박스(bounding Box), 윤곽선 맵(Contour Map) 및 히트 맵(Heatmap) 등의 판독 결과를 저장한 태그의 주소, VR, Value 등의 상세 스펙과 저장 데이터 형태 및 내용에 대한 정보 그리고 AXIR(영상 판독부)와 관련된 심층 합성곱 신경망의 버전, 다이콤 태그 상세스펙과 내용 등의 메타 정보를 모두 다이콤 파일에 저장이 가능하며, 이를 통하여 일반인 즉, 환자는 의료진으로부터 엑스레이 촬영 후 진료 시 의사의 소견을 공유할 수 있다.In addition, according to embodiments of the present invention, the detection score inferred using the AXIR (image reading unit) of the present invention at the time of storing the daicom file after image processing by acquiring a digital X-ray image (Screening Score) , information on detailed specifications such as address, VR, and value of the tag that stores the reading results such as , bounding box, contour map, and heatmap, as well as the form and content of stored data, and AXIR ( Meta information such as the version of the deep convolutional neural network related to the image reader) and the detailed specifications and contents of the Daicom tag can all be stored in the Daicom file. can share their opinions.
그리고 본 발명의 실시예들에 따르면, 영상 판독부의 판독결과를 다이콤 태그에 저장 시 판독에 사용한 심층 합성곱 신경망에 대한 버전 및 메타 정보를 상세 스펙에 포함 저장함으로써, 본 발명의 다이콤 태그 상세 스펙 및 내용을 사용하는 일반 이미지 뷰어를 개발하는 회사 및 개개인에게 유용한 정보를 제공할 수 있고 또한 그들의 의견을 수렴하여 반영할 수 있다.And, according to the embodiments of the present invention, when the reading result of the image reading unit is stored in the DICOM tag, the version and meta information for the deep convolutional neural network used for reading are included and stored in the detailed specification, so that the DICOM tag of the present invention is detailed. Useful information can be provided to companies and individuals developing general image viewers using specifications and contents, and their opinions can be collected and reflected.
또한, 본 발명의 실시예들에 따르면, 학습된 복수 개의 고 정확도, 고 민감도 및 고 특이도를 가진 딥러닝 기반의 학습 모델을 적용함으로써, 다양한 진단 서비스의 구성 및 제공이 가능하고 모델을 용이하게 갱신할 수 있다.In addition, according to the embodiments of the present invention, by applying a plurality of learned deep learning-based learning models having high accuracy, high sensitivity and high specificity, it is possible to configure and provide various diagnostic services and to facilitate the model Can be updated.
그리고 본 발명의 실시예들에 따르면, 환자가 엑스-레이 촬영에서부터 그 진단결과를 산출하기까지의 과정에서 실시간으로 의사 및 의료 관계자에게 필요한 정보를 제공하여 의료 워크플로우(Medical Work Flow)를 합리화, 효율화 및 최적화가 가능하게 하여 의료기관의 환자 진료율 제고가 가능하여 비용 절감을 할 수 있다.And, according to embodiments of the present invention, medical workflow is streamlined by providing necessary information to doctors and medical personnel in real time in the process from the patient's X-ray imaging to calculating the diagnosis result, By enabling efficiency and optimization, it is possible to increase the patient treatment rate in medical institutions, thereby reducing costs.
도 1은, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 인공지능 기반 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 시스템의 설명에 제공된 도면,1 is a view provided for the explanation of an artificial intelligence-based real-time automatic X-ray image reading system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
도 2는, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부의 설명에 제공된 도면,2 is a view provided for explanation of an image console viewer unit according to an embodiment of the present invention;
도 3은, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 영상 판독부의 설명에 제공된 도면,3 is a view provided for explanation of an image reading unit according to an embodiment of the present invention;
도 4는, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 이미지 뷰어부의 설명에 제공된 도면,4 is a view provided for explanation of an image viewer unit according to an embodiment of the present invention;
도 5 내지 도 6은, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 영상 판독부를 통한 판독 결과 및 메타 정보를 저장하기 위한 다이콤 태그의 주소, VR, VM, Description 및 Keyword 등이 예시된 도면,5 to 6 are diagrams illustrating an address, VR, VM, Description, and Keyword of a daicom tag for storing a reading result and meta information through an image reading unit according to an embodiment of the present invention;
도 7 내지 도 20는, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 영상 판독부를 통한 판독 결과 및 메타 정보에 대한 태그 정보(Private tag) 저장 전후의 다이콤 파일을 다이콤 파일 뷰어로 읽은 이미지 파일이 예시된 도면,7 to 20 are exemplified image files obtained by reading the DYCOM file before and after storing the tag information (Private tag) for the meta information and the reading result through the image reading unit according to an embodiment of the present invention with the DYCOM file viewer floor plan,
도 21은, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부의 동작 특성의 설명에 제공된 도면,21 is a view provided for explanation of operation characteristics of an image console viewer unit according to an embodiment of the present invention;
도 22 내지 도 23은, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 영상 판독부의 동작 특성의 설명에 제공된 도면,22 to 23 are views provided for explanation of operating characteristics of an image reading unit according to an embodiment of the present invention;
도 24 내지 도 25는, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 이미지 뷰어부의 동작 특성의 설명에 제공된 도면이다.24 to 25 are diagrams provided to explain the operation characteristics of the image viewer unit according to an embodiment of the present invention.
이하에서는 도면을 참조하여 본 발명을 보다 상세하게 설명한다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to the drawings.
도 1은, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 인공지능 기반 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 시스템(이하에서는 '실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 시스템'으로 총칭하기로 함)의 설명에 제공된 도면이다.1 is a diagram provided for explanation of an artificial intelligence-based real-time automatic X-ray image reading system (hereinafter, collectively referred to as 'real-time automatic X-ray image reading system') according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 실시예에 따른 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 시스템은, 의료현장에서 인공지능 자동 엑스레이 판독 솔루션을 이용하여 환자의 엑스레이 영상을 취득한 후 바로 의료진에게 실시간으로 결과를 제공할 수 있으며, 인공지능 기반 자동 엑스레이 영상의 판독 결과를 다이콤 표준에 맞추어 태그 정보(Private tag)를 생성하여 태그에 저장할 판독 결과의 데이터 형식에 따라 최적의 데이터 형식으로 변환 저장하여, 저장된 태그를 최적의 데이터 형식에 기반하여 해독하여 원 데이터 형식으로 변환하여 판독 결과를 표시할 수 있다.The real-time automatic X-ray image reading system according to this embodiment can provide real-time results to medical staff immediately after acquiring an X-ray image of a patient using an artificial intelligence automatic X-ray reading solution in a medical field, and artificial intelligence-based automatic X-ray image Creates tag information (Private tag) according to the Daicom standard, converts the read result to the optimal data format according to the data format of the read result to be stored in the tag, and stores it. It can be converted to data format to display the reading result.
