WO2020248156A1 - Pd-l1-targeting binding agent and use thereof - Google Patents
Pd-l1-targeting binding agent and use thereofDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2020248156A1 WO2020248156A1PCT/CN2019/090878CN2019090878WWO2020248156A1WO 2020248156 A1WO2020248156 A1WO 2020248156A1CN 2019090878 WCN2019090878 WCN 2019090878WWO 2020248156 A1WO2020248156 A1WO 2020248156A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- amino acid
- seq
- acid sequence
- cancer
- residue substitutions
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/395—Antibodies; Immunoglobulins; Immune serum, e.g. antilymphocytic serum
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P31/00—Antiinfectives, i.e. antibiotics, antiseptics, chemotherapeutics
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K16/00—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies
- C07K16/18—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans
- C07K16/28—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N15/00—Mutation or genetic engineering; DNA or RNA concerning genetic engineering, vectors, e.g. plasmids, or their isolation, preparation or purification; Use of hosts therefor
- C12N15/09—Recombinant DNA-technology
- C12N15/63—Introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors; Vectors; Use of hosts therefor; Regulation of expression
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N5/00—Undifferentiated human, animal or plant cells, e.g. cell lines; Tissues; Cultivation or maintenance thereof; Culture media therefor
- C12N5/10—Cells modified by introduction of foreign genetic material
Definitions
- the present inventionbelongs to the field of biomedicine, and specifically relates to targeted binding agents for PD-L1, nucleic acids encoding them and uses thereof.
- the present inventionrelates to monoclonal antibodies against PD-L1, nucleic acids encoding them, and uses of these antibodies.
- the inventionalso relates to cell lines expressing the targeted binding agent or antibody.
- the present inventionalso relates to the use of the targeted binding agent for diagnosis and treatment of diseases related to the activity and/or expression of PD-L1.
- the adaptive immune responseinvolves the activation, selection and clonal proliferation of two main types of lymphocytes, T cells and B cells. After encountering an antigen, T cells proliferate and differentiate into antigen-specific effector cells, while B cells proliferate and differentiate into antibody secreting cells.
- T cell activationis a multi-step process that requires some signal transduction events between T cells and antigen presenting cells (APC). For T cell activation to occur, two types of signals must be delivered to resting T cells. The first type is mediated by antigen-specific T cell receptors (TCR) and confers specificity for immune responses. The second type of co-stimulation regulates the size of the response and is delivered via a co-receptor on T cells.
- TCRantigen-specific T cell receptors
- the main costimulatory signalis delivered by binding to the ligand B7-1 or B7-2 on APC to activate the CD28 receptor on T cells.
- the binding of the same B7-1 or B7-2 ligand to the inhibitory CTLA-4 receptorresults in a weakening of the T cell response. Therefore, the CTLA-4 signal opposes CD28-mediated costimulation.
- CD28 costimulationsurpasses CTLA-4 inhibition.
- the temporary regulation of the expression of CD28 and CTLA-4maintains the balance between the activation signal and the inhibitory signal and ensures the formation of an effective immune response, while preventing the formation of autoimmunity.
- PD-L1also known as B7-H1
- B7-H1is a type I transmembrane protein with a size of about 53kD.
- PD-L1is expressed on a variety of immune cell types, including activated T cells, anergic/depleted T cells, natural B cells and activated B cells, as well as on myeloid dendritic cells (DC), monocytes and mast cells. It is also expressed on non-immune cells, including pancreatic islets, liver Kupffer Cells, vascular endothelial cells, and epithelial cells, such as tracheal epithelial cells and renal tubular epithelial cells, where its expression during inflammatory episodes is Enhanced.
- DCmyeloid dendritic cells
- PD-L1 expression levelsare up-regulated in a variety of tumors, including but not limited to breast cancer, colorectal cancer, lung cancer, kidney cancer, gastric cancer, bladder cancer, liver cancer, and pancreatic cancer, as well as black Prime tumor.
- PD-L1is a member of the B7 family of proteins, which contains two extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig) domains, an N-terminal V-type domain, followed by a C-type domain.
- the 30 amino acid long intracellular domaindoes not contain obvious signal transduction motifs, but contains possible sites for protein kinase C phosphorylation.
- Mouse PD-L1has 69% amino acid homology with human PD-L1 and shares a conserved structure.
- PD-L1binds to two alternative ligands, one of which is PD-1, a 50-55kD type I transmembrane receptor, which was originally identified in T cells undergoing activation-induced apoptosis.
- PD-1is expressed in activated T cells, B cells, monocytes and other cells of the immune system, and binds to PD-L1 and PD-L2.
- the secondis the B7 family member B7-1, which is expressed on activated T cells, B cells, monocytes and antigen presenting cells.
- PD-1is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, which contains a single Ig V-like domain in its extracellular domain.
- the cytoplasmic domain of PD-1contains two tyrosines, and the tyrosine closest to the membrane is located in the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-Based Inhibitory Motif, ITIM).
- ITIMimmunoreceptoreceptor Tyrosine-Based Inhibitory Motif
- Human and murine PD-1 proteinsshare about 60% amino acid homology, of which 4 N-glycosylation sites and amino acid residues that define the Ig-V domain are conserved.
- the ITIM in the cytoplasmic region and the ITIM-like motif around the tyrosine at the carboxyl terminal of PD-L1are also conserved between humans and mice.
- PD-L1 expressed in tumor cellshelps the detection and elimination of tumor escape from the immune system.
- PD-L1plays a role in this aspect through some selectable mechanisms, including driving the failure and anergy of tumors infiltrating T lymphocytes, stimulating the secretion of immunosuppressive cytokines into the tumor microenvironment, and stimulating inhibitory regulation T cells act and prevent tumor cells expressing PD-L1 from being lysed by tumor cell-specific cytotoxic T cells.
- the present inventionrelates to a targeted binding agent that specifically binds to PD-L1 and inhibits the biological activity of PD-L1.
- the present inventionrelates to a targeted binding agent that specifically binds to PD-L1 and thereby inhibits the activity of PD-L1.
- the present inventionrelates to a targeted binding agent that specifically binds to PD-L1 and thereby inhibits the binding of PD-L1 to PD-1.
- the present inventionrelates to a targeted binding agent that blocks PD-L1 induced T cell suppression and thereby enhances anti-tumor immunity.
- the present inventionalso relates to a targeted binding agent that can further stimulate one or more of the following activities, including T cell proliferation in mixed lymphocyte reaction, IFN- ⁇ Or IL-2 secretion.
- Embodiments of the present inventionrelate to targeted binding agents that specifically bind to PD-L1 and inhibit the biological activity of PD-L1.
- the targeted binding agentinhibits at least 5%, at least 10%, at least 15%, at least 20%, at least 25% of the biological activity of PD-L1 compared with the absence of the targeted binding agent. , At least 30%, at least 35%, at least 40%, at least 45%, at least 50%, at least 55%, at least 60%, at least 65%, at least 70%, at least 75%, at least 80%, at least 85%, at least 90% or at least 95%.
- Embodiments of the present inventionrelate to targeted binding agents that specifically bind to PD-L1 and thereby inhibit the activity of PD-L1.
- the targeted binding agentinhibits PD-L1 activity by at least 5%, at least 10%, at least 15%, at least 20%, at least 25%, At least 30%, at least 35%, at least 40%, at least 45%, at least 50%, at least 55%, at least 60%, at least 65%, at least 70%, at least 75%, at least 80%, at least 85%, at least 90 % Or at least 95%.
- Embodiments of the present inventionrelate to targeted binding agents that specifically bind to PD-L1 and thereby inhibit the binding to PD-1.
- the targeted binding agentinhibits the binding of PD-L1/PD-1 receptor ligand by at least 5%, at least 10%, at least 15%, at least 20% compared to when the targeted binding agent is not present. %, at least 25%, at least 30%, at least 35%, at least 40%, at least 45%, at least 50%, at least 55%, at least 60%, at least 65%, at least 70%, at least 75%, at least 80%, At least 85%, at least 90%, or at least 95%.
- Another embodiment of the present inventionrelates to a targeted binding agent that specifically binds to B7-H1 and thereby enhances anti-tumor immunity.
- the targeted binding agentenhances anti-tumor immunity by at least 5%, at least 10%, at least 15%, at least 20%, at least 25% compared to what would happen in the absence of the targeted binding agent , At least 30%, at least 35%, at least 40%, at least 45%, at least 50%, at least 55%, at least 60%, at least 65%, at least 70%, at least 75%, at least 80%, at least 85%, at least 90% or at least 95%.
- Another embodiment of the present inventionrelates to a targeted binding agent that specifically binds to B7-H1 and thereby inhibits cell proliferation.
- the targeted binding agentinhibits cell proliferation by at least 5%, at least 10%, at least 15%, at least 20%, at least 25%, at least 30%, at least 35%, at least 40%, at least 45%, at least 50%, at least 55%, at least 60%, at least 65%, at least 70%, at least 75%, at least 80%, at least 85%, at least 90% Or at least 95%.
- an antibody of the present inventionis less than or equal to 100nM, EC 50nM 1nM or 50. Further, in another embodiment, the antibodies of the invention having from about 1nM to about 100nM of up to 50 EC; EC or about 1nM to about 50nM up to 50; or from about 1nM to about 20nM up to 50 EC; or of about 50nM up to about 100nM EC 50; or from about 70nM to about 100nM until the EC 50.
- Further embodiments of the present inventionrelates specifically binds to PD-L1 and EC 50 of less than or equal to 100nM inhibiting targeted binding agent inhibits proliferation of PD-L1-mediated T cell.
- the antibody of the inventionhas an EC50 of less than or equal to 100 nM, for example, 90, 80, 70, 60, 50 , 40, 30, 20, or 10 nM.
- the antibodies of the inventionhaving about 100nM 10nM up to about 50 EC; EC or from about 50nM to about 10nM up to 50; or from about 20nM to about 10nM up to 50 EC; or of about 50nM up to about 100nM EC 50; or from about 70nM to about 100nM until the EC 50; or from about 80nM to about 100nM until the EC 50.
- Targeted binding agentsalso inhibit tumor cell adhesion, motility, invasion and cell metastasis, and targeted binding agents are useful for reducing tumor growth. Mechanisms that can achieve this may include, but are not limited to, inhibition of PD-L1 activity.
- the targeted binding agentis an antibody. In one embodiment of the invention, the targeted binding agent is a monoclonal antibody. In one embodiment of the invention, the targeted binding agent is a humanized antibody or fragment thereof.
- the monoclonal antibody hereinmay refer to the anti-PD-L1 antibody or the antibody of the present invention.
- Antibodies, monoclonal antibodies and human monoclonal antibodiesinclude IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 isotype antibodies.
- the targeted binding agentis a humanized monoclonal antibody of the IgG1 isotype.
- the IgG1 isotypeimproves the antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) of the antibody.
- the IgG1 isotypehas high stability.
- the targeted binding agenthas a desired therapeutic property selected from one or more of the following: high affinity for PD-L1, inhibiting PD-L1 activity in vitro or in vivo Ability, the ability to inhibit PD-L1-mediated tumor cell survival and the ability to inhibit PD-L1-mediated tumor-reactive T cell suppression, which can further reduce tumor cell proliferation, motility, invasion, metastasis and tumor growth.
- the present inventionincludes antibodies that specifically bind to PD-L1 with very high affinity.
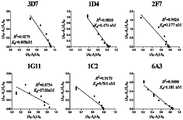
- the targeted binding agentbinds PD-L1 with a binding affinity (Kd) of less than 5 nM. In other embodiments, the targeted binding agent binds with a Kd of less than 4 nM, 3 nM, 2 nM, or 1 nM.
- the antibody of the present inventionis used at about 5 nM to about 1 nM; or about 5 nM to about 2 nM; or about 5 nM to about 3 nM; or about 5 nM to about 4 nM; or about 3 nM to about 1 nM; or about A Kd of 2nM to about 1nM binds PD-L1.
- the targeted binding agentbinds PD-L1 with a Kd of less than 950pM, 900pM, 800pM, 700pM, 600pM, 500pM, 400pM, 300pM, 200pM, or 100pM.
- the antibody of the present inventionis at about 900pM to about 100pM; or about 900pM to about 200pM; or about 900pM to about 300pM; or about 900pM to about 400pM; or about 900pM to about 500pM; or about 900pM to about 600pM; or about 900pM to about 700pM; or about 200pM to about 100pM; or about 300pM to about 200pM; or about 400pM to about 300pM Kd binds PD-L1.
- the targeted binding agentbinds PD-L1 with a Kd of less than 90pM, 80pM, 70pM, 60pM, 55pM, or 50pM. In some other embodiments, the targeted binding agent binds PD-L1 with a Kd of less than 60 pM. In some other embodiments, the targeted binding agent binds PD-L1 with a Kd of less than 55 pM.
- the antibody of the present inventionis used at about 100 pM to about 50 pM; or about 100 pM to about 70 pM; or about 100 pM to about 80 pM; or about 100 pM to about 90 pM; or about 70 pM to about 50 pM; or about 60pM to about 50pM; or about 55pM to about 50pM Kd binds PD-L1.
- Kdcan be evaluated using the methods described herein or well known to those of ordinary skill in the art (for example, the BIAcore method) (Biacore International AB, Uppsala, Sweden).
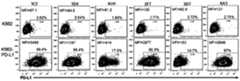
- the targeted binding agent or antibodycomprises a sequence comprising any one of the heavy chain sequences of antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7, or 6A3.
- Light chain promiscuityis very well established in the art. Therefore, a targeted binding agent containing any one of the sequences of the heavy chain sequence of the antibody 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7 or 6A3, another antibody disclosed herein, or The antibody may also comprise any one of 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7, or 6A3 shown in Table 2, the light chain sequence (VL) of other antibodies disclosed herein.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodycomprises a sequence comprising any of the heavy chain sequences of antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7 or 6A3 and further comprising antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, The corresponding light chain sequence of 2F7, 3D7 or 6A3.
- the antibodyis a fully human monoclonal antibody.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodycomprises a sequence comprising any one of the light chain sequences shown in Table 2. In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprises a sequence comprising any one of the light chain sequences of antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7, or 6A3.
- Another embodimentis a targeted binding agent or antibody that specifically binds to PD-L1, and includes a sequence that includes one of the CDR2 sequences and one of the CDR3 sequences shown in Table 2.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodyfurther comprises a sequence comprising the CDR3 sequence shown in Table 1.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodyfurther comprises a sequence comprising the CDR2 sequence and CDR3 sequence as shown in Table 1 and/or Table 2.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodyfurther comprises a sequence comprising: CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences as shown in Table 1 and/or Table 2.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodymay comprise a sequence comprising the CDR1 of any one of monoclonal antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7, or 6A3 as shown in Table 1. Either CDR2 or CDR3.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodymay comprise a sequence comprising CDR1, CDR2 of any one of monoclonal antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7 or 6A3 as shown in Table 2.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodymay comprise a sequence comprising CDR1, CDR2 of any one of monoclonal antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7 or 6A3 as shown in Table 1.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodymay comprise a sequence comprising CDR1, CDR2 of any one of monoclonal antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7 or 6A3 as shown in Table 2.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodymay comprise a sequence comprising CDR1, CDR2 of any one
- the targeted binding agent or antibodycomprises a sequence comprising the CDR1, CDR2, and CDR3 sequences of the heavy chain of monoclonal antibody 1C2 as shown in Table 1 and the single sequence as shown in Table 2.
- the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the light chain of antibody 1C2were cloned.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodycomprises a sequence comprising the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the heavy chain of monoclonal antibody 1D4 as shown in Table 1 and the single sequence as shown in Table 2.
- the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the light chain of antibody 1D4were cloned.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodycomprises a sequence comprising the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the heavy chain of monoclonal antibody 1G11 as shown in Table 1 and the single sequence as shown in Table 2.
- the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the light chain of antibody 1G11were cloned.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodycomprises a sequence comprising the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the heavy chain of monoclonal antibody 2F7 as shown in Table 1 and the single sequence as shown in Table 2.
- the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the light chain of antibody 2F7were cloned.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodycomprises a sequence comprising the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the heavy chain of the monoclonal antibody 3D7 as shown in Table 1 and the single sequence as shown in Table 2.
- the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the light chain of the antibody 3D7were cloned.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodycomprises a sequence comprising the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the heavy chain of monoclonal antibody 6A3 as shown in Table 1 and the single sequence as shown in Table 2.
- the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the light chain of antibody 6A3were cloned.
- the antibodyis a humanized antibody.
- the targeted binding agent or antibody of the present inventioncomprises the CDR3 sequence as shown in Table 1 or Table 2; or any of the CDR1, CDR2 or CDR3 sequences as shown in Table 1 or Table 2.
- the antibodyis a humanized antibody.
- the targeted binding agent or antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereofcomprises a heavy chain variable region having at least 90% homology with the amino acid of SEQ ID NO: 1, and comprises a heavy chain variable region with SEQ ID NO:
- the amino acid sequence of 2has a light chain variable region with at least 90% homology.
- the targeted binding agent or antibody, or antigen binding portion thereofcomprises a heavy chain variable region having at least 90% homology with the amino acid of SEQ ID NO: 3, and comprises a heavy chain variable region with SEQ ID NO:
- the amino acid sequence of 4has a light chain variable region with at least 90% homology.
- the targeted binding agent or antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereofcomprises a heavy chain variable region having at least 90% homology with the amino acid of SEQ ID NO: 5, and comprises a heavy chain variable region with SEQ ID NO: 5
- the amino acid sequence of 6has a light chain variable region with at least 90% homology.
- the targeted binding agent or antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereofcomprises a heavy chain variable region having at least 90% homology with the amino acid of SEQ ID NO: 7, and comprises the same as SEQ ID NO:
- the amino acid sequence of 8has a light chain variable region with at least 90% homology.
- the targeted binding agent or antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereofcomprises a heavy chain variable region having at least 90% homology with the amino acid of SEQ ID NO: 9 and comprises the same as SEQ ID NO:
- the amino acid sequence of 10has a light chain variable region with at least 90% homology.
- the targeted binding agent or antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereofcomprises a heavy chain variable region having at least 90% homology with the amino acid of SEQ ID NO: 11, and comprises a heavy chain variable region with SEQ ID NO:
- the amino acid sequence of 12has a light chain variable region with at least 90% homology.
- the targeted binding agent or antibodycomprises a variant or derivative of the CDR disclosed herein, spanning the framework region of the light chain sequence or heavy chain sequence disclosed herein and the CDR or the framework of the antibody disclosed herein Regions and CDRs (especially from FR1 to FR4 or CDR1 to CDR3).
- Variantsinclude a targeted binding agent or antibody, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprising a sequence having the continuous sequence of CDR1, CDR2 or CDR3 as shown in Table 1 or Table 2, the light disclosed herein Chain sequence or heavy chain sequence, or any of the monoclonal antibodies disclosed herein, up to 20, 16, 10, 9 or less, for example, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 amino acid additions, substitutions, deletions and/or insertions.
- Variantsinclude a targeted binding agent or antibody, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprising a sequence having the continuous sequence of CDR1, CDR2 or CDR3 as shown in Table 1 or Table 2, the light disclosed herein Chain sequence or heavy chain sequence, or 1, 2, 3 amino acid additions, substitutions, deletions and/or insertions in any of the monoclonal antibodies disclosed herein.
- Variantsinclude a targeted binding agent or antibody, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprising a sequence that is consistent with the continuous sequence of CDR1, CDR2 or CDR3 as shown in Table 1 or Table 2, and the light disclosed herein.
- Chain sequence or heavy chain sequenceor any of the monoclonal antibodies disclosed herein, have at least about 60%, 70%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, 98%, or about 99% amino acid homology Sex.
- the percent homology of two amino acid sequencescan be determined by any method known to those skilled in the art, including but not limited to, paired protein alignment.
- the variantincludes an alteration in the CDR sequence or light chain sequence or heavy chain sequence disclosed herein, the alteration is naturally occurring or through the use of recombinant DNA technology or mutation technology to engineer the natural sequence in vitro To introduce.
- Naturally occurring variantsinclude those produced in vivo in the corresponding germline nucleotide sequence during the production of antibodies against foreign antigens.
- the targeted binding agentcomprises:
- CDR1having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 13, 16, 19, 22, 25, or 28,
- CDR2having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 14, 17, 20, 23, 26, or 29, or having SEQ ID NO: CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in 15, 18, 21, 24, 27 or 30, or one or more of their variants;
- CDR1having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 31, 34, 37, 40, 43, or 46
- CDR2having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 32, 35, 38, 41, 44, or 47, or having SEQ ID NO: CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in NO: 33, 36, 39, 42, 45 or 48, or one or more of their variants;
- the sequence of the variantincludes up to 20, 16, 10, 9 or less, for example, an increase of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 amino acids , Substitution, deletion and/or insertion, or the sequence of the variant and any of the sequences have at least 60%, 70%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, 98% Or 99% homology.
- the targeted binding agentis a PD-L1 antibody or an antigen-binding fragment thereof comprising a heavy chain variable region and a light chain variable region, wherein:
- the heavy chain variable regioncomprises CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3, wherein:
- CDR1has the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 13, 16, 19, 22, 25, or 28 or contains 1, 2, or relative to SEQ ID NO: 13, 16, 19, 22, 25 or 28 Amino acid sequence with 3 amino acid residue substitutions;
- CDR2has the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 14, 17, 20, 23, 26 or 29 or contains 1, 2, or relative to SEQ ID NO: 14, 17, 20, 23, 26 or 29 Amino acid sequence with 3 amino acid residue substitutions;
- CDR3has the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 15, 18, 21, 24, 27 or 30 or contains 1, 2 or 1 relative to SEQ ID NO: 15, 18, 21, 24, 27 or 30 Amino acid sequence with 3 amino acid residue substitutions;
- the light chain variable regioncomprises CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3, wherein:
- CDR1has the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 31, 34, 37, 40, 43 or 46 or contains 1, 2 or 1 relative to SEQ ID NO: 31, 34, 37, 40, 43 or 46 Amino acid sequence with 3 amino acid residue substitutions;
- CDR2has the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 32, 35, 38, 41, 44 or 47 or contains 1, 2 or 1 relative to SEQ ID NO: 32, 35, 38, 41, 44 or 47 Amino acid sequence with 3 amino acid residue substitutions;
- CDR3has the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 33, 36, 39, 42, 45 or 48 or contains 1, 2 or 1 relative to SEQ ID NO: 33, 36, 39, 42, 45 or 48 Amino acid sequence with 3 amino acid residue substitutions.
- the variantincludes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
- VH sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO:1 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO:1;
- VL sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 2 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 2.
- the variantincludes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
- VH sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 3 or an amino acid sequence containing 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 3;
- VL sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 4 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 4.
- the variantincludes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
- VH sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 5 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 5;
- VL sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 6 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 6.
- the variantincludes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
- VH sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 7 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 7;
- VL sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 8 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 8.
- the variantincludes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
- VH sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 9 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 9;
- VL sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 10 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 10.
- the variantincludes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
- VH sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 11 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 11;
- VL sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 12 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 12.
- the variantincludes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
- VH CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 13 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 13;
- VH CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 14 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 14;
- VH CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 15 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 15;
- VL CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 31 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 31;
- VL CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 32 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 32;
- VL CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 33 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 33.
- the variantincludes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
- VH CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 16 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 16;
- VH CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 17 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 17;
- VH CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 18 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 18;
- VL CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 34 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 34;
- VL CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 35 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 35;
- VL CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 36 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 36.
- the variantincludes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
- VH CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 19 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 19;
- VH CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 20 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 20;
- VH CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 21 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 21;
- VL CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 37 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 37;
- VL CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 38 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 38;
- VL CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 39 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 39.
- the variantincludes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
- VH CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 22 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 22;
- VH CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 23 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 23;
- VH CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 24 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 24;
- VL CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 40 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 40;
- VL CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 41 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 41;
- VL CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 42 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 42.
- the variantincludes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
- VH CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 25 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 25;
- VH CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 26 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 26;
- VH CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 27 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 27;
- VL CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 43 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 43;
- VL CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 44 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 44;
- VL CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 45 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 45.
- the variantincludes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
- VH CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 28 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 28;
- VH CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 29 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 29;
- VH CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 30 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 30;
- VL CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 46 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 46;
- VL CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 47 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 47;
- VL CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 48 or an amino acid sequence containing 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 48.
- the antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereofcomprises the heavy chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 13, the heavy chain CDR2 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 14 and the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 15
- the heavy chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 31the light chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 32, and the light chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 33.
- the antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereofcomprises: the heavy chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 16, the heavy chain CDR2 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 17, the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 18
- the antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereofcomprises: heavy chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 19, heavy chain CDR2 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 20, and amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 21
- the antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereofcomprises: heavy chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 22, heavy chain CDR2 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 23, and amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 24
- the antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereofcomprises: the heavy chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 25, the heavy chain CDR2 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 26, and the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 27
- the antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereofcomprises: heavy chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 28, heavy chain CDR2 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 29, and amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 30
- the derivativemay be a heterogeneous antibody, that is, an antibody in which two or more antibodies are linked together.
- Derivativesinclude antibodies that have been chemically modified. Examples include covalent bonding of one or more polymers, such as water-soluble polymers, N-linked or O-linked carbohydrates, sugars, phosphates, and/or other such molecules. Derivatives are modified in such a way that the type or location of the bound molecule is different from the naturally occurring antibody or the starting antibody. Derivatives also include the deletion of one or more chemical groups naturally occurring in the antibody.
- an isolated nucleic acid encoding the targeted binding agent, vectors and host cells containing such nucleic acid, and recombinant technology for producing the targeted binding agentare provided.
- the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1is shown in SEQ ID NO: 71; preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 72;
- the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3is shown in SEQ ID NO: 73; preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 4 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 74;
- the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 5is shown in SEQ ID NO: 75; preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 6 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 76;
- the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 7is shown in SEQ ID NO: 77; preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown
- a vectoris provided, which is suitable for expressing a nucleic acid encoding any of the aforementioned anti-PD-L1 antibodies.
- the vectorfurther comprises a host cell suitable for expressing the nucleic acid.
- the host cellis a eukaryotic cell or a prokaryotic cell.
- the eukaryotic cellis a mammalian cell, such as Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO).
- a method for preparing an anti-PD-L1 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereofincludes culturing a nucleic acid containing a form suitable for expression under conditions suitable for the production of such antibody or fragment.
- the nucleic acidencodes any of the aforementioned anti-PD-L1 antibodies or antigen-binding fragments, and the antibodies or fragments are recovered.
- the nucleic acid encoding itis isolated and inserted into a replicable vector for further cloning (DNA amplification) or expression.
- the DNA encoding the monoclonal antibodycan be easily separated and sequenced using conventional procedures (for example, using oligonucleotide probes that can specifically bind to the genes encoding the heavy and light chains of the antibody).
- Many carriersare available.
- the choice of vectordepends in part on the host cell to be used. Generally, the preferred host cell is of prokaryotic or eukaryotic (usually mammalian) origin.
- a chimeric antigen receptor of a PD-L1 antibodywhich comprises a PD-L1 antibody variable region sequence.
- the chimeric antigen receptor of the PD-L1 antibodyfurther comprises one or more elements selected from the group consisting of: signal peptide, linker sequence, transmembrane domain, internal domain and costimulatory Structure domain.
- the chimeric antigen receptor of the PD-L1 antibodycomprises the CD8 antigen signal peptide, the light chain variable region of the PD-L1 antibody, the heavy chain variable region of the PD-L1 antibody, the CD28 element, the 4- 1BBL element and CD3 ⁇ element.
- the coding nucleic acid sequence of the CD8 antigen signal peptideis shown in SEQ ID NO: 51, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 52.
- the coding nucleic acid sequence of the CD28 elementis shown in SEQ ID NO:53, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:54.
- the coding nucleic acid sequence of the 4-1BBL elementis shown in SEQ ID NO: 55, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 56.
- the coding nucleic acid sequence of the CD3 ⁇ elementis shown in SEQ ID NO: 57, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 58.
- the nucleic acid sequence encoding the chimeric antigen receptoris selected from the sequence shown in 59, 61, 63, 65, 67 or 69, and the corresponding amino acid sequence is selected from 60, 62, 64, 66, 68 or 70 shown in the sequence.
- a nucleic acid encoding a chimeric antigen receptor of a PD-L1 antibodyis provided.
- a recombinant vector, expression cassette, recombinant virus or recombinant cell containing the nucleic acidis provided.
- a CAR constructcomprising a nucleic acid encoding a chimeric antigen receptor.
- a T cellis provided, which is transduced with the CAR construct.
- a method for preparing PD-L1 CAR-T cellsincludes the following steps:
- the vectorcan be a eukaryotic expression vector or a lentiviral vector, preferably a lentiviral vector, Preferably, the vector is a lentiviral vector pHAGE-EF1 ⁇ -MCS-ZsGreen;
- step (b)Transfect or infect host T cells with the vector constructed in step (a) to produce CAR-T cells with CAR elements that can recognize human PD-L1.
- a method for preparing PD-L1 CAR-T cellsincludes the following steps:
- the vectorcan be a eukaryotic expression vector or a lentiviral vector, preferably a lentiviral vector;
- the vectoris a lentiviral vector pHAGE-EF1 ⁇ -MCS-ZsGreen;
- step (b)Transfect the vector constructed in step (a) into a packaging cell line to produce lentiviral particles with CAR elements that can recognize human PD-L1;
- the CAR elementcomprises the following sequence:
- VH sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO:1 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO:1;
- VL sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 2 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 2;
- the CAR elementcomprises the following sequence:
- VH sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 3 or an amino acid sequence containing 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 3;
- VL sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 4 or an amino acid sequence containing 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 4;
- the CAR elementcomprises the following sequence:
- VH sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 5 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 5;
- VL sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 6 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 6;
- the CAR elementcomprises the following sequence:
- VH sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 7 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 7;
- VL sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 8 or an amino acid sequence containing 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 8;
- the CAR elementcomprises the following sequence:
- VH sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 9 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 9;
- VL sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 10 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 10;
- the CAR elementcomprises the following sequence:
- VH sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 11 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 11;
- VL sequencehaving the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 12 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 12;
- the CAR elementcomprises the following sequence:
- VH CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 13 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 13;
- VH CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 14 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 14;
- VH CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 15 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 15;
- VL CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 31 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 31;
- VL CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 32 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 32;
- VL CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 33 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 33.
- the CAR elementcomprises the following sequence:
- VH CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 16 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 16;
- VH CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 17 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 17;
- VH CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 18 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 18;
- VL CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 34 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 34;
- VL CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 35 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 35;
- VL CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 36 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 36.
- the CAR elementcomprises the following sequence:
- VH CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 19 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 19;
- VH CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 20 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 20;
- VH CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 21 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 21;
- VL CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 37 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 37;
- VL CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 38 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 38;
- VL CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 39 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 39.
- the CAR elementcomprises the following sequence:
- VH CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 22 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 22;
- VH CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 23 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 23;
- VH CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 24 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 24;
- VL CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 40 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 40;
- VL CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 41 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 41;
- VL CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 42 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 42.
- the CAR elementcomprises the following sequence:
- VH CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 25 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 25;
- VH CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 26 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 26;
- VH CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 27 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 27;
- VL CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 43 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 43;
- VL CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 44 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 44;
- VL CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 45 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 45.
- the CAR elementcomprises the following sequence:
- VH CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 28 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 28;
- VH CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 29 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 29;
- VH CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 30 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 30;
- VL CDR1having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 46 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 46;
- VL CDR2having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 47 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 47;
- VL CDR3having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 48 or an amino acid sequence containing 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 48.
- CDR regionor “CDR” is intended to mean the hypervariable regions of the heavy and light chains of an antibody that confer antigen binding specificity to the antibody.
- CDRcan be defined according to the Kabat system (Kabat, E.A., etc. (1991) Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, 5th edition. US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Service, NIH, Washington) and more recent versions.
- Antibodiesusually contain 3 heavy chain CDRs and 3 light chain CDRs.
