WO2021162355A1 - Method and apparatus for providing guide data for intravascular medical tool insertion device - Google Patents
Method and apparatus for providing guide data for intravascular medical tool insertion deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2021162355A1 WO2021162355A1PCT/KR2021/001537KR2021001537WWO2021162355A1WO 2021162355 A1WO2021162355 A1WO 2021162355A1KR 2021001537 WKR2021001537 WKR 2021001537WWO 2021162355 A1WO2021162355 A1WO 2021162355A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- blood vessel
- target area
- intermediate target
- medical tool
- processor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/20—Surgical navigation systems; Devices for tracking or guiding surgical instruments, e.g. for frameless stereotaxis
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/10—Computer-aided planning, simulation or modelling of surgical operations
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/30—Surgical robots
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M25/00—Catheters; Hollow probes
- A61M25/01—Introducing, guiding, advancing, emplacing or holding catheters
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M25/00—Catheters; Hollow probes
- A61M25/01—Introducing, guiding, advancing, emplacing or holding catheters
- A61M25/0105—Steering means as part of the catheter or advancing means; Markers for positioning
- A61M25/0113—Mechanical advancing means, e.g. catheter dispensers
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N20/00—Machine learning
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/10—Computer-aided planning, simulation or modelling of surgical operations
- A61B2034/101—Computer-aided simulation of surgical operations
- A61B2034/102—Modelling of surgical devices, implants or prosthesis
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/10—Computer-aided planning, simulation or modelling of surgical operations
- A61B2034/101—Computer-aided simulation of surgical operations
- A61B2034/105—Modelling of the patient, e.g. for ligaments or bones
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/10—Computer-aided planning, simulation or modelling of surgical operations
- A61B2034/107—Visualisation of planned trajectories or target regions
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/20—Surgical navigation systems; Devices for tracking or guiding surgical instruments, e.g. for frameless stereotaxis
- A61B2034/2046—Tracking techniques
- A61B2034/2065—Tracking using image or pattern recognition
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/30—Surgical robots
- A61B2034/303—Surgical robots specifically adapted for manipulations within body lumens, e.g. within lumen of gut, spine, or blood vessels
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M25/00—Catheters; Hollow probes
- A61M25/01—Introducing, guiding, advancing, emplacing or holding catheters
- A61M25/0105—Steering means as part of the catheter or advancing means; Markers for positioning
- A61M2025/0166—Sensors, electrodes or the like for guiding the catheter to a target zone, e.g. image guided or magnetically guided
Definitions
- a guide wireis a tool for setting a route for transporting a stent, etc. into a blood vessel through a catheter.
- visual information based on medical imagessuch as angiography and fine hand Tactile information based on the senses of
- a method of providing guide data for a medical tool insertion deviceperformed by a processor, the method comprising: setting an initial position of a distal end of a medical tool inserted into a blood vessel in a blood vessel image as a starting point; , determining a middle target point in a path from the starting point to a destination point based on a blood vessel branch point, and in at least a partial area of the blood vessel image. and providing guide data including at least a portion of the intermediate target area.
- the guide data providing methodincludes generating blood vessel structure data by obtaining connection information between branch points of blood vessels from the blood vessel image, and searching for a path to the target region based on the blood vessel structure data.
- the determining of the intermediate target areaincludes generating a basic intermediate target area at a position corresponding to a branching point in the blood vessel image, and selecting an additional intermediate target area based on a distance between the basic intermediate target areas. determining whether to create or not.
- the determining of the intermediate target areasmay include determining the number of the additional intermediate target areas to be generated between the basic intermediate target areas according to a distance between the basic intermediate target areas.
- the method of providing guide dataincludes outputting an intermediate target area graphic object to a position where the intermediate target area is generated in the blood vessel image, and when it is determined that the tip of the medical tool reaches the target area selected from the intermediate target area , deleting the graphic object of the target region from the blood vessel image.
- the method for guiding a medical tool inserted into a blood vesselincludes setting an initial position of the tip of the medical tool in a blood vessel image as a starting point, within a path from the starting point to a destination point. determining a middle target point based on a blood vessel branch point, corresponding to at least a portion of the blood vessel image, and providing guide data including at least a portion of the intermediate target area generating, and moving the distal end of the medical tool to the intermediate target area by driving the medical tool insertion device based on the guide data.
- a point different from the target area in the intermediate target area is set as the next target areamay include steps.
- the next target areamay be an intermediate target area closest to the target area along a traveling direction of the distal end of the medical tool.
- the guide data providing methodmay search for a path for moving a medical tool (eg, a medical tool) of the medical tool insertion apparatus to a target region within a blood vessel. After searching for the optimal path, the medical tool insertion apparatus for controlling the medical tool may provide a recognizable intermediate destination by generating an intermediate target area on the path.
- a medical tooleg, a medical tool
- the method for guiding a device for inserting a medical toolmay generate a basic intermediate target area based on a blood vessel branch point and then generate an additional intermediate target area according to a distance between the basic intermediate target areas, the mobile device may Even in the partial blood vessel image divided from the blood vessel image, the tip of the medical tool can be moved to the intermediate destination. Accordingly, the processor performing the method for guiding the apparatus for inserting a medical tool can precisely move the medical tool to the target area without remote control by an operator.
- FIG. 1is a diagram illustrating an operation of an apparatus for inserting a medical tool and a medical tool according to an exemplary embodiment.
- FIG. 2is a flowchart illustrating a method of providing guide data according to an exemplary embodiment.
- FIG. 3is a diagram illustrating generation of a blood vessel structure image in which an intermediate target region is generated from a blood vessel image according to an exemplary embodiment.
- FIG. 4is a diagram illustrating generation of blood vessel structure data from a blood vessel image according to an exemplary embodiment.
- FIG. 5is a diagram illustrating generating a path from blood vessel structure data to a target region and generating a location corresponding to a branch point of a blood vessel as a basic intermediate target region according to an exemplary embodiment.
- FIG. 6is a flowchart illustrating the creation of an additional intermediate target area according to an embodiment.
- FIG. 7is a diagram illustrating generation of an additional intermediate target region from an image of a blood vessel structure in which a basic intermediate target region is generated, according to an exemplary embodiment.
- FIG. 8is a diagram illustrating movement of a medical tool insertion device from a starting point to a destination area according to an exemplary embodiment
- FIG. 9is a block diagram schematically illustrating a configuration of a system for moving a medical tool insertion device according to an embodiment.
- first or secondmay be used to describe various components, these terms should be interpreted only for the purpose of distinguishing one component from another.
- a first componentmay be termed a second component, and similarly, a second component may also be termed a first component.
- FIG. 1is a diagram illustrating operations of a medical tool insertion apparatus 110 and a medical tool 120 according to an exemplary embodiment.
- the medical tool insertion apparatus 110may move the medical tool 120 to the blood vessel target area according to a driving command from the processor.
- the medical tool insertion device 110may move the distal end of the medical tool 120 to the blood vessel target region.
- the medical tool insertion device 110may be implemented as a robot for performing surgery, for example, a robot for controlling a medical tool for cardiovascular intervention.
- the medical tool 120is a member inserted into a blood vessel, and may include a medical tool disposed at the tip of the medical tool 120 and a medical wire connecting the medical tool to the driving unit.
- the medical wiremay include, for example, a catheter or a guidewire.
- the guide wiremay refer to a medical wire used for inserting and guiding the above-described medical tool to a target site of a blood vessel.
- the medical toolmay be a surgical tool operated under the control of a doctor, for example, an introducer kit.
- the medical tool insertion device 110may determine the above-described driving command by using the guide data. For example, the medical tool insertion apparatus 110 may output a driving command from the guide data by performing an operation according to the machine learning model.
- the machine learning modelis a model designed and trained to receive guide data and output guide data, and may be implemented as, for example, a neural network model.
- the driving commandmay represent a command for operating a driving unit connected to the medical tool 120 to move and rotate the medical tool 120 .
- the driving commandmay be, for example, a forward command, a reverse command, a clockwise rotation command, and a counterclockwise rotation command, but is not limited thereto.
- the guide datamay represent data in which guide information is mapped to a blood vessel image or a blood vessel structure image.
- the blood vessel structure imageis an image in which a specific blood vessel is extracted from the blood vessel image, and may be an image obtained by preprocessing the blood vessel image.
- the blood vessel structure imagewill be described with reference to FIG. 3 below.
- the blood vessel imagemay be an image generated using corona angiography (CAG) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In the blood vessel image, not only blood vessels but also the medical tool 120 may be photographed.
- CAGcorona angiography
- MRImagnetic resonance imaging
- the guide informationis information for guiding the movement and rotation of the medical tool 120, and may include, for example, information about a point where the medical tool 120 should start, a point through which the medical tool 120 should start, and information about a target area in a blood vessel. have.
- the information about each pointmay include, but is not limited to, image coordinates in the blood vessel structure image of the corresponding point.
- guide informationmay be visually mapped to the blood vessel structure image. For example, a graphic object corresponding to each target region may be visualized in the blood vessel structure image, and the blood vessel structure image in which the target region is visualized may be represented as a guide image.
- the medical tool insertion device 110may receive guide data from an external device (eg, a guide data providing device).
- the guide data providing apparatusmay receive and analyze a blood vessel image from the blood vessel imaging device 130 , and generate guide data from the blood vessel image.
- the medical tool insertion device 110may be implemented integrally with the guide data providing device described above. In this case, the medical tool insertion apparatus 110 may receive a blood vessel image from the blood vessel imaging device 130 , and may generate guide data by analyzing the received blood vessel image.
- the processor of the medical tool insertion apparatus 110may determine to drive the medical tool 120 based on a result of analyzing the blood vessel image.
- the medical tool insertion apparatus 110may generate guide data by analyzing the received blood vessel image, and may determine a driving command from the generated guide data. For example, the medical tool insertion apparatus 110 may select one of a forward command, a backward command, a clockwise rotation command, and a counterclockwise rotation command from the guide data as an operation command.
- the driving unit of the medical tool insertion device 110may be driven according to a selected operation command. For example, the driving unit may advance the medical tool 120 in response to the forward command. The driving unit may retract the medical tool 120 in response to the reverse command.
- the driving unitmay rotate the guide wire clockwise with respect to the longitudinal axis of the guide wire in response to the clockwise rotation command. In response to the counterclockwise rotation command, the driving unit may rotate the guide wire counterclockwise with respect to the longitudinal axis of the guide wire.
- the medical tool insertion apparatus 110may move the distal end of the medical tool 120 to a point guided by the guide data by determining a series of operation commands using the guide data generated by analyzing the blood vessel image. .
- the medical tool insertion apparatus 110may move the distal end of the medical tool 120 to the final target area by repeating the operation determination using the guide data. After the distal end of the medical tool 120, for example, the medical tool reaches the target area, the medical tool may perform a surgical operation under the control of the doctor.
- FIG. 2is a flowchart illustrating a method of providing guide data according to an exemplary embodiment.
- the processormay set the initial position of the tip of the medical tool inserted into the blood vessel in the blood vessel image as the starting point.
- the initial positionmay be a position corresponding to a point in the blood vessel at a time point at which the tip of the medical tool is first identified in the blood vessel region.
- a starting pointmay be set in the vascular structure image in which a specific blood vessel is extracted from the blood vessel image.
- the processormay determine an intermediate target area within a path from the starting point to the target area based on the blood vessel branch point.
- the target regionmay be a location in the blood vessel image designated by an operator or a processor.
- the processormay identify the branching point of the blood vessel as a location corresponding to the branching point of the blood vessel.
- the processormay determine a path from the starting point to the target region as the shortest distance in the blood vessel image.
- the processormay determine the route based on the blood vessel structure data generated by obtaining connection information between branch points of the blood vessel. Determining a path by the processor from the starting point to the destination area will be described in detail with reference to FIGS. 4 and 5 .