이를 위하여, 본 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 시스템은, 엑스레이 영상 획득부(100), 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200), 영상 판독부(300), 영상 관리부(400) 및 이미지 뷰어부(500)를 포함할 수 있다.To this end, the real-time automatic X-ray image reading system includes an X-ray
엑스레이 영상 획득부(100)는, 환자의 엑스레이 영상을 획득하기 위해 마련된다.The X-ray
구체적으로, 엑스레이 영상 획득부(100)는, 환자로부터 엑스레이 영상을 획득하기 위한 엑스레이 발생기, 디지털 평판 엑스레이 디텍터 및 제어 판넬 등으로 구성되며, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)와 통신을 하며 주요 기능은 환자의 엑스레이 영상을 취득하여 파일 확장자가 로우(RAW)인 원시파일을 생성할 수 있다.Specifically, the X-ray
이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)는, 컴퓨터 장치로 구현되어, 영상 획득부로부터 수신되는 엑스레이 영상을 대상으로 전처리 과정을 수행하여 기설정된 포맷의 이미지 파일로 변환하도록 할 수 있다.The
구체적으로, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)는, 엑스레이 영상 획득부(100)와 통신을 하며 디지털 평판 엑스레이 디텍터(Digital flat Panel X-ray Detector)의 특성을 교정하고, 환자가 엑스레이 영상 취득을 엑스레이 영상 획득부(100)를 제어하고, 또한 취득한 엑스레이 영상 파일 수신하여 다양한 이미지 처리를 하고 환자에 대한 정보를 등록하여 기록할 수 있다.Specifically, the
구체적으로, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)는, 영상 판독부(300)와 정보를 주고 받으며, 영상 관리부(400)와 DICOM(Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) 표준의 의료 영상을 송수신할 수 있다.Specifically, the
영상 판독부(300)는, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)로부터 수신되는 이미지 파일을 입력으로, 인공지능 기반의 영상 판독을 수행하고, 영상 판독 결과가 포함된 태그 정보를 생성하여, 이미지 파일에 부가하여, 인코딩할 수 있다.The
구체적으로, 영상 판독부(300)는, AXIR(Automatic X-ray Image Reader)로 구현되어, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)가 전송한 의료 영상을 입력으로 하여 기학습된 인공지능 기반의 심층 합성곱 신경망을 이용하여 의료 영상의 병변을 분류 및 검출하여 판독하고, 영상 판독 결과가 포함된 태그 정보(Private tag)를 생성하여, 이미지 파일로 변환된 의료 영상에 부가하여, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)로 전송할 수 있다.Specifically, the
예를 들면, 영상 판독부(300)는, 엑스레이 영상을 학습 데이터로 엑스레이 영상 내 질환 및 병변의 검출을 위해 학습된 이미지 학습 모델을 이용하여, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)로부터 수신되는 이미지 파일을 판독하고, 각 질환 및 병변에 대해 검출 점수(Screening Score), 윤곽선 맵 정보 또는 히트 맵 정보가 포함된 태그 정보를 이미지 파일에 부가할 수 있다.For example, the
즉, 영상 판독부(300)는, 영상 판독 결과에 대한 필수 항목으로 각 질환 및 병변에 대한 판독결과(Positive, Negative), 검출(Screening) 결과, 검출 점수(Screening Scores), 윤곽선 맵 정보(Contour Map Information) 및 히트 맵 정보(Heat Map information)이 포함되도록 할 수 있다.That is, the
그리고 이때, 영상 판독부(300)는, 영상 판독 결과가 이미지 파일과 함께 표시되는 경우, 태그 정보에 이미지, 문자 및 숫자로 구현되는 영상 판독 결과와 영상 판독 결과의 표시 위치에 대한 위치 정보를 기반으로 태그 정보를 생성할 수 있다.And at this time, the
한편, 영상 판독부(300)는, 판독 기준이 되는 임계 점수(Threshold Score)를 lower Sensitivity(0.3), low Sensitivity(0.4), Default Sensitivity(0.5), High Specificity(0.6), Higher Specificity(0.7)으로 구분하여 각각 태그 정보를 생성할 수 있다.On the other hand, the
구체적으로, 영상 판독부(300)는, 판독 기준이 되는 임계 점수(Threshold Score)에 따라 태그 정보에 포함되는 세부 항목 및 세부 내용에 대한 정보를 룩업테이블(Lookup Table)에 기록하고, 의료 영상의 판독 시, 룩업테이블을 기반으로, 태그 정보에 포함되어야 하는 필수 항목의 세부 항목 및 세부 내용이 결정되고, 이를 기반으로 태그 정보를 생성할 수 있다.Specifically, the
여기서, 영상 판독부(300)는, 판독 기준이 되는 임계 점수(Threshold Score)가 Default Sensitivity(0.5)를 기준으로 높을수록, 세부 항목 및 세부 내용이 간략하게 표시되어, 특이도(specificity)가 증가하고, 반면 검출도(sensitivity)가 감소하는 방향으로 표시되며, 0.5를 기준으로 낮을수록 자세하게 표시되어, 세부 항목 및 세부 내용의 검출도가 증가하는 대신, 특이도가 감소하는 방향으로 표시되도록 설정될 수 있다.Here, in the
더불어, 이미지 뷰어부(500)는, 사용자의 입력에 따라 판독 기준이 되는 임계 점수(Threshold Score)가 결정되면, 결정된 판독 기준이 되는 임계 점수(Threshold Score)에 따라 화면에 표시되는 영상 판독 결과의 세부 항목 및 세부 내용이 결정되도록 할 수 있다.In addition, the
영상 관리부(400)는 태그 정보가 부가된 이미지 파일을 저장할 수 있다.The
구체적으로, 영상 관리부(400)는, 의료 영상의 저장 및 전송을 수행하는 PACS(Picture Achieve and Communication System)로 구현되어, 본 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 시스템이 처리하는 의료 영상들을 저장하고, 전송할 수 있다.Specifically, the
이미지 뷰어부(500)는, 영상 관리부(400)에 저장된 태그 정보가 부가된 이미지 파일을 수신하여, 해독(디코딩)하고, 해독 결과를 화면에 표시(디스플레이)할 수 있다.The
구체적으로, 이미지 뷰어부(500)는, 영상 관리부(400)에 저장된 의료 영상을 액세스(Access)하여 모니터 화면에 표시하는 인터페이스를 위한 컴퓨팅 장치 또는 프로그램으로 구현되며, 영상 판독부(300)가 판독하여 이미지 파일로 변환된 의료 영상에 부가한 태그 정보를 해독하여, 판독 결과를 이미지 또는 문자 및 숫자로 변환하여 기존 의료 영상 이미지에 중첩, 생성하여 의료진에게 제공할 수 있다.Specifically, the
이를 통해, 의료진은, 다양한 판독결과를 참조하여 의료 영상의 이상 유무 및 병변을 보다 쉽고 정확하게 판독할 수 있다.Through this, the medical staff can more easily and accurately read the presence or absence of abnormalities and lesions in the medical image with reference to various reading results.