- the term CDRis used herein to indicate that, depending on the situation, one of these regions or some or even all of these regions contains most of the amino acid residues responsible for binding by the affinity of the antibody to the antigen or epitope recognized by the antibody.
- the third CDR (HCDR3) of the heavy chainhas a larger size of variability (larger diversity is basically due to the gene arrangement mechanism that makes it produced). Although the longest known size is 26, it can be as short as 2 amino acids.
- the length of the CDRcan also vary according to the adaptable length of the specific basic framework. Functionally, HCDR3 plays an important role in determining the specificity of antibodies (Segal et al., PNAS, 71: 4298-4302, 1974, Amit, Science, 233: 747-753, 1986, Chothia, J. Mol.
- CDR groupincludes CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3. Therefore, the HCDR group refers to HCDR1, HCDR2, and HCDR3, and the LCDR group refers to LCDR1, LCDR2, and LCDR3.
- VH and VL regions and CDR variants of the present inventionincluding those whose amino acid sequences are listed herein and which can be applied to PD-L1 targeted binding agents and antibodies, can be required by sequence change or mutation methods and screening. The characteristics of antigen targeting are obtained.
- required propertiesinclude, but are not limited to: increased binding affinity to antigen relative to known antibodies specific to antigen; neutralization of increased antigen activity relative to known antibodies specific to antigen (if the activity is already Known); specific ability to compete with known antibodies or ligands for antigen at a specific molar ratio; the ability to immunoprecipitate ligand-receptor complexes; the ability to bind to specific epitopes; linear epitopes, For example, peptide sequences identified by peptide binding scanning, for example, peptides screened in linear and/or defined conformations; conformational epitopes, formed by non-contiguous residues; ability to modulate new biological activities of B7-H1 or downstream molecules ; The ability to bind and/or neutralize B7-H1 and/or any other required properties.
- the properties of antibodiescan be derived from empirical and theoretical models of antibody sequence, functional structure, and three-dimensional structure (for example, analysis of possible contact residues or calculated physicochemical properties, and these properties can be considered individually and in combination.
- the antibody antigen binding site composed of VH domain and VL domainis usually formed by 6 polypeptide loops: 3 from the light chain variable domain (VL) and three from the heavy chain variable domain (VH).
- VLlight chain variable domain
- VHheavy chain variable domain
- the binding site loophas a small amount of main One of the chain conformations: canonical structure. It has been shown that the canonical structure formed in a specific loop is determined by its size and the presence of certain residues at key positions in both the loop and the framework region.
- sequence-structure relationshipcan be used to predict those residues in antibodies of known sequences (except for the unknown three-dimensional structure), which are important in maintaining the three-dimensional structure of its CDR loops and thereby maintaining binding specificity. These predictions can be supported by comparing the predictions with the output from the leading optimal experiment.
- any freely available or commercial software packagesuch as WAM
- WAMany freely available or commercial software package
- a protein visualization and analysis software packagesuch as Insight II (Accelrys, Inc.) or Deep View, can then be used to evaluate the possible substitutions at each position in the CDR. This information can then be used to perform substitutions that may have minimal or beneficial effects on activity or impart other desired properties.
- polypeptide fragmentrefers to a polypeptide having amino-terminal and/or carboxy-terminal deletions, but where the remaining amino acid sequence is the same as the corresponding position in the deduced naturally occurring sequence, for example, from a full-length cDNA sequence. Fragments are generally at least 5, 6, 8, or 10 amino acids in length, preferably at least 14 amino acids in length, more preferably at least 20 amino acids in length, usually at least 50 amino acids in length, and even more preferably at least in length 70 amino acids.
- analogrefers to a polypeptide consisting of a fragment of at least 25 amino acids that has sufficient identity with a portion of the deduced amino acid sequence, and which has at least one of the following properties: (1) In appropriate Under binding conditions, specific binding to PD-L1, (2) the ability to block appropriate PD-L1 protein binding, or (3) the ability to inhibit PD-L1 activity.
- polypeptide analogscontain conservative amino acid substitutions (or additions or deletions) with respect to naturally occurring sequences.
- the analogis generally at least 20 amino acids in length, preferably at least 50 amino acids or longer in length, and can generally be as long as a full-length naturally occurring polypeptide.
- Peptide analogsare often used in the pharmaceutical industry as non-peptide drugs with properties similar to template peptides. These types of non-peptide compounds are referred to as "peptidomimetics" or "peptoids". Fauchere, J. Adv. Drug Res. 15:29 (1986); Veber and Freidinger TINS page 392 (1985); and Evans et al. J. Med. Chem. 30:1229 (1987), which are incorporated herein by reference. Computer-based molecular modeling is often used to develop such compounds. Peptidomimetics that are structurally similar to therapeutically useful peptides can be used to produce equivalent therapeutic or preventive effects.
- the systematic substitution of one or more amino acids of the consensus sequence with the same type of D-amino acidfor example, D-lysine instead of L-lysine
- D-lysineinstead of L-lysine
- antibodyused herein can be a single chain antibody, oligoclonal antibody, polyclonal antibody, monoclonal antibody (including full-length monoclonal antibody), camelized, alone or in combination with other amino acid sequences provided by known techniques.
- Antibodiescan be derived from any species.
- the antibodycomprises a polypeptide or a group of polypeptides, which consists of at least one binding domain formed from the folding of a polypeptide chain with a three-dimensional binding space, wherein the inner surface shape and charge distribution are complementary to the characteristics of the antigen's epitope .
- Antibodiesgenerally have a tetrameric form, consisting of two identical pairs of polypeptide chains, each pair having a "light” chain and a "heavy” chain. The variable region of each light/heavy chain forms an antibody binding site. Natural antibodies are usually heterotetrameric glycoproteins with a molecular weight of about 150Kd, composed of two identical light chains and two identical heavy chains.
- Each light chainis connected to the heavy chain by a covalent disulfide bond, and the number of disulfide bonds between the heavy chains of different immunoglobulin isotypes is different.
- Each heavy and light chainalso has regularly spaced intrachain disulfide bonds.
- Each heavy chainhas a variable region (VH) at one end, followed by a constant region.
- Each light chainhas a variable region (VL) at one end and a constant region at the other end; the constant region of the light chain is opposite to the first constant region of the heavy chain, and the variable region of the light chain is the same as the variable region of the heavy chain. District relative.
- the light chainis classified as lambda chain or kappa chain based on the amino acid sequence of the light chain constant region.
- the variable region of the kappa light chainmay also be referred to herein as VK.
- variable regioncan also be used to describe the variable region of a heavy or light chain. Specific amino acid residues form the boundary between the variable region of the light chain and the variable region of the heavy chain.
- the variable region of each light/heavy chain pairforms an antibody binding site.
- the antibodycan be derived from any mammal, including, but not limited to, humans, monkeys, pigs, horses, rabbits, dogs, cats, mice and the like.
- antibodyincludes binding fragments of the antibodies of the present invention, and exemplary fragments include single-chain Fv (scFv), single-chain antibodies, single-domain antibodies, domain antibodies, Fv fragments, Fab fragments, F(ab)' fragments , F(ab′)2 fragments, antibody fragments showing the required biological activity, disulfide bond stabilized variable regions (dsFv), dimeric variable regions (diabodies), anti-idiotypic antibodies, intracellular antibodies , Linear antibodies, single-chain antibody molecules and multispecific antibodies formed from antibody fragments and any of the above epitope binding fragments.
- antibodiesinclude immunoglobulin molecules and immunologically active fragments of immunoglobulin molecules, that is, molecules containing antigen binding sites.
- Immunoglobulin moleculescan be of any type (e.g., IgG, IgE, IgM, IgD, IgA, and IgY), of any type (e.g., IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4, IgA1, and IgA2) or subclass.
- Enzyme (papain) digestion of the antibodyproduces two identical antigen-binding fragments, also called “Fab” fragments, and "Fc” fragments, which have no antigen-binding activity but have the ability to crystallize.
- Enzyme (pepsin) digestion of the antibodyproduces F(ab')2 fragments, where the two arms of the antibody molecule remain connected and contain two antigen binding sites. F(ab')2 fragments have the ability to cross-link antigens.
- Fvrefers to the smallest fragment of an antibody that retains both the antigen recognition site and the antigen binding site. This region is composed of a dimer of a heavy chain variable region and a light chain variable region that are tightly non-covalently bonded or covalently bonded.
- the 3 CDRs of each variable regioninteract to define the antigen binding site on the surface of the VH-VL dimer.
- the 6 CDRsconfer antigen binding specificity to the antibody.
- a single variable regionor only half of the 3 CDRs specific to the antigen still has the ability to recognize and bind to the antigen.
- Fabrefers to a fragment of an antibody, which, in addition to the heavy chain variable region and the light chain variable region, also includes the light chain constant domain and the CH1 region of the heavy chain.
- dAbrefers to a fragment of an antibody that is the smallest functional binding unit of a human antibody.
- DAbis a single domain antibody and contains the VH of the antibody heavy chain or the VL of the antibody light chain.
- Each dAbcontains 3 of the 6 naturally occurring CDRs (Ward et al., Binding activities of a repertoire of single immunoglobulin variable domains secreted from Escherichia coli. Nature 341, 544-546 (1989); Holt et al., Domain antibodies: protein for therapy , Trends Biotechnol. 21, 484-49 (2003)).
- Their molecular weightranges from 11kDa to 15kDa, they are 4 times smaller than the antigen-binding fragment (Fab) 2 and half the molecular size of the single-chain Fv (scFv).
- camel originrefers to antibody molecules composed of heavy chain dimers, which lack light chains but have a large number of antigen-binding components (Hamers-Casterman C, Atarhouch T, Muyldermans S, Robinson G, Hamers C, Songa EB, Bendahman N, Hamers R (1993) Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature363:446-448).
- diabodiesrefers to small antibody fragments with two antigen binding sites, the fragments of which include the heavy chain variable region connected to the light chain variable region in the same polypeptide chain. By using a sufficiently short linker to pair two domains on the same chain, the domains are paired with the complementary domains of another chain and two antigen binding sites are constructed. Diabodies are more fully described in, for example, EP404,097; WO93/11161; and Hollinger et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90: 6444-6448 (1993).
- binding fragmentsare (Ward, ES, et al., (1989) Nature 341, 544-546) Fab fragments composed of VL, VH, CL and CH1 domains; (McCafferty et al., (1990) Nature, 348, 552-554) by VH (Holt et al., (2003) Trends in Biotechnology 21,484-490) Fv fragment composed of the VL and VH domains of a single antibody; dAb fragment (Ward, ES etc., Nature 341,544-546 ( 1989), McCafferty et al., (1990) Nature, 348,552-554, Holt et al., (2003) Trends in Biotechnology 21, 484-490), which consist of VH or VL domains; isolated CDR regions; F(ab')2 fragments, A bivalent fragment containing two linked Fab fragments; a single-chain Fv molecule (sc
- Fv, scFv or diabody moleculescan be stabilized by the incorporation of a disulfide bridge connecting the VH and VL domains (Reiter, Y. et al., Nature Biotech, 14, 1239-1245, 1996).
- Minibodies containing scFvs that bind to the CH3 domaincan also be produced (Hu, S. et al., (1996) Cancer Res., 56, 3055-3061).
- binding fragmentsare Fab', which differ from Fab fragments due to the addition of several residues to the carboxy terminus of the CH1 domain of the heavy chain, the residues including one or more cysteines from the hinge region of an antibody , And Fab'-SH, which are Fab' fragments in which the cysteine residues of the constant domain carry free thiol groups.
- variablerefers to the fact that certain parts of antibody variable regions differ greatly in sequence between antibodies and are responsible for the binding specificity of each specific antibody to its specific antigen. However, the variability is not evenly distributed in the variable domains of antibodies. It is concentrated in fragments called complementarity determining regions (CDR) in both the light chain variable domain and the heavy chain variable domain. The highly conserved part of the variable region is called the framework region (FR).
- CDRcomplementarity determining regions
- FRframework region
- the variable regions of the heavy and light chains of natural antibodieseach contain 4 FR regions, which adopt a ⁇ -sheet configuration to a large extent and are connected by 3 CDRs, which form a connected ⁇ -sheet structure and in some In this case, a loop that forms part of the ⁇ -sheet structure.
- the CDRs in each chainare closely combined with the CDRs from other chains through the FR region, which helps to form the antigen binding site of the antibody (see, Kabat et al., Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, 5th edition, Public Health Service , National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD (1991)).
- the constant regiongenerally does not directly participate in antigen binding, but can affect antigen binding affinity and can exhibit various effector functions, such as ADCC, CDC, and/or antibody involvement in apoptosis.
- hypervariable regionrefers to the amino acid residues of an antibody related to its binding to an antigen.
- the hypervariable regionincludes amino acid residues of the "complementarity determining region” or "CDR" (e.g., residues 24-34 (L1), residues 50-56 (L2), and 89 of the light chain variable region). -97 residues (L3) and 31-35 residues (H1), 50-65 residues (H2) and 95-102 residues (H3) of the heavy chain variable region (Kabat et al. , Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, 5th edition.
- CDRcomplementarity determining region
- Targeted binding proteinrefers to agents that preferentially bind to a target site, such as antibodies or binding fragments thereof.
- the targeted binding agentis specific for only one target site. In other embodiments, the targeted binding agent is specific for more than one target site.
- the targeted binding agentmay be a monoclonal antibody and the target site may be an epitope.
- the targeted binding agentmay comprise at least one antigen binding domain (e.g., CDR) of an antibody, wherein the domain is fused to or contained in a heterologous protein scaffold, for example, a non-antibody protein scaffold.
- CDRantigen binding domain
- binding fragmentof the antibody is produced by recombinant DNA technology, or by enzymatic or chemical cleavage of the intact antibody. Binding fragments include Fab, Fab', F(ab')2, Fv, dAb, and single chain antibodies. Antibodies other than "bispecific” or “bifunctional” antibodies are understood to have the same each binding site. When excess antibody reduces the amount of receptor bound to the counter receptor by at least about 20%, 40%, 60%, or 80%, and more usually more than about 85% (as measured in an in vitro competitive binding assay ), the antibody basically inhibits the binding of the receptor to the counter receptor.
- epitopeincludes any protein determinant capable of specifically binding to an immunoglobulin or T cell receptor.
- Epitope determinantsusually consist of surface groups (such as amino acids or sugar side chains) of chemically active molecules, and may (but not always) have specific three-dimensional structural characteristics, as well as specific charge characteristics.
- the dissociation constantis ⁇ 1 ⁇ M, preferably ⁇ 100 ⁇ M and most preferably ⁇ 10 ⁇ M, the antibody is said to specifically bind to the antigen.
- the term "medicament”represents a chemical compound, a mixture of chemical compounds, a biological macromolecule, or an extract made from biological materials.
- the "active" or “active” of the PD-L1 polypeptiderefers to the part of the PD-L1 polypeptide that has the biological activity or immunological activity of the natural PD-L1 polypeptide.
- "Biological” as used hereinrefers to the biological function caused by the activity of the native PD-L1 polypeptide. Preferred biological activities of PD-L1 include, for example, cell proliferation, cell adhesion and invasion induced by PD-L1.
- mammalrefers to any animal that is considered a mammal. Preferably, the mammal is a human.
- animalincludes animals that are considered mammals.
- the animalis a human.
- patientincludes humans and test animals.
- mAbrefers to a monoclonal antibody.
- liposomerefers to a small vesicle that can be used to deliver a drug that can contain the PD-L1 polypeptide of the present invention or an antibody to such a PD-L1 polypeptide to a mammal.
- Labelrefers to the addition of a detectable moiety to a polypeptide, such as a radioactive label, a fluorescent label, an enzyme label, a chemiluminescent label, or a biotin-based.
- the radioisotope or radionuclidemay include 3 H, 14 C, 15 N, 35 S, 90 Y, 99 Tc, 111 In, 125 I, 131 I, the fluorescent label may include rhodamine, rare earth phosphor or FITC, and the enzyme Labels may include horseradish peroxidase, ⁇ -galactosidase, luciferase, alkaline phosphatase.
- Additional markersinclude, by way of example and not limitation: enzymes such as glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, ⁇ -D-galactosidase, glucose oxidase, glucoamylase, carbonic anhydrase, acetylcholinesterase, Lysozyme, malate dehydrogenase and peroxidase; dyes; additional fluorescent labels or fluorescent agents include, for example, fluorescein and its derivatives, fluorochromes, GFP (green fluorescent protein), dansyl, umbelliferone , Phycoerythrin, phycocyanin, allophycocyanin, o-phthalaldehyde and fluorescein; fluorophores such as cryptate rare earth compounds and chelates, such as europium, etc.
- enzymessuch as glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, ⁇ -D-galactosidase, glucose oxidase, glucoamylase, carbonic anhydrase
- chemiluminescence labeling or chemical Luminescent substancessuch as isoluminol, luminol and dioxane; sensitizers; coenzymes; enzyme substrates; particles, such as latex particles or carbon particles; metal sols; microcrystals; liposomes; cells, etc.
- toxin moietiessuch as those selected from Pseudomonas exotoxin (PE or its cytotoxicity) Fragment or mutant), diphtheria toxin or its cytotoxic fragment or mutant, botulinum toxin A, B, C, D, E or F, ricin or its cytotoxic fragment such as ricin A, acacia toxin Or its cytotoxic fragment, saporin or its cytotoxic fragment, pokeweed antiviral toxin or its cytotoxic fragment, and bryodin1 or its cytotoxic fragment.
- Pseudomonas exotoxinPE or its cytotoxicity
- diphtheria toxin or its cytotoxic fragment or mutantdiphtheria toxin or its cytotoxic fragment or mutant
- botulinum toxin A, B, C, D, E or Fbotulinum toxin A, B, C, D, E or F
- ricin or its cytotoxic fragmentsuch as ricin A, acacia
- pharmaceutical agent or drugrefers to a chemical compound or composition capable of inducing a desired therapeutic effect when properly administered to a patient.
- Other chemical terms used hereinare used according to conventional usage in the field, as exemplified by The McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Chemical Terms (Parker, S., ed., McGraw-Hill, San Francisco (1985)).
- substantially puremeans that the subject substance is the main substance present (that is, its moles in the composition are more abundant than any other individual substance), and preferably the substantially pure composition
- a fractionis a composition in which the subject substance accounts for at least 50% by mole of all macromolecular substances present.
- a substantially pure compositionwill account for greater than about 80% of all macromolecular species present in the composition, more preferably greater than about 85%, 90%, 95%, and 99%.
- the subject substanceis purified to be substantially homogeneous (contaminant substances cannot be detected in the composition by conventional detection methods), wherein the composition consists essentially of a single macromolecular substance.
- ADCCantibody-dependent cytotoxicity
- non-specific cytotoxic cellssuch as natural killer (NK) cells, monocytes, neutrophils
- FcRFc receptors
- the main cells that mediate ADCCare NK cells, which only express FcyRIII, while monocytes express FcyRI, FcyRII and FcyRIII.
- FcR expression on hematopoietic cellsis summarized in Table 9 on page 464 of Ravetch and Kinet, Annu. Rev. Immunol 9:457-92 (1991).
- an in vitro ADCC assaycan be performed, such as described in US Patent No. 5,500,362 or No. 5,821,337. Effector cells used in such assays include peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and NK cells.
- PBMCperipheral blood mononuclear cells
- NK cellsAlternatively, or in addition, the ADCC activity of the target molecule can be assessed in vivo, for example, in an animal model such as that disclosed in Clynes et al. PNAS (USA) 95:652-656 (1988).
- C1qthe first component of complement
- C1qis a large, ⁇ 410kD complex glycoprotein (Cooper, N.R.1985.Adv.Immunol.37:151) that exists in human serum at a concentration of 70 ⁇ g/mL.
- C1r, C1s, and C1q together with two serine proteasesform the first component of complement—complex C1.
- At least two of the N-terminal spherical heads of C1qmust bind to the Fc of Igs for C1 activation to initiate the complement cascade (Cooper, N.R. 1985. Adv. Immunol. 37: 151).
- antibody half-lifemeans the pharmacokinetic properties of the antibody, which is a measure of the average survival time of the antibody molecule after administration.
- Antibody half-lifecan be expressed as the time required to eliminate 50% of the known amount of immunoglobulin from the patient's body or its specific compartments or other tissues, for example, as measured in serum or plasma, ie circulating half life.
- the half-lifemay vary according to the immunoglobulin or the type of immunoglobulin. Generally, an increase in the half-life of an antibody results in an increase in the circulating mean residence time (MRT) of the administered antibody.
- MRTmean residence time
- isotyperefers to the classification of antibody heavy chain constant regions or light chain constant regions.
- the constant region of an antibodydoes not participate in binding antigen, but exhibits a variety of effector functions.
- a given human antibody or immunoglobulincan be assigned to one of the five main immunoglobulin classes: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM.
- Some of these classescan be further divided into subclasses (isotypes), for example, IgG1 ( ⁇ 1), IgG2 ( ⁇ 2), IgG3 ( ⁇ 3) and IgG4 ( ⁇ 4), and IgA1 and IgA2.
- the heavy chain constant regions corresponding to different types of immunoglobulinsare called ⁇ , ⁇ , ⁇ , ⁇ , and ⁇ , respectively.
- the structures and three-dimensional configurations of different kinds of immunoglobulinsare well known.
- human immunoglobulin classesonly human IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4 and IgM are known to activate complement. It is known that human IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4 bind to Fc ⁇ receptors, which mediate multiple effector functions including ADCC.
- the light chain constant regioncan be classified into two main categories, kappa and lambda.
- therapeutic antibodiesrequire complement-dependent cytotoxicity.
- complement-dependent cytotoxicityThere are many antibody isotypes with complement-dependent cytotoxicity, including but not limited to the following: murine IgM, murine IgG2a, murine IgG2b, murine IgG3, human IgM, human IgA, human IgG1, and human IgG3.
- therapeutic antibodiesneed to bind to Fc receptors on effector cells and participate in antibody-dependent cytotoxicity.
- antibody isotypes with antibody-dependent cytotoxic antibodiesincluding but not limited to the following: murine IgG2a, murine IgG2b, murine IgG3, human IgG1, and human IgG3.
- the antibody produced initiallydoes not have to have the said isotype, and the antibody can be isotype switched using conventional techniques well known in the art.
- the technologiesinclude direct recombination technology (see U.S. Patent No. 4,816,397) and the use of cell-cell fusion technology (see U.S. Patent Nos. 5,916,771 and 6,207,418).
- the “whole blood assay”uses unfractionated blood as a source of natural effectors. Blood contains complement in plasma, as well as FcR-expressing cellular effectors, such as polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) and monocytes (MNC). In this way, the whole blood assay allows the simultaneous evaluation of the synergy of the effector mechanisms of ADCC and CDC in vitro.
- PMNpolymorphonuclear leukocytes
- MNCmonocytes
- a “therapeutically effective” amountis an amount that provides some improvement or benefit to the subject.
- a “therapeutically effective” amountis an amount that provides a certain alleviation, relief, and/or reduction of at least one clinical symptom.
- the clinical symptoms associated with the disease that can be treated by the method of the present inventionare well known to those skilled in the art. Moreover, those skilled in the art will understand that the therapeutic effect need not be thorough or curative, as long as it provides certain benefits to the subject.
- Exemplary cancersinclude bladder tumors, breast tumors, prostate tumors, basal cell carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, bladder cancer, bone cancer, brain and CNS cancer (e.g. glioma), cervical cancer, choriocarcinoma, colon and rectal cancer , Connective tissue cancer, cancer of the digestive system; endometrial cancer, esophageal cancer; eye cancer, head and neck cancer, gastric cancer; intraepithelial tumor; kidney cancer; laryngeal cancer; leukemia; liver cancer; lung cancer (such as small cell and non-small cell lung cancer) ); Lymphoma, including Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma; melanoma; myeloma, neuroblastoma, oral cancer (for example, lips, tongue, mouth and pharynx); ovarian cancer; Pancreatic cancer, retinoblastoma; rhabdomyosarcoma; rectal cancer, kidney cancer,
- Exemplary chronic infectionsinclude HIV infection, hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection.
- Each tetrameris composed of two pairs of identical polypeptide chains, each pair having a "light" chain (about 25kD) and a "heavy” chain (about 50-70kD).
- the amino terminal portion of each chainincludes a variable region of about 100 to 110 or more amino acids, which is mainly responsible for antigen recognition.
- the carboxy terminal part of each chaindefines the constant region that is mainly responsible for effector functions.
- Light chainsare classified into kappa light chains and lambda light chains.
- Heavy chainsare classified as mu, delta, gamma, alpha or epsilon, and define the isotype of the antibody as IgM, IgD, IgA, and IgE, respectively.
- variable and constant regionsare connected by a "J" region of about 12 or more amino acids, where the heavy chain also includes a "D” region of about 10 or more amino acids.
- JJoint Immunology Ch. 7
- Ddouble-chain region
- a complete antibodyhas two binding sites. Except in bifunctional or bispecific antibodies, the two binding sites are the same.
- the chainsall show the same general structure: relatively conservative framework regions (FR) connected by 3 hypervariable regions (also called CDRs).
- the CDRs from the two chains of each pairare aligned by the framework regions to enable binding to a specific epitope.
- FR1, CDR1, FR2, CDR2, FR3, CDR3, and FR4 domainsFrom N-terminus to C-terminus, both the light chain and the heavy chain contain FR1, CDR1, FR2, CDR2, FR3, CDR3, and FR4 domains.
- amino acidsare assigned to each domain Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md. (1987 and 1991)), or Chothia & Lesk J. Mol. Biol. 196: 901-917 (1987) ; Chothia et al., Nature 342:878-883 (1989).
- Bispecific or bifunctional antibodiesare artificial hybrid antibodies with two different heavy/light chain pairs and two different binding sites.
- Bispecific antibodiescan be produced by various methods including fusion of hybridomas or linking of Fab' fragments. See Songsivilai & Lachmann Clin. Exp. Immunol. 79: 315-321 (1990), Kostelny et al. J. Immunol. 148: 1547-1553 (1992).
- Bispecific antibodiesdo not exist in the form of fragments with a single binding site (for example, Fab, Fab' and Fv).
- VH and VLare paired to provide an antibody antigen binding site, although a separate VH or VL can be used to bind the antigen.
- Human antibodiesavoid certain problems associated with antibodies with mouse or rat variable and/or constant regions.
- Mouse or rat-derived antibodiescan lead to rapid elimination of antibodies or can lead to an immune response by the patient against the antibodies.
- fully human antibodiescan produce fully human antibodies by introducing functional human antibody loci into rodents, other mammals, or animals. To generate.
- the recovered lymphocytesare fused with a bone marrow type cell line to prepare a permanent hybridoma cell line.
- These hybridoma cell linesare screened and selected to identify hybridoma cell lines that produce antibodies specific for the target antigen.
- Provided hereinare methods for the generation of multiple hybridoma cell lines specific for PD-L1.
- the characterization of the antibodies produced by the cell lineincluding the nucleotide and amino acid sequence analysis of the heavy and light chains of the antibody.
- B cellscan be assayed directly.
- CD19+ B cellscan be isolated from hyperimmunized mice and allowed to proliferate and differentiate into antibody-secreting plasma cells. The antibody from the cell supernatant was then screened for reactivity against PD-L1 immunogen by ELISA. The supernatant can also be screened for immunoreactivity against PD-L1 fragments to further mark different antibodies that bind to the target functional domain on B7-H1.
- Antibodiescan also be screened for other related human proteins and directed against rats, mice, and non-human primates, such as cynomolgus monkeys, orthologs of B7-H1, and ultimately determine species cross-reactivity.
- B cells from wells containing the antibody of interestcan be immortalized by a variety of methods, including fusion to generate hybridomas from separate wells or from combined wells, or by infection with EBV or by known immortalization
- the geneis transfected and then inoculated in a suitable medium.
- the B7-H1 specific hemolytic plaque assayis then used to isolate individual plasma cells that secrete antibodies with desired properties (see, for example, Babcook et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93:7843-48 (1996)).
- the cells targeted for lysisare preferably sheep red blood cells (SRBC) covered with B7-H1 antigen.
- SRBCsheep red blood cells
- antibodies as described hereincan be expressed in cell lines other than hybridoma cell lines. Sequences encoding specific antibodies can be used to transform suitable mammalian host cells. Transformation can be performed by any known method for introducing polynucleotides into host cells, including, for example, packaging the polynucleotides in a virus (or in a viral vector) and transducing with the virus (or vector) Host cells, or by transfection procedures known in the art, as shown in U.S. Patent Nos. 4,399,216, 4,912,040, 4,740,461, and 4,959,455 (which patents are incorporated herein by reference). The transformation method used depends on the host to be transformed.
- Methods for introducing heterologous polynucleotides into mammalian cellsinclude dextran-mediated transfection, calcium phosphate precipitation, polybrene-mediated transfection, and protoplast fusion , Electroporation, encapsulation of polynucleotides in liposomes, and direct DNA microinjection into the nucleus.
- myeloma, CHO cells or other cell lines with heavy chains of any desired isotypeare prepared, and myeloma, CHO cells or other cell lines with light chains are prepared.
- the cellscan then be fused and cell lines expressing intact antibodies can be isolated.
- antibody candidatesare generated that meet the required "structural" attributes as described above, and through isotype conversion they can generally have at least some of the required "functional” attributes.
- a myeloma, CHO cell or other cell line with a heavy chain of the desired isotypeis prepared and a myeloma, CHO cell or other cell line with a light chain is prepared.
- the cellscan then be fused and cell lines expressing intact antibodies can be isolated.
- antibody candidatesare generated that meet the required "structural" attributes as described above, and through isotype conversion they can generally have at least some of the required "functional” attributes.
- Embodiments of the inventioninclude the antibodies listed below.
- the underlineindicates the CDR region.
- the CDR sequence and its numbering of each antibody heavy chainare shown in Table 1, and the CDR sequence and its numbering of the antibody light chain are shown in Table 2.
- the embodiment of the present inventionincludes a pharmaceutical preparation of a PD-L1 targeted binding agent for treating diseases; preferably, the PD-L1 targeted binding agent is an anti-PD-L1 antibody.
- the formulationwill inhibit the binding of PD-L1 to one or more of its cognate ligands, thereby treating pathological conditions.
- the antibody of the present inventionpreferably has sufficient affinity to effectively inhibit the activity of PD-L1, or inhibit the binding of PD-L1 to one or more of its cognate ligands, and preferably has a sufficient duration of action to allow in humans Infrequent administration. The extended duration of action will allow for a less frequent and more convenient dosing regimen via alternate parenteral routes such as subcutaneous or intramuscular injections.
- Sterile preparationscan be produced, for example, by filtration through a sterile filter membrane before or after freeze-drying and reconstitution of the antibody.
- Antibodiesare generally stored in lyophilized form or in solution.
- the therapeutic antibody compositionis generally placed in a container with a sterile access port, for example, an intravenous solution pack or a vial with a connector that allows the preparation to be retrieved, such as a stopper pierceable by a hypodermic injection needle.
- the PD-L1 targeted binding agentcan be used to treat cancer. It includes administering an effective amount of PD-L1 targeted binding agent or a composition containing the same to the patient.
- the canceris selected from the group consisting of: bladder tumor, breast tumor, prostate tumor, basal cell carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, bladder cancer, bone cancer, brain and CNS cancer (e.g.
- gliomaglioma), cervical cancer, choriocarcinoma Cancer, colon and rectal cancer, connective tissue cancer, cancer of the digestive system; endometrial cancer, esophageal cancer; eye cancer, head and neck cancer, gastric cancer; intraepithelial tumor; kidney cancer; laryngeal cancer; leukemia; liver cancer; lung cancer (such as small Cell and non-small cell lung cancer); lymphoma, including Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma; melanoma; myeloma, neuroblastoma, oral cancer (for example, lip, tongue, mouth and Pharynx); ovarian cancer; pancreatic cancer, retinoblastoma; rhabdomyosarcoma; rectal cancer, kidney cancer, cancer of the respiratory system; sarcoma; skin cancer; stomach cancer; testicular cancer; thyroid cancer; uterine cancer, cancer of the urinary system, and Other cancers and s
- the PD-L1 targeted binding agentcan be used in combination with a chemotherapeutic agent.