- the processormay determine an intermediate target area within the path. For example, the processor may set basic intermediate target regions based on the branching point of a blood vessel, and may set additional intermediate target regions according to a distance between the basic intermediate target regions. Setting the basic intermediate target area and the additional intermediate target area will be described in detail with reference to FIGS. 6 and 7 .
- the guide data providing deviceprovides the guide data in which the intermediate target area including the basic intermediate target area and the additional intermediate target area is set to the medical tool insertion device.
- the medical tool insertion apparatusmay move the distal end of the medical tool to the intermediate target area set in a series of images corresponding to each partial area.
- the medical tool insertion devicecan move the medical tool tip to the final target area.
- the processormay provide guide data corresponding to at least a partial region of the blood vessel image and including at least a part of the intermediate target region.
- the guide datamay be data in which guide information (eg, a position of a starting point, a target region, and an intermediate target region) is set in a blood vessel image or a blood vessel structure image.
- the guide datamay include a guide image visualized by overlapping graphic objects corresponding to a start point, a target region, and an intermediate target region on a blood vessel image or a blood vessel structure image.
- the processormay determine whether the distal end of the medical tool has reached the target area or the intermediate target area based on whether the distal end of the medical tool overlaps the target area or the intermediate target area by a predetermined area in the blood vessel image. .
- the processormay calculate a ratio of the medical tool tip portion among the target region or the intermediate target region in the blood vessel image, and when the calculated ratio is greater than or equal to the threshold ratio, it may be determined that the medical tool tip has reached the target region or the intermediate target region.
- Steps 210 to 230 of FIG. 2 described abovemay be performed by the processor of the guide data providing apparatus, but are not limited thereto, and may be performed by the processor of the medical tool insertion apparatus.
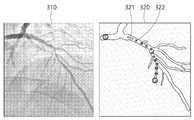
- FIG. 3is a diagram illustrating generation of a blood vessel structure image 320 in which an intermediate target region 322 is generated from a blood vessel image 310 according to an exemplary embodiment.
- the processormay receive the blood vessel structure image 320 generated from the blood vessel image 310 , but the present invention is not limited thereto and the processor may directly generate the blood vessel structure image 320 .
- the blood vessel structure image 320may be an image in which a blood vessel identified from the blood vessel image 310 and the structure and connection relationship of the blood vessel are displayed.
- the processormay generate the blood vessel structure image 320 by dividing the blood vessel region and the background region from the blood vessel image 310 by using an edge detecting method.
- the boundary detection methodmay be a boundary detection of a region in which the grayscale level of an arbitrary pixel and neighboring pixels rapidly changes, but is not limited thereto, and may be another method of detecting a boundary between a blood vessel region and a background region. may be
- the processormay extract a target blood vessel from an image in which the blood vessel region and the background region are separated, based on a thickness of a blood vessel in the blood vessel region and a grayscale level in the image.
- the blood vessel image 310may include a blood vessel other than the cardiovascular system.
- the blood vessel in which the molding agent is injectedmay have a lower grayscale level than the blood vessel in which the molding agent is not injected, and the blood vessel in which the medical tool 321 is movable may have a thicker vessel than the blood vessel in which the molding agent is not injected.
- the processormay determine a blood vessel having a thickness greater than a threshold thickness and a grayscale level lower than the threshold grayscale level among the blood vessel regions as cardiovascular.
- the present inventionis not limited thereto, and the processor may distinguish a blood vessel region to be extracted using a trained machine learning model.
- the processormay search for a path from a starting point to a target region using the blood vessel structure image 320 , and includes a starting point, a target region, and an intermediate target region 322 based on the searched path.
- a blood vessel structure image 320 including guide datamay be provided.
- FIG. 4is a diagram illustrating generation of blood vessel structure data from a blood vessel image according to an exemplary embodiment.
- the processormay extract a blood vessel region from the blood vessel image 410 , and may recognize a location where a blood vessel branch starts in the blood vessel region as a blood vessel branch point.
- the recognized blood vesselis shown as a solid line, and the position identified as a branch point of the vessel and the distal point of the vessel are shown as nodes.
- the processormay identify a branching point and a branching blood vessel from the blood vessel image 410 .
- the processormay identify a branch point while scanning along the blood vessel from the starting point to the end of the blood vessel, and may identify a blood vessel branching from the identified branch point.
- the branching pointmay include a blood vessel extending from the inlet to the end of the blood vessel and one or more remaining blood vessels branching from the branching point.
- the branching pointmay indicate a point within a blood vessel at which a blood vessel branches into at least two or more blood vessel branches.
- the processormay identify a point where two or more blood vessel branches are formed as a branch point while scanning the blood vessel, and identify a blood vessel connecting the branch point to another branch point.
- the processormay generate the blood vessel structure data 430 based on the branch point identified from the blood vessel image 420 and connection information of the branched blood vessel.
- the processormay generate node data indicating a branching point and edge data indicating a branched blood vessel. Since a branched blood vessel is connected to two different branching points, the processor can connect two node data to one edge data, and the node data can map edge data corresponding to the number of branched blood vessels. .
- the connection information between the branching point and the branched blood vesselmay be information indicating a connection relationship between the branching point and the branched blood vessel.
- the connection informationmay be generated using edge data mapped to node data and node data that is a connection target of the edge data.
- the processormay structure the blood vessel data based on the connection information. For example, the processor may create a tree structure in which the node and the edge are connected by using a branch point closest to the blood vessel introduction part as a root node.
- the root nodeis a node corresponding to the highest branching point, and may be, for example, a node corresponding to a starting point.
- FIG. 5is a diagram illustrating generation of a path from blood vessel structure data to a target region 522 and generating a location corresponding to a branch point of a blood vessel as a basic intermediate target region according to an exemplary embodiment.
- the processormay search for a path from a root node corresponding to the starting point 521 to a node or an edge corresponding to the target region 522 from the blood vessel structure data formed in a tree-type graph.
- the processormay search for a path based on the number of nodes that must pass from the root node to the node or edge corresponding to the destination region 522 , and searches for a path from the root node to a specific node through the minimum node. can do.
- the blood vessel structure datais formed in a tree-type graph, and the processor may acquire the level of each node while forming the blood vessel structure data.
- the level of a nodemay mean how many nodes must pass from the root node to reach a specific node.
- the specific node corresponding to the target region 522may be a leaf node that does not have a child node at the bottom of the tree graph, and the processor is configured to operate at the level of the leaf node and the root node.
- the shortest pathcan be calculated based on the difference.
- the processormay determine, as the shortest path, a path in which the number of nodes passed from the root node to the specific node corresponds to a level difference between the leaf node and the root node.
- the part corresponding to the target area 522may be an edge rather than a node. In this case, the processor may search for a shortest path to reach one of the two nodes to which the edge is connected.
- a method for searching for a path from the starting point 521 to the destination region 522may be using a tree traversal method as well as using a level difference from a root node to a specific node.
- the processormay determine a location in the image 530 corresponding to nodes on the path as the intermediate target region 531 .
- the processorvisualizes the starting point 521 , the target area 522 , and the intermediate target area 531 as graphic objects at positions corresponding to the starting point 521 , the target area 522 , and the intermediate target area 531 . can do.
- the processormay overlap and display the start point 521 , the target area 522 , and the intermediate target area 531 at positions corresponding to the respective points in the image 530 .
- FIG. 6is a flowchart illustrating the creation of an additional intermediate target area according to an embodiment.
- the processormay set an intermediate target area at a position corresponding to a branch point in the blood vessel image as a basic intermediate target area, and calculate a distance between adjacent basic intermediate target areas in units of image pixels.
- the processormay determine whether to additionally set the intermediate target area according to the distance between the undulation target areas calculated in units of image pixels. When the processor determines that the distance between the basic intermediate target areas is greater than the threshold distance, the processor may proceed to step 630 , and when it is determined that the distance between the basic intermediate target areas is smaller than the threshold distance, it may determine that it is not necessary to set an additional intermediate target area.
- the additional intermediate target areamay be generated.
- the guide data providing apparatus or the medical tool insertion apparatusmay generate the guide patch image by dividing and enlarging the blood vessel image or the blood vessel structure image in units of patches.
- the guide patch imagemay be used to accurately determine the operation of the medical tool insertion device.
- the guide data devicemay generate an additional intermediate target area on the movement path found in the blood vessel image of the divided patch area. Since the additional intermediate target area is created on the path that the medical tool tip must pass, the medical tool insertion device can accurately move the medical tool tip to the final target area simply by moving the medical tool tip to the additional intermediate target area within the segmented patch area. have.
- the additional intermediate target regionmay provide information on the exact position to which the medical tool tip should be moved on some paths shown in the divided patch regions among the entire paths.
- the processormay determine the threshold distance according to the patch size. For example, when a blood vessel image is enlarged with a square patch, the length of one side of the square may be set as a threshold distance.
- the medical tool insertion apparatususes the patch image, for example, Using the machine learning model, it is possible to calculate a series of motion commands for moving the tip of the medical tool to the next target area.
- the processormay change the threshold distance according to the size of the patch for enlarging the blood vessel image.
- the size of the patchmay be changed in real time according to the complexity of the vascular structure.
- the size of the rectangular patchhas a default value of 84 x 84 pixels, and may increase or decrease according to the complexity of the vascular structure.
- the processormay determine the threshold distance to be 84 pixels, which is the length of one side of the square patch, but may also be determined to be 50 pixels according to the operator's choice.
- FIG. 7is a diagram illustrating generation of an additional intermediate target region from an image of a blood vessel structure in which a basic intermediate target region is generated, according to an exemplary embodiment.
- the processormay generate an image 720 in which additional intermediate target areas 721 are set from the image 710 in which basic intermediate target areas 711 and 712 are set.
- the additional intermediate target areas 721may be set according to a distance between the basic intermediate target areas 711 and 712 .
- the medical tool insertion apparatusmay determine the operation command using a patch image including a partial path instead of using the image of the entire blood vessel region.
- the patch imageis a patch divided from the blood vessel image or the blood vessel structure image, and may include some paths between the basic intermediate target regions 711 and 712 .
- the medical tool insertion apparatusmay segment the patch image corresponding to the current position of the distal end of the medical tool based on the path searched for in the entire blood vessel region.
- the segmented patch imagemay include at least one additional intermediate target region 721 together with the distal end of the medical tool. This is because the additional intermediate target area 721 is set according to the distance between the basic intermediate target areas as described above with reference to FIG. 6 . Accordingly, the medical tool insertion device may calculate an operation command from the machine learning model by using the current position of the tip of the medical tool and the additional intermediate target region 721 .
- the distance between the basic intermediate target regions 711 and 712may vary depending on the blood vessel structure of the recipient.
- the processormay determine the number of additional intermediate target areas 721 according to a distance between the basic intermediate target areas 711 and 712 .
- the processormay determine the distance between the additional intermediate target areas 721 by comparing the distance between the basic intermediate target areas 711 , 712 with a distance that is a multiple of the threshold distance. That is, the processor may calculate n (n is a natural number) satisfying Equation 1, and determine n as the number of additional intermediate target areas 721 generated between the basic intermediate target areas 711 and 712 .
- the processordivides the additional intermediate target areas 721 between the basic intermediate target areas 711 and 712 at equal intervals. It may be created and visualized as an intermediate target area by overlapping the intermediate target area graphic object on the blood vessel image or the blood vessel structure image.
- the processormay generate the additional intermediate target area 721 at equal intervals between the basic intermediate target areas 711 and 712 , but is not limited thereto, and at least one intermediate target area 721 may be used in an image enlarged in units of patches. Other embodiments that allow the identification of target areas may also emerge. Since the additional intermediate target area 721 is visualized, each patch image divided into patch units may include the intermediate target area. Accordingly, the medical tool insertion apparatus may calculate an operation command for moving the distal end of the medical tool to the newly created intermediate target area using the patch image.