또한, 이미지 뷰어부(500)는, 이미지 파일을 화면에 표시하는 경우, 이미지 파일에 부가된 태그 정보를 해독하여, 태그 정보에 포함된 이미지, 문자 또는 숫자가 이미지 파일과 함께 표시되도록 하되, 이미지, 문자 또는 숫자의 표시 위치가, 각각의 위치 정보를 기반으로 이미지 파일 내에서 개별적으로 결정되도록 할 수 있다.In addition, the
다른 예를 들면, 이미지 뷰어부(500)는, 이미지 파일 및 태그 정보 판독 시, 바이트로 저장된 윤곽선 맵(Contour Maps)과 히트 맵(Heat Maps)을 각각의 어레이 형상(Array Shape)에 따라 어레이(Array)로 변환시킨 후 리스트(List) 및 튜플(Tuple)로 변환하여 변환된 정보 기반 윤곽선 맵(Contour Maps) 및 히트 맵(Heat Maps)를 생성하고, 이미지 파일에 태그 정보가 포함되는 경우, 태그 정보에 포함된 영상 판독 결과를 표시하는 아이콘 및 메뉴가 활성화되어, 이미지 파일이 표시되는 화면에 함께 표시되도록 하고, 표시된 아이콘 및 메뉴를 이용하여 영상 판독 결과의 표시를 요청하는 경우, 영상 판독 결과가 이미지 파일과 함께 표시되도록 할 수 있다.For another example, the
도 2는, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)의 설명에 제공된 도면이다.2 is a diagram provided to explain the
도 2를 참조하면, 본 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)는, 영상 획득부로부터 수신되는 엑스레이 영상을 대상으로 전처리 과정을 수행하여 기설정된 포맷의 이미지 파일로 변환하도록 하기 위해, 이미지 프로세서(Image Processor)(210), 엑스-레이 컨트롤러(X-ray Controller)(220), 이미지 콘솔 메인 모듈(Image Console Main Module)(230) 및 다이콤 핸들러 및 태그 정보 디코더(DICOM Handler & Private tag Decoder)(240)를 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 2 , the
이미지 프로세서(Image Processor)(210)는, 엑스레이 영상 획득부(100)로부터 파일 확장자가 로우(raw)인 원시파일을 수신하여 노이즈 켄슬링(Noise Cancelling), 감마 교정(Gamma Correction), 밝기 최적화(Brightness Optimization), AHE(Adaptive Histogram Equalization), 전체 대비 조정(Global Contrast Adjustment), 부분 대비 강화(Local Contrast Enhancement), 이미지 선명도 및 평활도 강화(Image Sharpness & Smoothness Enhancing), 멀티 주파수 프로세싱(Multi-frequency Processing) 등의 여러가지 이미지 향상을 위한 이미지 프로세싱을 수행하여, 이미지 프로세싱이 완료된 의료 영상을 이미지 파일로 변환시켜, 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상을 생성할 수 있다.The
엑스-레이 컨트롤러(X-ray Controller)(220)는, 엑스레이 영상 획득부(100)의 제어 및 교정을 위해 마련된다.The
이미지 콘솔 메인 모듈(Image Console Main Module)(230)은 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)의 제반 기능을 수행하고 의료진에서 인터페이스를 제공할 수 있다.The image console
구체적으로, 이미지 콘솔 메인 모듈(Image Console Main Module)(230)은 의료진이 환자 정보를 등록하거나 또는 엑스레이 영상 획득부(100)를 제어하여 엑스레이 영상을 획득하고, 영상 관리부(400)에 의료 영상을 전달하거나 또는 수신하는 기능을 수행할 수 있다.Specifically, the image console main module (Image Console Main Module) 230 acquires an X-ray image by a medical staff registering patient information or controlling the X-ray
다이콤 핸들러 & 태그 정보 디코더(DICOM Handler & Private tag Decoder)(240)는, 이미지 프로세서(Image Processor)(210)를 통해 생성된 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상을 영상 판독부(300)에 전달하고, 영상 판독부(300)를 통해, 의료 영상이 판독되면, 판독 결과를 포함하는 태그 정보가 부가된 의료 영상을 수신하여, 영상 관리부(400)에 전달하고, 판독 결과에 대한 태그 정보를 해독하여 판독 결과를 생성할 수 있다.The DICOM Handler &
도 3은, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 영상 판독부(300)의 설명에 제공된 도면이다.3 is a diagram provided to explain the
도 3을 참조하면, 영상 판독부(300)는, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)로부터 수신되는 이미지 파일을 입력으로, 인공지능 기반의 영상 판독을 수행하고, 영상 판독 결과가 포함된 태그 정보를 생성하여, 이미지 파일에 부가하기 위해, 이미지 전처리 프로세싱(Image Pre-processing)(310), 이미지 분류 모델(Image Classification Model)(320), 객체 추적 모델(Object Detection Model)(330) 및 다이콤 태그 생성기(Inference Result DICOM Tag Adder)(340)를 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 3 , the
이미지 전처리 프로세싱(Image Pre-processing)(310)은, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)로부터 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상이 수신되면, 수신된 의료 영상의 이미지 픽셀 어레이(Image Pixel Array)를 읽어, 십층 합성곱 신경망의 입력텐서(Input Tensor)의 사이즈에 맞추기 위해, 다운샘플링(Down Sampling)하고, 이미지 정규화(Normalization) 및 표준화(standardization) 처리를 수행할 수 있다.In the
이미지 분류 모델(Image Classification Model)(320) 및 객체 추적 모델(Object Detection Model)(330)은, 기학습된 인공지능 기반의 심층 합성곱 신경망을 이용하여, 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상을 판독하고, 판독 결과로서 각 병변에 대한 검출 점수(Screening Score), 히트 맵(Heatmap), 윤곽선맵(Contour Map), 바운딩박스(Bounding Box)을 생성할 수 있다.An
구체적으로 예를 들면, 이미지 분류 모델(Image Classification Model)(320) 및 객체 추적 모델(Object Detection Model)(330)은 태그 정보에 질환 및 병변 명에 대한 문자열(String)이 포함되도록 하는 경우, 문자열의 VR(Value Representation)을 LO(long String)에 적용하여 태그 정보에 포함되도록 하고, 태그 정보에 정수 및 부동소수점인 검출 점수(Screening Scores)가 포함되도록 하는 경우, 검출 점수를 DS(Decimal String)에 적용하여 태그 정보에 포함되도록 하고, 태그 정보에 컨트롤 맵(Control Maps), 히트 맵(Heat Maps) 또는 이미지형태(Image Shape)의 튜플(Tuple), 리스트(List) 및 어레이(Array)가 포함되도록 하는 경우, 컨트롤 맵(Control Maps), 히트 맵(Heat Maps) 또는 이미지형태(Image Shape)의 튜플(Tuple), 리스트(List) 및 어레이(Array)에 대한 정보를 바이트로 변환시킨 후, 16비트에 대한 바이트를 OW(Other Word String)에 적용하고, 8비트에 대한 바이트를 OB(Other Byte String)에 적용하여 태그 정보에 포함되도록 할 수 있다.Specifically, for example, when the
다이콤 태그 생성기(Inference Result DICOM Tag Adder)(340)는, 의료 영상의 병변 분류 및 검출 결과를 저장하기 위해 태그 정보를 생성하고, 태그 정보에 저장하는 데이터 타입에 따라 데이터 타입을 변환하여 인코딩하고, 인코딩 결과를 저장할 수 있다.The DICOM tag generator (Inference Result DICOM Tag Adder) 340 generates tag information to store the lesion classification and detection result of the medical image, converts the data type according to the data type stored in the tag information, and encodes it , the encoding result can be saved.
