WO2018076503A1 - Positioning system and medical positioning system for diagnosing of target object in body - Google Patents
Positioning system and medical positioning system for diagnosing of target object in bodyDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2018076503A1 WO2018076503A1PCT/CN2016/110725CN2016110725WWO2018076503A1WO 2018076503 A1WO2018076503 A1WO 2018076503A1CN 2016110725 WCN2016110725 WCN 2016110725WWO 2018076503 A1WO2018076503 A1WO 2018076503A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- virtual
- sight
- coordinate
- target object
- image
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/10—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges for stereotaxic surgery, e.g. frame-based stereotaxis
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/10—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges for stereotaxic surgery, e.g. frame-based stereotaxis
- A61B90/11—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges for stereotaxic surgery, e.g. frame-based stereotaxis with guides for needles or instruments, e.g. arcuate slides or ball joints
- A61B90/13—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges for stereotaxic surgery, e.g. frame-based stereotaxis with guides for needles or instruments, e.g. arcuate slides or ball joints guided by light, e.g. laser pointers
Definitions
- Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgeryis a minimally invasive surgical technique that combines television technology with endoscopic techniques.
- the intrathoracic structureis observed through a small incision using a miniature imaging device and a special surgical instrument, and some living diseases such as pleural diseases, spontaneous pneumothorax and bullae, lung tumors, mediastinal diseases, and esophageal diseases are performed.
- Tissue examination and treatmentAs a medical examination tool, the endoscope has the characteristics of small wound surface, simple operation, and true display image. It has been used in many medical fields.
- an endoscopeWhen using an endoscope, it is necessary to extend the endoscope from the mouth or nasal cavity into the human body, and with the assistance of the endoscope navigation system, enter different human organs.
- the doctorobserves the organ to be displayed based on the image taken by the endoscope, thereby realizing functions such as organ lesions that X-rays cannot display. For example, it is possible to observe ulcers in the stomach and develop an optimal treatment plan accordingly.
- the endoscopewhen the endoscope is used to find and determine the position of the lesion, when the operation is performed, only the image of the lesion position can be obtained, and the position of the lesion is analyzed as the position of the user, and the position of the lesion is determined according to the inference.
- Surgerythe position of the operation in the process is determined by the user based on the image of the location of the lesion, the skill of the physician is high, and the surgeon cannot accurately determine the surgical position.
- an embodiment of the present inventionprovides a positioning system and a medical positioning system for locating a target object in a body to accurately position the target object in the body of the diagnostic body in vitro.
- the embodiment of the present inventionprovides the following technical solutions:
- a diagnostic target object location systemincludes:
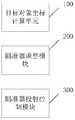
- a target object coordinate calculation unitconfigured to calculate coordinate information of the target object after the endoscopic device reaches the target position of the diagnostic body
- a sight adjustment moduleadjusting an aiming direction of the sight located outside the diagnostic body according to the coordinate information of the target object, such that the aiming direction of the sight passes through the target object;
- a sight projection control moduleis configured to control the sight to perform beam projection on the diagnostic body.
- the sight adjustment modulecomprises:
- a coordinate calculation unitconfigured to calculate a real coordinate of the endoscopic device of the endoscopic device in the electromagnetic navigation system; and obtain an endoscope of the endoscopic device in the virtual three-dimensional model according to a transformation matrix between the electromagnetic navigation system and the virtual three-dimensional model Virtual coordinate of the device; calculating the virtual coordinate of the object in the virtual three-dimensional model according to the virtual coordinate of the endoscopic device and the direction information of the endoscopic device; calculating the true coordinate and the true aiming direction of the sight of the sight in the electromagnetic navigation system; Obtaining a virtual coordinate of the sight and a virtual aiming direction of the sight in the virtual three-dimensional model according to a transformation matrix between the electromagnetic navigation system and the virtual three-dimensional model, wherein the virtual three-dimensional model is a virtual three-dimensional model of the diagnostic body;
- An aiming direction adjusting unitis configured to adjust an aiming direction of the sight such that a virtual aiming direction in the virtual three-dimensional model passes through the object virtual coordinates.