- the PD-L1 targeted binding agentcan be used to treat infections and can be used in combination with antibiotics.
- the antibioticis an antiviral agent; also preferably, the antiviral agent is a reverse transcriptase inhibitor; more preferably, the reverse transcriptase inhibitor is a polymerase inhibitor.
- the infectionis a chronic infection, such as HIV, hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection.
- the infectionis caused by a pathogen selected from the group consisting of bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa.
- the PD-L1 targeted binding agentcan also be used in combination with at least one vaccine.
- Figure 1shows the results of purification of PD-L1.
- Figure 2is a graph showing the results of affinity determination of anti-PD-L1 antibodies.
- Figure 3is an immunofluorescence staining image of anti-PD-L1 antibody.
- Figure 4is a graph showing the results of the EC50 determination of immunofluorescence titer of anti-PD-L1 antibody.
- Figure 5is a graph showing the results of affinity determination of the humanized anti-PD-L1 antibody.
- Figure 6is a graph showing the EC50 determination result of immunofluorescence titer of humanized anti-PD-L1 antibody.
- Figure 7shows the results of the K562-PD-L1 film surface binding test.
- Figure 8is a graph showing the results of the PD-L1 binding test on the surface of Raji-PD-L1 membrane.
- Figure 9shows the results of the PD-L1 binding test on the membrane surface.
- Figure 10is a schematic diagram of the PD-L1 CAR element structure.
- Figure 11is a graph of PD-L1 chimeric antigen receptor (PD-L1 CAR) activity.
- Example 1Expression and purification of recombinant human PD-L1-his protein
- the pVKD1.0-hPD-L1-his vectorwas transfected into 293T cells mediated by PEI, the supernatant was collected, and purified by nickel column chromatography, and then purified by ultrafiltration to obtain the purified human PD-L1-his recombinant protein, the specific method Please refer to the kit instructions (GE Healthcare, article number: 17-5247-01). The purification results are shown in Figure 1.
- Example 2Mouse immunity, hybridoma fusion and clone screening
- miceFive female BALB/c mice aged 6-8 weeks were purchased from the Animal Experiment Center of Soochow University and raised in the SPF animal room of the Animal Experiment Center of Soochow University. After fully emulsifying the human PD-L1-his recombinant protein in Example 1 with complete Freund's adjuvant, complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) or incomplete Freund's adjuvant (IFA), the back was injected subcutaneously at 10 ⁇ g/mouse. Immunize BALB/c mice 3 to 4 times at intervals of one month.
- CFAcomplete Freund's adjuvant
- IFAincomplete Freund's adjuvant
- micewere immunized with 50 ⁇ g human PD-L1-His recombinant protein by intraperitoneal injection. The immunized mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and spleen cells of the mice were obtained. The mouse spleen cells and SP 2/0 myeloma cells were washed three times with serum-free DMEM medium, then centrifuged at 500 g for 5 minutes, resuspended in 10 mL serum-free DMEM medium, and the cells were counted.
- SP 2/0 myeloma cells5:1 and mix, centrifuge at 500 g for 5 minutes, remove the supernatant and use 1 mL of 50% PEG for cell fusion. After the fusion is completed, centrifuge at 500g for 5 minutes, remove the supernatant, resuspend in DMEM medium containing 20% FBS, add 2 ⁇ 10 5 cells/well to a 96-well plate, and incubate overnight at 37°C. On the next day, HAT-containing hybridoma selection medium (Sigma, catalog number A9666) was added, 100 ⁇ L/well. Afterwards, every 3 days, half of the medium was removed and supplemented with hybridoma selection medium. On the 14th day, 100 ⁇ L of supernatant was taken from each well, and the antibody activity in the hybridoma supernatant was screened by ELISA.
- HAT-containing hybridoma selection mediumSigma, catalog number A9666
- the ELISA methodis well known in the art and is briefly described as follows.
- the 96-well microtiter platewas purchased from Jianghai Glass Instrument Factory. Recombinant human PD-L1-his protein was provided by Suzhou Industrial Park Weike Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
- the proteinwas coated with NaHCO 3 buffer (pH 9.6) at 4°C overnight, and the coating concentration was 1 ⁇ g/mL.
- PBSphosphate buffered saline
- BSAbovine serum albumin
- PBSTphosphate buffered saline
- Tween 20phosphate buffered saline
- the wells with an OD value> 1.0were defined as positive clones.
- the positive cell cloneswere picked from the 96-well cell culture plate and transferred to 24-well culture. Two days later, the above-mentioned ELSIA method was used to retest the supernatant antibody activity. Retest positive clones were transferred to a 6-well plate for culture, and then the cells were collected for subsequent experiments. The results of the titration after the retest are shown in Table 3. Select clones with titer> 1000 after retest for further study.
- the hybridoma cellswere lysed and treated with Trizol reagent (Thermo, catalog number 15596026), and then the hybridoma cell RNA was extracted.
- Trizol reagentThermo, catalog number 15596026
- the specific methodis well known in the art, please refer to the Trizol reagent manual.
- the amplified productis ligated to the pMD19T vector (Bao Biological, Item No. 6013) and sent for sequencing. At least 10 clones of each VH and VL are sent for sequencing to obtain antibody VH and VL nucleic acid sequences. And analyze the CDR region sequence of each antibody, see Table 1 and Table 2 for the CDR region sequence of each antibody.
- the hybridoma cells obtained in Example 2were amplified with DMEM medium containing 10% FBS, and the hybridoma supernatant was collected and purified with a protein A column (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 28985254).
- a protein A columnGE Healthcare, catalog number: 28985254
- the kit instructions to obtain The EC50 titer of each purified mouse monoclonal antibodywas determined by ELISA method.
- the method of ELISAis well known to those skilled in the art and is briefly described as follows.
- the 96-well microtiter platewas purchased from Jianghai Glass Instrument Factory.
- the recombinant human PD-L1-his proteinprepared in Example 1.
- the proteinwas coated with NaHCO 3 buffer (pH 9.6) at 4°C overnight, and the coating concentration was 1 ⁇ g/mL.
- PBSphosphate buffered saline
- BSAbovine serum albumin
- PBSTphosphate buffered saline
- TMB3,3,5,5-tetramethylbenzidine
- the EC50 titers of anti-PD-L1 antibodiesare shown in Table 4.
- Friguet methodJ Immunol Methods. 1985; 77: 305-19 was used to determine the equilibrium dissociation constant Kd of each antibody, that is, the affinity of the antibody.
- the main stepsare briefly described as follows.
- the 96-well microtiter platewas purchased from Jianghai Glass Instrument Factory.
- the recombinant human PD-L1-his proteinwas prepared in Example 1.
- the proteinwas coated with NaHCO 3 buffer (pH 9.6) at 4°C overnight, and the coating concentration was 5 ⁇ g/mL.
- PBSphosphate buffered saline
- FBSfetal bovine serum
- PBSphosphate buffered saline
- FBSfetal bovine serum
- the VH regions of each antibody gene obtained in Example 3were cloned into the vector Abvec-hIgG1 (GenBank: FJ475055.1) with the human IgG1 CH1 structural region and its Fc structural region by molecular biology techniques well known in the art.
- the VL regions of each antibody gene obtained in Example 3were cloned into the vector AbVec-hIgKappa (GenBank: FJ475056.1) with human kappa light chain constant region by molecular biology techniques well known in the art. Then, the plasmids expressing the humanized heavy chain and the humanized light chain were co-transfected into 293T cells, and the supernatant was collected to obtain the anti-PD-L1 humanized antibody.
- the cell transfection supernatant containing the humanized antibody obtained in Example 5was purified by a protein A column (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 17-0402-01), and the specific method refers to the kit instructions. Each purified humanized antibody was obtained, and the results are shown in Table 7.
- Example 7Determination of EC50 titer of humanized antibody
- the EC50 activity of anti-PD-L1 antibodywas determined by ELISA.
- the method of ELISAis well known to those skilled in the art and is briefly described as follows.
- the 96-well microtiter platewas purchased from Jianghai Glass Instrument Factory.
- the recombinant human PD-L1-his protein prepared in Example 1was coated with NaHCO 3 buffer (pH 9.6) at 4°C overnight, and the coating concentration was 1 ⁇ g/mL.
- PBSphosphate buffered saline
- BSAbovine serum albumin
- PBSTphosphate buffered saline
- TMB3,3,5,5-tetramethylbenzidine
- Example 8Affinity determination of humanized anti-PD-L1 antibody
- the Kd value of the humanized antibodywas measured by the Friguet method in Example 4. The results are shown in Figure 5, and the results are summarized in Table 9.
- Example 9Affinity of humanized anti-PD-L1 antibody (immunofluorescence method)
- Example 4The immunofluorescence method in Example 4 was used to determine the affinity of the humanized antibody for binding to natural PD-L1.
- Example 10Ability of anti-PD-L1 antibody to bind to PD-L1 antigen on the surface of tumor cell membrane
- Flow cytometrywas used to detect the ability of anti-PD-L1 antibody to bind the PD-L1 antigen on the surface of tumor cell membrane.
- the total volume of the staining systemis 50 ⁇ L of PBS buffer (staining buffer) containing 2% FBS.
- the primary antibodyis the anti-PD-L1 antibody obtained in Example 2.
- the final concentration of the antibodyis adjusted to 2 ⁇ g/mL and incubated at 4°C 30min. After finishing, add 500 ⁇ L of staining buffer to each tube for elution twice, and centrifuge at 800g for 3 minutes each time. After the primary antibody staining, prepare the secondary antibody staining mixture, add the secondary antibody donkey anti-mouse-IgG (H+L) (AF647 Conjugate, Abcam) at 1:1000, and the total volume of the staining system is also 50 ⁇ L of staining buffer. Stain for 30 minutes at 4°C, add 500 ⁇ L of staining buffer to each tube for elution twice, and centrifuge at 800g for 3 minutes each time.
- H+Lsecondary antibody donkey anti-mouse-IgG
- Example 11Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody
- VL and VH regions of the PD-L1 antibodywere spliced for gene synthesis, and the synthesized PD-L1 chimeric antigen receptor genes were all transferred to the lentiviral vector pHAGE-EF1 ⁇ -MCS-ZsGreen (purchased from Harvard Medical School, catalog number :EvNO00061636), so as to obtain the CAR that can recognize human PD-L1 based on 6 PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies: 1C2 CAR, 1D4 CAR, 1G11 CAR, 2F7 CAR, 3D7 CAR and 6A3 CAR (PD-L1 CAR element structure diagram see Figure 10).
- CD8 SPrepresents the sequence derived from the human CD8 antigen signal peptide (CD8 SP)
- PD-L1 VLrepresents the VL sequence of the anti-PD-L1 antibody
- PD-L1 VHrepresents the VH sequence of the anti-PD-L1 antibody
- CD28, 4 -1BBL and CD3 ⁇represent their respective components, which are commonly used components for CAR construction.
- the coding nucleic acid sequence of CD8 SPis shown in SEQ ID NO: 51, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 52;
- the coding nucleic acid sequence of CD28 elementis shown in SEQ ID NO: 53, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.
- the coding nucleic acid sequence of the 4-1BBL elementis shown in SEQ ID NO: 55, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 56; the coding nucleic acid sequence of the CD3 ⁇ element is shown in SEQ ID NO: 57, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 57. As shown in SEQ ID NO: 58.
- the coding nucleic acid sequence of 1C2 CARis shown in SEQ ID NO: 59, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 60; the coding nucleic acid sequence of 1D4 CAR is shown in SEQ ID NO: 61, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 62 Show; 1G11 CAR coding nucleic acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 63, amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 64; 2F7 CAR coding nucleic acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 64, and amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 66; 3D7 CAR coding nucleic acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 67, amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 68; 6A3 CAR coding nucleic acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 69, and amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 70 shown.
- Transfect the lentivirus packaging plasmid into 293T cellscollect the virus supernatant after 48 hours of transfection, centrifuge at 3000 rpm, 4°C for 10 minutes to remove cell debris, filter through a 0.45 ⁇ m filter, and add lentivirus concentrate at a volume ratio of 1:5 PEG8000 (5 ⁇ ), concentrated overnight, 4000g, 4°C for 20 minutes to obtain lentivirus precipitation, resuspend the lentivirus in RPMI1640 medium, and store at -80°C.
- JE6-1a concentrated virus to infect Jurkat E6-1 (ATCC catalog number: TIB-152 TM , referred to as JE6-1), control the number of cells during infection to 2 ⁇ 10 5 , and add the final concentration of 10 ⁇ g/mL sulfuric acid, a pro-infection reagent Fish protein.
- Use centrifugal infection method1000g, centrifugal infection at 32°C for 1 hour. 6-8 hours after the end of the centrifugal infection, change to a fresh medium RPMI1640, and continue to grow and expand the infected JE6-1. After the cells are expanded to a certain number, the PD-L1 CAR positive cells are sorted by flow cytometry.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Communicable Diseases (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Plant Pathology (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Peptides Or Proteins (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese本发明属于生物医药领域,具体涉及针对PD-L1的靶向结合剂、编码它们的核酸及其用途。在一些实施方案中,本发明涉及针对PD-L1的单克隆抗体、编码它们的核酸和这些抗体的用途。本发明也涉及表达所述靶向结合剂或抗体的细胞系。此外,本发明还涉及所述的靶向结合剂用于诊断和用于治疗与PD-L1的活性和/或表达相关的疾病。The present invention belongs to the field of biomedicine, and specifically relates to targeted binding agents for PD-L1, nucleic acids encoding them and uses thereof. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to monoclonal antibodies against PD-L1, nucleic acids encoding them, and uses of these antibodies. The invention also relates to cell lines expressing the targeted binding agent or antibody. In addition, the present invention also relates to the use of the targeted binding agent for diagnosis and treatment of diseases related to the activity and/or expression of PD-L1.
适应性免疫应答涉及T细胞和B细胞的两种主要类别的淋巴细胞的激活、选择和克隆增殖。遇到抗原之后,T细胞增殖并分化为抗原特异性效应细胞,而B细胞增殖并分化为抗体分泌细胞。T细胞激活是多步骤过程,需要T细胞和抗原呈递细胞(APC)之间的一些信号转导事件。对于要发生的T细胞激活,必须向静止T细胞递送两种类型的信号。第一种类型是通过抗原特异性T细胞受体(TCR)来介导,并赋予对免疫应答的特异性。第二种共刺激类型调节应答的大小并通过T细胞上的辅助受体来递送。The adaptive immune response involves the activation, selection and clonal proliferation of two main types of lymphocytes, T cells and B cells. After encountering an antigen, T cells proliferate and differentiate into antigen-specific effector cells, while B cells proliferate and differentiate into antibody secreting cells. T cell activation is a multi-step process that requires some signal transduction events between T cells and antigen presenting cells (APC). For T cell activation to occur, two types of signals must be delivered to resting T cells. The first type is mediated by antigen-specific T cell receptors (TCR) and confers specificity for immune responses. The second type of co-stimulation regulates the size of the response and is delivered via a co-receptor on T cells.
主要的共刺激信号通过结合APC上的配体B7-1或B7-2激活T细胞上的CD28受体来递送。相比之下,同样的B7-1或B7-2配体与抑制性CTLA-4受体的结合导致T细胞应答的弱化。因此,CTLA-4信号对抗由CD28介导的共刺激。在高抗原浓度时,CD28共刺激超越了CTLA-4抑制作用。CD28和CTLA-4表达的暂时调节维持了激活信号和抑制信号之间的平衡并确保了有效的免疫应答的形成,同时防范自身免疫的形成。The main costimulatory signal is delivered by binding to the ligand B7-1 or B7-2 on APC to activate the CD28 receptor on T cells. In contrast, the binding of the same B7-1 or B7-2 ligand to the inhibitory CTLA-4 receptor results in a weakening of the T cell response. Therefore, the CTLA-4 signal opposes CD28-mediated costimulation. At high antigen concentrations, CD28 costimulation surpasses CTLA-4 inhibition. The temporary regulation of the expression of CD28 and CTLA-4 maintains the balance between the activation signal and the inhibitory signal and ensures the formation of an effective immune response, while preventing the formation of autoimmunity.
PD-L1,又称作B7-H1,是大小约53kD的I型跨膜蛋白。在人中,PD-L1在多种免疫细胞类型上表达,包括在活化的T细胞、无反应性的/衰竭的T细胞、天然B细胞和活化B细胞上表达,以及在髓系树突细胞(DC)、单核细胞和肥大细胞上表达。其还在非免疫细胞,包括胰岛、肝脏库普弗细胞(Kupffer Cell)、血管内皮细胞和上皮细胞,例如,气管上皮细胞和肾小管上皮细胞上表达,其中在炎性发作过程中其表达是增强的。此外,研究还发现PD-L1在多种肿瘤中表达水平上调,所述多种肿瘤包括但不限于乳腺癌、结肠直肠癌、肺癌、肾癌、胃癌、膀胱癌、肝癌和胰腺癌,以及黑素瘤。PD-L1, also known as B7-H1, is a type I transmembrane protein with a size of about 53kD. In humans, PD-L1 is expressed on a variety of immune cell types, including activated T cells, anergic/depleted T cells, natural B cells and activated B cells, as well as on myeloid dendritic cells (DC), monocytes and mast cells. It is also expressed on non-immune cells, including pancreatic islets, liver Kupffer Cells, vascular endothelial cells, and epithelial cells, such as tracheal epithelial cells and renal tubular epithelial cells, where its expression during inflammatory episodes is Enhanced. In addition, studies have also found that PD-L1 expression levels are up-regulated in a variety of tumors, including but not limited to breast cancer, colorectal cancer, lung cancer, kidney cancer, gastric cancer, bladder cancer, liver cancer, and pancreatic cancer, as well as black Prime tumor.
PD-L1是B7家族蛋白的成员,其含有两个胞外免疫球蛋白(Ig)结 构域,一个N末端V型结构域,之后是C型结构域。30个氨基酸长度的胞内结构域不含明显的信号转导基序,但含有蛋白激酶C磷酸化的可能位点。小鼠PD-L1与人PD-L1具有69%氨基酸同源性,并且共有保守结构。PD-L1 is a member of the B7 family of proteins, which contains two extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig) domains, an N-terminal V-type domain, followed by a C-type domain. The 30 amino acid long intracellular domain does not contain obvious signal transduction motifs, but contains possible sites for protein kinase C phosphorylation. Mouse PD-L1 has 69% amino acid homology with human PD-L1 and shares a conserved structure.
已知PD-L1与两个可替代性配体结合,其中之一的PD-1为50-55kD的I型跨膜受体,其最初鉴定于经历激活诱导的凋亡的T细胞中。PD-1表达于活化T细胞、B细胞和单核细胞以及免疫系统的其它细胞中,并与PD-L1和PD-L2结合。第二是B7家族成员B7-1,其表达于活化T细胞、B细胞、单核细胞和抗原呈递细胞。It is known that PD-L1 binds to two alternative ligands, one of which is PD-1, a 50-55kD type I transmembrane receptor, which was originally identified in T cells undergoing activation-induced apoptosis. PD-1 is expressed in activated T cells, B cells, monocytes and other cells of the immune system, and binds to PD-L1 and PD-L2. The second is the B7 family member B7-1, which is expressed on activated T cells, B cells, monocytes and antigen presenting cells.
PD-1是免疫球蛋白超家族的成员,其在其胞外区中含有单一的Ig V样结构域。PD-1胞浆域含有两个酪氨酸,最接近膜的酪氨酸位于免疫受体酪氨酸抑制基序(Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-Based Inhibitory Motif,ITIM)中。ITIM的存在表明该分子以通过募集胞浆磷酸酶来抑制抗原受体信号转导来发挥作用。人和鼠PD-1蛋白共有约60%的氨基酸同源性,其中保守的是4个N-糖基化位点,和限定Ig-V结构域的氨基酸残基。胞浆区中的ITIM和围绕PD-L1羧基末端的酪氨酸的ITIM样基序(人和小鼠中的TEYATI)在人和鼠之间也是保守的。PD-1 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, which contains a single Ig V-like domain in its extracellular domain. The cytoplasmic domain of PD-1 contains two tyrosines, and the tyrosine closest to the membrane is located in the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-Based Inhibitory Motif, ITIM). The presence of ITIM indicates that the molecule functions by recruiting cytosolic phosphatase to inhibit antigen receptor signal transduction. Human and murine PD-1 proteins share about 60% amino acid homology, of which 4 N-glycosylation sites and amino acid residues that define the Ig-V domain are conserved. The ITIM in the cytoplasmic region and the ITIM-like motif around the tyrosine at the carboxyl terminal of PD-L1 (TEYATI in humans and mice) are also conserved between humans and mice.
研究认为经由PD-L1轴线的信号转导通过负向调控T细胞应答在免疫系统中起关键作用。该调控参与了T细胞发育、慢性炎症应答和外周耐受。这些功能的关键性质表现在自身免疫表型的PD-1缺陷的小鼠中示出。C57BL/6小鼠中的PD-1缺陷导致了慢性进行性狼疮样肾小球肾炎和关节炎。在BAL b/c小鼠中,PD-1缺陷导致由于心脏组织特异性自身反应性抗体的存在引起的严重的心肌病。经由PD-L1/B7-1的信号转导的功能尚不清楚,但认为其也参与向T细胞和抗原呈递细胞递送负调控信号。Research suggests that signal transduction via the PD-L1 axis plays a key role in the immune system by negatively regulating T cell responses. This regulation is involved in T cell development, chronic inflammatory response and peripheral tolerance. The key properties of these functions are shown in PD-1 deficient mice with an autoimmune phenotype. PD-1 deficiency in C57BL/6 mice leads to chronic progressive lupus-like glomerulonephritis and arthritis. In BAL b/c mice, PD-1 deficiency leads to severe cardiomyopathy due to the presence of autoreactive antibodies specific to heart tissue. The function of signal transduction via PD-L1/B7-1 is unclear, but it is thought that it is also involved in the delivery of negative regulatory signals to T cells and antigen-presenting cells.
研究认为表达于肿瘤细胞的PD-L1有助于肿瘤逃逸免疫系统的检测和清除。PD-L1经由一些可选择的机制在该方面起作用,所述机制包括驱使浸润T淋巴细胞的肿瘤的衰竭和无反应性、刺激免疫抑制性细胞因子分泌到肿瘤微环境中、刺激抑制性调控T细胞起作用并防止表达PD-L1的肿瘤细胞被肿瘤细胞特异性细胞毒性T细胞裂解。Research suggests that PD-L1 expressed in tumor cells helps the detection and elimination of tumor escape from the immune system. PD-L1 plays a role in this aspect through some selectable mechanisms, including driving the failure and anergy of tumors infiltrating T lymphocytes, stimulating the secretion of immunosuppressive cytokines into the tumor microenvironment, and stimulating inhibitory regulation T cells act and prevent tumor cells expressing PD-L1 from being lysed by tumor cell-specific cytotoxic T cells.
总之,存在提供用于与免疫反应的抑制有关的疾患的安全且有效的治疗方法的需要,所述疾患例如癌症和慢性病毒感染。这些疾患中涉及的免疫应答的调节可通过对PD-1/PD-L1通路进行操作来实现。In summary, there is a need to provide safe and effective treatments for conditions related to suppression of immune responses, such as cancer and chronic viral infections. The regulation of the immune response involved in these diseases can be achieved by manipulating the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway.
发明内容Summary of the invention
本发明涉及与PD-L1特异性结合并抑制PD-L1的生物活性的靶向结合剂。在本发明的一个实施方案中,本发明涉及与PD-L1特异性结合并从 而抑制PD-L1活性的靶向结合剂。在本发明的另一个实施方案中,本发明涉及与PD-L1特异性结合并从而抑制PD-L1与PD-1的结合的靶向结合剂。在本发明的又一个实施方案中,本发明涉及阻断PD-L1诱导的T细胞抑制并从而增强抗肿瘤免疫力的靶向结合剂。在本发明又一个另外的实施方案中,本发明还涉及可进一步刺激以下活性中的一种或多种的靶向结合剂,所述活性包括混合淋巴细胞反应中的T细胞增殖、IFN-γ或IL-2分泌。The present invention relates to a targeted binding agent that specifically binds to PD-L1 and inhibits the biological activity of PD-L1. In one embodiment of the present invention, the present invention relates to a targeted binding agent that specifically binds to PD-L1 and thereby inhibits the activity of PD-L1. In another embodiment of the present invention, the present invention relates to a targeted binding agent that specifically binds to PD-L1 and thereby inhibits the binding of PD-L1 to PD-1. In yet another embodiment of the present invention, the present invention relates to a targeted binding agent that blocks PD-L1 induced T cell suppression and thereby enhances anti-tumor immunity. In yet another embodiment of the present invention, the present invention also relates to a targeted binding agent that can further stimulate one or more of the following activities, including T cell proliferation in mixed lymphocyte reaction, IFN-γ Or IL-2 secretion.
本发明的实施方案涉及与PD-L1特异性结合并抑制PD-L1的生物活性的靶向结合剂。在一个实施方案中,与不存在所述靶向结合剂时相比,靶向结合剂抑制了PD-L1生物活性的至少5%、至少10%、至少15%、至少20%、至少25%、至少30%、至少35%、至少40%、至少45%、至少50%、至少55%、至少60%、至少65%、至少70%、至少75%、至少80%、至少85%、至少90%或至少95%。Embodiments of the present invention relate to targeted binding agents that specifically bind to PD-L1 and inhibit the biological activity of PD-L1. In one embodiment, the targeted binding agent inhibits at least 5%, at least 10%, at least 15%, at least 20%, at least 25% of the biological activity of PD-L1 compared with the absence of the targeted binding agent. , At least 30%, at least 35%, at least 40%, at least 45%, at least 50%, at least 55%, at least 60%, at least 65%, at least 70%, at least 75%, at least 80%, at least 85%, at least 90% or at least 95%.
本发明的实施方案涉及与PD-L1特异性结合并从而抑制PD-L1活性的靶向结合剂。在一个实施方案中,与不存在所述靶向结合剂时相比,靶向结合剂抑制了PD-L1活性的至少5%、至少10%、至少15%、至少20%、至少25%、至少30%、至少35%、至少40%、至少45%、至少50%、至少55%、至少60%、至少65%、至少70%、至少75%、至少80%、至少85%、至少90%或至少95%。Embodiments of the present invention relate to targeted binding agents that specifically bind to PD-L1 and thereby inhibit the activity of PD-L1. In one embodiment, the targeted binding agent inhibits PD-L1 activity by at least 5%, at least 10%, at least 15%, at least 20%, at least 25%, At least 30%, at least 35%, at least 40%, at least 45%, at least 50%, at least 55%, at least 60%, at least 65%, at least 70%, at least 75%, at least 80%, at least 85%, at least 90 % Or at least 95%.
本发明的实施方案涉及与PD-L1特异性结合并从而抑制与PD-1的结合的靶向结合剂。在一个实施方案中,与不存在靶向结合剂时相比,靶向结合剂抑制了PD-L1/PD-1受体配体结合的至少5%、至少10%、至少15%、至少20%、至少25%、至少30%、至少35%、至少40%、至少45%、至少50%、至少55%、至少60%、至少65%、至少70%、至少75%、至少80%、至少85%、至少90%或至少95%。Embodiments of the present invention relate to targeted binding agents that specifically bind to PD-L1 and thereby inhibit the binding to PD-1. In one embodiment, the targeted binding agent inhibits the binding of PD-L1/PD-1 receptor ligand by at least 5%, at least 10%, at least 15%, at least 20% compared to when the targeted binding agent is not present. %, at least 25%, at least 30%, at least 35%, at least 40%, at least 45%, at least 50%, at least 55%, at least 60%, at least 65%, at least 70%, at least 75%, at least 80%, At least 85%, at least 90%, or at least 95%.
本发明的另外的实施方案涉及与B7-H1特异性结合并从而增强抗肿瘤免疫力的靶向结合剂。在一个实施方案中,与不存在靶向结合剂时将发生的相比,靶向结合剂增强了抗肿瘤免疫力的至少5%、至少10%、至少15%、至少20%、至少25%、至少30%、至少35%、至少40%、至少45%、至少50%、至少55%、至少60%、至少65%、至少70%、至少75%、至少80%、至少85%、至少90%或至少95%。Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a targeted binding agent that specifically binds to B7-H1 and thereby enhances anti-tumor immunity. In one embodiment, the targeted binding agent enhances anti-tumor immunity by at least 5%, at least 10%, at least 15%, at least 20%, at least 25% compared to what would happen in the absence of the targeted binding agent , At least 30%, at least 35%, at least 40%, at least 45%, at least 50%, at least 55%, at least 60%, at least 65%, at least 70%, at least 75%, at least 80%, at least 85%, at least 90% or at least 95%.
本发明的另外的实施方案涉及与B7-H1特异性结合并从而抑制细胞增殖的靶向结合剂。在一个实施方案中,与不存在靶向结合剂时将发生的相比,靶向结合剂抑制了细胞增殖的至少5%、至少10%、至少15%、至少20%、至少25%、至少30%、至少35%、至少40%、至少45%、至少50%、至少55%、至少60%、至少65%、至少70%、至少75%、至少80%、 至少85%、至少90%或至少95%。Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a targeted binding agent that specifically binds to B7-H1 and thereby inhibits cell proliferation. In one embodiment, the targeted binding agent inhibits cell proliferation by at least 5%, at least 10%, at least 15%, at least 20%, at least 25%, at least 30%, at least 35%, at least 40%, at least 45%, at least 50%, at least 55%, at least 60%, at least 65%, at least 70%, at least 75%, at least 80%, at least 85%, at least 90% Or at least 95%.
本发明的另外的实施方案涉及与PD-L1特异性结合并提高针对表达B7-H1的肿瘤细胞的特异性溶细胞(CTL)活性的靶向结合剂。在一个实施方案中,本发明的抗体具有小于或等于100nM、50nM或1nM的EC50。而且,在另一个实施方案中,本发明的抗体具有约100nM直至约1nM的EC50;或约50nM直至约1nM的EC50;或约20nM直至约1nM的EC50;或约100nM直至约50nM的EC50;或约100nM直至约70nM的EC50。Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a targeted binding agent that specifically binds to PD-L1 and increases specific cytolytic (CTL) activity against tumor cells expressing B7-H1. In one embodiment, an antibody of the present invention is less than or equal to 100nM, EC 50nM 1nM or50. Further, in another embodiment, the antibodies of the invention having from about 1nM to about 100nM of up to50 EC; EC or about 1nM to about 50nM up to50; or from about 1nM to about 20nM up to50 EC; or of about 50nM up to about 100nM EC50; or from about 70nM to about 100nM until the EC50.
本发明的另外的实施方案涉及与PD-L1特异性结合并以小于或等于100nM的EC50抑制PD-L1介导的T细胞增殖的抑制的靶向结合剂。在一个实施方案中,本发明的抗体具有小于或等于100nM,例如,90、80、70、60、50、40、30、20或10nM的EC50。而且,在另一个实施方案中,本发明的抗体具有约100nM直至约10nM的EC50;或约50nM直至约10nM的EC50;或约20nM直至约10nM的EC50;或约100nM直至约50nM的EC50;或约100nM直至约70nM的EC50;或约100nM直至约80nM的EC50。Further embodiments of the present invention relates specifically binds to PD-L1 and EC50 of less than or equal to 100nM inhibiting targeted binding agent inhibits proliferation of PD-L1-mediated T cell. In one embodiment, the antibody of the invention has an EC50 of less than or equal to 100 nM, for example, 90, 80, 70, 60,50 , 40, 30, 20, or 10 nM. Further, in another embodiment, the antibodies of the invention having about 100nM 10nM up to about50 EC; EC or from about 50nM to about 10nM up to50; or from about 20nM to about 10nM up to50 EC; or of about 50nM up to about 100nM EC50; or from about 70nM to about 100nM until the EC50; or from about 80nM to about 100nM until the EC50.