즉, 다이콤 태그 생성기(Inference Result DICOM Tag Adder)(340)는, 판독 결과가 문자열(String) 또는 숫자(Number, integer or floating point)이면 그대로 저장을 하고, 판독 결과가 튜플(Tuple) 또는 리스트(List)이면, 어레이(Array)로 변환하고, 변환된 어레이를 바이트(Byte)로 변환하여 저장할 수 있다.That is, the DICOM tag generator (Inference Result DICOM Tag Adder) 340 stores as it is if the read result is a string or a number (Number, integer or floating point), and the read result is a tuple or list If it is (List), it can be converted into an array (Array), and the converted array can be converted into bytes and stored.
또한, 판독 결과 이외에 이미지 뷰어부(500)가 판독 결과에 대한 태그 정보를 정확히 해독하고 처리하여 판독 결과를 생성하는데 필요한 메타 정보를 함께 저장할 수 있다.In addition, in addition to the reading result, the
여기서 메타 정보에는, 이미지 분류 모델(Image Classification Model)(320) 및 객체 추적 모델(Object Detection Model)(330)에 대한 버전 정보를 포함하여, 판독 결과에 대한 데이터의 타입(Type), 사이즈(Size), 형태(Shape), 데이터 바이트 수 등이 포함될 수 있다.Here, the meta information includes version information on the
이를 통하여, 영상 판독부(300)는, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)로부터 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상을 수신하여, 수신한 의료 영상에 대한 판독 결과와 이미지 뷰어부(500)가 다이콤 태그에 포함된 판독 결과를 정확히 해독하고 판독 결과를 생성하기 위한 메타정보를 함께 저장한 의료 영상을 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)로 전달할 수 있다.Through this, the
도 4는, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 이미지 뷰어부(500)의 설명에 제공된 도면이다.4 is a diagram provided to explain the
도 4를 참조하면, 이미지 뷰어부(500)는, 영상 관리부(400)에 저장된 태그 정보가 부가된 이미지 파일을 수신하여, 해독(디코딩)하고, 해독 결과를 화면에 디스플레이하기 위해, 이미지 뷰잉 메인 모듈(Image Viewing Main Module)(510), 태그 정보 디코더(Private tag Decoder)(520) 및 판독기(Inference Result Constructor)(530)를 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 4 , the
이미지 뷰잉 메인 모듈(Image Viewing Main Module)(510)은, 수신된 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상을 읽어, 의료 영상에 부가된 태그 정보가 태그 정보 디코더(Private tag Decoder)(520)를 통해, 해독되도록 하고, 해독된 태그 정보에 포함된 판독 결과 및 메타 정보를 의료 영상에 중첩시켜 화면에 함께 표시할 수 있다.The image viewing
태그 정보 디코더(Private tag Decoder)(520)는, 태그 정보를 해독하여 해독 결과에 입각하여 판독 결과에 대한 바이트를 어레이로 변환하고 해독한 이미지형태(Image Shape), 데이터 바이트 수 등의 메타정보를 이용하여 어레이(Array)의 리사이즈(Resize)하거나 어레이(Array)를 리스트(List)와 튜플(Tuple)로 변환하여 판독 결과를 생성할 수 있다.The tag information decoder (Private tag Decoder) 520 decodes the tag information, converts the bytes for the read result into an array based on the decoding result, and converts meta information such as the decoded image shape and the number of data bytes. A read result can be generated by resizing an array or converting an array into a list and a tuple.
판독기(Inference Result Constructor)(530)는, 의료 영상에 생성한 검출 점수(Screening Score), 바운딩 박스, 윤곽선 맵, 히트 맵 등의 판독 결과 의료 영상에 중첩하여 의료진에게 제공하여 병변의 판독을 돕는 역할을 수행할 수 있다.The reader (Inference Result Constructor) 530 superimposes the reading results of the detection score, bounding box, contour map, heat map, etc. generated on the medical image on the medical image to provide the medical team with a role to help the reading of the lesion can be performed.
도 5 내지 도 6은, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 영상 판독부(300)를 통한 판독 결과 및 메타 정보를 저장하기 위한 다이콤 태그의 주소, VR, VM, Description 및 Keyword 등이 예시된 도면이다.5 to 6 are diagrams illustrating an address, VR, VM, Description, and Keyword of a Daicom tag for storing a reading result and meta information through the
도 5 내지 도 6을 참조하면, 태그 정보의 그룹 넘버(Group Number)에 0x1001을 할당하였고, 엘레먼트 넘버(Element Number)를 0x1001에서 0x100F까지 할당하였고 판독한 의료 영상의 파일명, 이미지 형태, 병변명, 검출확률, 바운딩 박스, 윤곽선 맵의 수, 각 윤곽선 좌표 형태 및 각 윤곽선 맵의 좌표값들, 히트 맵 등을 저장할 수 있는 태그 리스트이다.5 to 6, 0x1001 is assigned to the group number of the tag information, the element number is assigned from 0x1001 to 0x100F, and the file name, image type, lesion name, and It is a tag list that can store detection probability, bounding box, number of contour maps, shape of each contour coordinate, coordinate values of each contour map, heat map, and the like.
여기서, 각 태그의 VR(value Representation)은 태그에 저장되는 Data Type을 나타낸다. "LO"는 long String, "OW"은 Other Word String을, "DS"는 Decimal String을 의미한다. "OB"는 Other Byte String을 나타낸다.Here, the VR (value representation) of each tag indicates the data type stored in the tag. "LO" stands for long String, "OW" stands for Other Word String, and "DS" stands for Decimal String. "OB" stands for Other Byte String.
그리고 "OW"는 Value가 255를 초과하는 Unsigned Integer인 이미지형태(Image Shape), Bounding Box의 Coordinates, Contour Shape 및 Contour Coordinates를 저장하는데 사용된다.And "OW" is used to store Image Shape, which is an Unsigned Integer whose Value exceeds 255, Coordinates of Bounding Box, Contour Shape and Contour Coordinates.
또한, "OB"는 히트 맵(Heatmap)을 저장하는데 사용한다. 히트 맵(Heatmap)은 0에서 1 사이의 값을 갖는 싱글 채널(Single Channel)을 저장할 때에 데이터 타입(Data Type)을 Float32로 하고 "OW" VR을 적용할 수 있다.Also, "OB" is used to store a heat map. When a heatmap stores a single channel having a value between 0 and 1, the data type is Float32 and "OW" VR can be applied.
이 경우 다이콤 태그를 해독하여 히트 맵(Heatmap)을 구현하는 이미지 뷰어부(500)에서 칼러 히트 맵(Heatmap)을 생성하여야 한다. 본 실시예에서는 이미지 뷰어부(500)의 부담을 줄이기 위해서 히트 맵 태그 저장시, 칼러 히트 맵(Heatmap)을 생성하여 저장할 수 있다.In this case, the
도 6은 이미지 뷰어부(500) 또는 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)에서 태그 정보를 정확히 해독하기 위한 메타 정보가 예시된 도면이다.FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating meta information for accurately decoding tag information in the
태그 정보를 생성한 회사명(Solution Provider)로 "래디센"이 저장되면, 바운딩박스 정보의 저장 순서, 히트 맵의 높이 및 폭 정보, 히트 맵 데이터의 바이트 수, 병변명 리스트 및 일반 정보 등이 저장될 수 있다. 여기서, VR"UT"는 Unlimited Text를 나타낸다.When "Radisen" is saved as the name of the company (Solution Provider) that created the tag information, the storage order of the bounding box information, the height and width information of the heat map, the number of bytes of the heat map data, the lesion name list and general information, etc. can be saved. Here, VR "UT" represents Unlimited Text.