- the aiming direction adjusting unitis specifically configured to:
- the methodfurther includes:
- An annotation unitconfigured to acquire a virtual image in a virtual aiming direction of the sight in the virtual three-dimensional model, recorded as a virtual location image, and fuse the virtual location image with a real image collected by the endoscopic device, where Marking the position of the virtual target in the virtual target image in the real image;
- the virtual imageis: centered on a central axis of the virtual aiming direction, preset A virtual image within a radius range, and a target corresponding to a center position of the virtual image is a virtual target.
- the methodfurther includes:
- An image analyzing unitconfigured to acquire the virtual location image and the real image, calculate a similarity between the virtual location image and the real image, determine whether the similarity is greater than a preset value, and if not, to the virtual three-dimensional model and The coordinate transformation matrix between the electromagnetic navigation systems is adjusted until the similarity between the virtual position image and the real image is made larger than a preset value.
- the image analysis unitcomprises:
- a similarity calculation unitconfigured to acquire the virtual location image and the real image, calculate a similarity between the virtual location image and the real image, determine whether the similarity is greater than a preset value, and if not, adjust to the coordinate system
- the unitoutputs a trigger signal
- a coordinate system adjustment unitconfigured to: acquire real coordinates of the endoscopic device, virtual coordinates of the endoscopic device, a real observation direction of the endoscopic device in the electromagnetic navigation system, and a virtual observation direction of the endoscopic device in the virtual three-dimensional model; The difference between the real coordinate position and the virtual coordinate is recorded as a coordinate difference value; the difference between the real direction and the virtual direction is recorded as a direction difference value; and the adjustment is performed according to the coordinate difference value and the direction difference value
- the methodfurther includes:
- the direction matching failure submoduleis configured to output a first preset prompt signal when an angle difference between the virtual aiming direction of the sight and the aiming line is outside the allowable range.
- the image analyzing unitis further configured to:
- the second preset prompt signalis output.
- the permission rangeis not more than 10°.
- the preset valueis 0.5.
- a medical positioning systemcomprising: a computer using the diagnostic target object positioning system disclosed in any one of the above, an endoscope device, a sight, an electromagnetic navigation system, a CT device, a display and a computer connected to the computer;
- the CT deviceis configured to scan a diagnostic body to obtain a virtual three-dimensional model of the diagnostic body
- the displayis configured to display image information collected by the endoscopic device.
- the electromagnetic navigation systemcomprises at least: a tiled magnetic field generator, and a magnetic field generating host connected to the magnetic field generator;
- the magnetic field generatoris configured to generate a magnetic field signal under the control of a magnetic field generator host, and the inner endoscope and the sight built in the sight are sensed to calculate that the endoscopic device and the sight are built in the electromagnetic navigation system Location information and aiming direction information.
- the medical positioning systemis a TV-assisted thoracoscopic surgery system or a needle biopsy system.
- the coordinate information of the target objectmay be determined by using the position information of the endoscopic device, and the external scope sight is aimed
- the position of the target body on the target pathis recorded as a calibration position. It can be seen that the calibration position can be automatically positioned by the device, the skill requirement of the staff is low, and the positioning process is fast and accurate.
- FIG. 1is a schematic structural diagram of a system for locating a target object positioning system in a body according to an embodiment of the present application
- FIG. 2is a schematic structural diagram of a system of the sight adjustment module disclosed in the embodiment of the present application.
- FIG. 3is a schematic structural diagram of a system for locating a target object positioning system in a body according to another embodiment of the present application.
- FIG. 4is a schematic structural diagram of a system for locating a target object positioning system in a body according to another embodiment of the present disclosure
- FIG. 5is a schematic structural diagram of a medical positioning system disclosed in an embodiment of the present application.