靶向结合剂还抑制肿瘤细胞黏附、运动性、侵入和细胞转移,并且靶向结合剂对于降低肿瘤生长是有用的。可实现如此的机制可包括但不限于,抑制PD-L1活性。Targeted binding agents also inhibit tumor cell adhesion, motility, invasion and cell metastasis, and targeted binding agents are useful for reducing tumor growth. Mechanisms that can achieve this may include, but are not limited to, inhibition of PD-L1 activity.
在本发明的一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂是抗体。在本发明的一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂是单克隆抗体。在本发明的一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂是人源化抗体或其片段。所述单克隆抗体在本文中可指抗PD-L1抗体或本发明的抗体。In one embodiment of the invention, the targeted binding agent is an antibody. In one embodiment of the invention, the targeted binding agent is a monoclonal antibody. In one embodiment of the invention, the targeted binding agent is a humanized antibody or fragment thereof. The monoclonal antibody herein may refer to the anti-PD-L1 antibody or the antibody of the present invention.
抗体、单克隆抗体和人单克隆抗体包括IgG1、IgG2、IgG3和IgG4同种型抗体。在本发明的一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂是IgG1同种型的人源化单克隆抗体。IgG1同种型提高了抗体的抗体依赖性细胞毒性(ADCC)。此外,IgG1同种型具有较高的稳定性。Antibodies, monoclonal antibodies and human monoclonal antibodies include IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 isotype antibodies. In one embodiment of the invention, the targeted binding agent is a humanized monoclonal antibody of the IgG1 isotype. The IgG1 isotype improves the antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) of the antibody. In addition, the IgG1 isotype has high stability.
在本发明的一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂具有选自以下中的一个或多个的需要的治疗性质:对PD-L1的高亲和性、在体外或在体内抑制PD-L1活性的能力、抑制PD-L1介导的肿瘤细胞存活的能力和抑制PD-L1介导的肿瘤反应性T细胞的抑制的能力,其可进而降低肿瘤细胞增殖、运动性、侵入、转移和肿瘤生长。In one embodiment of the present invention, the targeted binding agent has a desired therapeutic property selected from one or more of the following: high affinity for PD-L1, inhibiting PD-L1 activity in vitro or in vivo Ability, the ability to inhibit PD-L1-mediated tumor cell survival and the ability to inhibit PD-L1-mediated tumor-reactive T cell suppression, which can further reduce tumor cell proliferation, motility, invasion, metastasis and tumor growth.
在一个实施方案中,本发明包括以非常高的亲和力与PD-L1特异性结合的抗体。在本发明的一些实施方案中,靶向结合剂以小于5nM的结合亲和力(Kd)结合PD-L1。在其它实施方案中,靶向结合剂以小于4nM、3nM、2nM或1nM的Kd结合。而且,在一些其它实施方案中,本发明的抗体以约5nM至约1nM;或约5nM至约2nM;或约5nM至约3nM;或约5nM 至约4nM;或约3nM至约1nM;或约2nM至约1nM的Kd结合PD-L1。在本发明的一些实施方案中,靶向结合剂以小于950pM、900pM、800pM、700pM、600pM、500pM、400pM、300pM、200pM或100pM的Kd结合PD-L1。而且,在一些其它实施方案中,本发明的抗体以约900pM至约100pM;或约900pM至约200pM;或约900pM至约300pM;或约900pM至约400pM;或约900pM至约500pM;或约900pM至约600pM;或约900pM至约700pM;或约200pM至约100pM;或约300pM至约200pM;或约400pM至约300pM的Kd结合PD-L1。在一些其它实施方案中,靶向结合剂以小于90pM、80pM、70pM、60pM、55pM或50pM的Kd结合PD-L1。在一些其它实施方案中,靶向结合剂以小于60pM的Kd结合PD-L1。在一些其它实施方案中,靶向结合剂以小于55pM的Kd结合PD-L1。而且,在一些其它实施方案中,本发明的抗体以约100pM至约50pM;或约100pM至约70pM;或约100pM至约80pM;或约100pM至约90pM;或约70pM至约50pM;或约60pM至约50pM;或约55pM至约50pM的Kd结合PD-L1。利用本文所描述的或本领域中普通技术人员熟知的方法(例如BIAcore法)(Biacore International AB,Uppsala,Sweden)可评估Kd。In one embodiment, the present invention includes antibodies that specifically bind to PD-L1 with very high affinity. In some embodiments of the invention, the targeted binding agent binds PD-L1 with a binding affinity (Kd) of less than 5 nM. In other embodiments, the targeted binding agent binds with a Kd of less than 4 nM, 3 nM, 2 nM, or 1 nM. Moreover, in some other embodiments, the antibody of the present invention is used at about 5 nM to about 1 nM; or about 5 nM to about 2 nM; or about 5 nM to about 3 nM; or about 5 nM to about 4 nM; or about 3 nM to about 1 nM; or about A Kd of 2nM to about 1nM binds PD-L1. In some embodiments of the present invention, the targeted binding agent binds PD-L1 with a Kd of less than 950pM, 900pM, 800pM, 700pM, 600pM, 500pM, 400pM, 300pM, 200pM, or 100pM. Moreover, in some other embodiments, the antibody of the present invention is at about 900pM to about 100pM; or about 900pM to about 200pM; or about 900pM to about 300pM; or about 900pM to about 400pM; or about 900pM to about 500pM; or about 900pM to about 600pM; or about 900pM to about 700pM; or about 200pM to about 100pM; or about 300pM to about 200pM; or about 400pM to about 300pM Kd binds PD-L1. In some other embodiments, the targeted binding agent binds PD-L1 with a Kd of less than 90pM, 80pM, 70pM, 60pM, 55pM, or 50pM. In some other embodiments, the targeted binding agent binds PD-L1 with a Kd of less than 60 pM. In some other embodiments, the targeted binding agent binds PD-L1 with a Kd of less than 55 pM. Moreover, in some other embodiments, the antibody of the present invention is used at about 100 pM to about 50 pM; or about 100 pM to about 70 pM; or about 100 pM to about 80 pM; or about 100 pM to about 90 pM; or about 70 pM to about 50 pM; or about 60pM to about 50pM; or about 55pM to about 50pM Kd binds PD-L1. Kd can be evaluated using the methods described herein or well known to those of ordinary skill in the art (for example, the BIAcore method) (Biacore International AB, Uppsala, Sweden).
在一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体包含这样的序列,该序列包含抗体1C2、1D4、1G11、2F7、3D7或6A3的重链序列中的任何一个。轻链混杂在本领域中非常确定,因而,包含含有抗体1C2、1D4、1G11、2F7、3D7或6A3、本文所公开的另一抗体的重链序列中的任何一个的序列的靶向结合剂或抗体还可包含示于表2中的1C2、1D4、1G11、2F7、3D7或6A3、本文所公开的其它抗体的轻链序列(VL)中的任何一个。在另一个实施方案中靶向结合剂或抗体包含这样的序列,该序列包含抗体1C2、1D4、1G11、2F7、3D7或6A3的重链序列中的任何一个且还包含抗体1C2、1D4、1G11、2F7、3D7或6A3的对应的轻链序列。在一些实施方案中,抗体是完全人单克隆抗体。In one embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprises a sequence comprising any one of the heavy chain sequences of antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7, or 6A3. Light chain promiscuity is very well established in the art. Therefore, a targeted binding agent containing any one of the sequences of the heavy chain sequence of the antibody 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7 or 6A3, another antibody disclosed herein, or The antibody may also comprise any one of 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7, or 6A3 shown in Table 2, the light chain sequence (VL) of other antibodies disclosed herein. In another embodiment the targeted binding agent or antibody comprises a sequence comprising any of the heavy chain sequences of antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7 or 6A3 and further comprising antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, The corresponding light chain sequence of 2F7, 3D7 or 6A3. In some embodiments, the antibody is a fully human monoclonal antibody.
在一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体包含这样的序列,该序列包含示于表2中的轻链序列中的任何一个。在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体包含这样的序列,该序列包含抗体1C2、1D4、1G11、2F7、3D7或6A3的轻链序列中的任何一个。In one embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprises a sequence comprising any one of the light chain sequences shown in Table 2. In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprises a sequence comprising any one of the light chain sequences of antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7, or 6A3.
另一个实施方案是与PD-L1特异性结合的靶向结合剂或抗体,且包含这样的序列,该序列包含示于表2中的CDR2序列的其中之一和CDR3序列的其中之一。在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体还包含这样的序列,该序列包含示于表1中的CDR3序列。在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体还包含这样的序列,该序列包含如表1和/或表2中所示的 CDR2序列和CDR3序列。在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体还包含这样的序列,该序列包含:如表1和/或表2中所示的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列。Another embodiment is a targeted binding agent or antibody that specifically binds to PD-L1, and includes a sequence that includes one of the CDR2 sequences and one of the CDR3 sequences shown in Table 2. In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody further comprises a sequence comprising the CDR3 sequence shown in Table 1. In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody further comprises a sequence comprising the CDR2 sequence and CDR3 sequence as shown in Table 1 and/or Table 2. In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody further comprises a sequence comprising: CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences as shown in Table 1 and/or Table 2.
在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体可包含这样的序列,该序列包含如表1中所示的单克隆抗体1C2、1D4、1G11、2F7、3D7或6A3中的任何一个的CDR1、CDR2或CDR3中的任何一个。在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体可包含这样的序列,该序列包含如表2中所示的单克隆抗体1C2、1D4、1G11、2F7、3D7或6A3的任何一个的CDR1、CDR2或CDR3中的任何一个。在一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体可包含这样的序列,该序列包含如表1中所示的单克隆抗体1C2、1D4、1G11、2F7、3D7或6A3中的任何一个的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3。在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体可包含这样的序列,该序列包含如表2中所示的单克隆抗体1C2、1D4、1G11、2F7、3D7或6A3的任何一个的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3。In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody may comprise a sequence comprising the CDR1 of any one of monoclonal antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7, or 6A3 as shown in Table 1. Either CDR2 or CDR3. In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody may comprise a sequence comprising CDR1, CDR2 of any one of monoclonal antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7 or 6A3 as shown in Table 2. Or any of CDR3. In one embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody may comprise a sequence comprising CDR1, CDR2 of any one of monoclonal antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7 or 6A3 as shown in Table 1. And CDR3. In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody may comprise a sequence comprising CDR1, CDR2 of any one of monoclonal antibodies 1C2, 1D4, 1G11, 2F7, 3D7 or 6A3 as shown in Table 2. And CDR3.
在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体包含这样的序列,该序列包含如表1中所示的单克隆抗体1C2重链的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列和如表2中所示的单克隆抗体1C2轻链的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列。在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体包含这样的序列,该序列包含如表1中所示的单克隆抗体1D4重链的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列和如表2中所示的单克隆抗体1D4轻链的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列。在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体包含这样的序列,该序列包含如表1中所示的单克隆抗体1G11重链的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列和如表2中所示的单克隆抗体1G11轻链的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列。在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体包含这样的序列,该序列包含如表1中所示的单克隆抗体2F7重链的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列和如表2中所示的单克隆抗体2F7轻链的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列。In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprises a sequence comprising the CDR1, CDR2, and CDR3 sequences of the heavy chain of monoclonal antibody 1C2 as shown in Table 1 and the single sequence as shown in Table 2. The CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the light chain of antibody 1C2 were cloned. In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprises a sequence comprising the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the heavy chain of monoclonal antibody 1D4 as shown in Table 1 and the single sequence as shown in Table 2. The CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the light chain of antibody 1D4 were cloned. In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprises a sequence comprising the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the heavy chain of monoclonal antibody 1G11 as shown in Table 1 and the single sequence as shown in Table 2. The CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the light chain of antibody 1G11 were cloned. In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprises a sequence comprising the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the heavy chain of monoclonal antibody 2F7 as shown in Table 1 and the single sequence as shown in Table 2. The CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the light chain of antibody 2F7 were cloned.
在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体包含这样的序列,该序列包含如表1中所示的单克隆抗体3D7重链的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列和如表2中所示的单克隆抗体3D7轻链的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列。在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体包含这样的序列,该序列包含如表1中所示的单克隆抗体6A3重链的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列和如表2中所示的单克隆抗体6A3轻链的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列。在一些实施方案中,抗体是人源化抗体。In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprises a sequence comprising the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the heavy chain of the monoclonal antibody 3D7 as shown in Table 1 and the single sequence as shown in Table 2. The CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the light chain of the antibody 3D7 were cloned. In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprises a sequence comprising the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the heavy chain of monoclonal antibody 6A3 as shown in Table 1 and the single sequence as shown in Table 2. The CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 sequences of the light chain of antibody 6A3 were cloned. In some embodiments, the antibody is a humanized antibody.
值得注意地是,本领域中的普通技术人员可容易地完成CDR的测定。参见例如,Kabat等,Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest(免疫 学目的蛋白序列),第5版,NIH出版91-3242,Bethesda MD(1991),第1-3卷。Kabat提供了来自大量物种抗体同种型的免疫球蛋白链的多个序列比对。根据单一编号系统,Kabat编号系统对所比对的序列进行编号。Kabat序列已自1991年更新且作为电子序列数据库是可获得的(目前可从Kabat数据库网站获得;另见Nucleic Acids Research,2000,28(1),214-218)。通过与Kabat参考序列进行比对,根据Kabat可对任何免疫球蛋白序列进行编号。因此,Kabat编号系统提供了用于对免疫球蛋白链进行编号的统一系统。It is worth noting that a person of ordinary skill in the art can easily complete the CDR determination. See, for example, Kabat et al., Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, 5th edition, NIH Publication 91-3242, Bethesda MD (1991), Vols 1-3. Kabat provides multiple sequence alignments of immunoglobulin chains from a large number of species antibody isotypes. According to a single numbering system, the Kabat numbering system numbers the aligned sequences. The Kabat sequence has been updated since 1991 and is available as an electronic sequence database (currently available from the Kabat database website; see also Nucleic Acids Research, 2000, 28(1), 214-218). By comparing with the Kabat reference sequence, any immunoglobulin sequence can be numbered according to Kabat. Therefore, the Kabat numbering system provides a unified system for numbering immunoglobulin chains.
在另一个实施方案中,本发明的靶向结合剂或抗体包含如表1或表2中所示的CDR3序列;或如表1或表2中所示的CDR1、CDR2或CDR3序列中的任何一个;或如表1中所示的重链可变区序列的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列;或如表2中所显示的轻链可变区序列的CDR1、CDR2和CDR3序列。In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody of the present invention comprises the CDR3 sequence as shown in Table 1 or Table 2; or any of the CDR1, CDR2 or CDR3 sequences as shown in Table 1 or Table 2. One; or the CDR1, CDR2, and CDR3 sequences of the heavy chain variable region sequence shown in Table 1; or the CDR1, CDR2, and CDR3 sequences of the light chain variable region sequence shown in Table 2.
在一些实施方案中,抗体是人源化抗体。In some embodiments, the antibody is a humanized antibody.
在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体,或其抗原结合部分,包含与SEQ ID NO:1的氨基酸具有至少90%同源性的重链可变区,且包含与SEQ ID NO:2的氨基酸序列具有至少90%同源性的轻链可变区。In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, comprises a heavy chain variable region having at least 90% homology with the amino acid of SEQ ID NO: 1, and comprises a heavy chain variable region with SEQ ID NO: The amino acid sequence of 2 has a light chain variable region with at least 90% homology.
在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体,或其抗原结合部分,包含与SEQ ID NO:3的氨基酸具有至少90%同源性的重链可变区,且包含与SEQ ID NO:4的氨基酸序列具有至少90%同源性的轻链可变区。In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody, or antigen binding portion thereof, comprises a heavy chain variable region having at least 90% homology with the amino acid of SEQ ID NO: 3, and comprises a heavy chain variable region with SEQ ID NO: The amino acid sequence of 4 has a light chain variable region with at least 90% homology.
在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体,或其抗原结合部分,包含与SEQ ID NO:5的氨基酸具有至少90%同源性的重链可变区,且包含与SEQ ID NO:6的氨基酸序列具有至少90%同源性的轻链可变区。In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, comprises a heavy chain variable region having at least 90% homology with the amino acid of SEQ ID NO: 5, and comprises a heavy chain variable region with SEQ ID NO: 5 The amino acid sequence of 6 has a light chain variable region with at least 90% homology.
在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体,或其抗原结合部分,包含与SEQ ID NO:7的氨基酸具有至少90%同源性的重链可变区,且包含与SEQ ID NO:8的氨基酸序列具有至少90%同源性的轻链可变区。In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, comprises a heavy chain variable region having at least 90% homology with the amino acid of SEQ ID NO: 7, and comprises the same as SEQ ID NO: The amino acid sequence of 8 has a light chain variable region with at least 90% homology.
在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体,或其抗原结合部分,包含与SEQ ID NO:9的氨基酸具有至少90%同源性的重链可变区,且包含与SEQ ID NO:10的氨基酸序列具有至少90%同源性的轻链可变区。In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, comprises a heavy chain variable region having at least 90% homology with the amino acid of SEQ ID NO: 9 and comprises the same as SEQ ID NO: The amino acid sequence of 10 has a light chain variable region with at least 90% homology.
在另一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体,或其抗原结合部分,包含与SEQ ID NO:11的氨基酸具有至少90%同源性的重链可变区,且包含与SEQ ID NO:12的氨基酸序列具有至少90%同源性的轻链可变区。In another embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, comprises a heavy chain variable region having at least 90% homology with the amino acid of SEQ ID NO: 11, and comprises a heavy chain variable region with SEQ ID NO: The amino acid sequence of 12 has a light chain variable region with at least 90% homology.
在一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂或抗体包含本文所公开的CDR的变体或衍生物,跨越本文所公开的轻链序列或重链序列的框架区和CDR或本文所公开的抗体的框架区和CDR(尤其从FR1至FR4或CDR1至CDR3) 的连续序列。变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,所述靶向结合剂或抗体包含这样的序列,该序列具有如表1或表2中所示的CDR1、CDR2或CDR3的连续序列、本文所公开的轻链序列或重链序列、或本文所公开的单克隆抗体的任何中的多达20个、16个、10个、9个或更少,例如,1个、2个、3个、4个、5个或6个氨基酸增加、置换、缺失和/或插入。变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,所述靶向结合剂或抗体包含这样的序列,该序列具有如表1或表2中所示的CDR1、CDR2或CDR3的连续序列、本文所公开的轻链序列或重链序列、或本文所公开的单克隆抗体的任何中的1个、2个、3个氨基酸增加、置换、缺失和/或插入。变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,所述靶向结合剂或抗体包含这样的序列,该序列与如表1或表2中所示的CDR1、CDR2或CDR3的连续序列、本文所公开的轻链序列或重链序列、或本文所公开的单克隆抗体中的任何一者具有至少约60%、70%、80%、85%、90%、95%、98%或约99%氨基酸同源性。两个氨基酸序列的同源性百分比可通过本领域中的技术人员已知的任何方法来确定,所述方法包括但不限于,成对蛋白质比对。在一个实施方案中,变体包括本文所公开的CDR序列或轻链序列或重链序列中的改变,所述改变是天然存在的或通过利用重组DNA技术或突变技术对天然序列进行体外工程化来引入。天然存在的变体包括在针对外源抗原的抗体的生成过程中对应种系核苷酸序列中体内生成的那些。In one embodiment, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprises a variant or derivative of the CDR disclosed herein, spanning the framework region of the light chain sequence or heavy chain sequence disclosed herein and the CDR or the framework of the antibody disclosed herein Regions and CDRs (especially from FR1 to FR4 or CDR1 to CDR3). Variants include a targeted binding agent or antibody, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprising a sequence having the continuous sequence of CDR1, CDR2 or CDR3 as shown in Table 1 or Table 2, the light disclosed herein Chain sequence or heavy chain sequence, or any of the monoclonal antibodies disclosed herein, up to 20, 16, 10, 9 or less, for example, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 amino acid additions, substitutions, deletions and/or insertions. Variants include a targeted binding agent or antibody, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprising a sequence having the continuous sequence of CDR1, CDR2 or CDR3 as shown in Table 1 or Table 2, the light disclosed herein Chain sequence or heavy chain sequence, or 1, 2, 3 amino acid additions, substitutions, deletions and/or insertions in any of the monoclonal antibodies disclosed herein. Variants include a targeted binding agent or antibody, the targeted binding agent or antibody comprising a sequence that is consistent with the continuous sequence of CDR1, CDR2 or CDR3 as shown in Table 1 or Table 2, and the light disclosed herein. Chain sequence or heavy chain sequence, or any of the monoclonal antibodies disclosed herein, have at least about 60%, 70%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, 98%, or about 99% amino acid homology Sex. The percent homology of two amino acid sequences can be determined by any method known to those skilled in the art, including but not limited to, paired protein alignment. In one embodiment, the variant includes an alteration in the CDR sequence or light chain sequence or heavy chain sequence disclosed herein, the alteration is naturally occurring or through the use of recombinant DNA technology or mutation technology to engineer the natural sequence in vitro To introduce. Naturally occurring variants include those produced in vivo in the corresponding germline nucleotide sequence during the production of antibodies against foreign antigens.
在一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂包含:In one embodiment, the targeted binding agent comprises:
具有SEQ ID NO:13、16、19、22、25或28所示氨基酸序列的CDR1,具有SEQ ID NO:14、17、20、23、26或29所示氨基酸序列的CDR2,或具有SEQ ID NO:15、18、21、24、27或30所示氨基酸序列的CDR3,或它们的变体中的一个或多个;和/或CDR1 having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 13, 16, 19, 22, 25, or 28, CDR2 having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 14, 17, 20, 23, 26, or 29, or having SEQ ID NO: CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in 15, 18, 21, 24, 27 or 30, or one or more of their variants; and/or
具有SEQ ID NO:31、34、37、40、43或46所示氨基酸序列的CDR1,具有SEQ ID NO:32、35、38、41、44或47所示氨基酸序列的CDR2,或具有SEQ ID NO:33、36、39、42、45或48所示氨基酸序列的CDR3,或它们的变体中的一个或多个;CDR1 having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 31, 34, 37, 40, 43, or 46, CDR2 having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 32, 35, 38, 41, 44, or 47, or having SEQ ID NO: CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in NO: 33, 36, 39, 42, 45 or 48, or one or more of their variants;
优选地,所述变体的序列为包括多达20个、16个、10个、9个或更少,例如,1个、2个、3个、4个、5个或6个氨基酸的增加、置换、缺失和/或插入的任一所述序列,或所述变体的序列与任一所述序列具有至少60%、70%、80%、85%、90%、95%、98%或99%同源性。Preferably, the sequence of the variant includes up to 20, 16, 10, 9 or less, for example, an increase of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 amino acids , Substitution, deletion and/or insertion, or the sequence of the variant and any of the sequences have at least 60%, 70%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, 98% Or 99% homology.
在一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂为包含重链可变区和轻链可变区的PD-L1抗体或其抗原结合片段,其中:In one embodiment, the targeted binding agent is a PD-L1 antibody or an antigen-binding fragment thereof comprising a heavy chain variable region and a light chain variable region, wherein:
(i)所述重链可变区包含CDR1、CDR2和CDR3,其中:(i) The heavy chain variable region comprises CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3, wherein:
(a)CDR1具有与SEQ ID NO:13、16、19、22、25或28相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:13、16、19、22、25或28包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列;(a) CDR1 has the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 13, 16, 19, 22, 25, or 28 or contains 1, 2, or relative to SEQ ID NO: 13, 16, 19, 22, 25 or 28 Amino acid sequence with 3 amino acid residue substitutions;
(b)CDR2具有与SEQ ID NO:14、17、20、23、26或29相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:14、17、20、23、26或29包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列;(b) CDR2 has the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 14, 17, 20, 23, 26 or 29 or contains 1, 2, or relative to SEQ ID NO: 14, 17, 20, 23, 26 or 29 Amino acid sequence with 3 amino acid residue substitutions;
(c)CDR3具有与SEQ ID NO:15、18、21、24、27或30相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:15、18、21、24、27或30包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列;(c) CDR3 has the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 15, 18, 21, 24, 27 or 30 or contains 1, 2 or 1 relative to SEQ ID NO: 15, 18, 21, 24, 27 or 30 Amino acid sequence with 3 amino acid residue substitutions;
(ii)所述轻链可变区包含CDR1、CDR2和CDR3,其中:(ii) The light chain variable region comprises CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3, wherein:
(d)CDR1具有与SEQ ID NO:31、34、37、40、43或46相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:31、34、37、40、43或46包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列;(d) CDR1 has the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 31, 34, 37, 40, 43 or 46 or contains 1, 2 or 1 relative to SEQ ID NO: 31, 34, 37, 40, 43 or 46 Amino acid sequence with 3 amino acid residue substitutions;
(e)CDR2具有与SEQ ID NO:32、35、38、41、44或47相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:32、35、38、41、44或47包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列;(e) CDR2 has the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 32, 35, 38, 41, 44 or 47 or contains 1, 2 or 1 relative to SEQ ID NO: 32, 35, 38, 41, 44 or 47 Amino acid sequence with 3 amino acid residue substitutions;
(f)CDR3具有与SEQ ID NO:33、36、39、42、45或48相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:33、36、39、42、45或48包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列。(f) CDR3 has the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 33, 36, 39, 42, 45 or 48 or contains 1, 2 or 1 relative to SEQ ID NO: 33, 36, 39, 42, 45 or 48 Amino acid sequence with 3 amino acid residue substitutions.
在一个实施方案中,变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,其包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the variant includes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:1相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:1包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH序列;(a) A VH sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO:1 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO:1;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:2相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:2包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL序列。(b) A VL sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 2 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 2.
在一个实施方案中,变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,其包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the variant includes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:3相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:3包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH序列;(a) A VH sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 3 or an amino acid sequence containing 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 3;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:4相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:4包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL序列。(b) A VL sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 4 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 4.
在一个实施方案中,变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,其包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the variant includes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:5相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:5包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH序列;(a) A VH sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 5 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 5;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:6相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:6包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL序列。(b) A VL sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 6 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 6.
在一个实施方案中,变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,其包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the variant includes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:7相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:7包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH序列;(a) A VH sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 7 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 7;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:8相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:8包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL序列。(b) A VL sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 8 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 8.
在一个实施方案中,变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,其包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the variant includes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:9相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:9包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH序列;(a) A VH sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 9 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 9;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:10相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:10包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL序列。(b) A VL sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 10 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 10.
在一个实施方案中,变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,其包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the variant includes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:11相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:11包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH序列;(a) A VH sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 11 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 11;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:12相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:12包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL序列。(b) A VL sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 12 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 12.
在另一个实施方案中,变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,其包含以下序列:In another embodiment, the variant includes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:13相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:13包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR1;(a) VH CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 13 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 13;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:14相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:14包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR2;(b) VH CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 14 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 14;
(c)具有与SEQ ID NO:15相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:15包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR3;(c) VH CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 15 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 15;
(d)具有与SEQ ID NO:31相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:31包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR1;(d) VL CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 31 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 31;
(e)具有与SEQ ID NO:32相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:32包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR2;(e) VL CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 32 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 32;
(f)具有与SEQ ID NO:33相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:33包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR3。(f) VL CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 33 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 33.
在另一个实施方案中,变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,其包含以下序列:In another embodiment, the variant includes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:16相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:16包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR1;(a) VH CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 16 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 16;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:17相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:17包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR2;(b) VH CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 17 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 17;
(c)具有与SEQ ID NO:18相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:18包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR3;(c) VH CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 18 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 18;
(d)具有与SEQ ID NO:34相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:34 包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR1;(d) VL CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 34 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 34;
(e)具有与SEQ ID NO:35相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:35包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR2;(e) VL CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 35 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 35;
(f)具有与SEQ ID NO:36相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:36包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR3。(f) VL CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 36 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 36.
在另一个实施方案中,变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,其包含以下序列:In another embodiment, the variant includes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:19相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:19包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR1;(a) VH CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 19 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 19;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:20相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:20包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR2;(b) VH CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 20 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 20;
(c)具有与SEQ ID NO:21相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:21包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR3;(c) VH CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 21 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 21;
(d)具有与SEQ ID NO:37相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:37包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR1;(d) VL CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 37 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 37;
(e)具有与SEQ ID NO:38相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:38包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR2;(e) VL CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 38 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 38;
(f)具有与SEQ ID NO:39相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:39包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR3。(f) VL CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 39 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 39.
在另一个实施方案中,变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,其包含以下序列:In another embodiment, the variant includes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:22相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:22包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR1;(a) VH CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 22 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 22;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:23相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:23包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR2;(b) VH CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 23 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 23;
(c)具有与SEQ ID NO:24相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:24包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR3;(c) VH CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 24 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 24;
(d)具有与SEQ ID NO:40相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:40包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR1;(d) VL CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 40 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 40;
(e)具有与SEQ ID NO:41相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:41包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR2;(e) VL CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 41 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 41;
(f)具有与SEQ ID NO:42相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:42包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR3。(f) VL CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 42 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 42.
在另一个实施方案中,变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,其包含以下序列:In another embodiment, the variant includes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:25相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:25包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR1;(a) VH CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 25 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 25;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:26相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:26 包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR2;(b) VH CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 26 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 26;
(c)具有与SEQ ID NO:27相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:27包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR3;(c) VH CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 27 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 27;
(d)具有与SEQ ID NO:43相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:43包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR1;(d) VL CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 43 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 43;
(e)具有与SEQ ID NO:44相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:44包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR2;(e) VL CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 44 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 44;
(f)具有与SEQ ID NO:45相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:45包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR3。(f) VL CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 45 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 45.
在另一个实施方案中,变体包括靶向结合剂或抗体,其包含以下序列:In another embodiment, the variant includes a targeted binding agent or antibody, which comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:28相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:28包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR1;(a) VH CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 28 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 28;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:29相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:29包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR2;(b) VH CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 29 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 29;
(c)具有与SEQ ID NO:30相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:30包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR3;(c) VH CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 30 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 30;
(d)具有与SEQ ID NO:46相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:46包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR1;(d) VL CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 46 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 46;
(e)具有与SEQ ID NO:47相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:47包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR2;(e) VL CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 47 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 47;
(f)具有与SEQ ID NO:48相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:48包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR3。(f) VL CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 48 or an amino acid sequence containing 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 48.
优选地,所述抗体或其抗原结合片段包含:SEQ ID NO:13所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR1、SEQ ID NO:14所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR2、SEQ ID NO:15所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR3、SEQ ID NO:31所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR1、SEQ ID NO:32所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR2、和SEQ ID NO:33所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR3。Preferably, the antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof comprises the heavy chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 13, the heavy chain CDR2 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 14 and the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 15 The heavy chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 31, the light chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 32, and the light chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 33.
优选地,所述抗体或其抗原结合片段包含:SEQ ID NO:16所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR1、SEQ ID NO:17所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR2、SEQ ID NO:18所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR3、SEQ ID NO:34所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR1、SEQ ID NO:35所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR2、和SEQ ID NO:36所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR3。Preferably, the antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof comprises: the heavy chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 16, the heavy chain CDR2 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 17, the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 18 The heavy chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 34, the light chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 35, and the light chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 36.
优选地,所述抗体或其抗原结合片段包含:SEQ ID NO:19所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR1、SEQ ID NO:20所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR2、SEQ ID NO:21所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR3、SEQ ID NO:37所示氨基酸序列 的轻链CDR1、SEQ ID NO:38所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR2、和SEQ ID NO:39所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR3。Preferably, the antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof comprises: heavy chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 19, heavy chain CDR2 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 20, and amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 21 The heavy chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 37, the light chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 38, and the light chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 39.
优选地,所述抗体或其抗原结合片段包含:SEQ ID NO:22所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR1、SEQ ID NO:23所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR2、SEQ ID NO:24所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR3、SEQ ID NO:40所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR1、SEQ ID NO:41所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR2、和SEQ ID NO:42所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR3。Preferably, the antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof comprises: heavy chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 22, heavy chain CDR2 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 23, and amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 24 The heavy chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 40, the light chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 41, and the light chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 42.