- FIG. 8is a diagram illustrating movement of a medical tool insertion device from a starting point to a destination area according to an exemplary embodiment
- the processor providing guide dataoutputs the intermediate target area graphic objects 811 and 812 at the location where the intermediate target area is generated in the blood vessel image, and the distal end of the medical tool reaches the target area selected from the intermediate target area. If it is determined that , the graphic object 811 of the target region may be deleted from the blood vessel image.
- the processormay determine an intermediate target area closest to the distal end of the medical tool as the target area along the progress direction of the medical tool from the blood vessel image. By deleting the graphic object of the target area when the tip of the medical tool reaches the target area, the processor can visualize in real time a situation in which the tip of the medical tool is moved to the target area 821 .
- the processorWhen the processor according to an embodiment recognizes that the graphic object of the target area is deleted, the processor provides an index for evaluating the operation of the medical tool insertion apparatus, so that the medical tool insertion apparatus can learn the operation by itself. That is, it is possible to provide data used for training a machine learning model through an artificial neural network.
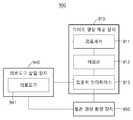
- FIG. 9is a block diagram schematically showing the configuration of a medical tool guide device according to an embodiment.
- a medical tool guide system 900 for moving a medical tool 941 inserted into a blood vesselmay include a medical tool insertion device 940 and a guide data providing device 910 .
- the guide data providing device 910may receive a blood vessel image or a blood vessel structure image from the blood vessel imaging device 950 through the input/output interface 913 , and transmit guide data including the guide image to the medical tool insertion device 940 . can be created and provided.
- the memory 912 of the guide data providing apparatus 910may at least temporarily store data and guide images generated by the processor 911 .
- the processor 911 of the guide data providing device 910sets the initial position of the distal end 941 of the medical tool as the starting point in the blood vessel image, and sets the intermediate target area within the path from the starting point to the target area as the blood vessel branching point.
- Guide data determined as a reference, corresponding to at least a partial region of the blood vessel image, and including at least a part of an intermediate target regionmay be provided. Since the operation of the processor 911 of the guide data providing apparatus 910 has been described above, a detailed description thereof will be omitted.
- the medical tool insertion device 940may move the medical tool 941 based on the guide data received from the guide data providing device 910 .
- the processor 911 of the guide data providing device 910 or the processor of the medical tool insertion device 940is an operation command for moving the medical tool 941 based on guide data including a guide image.
- the guide data providing apparatus 910 and the medical tool insertion apparatus 940may be divided according to functions.
- the guide data providing device 910 and the medical tool insertion device 940may be devices that perform different functions within a single device housing. That is, the processors of the guide data providing apparatus 910 and the medical tool insertion apparatus 940 may perform different functions as one processor.
- the present inventionis not limited thereto, and the guide data providing device 910 and the medical tool insertion device 940 may be implemented as separate devices independent of each other.
- the processormay drive the medical tool insertion device 940 based on the generated guide data.
- the processormay set a point different from the target area among the intermediate target areas as the next target area.
- the next target areamay be an intermediate target area closest to the target area along the moving direction of the distal end 941 of the medical tool.
- the processorreaches the target area, the medical tool tip 941 can be moved to a series of intermediate target areas by continuously setting the next target area, and finally the medical tool tip 941 can be positioned as the target area. have.
- the embodiments described abovemay be implemented by a hardware component, a software component, and/or a combination of a hardware component and a software component.
- the apparatus, methods and components described in the embodimentsmay include, for example, a processor, a controller, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU), a digital signal processor, a microcomputer, a field programmable gate (FPGA) array), a programmable logic unit (PLU), a microprocessor, or any other device capable of executing and responding to instructions.
- the processing devicemay execute an operating system (OS) and one or more software applications running on the operating system.
- the processing devicemay also access, store, manipulate, process, and generate data in response to execution of the software.
- OSoperating system
- the processing devicemay also access, store, manipulate, process, and generate data in response to execution of the software.
- the processing deviceincludes a plurality of processing elements and/or a plurality of types of processing elements. It can be seen that can include For example, the processing device may include a plurality of processors or one processor and one controller. Other processing configurations are also possible, such as parallel processors.
- the softwaremay comprise a computer program, code, instructions, or a combination of one or more thereof, which configures a processing device to operate as desired or is independently or collectively processed You can command the device.
- the software and/or datamay be any kind of machine, component, physical device, virtual equipment, computer storage medium or device, to be interpreted by or to provide instructions or data to the processing device. , or may be permanently or temporarily embody in a transmitted signal wave.
- the softwaremay be distributed over networked computer systems, and stored or executed in a distributed manner. Software and data may be stored in one or more computer-readable recording media.
- the method according to the embodimentmay be implemented in the form of program instructions that can be executed through various computer means and recorded in a computer-readable medium.
- the computer-readable mediummay include program instructions, data files, data structures, etc. alone or in combination.
- the program instructions recorded on the mediummay be specially designed and configured for the embodiment, or may be known and available to those skilled in the art of computer software.
- Examples of the computer-readable recording mediuminclude magnetic media such as hard disks, floppy disks and magnetic tapes, optical media such as CD-ROMs and DVDs, and magnetic such as floppy disks.
- -includes magneto-optical media, and hardware devices specially configured to store and execute program instructions, such as ROM, RAM, flash memory, and the like.
- Examples of program instructionsinclude not only machine language codes such as those generated by a compiler, but also high-level language codes that can be executed by a computer using an interpreter or the like.
- the hardware devices described abovemay be configured to operate as one or more software modules to perform the operations of the embodiments, and vice versa.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Robotics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Pulmonology (AREA)
- Anesthesiology (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Apparatus For Radiation Diagnosis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromKorean이하, 의료 도구 삽입 장치를 위해 가이드 데이터를 제공하는 방법에 관한 기술이 제공된다.Hereinafter, techniques for providing guide data for a medical tool insertion device are provided.
심혈관, 뇌혈관, 말초혈관을 치료할 때 카테터를 이용하여 스텐트 등을 삽입하는 중재 시술이 널리 보급되어 있다. 가이드와이어는 카테터를 통과하여 혈관 내에 스텐트 등을 이송하는 경로를 설정하기 위한 도구로서, 가이드와이어를 질환이 있는 혈관의 말단까지 이송시키기 위해서 혈관 조영술(angiography)등 의료영상 기반의 시각 정보와 미세한 손의 감각에 기반한 촉각 정보등을 활용된다.When treating cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and peripheral blood vessels, an interventional procedure that inserts a stent using a catheter is widespread. A guide wire is a tool for setting a route for transporting a stent, etc. into a blood vessel through a catheter. In order to transport the guide wire to the end of a diseased blood vessel, visual information based on medical images such as angiography and fine hand Tactile information based on the senses of
최근 방사선 노출 등 시술자의 신체적 부담을 경감하고 시술도구의 정밀한 제어를 위하여 원격로봇 등이 개발되고 있다. 시술로봇은 FDA를 통과하여 상용화가 진행되고 있으나, 간단한 시술 동작을 하기 위해서 새로운 도구에 적응하기 위한 학습이 필요한 실정이다. 가이드와이어를 뒤로 움직이거나 일정한 각도로 회전하는 등 해당 동작을 직접 하지 않더라도 로봇이 대신하는 기능이 더해지고 있으나, 시술에서 차지하는 비중은 적다.Recently, remote robots have been developed to reduce the operator's physical burden, such as radiation exposure, and to precisely control surgical tools. Although the surgical robot has passed the FDA and is being commercialized, it is necessary to learn to adapt to a new tool in order to perform a simple procedure. Even if you do not directly perform the corresponding motion, such as moving the guide wire backwards or rotating it at a certain angle, a function that the robot takes over is being added, but the proportion of the operation is small.
일실시예에 따르면, 프로세서에 의해 수행되는 의료 도구 삽입 장치를 위한 가이드 데이터를 제공하는 방법에 있어서, 혈관 영상에서 혈관에 삽입된 의료도구 선단부의 초기 위치를 시작 지점(starting point)으로 설정하는 단계, 상기 시작 지점으로부터 목적 영역(destination point)까지의 경로 내에서 중간 목표 영역(middle target point)을 혈관 분지 지점(blood vessel branch point)을 기준으로 결정하는 단계, 및 상기 혈관 영상의 적어도 일부 영역에 대응하고, 상기 중간 목표 영역 중 적어도 일부를 포함하는 가이드 데이터를 제공하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.According to one embodiment, there is provided a method of providing guide data for a medical tool insertion device performed by a processor, the method comprising: setting an initial position of a distal end of a medical tool inserted into a blood vessel in a blood vessel image as a starting point; , determining a middle target point in a path from the starting point to a destination point based on a blood vessel branch point, and in at least a partial area of the blood vessel image. and providing guide data including at least a portion of the intermediate target area.
일측에 따른 가이드 데이터 제공 방법은 상기 혈관 영상으로부터 혈관의 분지 지점들 간의 연결정보를 획득함으로써 혈관 구조 데이터를 생성하는 단계, 및 상기 혈관 구조 데이터에 기초하여 상기 목적 영역까지의 경로를 검색하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The guide data providing method according to one side includes generating blood vessel structure data by obtaining connection information between branch points of blood vessels from the blood vessel image, and searching for a path to the target region based on the blood vessel structure data. may include
또한, 상기 중간 목표 영역을 결정하는 단계는 상기 혈관 영상에서 분지 지점에 대응하는 위치(position)에 기본 중간 목표 영역을 생성하는 단계, 및 상기 기본 중간 목표 영역 간의 거리에 기초하여 추가 중간 목표 영역을 생성할지 여부를 결정하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In addition, the determining of the intermediate target area includes generating a basic intermediate target area at a position corresponding to a branching point in the blood vessel image, and selecting an additional intermediate target area based on a distance between the basic intermediate target areas. determining whether to create or not.
상기 중간 목표 영역을 결정하는 단계는 상기 기본 중간 목표 영역 간의 거리에 따라 상기 기본 중간 목표 영역 사이에 생성할 상기 추가 중간 목표 영역의 개수를 결정하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The determining of the intermediate target areas may include determining the number of the additional intermediate target areas to be generated between the basic intermediate target areas according to a distance between the basic intermediate target areas.
아울러, 가이드 데이터를 제공하는 방법은 상기 혈관 영상에서 상기 중간 목표 영역이 생성된 위치에 중간 목표 영역 그래픽 오브젝트를 출력하는 단계 및 상기 의료도구 선단부가 상기 중간 목표 영역으로부터 선택된 대상 영역에 도달하였다고 판단한 경우, 상기 혈관 영상에서 상기 대상 영역의 그래픽 오브젝트를 삭제하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In addition, the method of providing guide data includes outputting an intermediate target area graphic object to a position where the intermediate target area is generated in the blood vessel image, and when it is determined that the tip of the medical tool reaches the target area selected from the intermediate target area , deleting the graphic object of the target region from the blood vessel image.
일실시예에 따른 혈관에 삽입된 의료도구 가이드 방법은 혈관 영상에서 상기 의료도구 선단부의 초기 위치를 시작 지점(starting point)으로 설정하는 단계, 상기 시작 지점으로부터 목적 영역(destination point)까지의 경로 내에서 중간 목표 영역(middle target point)을 혈관 분지 지점(blood vessel branch point)을 기준으로 결정하는 단계, 상기 혈관 영상의 적어도 일부 영역에 대응하고, 상기 중간 목표 영역 중 적어도 일부를 포함하는 가이드 데이터를 생성하는 단계, 및 상기 가이드 데이터에 기초하여 상기 의료 도구 삽입 장치를 구동함으로써 상기 의료도구 선단부를 상기 중간 목표 영역으로 이동시키는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The method for guiding a medical tool inserted into a blood vessel according to an embodiment includes setting an initial position of the tip of the medical tool in a blood vessel image as a starting point, within a path from the starting point to a destination point. determining a middle target point based on a blood vessel branch point, corresponding to at least a portion of the blood vessel image, and providing guide data including at least a portion of the intermediate target area generating, and moving the distal end of the medical tool to the intermediate target area by driving the medical tool insertion device based on the guide data.