- the present applicationdiscloses a system for locating a target object in a system for locating a target object by using an endoscopic device.
- the disclosed in vivo target object location systemmay include:
- the target object coordinate calculation unit 100is configured to calculate coordinate information of the target object after the endoscopic device reaches the target position of the diagnostic body (the location where the target object is located);
- the endoscopic devicemay be an endoscopic device, such as a bronchial endoscope, a gastrointestinal endoscope, etc., and the user may control the movement path of the endoscopic device in the diagnostic body in combination with other auxiliary systems, ultimately causing the inner
- the deviceis located at a position where the target object is located, and the coordinate position information of the endoscopic device is located through the positioning system;
- the sight adjustment module 200adjusts an aiming direction of the sight located outside the diagnostic body according to the coordinate information of the target object, so that the aiming direction of the sight passes through the target object;
- the calibration positionis the position to be operated on (for example, the operation position).
- the usercan adjust the position of the sight to adjust the calibration position of the body chart, and finally Select a reasonable location among the multiple calibration locations;
- the sight projection control module 300is configured to control the sight to perform beam projection on the diagnostic body to determine a calibration position outside the diagnosis.
- the coordinate information of the target objectmay be determined by the position information of the endoscopic device, and the external scope sight is aimed at the target.
- the position of the diagnostic body surface on the aiming pathis recorded as the calibration position. It can be seen that the calibration position can be automatically positioned by the device, the skill requirement of the staff is low, and the positioning process is fast and accurate.
- the real coordinates of each device in the foregoing solution of the present applicationmay be determined by an electromagnetic navigation system, where the real coordinates are coordinates of each device in the electromagnetic navigation system, wherein the electromagnetic navigation
- the systemincludes at least: a magnetic field generator, a magnetic field generating host coupled to the magnetic field generator, the magnetic field generator being tiled on a horizontal surface, the diagnostic body being placed on a magnetic field generator, the magnetic field generator being in a magnetic field generator host A magnetic field signal is generated under control, and coordinate information of the sight, endoscopic device, etc. is located by the magnetic field signal.
- a virtual three-dimensional model of the diagnostic bodyis also established in advance, and the electromagnetic navigation system is combined with the virtual three-dimensional model to locate the endoscopic device obtained by the electromagnetic navigation system.
- the coordinate informationmaps the coordinates of the endoscopic device into the virtual three-dimensional model through the coordinate transformation matrix to calibrate the position information of the endoscopic device in the diagnostic body in the virtual three-dimensional model.
- the sight adjusting module 200may include:
- the coordinate calculation unit 210is configured to calculate the real coordinates of the endoscopic device of the endoscopic device in the electromagnetic navigation system; and calculate the real coordinate of the object of the target object in the electromagnetic navigation system according to the real coordinates of the endoscopic device and the aiming direction of the endoscopic device; Calculating the true coordinate and true aiming direction of the sight of the sight in the electromagnetic navigation system;
- each of the endoscopic device and the sightis configured with a navigation sensor
- the electromagnetic navigation systemis configured to sense the a navigation sensor built in the endoscopic device and the sight, sensing coordinate position information of the endoscopic device and the sight in the electromagnetic navigation system, and aiming direction information of the endoscopic device and the sight, through the electromagnetic navigation system and A coordinate transformation matrix between the virtual three-dimensional models, which can map the position information and the aiming direction of the endoscopic device and the sight to the In a virtual three-dimensional model;
- the aiming direction adjusting unit 220is configured to adjust an aiming direction of the sight, such that an aiming direction of the sight passes through the object virtual coordinates in the electromagnetic navigation system.
- the systemcan also use the virtual three-dimensional model to present the current aiming situation to the user, that is, the coordinate calculating unit 210 is specifically configured to combine the electromagnetic navigation system and the virtual three-dimensional model.