이를 통해, 메타 정보를 이용하여 이미지뷰어 소프트웨어를 개발하고 유지하는 소프트웨어 엔지니어는, 다이콤 태그 정보의 정보를 정확히 해독하고 의료 영상의 판독 결과를 생성하여 의료진에게 이미지화하여 제공할 수 있다.Through this, a software engineer who develops and maintains the image viewer software using meta information can accurately decode the information of the daicom tag information, generate the reading result of the medical image, and provide the image to the medical staff.
도 7 내지 도 20은, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 영상 판독부(300)를 통한 판독 결과 및 메타 정보에 대한 태그 정보(Private tag) 저장 전후의 다이콤 파일을 다이콤 파일 뷰어로 읽은 이미지 파일이 예시된 도면이다.7 to 20 are images of reading the DYCOM file before and after storing the tag information (Private tag) for the reading result and meta information through the
도 7 및 도 13은 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)가 생성한 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상을 일반 다이콤 뷰어를 사용하여 나타낸 것이며, 의료 영상 이미지와 다이콤 태그 일부를 표현하였으며 특히 영상 판독부(300)의 판독 결과에 대한 태그 정보가 없음을 나타낸다. 7 and 13 show the medical image in the form of a daicom file generated by the
도 8 및 도 14는, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)가 생성한 의료 영상에 대해서 영상 판독부(300)가 판독한 결과를 태그 정보를 추가한 저장한 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상을 일반 다이콤 뷰어를 사용하여 나타낸 것이다.8 and 14 show a medical image in the form of a daicom file in which tag information is added to the result of reading the medical image generated by the
도 8은, 도 7의 의료 영상에 대한 영상 판독부(300)의 판독 결과에 대한 태그 정보가 바운딩 박스 안에 도시한 바와 같이 저장되어 있음을 나타낸 것이다.FIG. 8 shows that tag information on the reading result of the
도 9 및 도 15는 의료 영상에 대한 판독 결과로서 바운딩 박스를 이미지에 중첩하여 나타낸 것이며, 도 10 및 도 16은 윤곽선맵 (Contour Map)을 이미지에 중첩하여 나타낸 것이며, 도 9 및 도 17은 히트 맵(Heat Map)을 이미지에 중첩하여 나타낸 것이며, 도 12 및 도 18은 검출 점수(Screening Score)을 이미지와 함께 나타낸 것이다.9 and 15 are a reading result of a medical image, showing a bounding box superimposed on an image, FIGS. 10 and 16 are showing a contour map superimposed on an image, and FIGS. 9 and 17 are hits A map (Heat Map) is shown by superimposing it on an image, and FIGS. 12 and 18 show a detection score (Screening Score) with an image.
한편, 도 19는 의료 영상에서 영상 판독부(300)가 복수개의 병변에 대해 판독한 결과의 일예를 나타낸 것이며, 이는 태그 정보를 병변의 수만큼 추가로 생성하여 프라이빗 다이콤 태그에 저장할 수 있음을 나타낸 것이다.Meanwhile, FIG. 19 shows an example of a result of the
또한, 도 20은 의료 영상에 대한 영상 판독부(300)의 복수개의 검출결과로 복수개의 바운딩 박스를 이미지에 중첩하여 나타낸 일 예이다. 이 또한 바운딩 박스의 수 만큼 바운딩 박스의 좌표, 병변명 및 검출 확률 등을 태그 정보에 추가로 저장할 수 있음을 나타낸 것이다.Also, FIG. 20 is an example showing a plurality of detection results of the
도 21은, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)의 동작 특성의 설명에 제공된 도면이다.21 is a diagram provided to explain the operating characteristics of the
본 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 시스템을 이용하는 실시간 자동 엑스레이 영상 판독 방법은, 엑스레이 영상 획득부(100)가, 환자로부터 엑스레이 영상을 취득하면, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)가, 엑스레이 영상 확득부로부터 원시 이미지를 수신하여, 이미지 처리를 하여 다이콤 파일과 같은 기설정된 포맷의 이미지 파일로 변환시키고, 이미지 파일로 변환된 의료 영상을 영상 판독부(300)에 전달하게 된다.In the real-time automatic X-ray image reading method using this real-time automatic X-ray image reading system, when the X-ray
여기서, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)는 엑스레이 영상을 획득하도록 엑스레이 영상 획득부(100)를 제어하며, 엑스레이 영상 획득부(100)의 영상 획득 조건을 변경하거나 또는 엑스레이 디텍터의 교정 기능도 수행 할 수 있으며, 환자 설정, 환자 예약 및 모니터링, 사용자 설정, 이미지 향상 프로세싱. 영상 관리부(400) 통신 및 의료 영상 저장, 검색, 전달 등 다양한 기능을 수행할 수 있다.Here, the
구체적으로, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)는 통상의 시스템 초기화 동작 완료 후(S2010), 사용자로부터 요청을 대기하는 상태가 유지되며(S2020), 사용자의 요청이 발생되면, 요청 내용에 준하여 처리를 수행할 수 있다(S2040).Specifically, the
이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)는 요청사항이 이미지 획득인 경우(S2030-Yes), 엑스레이 영상 획득부(100)로부터 로우 타입(Raw Type)의 원시파일을 읽어, 이미지 향상을 위한 이미지 프로세싱 작업을 수행할 수 있다(S2050).When the request is image acquisition (S2030-Yes), the
그리고 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)는 이미지 프로세싱을 완료하면, 의료용 디지털 통신 및 영상 표준에 맞추어 표준 다이콤 태그에 대한 정보를 추가하여, 의료 영상을 다이콤 파일로 생성할 수 있다(S2060).In addition, when the image processing is completed, the
또한, 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)는 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상의 생성 후에 바로 영상 관리부(400)에 전달하지 않고, 영상 판독부(300)에 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상을 전달할 수 있다(S2070).In addition, the
이때, 영상 판독부(300)는 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상에 대한 판독 결과를 기반으로 태그 정보를 생성하여, 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상에 부가하고, 태그 정보가 부가된 의료 영상을 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)로 전달할 수 있다.In this case, the
이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)는 의료 영상의 판독 결과를 저장한 태그 정보를 가진 의료 영상을 영상 관리부(400)에 전달한다.The
상기의 동작을 통하여 엑스레이 영상을 획득하자 마자 본 발명의 영상 판독부(300) 솔루션을 적용하여 바로 판독을 하여 그 결과를 다이콤 표준의 의료 영상에 판독 결과를 저장하는 동작을 수행하게 된다.As soon as the X-ray image is acquired through the above operation, the
도 22 내지 도 23은, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 영상 판독부(300)의 동작 특성의 설명에 제공된 도면이다.22 to 23 are diagrams provided to explain the operating characteristics of the
도 22는, 영상 판독부(300)의 의료 영상 판독 및 판독 결과를 다이콤 태그 정보에 저장하여 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상을 업데이트 한 후에 다시 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)로 전달하는 순서도이다.22 is a flowchart of the
영상 판독부(300)는, 이미지 파일로 변환된 의료 영상이 수신되면, 기학습된 인공지능 기반의 심층 합성곱 신경망을 이용하여 의료 영상의 병변 분류 및 검출을 하여 판독을 하고 그 판독 결과를 포함하는 태그 정보를 생성하여, 의료 영상에 부가하고, 태그 정보가 부가된 의료 영상을 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)에 전송하게 된다.When a medical image converted into an image file is received, the
구체적으로, 영상 판독부(300)는 시스템이 초기화되면(S2110), 시스템 초기화 동안에 의료 영상 판독을 위한 심층 합성곱 신경말 모델을 메모리에 상주하여 판독을 할 수 있도록 제반 동작 및 기능을 수행하며 스탠바이 상태에서 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)로부터 의료 영상이 전달되었는지를 확인할 수 있다(S2120).Specifically, when the system is initialized ( S2110 ), the
그리고 영상 판독부(300)는 의료 영상이 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)로부터 전달되면, 심층 합성곱 신경망을 이용하여 의료 영상에 대한 병변 유무 및 위치를 판독하여(S2130), 판독한 결과를 다이콤 태그 정보에 최적인 상태로 저장하기 위해서 판독 결과를 분류하고 변환할 수 있다(S2140).And, when the medical image is transmitted from the
또한, 영상 판독부(300)는 저장하고자 하는 각각의 판독 결과에 대해 태그 정보를 생성하고(S2150), 영상 판독부(300)의 판독 결과와 메타 정보를 각각의 태그에 저장할 수 있다(S2160, S2170).In addition, the
영상 판독부(300)는 기존의 다이콤 의료 영상에 태그 정보를 추가하여 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상을 업데이트하고(S2180), 이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)로 다이콤 파일 형태의 의료 영상을 전달할 수 있다(S2190).The
여기서 판독 결과를 분류하고 변환하는 사유는 다음과 같다.Here, the reasons for classifying and converting the reading results are as follows.