일측에 따른 상기 중간 목표 영역으로 이동시키는 단계는 상기 중간 목표 영역으로부터 선택된 대상 영역에 상기 의료도구 선단부가 도달하였다고 판단되는 경우, 상기 중간 목표 영역 중 상기 대상 영역과 다른 지점을 다음 대상 영역으로 설정하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In the step of moving to the intermediate target area according to one side, when it is determined that the tip of the medical tool has reached the target area selected from the intermediate target area, a point different from the target area in the intermediate target area is set as the next target area may include steps.
상기 다음 대상 영역은 상기 의료도구 선단부의 진행 방향을 따라 상기 대상 영역에 가장 인접한 중간 목표 영역일 수 있다.The next target area may be an intermediate target area closest to the target area along a traveling direction of the distal end of the medical tool.
일실시예에 따른 가이드 데이터 제공 방법은 혈관 내 목적 영역까지 의료 도구 삽입 장치의 의료도구(예를 들어, 의료 도구(medical tool))를 이동시키기 위한 경로를 탐색할 수 있다. 최적 경로를 탐색한 후, 경로 상에 중간 목표 영역을 생성함으로써 의료도구를 제어하는 의료 도구 삽입 장치가 인식 가능한 중간 목적지를 제공할 수 있다.The guide data providing method according to an embodiment may search for a path for moving a medical tool (eg, a medical tool) of the medical tool insertion apparatus to a target region within a blood vessel. After searching for the optimal path, the medical tool insertion apparatus for controlling the medical tool may provide a recognizable intermediate destination by generating an intermediate target area on the path.
또한, 일실시예에 따른 의료 도구 삽입 장치 가이드 방법은 혈관 분지 지점을 기준으로 기본 중간 목표 영역을 생성한 후, 기본 중간 목표 영역 간의 거리에 따라 추가 중간 목표 영역을 생성할 수 있으므로, 이동 장치는 혈관 영상으로부터 분할된 부분 혈관 영상에서도 의료도구 선단부를 중간 목적지로 이동시킬 수 있다. 따라서, 의료 도구 삽입 장치 가이드 방법을 수행하는 프로세서는 시술자의 원격 조종 없이도 목적 영역까지 의료도구를 정교하게 이동시킬 수 있다.In addition, since the method for guiding a device for inserting a medical tool according to an embodiment may generate a basic intermediate target area based on a blood vessel branch point and then generate an additional intermediate target area according to a distance between the basic intermediate target areas, the mobile device may Even in the partial blood vessel image divided from the blood vessel image, the tip of the medical tool can be moved to the intermediate destination. Accordingly, the processor performing the method for guiding the apparatus for inserting a medical tool can precisely move the medical tool to the target area without remote control by an operator.
도 1은 일실시예에 따른 의료 도구 삽입 장치 및 의료도구의 동작을 도시한 도면이다.1 is a diagram illustrating an operation of an apparatus for inserting a medical tool and a medical tool according to an exemplary embodiment.
도 2는 일실시예에 따른 가이드 데이터 제공 방법을 도시한 흐름도이다.2 is a flowchart illustrating a method of providing guide data according to an exemplary embodiment.
도 3은 일실시예에 따른 혈관 영상으로부터 중간 목표 영역이 생성된 혈관 구조 영상을 생성하는 것을 도시한 도면이다.3 is a diagram illustrating generation of a blood vessel structure image in which an intermediate target region is generated from a blood vessel image according to an exemplary embodiment.
도 4는 일실시예에 따라 혈관 영상으로부터 혈관 구조 데이터를 생성하는 것을 도시한 도면이다.4 is a diagram illustrating generation of blood vessel structure data from a blood vessel image according to an exemplary embodiment.
도 5는 일실시예에 따라 혈관 구조 데이터로부터 목적 영역까지의 경로를 생성하고, 혈관 분지 지점에 해당하는 위치를 기본 중간 목표 영역으로 생성하는 것을 도시한 도면이다.FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating generating a path from blood vessel structure data to a target region and generating a location corresponding to a branch point of a blood vessel as a basic intermediate target region according to an exemplary embodiment.
도 6은 일실시예에 따라 추가 중간 목표 영역을 생성하는 것을 나타낸 흐름도이다.6 is a flowchart illustrating the creation of an additional intermediate target area according to an embodiment.
도 7은 일실시예에 따라 기본 중간 목표 영역이 생성된 혈관 구조 영상으로부터 추가 중간 목표 영역을 생성하는 것을 도시한 도면이다.7 is a diagram illustrating generation of an additional intermediate target region from an image of a blood vessel structure in which a basic intermediate target region is generated, according to an exemplary embodiment.
도 8은 일실시예에 따라 의료 도구 삽입 장치가 시작 지점으로부터 목적 영역까지 이동하는 것을 도시한 도면이다.8 is a diagram illustrating movement of a medical tool insertion device from a starting point to a destination area according to an exemplary embodiment;
도 9는 일실시예에 따라 의료 도구 삽입 장치를 이동시키는 시스템의 구성을 대략적으로 나타낸 블록도이다.9 is a block diagram schematically illustrating a configuration of a system for moving a medical tool insertion device according to an embodiment.
실시예들에 대한 특정한 구조적 또는 기능적 설명들은 단지 예시를 위한 목적으로 개시된 것으로서, 다양한 형태로 변경되어 실시될 수 있다. 따라서, 실시예들은 특정한 개시형태로 한정되는 것이 아니며, 본 명세서의 범위는 기술적 사상에 포함되는 변경, 균등물, 또는 대체물을 포함한다.Specific structural or functional descriptions of the embodiments are disclosed for purposes of illustration only, and may be changed and implemented in various forms. Accordingly, the embodiments are not limited to a specific disclosure form, and the scope of the present specification includes changes, equivalents, or substitutes included in the technical spirit.
제1 또는 제2 등의 용어를 다양한 구성요소들을 설명하는데 사용될 수 있지만, 이런 용어들은 하나의 구성요소를 다른 구성요소로부터 구별하는 목적으로만 해석되어야 한다. 예를 들어, 제1 구성요소는 제2 구성요소로 명명될 수 있고, 유사하게 제2 구성요소는 제1 구성요소로도 명명될 수 있다.Although terms such as first or second may be used to describe various components, these terms should be interpreted only for the purpose of distinguishing one component from another. For example, a first component may be termed a second component, and similarly, a second component may also be termed a first component.
어떤 구성요소가 다른 구성요소에 "연결되어" 있다고 언급된 때에는, 그 다른 구성요소에 직접적으로 연결되어 있거나 또는 접속되어 있을 수도 있지만, 중간에 다른 구성요소가 존재할 수도 있다고 이해되어야 할 것이다.When a component is referred to as being “connected to” another component, it may be directly connected or connected to the other component, but it should be understood that another component may exist in between.
단수의 표현은 문맥상 명백하게 다르게 뜻하지 않는 한, 복수의 표현을 포함한다. 본 명세서에서, "포함하다" 또는 "가지다" 등의 용어는 설명된 특징, 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부분품 또는 이들을 조합한 것이 존재함으로 지정하려는 것이지, 하나 또는 그 이상의 다른 특징들이나 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부분품 또는 이들을 조합한 것들의 존재 또는 부가 가능성을 미리 배제하지 않는 것으로 이해되어야 한다.The singular expression includes the plural expression unless the context clearly dictates otherwise. In this specification, terms such as "comprise" or "have" are intended to designate that the described feature, number, step, operation, component, part, or combination thereof exists, and includes one or more other features or numbers, It should be understood that the possibility of the presence or addition of steps, operations, components, parts or combinations thereof is not precluded in advance.
다르게 정의되지 않는 한, 기술적이거나 과학적인 용어를 포함해서 여기서 사용되는 모든 용어들은 해당 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 의해 일반적으로 이해되는 것과 동일한 의미를 가진다. 일반적으로 사용되는 사전에 정의되어 있는 것과 같은 용어들은 관련 기술의 문맥상 가지는 의미와 일치하는 의미를 갖는 것으로 해석되어야 하며, 본 명세서에서 명백하게 정의하지 않는 한, 이상적이거나 과도하게 형식적인 의미로 해석되지 않는다. 이하, 실시예들을 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 상세하게 설명한다. 각 도면에 제시된 동일한 참조 부호는 동일한 부재를 나타낸다.Unless defined otherwise, all terms used herein, including technical or scientific terms, have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art. Terms such as those defined in a commonly used dictionary should be interpreted as having a meaning consistent with the meaning in the context of the related art, and should not be interpreted in an ideal or excessively formal meaning unless explicitly defined in the present specification. does not Hereinafter, embodiments will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. Like reference numerals in each figure indicate like elements.