- Describe the real coordinates of the target object in the electromagnetic navigation systemand then Obtaining the virtual coordinates of the target object in the virtual three-dimensional model according to the transformation matrix between the electromagnetic navigation system and the virtual three-dimensional model; calculating the true coordinate and the true aiming direction of the sight of the sight in the electromagnetic navigation system; Converting matrix between the system and the virtual three-dimensional model converts the real coordinate and the real aiming direction of the sight to obtain a virtual coordinate of the sight and a virtual aiming direction of the sight in the virtual three-dimensional model;
- the aiming direction adjusting unit 220is specifically configured to adjust an aiming direction of the sight such that a virtual aiming direction in the virtual three-dimensional model passes through the object virtual coordinates.
- the aiming direction adjusting unit 220is configured to determine, according to the sight virtual coordinate and the virtual aiming direction of the sight in the virtual three-dimensional model, whether the sight of the sight is aimed at the virtual coordinate of the object, and if not, The aiming direction and/or coordinate position of the sight is adjusted such that the virtual coordinates of the object in the virtual three-dimensional model are located in the virtual aiming direction of the sight.
- the aiming direction adjusting unit 220adjusts the aiming direction of the sight to make the aiming direction of the sight pass through the target object, and adjust the aiming direction of the sight.
- the aiming directionis adjusted.
- the aiming direction adjusting unit 220is specifically configured to: use the sight in the electromagnetic navigation system.
- the true coordinate of the sight and the real coordinate of the objectare taken as a straight line, and the aiming direction of the sight in the electromagnetic navigation system is acquired and adjusted to be consistent with the direction of the aiming line.
- the aiming direction adjusting unit 220is specifically configured to: use a straight line passing through the virtual coordinate of the sight and the virtual coordinate of the object as an aiming line; Whether the angular difference between the virtual aiming direction of the sight and the aiming line is within a permitted range, and if not, adjusting the true aiming direction of the sight until the virtual aiming direction of the sight is made The angle difference of the aiming line is within the permissible range.
- the endoscopic devicein order to facilitate the user to observe the real image collected by the endoscopic device, the endoscopic device can accurately collect the real image of the target object in the specific implementation process.
- the image information collected by the endoscopic deviceneeds to be displayed in real time through the display device, in order to further display to the user the in-vivo position of the diagnostic body currently aimed by the sight,
- the systemcan also include:
- An annotation unitconfigured to acquire a virtual image in a virtual aiming direction of the sight in the virtual three-dimensional model, recorded as a virtual location image, and when acquiring the virtual location image, the image information collected by the endoscopic device and Performing image matching on the virtual three-dimensional model, and marking, in the virtual three-dimensional model, area information of the image currently acquired by the endoscopic device in the virtual three-dimensional model, that is, a virtual shooting area, when the sight is aimed After the target object, the aiming direction of the sight necessarily passes through the virtual shooting area, and the virtual shooting area facing the aiming direction of the sight is recorded as a virtual position image, and in the display device, The virtual position image is merged with the real image collected by the endoscopic device, and the position of the virtual target in the virtual target image is marked in the real image, and displayed by the display device, thereby enabling the user to make a quicker determination The aiming object of the sight;
- the virtual imageis: a virtual shooting area within a predetermined radius within a center axis of the virtual aiming direction, and a target corresponding to a center position of the virtual shooting area is a virtual three-dimensional model The virtual target corresponding to the target object.
- the electromagnetic navigation system and the virtual threeThe transformation matrix between the dimensional models is the transformation matrix calculated by the user based on experience. In actual use, there must be certain errors. For this, in the above system work process, the obtained virtual position image and real image are also needed. Compare and judge the similarity between the two. If the similarity between the two is higher than the preset value, it indicates that the two images correspond to the same target object. At this time, the transformation matrix can accurately realize the electromagnetic navigation system and virtual Coordinate transformation between 3D models.
