WO2018179338A1 - Machine learning device and image recognition device - Google Patents
Machine learning device and image recognition deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2018179338A1 WO2018179338A1PCT/JP2017/013603JP2017013603WWO2018179338A1WO 2018179338 A1WO2018179338 A1WO 2018179338A1JP 2017013603 WJP2017013603 WJP 2017013603WWO 2018179338 A1WO2018179338 A1WO 2018179338A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- image
- neural network
- feature amount
- unit
- feature
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/0464—Convolutional networks [CNN, ConvNet]
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/045—Combinations of networks
- G06N3/0455—Auto-encoder networks; Encoder-decoder networks
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G06N3/0895—Weakly supervised learning, e.g. semi-supervised or self-supervised learning
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T1/00—General purpose image data processing
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
Definitions
- the present inventionrelates to a machine learning device that inputs a learning image and outputs a feature value of the learning image and updates a neural network parameter, and an image recognition device that searches for a registered image similar to a recognition target image. It is.
- Non-Patent Document 1discloses a machine learning device that updates a parameter of a model for extracting a feature amount of an image by performing machine learning for classifying images. Since this machine learning device is a device that uses a supervised learning method, machine learning is performed using teacher data.
- the conventional machine learning apparatusis configured as described above, it is necessary to collect a large amount of teacher data when performing machine learning. For this reason, when it is difficult to collect a large amount of teacher data, it is not possible to update and optimize the parameters of the model for extracting the feature amount of the image. As a result, there is a problem that the accuracy of the feature amount extracted by the model may be deteriorated.
- the present inventionhas been made to solve the above-described problems, and can update the parameters of a neural network that inputs a learning image and outputs a feature amount of the learning image without using teacher data.
- the purposeis to obtain a machine learning device.
- Another object of the present inventionis to obtain an image recognition device that can search for a registered image similar to a recognition target image using a neural network whose parameters are updated by a machine learning device.
- the machine learning deviceincludes a binary image conversion unit that converts a learning image, which is a learning target image, into a binary image, and a first neural that inputs the learning image and outputs a feature amount of the learning image.
- a feature amount extraction unithaving a network and a second neural network that inputs a feature amount output from the first neural network and outputs a reconstructed image that is an image reconstructed from a learning image as a binary image
- An image reconstructing unit, and the parameter updating unitincludes a first neural network according to a difference between the reconstructed image output from the second neural network and the binary image converted by the binary image converting unit. Each of the parameter and the parameter of the second neural network is updated.
- a binary image conversion unitthat converts a learning image into a binary image
- a feature amount extraction unitthat includes a first neural network that inputs the learning image and outputs the feature amount of the learning image
- An image reconstruction unithaving a second neural network that inputs a feature amount output from the first neural network and outputs a reconstructed image
- a parameter update unitis output from the second neural network. Since each of the first neural network parameter and the second neural network parameter is updated according to the difference between the reconstructed image and the binary image converted by the binary image conversion unit, the teacher data Without using the parameter of the first neural network that inputs the learning image and outputs the feature amount of the learning image. There is an advantage of being able to update the data.
- FIG. 2is a hardware configuration diagram of a computer when the image recognition apparatus is realized by software or firmware. It is a flowchart which shows the processing content in the sampling part 2 of the machine learning apparatus by Embodiment 1 of this invention.
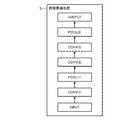
- FIG. 1is a block diagram showing a machine learning apparatus according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention
- FIG. 2is a hardware block diagram showing a machine learning apparatus according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
- the machine learning apparatus according to the first embodimentuses a document image that is an image showing a document as a learning image that is an image to be learned.
- a form image that is an image showing a formmay be used.
- the learning image storage unit 1is realized by, for example, the learning image storage circuit 11 shown in FIG. 2, and stores a plurality of document images acquired in advance.
- the document image stored in the learning image storage unit 1is assumed to be a gray scale image, for example. For this reason, in the case of a color image, it is assumed that the color image is converted into a grayscale image before being stored in the learning image storage unit 1.
- the document image acquisition methodis not particularly limited, and may be, for example, a document image read by a scanner or a document image taken by a camera. However, when using an image taken by a camera as a document image, the photographed image is corrected as seen from directly in front of the document, and the area where the document is reflected is selected from the corrected photographed image. Cut out as an image.
- the paper size of a documentcan be specified, and the learning image storage unit 1 stores a document image showing a document of the same paper size.
- the document images stored in the learning image storage unit 1are all document images in which documents of the same paper size are shown.
- the sampling unit 2is realized by, for example, the sampling circuit 12 shown in FIG.
- the sampling unit 2performs a process of sequentially selecting any one document image from a plurality of document images stored in the learning image storage unit 1. Further, the sampling unit 2 performs image processing for changing the image size of the selected document image and rotating the selected document image. Further, the sampling unit 2 extracts a region having the same size as the binary image converted by the binary image conversion unit 3 from the document image after the image processing, and uses the extracted region as a document image. A process of outputting to each of the conversion unit 3 and the image generation unit 4 is performed.
- the binary image conversion unit 3is realized by, for example, a binary image conversion circuit 13 shown in FIG.
- the binary image conversion unit 3converts the document image output from the sampling unit 2 into a binary image, and performs a process of outputting the converted binary image to the parameter update unit 7.
- the image generation unit 4is realized by, for example, the image generation circuit 14 illustrated in FIG.
- the image generation unit 4adjusts the pixel value of the document image output from the sampling unit 2 to generate a document image affected by the disturbance, and outputs the generated document image to the feature amount extraction unit 5 To implement.
- Disturbancesinclude the factors of the image acquisition equipment in addition to the factors of the environment in which the document image is taken.
- the document image adjustment processingincludes, for example, processing for adding Gaussian noise and sesame salt noise to the document image, processing for performing Gaussian blurring of the document image, processing for adjusting the sharpness, contrast, and brightness value of the document image. It is done.
- the feature quantity extraction unit 5is realized by, for example, a feature quantity extraction circuit 15 shown in FIG.
- the feature amount extraction unit 5has a first neural network that inputs the document image output from the image generation unit 4 and outputs the feature amount of the document image.
- the first neural network included in the feature quantity extraction unit 5is a convolutional neural network (CNN).
- the image reconstruction unit 6is realized by, for example, an image reconstruction circuit 16 illustrated in FIG.
- the image reconstruction unit 6inputs the feature amount output from the first neural network included in the feature amount extraction unit 5, and reconstructs a reconstructed image that is an image reconstructed as a binary image.
- a second neural network for outputis included. In the first embodiment, it is assumed that the second neural network included in the image reconstruction unit 6 has CNN.
- the parameter update unit 7is realized by, for example, the parameter update circuit 17 shown in FIG.
- the parameter update unit 7extracts feature amounts according to the difference between the reconstructed image output from the second neural network included in the image reconstructing unit 6 and the binary image output from the binary image conversion unit 3.
- a process of updating the parameters of the first neural network included in the unit 5 and the parameters of the second neural network included in the image reconstruction unit 6is performed.
- the parameter storage unit 8is realized by, for example, the parameter storage circuit 18 illustrated in FIG. 2, and stores each of the parameters of the first neural network and the parameters of the second neural network updated by the parameter update unit 7. To do.
- a learning image storage unit 1a sampling unit 2, a binary image conversion unit 3, an image generation unit 4, a feature amount extraction unit 5, an image reconstruction unit 6, and a parameter update unit 7 that are components of the machine learning device.
- Each of the parameter storage units 8is assumed to be realized by dedicated hardware as shown in FIG. That is, what is realized by the learning image storage circuit 11, the sampling circuit 12, the binary image conversion circuit 13, the image generation circuit 14, the feature amount extraction circuit 15, the image reconstruction circuit 16, the parameter update circuit 17 and the parameter storage circuit 18. Is assumed.
- each of the learning image storage circuit 11 and the parameter storage circuit 18includes, for example, a RAM (Random Access Memory), a ROM (Read Only Memory), a flash memory, an EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory), and an EEPROM (Electrically Easy Memory).
- RAMRandom Access Memory
- ROMRead Only Memory
- flash memoryan EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory)
- EEPROMElectrically Easy Memory
- Non-volatile or volatile semiconductor memoriessuch as Read Only Memory), magnetic disks, flexible disks, optical disks, compact disks, mini disks, DVDs (Digital Versatile Discs), and the like are applicable.
- the sampling circuit 12, the binary image conversion circuit 13, the image generation circuit 14, the feature amount extraction circuit 15, the image reconstruction circuit 16, and the parameter update circuit 17are, for example, a single circuit, a composite circuit, a programmed processor, A parallel-programmed processor, an ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit), an FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array), or a combination thereof is applicable.
- the components of the machine learning deviceare not limited to those realized by dedicated hardware, and the machine learning device may be realized by software, firmware, or a combination of software and firmware.
- Software or firmwareis stored as a program in the memory of a computer.
- the computermeans hardware that executes a program, and includes, for example, a CPU (Central Processing Unit), a central processing unit, a processing unit, an arithmetic unit, a microprocessor, a microcomputer, a processor, a DSP (Digital Signal Processor), and the like. .
- FIG. 3is a hardware configuration diagram of a computer when the machine learning device is realized by software or firmware.
- the learning image storage unit 1 and the parameter storage unit 8are configured on the memory 21 or the storage 22 of the computer, and the sampling unit 2, the binary image conversion unit 3, the image A program for causing the computer to execute the processing procedures of the generation unit 4, the feature amount extraction unit 5, the image reconstruction unit 6, and the parameter update unit 7 is stored in the memory 21 or the storage 22, and the processor 23 of the computer stores the memory 21 or the storage
- the program stored in the program 22may be executed.
- an image input unit 24is an input interface device for inputting a document image
- a result output unit 25receives a reconstructed image output from the second neural network included in the image reconstructing unit 6. It is an output interface device that outputs.
- FIG. 2shows an example in which each component of the machine learning device is realized by dedicated hardware
- FIG. 3shows an example in which the machine learning device is realized by software, firmware, etc. Some components in the machine learning device may be realized by dedicated hardware, and the remaining components may be realized by software, firmware, or the like.
- FIG. 4is a block diagram showing an image recognition apparatus according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention
- FIG. 5is a hardware block diagram showing the image recognition apparatus according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention
- the registered image storage unit 31is realized by, for example, the registered image storage circuit 41 illustrated in FIG. 5, and stores one or more document images (learning target images) as registered images.
- This registered imagemay be the same document image as the document image stored in the learning image storage unit 1 of the machine learning device in FIG. 1, or may be stored in the learning image storage unit 1 of the machine learning device in FIG.
- the document imagemay be different from the existing document image.
- the recognition target image storage unit 32is realized by, for example, the recognition target image storage circuit 42 illustrated in FIG. 5, and stores a recognition target image that is a recognition target document image.
- the feature amount detection unit 33is realized by, for example, a feature amount detection circuit 43 illustrated in FIG.
- the feature amount detection unit 33includes a first feature amount detection unit 34, an image regeneration unit 35, and a second feature amount detection unit 36.
- the feature amount detection unit 33is stored in the registered image storage unit 31 using the mounted neural network.
- the feature amount detection unit 33uses the implemented neural network as a preprocessing for starting the search process in which the image search unit 38 searches for a registered image similar to the recognition target image, and uses the mounted recognition target image storage unit 32.
- the recognition target image stored inis input, and the feature amount of the recognition target image is output.
- the first feature amount detecting unit 34performs the registration process as shown in FIG.
- the first neural networkwhose parameters are updated by the parameter updating unit 7 of the machine learning apparatus is provided.
- the first feature amount detection unit 34performs the preprocessing of the search process
- the first neural network that is implementedinputs the recognition target image stored in the recognition target image storage unit 32.
- the feature amount of the recognition target imageis output.
- the first neural network included in the first feature quantity detection unit 34is the same neural network as the first neural network included in the feature quantity extraction unit 5 of the machine learning device in FIG.
- the image regeneration unit 35inputs the feature amount of the registered image output from the first neural network included in the first feature amount detection unit 34, and the registered image As a neural network that outputs a reconstructed registered image that is an image reconstructed, the second neural network whose parameters are updated by the parameter updating unit 7 of the machine learning device of FIG. 1 is provided.
- the image regenerating unit 35outputs the mounted second neural network from the first neural network included in the first feature amount detecting unit 34.
- the feature amount of the recognized recognition target imageis input, and a reconstructed recognition image that is a reconstructed image of the recognition target image is output.
- the second neural network included in the image regeneration unit 35is the same neural network as the second neural network included in the image reconstruction unit 6 of the machine learning device in FIG.
- the second feature amount detection unit 36When performing the registration process, the second feature amount detection unit 36 inputs the reconstructed registration image output from the second neural network included in the image regenerating unit 35, and reconstructs and registers it. As a neural network that outputs image feature amounts, the first neural network whose parameters are updated by the parameter updating unit 7 of the machine learning device of FIG. 1 is provided. When the preprocessing of the search processing is performed, the second feature amount detection unit 36 outputs the mounted first neural network from the second neural network included in the image regeneration unit 35. The reconstructed recognition image is input, and the feature amount of the reconstructed recognition image is output.
- the first neural network included in the second feature amount detection unit 36is the same neural network as the first neural network included in the feature amount extraction unit 5 of the machine learning device in FIG.
- the feature amount storage unit 37is realized by, for example, a feature amount storage circuit 44 illustrated in FIG.
- the feature amount storage unit 37outputs from the first neural network included in the first feature amount detection unit 34 as the feature amount of the registered image output from the neural network included in the feature amount detection unit 36.
- Each of the registered feature values of the registered image and the feature amounts of the reconstructed registered image output from the first neural network included in the second feature value detection unit 36is stored.
- the image search unit 38is realized by, for example, an image search circuit 45 shown in FIG.
- the image storage unit 38 a of the image search unit 38stores the reconstructed registered image output from the image regeneration unit 35.
- the image storage unit 38a of the image search unit 38stores the reconstruction registration image output from the image regeneration unit 35.
- the image regeneration unit 35performs the reconstruction registration. You may make it provide the image memory
- the image recognition apparatus in FIG. 4may include a reconstructed registered image storage unit that stores the reconstructed registered image output from the image regenerating unit 35.
- the image search unit 38includes the feature amounts of one or more registered images output from the first feature amount detection unit 34 among the feature amounts of one or more registered images stored in the feature amount storage unit 37. Then, a process of calculating the similarity with the feature quantity of the recognition target image output from the first feature quantity detection unit 34 is performed. The image search unit 38 identifies a registered image having the highest calculated similarity among one or more registered images stored in the registered image storage unit 31, and the identified registered image is similar to the recognition target image. The process of outputting as a search result of the registered image is executed. The image search unit 38 also includes one or more feature amounts of one or more reconstructed registered images output from the second feature amount detection unit 36 among the one or more feature amounts stored in the feature amount storage unit 37.
- the image search unit 38identifies a reconstructed registered image having the highest calculated similarity among one or more reconstructed registered images stored in the image storage unit 38a, and corresponds to the identified reconstructed registered image.
- the registration image to be outputis output as a search result of registered images similar to the recognition target image.
- each of the registered image storage unit 31, the recognition target image storage unit 32, the feature amount detection unit 33, the feature amount storage unit 37, and the image search unit 38which are components of the image recognition apparatus, is illustrated in FIG. 5. It is assumed that it is realized by special hardware. That is, it is assumed to be realized by the registered image storage circuit 41, the recognition target image storage circuit 42, the feature amount detection circuit 43, the feature amount storage circuit 44, and the image search circuit 45.
- each of the registered image storage circuit 41, the recognition target image storage circuit 42, and the feature amount storage circuit 44includes, for example, a nonvolatile or volatile semiconductor memory such as a RAM, a ROM, a flash memory, an EPROM, an EEPROM, or a magnetic field.
- Discs, flexible discs, optical discs, compact discs, mini discs, DVDs and the likeare applicable.
- the feature quantity detection circuit 43 and the image search circuit 45correspond to, for example, a single circuit, a composite circuit, a programmed processor, a parallel programmed processor, an ASIC, an FPGA, or a combination thereof.
- FIG. 6is a hardware configuration diagram of a computer when the image recognition apparatus is realized by software or firmware.
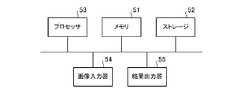
- the registered image storage unit 31, the recognition target image storage unit 32, and the feature amount storage unit 37are configured on the memory 51 or the storage 52 of the computer, and the feature amount detection unit 33 and a program for causing the computer to execute the processing procedure of the image search unit 38 are stored in the memory 51 or the storage 52, and the processor 53 of the computer executes the program stored in the memory 51 or the storage 52.
- an image input device 54is an input interface device that inputs a registered image or a recognition target image
- a result output device 55is an output interface device that outputs a search result of a registered image by the image search unit 38.
- FIG. 5shows an example in which each component of the image recognition apparatus is realized by dedicated hardware
- FIG. 6shows an example in which the image recognition apparatus is realized by software, firmware, etc. Some components in the image recognition apparatus may be realized by dedicated hardware, and the remaining components may be realized by software, firmware, or the like.
- the learning image storage unit 1stores a plurality of document images acquired in advance.
- the document image stored in the learning image storage unit 1is, for example, a gray scale image.
- the color imageis converted into a grayscale image before being stored in the learning image storage unit 1.
- the sampling unit 2selects any one document image from a plurality of document images stored in the learning image storage unit 1, and converts the selected document image into a binary image conversion unit 3 and an image generation unit 4. Output to each of.
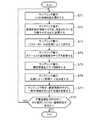
- FIG. 7is a flowchart showing the processing contents in the sampling unit 2 of the machine learning device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Hereinafter, the processing content of the sampling unit 2 will be described in detail with reference to FIG.
- the sampling unit 2randomly selects any one of the document images stored in the learning image storage unit 1 (step ST1 in FIG. 7).
- the sampling unit 2changes the image size of the selected document image to a preset image size (H, W) (step ST2 in FIG. 7).
- His the height of the document image
- Wis the width of the document image.
- the sampling unit 2the parameters P 1 indicating the image scale S determined by a random number, obtaining the parameter P 2 indicating the rotation angle ⁇ of the image by the random number (step ST3 in FIG. 7).