优选地,所述抗体或其抗原结合片段包含:SEQ ID NO:25所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR1、SEQ ID NO:26所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR2、SEQ ID NO:27所氨基酸序列示的重链CDR3、SEQ ID NO:43所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR1、SEQ ID NO:44所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR2、和SEQ ID NO:45所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR3。Preferably, the antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof comprises: the heavy chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 25, the heavy chain CDR2 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 26, and the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 27 The heavy chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 43, the light chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 44, and the light chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 45.
优选地,所述抗体或其抗原结合片段包含:SEQ ID NO:28所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR1、SEQ ID NO:29所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR2、SEQ ID NO:30所示氨基酸序列的重链CDR3、SEQ ID NO:46所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR1、SEQ ID NO:47所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR2、和SEQ ID NO:48所示氨基酸序列的轻链CDR3。Preferably, the antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof comprises: heavy chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 28, heavy chain CDR2 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 29, and amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 30 The heavy chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 46, the light chain CDR1 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 47, and the light chain CDR3 of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 48.
在一个实施方案中,衍生物可以是异种抗体,即其中两个或多个抗体连接在一起的抗体。衍生物包括已经过化学修饰的抗体。实例包括一种或多种聚合物的共价结合,比如水可溶性聚合物、N-连接的或O-连接的碳水化合物、糖、磷酸盐、和/或其它这样的分子。衍生物以所结合的分子的类型或位置不同于天然存在的抗体或起始抗体的方式来修饰。衍生物还包括抗体中天然存在的一种或多种化学基团的缺失。In one embodiment, the derivative may be a heterogeneous antibody, that is, an antibody in which two or more antibodies are linked together. Derivatives include antibodies that have been chemically modified. Examples include covalent bonding of one or more polymers, such as water-soluble polymers, N-linked or O-linked carbohydrates, sugars, phosphates, and/or other such molecules. Derivatives are modified in such a way that the type or location of the bound molecule is different from the naturally occurring antibody or the starting antibody. Derivatives also include the deletion of one or more chemical groups naturally occurring in the antibody.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,提供编码所述靶向结合剂的分离的核酸、包含此类核酸的载体和宿主细胞和用于产生所述靶向结合剂的重组技术。In some embodiments of the present invention, an isolated nucleic acid encoding the targeted binding agent, vectors and host cells containing such nucleic acid, and recombinant technology for producing the targeted binding agent are provided.
优选地,SEQ ID NO:1所示氨基酸序列的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:71所示;优选地,SEQ ID NO:2所示氨基酸序列的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:72所示;优选地,SEQ ID NO:3所示氨基酸序列的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:73所示;优选地,SEQ ID NO:4所示氨基酸序列的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:74所示;优选地,SEQ ID NO:5所示氨基酸序列的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:75所示;优选地,SEQ ID NO:6所示氨基酸序列的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:76所示;优选地,SEQ ID NO:7所示氨基酸序列的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:77所示;优选地,SEQ ID NO:8所示氨基酸序列的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:78所示;优选地,SEQ ID NO:9所示氨基酸序列的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:79所示;优选地,SEQ ID NO:10所示氨基酸序列的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:80所示;优选地,SEQ ID NO:11所示氨基酸序列的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:81所示;优选地,SEQ ID NO:12所示氨基酸序列的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:82所示。Preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 71; preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 72; Preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 73; preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 4 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 74; Preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 5 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 75; preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 6 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 76; Preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 7 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 77; preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 8 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 78; Preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 9 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 79; preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 10 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 80; Preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 11 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 81; preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 12 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 82.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,提供一种载体,该载体适合用于表达编码前述任何一种抗-PD-L1抗体的核酸。在又一个具体方面中,所述载体还包含适合用于表达该核酸的宿主细胞。在又一个具体方面中,所述宿主细胞是真核细胞或原核细胞。在又一个具体方面中,所述真核细胞是哺乳动物细胞,如中国仓鼠卵巢(CHO)。In some embodiments of the present invention, a vector is provided, which is suitable for expressing a nucleic acid encoding any of the aforementioned anti-PD-L1 antibodies. In yet another specific aspect, the vector further comprises a host cell suitable for expressing the nucleic acid. In yet another specific aspect, the host cell is a eukaryotic cell or a prokaryotic cell. In yet another specific aspect, the eukaryotic cell is a mammalian cell, such as Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO).
在本发明的一些实施方案中,提供制备抗-PD-L1抗体或其抗原结合片段的方法,其包括在适合用于产生此类抗体或片段的条件下,培养含有适合于表达的形式的核酸的宿主细胞,该核酸编码前述任何一种抗-PD-L1抗体或抗原结合片段,并且回收所述抗体或片段。In some embodiments of the present invention, a method for preparing an anti-PD-L1 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof is provided, which includes culturing a nucleic acid containing a form suitable for expression under conditions suitable for the production of such antibody or fragment The nucleic acid encodes any of the aforementioned anti-PD-L1 antibodies or antigen-binding fragments, and the antibodies or fragments are recovered.
为了重组产生抗体,分离编码它的核酸,并将其插入可复制载体,用于进一步克隆(DNA扩增)或表达。可使用常规流程容易的分离编码单克隆抗体的DNA并测序(如使用能够与编码抗体重链和轻链的基因特异结合的寡核苷酸探针)。可利用许多载体。载体的选择部分取决于将要使用的宿主细胞。通常,优选的宿主细胞是原核或真核(通常是哺乳动物)起源的。To produce an antibody recombinantly, the nucleic acid encoding it is isolated and inserted into a replicable vector for further cloning (DNA amplification) or expression. The DNA encoding the monoclonal antibody can be easily separated and sequenced using conventional procedures (for example, using oligonucleotide probes that can specifically bind to the genes encoding the heavy and light chains of the antibody). Many carriers are available. The choice of vector depends in part on the host cell to be used. Generally, the preferred host cell is of prokaryotic or eukaryotic (usually mammalian) origin.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,提供了一种PD-L1抗体的嵌合抗原受体,其包含PD-L1抗体可变区序列。优选地,所述的PD-L1抗体的嵌合抗原受体,其还包含一个或多个选自由以下组成的组的元件:信号肽、接头序列、跨膜结构域、内部结构域和共刺激结构域。更优选地,所述的PD-L1抗体的嵌合抗原受体包含CD8抗原信号肽、PD-L1抗体的轻链可变区、PD-L1抗体的重链可变区、CD28元件、4-1BBL元件以及CD3ζ元件。优选地,CD8抗原信号肽的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:51所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:52所示。优选地,所述CD28元件的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:53所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:54所示。优选地,所述4-1BBL元件的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:55所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:56所示。优选地,所述CD3ζ元件的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:57所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:58所示。更优选地,所述嵌合抗原受体的编码核酸序列选自59、61、63、65、67或69所示的序列,其相应的氨基酸序列选自60、62、64、66、68或70所示的序列。In some embodiments of the present invention, there is provided a chimeric antigen receptor of a PD-L1 antibody, which comprises a PD-L1 antibody variable region sequence. Preferably, the chimeric antigen receptor of the PD-L1 antibody further comprises one or more elements selected from the group consisting of: signal peptide, linker sequence, transmembrane domain, internal domain and costimulatory Structure domain. More preferably, the chimeric antigen receptor of the PD-L1 antibody comprises the CD8 antigen signal peptide, the light chain variable region of the PD-L1 antibody, the heavy chain variable region of the PD-L1 antibody, the CD28 element, the 4- 1BBL element and CD3ζ element. Preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the CD8 antigen signal peptide is shown in SEQ ID NO: 51, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 52. Preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the CD28 element is shown in SEQ ID NO:53, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:54. Preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the 4-1BBL element is shown in SEQ ID NO: 55, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 56. Preferably, the coding nucleic acid sequence of the CD3ζ element is shown in SEQ ID NO: 57, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 58. More preferably, the nucleic acid sequence encoding the chimeric antigen receptor is selected from the sequence shown in 59, 61, 63, 65, 67 or 69, and the corresponding amino acid sequence is selected from 60, 62, 64, 66, 68 or 70 shown in the sequence.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,提供了编码PD-L1抗体的嵌合抗原受体 的核酸。In some embodiments of the present invention, a nucleic acid encoding a chimeric antigen receptor of a PD-L1 antibody is provided.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,提供了含有所述核酸的重组载体、表达盒、重组病毒或重组细胞。In some embodiments of the present invention, a recombinant vector, expression cassette, recombinant virus or recombinant cell containing the nucleic acid is provided.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,提供了一种CAR构建体,其包含编码嵌合抗原受体的核酸。In some embodiments of the present invention, there is provided a CAR construct comprising a nucleic acid encoding a chimeric antigen receptor.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,提供了一种T细胞,其用所述的CAR构建体转导。In some embodiments of the present invention, a T cell is provided, which is transduced with the CAR construct.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,还提供了一种PD-L1 CAR-T细胞的制备方法,所述方法包括以下步骤:In some embodiments of the present invention, a method for preparing PD-L1 CAR-T cells is also provided, and the method includes the following steps:
(a)构建含有可识别人PD-L1的CAR元件(即本文中的PD-L1抗体可变区序列)的载体,所述载体可以是真核表达载体或慢病毒载体,优选慢病毒载体,优选地,所述载体是慢病毒载体pHAGE-EF1α-MCS-ZsGreen;(a) Construct a vector containing a CAR element that can recognize human PD-L1 (that is, the PD-L1 antibody variable region sequence herein). The vector can be a eukaryotic expression vector or a lentiviral vector, preferably a lentiviral vector, Preferably, the vector is a lentiviral vector pHAGE-EF1α-MCS-ZsGreen;
(b)用步骤(a)构建的载体转染或感染宿主T细胞,产生带有带有可识别人PD-L1的CAR元件的CAR-T细胞。(b) Transfect or infect host T cells with the vector constructed in step (a) to produce CAR-T cells with CAR elements that can recognize human PD-L1.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,还提供了一种PD-L1 CAR-T细胞的制备方法,所述方法包括以下步骤:In some embodiments of the present invention, a method for preparing PD-L1 CAR-T cells is also provided, and the method includes the following steps:
(a)构建含有可识别人PD-L1的CAR元件(即本文中的PD-L1抗体可变区序列)的载体,所述载体可以是真核表达载体或慢病毒载体,优选慢病毒载体;优选地,所述载体是慢病毒载体pHAGE-EF1α-MCS-ZsGreen;(a) Constructing a vector containing a CAR element that can recognize human PD-L1 (ie, the PD-L1 antibody variable region sequence herein). The vector can be a eukaryotic expression vector or a lentiviral vector, preferably a lentiviral vector; Preferably, the vector is a lentiviral vector pHAGE-EF1α-MCS-ZsGreen;
(b)将步骤(a)构建的载体转染至包装细胞系中,产生带有可识别人PD-L1的CAR元件的慢病毒颗粒;(b) Transfect the vector constructed in step (a) into a packaging cell line to produce lentiviral particles with CAR elements that can recognize human PD-L1;
(c)将所述载体或慢病毒颗粒转染或感染宿主T细胞,产生带有带有可识别人PD-L1的CAR元件的CAR-T细胞。(c) Transfecting or infecting host T cells with the vector or lentiviral particles to produce CAR-T cells with CAR elements that can recognize human PD-L1.
在一个实施方案中,CAR元件包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the CAR element comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:1相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:1包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH序列;(a) A VH sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO:1 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO:1;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:2相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:2包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL序列;(b) A VL sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 2 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 2;
在一个实施方案中,CAR元件包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the CAR element comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:3相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:3包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH序列;(a) A VH sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 3 or an amino acid sequence containing 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 3;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:4相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:4包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL序列;(b) A VL sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 4 or an amino acid sequence containing 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 4;
在一个实施方案中,CAR元件包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the CAR element comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:5相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:5包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH序列;(a) A VH sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 5 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 5;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:6相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:6包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL序列;(b) A VL sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 6 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 6;
在一个实施方案中,CAR元件包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the CAR element comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:7相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:7包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH序列;(a) A VH sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 7 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 7;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:8相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:8包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL序列;(b) A VL sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 8 or an amino acid sequence containing 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 8;
在一个实施方案中,CAR元件包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the CAR element comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:9相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:9包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH序列;(a) A VH sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 9 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 9;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:10相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:10包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL序列;(b) A VL sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 10 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 10;
在一个实施方案中,CAR元件包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the CAR element comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:11相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:11包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH序列;(a) A VH sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 11 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 11;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:12相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:12包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL序列;(b) A VL sequence having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 12 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 12;
在一个实施方案中,CAR元件包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the CAR element comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:13相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:13包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR1;(a) VH CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 13 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 13;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:14相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:14包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR2;(b) VH CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 14 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 14;
(c)具有与SEQ ID NO:15相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:15包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR3;(c) VH CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 15 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 15;
(d)具有与SEQ ID NO:31相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:31包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR1;(d) VL CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 31 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 31;
(e)具有与SEQ ID NO:32相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:32包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR2;(e) VL CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 32 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 32;
(f)具有与SEQ ID NO:33相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:33包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR3。(f) VL CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 33 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 33.
在一个实施方案中,CAR元件包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the CAR element comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:16相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:16 包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR1;(a) VH CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 16 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 16;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:17相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:17包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR2;(b) VH CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 17 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 17;
(c)具有与SEQ ID NO:18相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:18包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR3;(c) VH CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 18 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 18;
(d)具有与SEQ ID NO:34相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:34包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR1;(d) VL CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 34 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 34;
(e)具有与SEQ ID NO:35相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:35包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR2;(e) VL CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 35 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 35;
(f)具有与SEQ ID NO:36相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:36包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR3。(f) VL CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 36 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 36.
在一个实施方案中,CAR元件包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the CAR element comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:19相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:19包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR1;(a) VH CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 19 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 19;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:20相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:20包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR2;(b) VH CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 20 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 20;
(c)具有与SEQ ID NO:21相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:21包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR3;(c) VH CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 21 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 21;
(d)具有与SEQ ID NO:37相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:37包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR1;(d) VL CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 37 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 37;
(e)具有与SEQ ID NO:38相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:38包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR2;(e) VL CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 38 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 38;
(f)具有与SEQ ID NO:39相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:39包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR3。(f) VL CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 39 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 39.
在一个实施方案中,CAR元件包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the CAR element comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:22相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:22包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR1;(a) VH CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 22 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 22;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:23相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:23包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR2;(b) VH CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 23 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 23;
(c)具有与SEQ ID NO:24相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:24包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR3;(c) VH CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 24 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 24;
(d)具有与SEQ ID NO:40相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:40包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR1;(d) VL CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 40 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 40;
(e)具有与SEQ ID NO:41相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:41包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR2;(e) VL CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 41 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 41;
(f)具有与SEQ ID NO:42相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:42包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR3。(f) VL CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 42 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 42.
在一个实施方案中,CAR元件包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the CAR element comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:25相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:25包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR1;(a) VH CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 25 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 25;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:26相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:26包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR2;(b) VH CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 26 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 26;
(c)具有与SEQ ID NO:27相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:27包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR3;(c) VH CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 27 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 27;
(d)具有与SEQ ID NO:43相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:43包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR1;(d) VL CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 43 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 43;
(e)具有与SEQ ID NO:44相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:44包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR2;(e) VL CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 44 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 44;
(f)具有与SEQ ID NO:45相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:45包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR3。(f) VL CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 45 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 45.
在一个实施方案中,CAR元件包含以下序列:In one embodiment, the CAR element comprises the following sequence:
(a)具有与SEQ ID NO:28相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:28包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR1;(a) VH CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 28 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 28;
(b)具有与SEQ ID NO:29相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:29包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR2;(b) VH CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 29 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 29;
(c)具有与SEQ ID NO:30相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:30包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VH CDR3;(c) VH CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 30 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 30;
(d)具有与SEQ ID NO:46相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:46包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR1;(d) VL CDR1 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 46 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 46;
(e)具有与SEQ ID NO:47相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:47包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR2;(e) VL CDR2 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 47 or an amino acid sequence with 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 47;
(f)具有与SEQ ID NO:48相同的氨基酸序列或相对于SEQ ID NO:48包含1个、2个或3个氨基酸残基置换的氨基酸序列的VL CDR3。(f) VL CDR3 having the same amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 48 or an amino acid sequence containing 1, 2, or 3 amino acid residue substitutions relative to SEQ ID NO: 48.
术语“CDR区”或“CDR”意在表示赋予抗体抗原结合特异性的抗体的重链和轻链的高变区。CDR可根据Kabat系统(Kabat,E.A.等(1991)Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest,第5版.US Department of Health and Human Services,Public Service,NIH,Washington)和更近的版本来定义。抗体通常含有3个重链CDR和3个轻链CDR。本文使用术语CDR来表示,根据情况,这些区域之一或这些区域的一些或甚至全部,这些区域含有负责通过抗体对其识别的抗原或表位的亲和力进行结合的氨基酸 残基的大部分。The term "CDR region" or "CDR" is intended to mean the hypervariable regions of the heavy and light chains of an antibody that confer antigen binding specificity to the antibody. CDR can be defined according to the Kabat system (Kabat, E.A., etc. (1991) Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, 5th edition. US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Service, NIH, Washington) and more recent versions. Antibodies usually contain 3 heavy chain CDRs and 3 light chain CDRs. The term CDR is used herein to indicate that, depending on the situation, one of these regions or some or even all of these regions contains most of the amino acid residues responsible for binding by the affinity of the antibody to the antigen or epitope recognized by the antibody.
重链的第三CDR(HCDR3)具有较大尺寸的可变性(较大多样性基本上由于使其产生的基因的排列机制)。虽然已知最长的尺寸为26,其可短至2个氨基酸。CDR长度还可根据特定的基本框架可适应的长度来变化。功能上,HCDR3在决定抗体的特异性中起重要作用(Segal等,PNAS,71:4298-4302,1974,Amit,Science,233:747-753,1986,Chothia,J.Mol.Biol.,196:901-917,1987,Chothia等,Nature,342:877-883,1989,Caton,J.Immunol.,144:1965-1968,1990,Sharon,PNAS,87:4814-4817,1990,Sharon等,J.Immunol.,144:4863-4869,1990,Kabat等,J.Immunol.,147:1709-1719,1991)。The third CDR (HCDR3) of the heavy chain has a larger size of variability (larger diversity is basically due to the gene arrangement mechanism that makes it produced). Although the longest known size is 26, it can be as short as 2 amino acids. The length of the CDR can also vary according to the adaptable length of the specific basic framework. Functionally, HCDR3 plays an important role in determining the specificity of antibodies (Segal et al., PNAS, 71: 4298-4302, 1974, Amit, Science, 233: 747-753, 1986, Chothia, J. Mol. Biol., 196 :901-917,1987, Chothia etc., Nature, 342:877-883,1989, Caton, J.Immunol., 144:1965-1968,1990, Sharon, PNAS, 87:4814-4817,1990, Sharon etc., J. Immunol., 144:4863-4869, 1990, Kabat et al., J. Immunol., 147:1709-1719, 1991).
本文所提到的术语“CDR组”包括CDR1、CDR2和CDR3。因此,HCDR组指HCDR1、HCDR2和HCDR3,和LCDR组指LCDR1、LCDR2和LCDR3。The term "CDR group" mentioned herein includes CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3. Therefore, the HCDR group refers to HCDR1, HCDR2, and HCDR3, and the LCDR group refers to LCDR1, LCDR2, and LCDR3.
本发明的VH和VL区和CDR的变体,包括其氨基酸序列在本文列出且其可应用于PD-L1的靶向结合剂和抗体的那些,可通过序列改变或突变方法和筛选具有需要的特性的抗原靶向来获得。需要的特性的实例包括但不限于:相对于对抗原特异的已知抗体,对抗原增高的结合亲和力;相对于对抗原特异性的已知抗体,增高的抗原活性的中和(如果活性是已知的);在特定的摩尔比率时与已知抗体或配体对抗原的特定的竞争能力;免疫沉淀配体-受体复合物的能力;与特定的表位结合的能力;线性表位,例如,利用肽结合扫描鉴定的肽序列,例如,利用线性和/或限定构象中筛选的肽;构象表位,由非连续残基所形成;调节B7-H1或下游分子的新型生物活性的能力;结合和/或中和B7-H1和/或任何其它需要的性质的能力。在CDR、抗体VH或VL区和抗原结合位点的氨基酸序列中进行置换所需的技术是本领域中可获得的。可产生本文所公开的抗体分子的变体并用于本发明。继计算机化学在将多变量数据分析技术应用于结构/性质活性关系中的先导之后(Wold等,Multivariate data analysis in chemistry.Chemometrics–Mathematics and Statistics in Chemistry(编:B.Kowalski),D.Reidel PublishingCompany,Dordrecht,Holland,1984),利用熟知的数学技术可推导定量的抗体活性-性质关系,所述数学技术诸如统计回归、模式识别和分类(Norman等,Applied RegressionAnalysis.Wiley-Interscience;第3版(April 1998);Kandel,Abraham&Backer,Eric.Computer-Assisted Reasoning in Cluster Analysis.Prentice Hall PTR,(5月11日,1995);Krzanowski,Wojtek.Principles of Multivariate Analysis:A User’s Perspective(Oxford Statistical Science Series,No22(Paper)).Oxford University Press;(December2000);Witten,Ian H.&Frank,Eibe.Data Mining:Practical Machine Learning To olsand Techniques with Java Implementations.Morgan Kaufmann;(October11,1999);Denison David G.T.(Editor),Christopher C.Holmes,Bani K.Mallick,Adrian F.M.Smith.Bayesian Methods for Nonlinear Classification and Regression(Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics).John Wiley&Sons;(July 2002);Ghose,Arup K.&Viswanadhan,Vellarkad N.Combinatorial Library Design and Evaluation Principles,Software,Tools,and Applications in Drug Discovery)。在一些情况中,抗体的性质可来源于抗体序列、功能结构和三维结构的经验和理论模型(例如,可能接触残基或计算的物理化学性质的分析,且可单独地和组合地考虑这些性质。由VH域和VL域组成的抗体抗原结合位点通常由6个多肽的环形成:来自轻链可变域(VL)的3个和来自重链可变域(VH)的三个。对已知原子结构的抗体的分析已阐明了抗体结合位点的序列和三维结构之间的关系。这些关系暗示,除VH结构域中的第3区(环),结合位点环具有少量的主链构象之一:典型结构。已显示在特定的环中形成的典型结构通过其大小和在环和框架区二者中的关键位点处某些残基的存在来确定。VH and VL regions and CDR variants of the present invention, including those whose amino acid sequences are listed herein and which can be applied to PD-L1 targeted binding agents and antibodies, can be required by sequence change or mutation methods and screening. The characteristics of antigen targeting are obtained. Examples of required properties include, but are not limited to: increased binding affinity to antigen relative to known antibodies specific to antigen; neutralization of increased antigen activity relative to known antibodies specific to antigen (if the activity is already Known); specific ability to compete with known antibodies or ligands for antigen at a specific molar ratio; the ability to immunoprecipitate ligand-receptor complexes; the ability to bind to specific epitopes; linear epitopes, For example, peptide sequences identified by peptide binding scanning, for example, peptides screened in linear and/or defined conformations; conformational epitopes, formed by non-contiguous residues; ability to modulate new biological activities of B7-H1 or downstream molecules ; The ability to bind and/or neutralize B7-H1 and/or any other required properties. The techniques required to make substitutions in the amino acid sequences of the CDRs, antibody VH or VL regions, and antigen binding sites are available in the art. Variants of the antibody molecules disclosed herein can be produced and used in the present invention. Following the lead of computer chemistry in applying multivariate data analysis techniques to structure/property-activity relationships (Wold et al., Multivariate data analysis in chemistry.Chemometrics--Mathematics and Statistics in Chemistry (Editor: B. Kowalski), D. Reidel Publishing Company , Dordrecht, Holland, 1984), using well-known mathematical techniques to derive quantitative antibody activity-property relationships, such as statistical regression, pattern recognition and classification (Norman et al., Applied Regression Analysis. Wiley-Interscience; 3rd edition ( April 1998); Kandel,Abraham&Backer,Eric.Computer-Assisted Reasoning in Cluster Analysis.Prentice Hall PTR, (May 11, 1995); Krzanowski,Wojtek.Principles of Multivariate, Analysis:A User'sPerspective(Oxcience Series 22 (Paper)). Oxford University Press; (December2000); Witten, Ian H. & Frank, Eibe. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning To ols and Techniques with Java Implementations Morgan Kaufmann; (October11, 1999); GT(Editor) David ,Christopher C. Holmes, Bani K. Mallick, Adrian FMSmith. Bayesian Methods for Nonlinear Classification and Regression (Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics). John Wiley&Sons; (July 2002); Ghose, Arupadhan K.&Viswanadhan Library Design and Evaluation Principles, Software, Tools, and Applications in Drug Discovery). In some cases, the properties of antibodies can be derived from empirical and theoretical models of antibody sequence, functional structure, and three-dimensional structure (for example, analysis of possible contact residues or calculated physicochemical properties, and these properties can be considered individually and in combination. The antibody antigen binding site composed of VH domain and VL domain is usually formed by 6 polypeptide loops: 3 from the light chain variable domain (VL) and three from the heavy chain variable domain (VH). Right. The analysis of antibodies with known atomic structure has clarified the relationship between the sequence of the antibody binding site and the three-dimensional structure. These relationships suggest that, except for the third region (loop) in the VH domain, the binding site loop has a small amount of main One of the chain conformations: canonical structure. It has been shown that the canonical structure formed in a specific loop is determined by its size and the presence of certain residues at key positions in both the loop and the framework region.
该序列-结构关系的研究可用于预测已知序列(除未知的三维结构之外)的抗体中的那些残基,其在维持其CDR环的三维结构且从而维持结合特异性中是重要的。这些预测可通过将预测与来自先导最优实验的输出信息相比较来支持。在一个结构方法中,可利用任何免费提供的或商业上的软件包(诸如WAM)来创建抗体分子的模型。然后可使用蛋白质可视和分析软件包(诸如Insight II(Accelrys,Inc.)或Deep View)来评估CDR中的每个位置处可能的置换。然后可利用该信息来进行可能对活性具有极小影响或有利的影响或赋予其它需要的性质的置换。The study of the sequence-structure relationship can be used to predict those residues in antibodies of known sequences (except for the unknown three-dimensional structure), which are important in maintaining the three-dimensional structure of its CDR loops and thereby maintaining binding specificity. These predictions can be supported by comparing the predictions with the output from the leading optimal experiment. In a structural approach, any freely available or commercial software package (such as WAM) can be used to create a model of the antibody molecule. A protein visualization and analysis software package, such as Insight II (Accelrys, Inc.) or Deep View, can then be used to evaluate the possible substitutions at each position in the CDR. This information can then be used to perform substitutions that may have minimal or beneficial effects on activity or impart other desired properties.
本文所用的术语“多肽片段”指具有氨基末端和/或羧基末端缺失的多肽,但其中其余的氨基酸序列与所推断的天然存在的序列中的对应的位置相同,例如来自全长cDNA序列。片段长度通常为至少5个、6个、8个或10个氨基酸,优选长度为至少14个氨基酸,更优选长度为至少20个氨基酸,通常长度为至少50个氨基酸,和甚至更优选长度为至少70个氨基酸。如本文所用的术语“类似物”指由与所推断的氨基酸序列的部分具有充分同一性的至少25个氨基酸的片段组成的多肽,且其具有以下性质中的至少一个:(1)在适宜的结合条件下,与PD-L1的特异性结合,(2)阻断适当的PD-L1蛋白结合的能力,或(3)抑制PD-L1活性的能力。通常,多肽类似物包含关于天然存在的序列的保守氨基酸置换(或增加或缺 失)。类似物长度通常为至少20个氨基酸,优选长度为至少50个氨基酸或更长,且可通常与全长天然存在的多肽一样长。The term "polypeptide fragment" as used herein refers to a polypeptide having amino-terminal and/or carboxy-terminal deletions, but where the remaining amino acid sequence is the same as the corresponding position in the deduced naturally occurring sequence, for example, from a full-length cDNA sequence. Fragments are generally at least 5, 6, 8, or 10 amino acids in length, preferably at least 14 amino acids in length, more preferably at least 20 amino acids in length, usually at least 50 amino acids in length, and even more preferably at least in length 70 amino acids. The term "analog" as used herein refers to a polypeptide consisting of a fragment of at least 25 amino acids that has sufficient identity with a portion of the deduced amino acid sequence, and which has at least one of the following properties: (1) In appropriate Under binding conditions, specific binding to PD-L1, (2) the ability to block appropriate PD-L1 protein binding, or (3) the ability to inhibit PD-L1 activity. Generally, polypeptide analogs contain conservative amino acid substitutions (or additions or deletions) with respect to naturally occurring sequences. The analog is generally at least 20 amino acids in length, preferably at least 50 amino acids or longer in length, and can generally be as long as a full-length naturally occurring polypeptide.
肽类似物常作为具有与模板肽类似的性质的非肽药物而用于药物工业中。这些类型的非肽化合物被称作“肽模拟物”或“类肽物”。Fauchere,J.Adv.Drug Res.15:29(1986);Veber和Freidinger TINS第392页(1985);和Evans等J.Med.Chem.30:1229(1987),其通过引用并入本文。常借助于计算机的分子建模来开发这样的化合物。与治疗上有用的肽在结构上相似的肽模拟物可用于产生等效治疗或预防作用。一般,类肽物在结构上与范例肽(paradigm polypeptide)(即,具有生化性质或药理活性的多肽)相似,诸如人抗体,但其具有通过本领域中熟知的方法用选自由--CH2NH--、--CH2S--、--CH2-CH2--、--CH=CH--(顺式和反式)、--COCH2--、--CH(OH)CH2--和--CH2SO--组成的组的链接任选地替换的一个或多个肽链接。共有序列的一个或多个氨基酸被相同类型的D-氨基酸的系统置换(例如,D-赖氨酸替代L-赖氨酸)可用来产生更稳定的肽。并且,可通过了本领域中已知的方法来产生包含共有序列或基本上相同的共有序列变异的限定肽(Rizo和Gierasch Ann.Rev.Biochem.61:387(1992),通过引用并入本文);例如,通过添加能够形成使肽环化的分子内二硫键的内部半胱氨酸残基。Peptide analogs are often used in the pharmaceutical industry as non-peptide drugs with properties similar to template peptides. These types of non-peptide compounds are referred to as "peptidomimetics" or "peptoids". Fauchere, J. Adv. Drug Res. 15:29 (1986); Veber and Freidinger TINS page 392 (1985); and Evans et al. J. Med. Chem. 30:1229 (1987), which are incorporated herein by reference. Computer-based molecular modeling is often used to develop such compounds. Peptidomimetics that are structurally similar to therapeutically useful peptides can be used to produce equivalent therapeutic or preventive effects. Generally, peptoids are structurally similar to paradigm polypeptides (i.e., polypeptides with biochemical properties or pharmacological activities), such as human antibodies, but they can be selected from the group consisting of -CH2NH- by methods well known in the art. -, --CH2S--, --CH2-CH2--, --CH=CH-- (cis and trans), --COCH2--, --CH(OH)CH2-- and --CH2SO -One or more peptide links optionally replaced by the links of the composed group. The systematic substitution of one or more amino acids of the consensus sequence with the same type of D-amino acid (for example, D-lysine instead of L-lysine) can be used to produce more stable peptides. In addition, methods known in the art can be used to generate defined peptides containing consensus sequences or substantially the same consensus sequence variation (Rizo and Gierasch Ann. Rev. Biochem. 61:387 (1992), incorporated herein by reference ); For example, by adding internal cysteine residues capable of forming intramolecular disulfide bonds to cyclize the peptide.