- the methodfurther includes:
- the image analyzing unit 400is configured to acquire the virtual location image and the real image, calculate a similarity between the virtual location image and the real image, determine whether the similarity is greater than a preset value, and if not, the virtual three-dimensional model The coordinate transformation matrix between the electromagnetic navigation system and the electromagnetic navigation system is adjusted until the similarity between the virtual position image and the real image is greater than a preset value.
- the image analyzing unit 400may include a similarity calculating unit 410 and a coordinate system adjusting unit 420:
- the similarity calculation unit 410is configured to acquire the virtual location image and the real image, calculate a similarity between the virtual location image and the real image, determine whether the similarity is greater than a preset value, and if not, to the coordinate system
- the adjustment unitoutputs a trigger signal
- the coordinate system adjusting unit 420is configured to: after acquiring the trigger signal, acquire real coordinates of the endoscopic device, virtual coordinates of the endoscopic device, real viewing direction of the endoscopic device in the electromagnetic navigation system, and the endoscopic device in the virtual three-dimensional model a virtual observation direction; the difference between the real coordinate position and the virtual coordinate is recorded as a coordinate difference; the difference between the real direction and the virtual direction is recorded as a difference value; a direction difference value, adjusting a coordinate transformation matrix between the virtual three-dimensional model and the electromagnetic navigation system such that a difference between the coordinate difference between the real coordinate position and the virtual coordinate, the true direction, and the virtual direction Within the scope of the license.
- a manual adjustment modemay be adopted, and of course, an automatic aiming mode may also be adopted, wherein the sight is intuitively judged for the convenience of the user.
- the aiming direction of the aiming lineis consistent with the aiming line.
- the direction matching failure sub-modulemay be further included, when the virtual aiming direction of the sight and the aiming line are When the angle difference is outside the permitted range, the first preset prompt signal for characterizing the direction mismatch is output to prompt the user that the aiming direction of the sight needs to be further adjusted.
- the size of the allowable range of the angular difference between the virtual aiming direction and the aiming linemay be determined according to the user's requirement for accuracy, if the user is precise to aiming
- the permission requirementis relatively high, and the permission range may be set to be appropriately small.
- the permission rangeis [0°, 10°], that is, as long as the two If the angle difference is not more than 10°, the virtual aiming direction of the sight can be considered to coincide with the direction of the aiming line.
- the image analysis unitis further configured to: when it is determined that the similarity between the virtual location image and the real image is less than a preset value, outputting to prompt the user or the system A second preset prompt signal for continuing adjustment of the coordinate transformation matrix between the electromagnetic navigation system and the virtual coordinate system is continued.
- the usercan set the size of the preset value for determining the similarity according to the requirement of the accuracy of the user.
- the preset valuemay be set to 0.5, that is, as long as the similarity between the two is considered to be greater than 0.5, the two images are considered to be identical.
- a medical positioning systemincluding an endoscopic device X1, a sight X2, an electromagnetic navigation system X3, and a CT device is also disclosed.
- the medical positioning systemmay be a television assisted thoracoscopic surgery system or a needle biopsy system;
- the CT deviceis configured to scan a diagnostic body to obtain a virtual three-dimensional model of the diagnostic body.
- the endoscopic device and the sightare provided with a navigation sensor, and the electromagnetic navigation system is used to establish an electromagnetic navigation coordinate system.
- the electromagnetic navigation coordinate systemmay sense the navigation sensor in the endoscopic device and the sight to determine the position information of the endoscopic device, the sight, and the aiming direction, and the computer has any of the above-mentioned applications of the present application.
- the diagnostic in vivo target object positioning system disclosed in the embodimentthe computer is configured to acquire and display a virtual three-dimensional model acquired by the CT device, and determine the endoscopic device according to a conversion matrix between the electromagnetic navigation system and the virtual three-dimensional model
- the position information in the virtual three-dimensional model, the displayis used to display image information collected by the endoscopic device.
- the sightcan emit three laser beams, and the three laser beams are distributed in a triangle shape, and the center position of the triangle is the aiming position of the sight.