- Sampling unit 2based on the image scale S shown parameter P 1, to implement the image processing for changing an image size of a document image selected (step ST4 in FIG. 7).
- the sampling unit 2the rotation axis center of the document image selected, by the rotation angle ⁇ indicated by the parameter P 2, performing the image processing for rotating the document image selected (step ST5 in FIG. 7).
- the sampling unit 2determines the coordinates (X, Y) of a part of the region cut out from the document image after the image processing by using a random number (step ST6 in FIG. 7).
- the coordinates (X, Y) of the partial areaare, for example, the coordinates of the upper left corner point of the partial area.
- the sampling unit 2performs a process of cutting out a part of the document image after the image processing, for example, a region where the coordinates of the upper left corner point are the determined coordinates (X, Y) (step in FIG. 7). ST7).
- the image size of the cutout areais an image size (h, w) set in advance.
- the sampling unit 2outputs a part of the cut out region as a document image to each of the binary image conversion unit 3 and the image generation unit 4.
- the sampling unit 2determines whether there are any document images that have not yet been selected among the plurality of document images stored in the learning image storage unit 1 (step ST8 in FIG. 7). If there remains a document image that has not yet been selected (step ST8: YES in FIG. 7), the sampling unit 2 repeatedly performs the processing of steps ST1 to ST8. If there is no document image that has not yet been selected (step ST8 in FIG. 7: NO), the sampling unit 2 ends the process.
- a document imagecan be generated as an approximately infinite learning sample from a document image that is a finite learning image. For this reason, as a generalization performance of learning results, an improvement in the ability to identify unknown objects is expected.
- the binary image conversion unit 3converts the document image output from the sampling unit 2 into a binary image, and outputs the converted binary image to the parameter update unit 7.
- an algorithm for converting a document image into a binary imagefor example, adaptive threshold processing (processing using an Adaptive Threshold function) can be used. However, what is necessary is just to be able to convert a document image into a binary image. A simple algorithm may be used.
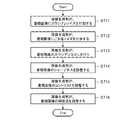
- FIG. 8is a flowchart showing the processing contents in the image generation unit 4 of the machine learning device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Hereinafter, the adjustment process of the image generation unit 4 will be specifically described with reference to FIG.
- the embodimentis not limited to the following six adjustment processes. For example, one or more and five or less adjustment processes are performed. Alternatively, seven or more adjustment processes may be performed.
- the order of the following six adjustment processesmay be any order. For example, the order can be determined by a random number.
- the image generation unit 4Upon receiving the document image output from the sampling unit 2, the image generation unit 4 adds, for example, a variance value determined by a random number as Gaussian noise to the luminance value of each pixel constituting the document image. Adjustment processing is performed (step ST11 in FIG. 8). Next, the image generation unit 4 determines a pixel to which sesame salt noise is added from each pixel constituting the document image based on a probability determined by a random number. Then, the image generation unit 4 adds sesame salt noise to the pixel by largely changing the determined luminance value of the pixel from the luminance values of the pixels around the pixel (step ST12 in FIG. 8).
- a variance value determined by a random numberas Gaussian noise
- the luminance value of a peripheral pixelis a luminance value on the black side of the threshold value used for the threshold processing of the binary image in the binary image conversion unit 3
- the luminance value of the pixelis set to the whitest luminance value.
- the luminance value of the surrounding pixelis a luminance value on the white side of the threshold value
- the luminance value of the pixelis set to the blackest luminance value.
- the image generation unit 4performs Gaussian blurring processing to blur the document image using, for example, a Gaussian function (step ST13 in FIG. 8).
- the image generation unit 4determines a parameter indicating sharpness using a random number, and performs a process of adjusting the sharpness of the document image according to the determined parameter (step ST14 in FIG. 8).
- the image generation unit 4determines a parameter indicating the contrast using a random number, and performs a process of adjusting the contrast of the document image according to the determined parameter (step ST15 in FIG. 8).
- the image generation unit 4determines a parameter indicating the luminance value by a random number, and performs a process of adjusting the luminance value of the document image according to the determined parameter (step ST16 in FIG. 8).
- the feature amount extraction unit 5has a first neural network that inputs the document image output from the image generation unit 4 and outputs the feature amount of the document image.
- the first neural network included in the feature amount extraction unit 5is CNN, and the first neural network includes a convolution layer that performs convolution of the feature amount of the document image and a pooling layer that performs pooling processing. It is out.
- FIG. 9is an explanatory diagram illustrating a configuration example of a first neural network included in the feature amount extraction unit 5.
- INPUTis an image input unit
- an image input from INPUTis a document image that is affected by a disturbance output from the image generation unit 4.
- OUTPUTis a feature value output unit, and the feature value output from OUTPUT is the feature value of the document image.
- CONV (1), CONV (2), and CONV (3)is a convolutional layer included in the first neural network. In the convolution layer, after performing the convolution of the feature amount of the document image, the calculation of the activation function is performed. In FIG. 9, the notation of the calculation of the activation function is omitted.
- Each of POOL (1) and POOL (2)is a pooling layer included in the first neural network.
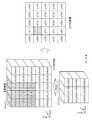
- FIG. 10is an explanatory diagram illustrating a convolution process in the convolution layer.
- the input feature amount shown in FIG. 10includes feature amounts of a plurality of regions in the document image input to the convolution layer, and the feature amounts of the plurality of regions correspond to an input feature amount map that is data of a two-dimensional structure.
- FIG. 10shows an example in which the document image has 25 regions (5 ⁇ 5 in the figure). That is, the document image shows an example in which the A direction has 5 areas and the B direction has 5 areas.
- the input feature amountincludes k (k is an integer of 1 or more) input feature amount maps. If the input feature amount includes two or more input feature amount maps, two or more input features are provided.
- the feature amount mapis expressed as data having a three-dimensional structure.
- the input feature amountis represented by a k map.
- the input feature The quantityincludes three input feature quantity maps as an input feature quantity map for R, an input feature quantity map for G, and an input feature quantity map for R.
- the convolution layerincludes a weight filter that is a convolution target, and the weight filter is called a kernel.
- the two-dimensional size of the kernelis 3 in the A direction and 3 in the B direction.
- the kernelis data having a three-dimensional structure and has the same depth size as the input feature amount map. Therefore, if the input feature quantity includes k input feature quantity maps, the kernel depth size is k. In FIG. 10, the kernel is represented by a k map.
- the feature quantity extraction unit 5performs the calculation of the convolution process shown in the following equation (1) while moving the kernel on the plane that is the input feature map.
- “c1 ⁇ b1 + pad A ” in x (c1 ⁇ b1 + pad A , c2 ⁇ b2 + pad B , b3)corresponds to “a1” in the input feature quantity x (a1, a2, a3)
- “c2 “ ⁇ b2 + pad B ”corresponds to “a2” in the input feature quantity x (a1, a2, a3)
- “b3”corresponds to “a3” in the input feature amount x (a1, a2, a3).
- w (b1, b2, b3)is a parameter indicating a kernel weight value, and is a parameter of the first neural network updated by the parameter updating unit 7.
- y (c1, c2)is an output feature amount of each region in the document image.
- the size of the output feature amount mapwhich is the feature amount of a plurality of regions output from the convolution layer, changes.
- FIG. 10shows an example in which the input feature value map and the output feature value map are maps of the same size.
- the feature quantity extraction unit 5may perform zero padding to fill the input feature quantity x (a1, a2, a3) having a negative index with zero.
- zero paddingis not essential, and zero padding may not be performed.
- parameters related to the convolution processinclude a stride parameter indicating the movement amount of the kernel.
- the feature quantity y (1, 1) of one area in the output feature quantityis the feature quantity x (a1, a2, a3) of nine areas in the input feature quantity, that is, x (0 , 0, 0), x (0, 1, 0), x (0, 2, 0), x (1, 0, 0), x (1, 1, 0), x (1, 2, 0) , X (2, 0, 0), x (2, 1, 0) and x (2, 2, 0).
- Expression (1)shows an example in which there is one kernel
- expression (2)shows calculation of convolution processing when there are a plurality of kernels.
- kis an index of the output feature amount map.
- the number of output feature amount mapsis the same as the number of kernels.
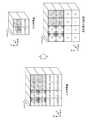
- FIG. 11is an explanatory diagram showing a pooling process in the pooling layer.
- the pooling process in the pooling layer which the feature-value extraction part 5 implementsdiffers from a general pooling process. That is, the pooling process performed by the feature quantity extraction unit 5 is similar to the general pooling process, for each local area that is a partial area of the output feature quantity map, for the feature quantity included in the local area. Among them, the maximum feature amount is extracted, and the extracted feature amount is output. Unlike the general pooling process, the pooling process performed by the feature quantity extraction unit 5 also outputs position information indicating the position in the document image where the extracted feature quantity exists.
- the structure of the pooling layerchanges depending on the two-dimensional size of the kernel, padding parameters, and stride parameters.
- the A directionis 2
- the B directionis 2
- the C directionis K with respect to the input feature quantity of (4 ⁇ 4 ⁇ K) in which the A direction is 4, the B direction is 4 and the C direction is K.
- an output feature amount (2 ⁇ 2 ⁇ K) in which the A direction is 2, the B direction is 2, and the C direction is Kis obtained.
- An exampleis shown.
- the kernel stride valueis 2 and the padding value is zero.
- the maximum feature amountis extracted from the feature amounts included in the local region for each (2 ⁇ 2 ⁇ K) local region in the input feature amount map by the pooling process.
- the feature quantity (0, 0, 0) of one area in the output feature quantityis the feature quantity x (a1, a2, a3) of four areas in the input feature quantity, that is, x ( Among the 0, 0, 0), x (0, 1, 0), x (1, 0, 0) and x (1, 1, 0), the maximum feature amount x (0, 0, 0) is obtained. Extracting.
- the extracted maximum feature quantity x (0, 0, 0)is output.
- position information indicating the position in the document image where the extracted maximum feature quantity x (0, 0, 0) existsis output.
- FIG. 11illustrates a position map indicating the local maximum value position as position information indicating the position in the document image where the maximum feature amount exists.
- the position mapis expressed as data having the same three-dimensional structure as the input feature amount.
- “1”is written in the position in the document image corresponding to the maximum feature value
- “0”is written in the position in the document image corresponding to the feature value other than the maximum feature value.
- the position informationis a position map having a three-dimensional structure.
- Equation (3)shows the pooling calculation.
- Expression (3)shows an example in which one feature value is output from a local region including four regions in the input feature value map using the operator f (.).
- the first embodimentshows an example in which the operator f (.) Is an operator that calculates the maximum value, and the pooling process in which such an operator f (.) Is used is the maximum pooling (Max). Called Pooling).
- the maximum value of the local areais calculated as one feature amount, and at the same time, position information indicating the position in the document image that is the maximum value is also calculated.
- position information indicating two or more positionsmay be output.
- the pooling process in the pooling layeris not limited to the maximum pooling, and may be another pooling process such as an average pooling (Average Pooling).
- the operator f (.) In Expression (3)is an operator that calculates an average value.
- the first neural network included in the feature amount extraction unit 5is CNN.
- the first neural networkis not limited to CNN.
- a multilayer structuresuch as a deep neural network is used. It may be a neural network.
- the image reconstruction unit 6inputs the feature amount output from the first neural network included in the feature amount extraction unit 5, and reconstructs a reconstructed image that is an image reconstructed as a binary image.
- a second neural network for outputis included.
- the second neural network included in the image reconstruction unit 6is a CNN, and the second neural network includes an inverse pooling layer that performs inverse pooling processing, and a convolution layer that performs convolution of feature values of a binary image. Including.
- FIG. 12is an explanatory diagram illustrating a configuration example of the second neural network included in the image reconstruction unit 6.
- INPUTis a feature quantity input unit
- the feature quantity input from INPUTis a feature quantity output from the first neural network included in the feature quantity extraction unit 5.
- OUTPUTis a feature value output unit, and the size of the output feature value, which is the feature value of a plurality of regions output from OUTPUT, is the same size as the size of the input feature value shown in FIG.
- Each of UNPOOL (1) and UNPOOL (2)is an inverse pooling layer included in the second neural network.
- UNDOOL (1) included in the second neural networkcorresponds to POOL (2) shown in FIG. 9, and UNDOOL (2) included in the second neural network is POOL (2) shown in FIG.
- Each of CONV (1), CONV (2), and CONV (3)is a convolutional layer included in the second neural network.
- the convolution layerthe activation function is calculated after convolution of the feature quantity of the reconstructed image.
- the notation of the activation function calculationis omitted.
- the convolutional layer included in the second neural network included in the image reconstruction unit 6is similar to the convolutional layer included in the first neural network included in the feature amount extraction unit 5.
- the size of the input feature map and the size of the output feature mapare the same.
- an output feature amount that is a feature amount of a plurality of regions output from the first neural network included in the feature amount extraction unit 5Needs to be restored to the size of the input feature quantity shown in FIG. That is, the size of the feature map, which is the output feature whose size is reduced by the pooling process of the pooling layer included in the first neural network included in the feature extractor 5, is reconstructed.
- the second neural network included in the image reconstruction unit 6includes an inverse pooling layer corresponding to the pooling layer included in the first neural network included in the feature amount extraction unit 5. It is out.
- FIG. 13is an explanatory diagram illustrating reverse pooling processing in the reverse pooling layer.
- the size of the output feature amount of the pooling layer corresponding to the reverse pooling layer And the size of the input feature amount of the inverse pooling layermatch.
- the size of the input feature amount of the pooling layer corresponding to the reverse pooling layer and the size of the output feature amount of the reverse pooling layermatch.
- the reverse pooling process shown in FIG. 13shows an example in which (2 ⁇ 2 ⁇ K) input feature values are converted to (4 ⁇ 4 ⁇ K) output feature values. In the reverse pooling process shown in FIG.
- the positional information acquired from the corresponding pooling layeris input, and among the output feature values of (4 ⁇ 4 ⁇ K), the maximum feature value indicated by the position information is used.
- the value of the input feature amountis inserted, and zero is inserted into the feature amount at a position other than the position of the maximum value indicated by the position information.
- the input feature quantity x (0, 0, 0)is inserted at the second position from the left in the A direction and the second position from the top in the B direction in the output feature quantity of (4 ⁇ 4 ⁇ K). . Further, the input feature quantity x (0, 1, 0) is inserted at the third position from the left in the A direction and the first position from the top in the B direction in the output feature quantity of (4 ⁇ 4 ⁇ K). . The input feature quantity x (1, 0, 0) is inserted at the second position from the left in the A direction and the third position from the top in the B direction in the output feature quantity of (4 ⁇ 4 ⁇ K). .
- the input feature quantity x (1, 1, 0)is inserted at the third position from the left in the A direction and the fourth position from the top in the B direction in the output feature quantity of (4 ⁇ 4 ⁇ K). Zeros are inserted at other positions of the output feature amount of (4 ⁇ 4 ⁇ K).
- the parameter update unit 7calculates a difference between the reconstructed image output from the second neural network included in the image reconstructing unit 6 and the binary image output from the binary image conversion unit 3.
- the parameter updating unit 7is configured so that the parameter of the first neural network that the feature amount extraction unit 5 has and the second neural network that the image reconstruction unit 6 has so that the calculated difference is minimized. Update each of the parameters. That is, the parameter updating unit 7 sets the parameter w (b1, b2, b3) indicating the kernel weight value in the first neural network and the kernel weight value in the second neural network so that the calculated difference is minimized. Each of the parameters w (b1, b2, b3) indicating is updated.
- the difference between the reconstructed image and the binary image calculated by the parameter updating unit 7may be, for example, a mean square error (MSE: Mean Square Error) between the reconstructed image and the binary image, or the reconstructed image. And a cross-entropy of a binary image. Further, for example, a stochastic gradient descent method or the like can be used as an optimization algorithm in which the parameter updating unit 7 updates the parameters so that the difference is minimized.
- MSEMean Square Error
- the parameter storage unit 8is a parameter w (b1, b2, b2) indicating kernel weight values in the first neural network updated by the parameter updating unit 7 as parameters of the first neural network updated by the parameter updating unit 7. b3) is stored.
- the parameter storage unit 8also includes a parameter w (b1, b1) indicating a kernel weight value in the second neural network updated by the parameter update unit 7 as a parameter of the second neural network updated by the parameter update unit 7. b2, b3) are stored.
- the first feature amount detection unit 34inputs the registered image stored in the registered image storage unit 31, outputs the feature amount of the registered image, and recognizes the recognition target stored in the recognition target image storage unit 32.
- a first neural network that inputs an image and outputs a feature amount of the recognition target imageis included.
- the first neural network included in the first feature quantity detection unit 34is the same neural network as the first neural network included in the feature quantity extraction unit 5 of the machine learning device in FIG. Therefore, the parameter w (b1, b2, b3) indicating the kernel weight value in the first neural network included in the first feature quantity detection unit 34 has the smallest difference between the reconstructed image and the binary image. 1 is optimized by the parameter updating unit 7 of the machine learning device of FIG.
- the image regeneration unit 35receives the feature amount of the registered image output from the first neural network included in the first feature amount detection unit 34, and is a reconstructed image that is an image obtained by reconstructing the registered image. This is an image in which a registered image is output and the feature quantity of the recognition target image output from the first neural network included in the first feature quantity detection unit 34 is input to reconstruct the recognition target image.
- a second neural network for outputting the reconstructed recognition imageis provided.
- the second neural network included in the image regeneration unit 35is the same neural network as the second neural network included in the image reconstruction unit 6 of the machine learning device in FIG.
- the parameter w (b1, b2, b3) indicating the kernel weight value in the second neural network possessed by the image regeneration unit 35is such that the difference between the reconstructed image and the binary image is minimized.
- the optimizationis performed by the parameter updating unit 7 of the machine learning device of FIG.
- the second feature amount detection unit 36receives the reconstruction registration image output from the second neural network included in the image regeneration unit 35, outputs the feature amount of the reconstruction registration image
- the image regeneration unit 35includes a first neural network that inputs the reconstruction recognition image output from the second neural network included in the image regeneration unit 35 and outputs the feature amount of the reconstruction recognition image.