도 1은 일실시예에 따른 의료 도구 삽입 장치(110) 및 의료도구(120)의 동작을 도시한 도면이다.1 is a diagram illustrating operations of a medical
일실시예에 따른 의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)는 프로세서에 의한 구동 명령에 따라 혈관 목적 영역까지 의료도구(120)를 이동시킬 수 있다. 예를 들어, 의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)는 의료도구(120)의 선단부를 혈관 목적 영역까지 이동시킬 수 있다. 의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)는 수술을 수행하기 위한 로봇으로 구현될 수 있으며, 예를 들어, 심혈관중재술을 위한 의료 도구를 제어하는 로봇일 수 있다.The medical
의료도구(120)는 혈관에 삽입되는 부재(member)로서, 의료도구(120)의 선단부에 배치되는 의료 도구(medical tool) 및 의료 도구를 구동부에 연결하는 의료용 와이어(medical wire)를 포함할 수 있다. 의료용 와이어는 예를 들어, 카테터(catheter) 또는 가이드와이어를 포함할 수 있다. 가이드와이어는 상술한 의료 도구를 혈관의 목적부위까지 삽입 및 가이드하기 위해 이용되는 의료용 와이어를 나타낼 수 있다. 의료 도구는 의사의 제어에 따라 작동되는 수술용 도구일 수 있고, 예를 들어, 인트로듀서 키트(introducer kit)일 수 있다.The
의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)는 가이드 데이터를 이용하여 상술한 구동 명령을 결정할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)는, 기계 학습 모델에 따른 연산을 수행함으로써, 가이드 데이터로부터 구동 명령을 출력할 수 있다. 기계 학습 모델은 가이드 데이터를 입력 받고 가이드 데이터를 출력하도록 설계 및 트레이닝된 모델로서, 예를 들어, 뉴럴 네트워크 모델로 구현될 수 있다.The medical
구동 명령은, 의료도구(120)와 연결되어 의료도구(120)를 이동 및 회전시키는 구동부를 동작시키기 위한 명령을 나타낼 수 있다. 구동 명령은 예를 들어, 전진 명령, 후진 명령, 시계 방향 회전 명령, 및 반시계 방향 회전 명령일 수 있으나, 이로 한정하는 것은 아니다.The driving command may represent a command for operating a driving unit connected to the
가이드 데이터는 혈관 영상 또는 혈관 구조 영상에 가이드 정보가 매핑된 데이터를 나타낼 수 있다. 혈관 구조 영상은 혈관 영상으로부터 특정 혈관이 추출된 영상으로서, 혈관 영상이 전처리된 영상일 수 있다. 혈관 구조 영상은 하기 도 3에서 설명한다. 혈관 영상은 혈관조영술(coronary angiography, 이하 CAG) 또는 자기공명영상(Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 이하 MRI)를 이용하여 생성된 영상일 수 있다. 혈관 영상에서는 혈관뿐만 아니라 의료도구(120)도 촬영될 수 있다.The guide data may represent data in which guide information is mapped to a blood vessel image or a blood vessel structure image. The blood vessel structure image is an image in which a specific blood vessel is extracted from the blood vessel image, and may be an image obtained by preprocessing the blood vessel image. The blood vessel structure image will be described with reference to FIG. 3 below. The blood vessel image may be an image generated using corona angiography (CAG) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In the blood vessel image, not only blood vessels but also the
가이드 정보는 의료도구(120)의 이동 및 회전을 가이드하기 위한 정보로서, 예를 들어, 혈관 내에서 의료도구(120)가 출발해야하는 지점, 경유해야하는 지점, 및 목적 영역에 관한 정보를 포함할 수 있다. 각 지점에 관한 정보는 해당 지점의 혈관 구조 영상 내 영상 좌표를 포함할 수 있으나, 이로 한정하는 것은 아니다. 일 실시예에 따르면 혈관 구조 영상에 가이드 정보가 시각적으로 매핑될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 각 목표 영역에 대응하는 그래픽 오브젝트가 혈관 구조 영상에 시각화될 수 있고, 목표 영역이 시각화된 혈관 구조 영상을 가이드 영상이라고 나타낼 수 있다.The guide information is information for guiding the movement and rotation of the
예를 들어, 의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)는 외부 장치(예를 들어, 가이드 데이터 제공 장치)로부터 가이드 데이터를 수신할 수 있다. 가이드 데이터 제공 장치는 혈관 촬영 장치(130)로부터 혈관 영상을 수신 및 분석하고, 혈관 영상으로부터 가이드 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 다른 예를 들어, 의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)는 상술한 가이드 데이터 제공 장치와 일체로 구현될 수 있다. 이 경우, 의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)는 혈관 촬영 장치(130)로부터 혈관 영상을 수신하고, 수신된 혈관 영상을 분석하여 가이드 데이터를 생성할 수 있다.For example, the medical
의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)의 프로세서는, 혈관 영상을 분석한 결과에 기초하여, 의료도구(120)의 구동을 결정할 수 있다. 의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)는 수신된 혈관 영상을 분석하여 가이드 데이터를 생성하고, 생성된 가이드 데이터로부터 구동 명령을 결정할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)는 가이드 데이터로부터 전진 명령, 후진 명령, 시계 방향 회전 명령, 및 반시계 방향 회전 명령 중 하나를 동작 명령으로 선택할 수 있다. 의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)의 구동부는 선택된 동작 명령에 따라 구동할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 구동부는 전진 명령에 응답하여 의료도구(120)를 전진시킬 수 있다. 구동부는 후진 명령에 응답하여 의료도구(120)를 후퇴시킬 수 있다. 구동부는 시계 방향 회전 명령에 응답하여, 가이드와이어의 길이 축을 기준으로 가이드와이어를 시계 방향으로 회전시킬 수 있다. 구동부는 반시계 방향 회전 명령에 응답하여, 가이드와이어의 길이 축을 기준으로 가이드와이어를 반시계 방향으로 회전시킬 수 있다.The processor of the medical
따라서, 의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)는 혈관 영상을 분석함으로써 생성된 가이드 데이터를 이용하여 일련의 동작 명령들을 결정함으로써, 가이드 데이터에 의해 가이드되는 지점으로 의료도구(120)의 선단부를 이동시킬 수 있다. 의료 도구 삽입 장치(110)는 가이드 데이터를 이용한 동작 결정을 반복함으로써, 의료도구(120)의 선단부를 최종 목적 영역까지 이동시킬 수 있다. 의료도구(120)의 선단부, 예를 들어, 의료 도구가 목적 영역까지 도달한 후, 의료 도구는 의사의 제어에 따른 수술 동작을 수행할 수 있다.Accordingly, the medical
도 2는 일실시예에 따른 가이드 데이터 제공 방법을 도시한 흐름도이다.2 is a flowchart illustrating a method of providing guide data according to an exemplary embodiment.
단계(210)에서, 일실시예에 따른 프로세서는 혈관 영상에서 혈관에 삽입된 의료도구 선단부의 초기 위치를 시작 지점으로 설정할 수 있다. 초기 위치는 혈관 영역에서 의료도구 선단부가 처음 식별된 시점(time point)의 혈관 내 지점에 대응하는 위치일 수 있다. 하기 도 3에 도시되는 바와 같이, 혈관 영상으로부터 특정 혈관이 추출된 혈관 구조 영상에 시작 지점이 설정될 수 있다.In
단계(220)에서, 프로세서는 시작 지점으로부터 목적 영역까지의 경로 내에서 중간 목표 영역을 혈관 분지 지점을 기준으로 결정할 수 있다. 목적 영역은 시술자 또는 프로세서에 의해 지정된 혈관 영상 내 위치일 수 있다. 프로세서는 혈관 분지 지점을 혈관이 분기되는 지점에 대응하는 위치로 식별할 수 있다. 프로세서는 시작 지점으로부터 목적 영역까지의 경로를 혈관 영상에서의 최단 거리로 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서는 혈관의 분지 지점들 간의 연결정보를 획득함으로써 생성된 혈관 구조 데이터에 기초하여 경로를 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서가 시작 지점으로부터 목적 영역까지의 경로를 결정하는 것은 도 4 및 도 5를 통해 상세히 서술한다.In
일실시예에 따른 프로세서는 경로 내에서 중간 목표 영역을 결정할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 프로세서는 혈관 분지 지점을 기준으로 기본 중간 목표 영역들을 설정하고, 기본 중간 목표 영역들 사이의 거리에 따라 추가 중간 목표 영역을 설정할 수 있다. 기본 중간 목표 영역 및 추가 중간 목표 영역을 설정하는 것은 도 6및 도 7을 통해 상세히 서술한다. 가이드 데이터 제공 장치는 기본 중간 목표 영역 및 추가 중간 목표 영역을 포함한 중간 목표 영역이 설정된 가이드 데이터를 의료 도구 삽입 장치로 제공함으로써, 의료 도구 삽입 장치는 가이드 데이터의 혈관 전체 영역 중 일부 영역이 확대된 영상을 이용하여 의료도구 선단부를 시작 지점으로부터 목적 영역까지 도달시킬 수 있게 된다. 일부 영역이 확대된 영상에서 최종 목적 영역이 없더라도 중간 목표 영역이 설정되어 있으므로, 의료 도구 삽입 장치는 각 일부 영역에 대응하는 일련의 영상들에 설정된 중간 목표 영역으로 의료도구 선단부를 이동시킬 수 있다. 일련의 중간 목표 영역에 의료도구 선단부를 순차적으로 도달시킴으로써, 의료 도구 삽입 장치는 최종 목적 영역까지 의료도구 선단부를 이동시킬 수 있다.The processor according to an embodiment may determine an intermediate target area within the path. For example, the processor may set basic intermediate target regions based on the branching point of a blood vessel, and may set additional intermediate target regions according to a distance between the basic intermediate target regions. Setting the basic intermediate target area and the additional intermediate target area will be described in detail with reference to FIGS. 6 and 7 . The guide data providing device provides the guide data in which the intermediate target area including the basic intermediate target area and the additional intermediate target area is set to the medical tool insertion device. It is possible to reach the tip of the medical tool from the starting point to the target area using Since the intermediate target area is set even if there is no final target area in the image in which the partial area is enlarged, the medical tool insertion apparatus may move the distal end of the medical tool to the intermediate target area set in a series of images corresponding to each partial area. By sequentially reaching the medical tool tip at a series of intermediate target areas, the medical tool insertion device can move the medical tool tip to the final target area.
단계(230)에서, 프로세서는 혈관 영상의 적어도 일부 영역에 대응하고, 중간 목표 영역 중 적어도 일부를 포함하는 가이드 데이터를 제공할 수 있다. 가이드 데이터는 혈관 영상 또는 혈관 구조 영상에 가이드 정보(예를 들어, 시작 지점, 목적 영역, 중간 목표 영역의 위치)가 설정된 데이터일 수 있다. 예를 들어, 가이드 데이터는 혈관 영상 또는 혈관 구조 영상 상에 시작 지점, 목적 영역, 중간 목표 영역에 대응하는 그래픽 오브젝트가 오버랩(overlap)되어 시각화된 가이드 영상을 포함할 수 있다.In
일실시예에 따른 프로세서는 의료도구 선단부가 혈관 영상에서 목적 영역 또는 중간 목표 영역의 일정 영역만큼 중첩 되어있는지 여부에 기초하여 의료도구 선단부가 목적 영역 또는 중간 목표 영역에 도달하였는지 여부를 판단할 수 있다. 예시적으로, 프로세서는 혈관 영상에서 목적 영역 또는 중간 목표 영역 중 의료도구 선단부가 차지하는 비율을 계산할 수 있고, 계산된 비율이 임계 비율 이상인 경우 의료도구 선단부가 목적 영역 또는 중간 목표 영역에 도달하였다고 판단할 수 있다.The processor according to an embodiment may determine whether the distal end of the medical tool has reached the target area or the intermediate target area based on whether the distal end of the medical tool overlaps the target area or the intermediate target area by a predetermined area in the blood vessel image. . For example, the processor may calculate a ratio of the medical tool tip portion among the target region or the intermediate target region in the blood vessel image, and when the calculated ratio is greater than or equal to the threshold ratio, it may be determined that the medical tool tip has reached the target region or the intermediate target region. can
상술한 도 2의 단계들(210 내지 230)은 가이드 데이터 제공 장치의 프로세서에 의해 수행될 수 있으나, 이로 한정하는 것은 아니고, 의료 도구 삽입 장치의 프로세서에 의해 수행될 수도 있다.
도 3은 일실시예에 따른 혈관 영상(310)으로부터 중간 목표 영역(322)이 생성된 혈관 구조 영상(320)을 생성하는 것을 도시한 도면이다.FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating generation of a blood
일실시예에 따른 프로세서는 혈관 영상(310)으로부터 생성된 혈관 구조 영상(320)을 입력 받을 수 있으나, 이에 국한되지 않고 프로세서가 혈관 구조 영상(320)을 직접 생성할 수도 있다.The processor according to an embodiment may receive the blood
혈관 구조 영상(320)은 혈관 영상(310)으로부터 식별된 혈관 및 혈관의 구조, 연결관계가 표시된 영상일 수 있다. 일실시예에 따른 프로세서는 혈관 영상(310)으로부터 경계 검출(edge detecting) 방법을 이용하여 혈관 영역과 배경 영역을 구분함으로써 혈관 구조 영상(320)을 생성할 수 있다. 예시적으로, 경계 검출 방법은 임의의 픽셀과 주변 픽셀의 그레이스케일 레벨이 급격하게 변하는 영역을 경계로 검출하는 것일 수 있으나, 이에 국한되지 않고, 혈관 영역과 배경 영역 간의 경계를 검출하는 다른 방법일 수도 있다.The blood
일실시예에 따른 프로세서는, 혈관 영역과 배경 영역이 구분된 영상으로부터, 혈관 영역 중 혈관 굵기 및 영상에서의 그레이스케일 레벨에 기초하여 대상 혈관을 추출할 수 있다. 예시적으로, 대상 혈관으로서 심혈관을 추출하고자 하는 경우, 혈관 영상(310)에는 심혈관 뿐만 아니라 심혈관 외의 혈관도 포함될 수 있다. 혈관 조영술을 이용하는 경우, 조형제가 주입된 혈관은 조형제가 주입되지 않은 혈관보다 그레이스케일 레벨이 더 낮을 수 있고, 의료도구(321)가 이동 가능한 혈관은 그렇지 않은 혈관에 비해 혈관 굵기가 더 두꺼울 수 있다. 따라서, 예시적으로 프로세서는 심혈관을 추출하기 위해 혈관 영역 중 혈관 굵기가 임계 굵기보다 두껍고 그레이스케일 레벨이 임계 그레이스케일 레벨보다 낮은 혈관을 심혈관으로 결정할 수 있다. 그러나 이에 국한되지 않고, 프로세서는 추출하고자 하는 혈관 영역을 트레이닝된 기계 학습 모델을 이용하여 구분할 수 있다.The processor according to an embodiment may extract a target blood vessel from an image in which the blood vessel region and the background region are separated, based on a thickness of a blood vessel in the blood vessel region and a grayscale level in the image. For example, when it is desired to extract a cardiovascular system as a target blood vessel, the
일실시예에 따른 프로세서는 혈관 구조 영상(320)을 이용하여 시작 지점으로부터 목적 영역까지의 경로를 검색할 수 있고, 검색된 경로에 기초하여 시작 지점, 목적 영역, 및 중간 목표 영역(322)을 포함하는 가이드 데이터가 포함된 혈관 구조 영상(320)을 제공할 수 있다.The processor according to an embodiment may search for a path from a starting point to a target region using the blood
도 4는 일실시예에 따라 혈관 영상으로부터 혈관 구조 데이터를 생성하는 것을 도시한 도면이다.4 is a diagram illustrating generation of blood vessel structure data from a blood vessel image according to an exemplary embodiment.