- the CT deviceis used to scan the diagnostic body to obtain a virtual three-dimensional model of the diagnostic body, and the virtual three-dimensional model is displayed by a computer.
- the computercontrols the built-in diagnostic in vivo target object positioning system action.
- the steps of a method or algorithm described in connection with the embodiments disclosed hereincan be implemented directly in hardware, a software module executed by a processor, or a combination of both.
- the software modulecan be placed in random access memory (RAM), memory, read only memory (ROM), electrically programmable ROM, electrically erasable programmable ROM, registers, hard disk, removable disk, CD-ROM, or technical field. Any other form of storage medium known.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Endoscopes (AREA)
- Apparatus For Radiation Diagnosis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese本申请要求于2016年10月28日提交中国专利局、申请号为201610971071.5、发明名称为“一种诊断体内目标对象定位系统和医疗定位系统”的国内申请的优先权,其全部内容通过引用结合在本申请中。This application claims the priority of the domestic application filed on October 28, 2016 by the Chinese Patent Office, application number 201610971071.5, and the invention titled "a diagnostic target target location system and medical positioning system", the entire contents of which are incorporated by reference. In this application.
电视辅助胸腔镜手术是由电视技术和内镜技术相结合而产生的微创外科技术。在手术过程中,利用微型摄像设备和特殊的手术器械,通过小切口观察胸内结构,进行一些胸膜疾病、自发性气胸和肺大疱、肺部肿瘤、纵膈疾病、食管疾病等疾病的活体组织检查和治疗。内窥镜作为一种医疗检查工具,具有创伤面小、操作简单、显示图像真实等特点,现已经在众多的医疗领域进行使用。Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that combines television technology with endoscopic techniques. During the operation, the intrathoracic structure is observed through a small incision using a miniature imaging device and a special surgical instrument, and some living diseases such as pleural diseases, spontaneous pneumothorax and bullae, lung tumors, mediastinal diseases, and esophageal diseases are performed. Tissue examination and treatment. As a medical examination tool, the endoscope has the characteristics of small wound surface, simple operation, and true display image. It has been used in many medical fields.
在使用内窥镜时,需要将内窥镜从口腔或鼻腔伸入人体,在内窥镜导航系统的协助下,进入不同的人体器官。医生根据内窥镜拍摄到的图像来观察需要显示的器官,进而实现X射线所不能显示的器官病变等功能。例如,可以观察胃内的溃疡情况,据此制定出最佳的治疗方案。When using an endoscope, it is necessary to extend the endoscope from the mouth or nasal cavity into the human body, and with the assistance of the endoscope navigation system, enter different human organs. The doctor observes the organ to be displayed based on the image taken by the endoscope, thereby realizing functions such as organ lesions that X-rays cannot display. For example, it is possible to observe ulcers in the stomach and develop an optimal treatment plan accordingly.
但是,传统技术方案中,当采用内窥镜找到并确定病灶位置后,在进行手术时,只能又得到的病灶位置的图像,分析病灶位置为用户的哪个位置,依据推断得到的病灶位置进行手术,在该过程中手术的位置由用户依据病灶位置的图像进行推断决定,对医师的技能要求较高,医师且无法精确的确定手术位置。However, in the conventional technical solution, when the endoscope is used to find and determine the position of the lesion, when the operation is performed, only the image of the lesion position can be obtained, and the position of the lesion is analyzed as the position of the user, and the position of the lesion is determined according to the inference. Surgery, the position of the operation in the process is determined by the user based on the image of the location of the lesion, the skill of the physician is high, and the surgeon cannot accurately determine the surgical position.
发明内容Summary of the invention
有鉴于此,本发明实施例提供一种对诊断体内目标对象定位的定位系统和医疗定位系统,以实现在诊断体的体外精确标定所述诊断体体内的目标对象的位置信息。In view of this, an embodiment of the present invention provides a positioning system and a medical positioning system for locating a target object in a body to accurately position the target object in the body of the diagnostic body in vitro.