- the first neural network included in the second feature amount detection unit 36is the same neural network as the first neural network included in the feature amount extraction unit 5 of the machine learning device in FIG. Accordingly, the parameter w (b1, b2, b3) indicating the kernel weight value in the first neural network possessed by the second feature quantity detection unit 36 has the smallest difference between the reconstructed image and the binary image. 1 is optimized by the parameter updating unit 7 of the machine learning device of FIG.
- the pooling layer included in the first neural network included in the second feature quantity detection unit 36does not need to output position information.
- the first neural network included in the feature amount extraction unit 5 and the second neural network included in the image reconstruction unit 6 of the machine learning device in FIG. 1is a CNN
- the first feature The first neural network included in the quantity detection unit 34 and the first neural network included in the second feature quantity detection unit 36have only a convolution layer kernel as a free parameter. For this reason, if the kernel sizes are the same, the parameter updated by the parameter update unit 7 can be used as a learned parameter. Therefore, the feature amount map of each convolution layer in the machine learning device of FIG.
- the size of each convolutional layer in the image recognition apparatusmay be different from the size map.
- the registered image storage unit 31stores one or more document images as registered images. This registered image may be the same document image as the document image stored in the learning image storage unit 1 of the machine learning device in FIG. 1, or may be stored in the learning image storage unit 1 of the machine learning device in FIG. The document image may be different from the existing document image.
- the recognition target image storage unit 32stores a recognition target image that is a document image to be recognized.
- the feature amount detection unit 33includes a registration process for registering the feature amount of the registered image stored in the registered image storage unit 31 in the feature amount storage unit 37, and a recognition target image stored in the recognition target image storage unit 32. In order to enable search processing for searching for similar registered images, pre-processing for extracting feature amounts of recognition target images is performed.
- the first feature amount detection unit 34 of the feature amount detection unit 33inputs one registered image in order from one or more registered images stored in the registered image storage unit 31.
- the first neural network included in the first feature quantity detection unit 34receives one registered image, the first neural network outputs the feature quantity of the registered image.
- the first feature amount detection unit 34stores the feature amount of the registered image in the feature amount storage unit 37 and outputs the feature amount of the registered image to the image regeneration unit 35.
- the image regeneration unit 35 of the feature amount detection unit 33inputs the feature amount of the registered image output from the first feature amount detection unit 34.
- the second neural network included in the image regeneration unit 35receives the feature amount of the registered image
- the second neural networkoutputs a reconstructed registered image that is an image obtained by reconstructing the registered image.
- the image regeneration unit 35outputs the reconstructed registration image to the second feature amount detection unit 36 and the image search unit 38.
- the image storage unit 38 a of the image search unit 38stores the reconstructed registered image output from the image regeneration unit 35. Note that the reconstructed registered image output from the image regenerating unit 35 is an image corresponding to the binary image of the registered image, but is an image reconstructed from the feature amount of the registered image. It does not necessarily match the image completely.
- the second feature quantity detection unit 36 of the feature quantity detection unit 33receives the reconstructed registration image output from the image regeneration unit 35.
- the first neural network included in the second feature amount detection unit 36inputs the reconstructed registered image
- the first neural networkoutputs the feature amount of the reconstructed registered image.
- the second feature quantity detection unit 36stores the feature quantity of the reconstructed registration image in the feature quantity storage unit 37. If the number of registered images stored in the registered image storage unit 31 is N, the feature amount storage unit 37 stores the feature amounts of the N registered images output from the first feature amount detection unit 34.
- the feature amounts of the N reconstructed registration images output from the second feature amount detection unit 36are stored.
- the feature amount of the reconstructed registered image output from the second feature amount detecting unit 36is a feature amount extracted from the reconstructed registered image that is an image reconstructed by the image regenerating unit 35, the first feature amount is extracted. The influence of disturbance is removed more than the feature amount of the registered image output from the first neural network included in the feature amount detection unit 34.
- the first feature amount detection unit 34 of the feature amount detection unit 33inputs a recognition target image that is a document image to be recognized that is stored in the recognition target image storage unit 32.
- the first neural network included in the first feature amount detection unit 34outputs the feature amount of the recognition target image.
- the first feature amount detection unit 34outputs the recognition target image.
- the feature amountis output to each of the image regeneration unit 35 and the image search unit 38.
- the image regeneration unit 35 included in the feature amount detection unit 33inputs the feature amount of the recognition target image output from the first feature amount detection unit 34.
- the second neural network of the image regeneration unit 35receives the feature amount of the recognition target image
- the second neural networkoutputs a reconstructed recognition image that is an image obtained by reconstructing the recognition target image.
- the image regeneration unit 35outputs the reconstructed recognition image to the second feature amount detection unit 36.
- the second feature amount detection unit 36 of the feature amount detection unit 33receives the reconstructed recognition image output from the image regeneration unit 35.
- the first neural network included in the second feature quantity detection unit 36receives the reconstruction recognition image
- the first neural networkoutputs the feature quantity of the reconstruction recognition image.
- the second feature amount detection unit 36outputs the feature amount of the reconstructed recognition image to the image search unit 38.
- the image search unit 38searches for a registered image similar to the recognition target image, the feature amount of the registered image output from the first feature amount detection unit 34 and the first feature amount detection unit It is not sufficient to simply compare the feature quantity of the recognition target image output from 34. Therefore, the feature quantity of the reconstructed registered image output from the second feature quantity detection unit 36 from which the influence of many disturbances has been removed, and the second feature quantity detection unit from which the influence of many disturbances has been removed. It is highly necessary to compare the feature amount of the reconstructed recognition image output from 36.
- the feature quantity to be compared by the image search unit 38is the feature quantity of the registered image output from the first feature quantity detection unit 34 and the feature quantity of the recognition target image. It is assumed that the feature amount of the reconstructed registered image and the feature amount of the reconstructed recognition image output from the feature amount detecting unit 36 is set in advance by the user.
- the setting in which the feature quantity to be compared by the image search unit 38 is the feature quantity of the registered image and the feature quantity of the recognition target image output from the first feature quantity detection unit 34is referred to as “setting A”.
- a setting in which the feature quantity to be compared by the image search unit 38 is the feature quantity of the reconstructed registered image and the feature quantity of the reconstructed recognition image output from the second feature quantity detection unit 36is referred to as “setting B”.
- the image search unit 38outputs one or more registrations output from the first feature amount detection unit 34 among the feature amounts of one or more registered images stored in the feature amount storage unit 37.
- the similarity between the feature quantity of the image and the feature quantity of the recognition target image output from the first feature quantity detection unit 34is calculated.
- the algorithm for calculating the similarity of the feature quantityis not particularly limited, and for example, cosine similarity can be used.
- the image search unit 38resembles the feature amount of one or more registered images output from the first feature amount detection unit 34 and the feature amount of the recognition target image output from the first feature amount detection unit 34. When the degree is calculated, a registered image with the highest calculated similarity is specified among one or more registered images stored in the registered image storage unit 31.
- the image search unit 38outputs the specified registered image as a search result of registered images similar to the recognition target image. In this case, when the image search unit 38 searches for a registered image similar to the recognition target image, it is not necessary for the image regeneration unit 35 and the second feature amount detection unit 36 to perform processing. The time until the search result is obtained can be shortened.
- the image search unit 38selects one or more re-outputs output from the second feature amount detection unit 36 among the feature amounts of one or more registered images stored in the feature amount storage unit 37.
- the similarity between the feature quantity of the construction registration image and the feature quantity of the reconstructed recognition image output from the second feature quantity detection unit 36is calculated.
- the image search unit 38includes the feature amount of one or more reconstructed registration images output from the second feature amount detection unit 36 and the feature amount of the reconstruction recognition image output from the second feature amount detection unit 36.
- the similarityis calculated, the reconstructed registered image having the highest calculated similarity is specified among one or more reconstructed registered images stored in the image storage unit 38a.
- the image search unit 38outputs a registered image corresponding to the identified reconstructed registered image as a search result of registered images similar to the recognition target image.
- the image regeneration unit 35 and the second feature amount detection unit 36need to perform preprocessing. Although it takes longer to obtain a registered image search result than in the case of A, even if the registration image and the environment in which the recognition target image is acquired are different, it is possible to search for a registered image that is similar to the recognition target image. Degradation of accuracy can be suppressed.
- the image search unit 38outputs the feature amount of one or more reconstructed registration images output from the second feature amount detection unit 36 and the second feature amount detection unit 36.
- the similarity with the feature amount of the reconstructed recognition imageis calculated.
- the present inventionis not limited to this.
- a method of calculating the similarity as followscan be considered.
- the image search unit 38resembles the feature amount of one or more registered images output from the first feature amount detection unit 34 and the feature amount of the recognition target image output from the first feature amount detection unit 34.
- the degreehereinafter referred to as similarity R1 is calculated.
- the image search unit 38also includes the feature quantities of one or more reconstructed registration images output from the second feature quantity detection unit 36 and the reconstruction recognition image output from the second feature quantity detection unit 36.
- a similarity with the feature amount(hereinafter referred to as similarity R2) is calculated.
- the image search unit 38calculates an average value of the similarity R1 and the similarity R2 or a weighted addition value of the similarity R1 and the similarity R2 as the final similarity R.
- the image search unit 38specifies a registered image having the highest calculated similarity R among one or more registered images.
- the image search unit 38outputs the specified registered image as a search result of registered images similar to the recognition target image.
- the image search unit 38calculates, for each registered image stored in the registered image storage unit 31, the similarity between the feature amount of the registered image and the feature amount of the recognition target image. Show.
- the image search unit 38performs the feature amount storage unit 37. The degree of similarity between the plurality of same-type registered images stored in the above and the feature amount of the recognition target image is calculated. Then, the image search unit 38 may calculate an average value of the calculated similarities as the similarity between the feature amount of the same type registered image and the feature amount of the recognition target image.
- the image search unit 38searches for the same type registered image similar to the recognition target image from among the M types of same type registered images.
- the binary image conversion unit 3that converts the learning image into a binary image, and the first that inputs the learning image and outputs the feature amount of the learning image.
- the parameter updating unit 7determines the parameters of the first neural network and the second neural network according to the difference between the reconstructed image output from the second neural network and the binary image converted by the binary image converting unit 3. Since each parameter is updated, the learning image is input and the feature value of the learning image is output without using teacher data. That offers an advantage of being able to update the parameters of the first neural network.
- the feature amount of the registered imageis output, and when the recognition target image is given, the feature amount having a neural network that outputs the feature amount of the recognition target image.
- a detection unit 33, a feature amount storage unit 37 that stores the feature amount of the registered image output from the neural network included in the feature amount detection unit 33, and one or more stored in the feature amount storage unit 37The feature amount of the registered image is compared with the feature amount of the recognition target image output from the neural network included in the feature amount detection unit 33, and similar to the recognition target image from one or more registered images.
- An image search unit 38 for searching for registered images, and the neural network parameters of the feature amount detection unit 33are updated by the machine learning device.
- the parametershave been updated by the machine learning device, an effect which can be retrieved registered image that is similar to the recognition target image.
- the usercan grasp the type of the recognition target image by confirming the type of the registered image searched by the image recognition apparatus.
- the registered image stored in the registered image storage unit 31 of the image recognition device of FIG. 4is the same image as the document image stored in the learning image storage unit 1 of the machine learning device of FIG. It has been described above that the image may be different from the document image stored in the learning image storage unit 1 of the machine learning device of FIG.
- the document image stored in the learning image storage unit 1is similar to the environment for acquiring the registered image and the recognition target image, or the document genre is the document image, the registered image, and the recognition target image. If the registered image and the recognition target image are different from the document image, a registered image similar to the recognition target image can be searched. That is, even when the machine learning apparatus of FIG.
- the acquisition environmentincludes not only the environment in which images are taken but also differences in image acquisition equipment.
- the genre of the documentsis similar, for example, an application form of a different bank or a form of a different administrative institution can be considered.
- Embodiment 2the initial state of the parameters of the first neural network included in the feature amount extraction unit 5 and the second neural network included in the image reconstruction unit 6 is particularly referred to. Absent.
- the first neural network included in the feature quantity extraction unit 5is a neural network in which parameters are learned in advance based on some learning data.
- the second neural network included in the image reconstruction unit 6is also a neural network in which parameters are learned in advance based on some learning data.
- the learning image storage unit 1 of the machine learning apparatus in FIG. 1stores a recognition target image as a document image. Based on the recognition target image, the parameter update unit 7 performs the same as in the first embodiment. It is assumed that the parameters of the first neural network and the parameters of the second neural network are updated. In this case, although the learning time is increased as compared with the first embodiment, a registered image similar to the recognition target image can be searched more accurately than the first embodiment.
- the present inventionis suitable for a machine learning apparatus that inputs a document image and updates a parameter of a neural network that outputs a feature amount of the document image.
- the present inventionis also suitable for an image recognition apparatus that searches for registered images that are similar to the recognition target image.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapaneseこの発明は、学習画像を入力して、学習画像の特徴量を出力するニューラルネットワークのパラメータを更新する機械学習装置と、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索する画像認識装置とに関するものである。The present invention relates to a machine learning device that inputs a learning image and outputs a feature value of the learning image and updates a neural network parameter, and an image recognition device that searches for a registered image similar to a recognition target image. It is.
画像を分類する機械学習を実施することで、画像の特徴量を抽出するモデルのパラメータを更新する機械学習装置が以下の非特許文献1に開示されている。
この機械学習装置は、教師あり学習手法を利用する装置であるため、教師データを使用して、機械学習を実施する。Non-Patent
Since this machine learning device is a device that uses a supervised learning method, machine learning is performed using teacher data.
従来の機械学習装置は以上のように構成されているので、機械学習を実施する際に、大量の教師データを収集する必要がある。このため、大量の教師データを収集することが困難である場合、画像の特徴量を抽出するモデルのパラメータを更新して最適化することができない。その結果、モデルにより抽出される特徴量の精度が劣化してしまうことがあるという課題があった。Since the conventional machine learning apparatus is configured as described above, it is necessary to collect a large amount of teacher data when performing machine learning. For this reason, when it is difficult to collect a large amount of teacher data, it is not possible to update and optimize the parameters of the model for extracting the feature amount of the image. As a result, there is a problem that the accuracy of the feature amount extracted by the model may be deteriorated.
この発明は上記のような課題を解決するためになされたもので、教師データを用いることなく、学習画像を入力して、学習画像の特徴量を出力するニューラルネットワークのパラメータを更新することができる機械学習装置を得ることを目的とする。
また、この発明は、機械学習装置によりパラメータが更新されたニューラルネットワークを用いて、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索することができる画像認識装置を得ることを目的とする。The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and can update the parameters of a neural network that inputs a learning image and outputs a feature amount of the learning image without using teacher data. The purpose is to obtain a machine learning device.
Another object of the present invention is to obtain an image recognition device that can search for a registered image similar to a recognition target image using a neural network whose parameters are updated by a machine learning device.
この発明に係る機械学習装置は、学習対象の画像である学習画像を二値画像に変換する二値画像変換部と、学習画像を入力して、学習画像の特徴量を出力する第1のニューラルネットワークを有する特徴量抽出部と、第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された特徴量を入力して、学習画像を二値画像として再構築した画像である再構築画像を出力する第2のニューラルネットワークを有する画像再構築部とを設け、パラメータ更新部が、第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築画像と、二値画像変換部により変換された二値画像との差分に従って第1のニューラルネットワークのパラメータ及び第2のニューラルネットワークのパラメータのそれぞれを更新するようにしたものである。The machine learning device according to the present invention includes a binary image conversion unit that converts a learning image, which is a learning target image, into a binary image, and a first neural that inputs the learning image and outputs a feature amount of the learning image. A feature amount extraction unit having a network and a second neural network that inputs a feature amount output from the first neural network and outputs a reconstructed image that is an image reconstructed from a learning image as a binary image An image reconstructing unit, and the parameter updating unit includes a first neural network according to a difference between the reconstructed image output from the second neural network and the binary image converted by the binary image converting unit. Each of the parameter and the parameter of the second neural network is updated.
この発明によれば、学習画像を二値画像に変換する二値画像変換部と、学習画像を入力して、学習画像の特徴量を出力する第1のニューラルネットワークを有する特徴量抽出部と、第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された特徴量を入力して、再構築画像を出力する第2のニューラルネットワークを有する画像再構築部とを設け、パラメータ更新部が、第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築画像と、二値画像変換部により変換された二値画像との差分に従って第1のニューラルネットワークのパラメータ及び第2のニューラルネットワークのパラメータのそれぞれを更新するように構成したので、教師データを用いることなく、学習画像を入力して、学習画像の特徴量を出力する第1のニューラルネットワークのパラメータを更新することができる効果がある。According to the present invention, a binary image conversion unit that converts a learning image into a binary image, a feature amount extraction unit that includes a first neural network that inputs the learning image and outputs the feature amount of the learning image, An image reconstruction unit having a second neural network that inputs a feature amount output from the first neural network and outputs a reconstructed image is provided, and a parameter update unit is output from the second neural network. Since each of the first neural network parameter and the second neural network parameter is updated according to the difference between the reconstructed image and the binary image converted by the binary image conversion unit, the teacher data Without using the parameter of the first neural network that inputs the learning image and outputs the feature amount of the learning image. There is an advantage of being able to update the data.
以下、この発明をより詳細に説明するために、この発明を実施するための形態について、添付の図面に従って説明する。Hereinafter, in order to explain the present invention in more detail, modes for carrying out the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
実施の形態1.
図1は、この発明の実施の形態1による機械学習装置を示す構成図であり、図2は、この発明の実施の形態1による機械学習装置を示すハードウェア構成図である。
この実施の形態1の機械学習装置は、学習対象の画像である学習画像として、書類が映っている画像である書類画像を利用するものとする。
ただし、これは一例に過ぎず、例えば、帳票が映っている画像である帳票画像を利用するものであってもよい。
図1及び図2において、学習画像記憶部1は、例えば図2に示す学習画像記憶回路11で実現されるものであり、事前に取得された複数の書類画像を記憶する。
学習画像記憶部1に記憶される書類画像は、例えば、グレースケールの画像であるものとする。このため、カラー画像の場合、学習画像記憶部1に記憶される前に、カラー画像がグレースケールの画像に変換されるものとする。
1 is a block diagram showing a machine learning apparatus according to
The machine learning apparatus according to the first embodiment uses a document image that is an image showing a document as a learning image that is an image to be learned.