일실시예에 따른 프로세서는 혈관 영상(410)으로부터 혈관 영역을 추출할 수 있고, 혈관 영역에서 혈관 분기가 시작되는 위치를 혈관 분지 지점으로 인식할 수 있다. 도 4에 도시된 이미지(420)에서, 인식된 혈관은 실선으로, 혈관 분지 지점으로 식별된 위치 및 혈관의 말단 지점은 노드로 도시된다.The processor according to an exemplary embodiment may extract a blood vessel region from the
프로세서는 혈관 영상(410)로부터 분지 지점 및 분기되는 혈관을 식별할 수 있다. 프로세서는 시작 지점부터 혈관 말단까지 혈관을 따라 스캐닝(scanning)하면서 분지점을 식별할 수 있고, 식별된 분지 지점으로부터 분기되는 혈관을 식별할 수 있다. 분지 지점은 혈관 도입부로부터 말단까지 진행되는 혈관과 해당 분지 지점에서 분기되는 하나 이상의 나머지 혈관들을 포함할 수 있다. 다시 말해, 분지 지점은 혈관이 적어도 2개 이상의 혈관 분지들로 분기되는 혈관 내 지점을 나타낼 수 있다. 프로세서는 혈관을 스캐닝하면서 2개 이상의 혈관 분지들이 형성된 지점을 분지 지점으로 식별하고, 분지점과 다른 분지점을 연결하는 혈관을 식별할 수 있다.The processor may identify a branching point and a branching blood vessel from the
프로세서는 혈관 이미지(420)로부터 식별된 분지 지점 및 분기된 혈관의 연결정보에 기초하여 혈관 구조 데이터(430)를 생성할 수 있다. 일실시예에 따르면, 프로세서는 분지 지점을 지시하는 노드(node) 데이터 및 분기된 혈관을 지시하는 엣지(edge) 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 분기된 혈관은 서로 다른 두개의 분지 지점과 연결되어 있으므로, 프로세서는 하나의 엣지 데이터에 두개의 노드 데이터를 연결시킬 수 있고, 노드 데이터는 분기되는 혈관의 개수에 대응하는 엣지 데이터를 매핑할 수 있다. 분지 지점 및 분기된 혈관의 연결정보는 분지 지점 및 분기된 혈관간의 연결 관계를 나타내는 정보일 수 있다. 연결정보는 노드 데이터에 매핑된 엣지 데이터와 엣지 데이터의 연결 대상이 되는 노드 데이터를 이용하여 생성될 수 있다. 프로세서는 연결정보에 기초하여 혈관을 데이터 구조화할 수 있는데, 예시적으로 프로세서는 혈관 도입부로부터 가장 인접한 분지 지점을 루트 노드(root node)로 하여 노드와 엣지가 연결된 트리 구조를 생성할 수 있다. 루트 노드는 최상위 분지 지점에 해당하는 노드로서, 예를 들어, 시작 지점에 해당하는 노드일 수 있다.The processor may generate the blood
도 5는 일실시예에 따라 혈관 구조 데이터로부터 목적 영역(522)까지의 경로를 생성하고, 혈관 분지 지점에 해당하는 위치를 기본 중간 목표 영역으로 생성하는 것을 도시한 도면이다.FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating generation of a path from blood vessel structure data to a
일실시예에 따른 프로세서는 트리 형식의 그래프로 형성된 혈관 구조 데이터로부터 시작 지점(521)에 대응하는 루트 노드부터 목적 영역(522)에 대응하는 노드 또는 엣지까지의 경로를 검색할 수 있다. 예시적으로 프로세서는 루트 노드부터 목적 영역(522)에 해당하는 노드 또는 엣지까지 거쳐야하는 노드 개수에 기초하여 경로를 검색할 수 있는데, 루트 노드부터 최소한의 노드를 거쳐 특정 노드까지 도달하는 경로를 검색할 수 있다.The processor according to an embodiment may search for a path from a root node corresponding to the
혈관 구조 데이터는 트리 형식의 그래프로 형성되고, 프로세서는 혈관 구조 데이터를 형성하면서 각 노드의 레벨(level)을 획득할 수 있다. 노드의 레벨은 루트 노드부터 몇 번의 노드를 거쳐야 특정 노드에 도달할 수 있는지를 의미하는 것일 수 있다.The blood vessel structure data is formed in a tree-type graph, and the processor may acquire the level of each node while forming the blood vessel structure data. The level of a node may mean how many nodes must pass from the root node to reach a specific node.
일실시예에 따르면, 목적 영역(522)에 대응하는 특정 노드는 트리 그래프의 최하단의 자식 노드(child node)를 갖지 않는 리프 노드(leaf node)일 수 있고, 프로세서는 리프 노드와 루트 노드의 레벨 차이에 기초하여 최단 경로를 계산할 수 있다. 프로세서는 루트 노드로부터 특정 노드까지의 경로 중 거쳐가는 노드의 개수가 리프 노드와 루트 노드의 레벨 차이에 해당하는 경로를 최단 경로로 결정할 수 있다. 다른 일실시예에 따르면, 목적 영역(522)에 대응하는 부분은 노드가 아닌 엣지일 수 있는데, 이 경우 프로세서는 엣지가 연결된 두 노드 중 하나에 도달하기 위한 최단 경로를 검색할 수 있다.According to an embodiment, the specific node corresponding to the
그러나, 시작 지점(521)으로부터 목적 영역(522)까지의 경로를 검색하기 위한 방법은 루트 노드로부터 특정 노드까지의 레벨 차이를 이용하는 것뿐만 아니라, 트리 순회(tree traversal) 방법을 이용하는 것일 수 있다.However, a method for searching for a path from the
프로세서는 시작 지점(521)으로부터 목적 영역(522)까지의 경로를 검색한 후, 경로 상의 노드들에 대응하는 영상(530)에서의 위치를 중간 목표 영역(531)으로 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서는 시작 지점(521), 목적 영역(522), 및 중간 목표 영역(531)에 해당하는 위치에 그래픽 오브젝트로 시작 지점(521), 목적 영역(522), 및 중간 목표 영역(531)을 시각화할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 프로세서는 시작 지점(521), 목적 영역(522), 및 중간 목표 영역(531)을 영상(530)에서 각 지점에 대응하는 위치에 오버랩하여 표시할 수 있다.After searching for a path from the
도 6은 일실시예에 따라 추가 중간 목표 영역을 생성하는 것을 나타낸 흐름도이다.6 is a flowchart illustrating the creation of an additional intermediate target area according to an embodiment.
단계(610)에서, 프로세서는 혈관 영상에서 분지 지점에 대응하는 위치의 중간 목표 영역을 기본 중간 목표 영역으로 설정하고, 인접한 기본 중간 목표 영역들 사이의 거리를 영상 픽셀 단위로 산출할 수 있다.In
단계(620)에서, 프로세서는 영상 픽셀 단위로 산출된 기복 목표 영역들 사이의 거리에 따라 중간 목표 영역을 추가로 설정할지 여부를 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서는 기본 중간 목표 영역들 사이의 거리가 임계 거리보다 크다고 판단한 경우, 단계(630)을 진행할 수 있고, 임계 거리보다 작다고 판단한 경우, 추가 중간 목표 영역을 설정하지 않아도 된다고 판단할 수 있다.In
단계(630)에서, 프로세서가 기본 중간 목표 영역들 사이의 거리가 임계 거리보다 크다고 판단한 경우, 추가 중간 목표 영역을 생성할 수 있다. 가이드 데이터 제공 장치 또는 의료 도구 삽입 장치는 혈관 영상 또는 혈관 구조 영상을 패치 단위로 분할 및 확대함으로써 가이드 패치 영상을 생성할 수 있다. 가이드 패치 영상은 의료 도구 삽입 장치의 동작을 정확히 결정하기 위해 사용될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 가이드 데이터 장치는 분할된 패치 영역의 혈관 영상 내에서 검색된 이동 경로 상에 추가 중간 목표 영역을 생성할 수 있다. 추가 중간 목표 영역은 의료도구 선단부가 통과해야 하는 경로 상에 생성되므로, 의료 도구 삽입 장치는 분할된 패치 영역 내의 추가 중간 목표 영역으로 의료도구 선단부를 이동시키는 것만으로도 최종 목적 영역까지 정확하게 이동시킬 수 있다. 다시 말해, 추가 중간 목표 영역은 전체 경로 중에서 분할된 패치 영역에 나타난 일부 경로 상에서 의료도구 선단부가 이동되어야 하는 정확한 위치에 관한 정보를 제공할 수 있다.In
일실시예에 따르면, 프로세서는 패치 크기에 따라 임계 거리를 결정할 수 있다. 예시적으로, 사각형의 패치로 혈관 영상을 확대하는 경우, 사각형의 한 변의 길이를 임계 거리로 설정할 수 있다. 기본 중간 목표 영역들 사이의 거리가 사각형 패치의 한 변의 길이보다 짧은 경우 확대된 패치 단위의 패치 영상이 적어도 두개의 중간 목표 영역을 포함하므로, 의료 도구 삽입 장치는 해당 패치 영상으로부터, 예를 들어, 기계 학습 모델을 이용하여, 의료도구 선단부를 다음 목표 영역으로 이동시키기 위한 일련의 동작 명령을 산출할 수 있다.According to an embodiment, the processor may determine the threshold distance according to the patch size. For example, when a blood vessel image is enlarged with a square patch, the length of one side of the square may be set as a threshold distance. When the distance between the basic intermediate target areas is shorter than the length of one side of the rectangular patch, since the patch image of the magnified patch unit includes at least two intermediate target areas, the medical tool insertion apparatus uses the patch image, for example, Using the machine learning model, it is possible to calculate a series of motion commands for moving the tip of the medical tool to the next target area.
또한, 일실시예에 따른 프로세서는 혈관 영상을 확대시키기 위한 패치의 크기에 따라 임계 거리를 변경할 수 있다. 예시적으로 패치 크기는 혈관 구조의 복잡도에 따라 실시간으로 변경될 수 있는데, 사각형 패치의 크기는 84 x 84 픽셀 크기를 기본 값으로 하고, 혈관 구조의 복잡도에 따라 커지거나 작아질 수 있다. 사각형 패치의 크기가 84 x 84 픽셀인 경우, 프로세서는 임계 거리를 사각형 패치 한변의 길이인 84 픽셀로 결정할 수 있으나, 시술자의 선택에 따라 50 픽셀로도 결정할 수 있다.Also, the processor according to an embodiment may change the threshold distance according to the size of the patch for enlarging the blood vessel image. For example, the size of the patch may be changed in real time according to the complexity of the vascular structure. The size of the rectangular patch has a default value of 84 x 84 pixels, and may increase or decrease according to the complexity of the vascular structure. When the size of the square patch is 84 x 84 pixels, the processor may determine the threshold distance to be 84 pixels, which is the length of one side of the square patch, but may also be determined to be 50 pixels according to the operator's choice.
도 7은 일실시예에 따라 기본 중간 목표 영역이 생성된 혈관 구조 영상으로부터 추가 중간 목표 영역을 생성하는 것을 도시한 도면이다.7 is a diagram illustrating generation of an additional intermediate target region from an image of a blood vessel structure in which a basic intermediate target region is generated, according to an exemplary embodiment.