판독 결과는 도 7 내지 도 20에 예시된 바와 같이 다양한 형태로 나타낼 수 있다. 검출확률 또는 점수(Screening Score), 바운딩 박스의 좌표정보, 클래스명 및 분류 확률, 윤곽선 맵의 좌표 정보 및 윤곽선 맵 개수, 클래스명, 히트 맵 픽셀 어레이 사이즈 정보 및 픽셀 값 등으로 표시가 된다.The reading result may be displayed in various forms as illustrated in FIGS. 7 to 20 . Detection probability or score, coordinate information of bounding box, class name and classification probability, coordinate information of outline map and number of outline maps, class name, heat map pixel array size information and pixel value are displayed.
그런데 이러한 다양한 판독 결과를 의료용 디지털 통신 및 영상 표준에 맞추어 다이콤 태그 정보에 바로 저장을 할 수 없으며 또한 저장된 태그 정보의 해독에 필요한 정보를 정확히 알아야만 태그 정보의 해독 및 원해의 판독 결과를 재생할 수 있기 때문이다.However, it is not possible to directly store these various reading results in the DICOM tag information in accordance with the medical digital communication and image standards, and to decode the tag information and reproduce the original reading result only if you know exactly the information required to decode the stored tag information. Because.
전술한 다양한 판독 결과는 데이터 클래스 및 데이터 속성에 따라 문자열, 숫자, 튜플, 리스트, 어레이 등으로 분류 가능하며, 또한 데이터가 정수인지 아니면 실수인지 여부와 각각의 경우에 있어서 숫자를 표현하는데 필요한 바이트 수에 따라 분류될 수 있으며, 다이콤 표준에 맞추어 전달하기 위해서는 1차원의 데이터 형태로 변환하여 전달을 하여야 한다.The various reading results described above can be classified into character strings, numbers, tuples, lists, arrays, etc. according to data classes and data attributes, and also whether the data are integers or real numbers, and the number of bytes required to represent the numbers in each case It can be classified according to the standard, and in order to transmit it according to the Daicom standard, it must be converted into a one-dimensional data form and transmitted.
그리고 다이콤 태그 정보를 해독하고 본래의 형태로 디코딩하기 위해서는 튜플, 리스트, 어레이를 바이트로 변환하여 저장을 하여야 한다,And in order to decode the DYCOM tag information and decode it in its original form, tuple, list, and array must be converted into bytes and stored.
이는, 바이트로 변환처리하지 않고 문자열로 저장을 하는 경우에는 저장된 태그 정보로부터 본래의 튜플, 리스트 및 어레이를 복원하기가 매우 어렵기 때문에, 정확도가 상대적으로 낮아질 수 있다.When storing as a character string without converting to bytes, it is very difficult to restore the original tuple, list, and array from the stored tag information, so the accuracy may be relatively low.
도 23은 본 발명의 태그 정보에 판독 결과를 저장하기 위한 판독 결과 분류 및 변환 방법을 설명하기 위한 동작 순서도이다.23 is an operation flowchart for explaining a read result classification and conversion method for storing a read result in tag information according to the present invention.
도 23을 참조하면, 영상 판독부(300)는 의료 영상을 판독하고, 판독 결과를 기반으로 태그 정보를 생성하기 위해, 판독 결과의 데이터 클래스 및 데이터 타입(속성)을 분류한다(S2210).Referring to FIG. 23 , the
영상 판독부(300)는 2차원 어레이로 표현되는 이미지 형태 또는 윤곽선 맵의 이미지 형태와 같이 데이터 클래스가 튜플(Tuple)이면(S2215-Yes), 튜플 값이 실수, 정수인지 여부와 필요한 바이트수에 입각하여 어레이로 변환을 하고(S2220), 다시 1차원의 바이트로 변환하여(S2225), 태그 정보를 생성하고 의료 영상에 부가할 수 있다.The
그리고 영상 판독부(300)는 윤곽선 맵 또는 바운딩 박스의 좌표와 같이 데이터 클래스가 리스트이면(S2230-Yes), 리스트의 값이 실수, 정수인지 여부와 필요한 바이트수에 입각하여 어레이로 변환하고(S2235), 다시 1차원의 바이트로 변환(S2240)하여, 태그 정보를 생성하고 의료 영상에 부가할 수 있다.And, if the data class is a list such as the contour map or the coordinates of the bounding box (S2230-Yes), the
또한, 영상 판독부(300)는 히트 맵과 같이 데이터 클래스가 어레이(Array)이면(S2245-Yes), 1차원의 바이트로 변환하여(S2250), 태그 정보를 생성하고 의료 영상에 부가할 수 있다.Also, if the data class is an array like a heat map (S2245-Yes), the
그리고 영상 판독부(300)는 판독 결과 병변에 해당하는 클래스명 그리고 검출 확률과 같은 데이터 클래스를 문자열 및 숫자 처리하여(S2260), 태그 정보를 생성하고 의료 영상에 부가할 수 있다.In addition, the
이렇게 해서 영상 판독부(300)는 다이콤 표준에 부합하면서 이미지 뷰어부(500)에서 효율적이고 효과적으로 프라이빗 다이콤 태그를 해독하여 다양한 판독 결과의 데이터 클래스 및 타입(속성)으로 복원하여 판독 결과를 생성하여 이미지와 중첩하여 나타낼 수 있게 한다.In this way, the
도 24 내지 도 25는, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 이미지 뷰어부(500)의 동작 특성의 설명에 제공된 도면이다.24 to 25 are diagrams provided to explain the operating characteristics of the
통상의 이미지 뷰어는 워크 스테이션, 랩톱, 태블릿을 위한 고성능 다중 모니터 뷰어이며 이미지 조작, 레이아웃 및 마크업을 통한 다양한 도구모음이 있고 보고서 작성기, CD/미디어 작성 및 교수형 프로토콜 등이 있으며, 통상 의료진이 환자 진료시 의료 영상을 디스플레이한 상태에서 판독을 하고 설명을 하고 진단결과를 입력하는 용도로 사용될 수 있다.A typical image viewer is a high-performance multi-monitor viewer for workstations, laptops, and tablets, has a variety of tool sets through image manipulation, layout and markup, and has a report writer, CD/media writing and hanging protocol, etc. It can be used to read, explain, and input a diagnosis result while a medical image is displayed during treatment.