However, this is only an example, and for example, a form image that is an image showing a form may be used.
1 and 2, the learning
The document image stored in the learning
書類画像の取得方式は、特に限定するものではなく、例えば、スキャナーによって読み取られた書類画像でもよいし、カメラによって撮影された書類画像でもよい。
ただし、カメラによって撮影された画像を書類画像として用いる場合には、書類の真正面から見ているように撮影画像に補正を施し、補正後の撮影画像の中から、書類が映っている領域を書類画像として切り出すようにする。
この実施の形態1では、書類の用紙サイズを特定することができるものとし、学習画像記憶部1には、同じ用紙サイズの書類が映っている書類画像が記憶されるものとする。
書類の用紙サイズを特定することができない場合、学習画像記憶部1に記憶される書類画像は、全て同じ用紙サイズの書類が映っている書類画像であるものとする。The document image acquisition method is not particularly limited, and may be, for example, a document image read by a scanner or a document image taken by a camera.
However, when using an image taken by a camera as a document image, the photographed image is corrected as seen from directly in front of the document, and the area where the document is reflected is selected from the corrected photographed image. Cut out as an image.
In the first embodiment, it is assumed that the paper size of a document can be specified, and the learning
When the paper size of the document cannot be specified, it is assumed that the document images stored in the learning
サンプリング部2は、例えば図2に示すサンプリング回路12で実現される。
サンプリング部2は、学習画像記憶部1に記憶されている複数の書類画像の中から、いずれか1つの書類画像を順番に選択する処理を実施する。
また、サンプリング部2は、選択した書類画像の画像サイズを変更するとともに、選択した書類画像を回転させる画像処理を実施する。
さらに、サンプリング部2は、画像処理後の書類画像の中から、二値画像変換部3により変換される二値画像と同じサイズの領域を抽出し、抽出した領域を書類画像として、二値画像変換部3及び画像生成部4のそれぞれに出力する処理を実施する。The
The
Further, the
Further, the
二値画像変換部3は、例えば図2に示す二値画像変換回路13で実現される。
二値画像変換部3は、サンプリング部2から出力された書類画像を二値画像に変換し、変換した二値画像をパラメータ更新部7に出力する処理を実施する。
画像生成部4は、例えば図2に示す画像生成回路14で実現される。
画像生成部4は、サンプリング部2から出力された書類画像の画素値を調整して、外乱の影響を受けている書類画像を生成し、生成した書類画像を特徴量抽出部5に出力する処理を実施する。
外乱としては、書類画像を撮影している環境の要因のほか、画像取得機材の要因も含まれる。
このため、書類画像の調整処理として、例えば、ガウシアンノイズ及びごま塩ノイズを書類画像に付加する処理、書類画像のガウシアンぼかしを行う処理、書類画像のシャープネス、コントラスト及び輝度値を調整する処理などが考えられる。The binary
The binary
The image generation unit 4 is realized by, for example, the
The image generation unit 4 adjusts the pixel value of the document image output from the
Disturbances include the factors of the image acquisition equipment in addition to the factors of the environment in which the document image is taken.
For this reason, the document image adjustment processing includes, for example, processing for adding Gaussian noise and sesame salt noise to the document image, processing for performing Gaussian blurring of the document image, processing for adjusting the sharpness, contrast, and brightness value of the document image. It is done.
特徴量抽出部5は、例えば図2に示す特徴量抽出回路15で実現される。
特徴量抽出部5は、画像生成部4から出力された書類画像を入力して、書類画像の特徴量を出力する第1のニューラルネットワークを有している。
この実施の形態1では、特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークは、畳み込みニューラルネットワーク(CNN:Convolutional Neural Net)をあるものとする。The feature
The feature
In the first embodiment, it is assumed that the first neural network included in the feature
画像再構築部6は、例えば図2に示す画像再構築回路16で実現される。
画像再構築部6は、特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された特徴量を入力して、書類画像を二値画像として再構築した画像である再構築画像を出力する第2のニューラルネットワークを有している。
この実施の形態1では、画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークは、CNNをあるものとする。The
The
In the first embodiment, it is assumed that the second neural network included in the
パラメータ更新部7は、例えば図2に示すパラメータ更新回路17で実現される。
パラメータ更新部7は、画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築画像と、二値画像変換部3から出力された二値画像との差分に従って特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークのパラメータ及び画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークのパラメータのそれぞれを更新する処理を実施する。
パラメータ記憶部8は、例えば図2に示すパラメータ記憶回路18で実現されるものであり、パラメータ更新部7により更新された第1のニューラルネットワークのパラメータ及び第2のニューラルネットワークのパラメータのそれぞれを記憶する。The parameter update unit 7 is realized by, for example, the
The parameter update unit 7 extracts feature amounts according to the difference between the reconstructed image output from the second neural network included in the
The parameter storage unit 8 is realized by, for example, the
図1では、機械学習装置の構成要素である学習画像記憶部1、サンプリング部2、二値画像変換部3、画像生成部4、特徴量抽出部5、画像再構築部6、パラメータ更新部7及びパラメータ記憶部8のそれぞれが、図2に示すような専用のハードウェアで実現されるものを想定している。即ち、学習画像記憶回路11、サンプリング回路12、二値画像変換回路13、画像生成回路14、特徴量抽出回路15、画像再構築回路16、パラメータ更新回路17及びパラメータ記憶回路18で実現されるものを想定している。In FIG. 1, a learning
ここで、学習画像記憶回路11及びパラメータ記憶回路18のそれぞれは、例えば、RAM(Random Access Memory)、ROM(Read Only Memory)、フラッシュメモリ、EPROM(Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory)、EEPROM(Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory)などの不揮発性又は揮発性の半導体メモリや、磁気ディスク、フレキシブルディスク、光ディスク、コンパクトディスク、ミニディスク、DVD(Digital Versatile Disc)などが該当する。Here, each of the learning image storage circuit 11 and the
また、サンプリング回路12、二値画像変換回路13、画像生成回路14、特徴量抽出回路15、画像再構築回路16及びパラメータ更新回路17は、例えば、単一回路、複合回路、プログラム化したプロセッサ、並列プログラム化したプロセッサ、ASIC(Application Specific Integrated Circuit)、FPGA(Field-Programmable Gate Array)、または、これらを組み合わせたものが該当する。The
ただし、機械学習装置の構成要素は、専用のハードウェアで実現されるものに限るものではなく、機械学習装置がソフトウェア、ファームウェア、または、ソフトウェアとファームウェアとの組み合わせで実現されるものであってもよい。
ソフトウェア又はファームウェアはプログラムとして、コンピュータのメモリに格納される。コンピュータは、プログラムを実行するハードウェアを意味し、例えば、CPU(Central Processing Unit)、中央処理装置、処理装置、演算装置、マイクロプロセッサ、マイクロコンピュータ、プロセッサ、DSP(Digital Signal Processor)などが該当する。However, the components of the machine learning device are not limited to those realized by dedicated hardware, and the machine learning device may be realized by software, firmware, or a combination of software and firmware. Good.
Software or firmware is stored as a program in the memory of a computer. The computer means hardware that executes a program, and includes, for example, a CPU (Central Processing Unit), a central processing unit, a processing unit, an arithmetic unit, a microprocessor, a microcomputer, a processor, a DSP (Digital Signal Processor), and the like. .
図3は、機械学習装置がソフトウェア又はファームウェアなどで実現される場合のコンピュータのハードウェア構成図である。
機械学習装置がソフトウェア又はファームウェアなどで実現される場合、学習画像記憶部1及びパラメータ記憶部8をコンピュータのメモリ21又はストレージ22上に構成するとともに、サンプリング部2、二値画像変換部3、画像生成部4、特徴量抽出部5、画像再構築部6及びパラメータ更新部7の処理手順をコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムをメモリ21又はストレージ22に格納し、コンピュータのプロセッサ23がメモリ21又はストレージ22に格納されているプログラムを実行するようにすればよい。
図3において、画像入力器24は、書類画像を入力する入力インタフェース機器であり、結果出力器25は、画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築画像を出力する出力インタフェース機器である。FIG. 3 is a hardware configuration diagram of a computer when the machine learning device is realized by software or firmware.
When the machine learning device is realized by software or firmware, the learning
In FIG. 3, an
また、図2では、機械学習装置の構成要素のそれぞれが専用のハードウェアで実現される例を示し、図3では、機械学習装置がソフトウェアやファームウェアなどで実現される例を示しているが、機械学習装置における一部の構成要素が専用のハードウェアで実現され、残りの構成要素がソフトウェアやファームウェアなどで実現されるものであってもよい。2 shows an example in which each component of the machine learning device is realized by dedicated hardware, and FIG. 3 shows an example in which the machine learning device is realized by software, firmware, etc. Some components in the machine learning device may be realized by dedicated hardware, and the remaining components may be realized by software, firmware, or the like.
図4は、この発明の実施の形態1による画像認識装置を示す構成図であり、図5は、この発明の実施の形態1による画像認識装置を示すハードウェア構成図である。
図4及び図5において、登録画像記憶部31は、例えば図5に示す登録画像記憶回路41で実現されるものであり、1つ以上の書類画像(学習対象の画像)を登録画像として記憶する。
この登録画像は、図1の機械学習装置の学習画像記憶部1に記憶されている書類画像と同じ書類画像であってもよいし、図1の機械学習装置の学習画像記憶部1に記憶されている書類画像と異なる書類画像であってもよい。
認識対象画像記憶部32は、例えば図5に示す認識対象画像記憶回路42で実現されるものであり、認識対象の書類画像である認識対象画像を記憶する。FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing an image recognition apparatus according to
4 and 5, the registered
This registered image may be the same document image as the document image stored in the learning
The recognition target
特徴量検出部33は、例えば図5に示す特徴量検出回路43で実現される。
特徴量検出部33は、第1の特徴量検出部34、画像再生成部35及び第2の特徴量検出部36を備えている。
特徴量検出部33は、登録画像の特徴量を特徴量記憶部37に登録する登録処理を実施する際には、実装しているニューラルネットワークを用いて、登録画像記憶部31に記憶されている登録画像を入力する毎に、当該登録画像の特徴量を出力する。
特徴量検出部33は、画像検索部38が認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索する検索処理を開始する前処理として、実装しているニューラルネットワークを用いて、認識対象画像記憶部32に記憶されている認識対象画像を入力して、認識対象画像の特徴量を出力する。The feature
The feature
When performing the registration process for registering the feature amount of the registered image in the feature
The feature
第1の特徴量検出部34は、登録処理を実施する際には、登録画像記憶部31に記憶されている登録画像を入力して、登録画像の特徴量を出力するニューラルネットワークとして、図1の機械学習装置のパラメータ更新部7によりパラメータが更新された第1のニューラルネットワークを有している。
第1の特徴量検出部34は、検索処理の前処理を実施する際には、実装している第1のニューラルネットワークが、認識対象画像記憶部32に記憶されている認識対象画像を入力して、認識対象画像の特徴量を出力する。
第1の特徴量検出部34が有している第1のニューラルネットワークは、図1の機械学習装置の特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークと同じニューラルネットワークである。As the neural network that inputs the registered image stored in the registered
When the first feature
The first neural network included in the first feature
画像再生成部35は、登録処理を実施する際には、第1の特徴量検出部34が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された登録画像の特徴量を入力して、登録画像を再構築した画像である再構築登録画像を出力するニューラルネットワークとして、図1の機械学習装置のパラメータ更新部7によりパラメータが更新された第2のニューラルネットワークを有している。
画像再生成部35は、検索処理の前処理を実施する際には、実装している第2のニューラルネットワークが、第1の特徴量検出部34が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された認識対象画像の特徴量を入力して、認識対象画像を再構築した画像である再構築認識画像を出力する。
画像再生成部35が有している第2のニューラルネットワークは、図1の機械学習装置の画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークと同じニューラルネットワークである。When the registration process is performed, the
When performing the preprocessing of the search process, the
The second neural network included in the
第2の特徴量検出部36は、登録処理を実施する際には、画像再生成部35が有している第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築登録画像を入力して、再構築登録画像の特徴量を出力するニューラルネットワークとして、図1の機械学習装置のパラメータ更新部7によりパラメータが更新された第1のニューラルネットワークを有している。
第2の特徴量検出部36は、検索処理の前処理を実施する際には、実装している第1のニューラルネットワークが、画像再生成部35が有している第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築認識画像を入力して、再構築認識画像の特徴量を出力する。
第2の特徴量検出部36が有している第1のニューラルネットワークは、図1の機械学習装置の特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークと同じニューラルネットワークである。When performing the registration process, the second feature
When the preprocessing of the search processing is performed, the second feature
The first neural network included in the second feature
特徴量記憶部37は、例えば図5に示す特徴量記憶回路44で実現される。
特徴量記憶部37は、特徴量検出部36が有しているニューラルネットワークから出力された登録画像の特徴量として、第1の特徴量検出部34が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された登録画像の特徴量及び第2の特徴量検出部36が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築登録画像の特徴量のそれぞれを記憶する。The feature
The feature
画像検索部38は、例えば図5に示す画像検索回路45で実現される。
画像検索部38の画像記憶部38aは、画像再生成部35から出力された再構築登録画像を記憶する。
この実施の形態1では、画像検索部38の画像記憶部38aが、画像再生成部35から出力された再構築登録画像を記憶するようにしているが、画像再生成部35が、再構築登録画像を記憶する画像記憶部を備えるようにしてもよい。あるいは、図4の画像認識装置が、画像再生成部35から出力された再構築登録画像を記憶する再構築登録画像記憶部を備えるようにしてもよい。
画像検索部38は、特徴量記憶部37により記憶されている1つ以上の登録画像の特徴量のうち、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された1つ以上の登録画像の特徴量と、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された認識対象画像の特徴量との類似度を算出する処理を実施する。
画像検索部38は、登録画像記憶部31により記憶されている1つ以上の登録画像の中で、算出した類似度が最も高い登録画像を特定し、特定した登録画像を、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像の検索結果として出力する処理を実施する。
また、画像検索部38は、特徴量記憶部37により記憶されている1つ以上の特徴量のうち、第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された1つ以上の再構築登録画像の特徴量と、第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された再構築認識画像の特徴量との類似度を算出する処理を実施する。
画像検索部38は、画像記憶部38aにより記憶されている1つ以上の再構築登録画像の中で、算出した類似度が最も高い再構築登録画像を特定し、特定した再構築登録画像に対応する登録画像を、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像の検索結果として出力する処理を実施する。The
The image storage unit 38 a of the
In the first embodiment, the image storage unit 38a of the
The
The
The
The
図4では、画像認識装置の構成要素である登録画像記憶部31、認識対象画像記憶部32、特徴量検出部33、特徴量記憶部37及び画像検索部38のそれぞれが、図5に示すような専用のハードウェアで実現されるものを想定している。即ち、登録画像記憶回路41、認識対象画像記憶回路42、特徴量検出回路43、特徴量記憶回路44及び画像検索回路45で実現されるものを想定している。In FIG. 4, each of the registered
ここで、登録画像記憶回路41、認識対象画像記憶回路42及び特徴量記憶回路44のそれぞれは、例えば、RAM、ROM、フラッシュメモリ、EPROM、EEPROMなどの不揮発性又は揮発性の半導体メモリや、磁気ディスク、フレキシブルディスク、光ディスク、コンパクトディスク、ミニディスク、DVDなどが該当する。
また、特徴量検出回路43及び画像検索回路45は、例えば、単一回路、複合回路、プログラム化したプロセッサ、並列プログラム化したプロセッサ、ASIC、FPGA、または、これらを組み合わせたものが該当する。Here, each of the registered
The feature
ただし、画像認識装置の構成要素は、専用のハードウェアで実現されるものに限るものではなく、機械学習装置がソフトウェア、ファームウェア、または、ソフトウェアとファームウェアとの組み合わせで実現されるものであってもよい。
図6は、画像認識装置がソフトウェア又はファームウェアなどで実現される場合のコンピュータのハードウェア構成図である。
画像認識装置がソフトウェア又はファームウェアなどで実現される場合、登録画像記憶部31、認識対象画像記憶部32及び特徴量記憶部37をコンピュータのメモリ51又はストレージ52上に構成するとともに、特徴量検出部33及び画像検索部38の処理手順をコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムをメモリ51又はストレージ52に格納し、コンピュータのプロセッサ53がメモリ51又はストレージ52に格納されているプログラムを実行するようにすればよい。
図6において、画像入力器54は、登録画像又は認識対象画像を入力する入力インタフェース機器であり、結果出力器55は、画像検索部38による登録画像の検索結果を出力する出力インタフェース機器である。However, the components of the image recognition device are not limited to those realized by dedicated hardware, and the machine learning device may be realized by software, firmware, or a combination of software and firmware. Good.
FIG. 6 is a hardware configuration diagram of a computer when the image recognition apparatus is realized by software or firmware.
When the image recognition device is realized by software or firmware, the registered
In FIG. 6, an
また、図5では、画像認識装置の構成要素のそれぞれが専用のハードウェアで実現される例を示し、図6では、画像認識装置がソフトウェアやファームウェアなどで実現される例を示しているが、画像認識装置における一部の構成要素が専用のハードウェアで実現され、残りの構成要素がソフトウェアやファームウェアなどで実現されるものであってもよい。5 shows an example in which each component of the image recognition apparatus is realized by dedicated hardware, and FIG. 6 shows an example in which the image recognition apparatus is realized by software, firmware, etc. Some components in the image recognition apparatus may be realized by dedicated hardware, and the remaining components may be realized by software, firmware, or the like.
次に動作について説明する。
最初に、図1の機械学習装置の動作について説明する。
学習画像記憶部1には、事前に取得された複数の書類画像が記憶される。
この実施の形態1では、学習画像記憶部1に記憶される書類画像は、例えば、グレースケールの画像であるものとする。このため、カラー画像の場合、学習画像記憶部1に記憶される前に、カラー画像がグレースケールの画像に変換されるものとする。Next, the operation will be described.