本文所用的“抗体”可以是单独的或与已知技术所提供的其它氨基酸序列组合的单链抗体、寡克隆抗体、多克隆抗体、单克隆抗体(包括全长的单克隆抗体)、驼化的抗体(camelised antibody)、嵌合抗体、CDR移植抗体、多特异性抗体、双特异性抗体、催化抗体、嵌合抗体、人源化抗体、完全人抗体、抗独特型抗体和可以溶解的形式或结合的形式来标记的抗体以及其片段、变体或衍生物。抗体可来源于任何物种。抗体包含多肽或多肽的组,其由至少一个结合结构域组成,所述结合结构域从具有三维结合空间的多肽链的折叠形成,其中内表面形状和电荷分布与抗原的抗原决定簇的特征互补。抗体通常具有四聚形式,包含两个相同的多肽链的对,每对具有一条“轻”链和一条“重”链。每条轻/重链的可变区形成抗体结合位点。天然抗体通常是分子量约150Kd的异源四聚体糖蛋白,由两条相同的轻链和两条相同的重链组成。每条轻链通过一个共价二硫键与重链连接,而不同免疫球蛋白同种型的重链之间的二硫键的数目不同。每条重链和轻链还具有规则间隔的链内二硫键。每条重链在一端具有可变区(VH),其后为恒定区。每条轻链在一端具有可变区(VL)且在另一端具有恒定区;轻链的恒定区与重链的第一个恒定区相对,且轻链的可变区与重链的可变区相对。基于轻链恒定区的氨基酸序列将轻链分类为λ链或κ链。κ轻链 的可变区在本文中还可表示为VK。The "antibody" used herein can be a single chain antibody, oligoclonal antibody, polyclonal antibody, monoclonal antibody (including full-length monoclonal antibody), camelized, alone or in combination with other amino acid sequences provided by known techniques. Camelised antibodies, chimeric antibodies, CDR grafted antibodies, multispecific antibodies, bispecific antibodies, catalytic antibodies, chimeric antibodies, humanized antibodies, fully human antibodies, anti-idiotypic antibodies and soluble forms Or labeled antibodies and their fragments, variants or derivatives in a combined form. Antibodies can be derived from any species. The antibody comprises a polypeptide or a group of polypeptides, which consists of at least one binding domain formed from the folding of a polypeptide chain with a three-dimensional binding space, wherein the inner surface shape and charge distribution are complementary to the characteristics of the antigen's epitope . Antibodies generally have a tetrameric form, consisting of two identical pairs of polypeptide chains, each pair having a "light" chain and a "heavy" chain. The variable region of each light/heavy chain forms an antibody binding site. Natural antibodies are usually heterotetrameric glycoproteins with a molecular weight of about 150Kd, composed of two identical light chains and two identical heavy chains. Each light chain is connected to the heavy chain by a covalent disulfide bond, and the number of disulfide bonds between the heavy chains of different immunoglobulin isotypes is different. Each heavy and light chain also has regularly spaced intrachain disulfide bonds. Each heavy chain has a variable region (VH) at one end, followed by a constant region. Each light chain has a variable region (VL) at one end and a constant region at the other end; the constant region of the light chain is opposite to the first constant region of the heavy chain, and the variable region of the light chain is the same as the variable region of the heavy chain. District relative. The light chain is classified as lambda chain or kappa chain based on the amino acid sequence of the light chain constant region. The variable region of the kappa light chain may also be referred to herein as VK.
术语“可变区”还可用来描述重链或轻链的可变区。特定的氨基酸残基在轻链可变区和重链可变区之间形成分界。每条轻/重链对的可变区形成抗体结合位点。所述抗体可来源于任何哺乳动物,包括但不限于,人、猴、猪、马、兔、狗、猫、小鼠等。The term "variable region" can also be used to describe the variable region of a heavy or light chain. Specific amino acid residues form the boundary between the variable region of the light chain and the variable region of the heavy chain. The variable region of each light/heavy chain pair forms an antibody binding site. The antibody can be derived from any mammal, including, but not limited to, humans, monkeys, pigs, horses, rabbits, dogs, cats, mice and the like.
术语“抗体”包括本发明的抗体的结合片段,示例性的片段包括单链Fv(scFv)、单链抗体、单结构域抗体、结构域抗体、Fv片段、Fab片段、F(ab)′片段、F(ab′)2片段,表现出需要的生物活性的抗体片段、二硫键稳定的可变区(dsFv)、二聚可变区(双链抗体)、抗独特型抗体、胞内抗体、线性抗体、单链抗体分子和从抗体片段形成的多特异性抗体和以上中任何的表位结合片段。尤其是,抗体包括免疫球蛋白分子和免疫球蛋白分子的免疫活性片段,即,含有抗原结合位点的分子。免疫球蛋白分子可以是任何类型的(例如,IgG、IgE、IgM、IgD、IgA和IgY),任何种类(例如,IgG1、IgG2、IgG3、IgG4、IgA1和IgA2)或亚类的。The term "antibody" includes binding fragments of the antibodies of the present invention, and exemplary fragments include single-chain Fv (scFv), single-chain antibodies, single-domain antibodies, domain antibodies, Fv fragments, Fab fragments, F(ab)' fragments , F(ab′)2 fragments, antibody fragments showing the required biological activity, disulfide bond stabilized variable regions (dsFv), dimeric variable regions (diabodies), anti-idiotypic antibodies, intracellular antibodies , Linear antibodies, single-chain antibody molecules and multispecific antibodies formed from antibody fragments and any of the above epitope binding fragments. In particular, antibodies include immunoglobulin molecules and immunologically active fragments of immunoglobulin molecules, that is, molecules containing antigen binding sites. Immunoglobulin molecules can be of any type (e.g., IgG, IgE, IgM, IgD, IgA, and IgY), of any type (e.g., IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4, IgA1, and IgA2) or subclass.
用酶(木瓜蛋白酶)消化抗体产生两个相同的抗原结合片段,也称作“Fab”片段,和“Fc”片段,其不具有抗原结合活性但具有结晶的能力。用酶(胃蛋白酶)消化抗体产生F(ab′)2片段,其中抗体分子的两个臂保持相连且包含两个抗原结合位点。F(ab′)2片段具有交联抗原的能力。Enzyme (papain) digestion of the antibody produces two identical antigen-binding fragments, also called "Fab" fragments, and "Fc" fragments, which have no antigen-binding activity but have the ability to crystallize. Enzyme (pepsin) digestion of the antibody produces F(ab')2 fragments, where the two arms of the antibody molecule remain connected and contain two antigen binding sites. F(ab')2 fragments have the ability to cross-link antigens.
当在本文使用时,“Fv”指保持抗原识别位点和抗原结合位点二者的抗体的最小片段。该区域由紧密的非共价结合或共价结合的一个重链可变区和一个轻链可变区的二聚体组成。在这种构型中:每个可变区的3个CDR相互作用以限定VH-VL二聚体的表面的抗原结合位点。总之,6个CDR赋予抗体抗原结合特异性。然而,即使在低于完整的结合位点的亲和力时,单一可变区(或仅包含对抗原特异的3个CDR的一半)还具有识别和结合抗原的能力。As used herein, "Fv" refers to the smallest fragment of an antibody that retains both the antigen recognition site and the antigen binding site. This region is composed of a dimer of a heavy chain variable region and a light chain variable region that are tightly non-covalently bonded or covalently bonded. In this configuration: the 3 CDRs of each variable region interact to define the antigen binding site on the surface of the VH-VL dimer. In total, the 6 CDRs confer antigen binding specificity to the antibody. However, even when the affinity is lower than the complete binding site, a single variable region (or only half of the 3 CDRs specific to the antigen) still has the ability to recognize and bind to the antigen.
当在本文中使用时,“Fab”指抗体的片段,除了包含重链可变区和轻链可变区之外,其还包含轻链恒定域和重链的CH1区。As used herein, "Fab" refers to a fragment of an antibody, which, in addition to the heavy chain variable region and the light chain variable region, also includes the light chain constant domain and the CH1 region of the heavy chain.
当在本文中使用时,“dAb”指作为人抗体的最小功能结合单位的抗体的片段。“dAb”是单一结构域抗体且包含抗体重链的VH或抗体轻链的VL。每个dAb含有6个天然存在的CDR中的3个(Ward等,Binding activitiesof a repertoire of single immunoglobulin variable domains secreted from Escherichia coli.Nature341,544-546(1989);Holt等,Domain antibodies:protein for therapy,Trends Biotechnol.21,484-49(2003))。其分子量范围从11kDa到15kDa,它们比抗原结合片段(Fab)2小4倍且是单链Fv(scFv)分子大小的一半。As used herein, "dAb" refers to a fragment of an antibody that is the smallest functional binding unit of a human antibody. "DAb" is a single domain antibody and contains the VH of the antibody heavy chain or the VL of the antibody light chain. Each dAb contains 3 of the 6 naturally occurring CDRs (Ward et al., Binding activities of a repertoire of single immunoglobulin variable domains secreted from Escherichia coli. Nature 341, 544-546 (1989); Holt et al., Domain antibodies: protein for therapy , Trends Biotechnol. 21, 484-49 (2003)). Their molecular weight ranges from 11kDa to 15kDa, they are 4 times smaller than the antigen-binding fragment (Fab) 2 and half the molecular size of the single-chain Fv (scFv).
当在本文中使用时,“驼源”指由重链二聚物组成的抗体分子,其缺少轻链,但却具有大量的抗原结合组成组分(Hamers-Casterman C,Atarhouch T,Muyldermans S,Robinson G,Hamers C,Songa EB,Bendahman N,Hamers R(1993)Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains.Nature363:446-448)。As used herein, "camel origin" refers to antibody molecules composed of heavy chain dimers, which lack light chains but have a large number of antigen-binding components (Hamers-Casterman C, Atarhouch T, Muyldermans S, Robinson G, Hamers C, Songa EB, Bendahman N, Hamers R (1993) Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature363:446-448).
术语“双链抗体”指具有两个抗原结合位点的小抗体片段,其片段包括在同一多肽链中与轻链可变区相连的重链可变区。通过利用足够短的连接物来使同一链上的两个结构域之间配对,促使结构域与另一链的互补域配对并构建两个抗原结合位点。双链抗体更充分地描述于,例如,EP404,097;WO93/11161;和Hollinger等,Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA,90:6444-6448(1993)。The term "diabodies" refers to small antibody fragments with two antigen binding sites, the fragments of which include the heavy chain variable region connected to the light chain variable region in the same polypeptide chain. By using a sufficiently short linker to pair two domains on the same chain, the domains are paired with the complementary domains of another chain and two antigen binding sites are constructed. Diabodies are more fully described in, for example, EP404,097; WO93/11161; and Hollinger et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90: 6444-6448 (1993).
已显示完整抗体的片段可执行结合抗原的功能。结合片段的实例是(Ward,E.S.等,(1989)Nature341,544-546)由VL、VH、CL和CH1结构域组成的Fab片段;(McCafferty等,(1990)Nature,348,552-554)由VH和CH1结构域组成的Fd片段);(Holt等,(2003)Trends in Biotechnology 21,484-490)由单一抗体的VL和VH域组成的Fv片段;dAb片段(Ward,E.S.等,Nature 341,544-546(1989),McCafferty等,(1990)Nature,348,552-554,Holt等,(2003)Trends in Biotechnology 21,484-490),其由VH或VL域组成;分离的CDR区;F(ab')2片段,包含两个相连的Fab片段的二价片段;单链Fv分子(scFv),其中VH域与VL域由肽连接物相连,其使两个结构域结合以形成抗原结合位点(Bird等,(1988)Science,242,423-426,Huston等,(1988)PNAS USA,85,5879-5883);双特异性单链Fv二聚体(PCT/US92/09965)和“双链抗体”,通过基因融合构建的多价片段或多特异性片段(WO94/13804;Holliger,P.(1993)等,Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA906444-6448)。Fv、scFv或双链抗体分子可通过连接VH和VL域的二硫桥的掺入来稳定(Reiter,Y.等,Nature Biotech,14,1239-1245,1996)。还可产生包含与CH3域结合的scFv的微抗体(Hu,S.等,(1996)Cancer Res.,56,3055-3061)。结合片段的其它实例是Fab′,其由于在重链CH1结构域的羧基末端添加了几个残基而不同于Fab片段,所述残基包括来自抗体铰链区的一个或多个半胱氨酸,和Fab′-SH,其是Fab′片段,其中恒定域的半胱氨酸残基携带游离的硫醇基。It has been shown that fragments of whole antibodies can perform the function of binding antigen. Examples of binding fragments are (Ward, ES, et al., (1989) Nature 341, 544-546) Fab fragments composed of VL, VH, CL and CH1 domains; (McCafferty et al., (1990) Nature, 348, 552-554) by VH (Holt et al., (2003) Trends in Biotechnology 21,484-490) Fv fragment composed of the VL and VH domains of a single antibody; dAb fragment (Ward, ES etc., Nature 341,544-546 ( 1989), McCafferty et al., (1990) Nature, 348,552-554, Holt et al., (2003) Trends in Biotechnology 21, 484-490), which consist of VH or VL domains; isolated CDR regions; F(ab')2 fragments, A bivalent fragment containing two linked Fab fragments; a single-chain Fv molecule (scFv), in which the VH domain and the VL domain are connected by a peptide linker, which allows the two domains to join to form an antigen binding site (Bird et al., ( 1988) Science, 242, 423-426, Huston et al., (1988) PNAS USA, 85, 5879-5883); bispecific single-chain Fv dimer (PCT/US92/09965) and "diabodies", through gene fusion Constructed multivalent fragments or multispecific fragments (WO94/13804; Holliger, P. (1993), etc., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA906444-6448). Fv, scFv or diabody molecules can be stabilized by the incorporation of a disulfide bridge connecting the VH and VL domains (Reiter, Y. et al., Nature Biotech, 14, 1239-1245, 1996). Minibodies containing scFvs that bind to the CH3 domain can also be produced (Hu, S. et al., (1996) Cancer Res., 56, 3055-3061). Other examples of binding fragments are Fab', which differ from Fab fragments due to the addition of several residues to the carboxy terminus of the CH1 domain of the heavy chain, the residues including one or more cysteines from the hinge region of an antibody , And Fab'-SH, which are Fab' fragments in which the cysteine residues of the constant domain carry free thiol groups.
术语“可变的”指以下事实:抗体可变区的某些部分在抗体之间在序列中具有很大不同,且负责每个特定的抗体与其特定的抗原的结合特异性。然而,可变性并不在抗体的可变域中均匀分布。其集中于轻链可变域和重链可变域二者中称作互补决定区(CDR)的片段中。可变区的高度保 守的部分称作框架区(FR)。天然抗体重链和轻链的可变区均包含4个FR区,很大程度地采用了β-折叠构型,由3个CDR连接,所述3个CDR形成连接β-折叠结构且在一些情况中形成β-折叠结构的部分的环。每条链中的CDR通过FR区与来自其它链的CDR紧密结合在一起,有助于形成抗体的抗原结合位点(参见,Kabat等,Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest,第5版,Public Health Service,National Institutes of Health,Bethesda,MD(1991))。恒定区一般不直接参与抗原结合,但可影响抗原结合亲和力并可表现出多种效应功能,比如ADCC、CDC和/或细胞凋亡中抗体的参与。The term "variable" refers to the fact that certain parts of antibody variable regions differ greatly in sequence between antibodies and are responsible for the binding specificity of each specific antibody to its specific antigen. However, the variability is not evenly distributed in the variable domains of antibodies. It is concentrated in fragments called complementarity determining regions (CDR) in both the light chain variable domain and the heavy chain variable domain. The highly conserved part of the variable region is called the framework region (FR). The variable regions of the heavy and light chains of natural antibodies each contain 4 FR regions, which adopt a β-sheet configuration to a large extent and are connected by 3 CDRs, which form a connected β-sheet structure and in some In this case, a loop that forms part of the β-sheet structure. The CDRs in each chain are closely combined with the CDRs from other chains through the FR region, which helps to form the antigen binding site of the antibody (see, Kabat et al., Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, 5th edition, Public Health Service , National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD (1991)). The constant region generally does not directly participate in antigen binding, but can affect antigen binding affinity and can exhibit various effector functions, such as ADCC, CDC, and/or antibody involvement in apoptosis.
术语“高变区”指与其与抗原的结合有关的抗体的氨基酸残基。高变区包括“互补决定区”或“CDR”的氨基酸残基(例如,轻链可变区的第24-34位残基(L1)、第50-56位残基(L2)和第89-97位残基(L3)和重链可变区的第31-35位残基(H1)、第50-65位残基(H2)和第95-102位残基(H3)(Kabat等,Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest,第5版.Public Health Service,National Institutes of Health,Bethesda,MD(1991))和/或来自“高变环”的那些残基(例如,轻链可变域中的第26-32位残基(L1)、第50-52位残基(L2)和第91-96位残基(L3)和重链可变域中的第26-32位残基(H1)、第53-55位残基(H2)和第96-101位残基(H3);Chothia和Lesk,J.Mol.Biol.,196:901-917(1987))。“框架”或“FR”残基是在CDR两侧的那些可变域残基。FR残基存在于嵌合抗体、人源化的抗体、人抗体、结构域抗体、双链抗体、疫苗体、线性抗体和双特异性抗体中。The term "hypervariable region" refers to the amino acid residues of an antibody related to its binding to an antigen. The hypervariable region includes amino acid residues of the "complementarity determining region" or "CDR" (e.g., residues 24-34 (L1), residues 50-56 (L2), and 89 of the light chain variable region). -97 residues (L3) and 31-35 residues (H1), 50-65 residues (H2) and 95-102 residues (H3) of the heavy chain variable region (Kabat et al. , Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, 5th edition. Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD (1991)) and/or those residues from the "hypervariable loop" (for example, in the light chain variable domain Residues 26-32 (L1), residues 50-52 (L2) and residues 91-96 (L3) and residues 26-32 in the heavy chain variable domain (H1 ), residues 53-55 (H2) and residues 96-101 (H3); Chothia and Lesk, J. Mol. Biol., 196:901-917 (1987)). "Framework" or " "FR" residues are those variable domain residues on both sides of the CDR. FR residues are found in chimeric antibodies, humanized antibodies, human antibodies, domain antibodies, diabodies, vaccinates, linear antibodies, and diabodies. Specific antibodies.
“靶向结合剂”、“靶向结合蛋白”、“特异性结合蛋白”和相似的术语指优先与靶位点结合的药剂,例如抗体或其结合片段。在一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂仅对一个靶位点是特异的。在其它实施方案中,靶向结合剂对多于一个的靶位点是特异的。在一个实施方案中,靶向结合剂可以是单克隆抗体且靶位点可以是表位。靶向结合剂可包含抗体的至少一个抗原结合结构域(例如,CDR),其中所述结构域融合于或含于异源蛋白支架中,例如,非抗体蛋白支架。"Targeted binding agent", "targeted binding protein", "specific binding protein" and similar terms refer to agents that preferentially bind to a target site, such as antibodies or binding fragments thereof. In one embodiment, the targeted binding agent is specific for only one target site. In other embodiments, the targeted binding agent is specific for more than one target site. In one embodiment, the targeted binding agent may be a monoclonal antibody and the target site may be an epitope. The targeted binding agent may comprise at least one antigen binding domain (e.g., CDR) of an antibody, wherein the domain is fused to or contained in a heterologous protein scaffold, for example, a non-antibody protein scaffold.
抗体的“结合片段”通过重组DNA技术来产生,或通过完整抗体的酶促裂解或化学裂解来产生。结合片段包括Fab、Fab′、F(ab′)2、Fv、dAb和单链抗体。不同于“双特异性”或“双功能”抗体的抗体被理解为其每个结合位点是相同的。当过量的抗体降低了与反受体结合的受体的量的至少约20%、40%、60%或80%,且更通常高于约85%时(如在体外竞争结合测定中所测量的),抗体基本上抑制受体与反受体的结合。The "binding fragment" of the antibody is produced by recombinant DNA technology, or by enzymatic or chemical cleavage of the intact antibody. Binding fragments include Fab, Fab', F(ab')2, Fv, dAb, and single chain antibodies. Antibodies other than "bispecific" or "bifunctional" antibodies are understood to have the same each binding site. When excess antibody reduces the amount of receptor bound to the counter receptor by at least about 20%, 40%, 60%, or 80%, and more usually more than about 85% (as measured in an in vitro competitive binding assay ), the antibody basically inhibits the binding of the receptor to the counter receptor.
术语“表位”包括能够与免疫球蛋白或T细胞受体特异性结合的任何蛋白决定簇。表位决定簇通常由具有化学活性的分子的表面基团(诸如氨基酸或糖侧链)组成,且可(但不总是)具有特定的三维结构特性,以及特定的电荷特性。当解离常数≤1μM,优选地≤100μM和最优选地≤10μM时,称抗体与抗原特异性结合。The term "epitope" includes any protein determinant capable of specifically binding to an immunoglobulin or T cell receptor. Epitope determinants usually consist of surface groups (such as amino acids or sugar side chains) of chemically active molecules, and may (but not always) have specific three-dimensional structural characteristics, as well as specific charge characteristics. When the dissociation constant is ≦1 μM, preferably ≦100 μM and most preferably ≦10 μM, the antibody is said to specifically bind to the antigen.
术语“药剂”代表化学化合物、化学化合物的混合物、生物大分子或由生物材料制成的提取物。The term "medicament" represents a chemical compound, a mixture of chemical compounds, a biological macromolecule, or an extract made from biological materials.
关于PD-L1多肽的“活性的”或“活性”指PD-L1多肽的具有天然PD-L1多肽的生物活性或免疫活性的部分。当在本文中使用时“生物的”指由天然PD-L1多肽的活性引起的生物学功能。优选的PD-L1生物活性包括,例如,PD-L1诱导的细胞增殖、细胞黏附和侵入。The "active" or "active" of the PD-L1 polypeptide refers to the part of the PD-L1 polypeptide that has the biological activity or immunological activity of the natural PD-L1 polypeptide. "Biological" as used herein refers to the biological function caused by the activity of the native PD-L1 polypeptide. Preferred biological activities of PD-L1 include, for example, cell proliferation, cell adhesion and invasion induced by PD-L1.
当在本文中使用时,“哺乳动物”指被认为是哺乳动物的任何动物。优选地,哺乳动物是人。As used herein, "mammal" refers to any animal that is considered a mammal. Preferably, the mammal is a human.
当在本文中使用时,“动物”包括被认为是哺乳动物的动物。优选地,动物是人。As used herein, "animal" includes animals that are considered mammals. Preferably, the animal is a human.
术语“患者”包括人和受试动物。The term "patient" includes humans and test animals.
术语“mAb”指单克隆抗体。The term "mAb" refers to a monoclonal antibody.
当在本文中使用时,“脂质体”指可用于将可包含本发明的PD-L1多肽或对于这种PD-L1多肽的抗体的药物递送至哺乳动物的小囊泡。As used herein, "liposome" refers to a small vesicle that can be used to deliver a drug that can contain the PD-L1 polypeptide of the present invention or an antibody to such a PD-L1 polypeptide to a mammal.
如本文所用的“标记”或“标记的”指将可检测的部分添加到多肽,所述可检测部分例如放射性标记、荧光标记、酶标记、化学发光标记的或生物素基。放射性同位素或放射性核素可包括3H、14C、15N、35S、90Y、99Tc、111In、125I、131I,荧光标记可包括罗丹明、稀土荧光粉或FITC,且酶标记可包括辣根过氧化物酶、β-半乳糖苷酶、荧光素酶、碱性磷酸酶。"Label" or "labeled" as used herein refers to the addition of a detectable moiety to a polypeptide, such as a radioactive label, a fluorescent label, an enzyme label, a chemiluminescent label, or a biotin-based. The radioisotope or radionuclide may include3 H,14 C,15 N,35 S,90 Y,99 Tc,111 In,125 I,131 I, the fluorescent label may include rhodamine, rare earth phosphor or FITC, and the enzyme Labels may include horseradish peroxidase, β-galactosidase, luciferase, alkaline phosphatase.
另外的标记包括,以示例的方式且不限于:酶,比如葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶、α-D-半乳糖苷酶、葡萄糖氧化酶、葡萄糖淀粉酶、碳酸酐酶、乙酰胆碱酯酶、溶菌酶、苹果酸脱氢酶和过氧化物酶;染料;另外的荧光标记或荧光剂包括,比如荧光素和其衍生物、荧色物、GFP(绿色荧光蛋白)、丹酰、伞形酮、藻红蛋白、藻蓝蛋白、别藻蓝蛋白、邻苯二甲醛和荧光胺;荧光团诸如穴状稀土化合物和螯合物,例如铕等(Perkin Elmer和Cisbio测定);化学发光标记或化学发光物,比如异鲁米诺、鲁米诺和二氧烷;敏化剂;辅酶;酶底物;颗粒,比如胶乳颗粒或碳颗粒;金属溶胶;微晶;脂质体;细胞等,其可进一步被染料、催化剂或其它可检测基团所标记;分子诸如生物素、地高辛或5-溴脱氧尿苷;毒素部分,比如例如选自由假单胞菌外毒素(PE或其细胞毒性片段或突变体)、白喉毒素或其细胞毒 性片段或突变体、肉毒杆菌毒素A、B、C、D、E或F、蓖麻毒素或其细胞毒性片段例如蓖麻毒素A、相思豆毒素或其细胞毒性片段、皂草素或其细胞毒性片段、美洲商陆抗病毒毒素或其细胞毒性片段和bryodin1或其细胞毒性片段组成的组的毒素部分。Additional markers include, by way of example and not limitation: enzymes such as glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, α-D-galactosidase, glucose oxidase, glucoamylase, carbonic anhydrase, acetylcholinesterase, Lysozyme, malate dehydrogenase and peroxidase; dyes; additional fluorescent labels or fluorescent agents include, for example, fluorescein and its derivatives, fluorochromes, GFP (green fluorescent protein), dansyl, umbelliferone , Phycoerythrin, phycocyanin, allophycocyanin, o-phthalaldehyde and fluorescein; fluorophores such as cryptate rare earth compounds and chelates, such as europium, etc. (Perkin Elmer and Cisbio determination); chemiluminescence labeling or chemical Luminescent substances, such as isoluminol, luminol and dioxane; sensitizers; coenzymes; enzyme substrates; particles, such as latex particles or carbon particles; metal sols; microcrystals; liposomes; cells, etc. It can be further labeled with dyes, catalysts or other detectable groups; molecules such as biotin, digoxin or 5-bromodeoxyuridine; toxin moieties, such as those selected from Pseudomonas exotoxin (PE or its cytotoxicity) Fragment or mutant), diphtheria toxin or its cytotoxic fragment or mutant, botulinum toxin A, B, C, D, E or F, ricin or its cytotoxic fragment such as ricin A, acacia toxin Or its cytotoxic fragment, saporin or its cytotoxic fragment, pokeweed antiviral toxin or its cytotoxic fragment, and bryodin1 or its cytotoxic fragment.
如本文所用的术语“药物剂或药物”指当合适地施用于患者时能够诱导需要的治疗作用的化学化合物或组合物。本文所用的其它化学术语根据本领域中的常规用法使用,如The McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Chemical Terms所例证(Parker,S.,编,McGraw-Hill,San Francisco(1985))。The term "pharmaceutical agent or drug" as used herein refers to a chemical compound or composition capable of inducing a desired therapeutic effect when properly administered to a patient. Other chemical terms used herein are used according to conventional usage in the field, as exemplified by The McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Chemical Terms (Parker, S., ed., McGraw-Hill, San Francisco (1985)).
如本文所用的,“基本上纯的”意为主题物质是所存在的主要物质(即其在组合物中的摩尔数占比任何其它单独的物质更丰富),且优选地基本上纯的组分是其中主题物质占存在的所有大分子物质的至少50%摩尔比的组合物。一般,基本上纯的组合物将占存在于组合物中的所有大分子物质的大于约80%,更优选地大于约85%、90%、95%和99%。最优选地,主题物质是纯化至基本均质的(通过常规检测方法在组合物中不可检测污染物物质),其中组合物基本上由单一的大分子物质组成。As used herein, "substantially pure" means that the subject substance is the main substance present (that is, its moles in the composition are more abundant than any other individual substance), and preferably the substantially pure composition A fraction is a composition in which the subject substance accounts for at least 50% by mole of all macromolecular substances present. Generally, a substantially pure composition will account for greater than about 80% of all macromolecular species present in the composition, more preferably greater than about 85%, 90%, 95%, and 99%. Most preferably, the subject substance is purified to be substantially homogeneous (contaminant substances cannot be detected in the composition by conventional detection methods), wherein the composition consists essentially of a single macromolecular substance.
“抗体依赖性细胞毒性”或“ADCC”指某种细胞介导的反应,其中表达Fc受体(FcR)的非特异性细胞毒性细胞(例如天然杀伤(NK)细胞、单核细胞、嗜中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞)识别靶细胞上结合的抗体并随之导致靶细胞的裂解。介导ADCC的主要细胞有NK细胞,仅表达FcγRIII,然而单核细胞表达FcγRI、FcγRII和FcγRIII。造血细胞上的FcR表达概括于Ravetch和Kinet,Annu.Rev.Immunol 9:457-92(1991)的第464页的表9中。为评估目标分子的ADCC活性,可进行体外ADCC测定,比如美国专利第5,500,362号或第5,821,337号中所描述的。用于这样的测定的效应细胞包括外周血单核细胞(PBMC)和NK细胞。可选地,或另外地,目标分子的ADCC活性可在体内进行评估,例如,在动物模型中,比如Clynes等PNAS(USA)95:652-656(1988)中所公开的。"Antibody-dependent cytotoxicity" or "ADCC" refers to a certain cell-mediated response in which non-specific cytotoxic cells (such as natural killer (NK) cells, monocytes, neutrophils) expressing Fc receptors (FcR) Granulocytes and macrophages) recognize the antibody bound on the target cell and subsequently cause the lysis of the target cell. The main cells that mediate ADCC are NK cells, which only express FcyRIII, while monocytes express FcyRI, FcyRII and FcyRIII. FcR expression on hematopoietic cells is summarized in Table 9 on page 464 of Ravetch and Kinet, Annu. Rev. Immunol 9:457-92 (1991). To evaluate the ADCC activity of the target molecule, an in vitro ADCC assay can be performed, such as described in US Patent No. 5,500,362 or No. 5,821,337. Effector cells used in such assays include peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and NK cells. Alternatively, or in addition, the ADCC activity of the target molecule can be assessed in vivo, for example, in an animal model such as that disclosed in Clynes et al. PNAS (USA) 95:652-656 (1988).
“补体依赖性细胞毒性”或“CDC”指抗体进行其细胞杀伤功能的机制。其通过补体的第一组分的成分C1q与在Igs、IgG或IgM的Fc结构域的结合来起始。C1q是以70μg/mL的浓度存在于人血清中的大的、~410kD的结构复杂的糖蛋白(Cooper,N.R.1985.Adv.Immunol.37:151)。C1r和C1s、C1q与两个丝氨酸蛋白酶共同形成补体的第一组分—复合物C1。C1q的N末端球形头部中的至少两个必须与Igs的Fc结合以进行C1激活,从而起始补体级联反应(Cooper,N.R.1985.Adv.Immunol.37:151)。"Complement-dependent cytotoxicity" or "CDC" refers to the mechanism by which an antibody performs its cell killing function. It is initiated by the binding of C1q, the first component of complement, to the Fc domain of Igs, IgG or IgM. C1q is a large, ~410kD complex glycoprotein (Cooper, N.R.1985.Adv.Immunol.37:151) that exists in human serum at a concentration of 70μg/mL. C1r, C1s, and C1q together with two serine proteases form the first component of complement—complex C1. At least two of the N-terminal spherical heads of C1q must bind to the Fc of Igs for C1 activation to initiate the complement cascade (Cooper, N.R. 1985. Adv. Immunol. 37: 151).