일실시예에 따른 프로세서는 기본 중간 목표 영역들(711, 712)이 설정된 영상(710)에서 추가 중간 목표 영역들(721)이 설정된 영상(720)을 생성할 수 있다. 추가 중간 목표 영역들(721)은 기본 중간 목표 영역들(711, 712) 간의 거리에 따라 설정될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 의료 도구 삽입 장치는, 전체 혈관 영역의 영상을 이용하는 대신, 일부 경로를 포함하는 패치 영상을 이용하여 동작 명령을 결정할 수 있다. 패치 영상은, 혈관 영상 또는 혈관 구조 영상으로부터 분할된 패치로서, 기본 중간 목표 영역들(711, 712) 사이의 일부 경로를 포함할 수 있다. 의료 도구 삽입 장치는, 전체 혈관 영역에서 검색된 경로를 기준으로 의료도구 선단부의 현재 위치에 대응하는 패치 영상을 분할할 수 있다. 분할된 패치 영상은 의료도구 선단부와 함께 적어도 하나의 추가 중간 목표 영역(721)을 포함할 수 있다. 추가 중간 목표 영역(721)이 도 6에서 상술한 바와 같이 기본 중간 목표 영역 간의 거리에 따라 설정되기 때문이다. 따라서 의료 도구 삽입 장치는 의료도구 선단부의 현재 위치 및 추가 중간 목표 영역(721)을 이용하여 기계 학습 모델로부터 동작 명령을 산출할 수 있다.The processor according to an embodiment may generate an
기본 중간 목표 영역(711, 712) 사이의 거리는 피시술자의 혈관 구조에 따라 다양할 수 있는데, 기본 중간 목표 영역(711, 712) 사이에 추가 중간 목표 영역(721)을 생성하기로 한 경우, 일실시예에 따른 프로세서는 기본 중간 목표 영역(711, 712) 사이의 거리에 따라 추가 중간 목표 영역(721)의 개수를 결정할 수 있다. 예시적으로, 프로세서는 기본 중간 목표 영역(711, 712) 사이의 거리와 임계 거리의 배수 거리를 비교함으로써 추가 중간 목표 영역(721) 사이의 거리를 결정할 수 있다. 즉, 프로세서는 수학식 1을 만족하는 n(n은 자연수)을 계산하고, n을 기본 중간 목표 영역(711, 712) 사이에 생성되는 추가 중간 목표 영역(721)의 개수로 결정할 수 있다.The distance between the basic
기본 중간 목표 영역(711, 712) 사이에 생성되는 추가 중간 목표 영역(721)의 개수가 결정되면, 프로세서는 추가 중간 목표 영역(721)을 기본 중간 목표 영역(711, 712) 사이에 등간격으로 생성하고, 중간 목표 영역 그래픽 오브젝트를 혈관 영상 또는 혈관 구조 영상에 오버랩함으로써 중간 목표 영역으로 시각화할 수 있다. 일실시예에 따른 프로세서는 추가 중간 목표 영역(721)을 기본 중간 목표 영역(711, 712) 사이에 등간격으로 생성할 수도 있지만, 이에 국한되지 않고, 패치 단위로 확대된 영상에서도 적어도 하나의 중간 목표 영역을 식별할 수 있도록 하는 다른 실시예로도 현출할 수 있다. 추가 중간 목표 영역(721)이 시각화됨으로써 패치 단위로 분할된 각 패치 영상은 중간 목표 영역을 포함할 수 있다. 따라서 의료 도구 삽입 장치는 패치 영상을 이용하여 의료도구 선단부를 새로 생성된 중간 목표 영역으로 이동시키기 위한 동작 명령을 산출할 수 있다.When the number of additional
도 8은 일실시예에 따라 의료 도구 삽입 장치가 시작 지점으로부터 목적 영역까지 이동하는 것을 도시한 도면이다.8 is a diagram illustrating movement of a medical tool insertion device from a starting point to a destination area according to an exemplary embodiment;
일실시예에 따른 가이드 데이터를 제공하는 프로세서는 혈관 영상에서 중간 목표 영역이 생성된 위치에 중간 목표 영역 그래픽 오브젝트(811, 812)를 출력하고, 의료도구 선단부가 중간 목표 영역으로부터 선택된 대상 영역에 도달하였다고 판단한 경우, 혈관 영상에서 대상 영역의 그래픽 오브젝트(811)를 삭제할 수 있다. 프로세서는 혈관 영상으로부터 의료도구의 진행 방향을 따라 의료도구 선단부와 가장 인접한 중간 목표 영역을 대상 영역으로 결정할 수 있다. 의료도구 선단부가 대상 영역에 도달하여 대상 영역의 그래픽 오브젝트를 삭제함으로써, 프로세서는 의료도구 선단부가 목적 영역(821)까지 이동되는 상황을 실시간으로 시각화할 수 있다.The processor providing guide data according to an embodiment outputs the intermediate target area
일실시예에 따른 프로세서는 대상 영역의 그래픽 오브젝트가 삭제되는 것을 인식하는 경우, 의료 도구 삽입 장치의 동작을 평가할 수 있는 지표를 제공함으로써, 의료 도구 삽입 장치가 동작을 스스로 학습하는데 활용할 수 있다. 즉, 인공신경망을 통해 기계 학습 모델을 트레이닝하는데 이용되는 데이터를 제공할 수 있다.When the processor according to an embodiment recognizes that the graphic object of the target area is deleted, the processor provides an index for evaluating the operation of the medical tool insertion apparatus, so that the medical tool insertion apparatus can learn the operation by itself. That is, it is possible to provide data used for training a machine learning model through an artificial neural network.
도 9는 일실시예에 따라 의료도구 가이드 장치의 구성을 대략적으로 나타낸 블록도이다.9 is a block diagram schematically showing the configuration of a medical tool guide device according to an embodiment.
일실시예에 따른 혈관에 삽입된 의료도구(941)를 이동시키기 위한 의료도구 가이드 시스템(900)은 의료 도구 삽입 장치(940) 및 가이드 데이터 제공 장치(910)를 포함할 수 있다.A medical
가이드 데이터 제공 장치(910)는 입출력 인터페이스(913)를 통해 혈관 영상 촬영 장치(950)로부터 혈관 영상 또는 혈관 구조 영상을 입력 받을 수 있고, 의료 도구 삽입 장치(940)로 가이드 영상을 포함한 가이드 데이터를 생성하여 제공할 수 있다. 가이드 데이터 제공 장치(910)의 메모리(912)는 프로세서(911)가 생성한 데이터 및 가이드 영상을 적어도 일시적으로 저장할 수 있다.The guide
가이드 데이터 제공 장치(910)의 프로세서(911)는 혈관 영상에서 의료도구 선단부(941)의 초기 위치를 시작 지점으로 설정하고, 시작 지점으로부터 목적 영역까지의 경로 내에서 중간 목표 영역을 혈관 분지 지점을 기준으로 결정하며, 혈관 영상의 적어도 일부 영역에 대응하고, 중간 목표 영역 중 적어도 일부를 포함하는 가이드 데이터를 제공할 수 있다. 가이드 데이터 제공 장치(910)의 프로세서(911)의 동작에 대해서는 선술하였으므로, 자세한 설명은 생략한다.The
의료 도구 삽입 장치(940)는 가이드 데이터 제공 장치(910)로부터 수신한 가이드 데이터에 기초하여 의료도구(941)를 이동시킬 수 있다. 일실시예에 따르면, 가이드 데이터 제공 장치(910)의 프로세서(911) 또는 의료 도구 삽입 장치(940)의 프로세서는 가이드 영상이 포함된 가이드 데이터에 기초하여 의료도구(941)를 이동시키기 위한 동작 명령을 생성할 수 있다.The medical
참고로, 도 9에서 가이드 데이터 제공 장치(910) 및 의료 도구 삽입 장치(940)는 기능에 따라 구분된 장치일 수 있다. 예를 들어, 가이드 데이터 제공 장치(910) 및 의료 도구 삽입 장치(940)는 하나의 장치 하우징 내부에서 서로 구별되는 기능을 수행하는 장치일 수 있다. 즉, 가이드 데이터 제공 장치(910) 및 의료 도구 삽입 장치(940)의 프로세서는 하나의 프로세서로 서로 다른 기능을 수행할 수 있다. 다만, 이로 한정하는 것은 아니고, 가이드 데이터 제공 장치(910) 및 의료 도구 삽입 장치(940)는 서로 독립된 개별 장치로 구현될 수도 있다.For reference, in FIG. 9 , the guide
프로세서는 생성된 가이드 데이터에 기초하여 의료 도구 삽입 장치(940)를 구동할 수 있다. 프로세서는 중간 목표 영역으로부터 선택된 대상 영역에 의료도구 선단부(941)가 도달하였다고 판단되는 경우, 중간 목표 영역 중 대상 영역과 다른 지점을 다음 대상 영역으로 설정할 수 있다. 다음 대상 영역은 의료도구 선단부(941)의 진행 방향을 따라 상기 대상 영역에 가장 인접한 중간 목표 영역일 수 있다. 프로세서가 대상 영역에 도달한 경우, 계속하여 다음 대상 영역을 설정함으로써 일련의 중간 목표 영역으로 의료도구 선단부(941)를 이동시킬 수 있고, 최종적으로 목적 영역으로 의료도구 선단부(941)를 위치시킬 수 있다.The processor may drive the medical
이상에서 설명된 실시예들은 하드웨어 구성요소, 소프트웨어 구성요소, 및/또는 하드웨어 구성요소 및 소프트웨어 구성요소의 조합으로 구현될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 실시예들에서 설명된 장치, 방법 및 구성요소는, 예를 들어, 프로세서, 콘트롤러, ALU(arithmetic logic unit), 디지털 신호 프로세서(digital signal processor), 마이크로컴퓨터, FPGA(field programmable gate array), PLU(programmable logic unit), 마이크로프로세서, 또는 명령(instruction)을 실행하고 응답할 수 있는 다른 어떠한 장치와 같이, 하나 이상의 범용 컴퓨터 또는 특수 목적 컴퓨터를 이용하여 구현될 수 있다. 처리 장치는 운영 체제(OS) 및 상기 운영 체제 상에서 수행되는 하나 이상의 소프트웨어 애플리케이션을 수행할 수 있다. 또한, 처리 장치는 소프트웨어의 실행에 응답하여, 데이터를 접근, 저장, 조작, 처리 및 생성할 수도 있다. 이해의 편의를 위하여, 처리 장치는 하나가 사용되는 것으로 설명된 경우도 있지만, 해당 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자는, 처리 장치가 복수 개의 처리 요소(processing element) 및/또는 복수 유형의 처리 요소를 포함할 수 있음을 알 수 있다. 예를 들어, 처리 장치는 복수 개의 프로세서 또는 하나의 프로세서 및 하나의 콘트롤러를 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 병렬 프로세서(parallel processor)와 같은, 다른 처리 구성(processing configuration)도 가능하다.The embodiments described above may be implemented by a hardware component, a software component, and/or a combination of a hardware component and a software component. For example, the apparatus, methods and components described in the embodiments may include, for example, a processor, a controller, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU), a digital signal processor, a microcomputer, a field programmable gate (FPGA) array), a programmable logic unit (PLU), a microprocessor, or any other device capable of executing and responding to instructions. The processing device may execute an operating system (OS) and one or more software applications running on the operating system. The processing device may also access, store, manipulate, process, and generate data in response to execution of the software. For convenience of understanding, although one processing device is sometimes described as being used, one of ordinary skill in the art will recognize that the processing device includes a plurality of processing elements and/or a plurality of types of processing elements. It can be seen that can include For example, the processing device may include a plurality of processors or one processor and one controller. Other processing configurations are also possible, such as parallel processors.