First, the operation of the machine learning device in FIG. 1 will be described.
The learning
In the first embodiment, it is assumed that the document image stored in the learning
サンプリング部2は、学習画像記憶部1に記憶されている複数の書類画像の中から、いずれか1つの書類画像を選択して、選択した書類画像を二値画像変換部3及び画像生成部4のそれぞれに出力する。
図7は、この発明の実施の形態1による機械学習装置のサンプリング部2における処理内容を示すフローチャートである。
以下、図7を参照しながら、サンプリング部2の処理内容を具体的に説明する。The
FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing the processing contents in the
Hereinafter, the processing content of the
サンプリング部2は、学習画像記憶部1に記憶されている複数の書類画像の中から、いずれか1つの書類画像をランダムに選択する(図7のステップST1)。
次に、サンプリング部2は、選択した書類画像の画像サイズを事前に設定されている画像サイズ(H,W)に変更する(図7のステップST2)。Hは書類画像の高さ、Wは書類画像の幅である。The
Next, the
次に、サンプリング部2は、画像スケールSを示すパラメータP1を乱数によって求め、画像の回転角度θを示すパラメータP2を乱数によって求める(図7のステップST3)。
サンプリング部2は、パラメータP1が示す画像スケールSに基づいて、選択した書類画像の画像サイズを変更する画像処理を実施する(図7のステップST4)。
また、サンプリング部2は、選択した書類画像の中心を回転軸として、パラメータP2が示す回転角度θだけ、選択した書類画像を回転させる画像処理を実施する(図7のステップST5)。Then, the
The
次に、サンプリング部2は、画像処理後の書類画像から切り出す一部の領域の座標(X,Y)を乱数によって決定する(図7のステップST6)。一部の領域の座標(X,Y)は、例えば、一部の領域の左上の角点の座標である。
サンプリング部2は、画像処理後の書類画像の中から、例えば、左上の角点の座標が、決定した座標(X,Y)である一部の領域を切り出す処理を実施する(図7のステップST7)。切り出し領域の画像サイズは、事前に設定されている画像サイズ(h,w)である。
サンプリング部2は、切り出した一部の領域を書類画像として、二値画像変換部3及び画像生成部4のそれぞれに出力する。Next, the
The
The
サンプリング部2は、学習画像記憶部1に記憶されている複数の書類画像の中に、未だ選択していない書類画像が残っているか否かを判定する(図7のステップST8)。
サンプリング部2は、未だ選択していない書類画像が残っていれば(図7のステップST8:YESの場合)、ステップST1~ST8の処理を繰り返し実施する。
サンプリング部2は、既に選択していない書類画像が残っていなければ(図7のステップST8:NOの場合)、処理を終了する。
サンプリング部2の処理によって、有限の学習画像である書類画像から、近似的に無限の学習サンプルとして書類画像を生成することができる。このため、学習結果の汎化性能として、未知の対象の識別能力の向上が期待される。The
If there remains a document image that has not yet been selected (step ST8: YES in FIG. 7), the
If there is no document image that has not yet been selected (step ST8 in FIG. 7: NO), the
By the processing of the
二値画像変換部3は、サンプリング部2から出力された書類画像を二値画像に変換し、変換した二値画像をパラメータ更新部7に出力する。
書類画像を二値画像に変換するアルゴリズムとして、例えば、適応的閾値処理(Adaptive Threshold関数を用いる処理)を利用することができるが、書類画像を二値画像に変換することができればよく、どのようなアルゴリズムを利用してもよい。The binary
As an algorithm for converting a document image into a binary image, for example, adaptive threshold processing (processing using an Adaptive Threshold function) can be used. However, what is necessary is just to be able to convert a document image into a binary image. A simple algorithm may be used.
画像生成部4は、サンプリング部2から書類画像が出力される毎に、当該書類画像の画素値を調整して、外乱の影響を受けている書類画像を生成し、生成した書類画像を特徴量抽出部5に出力する。
図8は、この発明の実施の形態1による機械学習装置の画像生成部4における処理内容を示すフローチャートである。
以下、図8を参照しながら、画像生成部4の調整処理を具体的に説明する。Each time a document image is output from the
FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing the processing contents in the image generation unit 4 of the machine learning device according to
Hereinafter, the adjustment process of the image generation unit 4 will be specifically described with reference to FIG.
この実施の形態1では、画像生成部4が以下の6つの調整処理を実施する例を説明するが、以下の6つの調整処理に限るものではなく、例えば、1つ以上5つ以下の調整処理、または、7つ以上の調整処理を実施するようにしてもよい。
また、以下の6つの調整処理の順序は、どのような順序でもよく、例えば、順序を乱数によって決定することができる。In the first embodiment, an example in which the image generation unit 4 performs the following six adjustment processes will be described. However, the embodiment is not limited to the following six adjustment processes. For example, one or more and five or less adjustment processes are performed. Alternatively, seven or more adjustment processes may be performed.
The order of the following six adjustment processes may be any order. For example, the order can be determined by a random number.
画像生成部4は、サンプリング部2から出力された書類画像を受けると、書類画像を構成している各々の画素の輝度値に対して、例えば、乱数で決めた分散値をガウシアンノイズとして付加する調整処理を実施する(図8のステップST11)。
次に、画像生成部4は、書類画像を構成している各々の画素の中から、ごま塩ノイズを付加する画素を、乱数で決めた確率に基づいて決定する。
そして、画像生成部4は、決定した画素の輝度値を、当該画素の周辺の画素の輝度値と大きく変えることで、当該画素にごま塩ノイズを付加する(図8のステップST12)。
例えば、周辺の画素の輝度値が、二値画像変換部3における二値画像の閾値処理に用いる閾値よりも黒側の輝度値であれば、当該画素の輝度値を最も白い輝度値とする。
一方、周辺の画素の輝度値が、閾値よりも白側の輝度値であれば、当該画素の輝度値を最も黒い輝度値とする。Upon receiving the document image output from the
Next, the image generation unit 4 determines a pixel to which sesame salt noise is added from each pixel constituting the document image based on a probability determined by a random number.
Then, the image generation unit 4 adds sesame salt noise to the pixel by largely changing the determined luminance value of the pixel from the luminance values of the pixels around the pixel (step ST12 in FIG. 8).
For example, if the luminance value of a peripheral pixel is a luminance value on the black side of the threshold value used for the threshold processing of the binary image in the binary
On the other hand, if the luminance value of the surrounding pixel is a luminance value on the white side of the threshold value, the luminance value of the pixel is set to the blackest luminance value.
次に、画像生成部4は、例えば、ガウス関数を用いて、書類画像をぼかすガウシアンぼかし処理を実施する(図8のステップST13)。
次に、画像生成部4は、シャープネスを示すパラメータを乱数によって決定し、決定したパラメータに従って書類画像のシャープネスを調整する処理を実施する(図8のステップST14)。Next, the image generation unit 4 performs Gaussian blurring processing to blur the document image using, for example, a Gaussian function (step ST13 in FIG. 8).
Next, the image generation unit 4 determines a parameter indicating sharpness using a random number, and performs a process of adjusting the sharpness of the document image according to the determined parameter (step ST14 in FIG. 8).
次に、画像生成部4は、コントラストを示すパラメータを乱数によって決定し、決定したパラメータに従って書類画像のコントラストを調整する処理を実施する(図8のステップST15)。
次に、画像生成部4は、輝度値を示すパラメータを乱数によって決定し、決定したパラメータに従って書類画像の輝度値を調整する処理を実施する(図8のステップST16)。
画像生成部4の調整処理によって、図4の画像認識装置に与えられる認識対象画像が、外乱の影響を受けている場合でも、認識対象画像に類似している画像の検索が可能になる。Next, the image generation unit 4 determines a parameter indicating the contrast using a random number, and performs a process of adjusting the contrast of the document image according to the determined parameter (step ST15 in FIG. 8).
Next, the image generation unit 4 determines a parameter indicating the luminance value by a random number, and performs a process of adjusting the luminance value of the document image according to the determined parameter (step ST16 in FIG. 8).
By the adjustment processing of the image generation unit 4, even when the recognition target image given to the image recognition apparatus in FIG. 4 is affected by disturbance, an image similar to the recognition target image can be searched.
特徴量抽出部5は、画像生成部4から出力された書類画像を入力して、書類画像の特徴量を出力する第1のニューラルネットワークを有している。
特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークはCNNであり、第1のニューラルネットワークは、書類画像の特徴量の畳み込みを行う畳み込み層と、プーリング処理を実施するプーリング層とを含んでいる。The feature
The first neural network included in the feature
図9は、特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークの構成例を示す説明図である。
図9において、INPUTは、画像の入力部であり、INPUTから入力される画像は、画像生成部4から出力された外乱の影響を受けている書類画像である。
OUTPUTは、特徴量の出力部であり、OUTPUTから出力される特徴量は、書類画像の特徴量である。
CONV(1)、CONV(2)及びCONV(3)のそれぞれは、第1のニューラルネットワークに含まれている畳み込み層である。畳み込み層では、書類画像の特徴量の畳み込みを実施した後、活性化関数の演算が行われるが、図9では、活性化関数の演算の表記を省略している。
POOL(1)及びPOOL(2)のそれぞれは、第1のニューラルネットワークに含まれているプーリング層である。FIG. 9 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a configuration example of a first neural network included in the feature
In FIG. 9, INPUT is an image input unit, and an image input from INPUT is a document image that is affected by a disturbance output from the image generation unit 4.
OUTPUT is a feature value output unit, and the feature value output from OUTPUT is the feature value of the document image.
Each of CONV (1), CONV (2), and CONV (3) is a convolutional layer included in the first neural network. In the convolution layer, after performing the convolution of the feature amount of the document image, the calculation of the activation function is performed. In FIG. 9, the notation of the calculation of the activation function is omitted.
Each of POOL (1) and POOL (2) is a pooling layer included in the first neural network.
図10は、畳み込み層における畳み込み処理を示す説明図である。
図10に示す入力特徴量は、畳み込み層に入力される書類画像における複数の領域の特徴量を含んでおり、複数の領域の特徴量は、2次元構造のデータである入力特徴量マップに相当する。
図10では、書類画像が25個の領域(図中、縦5×横5個の領域)を備えている例を示している。即ち、書類画像は、A方向が5、B方向が5の領域を備えている例を示している。。
また、入力特徴量は、k(kは1以上の整数)個の入力特徴量マップを備えており、入力特徴量が2つ以上の入力特徴量マップを備えていれば、2つ以上の入力特徴量マップは、3次元構造のデータとして表現される。図10では、入力特徴量をkマップで表記している。
例えば、書類画像が、R(赤色)、G(緑色)及びB(青色)の色成分を有するカラー画像が、色成分毎に、グレースケールの画像に変換されている画像である場合、入力特徴量は、R用の入力特徴量マップ、G用の入力特徴量マップ及びR用の入力特徴量マップとして、3個の入力特徴量マップを備える。FIG. 10 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a convolution process in the convolution layer.
The input feature amount shown in FIG. 10 includes feature amounts of a plurality of regions in the document image input to the convolution layer, and the feature amounts of the plurality of regions correspond to an input feature amount map that is data of a two-dimensional structure. To do.
FIG. 10 shows an example in which the document image has 25 regions (5 × 5 in the figure). That is, the document image shows an example in which the A direction has 5 areas and the B direction has 5 areas. .
The input feature amount includes k (k is an integer of 1 or more) input feature amount maps. If the input feature amount includes two or more input feature amount maps, two or more input features are provided. The feature amount map is expressed as data having a three-dimensional structure. In FIG. 10, the input feature amount is represented by a k map.
For example, when the document image is an image in which a color image having R (red), G (green), and B (blue) color components is converted into a grayscale image for each color component, the input feature The quantity includes three input feature quantity maps as an input feature quantity map for R, an input feature quantity map for G, and an input feature quantity map for R.
畳み込み層は、畳み込み対象である重みフィルタを備えており、重みフィルタは、カーネルと呼ばれる。
図10の例では、カーネルの2次元サイズは、A方向が3、B方向が3である。
また、カーネルは、3次元構造のデータであり、入力特徴量マップと同じ奥行サイズを持っている。したがって、入力特徴量がk個の入力特徴量マップを備えていれば、カーネルの奥行サイズはkとなる。図10では、カーネルをkマップで表記している。The convolution layer includes a weight filter that is a convolution target, and the weight filter is called a kernel.
In the example of FIG. 10, the two-dimensional size of the kernel is 3 in the A direction and 3 in the B direction.
The kernel is data having a three-dimensional structure and has the same depth size as the input feature amount map. Therefore, if the input feature quantity includes k input feature quantity maps, the kernel depth size is k. In FIG. 10, the kernel is represented by a k map.
特徴量抽出部5は、入力特徴マップである平面上を、カーネルを移動させながら、以下の式(1)に示す畳み込み処理の計算を実施する。
式(1)において、x(c1-b1+padA,c2-b2+padB,b3)における「c1-b1+padA」は、入力特徴量x(a1,a2,a3)における「a1」に対応し、「c2-b2+padB」は、入力特徴量x(a1,a2,a3)における「a2」に対応する。また、「b3」は、入力特徴量x(a1,a2,a3)における「a3」に対応する。
w(b1,b2,b3)は、カーネルの重み値を示すパラメータであり、パラメータ更新部7によって更新される第1のニューラルネットワークのパラメータである。
y(c1,c2)は、書類画像における各領域の出力特徴量である。The feature
In Expression (1), “c1−b1 + padA ” in x (c1−b1 + padA , c2−b2 + padB , b3) corresponds to “a1” in the input feature quantity x (a1, a2, a3), and “c2 “−b2 + padB ” corresponds to “a2” in the input feature quantity x (a1, a2, a3). Further, “b3” corresponds to “a3” in the input feature amount x (a1, a2, a3).
w (b1, b2, b3) is a parameter indicating a kernel weight value, and is a parameter of the first neural network updated by the parameter updating unit 7.
y (c1, c2) is an output feature amount of each region in the document image.
padA及びpadBのそれぞれは、事前に設定されるパッディングパラメータであり、畳み込み処理の計算時に、入力特徴マップの領域からカーネルがはみ出しても、計算可能な範囲を示すパラメータである。
例えば、padA=1であれば、入力特徴マップの領域からカーネルがA方向に1マスはみ出しても、畳み込み処理の計算が可能であるが、カーネルがA方向に2マスはみ出していれば、畳み込み処理の計算が不可能であることを意味している。
また、padB=2であれば、入力特徴マップの領域からカーネルがB方向に2マスはみ出しても、畳み込み処理の計算が可能であるが、カーネルがB方向に3マスはみ出していれば、畳み込み処理の計算が不可能であることを意味している。Each of padA and padB is a padding parameter set in advance, and is a parameter indicating a computable range even if the kernel protrudes from the area of the input feature map when calculating the convolution process.
For example, if padA = 1, it is possible to calculate the convolution process even if the kernel protrudes in the A direction from the area of the input feature map, but if the kernel protrudes in the A direction, the convolution process is possible. This means that processing cannot be calculated.
If padB = 2, the convolution processing can be calculated even if the kernel protrudes in the B direction from the area of the input feature map, but if the kernel protrudes in the B direction, the convolution process is possible. This means that processing cannot be calculated.
パッディングパラメータpadA,padBの値によって、畳み込み層から出力される複数の領域の特徴量である出力特徴量マップのサイズが変化する。図10では、入力特徴量マップと出力特徴量マップが同じサイズのマップである例を示している。
例えば、入力特徴マップの領域から-A方向にカーネルがはみ出しているとき、式(1)に示す畳み込み処理の計算では、一部の入力特徴量x(a1,a2,a3)のインデックスがマイナスになる。このとき、特徴量抽出部5は、インデックスがマイナスである入力特徴量x(a1,a2,a3)をゼロで埋めるゼロパッディングを実施するようにしてもよい。ただし、ゼロパッディングの実施は必須ではなく、ゼロパッディングを実施しないようにしてもよい。Depending on the values of the padding parameters padA and padB , the size of the output feature amount map, which is the feature amount of a plurality of regions output from the convolution layer, changes. FIG. 10 shows an example in which the input feature value map and the output feature value map are maps of the same size.
For example, when the kernel protrudes in the −A direction from the area of the input feature map, the index of some of the input feature values x (a1, a2, a3) becomes negative in the calculation of the convolution process shown in the equation (1). Become. At this time, the feature
畳み込み処理に関するパラメータは、カーネルの2次元サイズ及びパッディングパラメータpadA,padBのほかに、カーネルの移動量を示すストライドパラメータがある。
図10では、padA=1、padB=1、ストライドパラメータ=1であり、カーネルを1つずつ移動させながら、式(1)に示す畳み込み処理の計算を実施している例を示している。
例えば、出力特徴量の中の1個の領域の特徴量y(1,1)は、入力特徴量の中の9個の領域の特徴量x(a1,a2,a3)、即ち、x(0,0,0)、x(0,1,0)、x(0,2,0)、x(1,0,0)、x(1,1,0)、x(1,2,0)、x(2,0,0)、x(2,1,0)及びx(2,2,0)についての計算結果を示している。In addition to the two-dimensional kernel size and padding parameters padA and padB , parameters related to the convolution process include a stride parameter indicating the movement amount of the kernel.
FIG. 10 shows an example in which padA = 1, padB = 1, stride parameter = 1, and the calculation of the convolution processing shown in Expression (1) is performed while moving the kernels one by one. .
For example, the feature quantity y (1, 1) of one area in the output feature quantity is the feature quantity x (a1, a2, a3) of nine areas in the input feature quantity, that is, x (0 , 0, 0), x (0, 1, 0), x (0, 2, 0), x (1, 0, 0), x (1, 1, 0), x (1, 2, 0) , X (2, 0, 0), x (2, 1, 0) and x (2, 2, 0).