여기에서는 본 실시예와 관련하여 영상 판독부(300)가 판독한 결과를 참조하여 의사가 진단을 하는데 도움이 될 수 있도록 태그 정보를 해독하여 판독 결과를 재생하여 본래의 검출 점수(Screening Score), 바운딩 박스(Bounding Box), 윤곽선 맵(Contour Map) 및 히트 맵(Heat Map)을 생성하는 동작에 대해 기술하고자 한다.Here, with reference to the result read by the
이미지 콘솔 뷰어부(200)는 영상 판독부(300)으로부터 수신된 태그 정보가 저장된 의료 영상을 영상 관리부(400)에 전달하여 저장하도록 함으로써, 의료진이 이미지 뷰어부(500)를 사용하여 의료 영상을 읽어, 의료 영상의 판독 결과를 보고 판독하도록 할 수 있다.The
도 24를 참조하면, 이미지 뷰어부(500)는, 시스템의 초기화에 제반 필요한 동작을 다 수행을 하고(S2310), 사용자로부터 요청을 기다리며 요청 대기 상태를 유지할 수 있으며(S2320), 사용자의 요청이 발생되면, 요청 내용에 준하여 처리를 수행할 수 있다(S2340).Referring to FIG. 24 , the
그리고 이미지 뷰어부(500)는, 영상 판독부(300)의 판독 결과를 생성하라는 요청이 발생되면(S2330), 태그 정보를 해독하고(S2350), 데이터 클래스 및 타입(속성)을 디코딩하여(S2360), 판독 결과를 검출 점수(Screening Score), 바운딩 박스(Bounding Box), 윤곽선 맵(Contour Map) 및 히트 맵(Heat Map) 형태로 생성하여(S2370), 화면에 표시(디스플레이)하여, 의료진이 의료 영상을 판독하는데 도움이 되게 한다.And when a request to generate the reading result of the
도 25는, 이미지 뷰어부(500)가 태그 정보 정보를 정확히 복원하기 위한 동작을 나타낸 순서도이다.25 is a flowchart illustrating an operation of the
이미지 뷰어부(500)는 저장할 때의 순서와 정확히 역순으로 해독을 하여야 검출 점수(Screening Score), 바운딩 박스(Bounding Box), 윤곽선 맵(Contour Map) 및 히트 맵(Heat Map)을 정상적으로 디코딩을 수행할 수 있다.The
즉, 이미지 뷰어부(500)는 판독 결과의 데이터 클래스 및 데이터 타입(속성)을 분류하고(S2410), 1차원의 바이트 코드로부터 어레이로 변환하여 튜플, 리스트 및 어레이로 변환하고 히트 맵, 윤곽선맵 생성을 위해서 리사이징을 수행할 수 있다.That is, the
구체적으로, 이미지 뷰어부(500)는, 분류 결과, 바이트가 아닌 문자열 또는 숫자이면, 그대로 복원(디코딩)을 하고, 바이트인 경우(S2415-Yes), 문자열, 숫자로 변환하고(S2420), 튜플에 해당하는 바이트이면(S2425-Yes), 저장시와 동일한 실수 또는 정수 구분 및 필요한 바이트 수를 정확히 적용하여 어레이로 변환하고(S2430), 튜플로 변환하고(S2435), 리스트에 해당하는 바이트인 경우에는(S2440-Yes), 마찬가지로 저장시와 동일한 실수 또는 정수 구분 및 필요한 바이트 수를 정확히 적용하여 어레이로 변환하여(S2445), 변환된 어레이를 리스트로 변환하고(S2450), 리스트의 형태에 따라 리사이징하며(S2455), 이는 본래의 윤곽선맵을 복원하는 것과 관련이 있으며. 어레이에 해당하는 바이트인 경우에는 저장시의 정보를 이용하여 리사이징하여(S2455), 히트 맵을 복원하는 것과 관련이 있다.Specifically, as a result of the classification, if the
본 발명의 의료 영상 판독 결과를 이미지 뷰어부(500)로 처리하기 위해서는 상기에 기술한 바와 같이 복원에 필요한 정보를 활용하면 정확히 판독 결과를 태그 정보로부터 생성하는 것이 가능하고, 또한 다이콤 메타정보에 대한 태그를 해독하여 판독 결과 생성에 필요한 정확한 정보를 얻을 수 있어, 일반 이미지 뷰어부(500)를 개발하는 소프트웨어 엔지니어는 영상 판독부(300)로 판독한 결과를 생성할 수 있다.In order to process the medical image reading result of the present invention by the
한편, 본 실시예에 따른 장치와 방법의 기능을 수행하게 하는 컴퓨터 프로그램을 수록한 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 기록매체에도 본 발명의 기술적 사상이 적용될 수 있음은 물론이다. 또한, 본 발명의 다양한 실시예에 따른 기술적 사상은 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 기록매체에 기록된 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 코드 형태로 구현될 수도 있다. 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 기록매체는 컴퓨터에 의해 읽을 수 있고 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 어떤 데이터 저장 장치이더라도 가능하다. 예를 들어, 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 기록매체는 ROM, RAM, CD-ROM, 자기 테이프, 플로피 디스크, 광디스크, 하드 디스크 드라이브, 등이 될 수 있음은 물론이다. 또한, 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 기록매체에 저장된 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 코드 또는 프로그램은 컴퓨터간에 연결된 네트워크를 통해 전송될 수도 있다.On the other hand, it goes without saying that the technical idea of the present invention can also be applied to a computer-readable recording medium containing a computer program for performing the functions of the apparatus and method according to the present embodiment. In addition, the technical ideas according to various embodiments of the present invention may be implemented in the form of computer-readable codes recorded on a computer-readable recording medium. The computer-readable recording medium may be any data storage device readable by the computer and capable of storing data. For example, the computer-readable recording medium may be a ROM, RAM, CD-ROM, magnetic tape, floppy disk, optical disk, hard disk drive, or the like. In addition, the computer-readable code or program stored in the computer-readable recording medium may be transmitted through a network connected between computers.