本文所用的术语“抗体半衰期”意为抗体的药代动力学性质,其为施用后抗体分子的平均存活时间的量度。抗体半衰期可表示为从患者体中或 其特定的区室中或其它组织中消除已知的免疫球蛋白的量的50%所需的时间,例如,如血清或血浆中所测量的,即循环半衰期。半衰期可根据免疫球蛋白或免疫球蛋白的类别而不同。一般地,抗体半衰期的增加导致施用的抗体的循环中的平均停留时间(MRT)的增加。The term "antibody half-life" as used herein means the pharmacokinetic properties of the antibody, which is a measure of the average survival time of the antibody molecule after administration. Antibody half-life can be expressed as the time required to eliminate 50% of the known amount of immunoglobulin from the patient's body or its specific compartments or other tissues, for example, as measured in serum or plasma, ie circulating half life. The half-life may vary according to the immunoglobulin or the type of immunoglobulin. Generally, an increase in the half-life of an antibody results in an increase in the circulating mean residence time (MRT) of the administered antibody.
术语“同种型”指抗体重链恒定区或轻链恒定区的分类。抗体的恒定区不参与结合抗原,但表现出多种效应功能。根据重链恒定区的氨基酸序列,可将给定的人抗体或免疫球蛋白分配到5种主要免疫球蛋白种类的其中之一:IgA、IgD、IgE、IgG和IgM。这些种类中的一些可进一步分为亚类(同种型),例如,IgG1(γ1)、IgG2(γ2)、IgG3(γ3)和IgG4(γ4),和IgA1和IgA2。对应于不同种类的免疫球蛋白的重链恒定区分别称作α、δ、ε、γ和μ。不同种类的免疫球蛋白的结构和三维构型是熟知的。在多种人免疫球蛋白种类中,仅已知人IgG1、IgG2、IgG3、IgG4和IgM激活补体。已知人IgG1、IgG2、IgG3和IgG4结合Fcγ受体,其介导包括ADCC的多种效应功能。轻链恒定区可被分类为两个主要的种类,κ和λ。The term "isotype" refers to the classification of antibody heavy chain constant regions or light chain constant regions. The constant region of an antibody does not participate in binding antigen, but exhibits a variety of effector functions. According to the amino acid sequence of the constant region of the heavy chain, a given human antibody or immunoglobulin can be assigned to one of the five main immunoglobulin classes: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM. Some of these classes can be further divided into subclasses (isotypes), for example, IgG1 (γ1), IgG2 (γ2), IgG3 (γ3) and IgG4 (γ4), and IgA1 and IgA2. The heavy chain constant regions corresponding to different types of immunoglobulins are called α, δ, ε, γ, and μ, respectively. The structures and three-dimensional configurations of different kinds of immunoglobulins are well known. Among the various human immunoglobulin classes, only human IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4 and IgM are known to activate complement. It is known that human IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4 bind to Fcγ receptors, which mediate multiple effector functions including ADCC. The light chain constant region can be classified into two main categories, kappa and lambda.
如果需要的话,可转换抗体的同种型。例如,一些情况下,治疗性抗体需要补体依赖性细胞毒性。存在许多具有补体依赖性细胞毒性的抗体同种型,包括但不限于以下:鼠IgM、鼠IgG2a、鼠IgG2b、鼠IgG3、人IgM、人IgA、人IgG1和人IgG3。在其它实施方案中,治疗性抗体需要结合效应细胞上的Fc受体并参与抗体依赖性细胞毒性。存在许多具有抗体依赖性细胞毒性抗体的抗体同种型,包括但不限于以下:鼠IgG2a、鼠IgG2b、鼠IgG3、人IgG1和人IgG3。最初所产生的抗体不必具有所述同种型,可利用本领域中熟知的常规技术对抗体进行同种型转换。所述技术其中包括直接重组技术(参见美国专利第4,816,397号),细胞-细胞融合技术(参见美国专利第5,916,771号和第6,207,418号)的使用。If necessary, the isotype of the antibody can be switched. For example, in some cases, therapeutic antibodies require complement-dependent cytotoxicity. There are many antibody isotypes with complement-dependent cytotoxicity, including but not limited to the following: murine IgM, murine IgG2a, murine IgG2b, murine IgG3, human IgM, human IgA, human IgG1, and human IgG3. In other embodiments, therapeutic antibodies need to bind to Fc receptors on effector cells and participate in antibody-dependent cytotoxicity. There are many antibody isotypes with antibody-dependent cytotoxic antibodies, including but not limited to the following: murine IgG2a, murine IgG2b, murine IgG3, human IgG1, and human IgG3. The antibody produced initially does not have to have the said isotype, and the antibody can be isotype switched using conventional techniques well known in the art. The technologies include direct recombination technology (see U.S. Patent No. 4,816,397) and the use of cell-cell fusion technology (see U.S. Patent Nos. 5,916,771 and 6,207,418).
“全血测定”利用未分级分离的血液作为天然效应器的来源。血液在血浆中含有补体,以及FcR表达细胞效应器,比如多形核白细胞(PMN)和单核细胞(MNC)。这样,全血测定允许在体外同时评估ADCC和CDC二者效应器机制的协同作用。The "whole blood assay" uses unfractionated blood as a source of natural effectors. Blood contains complement in plasma, as well as FcR-expressing cellular effectors, such as polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) and monocytes (MNC). In this way, the whole blood assay allows the simultaneous evaluation of the synergy of the effector mechanisms of ADCC and CDC in vitro.
本文所用的“治疗有效的”量是向受治疗者提供某些改善或益处的量。换言之,“治疗有效的”量是提供至少一种临床症状的一定的缓和、缓解和/或减少的量。可通过本发明的方法治疗的与疾患有关的临床症状是本领域中的技术人员熟知的。而且,本领域中的技术人员将理解,治疗作用不必是彻底的或治愈的,只要向受治疗者提供了一定的益处。As used herein, a "therapeutically effective" amount is an amount that provides some improvement or benefit to the subject. In other words, a "therapeutically effective" amount is an amount that provides a certain alleviation, relief, and/or reduction of at least one clinical symptom. The clinical symptoms associated with the disease that can be treated by the method of the present invention are well known to those skilled in the art. Moreover, those skilled in the art will understand that the therapeutic effect need not be thorough or curative, as long as it provides certain benefits to the subject.
示例性癌症包括膀胱肿瘤、乳腺肿瘤、前列腺肿瘤、基底细胞癌、胆管癌、膀胱癌、骨癌、脑和CNS癌(例如神经胶质瘤)、子宫颈癌、绒 毛膜癌、结肠和直肠癌、结缔组织癌、消化系统的癌症;子宫内膜癌、食道癌;眼癌、头颈癌、胃癌;上皮内肿瘤;肾癌;喉癌;白血病;肝癌;肺癌(例如小细胞和非小细胞肺癌);淋巴瘤,包括霍奇金氏淋巴瘤和非霍奇金氏淋巴瘤;黑素瘤;骨髓瘤、成神经细胞瘤、口腔癌(例如,唇、舌、口和咽);卵巢癌;胰腺癌、成视网膜细胞瘤;横纹肌肉瘤;直肠癌、肾癌、呼吸系统的癌症;肉瘤;皮肤癌;胃癌;睾丸癌;甲状腺癌;子宫癌、泌尿系统的癌症,以及其它癌和肉瘤。Exemplary cancers include bladder tumors, breast tumors, prostate tumors, basal cell carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, bladder cancer, bone cancer, brain and CNS cancer (e.g. glioma), cervical cancer, choriocarcinoma, colon and rectal cancer , Connective tissue cancer, cancer of the digestive system; endometrial cancer, esophageal cancer; eye cancer, head and neck cancer, gastric cancer; intraepithelial tumor; kidney cancer; laryngeal cancer; leukemia; liver cancer; lung cancer (such as small cell and non-small cell lung cancer) ); Lymphoma, including Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma; melanoma; myeloma, neuroblastoma, oral cancer (for example, lips, tongue, mouth and pharynx); ovarian cancer; Pancreatic cancer, retinoblastoma; rhabdomyosarcoma; rectal cancer, kidney cancer, cancer of the respiratory system; sarcoma; skin cancer; stomach cancer; testicular cancer; thyroid cancer; cancer of the uterus, urinary system, and other cancers and sarcomas.
示例性慢性感染包括HIV感染、乙肝病毒(HBV)感染和丙肝病毒(HCV)感染。Exemplary chronic infections include HIV infection, hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection.
本文所用的术语“和/或”视作两个特定的特征或组分的每一项与另一项一起或不与另一项一起的特定的公开。例如“A和/或B”视作(i)A,(ii)B和(iii)A和B的每一项的特定的公开,如同每个单独在本文中列出。The term "and/or" as used herein is regarded as a specific disclosure of each of two specific features or components with or without the other. For example, "A and/or B" is regarded as the specific disclosure of each of (i) A, (ii) B, and (iii) A and B, as if each were individually listed herein.
抗体结构Antibody structure
已知基本抗体结构单元包括四聚体。每个四聚体由两对相同的多肽链组成,每对具有一条“轻”链(约25kD)和一条“重”链(约50-70kD)。每条链的氨基末端部分包括约100至110或更多的氨基酸的可变区,其主要负责抗原识别。每条链的羧基末端部分限定了主要负责效应功能的恒定区。轻链分类为κ轻链和λ轻链。重链分类为μ、δ、γ、α或ε,并分别定义抗体的同种型为IgM、IgD、IgA和IgE。在轻链和重链中,可变区和恒定区通过约12或更多个氨基酸的“J”区域连接,其中重链还包含约10个或更多个氨基酸的“D”区。一般参见,Fundamental Immunology Ch.7(Paul,W.,编,第2版.Raven Press,N.Y.(1989))。每条轻/重链对的可变区形成抗体结合位点。It is known that basic antibody structural units include tetramers. Each tetramer is composed of two pairs of identical polypeptide chains, each pair having a "light" chain (about 25kD) and a "heavy" chain (about 50-70kD). The amino terminal portion of each chain includes a variable region of about 100 to 110 or more amino acids, which is mainly responsible for antigen recognition. The carboxy terminal part of each chain defines the constant region that is mainly responsible for effector functions. Light chains are classified into kappa light chains and lambda light chains. Heavy chains are classified as mu, delta, gamma, alpha or epsilon, and define the isotype of the antibody as IgM, IgD, IgA, and IgE, respectively. In the light chain and the heavy chain, the variable and constant regions are connected by a "J" region of about 12 or more amino acids, where the heavy chain also includes a "D" region of about 10 or more amino acids. See generally, Fundamental Immunology Ch. 7 (Paul, W., ed., 2nd edition. Raven Press, N.Y. (1989)). The variable region of each light/heavy chain pair forms an antibody binding site.
这样,完整的抗体具有两个结合位点。除在双功能或双特异性抗体中,两个结合位点是相同的。In this way, a complete antibody has two binding sites. Except in bifunctional or bispecific antibodies, the two binding sites are the same.
链均表现出同样的一般结构:由3个高变区(也称CDR)连接的相对保守的框架区(FR)。来自每对的两条链的CDR通过框架区对齐,使能够与特定表位结合。从N末端到C末端,轻链和重链二者均包含FR1、CDR1、FR2、CDR2、FR3、CDR3和FR4结构域。根据Kabat的定义将氨基酸分配至每个结构域Sequences of Proteins ofImmunological Interest(National Institutes of Health,Bethesda,Md.(1987和1991)),或Chothia&Lesk J.Mol.Biol.196:901-917(1987);Chothia等,Nature 342:878-883(1989)。The chains all show the same general structure: relatively conservative framework regions (FR) connected by 3 hypervariable regions (also called CDRs). The CDRs from the two chains of each pair are aligned by the framework regions to enable binding to a specific epitope. From N-terminus to C-terminus, both the light chain and the heavy chain contain FR1, CDR1, FR2, CDR2, FR3, CDR3, and FR4 domains. According to Kabat's definition, amino acids are assigned to each domain Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md. (1987 and 1991)), or Chothia & Lesk J. Mol. Biol. 196: 901-917 (1987) ; Chothia et al., Nature 342:878-883 (1989).
双特异性或双功能抗体是具有两个不同的重/轻链对和两个不同的结 合位点的人工杂交抗体。双特异性抗体可通过包括杂交瘤的融合或Fab′片段的连接的多种方法来产生。参见Songsivilai&Lachmann Clin.Exp.Immunol.79:315-321(1990),Kostelny等J.Immunol.148:1547-1553(1992)。双特异性抗体不以具有单一结合位点的片段的形式(例如,Fab、Fab′和Fv)存在。Bispecific or bifunctional antibodies are artificial hybrid antibodies with two different heavy/light chain pairs and two different binding sites. Bispecific antibodies can be produced by various methods including fusion of hybridomas or linking of Fab' fragments. See Songsivilai & Lachmann Clin. Exp. Immunol. 79: 315-321 (1990), Kostelny et al. J. Immunol. 148: 1547-1553 (1992). Bispecific antibodies do not exist in the form of fragments with a single binding site (for example, Fab, Fab' and Fv).
通常,VH与VL配对以提供抗体抗原结合位点,虽然单独的VH或VL可用来结合抗原。Generally, VH and VL are paired to provide an antibody antigen binding site, although a separate VH or VL can be used to bind the antigen.
人抗体和抗体的人源化Human antibodies and humanization of antibodies
人抗体避免了与具有小鼠或大鼠可变区和/或恒定区的抗体有关的某些问题。小鼠或大鼠来源的抗体可导致抗体的快速清除或可导致由患者针对抗体产生免疫应答。为避免利用小鼠或大鼠来源的抗体,完全人抗体可通过将功能性的人抗体基因座导入到啮齿动物、其它哺乳动物或动物中而使啮齿动物、其它哺乳动物或动物产生完全人抗体来生成。Human antibodies avoid certain problems associated with antibodies with mouse or rat variable and/or constant regions. Mouse or rat-derived antibodies can lead to rapid elimination of antibodies or can lead to an immune response by the patient against the antibodies. To avoid the use of mouse or rat-derived antibodies, fully human antibodies can produce fully human antibodies by introducing functional human antibody loci into rodents, other mammals, or animals. To generate.
抗体的制备Antibody preparation
将回收的淋巴细胞与骨髓型细胞系融合以制备永久杂交瘤细胞系。筛选这些杂交瘤细胞系并进行选择以鉴定产生对目标抗原特异的抗体的杂交瘤细胞系。本文所提供的是用于产生对PD-L1特异的多种杂交瘤细胞系的产生的方法。而且,本文所提供的是由所述细胞系产生的抗体的表征,包括所述抗体的重链和轻链的核苷酸和氨基酸序列分析。The recovered lymphocytes are fused with a bone marrow type cell line to prepare a permanent hybridoma cell line. These hybridoma cell lines are screened and selected to identify hybridoma cell lines that produce antibodies specific for the target antigen. Provided herein are methods for the generation of multiple hybridoma cell lines specific for PD-L1. Moreover, what is provided herein is the characterization of the antibodies produced by the cell line, including the nucleotide and amino acid sequence analysis of the heavy and light chains of the antibody.
可选地,代替与骨髓瘤细胞融合以产生杂交瘤,可直接对B细胞进行测定。例如,可从超免疫小鼠中分离CD19+B细胞并允许其增殖并分化为抗体分泌的血浆细胞。然后通过ELISA筛选来自细胞上清液的抗体针对PD-L1免疫原的反应性。还可筛选上清液的针对PD-L1的片段的免疫反应性以进一步标出与B7-H1上目标功能结构域结合的不同抗体。还可筛选抗体其它相关人蛋白并针对大鼠、小鼠和非人灵长类,比如食蟹猕猴,B7-H1的直系同源物,最终来确定物种交叉反应性。可通过多种方法使来自含有目标抗体的孔的B细胞永生化,所述方法包括融合以从单独的孔或从合并的孔中生成杂交瘤,或通过用EBV感染或通过已知的永生化基因转染且然后接种于适宜的培养基中。可选地,然后利用B7-H1特异性的溶血性空斑测定来分离分泌具有期望特性的抗体的单独的血浆细胞(参见,例如Babcook等,Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA93:7843-48(1996))。靶向裂解的细胞优选地为用B7-H1抗原覆盖的绵羊红细胞(SRBC)。Alternatively, instead of fusing with myeloma cells to produce hybridomas, B cells can be assayed directly. For example, CD19+ B cells can be isolated from hyperimmunized mice and allowed to proliferate and differentiate into antibody-secreting plasma cells. The antibody from the cell supernatant was then screened for reactivity against PD-L1 immunogen by ELISA. The supernatant can also be screened for immunoreactivity against PD-L1 fragments to further mark different antibodies that bind to the target functional domain on B7-H1. Antibodies can also be screened for other related human proteins and directed against rats, mice, and non-human primates, such as cynomolgus monkeys, orthologs of B7-H1, and ultimately determine species cross-reactivity. B cells from wells containing the antibody of interest can be immortalized by a variety of methods, including fusion to generate hybridomas from separate wells or from combined wells, or by infection with EBV or by known immortalization The gene is transfected and then inoculated in a suitable medium. Optionally, the B7-H1 specific hemolytic plaque assay is then used to isolate individual plasma cells that secrete antibodies with desired properties (see, for example, Babcook et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93:7843-48 (1996)). The cells targeted for lysis are preferably sheep red blood cells (SRBC) covered with B7-H1 antigen.
如将所理解地,可在不同于杂交瘤细胞系的细胞系中表达如本文所描述的抗体。编码特定抗体的序列可用于转化适宜的哺乳动物宿主细胞。转化可通过用于将多核苷酸引入到宿主细胞中的任何已知的方法来进行,包 括例如,将多核苷酸包装在病毒中(或包装到病毒载体中)并用病毒(或载体)转导宿主细胞,或通过本领域中已知的转染程序,如美国专利第4,399,216号、第4,912,040号、第4,740,461号和第4,959,455号中所示出的(所述专利通过引用并入本文)。所用的转化方法取决于待转化的宿主。用于将异源多核苷酸引入到哺乳动物细胞中的方法是本领域中熟知的,且包括葡聚糖介导的转染、磷酸钙沉淀、聚凝胺介导的转染、原生质体融合、电穿孔、脂质体中的多核苷酸的封装和直接将DNA微注射到核中。As will be understood, antibodies as described herein can be expressed in cell lines other than hybridoma cell lines. Sequences encoding specific antibodies can be used to transform suitable mammalian host cells. Transformation can be performed by any known method for introducing polynucleotides into host cells, including, for example, packaging the polynucleotides in a virus (or in a viral vector) and transducing with the virus (or vector) Host cells, or by transfection procedures known in the art, as shown in U.S. Patent Nos. 4,399,216, 4,912,040, 4,740,461, and 4,959,455 (which patents are incorporated herein by reference). The transformation method used depends on the host to be transformed. Methods for introducing heterologous polynucleotides into mammalian cells are well known in the art, and include dextran-mediated transfection, calcium phosphate precipitation, polybrene-mediated transfection, and protoplast fusion , Electroporation, encapsulation of polynucleotides in liposomes, and direct DNA microinjection into the nucleus.
在细胞-细胞融合技术中,制备拥有具有任何需要的同种型的重链的骨髓瘤、CHO细胞或其它细胞系,制备具有轻链的骨髓瘤、CHO细胞或其它细胞系。之后可将所述细胞融合并可分离表达完整的抗体的细胞系。In the cell-cell fusion technology, myeloma, CHO cells or other cell lines with heavy chains of any desired isotype are prepared, and myeloma, CHO cells or other cell lines with light chains are prepared. The cells can then be fused and cell lines expressing intact antibodies can be isolated.
因此,生成了抗体候选物,其符合如上所述的需要的“结构”属性,通过同种型转换它们一般可具有至少某些需要的“功能”属性。Therefore, antibody candidates are generated that meet the required "structural" attributes as described above, and through isotype conversion they can generally have at least some of the required "functional" attributes.
在细胞-细胞融合技术中,制备了拥有具有需要的同种型的重链的骨髓瘤、CHO细胞或其它细胞系和制备了具有轻链的的骨髓瘤、CHO细胞或其它细胞系。之后可将所述细胞融合并可分离表达完整的抗体的细胞系。In the cell-cell fusion technology, a myeloma, CHO cell or other cell line with a heavy chain of the desired isotype is prepared and a myeloma, CHO cell or other cell line with a light chain is prepared. The cells can then be fused and cell lines expressing intact antibodies can be isolated.
因此,生成了抗体候选物,其符合如上所述的需要的“结构”属性,通过同种型转换它们一般可具有至少某些需要的“功能”属性。Therefore, antibody candidates are generated that meet the required "structural" attributes as described above, and through isotype conversion they can generally have at least some of the required "functional" attributes.
抗体序列Antibody sequence
本发明的实施方案包括以下所列的抗体。下划线表示CDR区。各个抗体重链的CDR序列及其编号如表1所示,抗体轻链的CDR序列及其编号如表2所示。Embodiments of the invention include the antibodies listed below. The underline indicates the CDR region. The CDR sequence and its numbering of each antibody heavy chain are shown in Table 1, and the CDR sequence and its numbering of the antibody light chain are shown in Table 2.
1C2 VH氨基酸序列(SEQ ID NO:1)119aa1C2 VH amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO:1) 119aa
1C2 VH核酸序列(SEQ ID NO:71)357bp1C2 VH nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 71) 357bp
1C2 VL氨基酸序列(SEQ ID NO:2)107aa1C2 VL amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 2) 107aa
1C2 VL核酸序列(SEQ ID NO:72)321bp1C2 VL nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 72) 321bp
1D4 VH氨基酸序列(SEQ ID NO:3)121aa1D4 VH amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 3) 121aa
1D4 VH核酸序列(SEQ ID NO:73)363bp1D4 VH nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 73) 363bp
1D4 VL氨基酸序列(SEQ ID NO:4)107aa1D4 VL amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 4) 107aa
1D4 VL核酸序列(SEQ ID NO:74)321bp1D4 VL nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 74) 321bp
1G11 VH氨基酸序列(SEQ ID NO:5)122aa1G11 VH amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 5) 122aa
1G11 VH核酸序列(SEQ ID NO:75)366bp1G11 VH nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 75) 366bp
1G11 VL氨基酸序列(SEQ ID NO:6)108aa1G11 VL amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 6) 108aa
1G11 VL核酸序列(SEQ ID NO:76)324bp1G11 VL nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 76) 324bp
2F7 VH氨基酸序列(SEQ ID NO:7)117aa2F7 VH amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 7) 117aa
2F7 VH核酸序列(SEQ ID NO:77)351bp2F7 VH nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 77) 351bp
2F7VL氨基酸序列(SEQ ID NO:8)111aa2F7VL amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 8) 111aa
2F7 VL核酸序列(SEQ ID NO:78)333bp2F7 VL nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 78) 333bp
3D7 VH氨基酸序列(SEQ ID NO:9)122aa3D7 VH amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 9) 122aa
3D7 VH核酸序列(SEQ ID NO:79)366bp3D7 VH nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 79) 366bp
3D7 VL氨基酸序列(SEQ ID NO:10)107aa3D7 VL amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 10) 107aa
3D7 VL核酸序列(SEQ ID NO:80)321bp3D7 VL nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 80) 321bp
6A3 VH氨基酸序列(SEQ ID NO:11)121aa6A3 VH amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 11) 121aa
6A3 VH核酸序列(SEQ ID NO:81)363bp6A3 VH nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 81) 363bp
6A3 VL氨基酸序列(SEQ ID NO:12)107aa6A3 VL amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 12) 107aa
6A3 VL核酸序列(SEQ ID NO:82)321bp6A3 VL nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 82) 321bp
表1抗PD-L1抗体重链CDR氨基酸序列及其编号Table 1 Anti-PD-L1 antibody heavy chain CDR amino acid sequence and its numbering
表2抗PD-L1抗体轻链CDR氨基酸序列及其编号Table 2 Anti-PD-L1 antibody light chain CDR amino acid sequence and its numbering
治疗施用和制剂Therapeutic administration and formulation
本发明的实施方案包括用于治疗疾病的PD-L1靶向结合剂的药物制剂;优选地,所述PD-L1靶向结合剂是抗PD-L1抗体。所述制剂将抑制PD-L1与其一个或多个其同源配体的结合,从而治疗病理病症。本发明的 抗体优选地具有足够的亲和力以有效地抑制PD-L1活性,或抑制PD-L1与其一个或多个同源配体的结合,和优选地具有足够的作用持续时间以允许在人中不频繁给药。延长的作用持续时间将允许通过交替的胃肠外途径(诸如皮下或肌内注射)的较不频繁的和更方便的给药方案。The embodiment of the present invention includes a pharmaceutical preparation of a PD-L1 targeted binding agent for treating diseases; preferably, the PD-L1 targeted binding agent is an anti-PD-L1 antibody. The formulation will inhibit the binding of PD-L1 to one or more of its cognate ligands, thereby treating pathological conditions. The antibody of the present invention preferably has sufficient affinity to effectively inhibit the activity of PD-L1, or inhibit the binding of PD-L1 to one or more of its cognate ligands, and preferably has a sufficient duration of action to allow in humans Infrequent administration. The extended duration of action will allow for a less frequent and more convenient dosing regimen via alternate parenteral routes such as subcutaneous or intramuscular injections.
可生成无菌制剂,例如,在抗体的冷冻干燥和重构之前或之后通过经过无菌滤膜进行过滤。抗体一般以冻干的形式或在溶液中贮存。治疗性抗体组合物一般置于具有无菌存取口的容器中,例如,具有允许取回制剂的接头的静脉内溶液包或药瓶,所述接头比如由皮下注射针头可刺穿的塞子。Sterile preparations can be produced, for example, by filtration through a sterile filter membrane before or after freeze-drying and reconstitution of the antibody. Antibodies are generally stored in lyophilized form or in solution. The therapeutic antibody composition is generally placed in a container with a sterile access port, for example, an intravenous solution pack or a vial with a connector that allows the preparation to be retrieved, such as a stopper pierceable by a hypodermic injection needle.
所述PD-L1靶向结合剂可用于治疗癌症。其包括向患者施用有效量的PD-L1靶向结合剂或包含其的组合物。所述癌症选自由以下组成的组:膀胱肿瘤、乳腺肿瘤、前列腺肿瘤、基底细胞癌、胆管癌、膀胱癌、骨癌、脑和CNS癌(例如神经胶质瘤)、子宫颈癌、绒毛膜癌、结肠和直肠癌、结缔组织癌、消化系统的癌症;子宫内膜癌、食道癌;眼癌、头颈癌、胃癌;上皮内肿瘤;肾癌;喉癌;白血病;肝癌;肺癌(例如小细胞和非小细胞肺癌);淋巴瘤,包括霍奇金氏淋巴瘤和非霍奇金氏淋巴瘤;黑素瘤;骨髓瘤、成神经细胞瘤、口腔癌(例如,唇、舌、口和咽);卵巢癌;胰腺癌、成视网膜细胞瘤;横纹肌肉瘤;直肠癌、肾癌、呼吸系统的癌症;肉瘤;皮肤癌;胃癌;睾丸癌;甲状腺癌;子宫癌、泌尿系统的癌症,以及其它癌和肉瘤。The PD-L1 targeted binding agent can be used to treat cancer. It includes administering an effective amount of PD-L1 targeted binding agent or a composition containing the same to the patient. The cancer is selected from the group consisting of: bladder tumor, breast tumor, prostate tumor, basal cell carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, bladder cancer, bone cancer, brain and CNS cancer (e.g. glioma), cervical cancer, choriocarcinoma Cancer, colon and rectal cancer, connective tissue cancer, cancer of the digestive system; endometrial cancer, esophageal cancer; eye cancer, head and neck cancer, gastric cancer; intraepithelial tumor; kidney cancer; laryngeal cancer; leukemia; liver cancer; lung cancer (such as small Cell and non-small cell lung cancer); lymphoma, including Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma; melanoma; myeloma, neuroblastoma, oral cancer (for example, lip, tongue, mouth and Pharynx); ovarian cancer; pancreatic cancer, retinoblastoma; rhabdomyosarcoma; rectal cancer, kidney cancer, cancer of the respiratory system; sarcoma; skin cancer; stomach cancer; testicular cancer; thyroid cancer; uterine cancer, cancer of the urinary system, and Other cancers and sarcomas.
所述PD-L1靶向结合剂可以与化疗剂联合使用。The PD-L1 targeted binding agent can be used in combination with a chemotherapeutic agent.
所述PD-L1靶向结合剂可用于治疗感染,可以与抗生素联合使用。优选地,所述抗生素是抗病毒剂;还优选地,所述抗病毒剂是逆转录酶抑制剂;更优选地,所述逆转录酶抑制剂是聚合酶抑制剂。所述感染是慢性感染,例如HIV、乙肝病毒(HBV)和丙肝病毒(HCV)感染。所述感染是由选自由细菌,病毒,真菌和原生动物组成的组的病原体导致的。The PD-L1 targeted binding agent can be used to treat infections and can be used in combination with antibiotics. Preferably, the antibiotic is an antiviral agent; also preferably, the antiviral agent is a reverse transcriptase inhibitor; more preferably, the reverse transcriptase inhibitor is a polymerase inhibitor. The infection is a chronic infection, such as HIV, hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. The infection is caused by a pathogen selected from the group consisting of bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa.
所述PD-L1靶向结合剂还可与至少一种疫苗联合使用。The PD-L1 targeted binding agent can also be used in combination with at least one vaccine.
附图的简要说明Brief description of the drawings
图1为PD-L1纯化结果图。Figure 1 shows the results of purification of PD-L1.
图2为抗PD-L1抗体的亲和力测定结果图。Figure 2 is a graph showing the results of affinity determination of anti-PD-L1 antibodies.
图3为抗PD-L1抗体免疫荧光染色图。Figure 3 is an immunofluorescence staining image of anti-PD-L1 antibody.
图4为抗PD-L1抗体的免疫荧光效价EC50测定结果图。Figure 4 is a graph showing the results of the EC50 determination of immunofluorescence titer of anti-PD-L1 antibody.
图5为人源化抗PD-L1抗体的亲和力测定结果图。Figure 5 is a graph showing the results of affinity determination of the humanized anti-PD-L1 antibody.
图6为人源化抗PD-L1抗体的免疫荧光效价EC50测定结果图。Figure 6 is a graph showing the EC50 determination result of immunofluorescence titer of humanized anti-PD-L1 antibody.
图7为K562-PD-L1膜表面结合试验结果图。Figure 7 shows the results of the K562-PD-L1 film surface binding test.
图8为Raji-PD-L1膜表面PD-L1结合试验结果图。Figure 8 is a graph showing the results of the PD-L1 binding test on the surface of Raji-PD-L1 membrane.
图9为膜表面PD-L1结合试验结果图。Figure 9 shows the results of the PD-L1 binding test on the membrane surface.
图10为PD-L1 CAR元件结构示意图。Figure 10 is a schematic diagram of the PD-L1 CAR element structure.
图11为PD-L1嵌合抗原受体(PD-L1 CAR)活性图。Figure 11 is a graph of PD-L1 chimeric antigen receptor (PD-L1 CAR) activity.
实施发明的最佳方式The best way to implement the invention
以下的实施例,包括所提供的进行的实验和获得的结果仅用于阐释的目的而不应理解为对本文的教导的限制。The following examples, including the provided experiments and results obtained are only for illustrative purposes and should not be construed as limiting the teachings herein.
实施例1:重组人PD-L1-his蛋白的表达与纯化Example 1: Expression and purification of recombinant human PD-L1-his protein
从NCBI数据库上获取人PD-L1胞外区蛋白序列(NP_054862.1),经哺乳动物密码子优化后,加上6个组氨酸标签编码序列,送金唯智公司合成,得到PD-L1-his的编码核酸序列(SEQ ID NO:49),其氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:50所示。通过本领域熟知的分子生物学方法将片段构建至真核表达载体pVKD1.0中(参见PCT/CN2017/104401,其公开号为WO2019061297A1),构建成表达人PD-L1胞外区肽段的真核表达载体pVKD1.0-hPD-L1-his。Obtain the human PD-L1 extracellular domain protein sequence (NP_054862.1) from the NCBI database. After mammalian codon optimization, 6 histidine tag coding sequences are added and sent to Jinweizhi Company for synthesis to obtain PD-L1-his The coding nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 49), and its amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 50. The fragment was constructed into the eukaryotic expression vector pVKD1.0 (see PCT/CN2017/104401, the publication number of which is WO2019061297A1) by molecular biology methods well-known in the art, and constructed to express the peptide of the extracellular region of human PD-L1. Nuclear expression vector pVKD1.0-hPD-L1-his.