入力データの様々なパターンの特徴を抽出するためには、複数のカーネルと入力特徴量との畳み込み処理の計算を実施することが望ましい。
式(1)は、カーネルが1つである例を示しており、以下の式(2)は、カーネルが複数である場合の畳み込み処理の計算を示している。
式(2)において、kは、出力特徴量マップのインデックスである。出力特徴量マップの個数は、カーネルの個数と同じである。In order to extract features of various patterns of input data, it is desirable to perform calculation of convolution processing between a plurality of kernels and input feature amounts.
Expression (1) shows an example in which there is one kernel, and the following expression (2) shows calculation of convolution processing when there are a plurality of kernels.
In Expression (2), k is an index of the output feature amount map. The number of output feature amount maps is the same as the number of kernels.
図11は、プーリング層におけるプーリング処理を示す説明図である。
この実施の形態1において、特徴量抽出部5が実施するプーリング層におけるプーリング処理は、一般的なプーリング処理と異なる。
即ち、特徴量抽出部5が実施するプーリング処理は、一般的なプーリング処理と同様に、出力特徴量マップの一部の領域である局所領域毎に、当該局所領域に含まれている特徴量の中で、最大の特徴量を抽出して、抽出した特徴量を出力する。
特徴量抽出部5が実施するプーリング処理は、一般的なプーリング処理と異なり、抽出した特徴量が存在している書類画像内の位置を示す位置情報についても出力する。FIG. 11 is an explanatory diagram showing a pooling process in the pooling layer.
In this
That is, the pooling process performed by the feature
Unlike the general pooling process, the pooling process performed by the feature
プーリング層は、図10に示す畳み込み層と同様に、カーネルの2次元サイズ、パッディングパラメータ及びストライドパラメータによって構造が変化する。
図11では、A方向が4、B方向が4及びC方向がKである(4×4×K)の入力特徴量に対して、A方向が2、B方向が2及びC方向がKである(2×2×K)のカーネルを用いて、プーリング処理を実施した結果、A方向が2、B方向が2及びC方向がKである(2×2×K)の出力特徴量が得られている例を示している。図11の例では、カーネルのストライド値は2、パッディング値はゼロである。Similar to the convolution layer shown in FIG. 10, the structure of the pooling layer changes depending on the two-dimensional size of the kernel, padding parameters, and stride parameters.
In FIG. 11, the A direction is 2, the B direction is 2, and the C direction is K with respect to the input feature quantity of (4 × 4 × K) in which the A direction is 4, the B direction is 4 and the C direction is K. As a result of performing the pooling process using a certain (2 × 2 × K) kernel, an output feature amount (2 × 2 × K) in which the A direction is 2, the B direction is 2, and the C direction is K is obtained. An example is shown. In the example of FIG. 11, the kernel stride value is 2 and the padding value is zero.
具体的には、プーリング処理によって、入力特徴量マップにおける(2×2×K)の局所領域毎に、当該局所領域に含まれている特徴量の中で、最大の特徴量を抽出している。
例えば、出力特徴量の中の1個の領域の特徴量(0,0,0)は、入力特徴量の中の4個の領域の特徴量x(a1,a2,a3)、即ち、x(0,0,0)、x(0,1,0)、x(1,0,0)及びx(1,1,0)の中で、最大の特徴量x(0,0,0)を抽出している。そして、抽出した最大の特徴量x(0,0,0)を出力している。
また、抽出した最大の特徴量x(0,0,0)が存在している書類画像内の位置を示す位置情報を出力している。Specifically, the maximum feature amount is extracted from the feature amounts included in the local region for each (2 × 2 × K) local region in the input feature amount map by the pooling process. .
For example, the feature quantity (0, 0, 0) of one area in the output feature quantity is the feature quantity x (a1, a2, a3) of four areas in the input feature quantity, that is, x ( Among the 0, 0, 0), x (0, 1, 0), x (1, 0, 0) and x (1, 1, 0), the maximum feature amount x (0, 0, 0) is obtained. Extracting. The extracted maximum feature quantity x (0, 0, 0) is output.
In addition, position information indicating the position in the document image where the extracted maximum feature quantity x (0, 0, 0) exists is output.
図11では、最大の特徴量が存在している書類画像内の位置を示す位置情報として、局所最大値位置を示す位置マップを例示している。
位置マップは、入力特徴量と同じ3次元構造のデータとして表現されている。
位置マップにおいて、最大の特徴量に対応する書類画像内の位置には“1”が表記され、最大の特徴量以外の特徴量に対応する書類画像内の位置には“0”が表記されている。
ここでは、位置情報が、3次元構造の位置マップである例を示しているが、最大の特徴量が存在している書類画像内の位置が分かればよく、位置情報のデータ構造は、どのような構造であってもよい。FIG. 11 illustrates a position map indicating the local maximum value position as position information indicating the position in the document image where the maximum feature amount exists.
The position map is expressed as data having the same three-dimensional structure as the input feature amount.
In the position map, “1” is written in the position in the document image corresponding to the maximum feature value, and “0” is written in the position in the document image corresponding to the feature value other than the maximum feature value. Yes.
In this example, the position information is a position map having a three-dimensional structure. However, it is only necessary to know the position in the document image where the maximum feature amount exists, and what is the data structure of the position information? It may be a simple structure.
以下の式(3)は、プーリング処理の計算を示している。
式(3)は、演算子f(.)を利用して、入力特徴量マップにおける4つの領域を含む局所領域から、1つの特徴量を出力する例を示している。
この実施の形態1では、演算子f(.)が、最大値を演算する演算子である例を示しており、このような演算子f(.)が用いられるプーリング処理は、最大プーリング(Max Pooling)と呼ばれる。
プーリング層におけるプーリング処理が最大プーリングである場合、1つの特徴量として局所領域の最大値を計算すると同時に、最大値となる書類画像内の位置を示す位置情報も計算される。4つの領域を含む局所領域の中に、最大値となる書類画像内の位置が2つ以上存在する場合、2つ以上の位置を示す位置情報を出力するようにしてもよい。
プーリング層におけるプーリング処理は、最大プーリングに限るものではなく、例えば、平均プーリング(Average Pooling)などの他のプーリング処理であってもよい。
プーリング層におけるプーリング処理が平均プーリングである場合、式(3)における演算子f(.)は、平均値を演算する演算子となる。Equation (3) below shows the pooling calculation.
Expression (3) shows an example in which one feature value is output from a local region including four regions in the input feature value map using the operator f (.).
The first embodiment shows an example in which the operator f (.) Is an operator that calculates the maximum value, and the pooling process in which such an operator f (.) Is used is the maximum pooling (Max). Called Pooling).
When the pooling process in the pooling layer is maximum pooling, the maximum value of the local area is calculated as one feature amount, and at the same time, position information indicating the position in the document image that is the maximum value is also calculated. When there are two or more positions in the document image having the maximum value in the local area including the four areas, position information indicating two or more positions may be output.
The pooling process in the pooling layer is not limited to the maximum pooling, and may be another pooling process such as an average pooling (Average Pooling).
When the pooling process in the pooling layer is average pooling, the operator f (.) In Expression (3) is an operator that calculates an average value.
なお、プーリング処理に関するパラメータの中には、パラメータ更新部7によって更新されるパラメータはない。
この実施の形態1では、特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークがCNNである例を示しているが、CNNに限るものではなく、例えば、ディープニューラルネットなどの多層構造を持つニューラルネットであってもよい。Note that there is no parameter updated by the parameter updating unit 7 among the parameters related to the pooling process.
In the first embodiment, the first neural network included in the feature
画像再構築部6は、特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された特徴量を入力して、書類画像を二値画像として再構築した画像である再構築画像を出力する第2のニューラルネットワークを有している。
画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークはCNNであり、第2のニューラルネットワークは、逆プーリング処理を実施する逆プーリング層と、二値画像の特徴量の畳み込みを行う畳み込み層とを含んでいる。The
The second neural network included in the
図12は、画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークの構成例を示す説明図である。
図12において、INPUTは、特徴量の入力部であり、INPUTから入力される特徴量は、特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された特徴量である。
OUTPUTは、特徴量の出力部であり、OUTPUTから出力される複数の領域の特徴量である出力特徴量のサイズは、図10に示す入力特徴量のサイズと同じサイズである。
UNPOOL(1)及びUNPOOL(2)のそれぞれは、第2のニューラルネットワークに含まれている逆プーリング層である。
第2のニューラルネットワークに含まれているUNPOOL(1)は、図9に示すPOOL(2)と対応し、第2のニューラルネットワークに含まれているUNPOOL(2)は、図9に示すPOOL(1)と対応している。
CONV(1)、CONV(2)及びCONV(3)のそれぞれは、第2のニューラルネットワークに含まれている畳み込み層である。畳み込み層では、再構築画像の特徴量の畳み込みを実施した後、活性化関数の演算が行われるが、図12では、活性化関数の演算の表記を省略している。FIG. 12 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a configuration example of the second neural network included in the
In FIG. 12, INPUT is a feature quantity input unit, and the feature quantity input from INPUT is a feature quantity output from the first neural network included in the feature
OUTPUT is a feature value output unit, and the size of the output feature value, which is the feature value of a plurality of regions output from OUTPUT, is the same size as the size of the input feature value shown in FIG.
Each of UNPOOL (1) and UNPOOL (2) is an inverse pooling layer included in the second neural network.
UNDOOL (1) included in the second neural network corresponds to POOL (2) shown in FIG. 9, and UNDOOL (2) included in the second neural network is POOL (2) shown in FIG. Corresponds to 1).
Each of CONV (1), CONV (2), and CONV (3) is a convolutional layer included in the second neural network. In the convolution layer, the activation function is calculated after convolution of the feature quantity of the reconstructed image. In FIG. 12, the notation of the activation function calculation is omitted.
画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークに含まれている畳み込み層は、特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークに含まれている畳み込み層と同様に、入力特徴量マップのサイズと出力特徴量マップのサイズとが同じである。
画像再構築部6が、期待された機械学習効果を達成するためには、特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された複数の領域の特徴量である出力特徴量のサイズを、図10に示す入力特徴量のサイズに戻す必要がある。
即ち、特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークに含まれているプーリング層のプーリング処理によって、サイズが小さくなっている出力特徴量である特徴量マップのサイズを、画像再構築部6が、当該プーリング処理が実施される前の入力特徴量のサイズに戻す必要がある。
このため、画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークは、特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットに含まれているプーリング層に対応する逆プーリング層を含んでいる。The convolutional layer included in the second neural network included in the
In order for the
That is, the size of the feature map, which is the output feature whose size is reduced by the pooling process of the pooling layer included in the first neural network included in the
Therefore, the second neural network included in the
具体的には、特徴量抽出部5が、図11に示すように、プーリング層のプーリング処理を実施することで、入力特徴量のサイズを4分の1の大きさにしている場合、画像再構築部6が、図13に示すように、逆プーリング層の逆プーリング処理を実施することで、入力特徴量のサイズを4倍にしている。
図13は、逆プーリング層における逆プーリング処理を示す説明図である。Specifically, as shown in FIG. 11, when the feature
FIG. 13 is an explanatory diagram illustrating reverse pooling processing in the reverse pooling layer.
画像再構築部6が実施する逆プーリング層の逆プーリング処理において、逆プーリング層と対応するプーリング層から出力された位置情報を利用するに際し、逆プーリング層と対応するプーリング層の出力特徴量のサイズと、当該逆プーリング層の入力特徴量のサイズとが一致している。また、逆プーリング層と対応するプーリング層の入力特徴量のサイズと当該逆プーリング層の出力特徴量のサイズとが一致している。
図13に示す逆プーリング処理では、(2×2×K)の入力特徴量を(4×4×K)の出力特徴量に変換する例を示している。
また、図13に示す逆プーリング処理では、対応するプーリング層から取得した位置情報を入力し、(4×4×K)の出力特徴量のうち、位置情報が示す最大値の位置の特徴量に、入力特徴量の値を挿入し、位置情報が示す最大値の位置以外の位置の特徴量に、ゼロを挿入している。In the reverse pooling process of the reverse pooling layer performed by the
The reverse pooling process shown in FIG. 13 shows an example in which (2 × 2 × K) input feature values are converted to (4 × 4 × K) output feature values.
In the reverse pooling process shown in FIG. 13, the positional information acquired from the corresponding pooling layer is input, and among the output feature values of (4 × 4 × K), the maximum feature value indicated by the position information is used. The value of the input feature amount is inserted, and zero is inserted into the feature amount at a position other than the position of the maximum value indicated by the position information.
例えば、入力特徴量x(0,0,0)は、(4×4×K)の出力特徴量において、A方向で左から2番目及びB方向で上から2番目の位置に挿入されている。
また、入力特徴量x(0,1,0)は、(4×4×K)の出力特徴量において、A方向で左から3番目及びB方向で上から1番目の位置に挿入されている。
また、入力特徴量x(1,0,0)は、(4×4×K)の出力特徴量において、A方向で左から2番目及びB方向で上から3番目の位置に挿入されている。
入力特徴量x(1,1,0)は、(4×4×K)の出力特徴量において、A方向で左から3番目及びB方向で上から4番目の位置に挿入されている。
(4×4×K)の出力特徴量の他の位置には、ゼロが挿入されている。For example, the input feature quantity x (0, 0, 0) is inserted at the second position from the left in the A direction and the second position from the top in the B direction in the output feature quantity of (4 × 4 × K). .
Further, the input feature quantity x (0, 1, 0) is inserted at the third position from the left in the A direction and the first position from the top in the B direction in the output feature quantity of (4 × 4 × K). .
The input feature quantity x (1, 0, 0) is inserted at the second position from the left in the A direction and the third position from the top in the B direction in the output feature quantity of (4 × 4 × K). .
The input feature quantity x (1, 1, 0) is inserted at the third position from the left in the A direction and the fourth position from the top in the B direction in the output feature quantity of (4 × 4 × K).
Zeros are inserted at other positions of the output feature amount of (4 × 4 × K).
パラメータ更新部7は、画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築画像と、二値画像変換部3から出力された二値画像との差分を算出する。
パラメータ更新部7は、算出した差分が最小になるように、特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークのパラメータ及び画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークのパラメータのそれぞれを更新する。
即ち、パラメータ更新部7は、算出した差分が最小になるように、第1のニューラルネットワークにおけるカーネルの重み値を示すパラメータw(b1,b2,b3)及び第2のニューラルネットワークにおけるカーネルの重み値を示すパラメータw(b1,b2,b3)のそれぞれを更新する。
パラメータ更新部7により算出される再構築画像と二値画像との差分としては、例えば、再構築画像と二値画像との平均2乗誤差(MSE:Mean Square Error)でもよいし、再構築画像と二値画像とのクロスエントロピーでもよい。
また、パラメータ更新部7が、差分が最小になるように、パラメータを更新する最適化アルゴリズムとして、例えば、確率的勾配降下法などを用いることができる。The parameter update unit 7 calculates a difference between the reconstructed image output from the second neural network included in the
The parameter updating unit 7 is configured so that the parameter of the first neural network that the feature
That is, the parameter updating unit 7 sets the parameter w (b1, b2, b3) indicating the kernel weight value in the first neural network and the kernel weight value in the second neural network so that the calculated difference is minimized. Each of the parameters w (b1, b2, b3) indicating is updated.
The difference between the reconstructed image and the binary image calculated by the parameter updating unit 7 may be, for example, a mean square error (MSE: Mean Square Error) between the reconstructed image and the binary image, or the reconstructed image. And a cross-entropy of a binary image.
Further, for example, a stochastic gradient descent method or the like can be used as an optimization algorithm in which the parameter updating unit 7 updates the parameters so that the difference is minimized.
パラメータ記憶部8は、パラメータ更新部7により更新された第1のニューラルネットワークのパラメータとして、パラメータ更新部7により更新された第1のニューラルネットワークにおけるカーネルの重み値を示すパラメータw(b1,b2,b3)を記憶する。
また、パラメータ記憶部8は、パラメータ更新部7により更新された第2のニューラルネットワークのパラメータとして、パラメータ更新部7により更新された第2のニューラルネットワークにおけるカーネルの重み値を示すパラメータw(b1,b2,b3)を記憶する。The parameter storage unit 8 is a parameter w (b1, b2, b2) indicating kernel weight values in the first neural network updated by the parameter updating unit 7 as parameters of the first neural network updated by the parameter updating unit 7. b3) is stored.
The parameter storage unit 8 also includes a parameter w (b1, b1) indicating a kernel weight value in the second neural network updated by the parameter update unit 7 as a parameter of the second neural network updated by the parameter update unit 7. b2, b3) are stored.
次に、図4の画像認識装置の動作について説明する。
第1の特徴量検出部34は、登録画像記憶部31に記憶されている登録画像を入力して、登録画像の特徴量を出力するとともに、認識対象画像記憶部32に記憶されている認識対象画像を入力して、認識対象画像の特徴量を出力する第1のニューラルネットワークを有している。
第1の特徴量検出部34が有している第1のニューラルネットワークは、図1の機械学習装置の特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークと同じニューラルネットワークである。
したがって、第1の特徴量検出部34が有している第1のニューラルネットワークにおけるカーネルの重み値を示すパラメータw(b1,b2,b3)は、再構築画像と二値画像との差分が最小になるように、図1の機械学習装置のパラメータ更新部7によって最適化されている。Next, the operation of the image recognition apparatus in FIG. 4 will be described.