소프트웨어는 컴퓨터 프로그램(computer program), 코드(code), 명령(instruction), 또는 이들 중 하나 이상의 조합을 포함할 수 있으며, 원하는 대로 동작하도록 처리 장치를 구성하거나 독립적으로 또는 결합적으로(collectively) 처리 장치를 명령할 수 있다. 소프트웨어 및/또는 데이터는, 처리 장치에 의하여 해석되거나 처리 장치에 명령 또는 데이터를 제공하기 위하여, 어떤 유형의 기계, 구성요소(component), 물리적 장치, 가상 장치(virtual equipment), 컴퓨터 저장 매체 또는 장치, 또는 전송되는 신호 파(signal wave)에 영구적으로, 또는 일시적으로 구체화(embody)될 수 있다. 소프트웨어는 네트워크로 연결된 컴퓨터 시스템 상에 분산되어서, 분산된 방법으로 저장되거나 실행될 수도 있다. 소프트웨어 및 데이터는 하나 이상의 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록 매체에 저장될 수 있다.The software may comprise a computer program, code, instructions, or a combination of one or more thereof, which configures a processing device to operate as desired or is independently or collectively processed You can command the device. The software and/or data may be any kind of machine, component, physical device, virtual equipment, computer storage medium or device, to be interpreted by or to provide instructions or data to the processing device. , or may be permanently or temporarily embody in a transmitted signal wave. The software may be distributed over networked computer systems, and stored or executed in a distributed manner. Software and data may be stored in one or more computer-readable recording media.
실시예에 따른 방법은 다양한 컴퓨터 수단을 통하여 수행될 수 있는 프로그램 명령 형태로 구현되어 컴퓨터 판독 가능 매체에 기록될 수 있다. 상기 컴퓨터 판독 가능 매체는 프로그램 명령, 데이터 파일, 데이터 구조 등을 단독으로 또는 조합하여 포함할 수 있다. 상기 매체에 기록되는 프로그램 명령은 실시예를 위하여 특별히 설계되고 구성된 것들이거나 컴퓨터 소프트웨어 당업자에게 공지되어 사용 가능한 것일 수도 있다. 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록 매체의 예에는 하드 디스크, 플로피 디스크 및 자기 테이프와 같은 자기 매체(magnetic media), CD-ROM, DVD와 같은 광기록 매체(optical media), 플롭티컬 디스크(floptical disk)와 같은 자기-광 매체(magneto-optical media), 및 롬(ROM), 램(RAM), 플래시 메모리 등과 같은 프로그램 명령을 저장하고 수행하도록 특별히 구성된 하드웨어 장치가 포함된다. 프로그램 명령의 예에는 컴파일러에 의해 만들어지는 것과 같은 기계어 코드뿐만 아니라 인터프리터 등을 사용해서 컴퓨터에 의해서 실행될 수 있는 고급 언어 코드를 포함한다. 상기된 하드웨어 장치는 실시예의 동작을 수행하기 위해 하나 이상의 소프트웨어 모듈로서 작동하도록 구성될 수 있으며, 그 역도 마찬가지이다.The method according to the embodiment may be implemented in the form of program instructions that can be executed through various computer means and recorded in a computer-readable medium. The computer-readable medium may include program instructions, data files, data structures, etc. alone or in combination. The program instructions recorded on the medium may be specially designed and configured for the embodiment, or may be known and available to those skilled in the art of computer software. Examples of the computer-readable recording medium include magnetic media such as hard disks, floppy disks and magnetic tapes, optical media such as CD-ROMs and DVDs, and magnetic such as floppy disks. - includes magneto-optical media, and hardware devices specially configured to store and execute program instructions, such as ROM, RAM, flash memory, and the like. Examples of program instructions include not only machine language codes such as those generated by a compiler, but also high-level language codes that can be executed by a computer using an interpreter or the like. The hardware devices described above may be configured to operate as one or more software modules to perform the operations of the embodiments, and vice versa.
이상과 같이 실시예들이 비록 한정된 도면에 의해 설명되었으나, 해당 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 상기를 기초로 다양한 기술적 수정 및 변형을 적용할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 설명된 기술들이 설명된 방법과 다른 순서로 수행되거나, 및/또는 설명된 시스템, 구조, 장치, 회로 등의 구성요소들이 설명된 방법과 다른 형태로 결합 또는 조합되거나, 다른 구성요소 또는 균등물에 의하여 대치되거나 치환되더라도 적절한 결과가 달성될 수 있다.As described above, although the embodiments have been described with reference to the limited drawings, those skilled in the art may apply various technical modifications and variations based on the above. For example, the described techniques are performed in a different order than the described method, and/or the described components of the system, structure, apparatus, circuit, etc. are combined or combined in a different form than the described method, or other components Or substituted or substituted by equivalents may achieve an appropriate result.
Claims (25)
Translated fromKoreanApplications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR10-2020-0015857 | 2020-02-10 | ||
| KR1020200015857AKR102356341B1 (en) | 2020-02-10 | 2020-02-10 | Method and apparatus to provide guide data for device to insert medical tool into vascular |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2021162355A1true WO2021162355A1 (en) | 2021-08-19 |
Family
ID=77291600
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/KR2021/001537CeasedWO2021162355A1 (en) | 2020-02-10 | 2021-02-05 | Method and apparatus for providing guide data for intravascular medical tool insertion device |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102356341B1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2021162355A1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115147357A (en)* | 2022-05-31 | 2022-10-04 | 深圳睿心智能医疗科技有限公司 | Automatic navigation method, device, equipment and medium for vascular intervention guide wire |
| CN116864098A (en)* | 2023-09-01 | 2023-10-10 | 泰州市榕兴医疗用品股份有限公司 | A method and system for obtaining force information of medical devices based on location information |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102473037B1 (en)* | 2022-04-18 | 2022-12-02 | 주식회사 메디픽셀 | Method and system for automatically controlling navigation of surgical tool based on reinforcement learning |
| WO2024014906A1 (en)* | 2022-07-13 | 2024-01-18 | 주식회사 로엔서지컬 | System and method for providing guidance for calculus removal |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101294858B1 (en)* | 2012-04-26 | 2013-08-09 | 가톨릭대학교 산학협력단 | Method for liver segment division using vascular structure information of portal vein and apparatus thereof |
| JP2014064824A (en)* | 2012-09-27 | 2014-04-17 | Fujifilm Corp | Shortest route searching device, method and program of tubular structure |
| KR20150128405A (en)* | 2014-05-09 | 2015-11-18 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method, apparatus and system for providing medical image |
| KR20160121735A (en)* | 2015-04-10 | 2016-10-20 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Apparatus and method for recommending operation route |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7486811B2 (en)* | 1996-09-16 | 2009-02-03 | The Research Foundation Of State University Of New York | System and method for performing a three-dimensional virtual examination of objects, such as internal organs |
| KR100822738B1 (en) | 2006-12-06 | 2008-04-17 | 고려대학교 산학협력단 | Route planning method of mobile robot |
| US20090156895A1 (en)* | 2007-01-31 | 2009-06-18 | The Penn State Research Foundation | Precise endoscopic planning and visualization |
- 2020
- 2020-02-10KRKR1020200015857Apatent/KR102356341B1/enactiveActive
- 2021
- 2021-02-05WOPCT/KR2021/001537patent/WO2021162355A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101294858B1 (en)* | 2012-04-26 | 2013-08-09 | 가톨릭대학교 산학협력단 | Method for liver segment division using vascular structure information of portal vein and apparatus thereof |
| JP2014064824A (en)* | 2012-09-27 | 2014-04-17 | Fujifilm Corp | Shortest route searching device, method and program of tubular structure |
| KR20150128405A (en)* | 2014-05-09 | 2015-11-18 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method, apparatus and system for providing medical image |
| KR20160121735A (en)* | 2015-04-10 | 2016-10-20 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Apparatus and method for recommending operation route |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| JIHOON KWEON, HWI KWON, JINWOO PARK, KYUNGHWAN KIM, HYUNGKYU KIM, YOUNGEON KIM, KYOSEOK SONG, JAE-HYUNG ROH, YOUNGJIN MOON, JAESOO: "Reinforcement learning for guidewire navigation in coronary phantom", TCT ABSTRACTS POSTERS 2019; SAN FRANCISCO, CA, USA; SEPTEMBER 25 - 29, 2019, 29 September 2019 (2019-09-29) - 29 September 2019 (2019-09-29), US, pages 1 - 1, XP009529735* |
| MEDIPIXEL: "[TCT 2019] Reinforcement Learning for Guidewire Navigation in Coronary Phantom", YOUTUBE, 2 October 2019 (2019-10-02), pages 1, XP054982174, Retrieved from the Internet <URL:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1imlCMfr4mI>* |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115147357A (en)* | 2022-05-31 | 2022-10-04 | 深圳睿心智能医疗科技有限公司 | Automatic navigation method, device, equipment and medium for vascular intervention guide wire |
| CN116864098A (en)* | 2023-09-01 | 2023-10-10 | 泰州市榕兴医疗用品股份有限公司 | A method and system for obtaining force information of medical devices based on location information |
| CN116864098B (en)* | 2023-09-01 | 2023-11-14 | 泰州市榕兴医疗用品股份有限公司 | Medical instrument stress information acquisition method and system based on position information |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20210101640A (en) | 2021-08-19 |
| KR102356341B1 (en) | 2022-01-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2021162355A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing guide data for intravascular medical tool insertion device | |
| WO2021162354A1 (en) | Method and device for extracting major vessel region on basis of vessel image | |
| WO2022050557A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for training operation determination model for medical instrument control device | |
| WO2021246612A1 (en) | Method and device for automatically processing blood vessel image | |
| WO2023277283A1 (en) | Blood vessel segmentation-based blood vessel image processing method and device | |
| KR20190100011A (en) | Method and apparatus for providing surgical information using surgical video | |
| WO2022114522A1 (en) | Blood vessel image extracting method and apparatus using plurality of prediction results | |
| WO2021246648A1 (en) | Method and device for processing blood vessel image on basis of user input | |
| KR102305965B1 (en) | Device and method for detecting guidewire | |
| WO2021145490A1 (en) | Method for determining hysteresis of surgical robot, method for compensating for same, and endoscopic surgery device | |
| WO2023191380A1 (en) | Lesion determination method and device | |
| WO2021071288A1 (en) | Fracture diagnosis model training method and device | |
| WO2021006472A1 (en) | Multiple bone density displaying method for establishing implant procedure plan, and image processing device therefor | |
| WO2021206517A1 (en) | Intraoperative vascular navigation method and system | |
| US11896323B2 (en) | System, method, and computer-accessible medium for automatically tracking and/or identifying at least one portion of an anatomical structure during a medical procedure | |
| WO2022145841A1 (en) | Method for interpreting lesion and apparatus therefor | |
| CN112069805A (en) | Text annotation method, device, equipment and storage medium combining RPA and AI | |
| WO2022108387A1 (en) | Method and device for generating clinical record data | |
| WO2022139068A1 (en) | Deep learning-based lung disease diagnosis assistance system and deep learning-based lung disease diagnosis assistance method | |
| WO2021162181A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for training machine learning model for determining operation of medical tool control device | |
| Deng et al. | Automatic endoscopic navigation based on attention-based network for nasotracheal Intubation | |
| CN118521599A (en) | Laparoscopic surgery image segmentation method and system based on spatial feature enhancement | |
| KR102418439B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for dividing blood vessel region and medical instrument tip region from vessel imaging | |
| KR102641492B1 (en) | Polyp detection method, device and computer program using endoscopy image | |
| Xu et al. | Study on the Path Planning Based on A* Algorithm for Vascular Intervention Robots |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | Ref document number:21753943 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 | |
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase | Ref country code:DE | |
| 32PN | Ep: public notification in the ep bulletin as address of the adressee cannot be established | Free format text:NOTING OF LOSS OF RIGHTS PURSUANT TO RULE 112(1) EPC (EPO FORM 1205A DATED 15.12.2023) | |
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase | Ref document number:21753943 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 |