将pVKD1.0-hPD-L1-his载体用PEI介导转染至293T细胞中,收集上清,并用镍柱层析,然后通过超滤得到纯化的人PD-L1-his重组蛋白,具体方法参看试剂盒说明书(GE Healthcare,货号:17-5247-01)。其纯化结果如图1。The pVKD1.0-hPD-L1-his vector was transfected into 293T cells mediated by PEI, the supernatant was collected, and purified by nickel column chromatography, and then purified by ultrafiltration to obtain the purified human PD-L1-his recombinant protein, the specific method Please refer to the kit instructions (GE Healthcare, article number: 17-5247-01). The purification results are shown in Figure 1.
实施例2:小鼠免疫、杂交瘤的融合和克隆筛查Example 2: Mouse immunity, hybridoma fusion and clone screening
从苏州大学动物实验中心购买5只6-8周龄的雌性BALB/c小鼠,并饲养于苏州大学动物实验中心SPF级动物房中。将实施例1中的人PD-L1-his重组蛋白与完全弗氏佐剂完全弗氏佐剂(CFA)或不完全弗氏佐剂(IFA)充分乳化后,背部皮下注射,10μg/只。每间隔一个月免疫一次,连续免疫BALB/c小鼠3到4次。Five female BALB/c mice aged 6-8 weeks were purchased from the Animal Experiment Center of Soochow University and raised in the SPF animal room of the Animal Experiment Center of Soochow University. After fully emulsifying the human PD-L1-his recombinant protein in Example 1 with complete Freund's adjuvant, complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) or incomplete Freund's adjuvant (IFA), the back was injected subcutaneously at 10 μg/mouse. Immunize BALB/
融合前一周,复苏SP 2/0骨髓瘤细胞,饲养于含10%FBS的DMEM培养基中,融合前三天,用50μg人PD-L1-His重组蛋白通过腹腔注射冲击免疫小鼠。通过颈脱位法处死免疫小鼠,并获取小鼠脾细胞。用无血清的DMEM培养基洗涤小鼠脾细胞和SP 2/0骨髓瘤细胞三遍,然后500g离心5分钟,分别重悬于10mL无血清DMEM培养基中,细胞计数。取脾细胞:SP 2/0骨髓瘤细胞=5:1的比例混合,500g离心5分钟,去上清后用 1mL 50%PEG进行细胞融合。融合完成后500g离心5分钟,去上清,用含20%FBS的DMEM培养基重悬,以2×105细胞/孔加入96孔板中,37℃过夜孵育。第二天,加入含HAT的杂交瘤选择培养基(Sigma,目录号A9666),100μL/孔。以后每隔3天,去除一半的培养基,并用杂交瘤选择培养基补充。在第14天,每孔取100μL上清,用ELISA法筛查杂交瘤上清中的抗体活性。One week before the fusion, the
ELISA方法为本领域熟知,简述如下。96孔酶标板购自江海玻璃仪器总厂。重组人PD-L1-his蛋白由苏州工业园区唯可达生物科技有限公司提供。用NaHCO3缓冲液(pH 9.6)包被蛋白,4℃过夜,包被浓度为1μg/mL。用含0.1%牛血清白蛋白(bovine serum albumin,BSA)的磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)37℃封闭30分钟,再用含0.5%吐温20的磷酸盐缓冲液(PBST)洗5遍后拍干,加入待测杂交瘤上清,100μL/孔,室温孵育1小时,PBST洗5遍后,1:5000孵育羊抗鼠HRP二抗(美国Santacruz公司,货号:sc-2005),37℃孵育30分钟,PBST洗5遍后拍干,用3,3,5,5-四甲基联苯胺(3,3,5,5-tetraamthyl benzidine,TMB)底物显色,37℃孵育15分钟,用2M稀硫酸终止后用酶标仪(美国Thermo公司)在450nm波长下读取吸光度(A)值。The ELISA method is well known in the art and is briefly described as follows. The 96-well microtiter plate was purchased from Jianghai Glass Instrument Factory. Recombinant human PD-L1-his protein was provided by Suzhou Industrial Park Weike Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The protein was coated with NaHCO3 buffer (pH 9.6) at 4°C overnight, and the coating concentration was 1 μg/mL. Block with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) at 37°C for 30 minutes, and then wash with phosphate buffered saline (PBST) containing 0.5
将OD值>1.0的孔定义为阳性克隆,从96孔细胞培养板中挑出阳性细胞克隆,然后转移至24孔培养,两天后再次运用上述的ELSIA法复测上清抗体活性。复测阳性的克隆转移至6孔板培养,然后收集细胞,进行后续实验。复测后滴定的结果如表3所示。选取复测后滴度>1000的克隆进行进一步研究。The wells with an OD value> 1.0 were defined as positive clones. The positive cell clones were picked from the 96-well cell culture plate and transferred to 24-well culture. Two days later, the above-mentioned ELSIA method was used to retest the supernatant antibody activity. Retest positive clones were transferred to a 6-well plate for culture, and then the cells were collected for subsequent experiments. The results of the titration after the retest are shown in Table 3. Select clones with titer> 1000 after retest for further study.
表3复测后杂交瘤上清OD450值Table 3 OD450 value of hybridoma supernatant after retest
实施例3:抗PD-L1抗体的序列获取并分析Example 3: Sequence acquisition and analysis of anti-PD-L1 antibody
用Trizol试剂(Thermo,货号15596026)裂解处理杂交瘤细胞,然后提取杂交瘤细胞RNA,具体方法本领域熟知,可参看Trizol试剂说明书。The hybridoma cells were lysed and treated with Trizol reagent (Thermo, catalog number 15596026), and then the hybridoma cell RNA was extracted. The specific method is well known in the art, please refer to the Trizol reagent manual.
用cDNA合成(逆转录)试剂盒(宝生物,货号2641Q)扩增cDNA第一链,具体方法参看试剂盒说明书。然后PCR分别扩增抗体重链VH区和轻链的VL区,具体方法参考Sherie L.Morrison“Cloning,Expression,and Modification of Antibody V Regions”in“Current Protocols in Immunology”,Volume 47,Issue 1。Amplify the first strand of cDNA with a cDNA synthesis (reverse transcription) kit (Bao Biological, article number 2641Q). For specific methods, refer to the kit instructions. Then PCR amplifies the VH region of the antibody heavy chain and the VL region of the light chain respectively. For specific methods, refer to Sherie L. Morrison "Cloning, Expression, and Modification of Antibody V Regions" in "Current Protocols in Immunology", Volume 47,
扩增后的产物连接至pMD19T载体(宝生物,货号6013),送测序,每个VH和VL各送至少10个克隆测序,得到抗体VH和VL核酸序列。并分析得到各个抗体的CDR区序列,各个抗体的CDR区序列见表1和表2。The amplified product is ligated to the pMD19T vector (Bao Biological, Item No. 6013) and sent for sequencing. At least 10 clones of each VH and VL are sent for sequencing to obtain antibody VH and VL nucleic acid sequences. And analyze the CDR region sequence of each antibody, see Table 1 and Table 2 for the CDR region sequence of each antibody.
实施例4:抗体纯化和亲和力测定Example 4: Antibody purification and affinity determination
将实施例2中获得的杂交瘤细胞用含10%FBS的DMEM培养基扩增,收集杂交瘤上清,用蛋白A柱(GE Healthcare,货号:28985254)纯化,具体方法参考试剂盒说明书,得到各个纯化后的小鼠单克隆抗体,并用ELISA方法测定抗体的EC50效价。ELISA的方法为本领域人员熟知,简述如下。96孔酶标板购自江海玻璃仪器总厂。实施例1制备的重组人PD-L1-his蛋白。用NaHCO3缓冲液(pH 9.6)包被蛋白,4℃过夜,包被浓度为1μg/mL。用含0.1%牛血清白蛋白(bovine serum albumin,BSA)的磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)37℃封闭30分钟,再用含0.5%吐温20的磷酸盐缓冲液(PBST)洗5遍后拍干,加入待测抗PD-L1抗体,100μL/孔,抗体起始浓度为100ng/mL,3倍或4倍梯度稀释,室温孵育1小时,PBST洗5遍后,1:5000孵育羊抗鼠HRP二抗(美国Santacruz公司,货号:sc-2005),37℃孵育30分钟,PBST洗5遍后拍干,用3,3,5,5-四甲基联苯胺(3,3,5,5-tetraamthyl benzidine,TMB)底物显色,37℃孵育15分钟,用2M稀硫酸终止后用酶标仪(美国Thermo公司)在450nm波长下读取吸光度(A)值。最后用GraphPad软件拟合曲线,计算EC50。The hybridoma cells obtained in Example 2 were amplified with DMEM medium containing 10% FBS, and the hybridoma supernatant was collected and purified with a protein A column (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 28985254). For specific methods, refer to the kit instructions to obtain The EC50 titer of each purified mouse monoclonal antibody was determined by ELISA method. The method of ELISA is well known to those skilled in the art and is briefly described as follows. The 96-well microtiter plate was purchased from Jianghai Glass Instrument Factory. The recombinant human PD-L1-his protein prepared in Example 1. The protein was coated with NaHCO3 buffer (pH 9.6) at 4°C overnight, and the coating concentration was 1 μg/mL. Block with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) at 37°C for 30 minutes, and then wash it with phosphate buffered saline (PBST) containing 0.5
抗PD-L1抗体的EC50效价见表4。The EC50 titers of anti-PD-L1 antibodies are shown in Table 4.
表4 PD-L1抗体EC50效价Table 4 EC50 titer of PD-L1 antibody
然后用Friguet法(J Immunol Methods.1985;77:305-19)测定各抗体的平衡解离常数Kd,即抗体的亲和力。主要步骤简述如下。96孔酶标板购自江海玻璃仪器总厂。重组人PD-L1-his蛋白由实施例1制备。用NaHCO3缓冲液(pH 9.6)包被蛋白,4℃过夜,包被浓度为5μg/mL。用含5%胎牛血清(FBS)的磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)37℃封闭30分钟。用含5%胎牛血清(FBS)的磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)(抗体稀释液)稀释PD-L1-his抗原蛋白,得到12个不同梯度的稀释液(0、0.349nM、0.697nM、1.395nM、2.79nM、5.58nM、11.2nM、22.3nM、44.6nM、89.3nM、178.4nM、357nM)后,然后加入恒定浓度的待测抗PD-L1抗体,100μL/孔,37℃孵育1小时。然后将共孵育复合物加入酶标板,室温2小时。PBST洗5遍后,1:5000孵育羊抗鼠HRP二抗(美国Santacruz公司,货号:sc-2005),37℃孵育30分钟,PBST洗5遍后拍干,用3,3,5,5-四甲基联苯胺(3,3,5,5-tetraamthyl benzidine,TMB)底物显色,37℃孵育15分钟,用2M稀硫酸终止后用酶标仪(美国Thermo公司)在450nm波长下读取吸光度(A)值。然后计算Kd值。图2为各抗体亲和力测定的结果,其最后结果汇总于表5。Then the Friguet method (J Immunol Methods. 1985; 77: 305-19) was used to determine the equilibrium dissociation constant Kd of each antibody, that is, the affinity of the antibody. The main steps are briefly described as follows. The 96-well microtiter plate was purchased from Jianghai Glass Instrument Factory. The recombinant human PD-L1-his protein was prepared in Example 1. The protein was coated with NaHCO3 buffer (pH 9.6) at 4°C overnight, and the coating concentration was 5 μg/mL. Block with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS) at 37°C for 30 minutes. Dilute the PD-L1-his antigen protein with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (antibody diluent) containing 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS) to obtain 12 different gradient dilutions (0, 0.349nM, 0.697nM, 1.395 nM, 2.79nM, 5.58nM, 11.2nM, 22.3nM, 44.6nM, 89.3nM, 178.4nM, 357nM), then add a constant concentration of anti-PD-L1 antibody to be tested, 100μL/well, and incubate at 37°C for 1 hour. Then add the co-incubation complex to the microtiter plate at room temperature for 2 hours. After washing 5 times with PBST, incubate goat anti-mouse HRP secondary antibody (Santacruz, USA, product number: sc-2005) at 1:5000, incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes, wash 5 times with PBST and pat dry,
表5抗PD-L1抗体亲和力Table 5 Anti-PD-L1 antibody affinity
最后,用免疫荧光法检测各PD-L1抗体与天然PD-L1蛋白的结合能力。用表达全长人PD-L1的质粒pVKD1.0-PD-L1-Full(苏州工业园区唯可达生物科技有限公司提供)转染至Hela细胞,48小时后先用含5%FBS的 PBS室温封闭30分钟,然后加入各个梯度的抗PD-L1抗体孵育,室温1小时,然后用PBS洗涤3遍后,加入1:1000稀释的羊抗鼠-PE二抗(Santa Cruz,货号:sc-3752),室温孵育30分钟后,用荧光显微镜观察(美国BioTek,Cytation 3)成像拍照。结果如图3所示,各个抗PD-L1抗体均能有效结果细胞膜表面表达的PD-L1蛋白。根据所得荧光强度,经计算分析,得到免疫荧光法染色的EC50效价,结果见图4,其最后结果汇总于表6。Finally, immunofluorescence was used to detect the binding ability of each PD-L1 antibody to the natural PD-L1 protein. Transfected into Hela cells with the plasmid pVKD1.0-PD-L1-Full (provided by Suzhou Industrial Park Weida Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) expressing full-length human PD-L1. After 48 hours, first use PBS containing 5% FBS at room temperature Block for 30 minutes, then add each gradient of anti-PD-L1 antibody to incubate at room temperature for 1 hour, then wash with PBS for 3 times, add 1:1000 diluted goat anti-mouse-PE secondary antibody (Santa Cruz, catalog number: sc-3752) ), after incubating at room temperature for 30 minutes, observe with a fluorescence microscope (BioTek,
表6抗PD-L1抗体EC50效价(免疫荧光法)Table 6 EC50 titer of anti-PD-L1 antibody (immunofluorescence method)
实施例5:抗体人源化改造和表达Example 5: Humanized antibody transformation and expression
将实施例3中获得的各个抗体基因VH区通过本领域熟知的分子生物学技术克隆至带有人IgG1 CH1结构区及其Fc结构区的载体Abvec-hIgG1(GenBank:FJ475055.1)上。将实施例3中获得的各个抗体基因VL区通过本领域熟知的分子生物学技术克隆至带有人κ轻链恒定区的载体AbVec-hIgKappa(GenBank:FJ475056.1)上。然后将分别表达人源化重链和人源化轻链的质粒共同转染至293T细胞中,收集上清,获取抗PD-L1人源化抗体。The VH regions of each antibody gene obtained in Example 3 were cloned into the vector Abvec-hIgG1 (GenBank: FJ475055.1) with the human IgG1 CH1 structural region and its Fc structural region by molecular biology techniques well known in the art. The VL regions of each antibody gene obtained in Example 3 were cloned into the vector AbVec-hIgKappa (GenBank: FJ475056.1) with human kappa light chain constant region by molecular biology techniques well known in the art. Then, the plasmids expressing the humanized heavy chain and the humanized light chain were co-transfected into 293T cells, and the supernatant was collected to obtain the anti-PD-L1 humanized antibody.
实施例6:人源化抗体纯化Example 6: Purification of humanized antibodies
将实施例5中获得的含有人源化抗体的细胞转染上清通过蛋白A柱(GE Healthcare,货号:17-0402-01)纯化,具体方法参考试剂盒说明书。得到各个纯化后的人源化抗体,结果见表7。The cell transfection supernatant containing the humanized antibody obtained in Example 5 was purified by a protein A column (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 17-0402-01), and the specific method refers to the kit instructions. Each purified humanized antibody was obtained, and the results are shown in Table 7.
表7人源化抗体纯化结果Table 7 Purification results of humanized antibodies
实施例7:人源化抗体EC50效价确定Example 7: Determination of EC50 titer of humanized antibody
ELISA法确定抗PD-L1抗体的EC50活性。ELISA的方法为本领域人员熟知,简述如下。96孔酶标板购自江海玻璃仪器总厂。实施例1制备的重组人PD-L1-his蛋白用NaHCO3缓冲液(pH 9.6)包被蛋白,4℃过夜,包被浓度为1μg/mL。用含0.1%牛血清白蛋白(bovine serum albumin,BSA)的磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)37℃封闭30分钟,再用含0.5%吐温20的磷酸盐缓冲液(PBST)洗5遍后拍干,加入待测抗PD-L1抗体,100μL/孔,抗体起始浓度为100ng/mL,3倍或4倍梯度稀释,室温孵育1小时,PBST洗5遍后,1:5000孵育羊抗鼠HRP二抗(美国Santacruz公司,货号:sc-2005),37℃孵育30分钟,PBST洗5遍后拍干,用3,3,5,5-四甲基联苯胺(3,3,5,5-tetraamthyl benzidine,TMB)底物显色,37℃孵育15分钟,用2M稀硫酸终止后用酶标仪(美国Thermo公司)在450nm波长下读取吸光度(A)值。最后用GraphPad软件拟合曲线,计算EC50。各抗PD-L1抗体EC50效价结果见表8。The EC50 activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody was determined by ELISA. The method of ELISA is well known to those skilled in the art and is briefly described as follows. The 96-well microtiter plate was purchased from Jianghai Glass Instrument Factory. The recombinant human PD-L1-his protein prepared in Example 1 was coated with NaHCO3 buffer (pH 9.6) at 4°C overnight, and the coating concentration was 1 μg/mL. Block with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) at 37°C for 30 minutes, and then wash it with phosphate buffered saline (PBST) containing 0.5
表8人源化抗体EC50效价Table 8 EC50 titers of humanized antibodies
实施例8:人源化抗PD-L1抗体的亲和力测定Example 8: Affinity determination of humanized anti-PD-L1 antibody
用实施例4中的Friguet法测定人源化抗体的Kd值,结果如图5,其结果汇总于表9。The Kd value of the humanized antibody was measured by the Friguet method in Example 4. The results are shown in Figure 5, and the results are summarized in Table 9.
表9人源化抗体亲和力Table 9 Humanized antibody affinity
实施例9:人源化抗PD-L1抗体的亲和力(免疫荧光法)Example 9: Affinity of humanized anti-PD-L1 antibody (immunofluorescence method)
用实施例4中的免疫荧光法测定人源化抗体结合天然PD-L1亲和力,结果如图6,其结果汇总于表10。The immunofluorescence method in Example 4 was used to determine the affinity of the humanized antibody for binding to natural PD-L1.
表10人源化抗体亲和力(免疫荧光法)Table 10 Humanized antibody affinity (immunofluorescence method)
实施例10:抗PD-L1抗体结合肿瘤细胞细胞膜表面PD-L1抗原的能力Example 10: Ability of anti-PD-L1 antibody to bind to PD-L1 antigen on the surface of tumor cell membrane
用流式细胞术检测抗PD-L1抗体结合肿瘤细胞细胞膜表面PD-L1抗原的能力。分别取106稳定表达人PD-L1的K562-PD-L1细胞(参见WO2018103734A1)和稳定表达人PD-L1的Raji-PD-L1细胞(购自Invivogen)于EP管(1.5mL)中,然后加入相应的抗PD-L1抗体,进行一抗孵育。染色体系总体积为50μL的含2%FBS的PBS缓冲液(染色缓冲液),一抗为实施例2中得到的抗PD-L1抗体,抗体终浓度均调整为2μg/mL,于4℃孵育30min。结束后,每管加入500μL的染色缓冲液洗脱两次,800g离心,每次3分钟。一抗染色结束后,配制二抗染色混合物,以1:1000加入二抗驴抗小鼠-IgG(H+L)(AF647 Conjugate,Abcam),染色体系总体积亦为50μL的染色缓冲液,于4℃染色30分钟,每管加入500μL的染色缓冲液洗脱两次,800g离心,每次3分钟。最后用300μL的染色缓冲液重悬细胞后进行流式检测。结果如图7和图8所示,所有抗PD-L1抗体均能有效结合细胞膜表面的PD-L1蛋白。总体结合效率见图9所示,其中1C2、6A3、2F7、1D4抗体对膜表面表达的PD-L1蛋白结合能力最高。Flow cytometry was used to detect the ability of anti-PD-L1 antibody to bind the PD-L1 antigen on the surface of tumor cell membrane. Take 106 K562-PD-L1 cells stably expressing human PD-L1 (see WO2018103734A1) and Raji-PD-L1 cells stably expressing human PD-L1 (purchased from Invivogen) in an EP tube (1.5 mL), and then Add the corresponding anti-PD-L1 antibody and incubate with the primary antibody. The total volume of the staining system is 50μL of PBS buffer (staining buffer) containing 2% FBS. The primary antibody is the anti-PD-L1 antibody obtained in Example 2. The final concentration of the antibody is adjusted to 2μg/mL and incubated at 4°C 30min. After finishing, add 500μL of staining buffer to each tube for elution twice, and centrifuge at 800g for 3 minutes each time. After the primary antibody staining, prepare the secondary antibody staining mixture, add the secondary antibody donkey anti-mouse-IgG (H+L) (AF647 Conjugate, Abcam) at 1:1000, and the total volume of the staining system is also 50μL of staining buffer. Stain for 30 minutes at 4°C, add 500μL of staining buffer to each tube for elution twice, and centrifuge at 800g for 3 minutes each time. Finally, the cells were resuspended in 300 μL of staining buffer for flow cytometry. The results are shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8. All anti-PD-L1 antibodies can effectively bind to the PD-L1 protein on the cell membrane surface. The overall binding efficiency is shown in Figure 9. Among them, 1C2, 6A3, 2F7, and 1D4 antibodies have the highest binding ability to the PD-L1 protein expressed on the membrane surface.
实施例11:抗PD-L1抗体的嵌合抗原受体(CAR)活性Example 11: Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody
将PD-L1抗体VL区和VH区拼接进行基因合成,合成后的PD-L1嵌合抗原受体基因,均转载至慢病毒载体pHAGE-EF1α-MCS-ZsGreen(购自哈佛大学医学院,货号:EvNO00061636),从而获得基于6个PD-L1单抗的可识别人PD-L1的CAR:1C2 CAR、1D4 CAR、1G11 CAR、2F7 CAR、3D7 CAR和6A3 CAR(PD-L1 CAR元件结构示意图见图10)。其中,CD8 SP代表源于人CD8抗原信号肽(CD8 SP)的序列,PD-L1 VL代表抗PD-L1抗体的VL序列,PD-L1 VH代表抗PD-L1抗体的VH序列,CD28、4-1BBL以及CD3ζ代表各自相应的元件,均为常用的CAR构建所需元件。具体地,CD8 SP的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:51所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:52所示;CD28元件的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:53所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:54所示;4-1BBL元件的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:55所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:56所示;CD3ζ元件的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:57所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:58所示。1C2 CAR的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:59所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:60所示;1D4 CAR的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:61所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:62所示;1G11 CAR的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:63所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:64所示;2F7 CAR的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:64所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:66所示;3D7 CAR的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:67所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:68所示;6A3 CAR的编码核酸序列如SEQ ID NO:69所示,氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO:70所示。The VL and VH regions of the PD-L1 antibody were spliced for gene synthesis, and the synthesized PD-L1 chimeric antigen receptor genes were all transferred to the lentiviral vector pHAGE-EF1α-MCS-ZsGreen (purchased from Harvard Medical School, catalog number :EvNO00061636), so as to obtain the CAR that can recognize human PD-L1 based on 6 PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies: 1C2 CAR, 1D4 CAR, 1G11 CAR, 2F7 CAR, 3D7 CAR and 6A3 CAR (PD-L1 CAR element structure diagram see Figure 10). Among them, CD8 SP represents the sequence derived from the human CD8 antigen signal peptide (CD8 SP), PD-L1 VL represents the VL sequence of the anti-PD-L1 antibody, PD-L1 VH represents the VH sequence of the anti-PD-L1 antibody, CD28, 4 -1BBL and CD3ζ represent their respective components, which are commonly used components for CAR construction. Specifically, the coding nucleic acid sequence of CD8 SP is shown in SEQ ID NO: 51, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 52; the coding nucleic acid sequence of CD28 element is shown in SEQ ID NO: 53, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO. The coding nucleic acid sequence of the 4-1BBL element is shown in SEQ ID NO: 55, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 56; the coding nucleic acid sequence of the CD3ζ element is shown in SEQ ID NO: 57, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 57. As shown in SEQ ID NO: 58. The coding nucleic acid sequence of 1C2 CAR is shown in SEQ ID NO: 59, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 60; the coding nucleic acid sequence of 1D4 CAR is shown in SEQ ID NO: 61, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 62 Show; 1G11 CAR coding nucleic acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 63, amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 64; 2F7 CAR coding nucleic acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 64, and amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 66; 3D7 CAR coding nucleic acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 67, amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 68; 6A3 CAR coding nucleic acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 69, and amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 70 shown.
将慢病毒包装质粒转染进293T细胞中,转染48h后收集病毒上清,3000rpm,4℃离心10分钟去除细胞碎片,再经0.45μm滤器过滤,以体积比1:5加入慢病毒浓缩液PEG8000(5×),浓缩过夜,4000g,4℃离心20分钟获得慢病毒沉淀,用RPMI1640培养基重悬慢病毒,-80℃保存。取一支浓缩的病毒感染Jurkat E6-1(ATCC目录号:TIB-152TM,简称JE6-1),感染时细胞数控制在2×105,加入终浓度为10μg/mL的促感染试剂硫酸鱼精蛋白。采用离心感染法,1000g,于32℃离心感染1小时。离心感染结束后6-8小时换成新鲜的培养基RPMI1640,继续培养扩增感染后的JE6-1。待细胞扩增到一定数量,采用流式细胞仪分选PD-L1 CAR阳性细胞。分别取105的PD-L1 CAR-T细胞与靶细胞(K562和K562-PD-L1),以1:1混合,400g,离心1分钟促进细胞接触,置于37℃孵箱,孵育24小时后收集上清于-20℃冻存备用。采用Human IL-2 ELISA kit(BD Biosciences)进行上清IL-2的检测,确定PD-L1 CAR活性。结果如图11所示,基于1C2,1D4,2F7,3D7和6A3的PD-L1 CAR均可识别肿瘤细胞膜表面PD-L1抗原而激活,分泌细胞因子IL-2。其中,1D4鼠源单抗的活化效果与阳性对照抗体(Avelumab,参看WO2016137985A1)相当。Transfect the lentivirus packaging plasmid into 293T cells, collect the virus supernatant after 48 hours of transfection, centrifuge at 3000 rpm, 4°C for 10 minutes to remove cell debris, filter through a 0.45 μm filter, and add lentivirus concentrate at a volume ratio of 1:5 PEG8000 (5×), concentrated overnight, 4000g, 4°C for 20 minutes to obtain lentivirus precipitation, resuspend the lentivirus in RPMI1640 medium, and store at -80°C. Take a concentrated virus to infect Jurkat E6-1 (ATCC catalog number: TIB-152TM , referred to as JE6-1), control the number of cells during infection to 2×105 , and add the final concentration of 10 μg/mL sulfuric acid, a pro-infection reagent Fish protein. Use centrifugal infection method, 1000g, centrifugal infection at 32℃ for 1 hour. 6-8 hours after the end of the centrifugal infection, change to a fresh medium RPMI1640, and continue to grow and expand the infected JE6-1. After the cells are expanded to a certain number, the PD-L1 CAR positive cells are sorted by flow cytometry. Take 105 PD-L1 CAR-T cells and target cells (K562 and K562-PD-L1) respectively, mix 1:1, 400g, centrifuge for 1 minute to promote cell contact, place in a 37℃ incubator, and incubate for 24 hours The supernatant was collected and frozen at -20°C for later use. The human IL-2 ELISA kit (BD Biosciences) was used to detect the supernatant IL-2 to determine the PD-L1 CAR activity. The results are shown in Figure 11. PD-L1 CARs based on 1C2, 1D4, 2F7, 3D7 and 6A3 can all recognize the PD-L1 antigen on the tumor cell membrane surface and activate it to secrete the cytokine IL-2. Among them, the activation effect of the 1D4 murine monoclonal antibody is equivalent to the positive control antibody (Avelumab, see WO2016137985A1).
Claims (21)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2019/090878WO2020248156A1 (en) | 2019-06-12 | 2019-06-12 | Pd-l1-targeting binding agent and use thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2019/090878WO2020248156A1 (en) | 2019-06-12 | 2019-06-12 | Pd-l1-targeting binding agent and use thereof |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2020248156A1true WO2020248156A1 (en) | 2020-12-17 |
Family
ID=73780824
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2019/090878CeasedWO2020248156A1 (en) | 2019-06-12 | 2019-06-12 | Pd-l1-targeting binding agent and use thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2020248156A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP4370213A4 (en)* | 2021-07-16 | 2025-06-04 | Instil Bio (Uk) Limited | CHIMERIC MOLECULES PROVIDING TARGETED CO-STIMULATION FOR ADOPTIVE CELL THERAPY |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101248089A (en)* | 2005-07-01 | 2008-08-20 | 米德列斯公司 | Human monoclonal antibodies to programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) |
| CN102245640A (en)* | 2008-12-09 | 2011-11-16 | 霍夫曼-拉罗奇有限公司 | Anti-PD-L1 antibodies and their use for enhancing T cell function |
| CN102264762A (en)* | 2008-09-26 | 2011-11-30 | 达纳-法伯癌症研究公司 | Human anti-PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 antibodies and applications thereof |
- 2019
- 2019-06-12WOPCT/CN2019/090878patent/WO2020248156A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101248089A (en)* | 2005-07-01 | 2008-08-20 | 米德列斯公司 | Human monoclonal antibodies to programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) |
| CN102264762A (en)* | 2008-09-26 | 2011-11-30 | 达纳-法伯癌症研究公司 | Human anti-PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 antibodies and applications thereof |
| CN102245640A (en)* | 2008-12-09 | 2011-11-16 | 霍夫曼-拉罗奇有限公司 | Anti-PD-L1 antibodies and their use for enhancing T cell function |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP4370213A4 (en)* | 2021-07-16 | 2025-06-04 | Instil Bio (Uk) Limited | CHIMERIC MOLECULES PROVIDING TARGETED CO-STIMULATION FOR ADOPTIVE CELL THERAPY |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7345578B2 (en) | Novel anti-PD-L1 antibody | |
| US12252536B2 (en) | Caninized antibodies | |
| JP6480561B2 (en) | Targeted binding agent for B7-H1 | |
| JP6797111B2 (en) | PD-L1 antibody that binds to canine PD-L1 | |
| US11472882B2 (en) | Anti-B7-H4 antibody, antigen-binding fragment thereof and pharmaceutical use thereof | |
| US20190367612A1 (en) | Anti-gprc5d antibody and molecule containing same | |
| JP7368453B2 (en) | High affinity antibodies against PD-1 and LAG-3 and bispecific binding proteins made therefrom | |
| IL293138A (en) | Antibodies to cd3 and bcma and bispecific binding proteins produced from them | |
| EP4249511A2 (en) | Anti-pd-l1/anti-lag3 bispecific antibodies and uses thereof | |
| CN118251419A (en) | Anti-TIGIT-anti-PD-L1 bispecific antibodies, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof | |
| CN112079924B (en) | PD-L1 targeted binding agents and their uses | |
| WO2020248156A1 (en) | Pd-l1-targeting binding agent and use thereof | |
| RU2807484C2 (en) | Antibody to pd-1, its antigen-binding fragment and its pharmaceutical use | |
| WO2025113640A1 (en) | Antibody binding to lilrb1/2 or pd1-lilrb1/2 and use thereof | |
| HK40067877A (en) | Antibodies to cd3 and bcma, and bispecific binding proteins made therefrom | |
| HK40044020A (en) | High affinity antibodies to pd-1 and lag-3 and bispecific binding proteins made therefrom |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | Ref document number:19933164 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 | |
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase | Ref country code:DE | |
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase | Ref document number:19933164 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 |