또한, 이상에서는 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예에 대하여 도시하고 설명하였지만, 본 발명은 상술한 특정의 실시예에 한정되지 아니하며, 청구범위에서 청구하는 본 발명의 요지를 벗어남이 없이 당해 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진자에 의해 다양한 변형실시가 가능한 것은 물론이고, 이러한 변형실시들은 본 발명의 기술적 사상이나 전망으로부터 개별적으로 이해되어져서는 안될 것이다.In addition, although preferred embodiments of the present invention have been illustrated and described above, the present invention is not limited to the specific embodiments described above, and the technical field to which the present invention belongs without departing from the gist of the present invention as claimed in the claims In addition, various modifications are possible by those of ordinary skill in the art, and these modifications should not be individually understood from the technical spirit or perspective of the present invention.
Claims (9)
Translated fromKoreanApplications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020200068149AKR102405314B1 (en) | 2020-06-05 | 2020-06-05 | Method and system for real-time automatic X-ray image reading based on artificial intelligence |
| KR10-2020-0068149 | 2020-06-05 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2021246770A1true WO2021246770A1 (en) | 2021-12-09 |
Family
ID=78831163
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/KR2021/006852CeasedWO2021246770A1 (en) | 2020-06-05 | 2021-06-02 | Method and system for automatically reading x-ray image in real time on basis of artificial intelligence |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102405314B1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2021246770A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114500498A (en)* | 2021-12-28 | 2022-05-13 | 武汉联影医疗科技有限公司 | DICOM file transmission and storage method, system, device and storage medium |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102442591B1 (en)* | 2022-01-24 | 2022-09-13 | 주식회사 에어스메디컬 | Method, program, and apparatus for generating label |
| KR102703557B1 (en)* | 2022-03-16 | 2024-09-04 | 연세대학교 산학협력단 | Medical image processing method for diagnosing supernumerary tooth in radiographic images |
| KR102564737B1 (en)* | 2022-05-25 | 2023-08-10 | 주식회사 래디센 | Method for training a device for denoising an X-ray image and computing device for the same |
| KR102838814B1 (en) | 2023-04-11 | 2025-07-24 | 한림대학교 산학협력단 | Apparatus for converting an anterior-posterior X-ray image into a posterior-anterior X-ray image |
| KR102838813B1 (en) | 2023-04-11 | 2025-07-24 | 한림대학교 산학협력단 | Device for predicting cardiac output using chest X-ray images |
| KR102838815B1 (en) | 2023-04-11 | 2025-07-24 | 한림대학교 산학협력단 | X-ray reading device for predicting the status of respiration and cardiac output |
| CN118319486B (en)* | 2024-04-25 | 2024-09-10 | 浙江大学医学院附属邵逸夫医院 | Cardiovascular intervention operation image guidance system based on artificial intelligence |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011067637A (en)* | 2004-05-31 | 2011-04-07 | Toshiba Corp | Dicom based medical image information processor and dicom based medical image information processing system |
| CN106951531A (en)* | 2017-03-21 | 2017-07-14 | 东软集团股份有限公司 | Data query method and device |
| KR20190071724A (en)* | 2016-10-12 | 2019-06-24 | 테라리콘, 인코포레이티드 | System and method for medical image interpretation |
| KR20190105220A (en)* | 2016-11-17 | 2019-09-16 | 테라리콘, 인코포레이티드 | Medical Image Identification and Interpretation |
| JP2019195627A (en)* | 2018-05-07 | 2019-11-14 | ゼブラ メディカル ビジョン リミテッド | System and device for analyzing anatomical image |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101628276B1 (en) | 2015-04-20 | 2016-06-08 | 주식회사 루닛 | System and method for pathological analysis based on cloud |
- 2020
- 2020-06-05KRKR1020200068149Apatent/KR102405314B1/enactiveActive
- 2021
- 2021-06-02WOPCT/KR2021/006852patent/WO2021246770A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011067637A (en)* | 2004-05-31 | 2011-04-07 | Toshiba Corp | Dicom based medical image information processor and dicom based medical image information processing system |
| KR20190071724A (en)* | 2016-10-12 | 2019-06-24 | 테라리콘, 인코포레이티드 | System and method for medical image interpretation |
| KR20190105220A (en)* | 2016-11-17 | 2019-09-16 | 테라리콘, 인코포레이티드 | Medical Image Identification and Interpretation |
| CN106951531A (en)* | 2017-03-21 | 2017-07-14 | 东软集团股份有限公司 | Data query method and device |
| JP2019195627A (en)* | 2018-05-07 | 2019-11-14 | ゼブラ メディカル ビジョン リミテッド | System and device for analyzing anatomical image |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114500498A (en)* | 2021-12-28 | 2022-05-13 | 武汉联影医疗科技有限公司 | DICOM file transmission and storage method, system, device and storage medium |
| CN114500498B (en)* | 2021-12-28 | 2023-12-08 | 武汉联影医疗科技有限公司 | DICOM file transmission and storage methods, systems, equipment and storage media |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20210152048A (en) | 2021-12-14 |
| KR102405314B1 (en) | 2022-06-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2021246770A1 (en) | Method and system for automatically reading x-ray image in real time on basis of artificial intelligence | |
| US7840041B2 (en) | Device for converting medical image data | |
| US6556698B1 (en) | Method and system for associating exposed radiographic films with proper patient information | |
| WO2020045987A1 (en) | System and method for providing deep learning-based virtual reality 3d embryo model | |
| JPH08508597A (en) | Information management in endoscopy system | |
| JP2005510324A (en) | Handling of image data generated by image data set operations | |
| WO2022050713A1 (en) | Method for reading chest image | |
| WO2017099375A1 (en) | Image processing apparatus and image processing method thereof | |
| WO2022131642A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for determining disease severity on basis of medical images | |
| WO2021137454A1 (en) | Artificial intelligence-based method and system for analyzing user medical information | |
| WO2021261727A1 (en) | Capsule endoscopy image reading system and method | |
| WO2023185805A1 (en) | Image processing method and apparatus | |
| WO2019124836A1 (en) | Method for mapping region of interest of first medical image onto second medical image, and device using same | |
| Fraser et al. | TeleMedMail: free software to facilitate telemedicine in developing countries | |
| WO2021033835A1 (en) | Server for generating electronic document, and method thereof | |
| WO2019221586A1 (en) | Medical image management system, method, and computer-readable recording medium | |
| Marchevsky et al. | Storage and distribution of pathology digital images using integrated web-based viewing systems | |
| WO2024005344A1 (en) | Thumbnail provision method for patient management system, and computing device performing same method | |
| WO2020197071A1 (en) | Electronic device and control method thereof | |
| WO2023090601A1 (en) | User terminal and method for providing body shape information for each body part of user | |
| JP3783895B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and method | |
| WO2015115720A1 (en) | Content generating service device for generating video on basis of plurality of user devices, method for generating video on basis of plurality of user devices, and recording medium having computer program recorded thereon | |
| WO2019132565A1 (en) | Method for generating multi-depth image | |
| JPH1131187A (en) | Diagnostic report generating system | |
| JPH10211173A (en) | Diagnostic report preparing device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | Ref document number:21817795 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 | |
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase | Ref country code:DE | |
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase | Ref document number:21817795 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 | |
| 32PN | Ep: public notification in the ep bulletin as address of the adressee cannot be established | Free format text:NOTING OF LOSS OF RIGHTS PURSUANT TO RULE 112(1) EPC (EPO FORM 1205A DATED 06.06.2023) |