The first feature
The first neural network included in the first feature
Therefore, the parameter w (b1, b2, b3) indicating the kernel weight value in the first neural network included in the first feature
画像再生成部35は、第1の特徴量検出部34が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された登録画像の特徴量を入力して、登録画像を再構築した画像である再構築登録画像を出力するとともに、第1の特徴量検出部34が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された認識対象画像の特徴量を入力して、認識対象画像を再構築した画像である再構築認識画像を出力する第2のニューラルネットワークを有している。
画像再生成部35が有している第2のニューラルネットワークは、図1の機械学習装置の画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークと同じニューラルネットワークである。
したがって、画像再生成部35が有している第2のニューラルネットワークにおけるカーネルの重み値を示すパラメータw(b1,b2,b3)は、再構築画像と二値画像との差分が最小になるように、図1の機械学習装置のパラメータ更新部7によって最適化されている。The
The second neural network included in the
Therefore, the parameter w (b1, b2, b3) indicating the kernel weight value in the second neural network possessed by the
第2の特徴量検出部36は、画像再生成部35が有している第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築登録画像を入力して、再構築登録画像の特徴量を出力するとともに、画像再生成部35が有している第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築認識画像を入力して、再構築認識画像の特徴量を出力する第1のニューラルネットワークを有している。
第2の特徴量検出部36が有している第1のニューラルネットワークは、図1の機械学習装置の特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークと同じニューラルネットワークである。
したがって、第2の特徴量検出部36が有している第1のニューラルネットワークにおけるカーネルの重み値を示すパラメータw(b1,b2,b3)は、再構築画像と二値画像との差分が最小になるように、図1の機械学習装置のパラメータ更新部7によって最適化されている。The second feature
The first neural network included in the second feature
Accordingly, the parameter w (b1, b2, b3) indicating the kernel weight value in the first neural network possessed by the second feature
なお、第2の特徴量検出部36が有している第1のニューラルネットワークに含まれているプーリング層は、位置情報を出力する必要がない。
図1の機械学習装置の特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワーク及び画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークのそれぞれがCNNである場合、第1の特徴量検出部34が有している第1のニューラルネットワーク及び第2の特徴量検出部36が有している第1のニューラルネットワークは、自由パラメータとして、畳み込み層のカーネルだけを持っている。このため、カーネルのサイズが同じであれば、パラメータ更新部7により更新されたパラメータを学習済みのパラメータとして利用できるため、図1の機械学習装置における各々の畳み込み層の特徴量マップと、図4の画像認識装置における各々の畳み込み層の特徴量マップとのサイズが異なっていてもよい。Note that the pooling layer included in the first neural network included in the second feature
When each of the first neural network included in the feature
登録画像記憶部31は、1つ以上の書類画像を登録画像として記憶している。
この登録画像は、図1の機械学習装置の学習画像記憶部1に記憶されている書類画像と同じ書類画像であってもよいし、図1の機械学習装置の学習画像記憶部1に記憶されている書類画像と異なる書類画像であってもよい。
認識対象画像記憶部32は、認識対象の書類画像である認識対象画像を記憶している。
特徴量検出部33は、登録画像記憶部31に記憶されている登録画像の特徴量を特徴量記憶部37に登録する登録処理と、認識対象画像記憶部32に記憶されている認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索する検索処理を可能にするために、認識対象画像の特徴量を抽出する前処理とを実施する。The registered
This registered image may be the same document image as the document image stored in the learning
The recognition target
The feature
最初に、特徴量検出部33の登録処理の動作について説明する。
特徴量検出部33の第1の特徴量検出部34は、登録画像記憶部31に記憶されている1つ以上の登録画像の中から、1つの登録画像を順番に入力する。
第1の特徴量検出部34が有している第1のニューラルネットワークは、1つの登録画像を入力すると、登録画像の特徴量を出力する。
第1の特徴量検出部34は、登録画像の特徴量を特徴量記憶部37に格納するとともに、登録画像の特徴量を画像再生成部35に出力する。First, the registration processing operation of the feature
The first feature
When the first neural network included in the first feature
The first feature
特徴量検出部33の画像再生成部35は、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された登録画像の特徴量を入力する。
画像再生成部35が有している第2のニューラルネットワークは、登録画像の特徴量を入力すると、登録画像を再構築した画像である再構築登録画像を出力する。
画像再生成部35は、再構築登録画像を第2の特徴量検出部36及び画像検索部38に出力する。
画像検索部38の画像記憶部38aは、画像再生成部35から出力された再構築登録画像を記憶する。
なお、画像再生成部35から出力される再構築登録画像は、登録画像の二値画像に相当する画像ではあるが、登録画像の特徴量から再構築した画像であるため、登録画像の二値画像と完全に一致しているとは限らない。The
When the second neural network included in the
The
The image storage unit 38 a of the
Note that the reconstructed registered image output from the
特徴量検出部33の第2の特徴量検出部36は、画像再生成部35から出力された再構築登録画像を入力する。
第2の特徴量検出部36が有している第1のニューラルネットワークは、再構築登録画像を入力すると、再構築登録画像の特徴量を出力する。
第2の特徴量検出部36は、再構築登録画像の特徴量を特徴量記憶部37に格納する。
登録画像記憶部31に記憶されている登録画像の個数がN個であれば、特徴量記憶部37には、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力されたN個の登録画像の特徴量と、第2の特徴量検出部36から出力されたN個の再構築登録画像の特徴量が記憶される。
第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された再構築登録画像の特徴量は、画像再生成部35により再構築された画像である再構築登録画像から抽出された特徴量であるため、第1の特徴量検出部34が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された登録画像の特徴量よりも、多くの外乱の影響が除去されている。The second feature
When the first neural network included in the second feature
The second feature
If the number of registered images stored in the registered
Since the feature amount of the reconstructed registered image output from the second feature
次に、特徴量検出部33による検索処理の前処理について説明する。
特徴量検出部33の第1の特徴量検出部34は、認識対象画像記憶部32に記憶されている認識対象の書類画像である認識対象画像を入力する。
第1の特徴量検出部34が有している第1のニューラルネットワークは、認識対象画像を入力すると、認識対象画像の特徴量を出力する
第1の特徴量検出部34は、認識対象画像の特徴量を画像再生成部35及び画像検索部38のそれぞれに出力する。Next, preprocessing of search processing by the feature
The first feature
When the recognition target image is input, the first neural network included in the first feature
特徴量検出部33が有している画像再生成部35は、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された認識対象画像の特徴量を入力する。
画像再生成部35の第2のニューラルネットワークは、認識対象画像の特徴量を入力すると、認識対象画像を再構築した画像である再構築認識画像を出力する。
画像再生成部35は、再構築認識画像を第2の特徴量検出部36に出力する。The
When the second neural network of the
The
特徴量検出部33の第2の特徴量検出部36は、画像再生成部35から出力された再構築認識画像を入力する。
第2の特徴量検出部36が有している第1のニューラルネットワークは、再構築認識画像を入力すると、再構築認識画像の特徴量を出力する。
第2の特徴量検出部36は、再構築認識画像の特徴量を画像検索部38に出力する。The second feature
When the first neural network included in the second feature
The second feature
登録画像記憶部31に記憶されている1つ以上の登録画像と、認識対象画像記憶部32に記憶されている認識対象画像とが、同じ環境下又は類似している環境下で取得された画像である場合、登録画像と認識対象画像とが受けている外乱の影響はほんとんど同じである。
このため、画像検索部38が、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索する際、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された登録画像の特徴量と、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された認識対象画像の特徴量とを比較すれば十分である。したがって、多くの外乱の影響が除去されている第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された再構築登録画像の特徴量と、多くの外乱の影響が除去されている第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された再構築認識画像の特徴量とを比較する必要性が低い。An image acquired in the same environment or an environment in which one or more registered images stored in the registered
For this reason, when the
登録画像記憶部31に記憶されている1つ以上の登録画像と、認識対象画像記憶部32に記憶されている認識対象画像とが、異なる環境下で取得された画像である場合、登録画像と認識対象画像とが受けている外乱の影響が異なる。
このため、画像検索部38が、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索する際、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された登録画像の特徴量と、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された認識対象画像の特徴量とを比較するだけでは不十分である。したがって、多くの外乱の影響が除去されている第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された再構築登録画像の特徴量と、多くの外乱の影響が除去されている第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された再構築認識画像の特徴量とを比較する必要性が高い。When one or more registered images stored in the registered
For this reason, when the
この実施の形態1では、画像検索部38による比較対象の特徴量が、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力される登録画像の特徴量と認識対象画像の特徴量とにするのか、第2の特徴量検出部36から出力される再構築登録画像の特徴量と再構築認識画像の特徴量とするのかは、事前にユーザによって設定されるものとする。
以下、画像検索部38による比較対象の特徴量が、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力される登録画像の特徴量と認識対象画像の特徴量とする設定を「設定A」と称する。
画像検索部38による比較対象の特徴量が、第2の特徴量検出部36から出力される再構築登録画像の特徴量と再構築認識画像の特徴量とする設定を「設定B」と称する。In the first embodiment, whether the feature quantity to be compared by the
Hereinafter, the setting in which the feature quantity to be compared by the
A setting in which the feature quantity to be compared by the
画像検索部38は、設定Aの場合、特徴量記憶部37により記憶されている1つ以上の登録画像の特徴量のうち、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された1つ以上の登録画像の特徴量と、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された認識対象画像の特徴量との類似度を算出する。
特徴量の類似度を算出するアルゴリズムは、特に限定するものではないが、例えば、コサイン類似度(Cosine Similarity)を使用することができる。
画像検索部38は、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された1つ以上の登録画像の特徴量と、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された認識対象画像の特徴量との類似度を算出すると、登録画像記憶部31により記憶されている1つ以上の登録画像の中で、算出した類似度が最も高い登録画像を特定する。
画像検索部38は、特定した登録画像を、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像の検索結果として出力する。
この場合、画像検索部38が、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索する際、画像再生成部35及び第2の特徴量検出部36が処理を実施する必要がないため、登録画像の検索結果が得られるまでの時間を短縮することができる。In the case of setting A, the
The algorithm for calculating the similarity of the feature quantity is not particularly limited, and for example, cosine similarity can be used.
The
The
In this case, when the
画像検索部38は、設定Bの場合、特徴量記憶部37により記憶されている1つ以上の登録画像の特徴量のうち、第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された1つ以上の再構築登録画像の特徴量と、第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された再構築認識画像の特徴量との類似度を算出する。
画像検索部38は、第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された1つ以上の再構築登録画像の特徴量と、第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された再構築認識画像の特徴量との類似度を算出すると、画像記憶部38aにより記憶されている1つ以上の再構築登録画像の中で、算出した類似度が最も高い再構築登録画像を特定する。
画像検索部38は、特定した再構築登録画像に対応する登録画像を、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像の検索結果として出力する。
この場合、画像検索部38が、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索する際、画像再生成部35及び第2の特徴量検出部36が前処理を実施する必要があるため、設定Aの場合よりも、登録画像の検索結果が得られるまでの時間が長くなるが、登録画像と認識対象画像が取得された環境が異なる場合でも、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像の検索精度の劣化を抑えることができる。In the case of setting B, the
The
The
In this case, when the
ここでは、設定Bの場合、画像検索部38が、第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された1つ以上の再構築登録画像の特徴量と、第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された再構築認識画像の特徴量との類似度を算出する例を示しているが、これに限るものではなく、例えば、以下のようにして、類似度を算出する方法が考えられる。
画像検索部38は、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された1つ以上の登録画像の特徴量と、第1の特徴量検出部34から出力された認識対象画像の特徴量との類似度(以下、類似度R1と称する)を算出する。
また、画像検索部38は、第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された1つ以上の再構築登録画像の特徴量と、第2の特徴量検出部36から出力された再構築認識画像の特徴量との類似度(以下、類似度R2と称する)を算出する。
そして、画像検索部38は、最終的な類似度Rとして、類似度R1と類似度R2の平均値、あるいは、類似度R1と類似度R2の重み付け加算値などを算出する。
画像検索部38は、最終的な類似度Rを算出すると、1つ以上の登録画像の中で、算出した類似度Rが最も高い登録画像を特定する。
画像検索部38は、特定した登録画像を、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像の検索結果として出力する。Here, in the case of setting B, the
The
The
Then, the
When the final similarity R is calculated, the
The
この実施の形態1では、画像検索部38が、登録画像記憶部31に記憶されている登録画像毎に、当該登録画像の特徴量と認識対象画像の特徴量との類似度を算出する例を示している。
同じ種類の登録画像(以下、同種登録画像と称する)が複数存在しており、複数の同種登録画像が登録画像記憶部31に記憶されている場合、画像検索部38が、特徴量記憶部37により記憶されている複数の同種登録画像と、認識対象画像の特徴量との類似度をそれぞれ算出する。
そして、画像検索部38が、同種登録画像の特徴量と認識対象画像の特徴量との類似度として、それぞれ算出した類似度の平均値を算出するようにしてもよい。
この場合、登録画像記憶部31に記憶されている登録画像の個数がN個であっても、登録画像記憶部31に記憶されている登録画像の種類がM(N≧M)であれば、画像検索部38は、M種類の同種登録画像の中から、認識対象画像と類似している同種登録画像を検索するようになる。In the first embodiment, the
When there are a plurality of registered images of the same type (hereinafter referred to as “same type registered images”) and a plurality of same type registered images are stored in the registered
Then, the
In this case, even if the number of registered images stored in the registered
以上で明らかなように、この実施の形態1によれば、学習画像を二値画像に変換する二値画像変換部3と、学習画像を入力して、学習画像の特徴量を出力する第1のニューラルネットワークを有する特徴量抽出部5と、第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された特徴量を入力して、再構築画像を出力する第2のニューラルネットワークを有する画像再構築部6とを設け、パラメータ更新部7が、第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築画像と、二値画像変換部3により変換された二値画像との差分に従って第1のニューラルネットワークのパラメータ及び第2のニューラルネットワークのパラメータのそれぞれを更新するように構成したので、教師データを用いることなく、学習画像を入力して、学習画像の特徴量を出力する第1のニューラルネットワークのパラメータを更新することができる効果を奏する。As is apparent from the above, according to the first embodiment, the binary
また、この実施の形態1によれば、登録画像が与えられると、登録画像の特徴量を出力し、認識対象画像が与えられると、認識対象画像の特徴量を出力するニューラルネットワークを有する特徴量検出部33と、特徴量検出部33が有しているニューラルネットワークから出力された登録画像の特徴量を記憶する特徴量記憶部37と、特徴量記憶部37により記憶されている1つ以上の登録画像の特徴量と、特徴量検出部33が有しているニューラルネットワークから出力された認識対象画像の特徴量とを比較して、1つ以上の登録画像の中から、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索する画像検索部38とを備え、特徴量検出部33が有しているニューラルネットワークのパラメータが機械学習装置によって更新されているように構成したので、機械学習装置によりパラメータが更新されたニューラルネットワークを用いて、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索することができる効果を奏する。
これにより、例えば、ユーザは、画像認識装置により検索された登録画像の種類を確認することで、認識対象画像の種類を把握することができるようになる。Further, according to the first embodiment, when a registered image is given, the feature amount of the registered image is output, and when the recognition target image is given, the feature amount having a neural network that outputs the feature amount of the recognition target image. A
Thereby, for example, the user can grasp the type of the recognition target image by confirming the type of the registered image searched by the image recognition apparatus.
この実施の形態1では、図4の画像認識装置の登録画像記憶部31に記憶される登録画像が、図1の機械学習装置の学習画像記憶部1に記憶されている書類画像と同じ画像であってもよいし、図1の機械学習装置の学習画像記憶部1に記憶されている書類画像と異なる画像であってもよい旨を上述している。
例えば、学習画像記憶部1に記憶される書類画像と、登録画像及び認識対象画像とを取得する環境が類似している場合、あるいは、書類のジャンルが、書類画像、登録画像及び認識対象画像の間で類似している場合、登録画像及び認識対象画像が、書類画像と異なる画像であっても、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索することができる。
即ち、図1の機械学習装置が、事前に書類画像と同じ登録画像及び認識対象画像を学習していない場合でも、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索することができる。
なお、取得する環境には、画像を撮影している環境のほか、画像取得機材の違いも含まれる。
書類のジャンルが類似する態様として、例えば、異なる銀行の申請書又は異なる行政機関の用紙などが考えられる。In the first embodiment, the registered image stored in the registered
For example, when the document image stored in the learning
That is, even when the machine learning apparatus of FIG. 1 does not learn the same registered image and recognition target image as the document image in advance, it is possible to search for a registered image similar to the recognition target image.
Note that the acquisition environment includes not only the environment in which images are taken but also differences in image acquisition equipment.
As an aspect in which the genre of the documents is similar, for example, an application form of a different bank or a form of a different administrative institution can be considered.
実施の形態2.
上記実施の形態1では、特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワーク及び画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークのパラメータの初期状態については、特に言及していない。
この実施の形態2では、特徴量抽出部5が有している第1のニューラルネットワークは、何らかの学習データに基づいて事前にパラメータが学習されているニューラルネットワークであるものとする。
また、画像再構築部6が有している第2のニューラルネットワークについても、何らかの学習データに基づいて事前にパラメータが学習されているニューラルネットワークであるものとする。
In the first embodiment, the initial state of the parameters of the first neural network included in the feature
In the second embodiment, the first neural network included in the feature
The second neural network included in the
また、図1の機械学習装置の学習画像記憶部1には、書類画像として認識対象画像が記憶されており、認識対象画像に基づいて、上記実施の形態1と同様に、パラメータ更新部7によって、第1のニューラルネットワークのパラメータ及び第2のニューラルネットワークのパラメータのそれぞれが更新されているものとする。
この場合、上記実施の形態1よりも学習時間が増加してしまうが、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を、上記実施の形態1よりも正確に検索することができるようになる。Further, the learning
In this case, although the learning time is increased as compared with the first embodiment, a registered image similar to the recognition target image can be searched more accurately than the first embodiment.
なお、本願発明はその発明の範囲内において、各実施の形態の自由な組み合わせ、あるいは各実施の形態の任意の構成要素の変形、もしくは各実施の形態において任意の構成要素の省略が可能である。In the present invention, within the scope of the invention, any combination of the embodiments, or any modification of any component in each embodiment, or omission of any component in each embodiment is possible. .
この発明は、書類画像を入力して、書類画像の特徴量を出力するニューラルネットワークのパラメータを更新する機械学習装置に適している。
また、この発明は、認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索する画像認識装置に適している。The present invention is suitable for a machine learning apparatus that inputs a document image and updates a parameter of a neural network that outputs a feature amount of the document image.
The present invention is also suitable for an image recognition apparatus that searches for registered images that are similar to the recognition target image.
1 学習画像記憶部、2 サンプリング部、3 二値画像変換部、4 画像生成部、5 特徴量抽出部、6 画像再構築部、7 パラメータ更新部、8 パラメータ記憶部、11 学習画像記憶回路、12 サンプリング回路、13 二値画像変換回路、14 画像生成回路、15 特徴量抽出回路、16 画像再構築回路、17 パラメータ更新回路、18 パラメータ記憶回路、21 メモリ、22 ストレージ、23 プロセッサ、24 画像入力器、25 結果出力器、31 登録画像記憶部、32 認識対象画像記憶部、33 特徴量検出部、34 第1の特徴量検出部、35 画像再生成部、36 第2の特徴量検出部、37 特徴量記憶部、38 画像検索部、38a 画像記憶部、41 登録画像記憶回路、42 認識対象画像記憶回路、43 特徴量検出回路、44 特徴量記憶回路、45 画像検索回路、51 メモリ、52 ストレージ、53 プロセッサ、54 画像入力器、55 結果出力器。1 learning image storage unit, 2 sampling unit, 3 binary image conversion unit, 4 image generation unit, 5 feature quantity extraction unit, 6 image reconstruction unit, 7 parameter update unit, 8 parameter storage unit, 11 learning image storage circuit, 12 sampling circuit, 13 binary image conversion circuit, 14 image generation circuit, 15 feature extraction circuit, 16 image reconstruction circuit, 17 parameter update circuit, 18 parameter storage circuit, 21 memory, 22 storage, 23 processor, 24
Claims (15)
Translated fromJapanese前記学習画像を入力して、前記学習画像の特徴量を出力する第1のニューラルネットワークを有する特徴量抽出部と、
前記第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された特徴量を入力して、前記学習画像を二値画像として再構築した画像である再構築画像を出力する第2のニューラルネットワークを有する画像再構築部と、
前記第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築画像と、前記二値画像変換部により変換された二値画像との差分に従って前記第1のニューラルネットワークのパラメータ及び前記第2のニューラルネットワークのパラメータのそれぞれを更新するパラメータ更新部と
を備えた機械学習装置。A binary image conversion unit that converts a learning image, which is an image to be learned, into a binary image;
A feature quantity extraction unit having a first neural network that inputs the learning image and outputs the feature quantity of the learning image;
An image reconstruction unit having a second neural network that inputs a feature amount output from the first neural network and outputs a reconstructed image that is an image reconstructed from the learning image as a binary image;
According to the difference between the reconstructed image output from the second neural network and the binary image converted by the binary image converter, the parameters of the first neural network and the parameters of the second neural network A machine learning device comprising: a parameter updating unit for updating each.
前記画像再構築部は、前記第2のニューラルネットワークとして、畳み込みニューラルネットワークであるCNNを有していることを特徴とする請求項1記載の機械学習装置。The feature quantity extraction unit has a CNN (Convolutional Neural Net) which is a convolutional neural network as the first neural network,
The machine learning device according to claim 1, wherein the image reconstruction unit includes a CNN that is a convolutional neural network as the second neural network.
前記畳み込み層の入力特徴量マップと、前記畳み込み層の出力特徴量マップとが同じサイズであることを特徴とする請求項5記載の機械学習装置。The first neural network includes a convolution layer for performing convolution of the feature amount of the learning image,
6. The machine learning device according to claim 5, wherein the input feature value map of the convolution layer and the output feature value map of the convolution layer have the same size.
前記ニューラルネットワークから出力された登録画像の特徴量を記憶する特徴量記憶部と、
前記特徴量記憶部により記憶されている1つ以上の登録画像の特徴量と、前記ニューラルネットワークから出力された認識対象画像の特徴量とを比較して、前記1つ以上の登録画像の中から、前記認識対象画像と類似している登録画像を検索する画像検索部とを備え、
前記特徴量検出部が有しているニューラルネットワークのパラメータが機械学習装置によって更新されていることを特徴とする画像認識装置。A neural network that outputs a feature amount of the registered image when a registered image that is a learning target image is given, and outputs a feature amount of the recognition target image when a recognition target image that is a recognition target learning image is given A feature amount detection unit having
A feature amount storage unit for storing a feature amount of a registered image output from the neural network;
The feature quantity of the one or more registered images stored in the feature quantity storage unit is compared with the feature quantity of the recognition target image output from the neural network, and the feature quantity is stored in the one or more registered images. An image search unit for searching for a registered image similar to the recognition target image,
An image recognition device, wherein a parameter of a neural network included in the feature amount detection unit is updated by a machine learning device.
学習対象の画像である学習画像を二値画像に変換する二値画像変換部と、
前記学習画像を入力して、前記学習画像の特徴量を出力する第1のニューラルネットワークを有する特徴量抽出部と、
前記第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された特徴量を入力して、前記学習画像を二値画像として再構築した画像である再構築画像を出力する第2のニューラルネットワークを有する画像再構築部と、
前記第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築画像と、前記二値画像変換部により変換された二値画像との差分に従って前記第1のニューラルネットワークのパラメータ及び前記第2のニューラルネットワークのパラメータのそれぞれを更新するパラメータ更新部とを備えており、
前記特徴量検出部が有しているニューラルネットワークは、前記パラメータ更新部によりパラメータが更新された前記第1及び第2のニューラルネットワークであることを特徴とする請求項9記載の画像認識装置。The machine learning device includes:
A binary image conversion unit that converts a learning image, which is an image to be learned, into a binary image;
A feature quantity extraction unit having a first neural network that inputs the learning image and outputs the feature quantity of the learning image;
An image reconstruction unit having a second neural network that inputs a feature amount output from the first neural network and outputs a reconstructed image that is an image reconstructed from the learning image as a binary image;
According to the difference between the reconstructed image output from the second neural network and the binary image converted by the binary image converter, the parameters of the first neural network and the parameters of the second neural network And a parameter update unit for updating each,
10. The image recognition apparatus according to claim 9, wherein the neural network included in the feature amount detection unit is the first and second neural networks whose parameters are updated by the parameter update unit.
前記登録画像を入力して、前記登録画像の特徴量を出力するとともに、前記認識対象画像を入力して、前記認識対象画像の特徴量を出力するニューラルネットワークとして、前記パラメータ更新部によりパラメータが更新された前記第1のニューラルネットワークを有する第1の特徴量検出部と、
前記第1の特徴量検出部が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された登録画像の特徴量を入力して、前記登録画像を再構築した画像である再構築登録画像を出力するとともに、前記第1の特徴量検出部が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された認識対象画像の特徴量を入力して、前記認識対象画像を再構築した画像である再構築認識画像を出力するニューラルネットワークとして、前記パラメータ更新部によりパラメータが更新された前記第2のニューラルネットワークを有する画像再生成部と、
前記画像再生成部が有している第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築登録画像を入力して、前記再構築登録画像の特徴量を出力するとともに、前記画像再生成部が有している第2のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築認識画像を入力して、前記再構築認識画像の特徴量を出力するニューラルネットワークとして、前記パラメータ更新部によりパラメータが更新された前記第1のニューラルネットワークを有する第2の特徴量検出部とを備えており、
前記特徴量記憶部は、前記特徴量検出部が有しているニューラルネットワークから出力された登録画像の特徴量として、前記第1の特徴量検出部が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された登録画像の特徴量及び前記第2の特徴量検出部が有している第1のニューラルネットワークから出力された再構築登録画像の特徴量のそれぞれを記憶することを特徴とする請求項10記載の画像認識装置。The feature amount detection unit includes:
The parameter update unit updates the parameters as a neural network that inputs the registered image and outputs the feature amount of the registered image, and inputs the recognition target image and outputs the feature amount of the recognition target image. A first feature amount detection unit having the first neural network,
The feature amount of the registered image output from the first neural network included in the first feature amount detection unit is input, and a reconstructed registered image that is an image obtained by reconstructing the registered image is output. A reconstructed recognition image that is an image obtained by reconstructing the recognition target image by inputting the feature amount of the recognition target image output from the first neural network included in the first feature amount detection unit. As an output neural network, an image regeneration unit having the second neural network whose parameters are updated by the parameter update unit;
The reconstructed registered image output from the second neural network included in the image regenerating unit is input, the feature amount of the reconstructed registered image is output, and the image regenerating unit includes The first neural network whose parameters are updated by the parameter update unit as a neural network that inputs the reconstructed recognition image output from the second neural network and outputs the feature quantity of the reconstructed recognition image And a second feature amount detection unit having
The feature quantity storage unit outputs from the first neural network included in the first feature quantity detection unit as a feature quantity of a registered image output from the neural network included in the feature quantity detection unit. 11. The stored registered image feature amount and the feature amount of the reconstructed registered image output from the first neural network included in the second feature amount detection unit are stored. The image recognition apparatus described.
前記画像検索部は、前記特徴量記憶部により記憶されている複数の同種登録画像と、前記ニューラルネットワークから出力された認識対象画像の特徴量との類似度をそれぞれ算出し、前記複数の同種登録画像を1つの登録画像とみなし、前記1つの登録画像の特徴量と前記認識対象画像の特徴量との類似度として、それぞれ算出した類似度の平均値を算出することを特徴とする請求項13記載の画像認識装置。In the feature amount storage unit, a plurality of same-type registered images that are registered images of the same type are stored,
The image search unit calculates the similarity between the plurality of same type registration images stored in the feature amount storage unit and the feature amount of the recognition target image output from the neural network, and the plurality of same type registrations. The image is regarded as one registered image, and an average value of the calculated similarities is calculated as the similarity between the feature amount of the one registered image and the feature amount of the recognition target image. The image recognition apparatus described.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017554102AJP6320649B1 (en) | 2017-03-31 | 2017-03-31 | Machine learning device and image recognition device |
| PCT/JP2017/013603WO2018179338A1 (en) | 2017-03-31 | 2017-03-31 | Machine learning device and image recognition device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/013603WO2018179338A1 (en) | 2017-03-31 | 2017-03-31 | Machine learning device and image recognition device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2018179338A1true WO2018179338A1 (en) | 2018-10-04 |
Family
ID=62105884
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/013603CeasedWO2018179338A1 (en) | 2017-03-31 | 2017-03-31 | Machine learning device and image recognition device |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6320649B1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2018179338A1 (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2020194864A1 (en)* | 2019-03-25 | 2020-10-01 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Feature specifying device, feature specifying method, and feature specifying program |
| CN112541876A (en)* | 2020-12-15 | 2021-03-23 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Satellite image processing method, network training method, related device and electronic equipment |
| WO2021131248A1 (en)* | 2019-12-24 | 2021-07-01 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Object search device and object search method |
| JP7585431B2 (en) | 2018-11-13 | 2024-11-18 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | Image search system and image search method |
| JP7611315B1 (en) | 2023-08-04 | 2025-01-09 | 三菱重工機械システム株式会社 | Learning image generation method, learning image generation device, learning image generation program, and learning model generation method |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019211912A (en)* | 2018-06-01 | 2019-12-12 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Learning device, search device, method, and program |
| WO2020129231A1 (en)* | 2018-12-21 | 2020-06-25 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Sound source direction estimation device, sound source direction estimation method and sound source direction estimation program |
| JP7269778B2 (en)* | 2019-04-04 | 2023-05-09 | 富士フイルムヘルスケア株式会社 | Ultrasonic imaging device and image processing device |
| JP7368995B2 (en)* | 2019-09-30 | 2023-10-25 | セコム株式会社 | Image recognition system, imaging device, recognition device, and image recognition method |
| JP7363929B2 (en)* | 2020-01-29 | 2023-10-18 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Learning device, search device, learning method, search method and program |
| CN113470831B (en)* | 2021-09-03 | 2021-11-16 | 武汉泰乐奇信息科技有限公司 | Big data conversion method and device based on data degeneracy |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005092465A (en)* | 2003-09-16 | 2005-04-07 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | Data recognition device |
| US20150238148A1 (en)* | 2013-10-17 | 2015-08-27 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Method and system for anatomical object detection using marginal space deep neural networks |
| JP2016004549A (en)* | 2014-06-19 | 2016-01-12 | ヤフー株式会社 | Specific apparatus, specific method, and specific program |
| US20170076438A1 (en)* | 2015-08-31 | 2017-03-16 | Cape Analytics, Inc. | Systems and methods for analyzing remote sensing imagery |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11212990A (en)* | 1998-01-26 | 1999-08-06 | Toray Ind Inc | Image retrieving device, image retrieving display method and production of product |
- 2017
- 2017-03-31WOPCT/JP2017/013603patent/WO2018179338A1/ennot_activeCeased
- 2017-03-31JPJP2017554102Apatent/JP6320649B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005092465A (en)* | 2003-09-16 | 2005-04-07 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | Data recognition device |
| US20150238148A1 (en)* | 2013-10-17 | 2015-08-27 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Method and system for anatomical object detection using marginal space deep neural networks |
| JP2016004549A (en)* | 2014-06-19 | 2016-01-12 | ヤフー株式会社 | Specific apparatus, specific method, and specific program |
| US20170076438A1 (en)* | 2015-08-31 | 2017-03-16 | Cape Analytics, Inc. | Systems and methods for analyzing remote sensing imagery |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| HITOSHI IBA, NEURO-EVOLUTION AND DEEP LEARNING, 20 October 2015 (2015-10-20), pages 57 - 60 , 81-111, ISBN: 978-4-274-21802-6* |
| NAOKI KUBO ET AL.: "Query-by-sketch image retrieval using pseudo-autoencoder", THE INSTITUTE OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERS OF JAPAI KENKYUKAI SHIRYO, 28 March 2016 (2016-03-28), pages 101 - 106* |
| TOMONORI SHINDO: "Deep Learning wa Banno ka Dai 3 Bu: Task Betsu Hen", NIKKEI ELECTRONICS, vol. 1156, 20 May 2015 (2015-05-20), pages 44 - 52, ISSN: 0385-1680* |
Cited By (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US12174882B2 (en) | 2018-11-13 | 2024-12-24 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Image retrieval system and image retrieval method |
| JP7585431B2 (en) | 2018-11-13 | 2024-11-18 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | Image search system and image search method |
| JP7357454B2 (en) | 2019-03-25 | 2023-10-06 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Feature identification device, feature identification method, and feature identification program |
| JP2020160582A (en)* | 2019-03-25 | 2020-10-01 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Feature specification device, feature specification method, and feature specification program |
| CN113661515B (en)* | 2019-03-25 | 2025-02-28 | 三菱电机株式会社 | Feature determination device, feature determination method, and computer-readable storage medium |
| WO2020194864A1 (en)* | 2019-03-25 | 2020-10-01 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Feature specifying device, feature specifying method, and feature specifying program |
| CN113661515A (en)* | 2019-03-25 | 2021-11-16 | 三菱电机株式会社 | Feature determination device, feature determination method, and feature determination program |
| JP2021101274A (en)* | 2019-12-24 | 2021-07-08 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Object search device and object search method |
| US12125284B2 (en) | 2019-12-24 | 2024-10-22 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Object search device and object search method |
| JP7196058B2 (en) | 2019-12-24 | 2022-12-26 | 株式会社日立製作所 | OBJECT SEARCH DEVICE AND OBJECT SEARCH METHOD |
| WO2021131248A1 (en)* | 2019-12-24 | 2021-07-01 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Object search device and object search method |
| CN112541876B (en)* | 2020-12-15 | 2023-08-04 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Satellite image processing method, network training method, related device and electronic equipment |
| CN112541876A (en)* | 2020-12-15 | 2021-03-23 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Satellite image processing method, network training method, related device and electronic equipment |
| JP7611315B1 (en) | 2023-08-04 | 2025-01-09 | 三菱重工機械システム株式会社 | Learning image generation method, learning image generation device, learning image generation program, and learning model generation method |
| WO2025032990A1 (en)* | 2023-08-04 | 2025-02-13 | 三菱重工機械システム株式会社 | Learning image generation method, learning image generation device, learning image generation program, and learning model generation method |
| JP2025023616A (en)* | 2023-08-04 | 2025-02-17 | 三菱重工機械システム株式会社 | Learning image generation method, learning image generation device, learning image generation program, and learning model generation method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2018179338A1 (en) | 2019-04-04 |
| JP6320649B1 (en) | 2018-05-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6320649B1 (en) | Machine learning device and image recognition device | |
| JP5602940B2 (en) | Daisy descriptor generation from precomputed scale space | |
| KR101183391B1 (en) | Image comparison by metric embeddings | |
| CN116664892B (en) | Multi-temporal remote sensing image registration method based on cross-attention and deformable convolution | |
| CN108961180B (en) | Infrared image enhancement method and system | |
| JP5261501B2 (en) | Permanent visual scene and object recognition | |
| CN111179173B (en) | Image splicing method based on discrete wavelet transform and gradient fusion algorithm | |
| CN105335952B (en) | Matching power flow computational methods and device and parallax value calculating method and equipment | |
| JP5289412B2 (en) | Local feature amount calculation apparatus and method, and corresponding point search apparatus and method | |
| CN109919971B (en) | Image processing method, apparatus, electronic device, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| EP2293243A2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image capture apparatus, image processing method, and program | |
| CN114299358B (en) | Image quality assessment method, device, electronic device and machine-readable storage medium | |
| CN111091567A (en) | Medical image registration method, medical device and storage medium | |
| JP6426441B2 (en) | Density measuring device, density measuring method, and program | |
| GB2587248A (en) | Analysing objects in a set of frames | |
| US20190279022A1 (en) | Object recognition method and device thereof | |
| JP2023145404A (en) | System and method for using pyramid and uniqueness matching priors to identify correspondences between images | |
| CN114612352A (en) | Multi-focus image fusion method, storage medium and computer | |
| CN111353325B (en) | Key point detection model training method and device | |
| CN108830863A (en) | Left ventricle dividing method, system and the computer readable storage medium of medical imaging | |
| CN117952901B (en) | Multi-source heterogeneous image change detection method and device based on generative adversarial network | |
| CN113205467A (en) | Image processing method and device based on fuzzy detection | |
| CN112862732A (en) | Multi-resolution image fusion method, device, equipment, medium and product | |
| CN117934568A (en) | Cross-modal image registration method based on multi-scale local salient principal direction features | |
| CN106557772B (en) | Method and device for extracting local feature and image processing method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase | Ref document number:2017554102 Country of ref document:JP Kind code of ref document:A | |
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | Ref document number:17903758 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 | |
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase | Ref country code:DE | |
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase | Ref document number:17903758 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 |