为实现上述目的,本发明实施例提供如下技术方案:To achieve the above objective, the embodiment of the present invention provides the following technical solutions:
一种诊断体内目标对象定位系统,包括:A diagnostic target object location system includes:
目标对象坐标计算单元,用于当内窥设备达到诊断体的目标位置后,计算目标对象的坐标信息;a target object coordinate calculation unit, configured to calculate coordinate information of the target object after the endoscopic device reaches the target position of the diagnostic body;
瞄准器调整模块,依据所述目标对象的坐标信息调整位于诊断体外部的瞄准器的瞄准方向,使得所述瞄准器的瞄准方向穿过所述目标对象;a sight adjustment module, adjusting an aiming direction of the sight located outside the diagnostic body according to the coordinate information of the target object, such that the aiming direction of the sight passes through the target object;
瞄准器投射控制模块,用于控制所述瞄准器在所述诊断体上进行光束投射。A sight projection control module is configured to control the sight to perform beam projection on the diagnostic body.
优选的,上述诊断体内目标对象定位系统中,所述瞄准器调整模块,包括:Preferably, in the above-mentioned diagnostic target object positioning system, the sight adjustment module comprises:
坐标计算单元,用于计算内窥设备在电磁导航系统中的内窥设备真实坐标;依据电磁导航系统和虚拟三维模型之间的转换矩阵,得到所述内窥设备在虚拟三维模型中的内窥设备虚拟坐标;依据内窥设备虚拟坐标和内窥设备的方向信息,计算得到目标对象在虚拟三维模型中的对象虚拟坐标;计算瞄准器在电磁导航系统中的瞄准器真实坐标和真实瞄准方向;依据电磁导航系统和虚拟三维模型之间的转换矩阵,得到所述瞄准器在虚拟三维模型中的瞄准器虚拟坐标和虚拟瞄准方向,其中,所述虚拟三维模型为诊断体的虚拟三维模型;a coordinate calculation unit, configured to calculate a real coordinate of the endoscopic device of the endoscopic device in the electromagnetic navigation system; and obtain an endoscope of the endoscopic device in the virtual three-dimensional model according to a transformation matrix between the electromagnetic navigation system and the virtual three-dimensional model Virtual coordinate of the device; calculating the virtual coordinate of the object in the virtual three-dimensional model according to the virtual coordinate of the endoscopic device and the direction information of the endoscopic device; calculating the true coordinate and the true aiming direction of the sight of the sight in the electromagnetic navigation system; Obtaining a virtual coordinate of the sight and a virtual aiming direction of the sight in the virtual three-dimensional model according to a transformation matrix between the electromagnetic navigation system and the virtual three-dimensional model, wherein the virtual three-dimensional model is a virtual three-dimensional model of the diagnostic body;
瞄准方向调整单元,用于调整所述瞄准器的瞄准方向,使得所述虚拟三维模型中的虚拟瞄准方向穿过所述对象虚拟坐标。An aiming direction adjusting unit is configured to adjust an aiming direction of the sight such that a virtual aiming direction in the virtual three-dimensional model passes through the object virtual coordinates.
优选的,上述诊断体内目标对象定位系统中,瞄准方向调整单元,具体用于:Preferably, in the above-mentioned diagnostic target object positioning system, the aiming direction adjusting unit is specifically configured to:
将穿过所述瞄准器虚拟坐标和对象虚拟坐标的直线作为瞄准直线;判断所述瞄准器的虚拟瞄准方向与所述瞄准直线的角度差值是否在许可范围之内,如果否,调整所述瞄准器的真实瞄准方向,直至使得所述瞄准器的虚拟瞄准方向与所述瞄准直线的角度差值位于许可范围之内。Taking a straight line passing through the virtual coordinate of the sight and the virtual coordinate of the object as an aiming line; determining whether an angle difference between the virtual aiming direction of the sight and the aiming line is within a permitted range, and if not, adjusting the angle The true aiming direction of the sight until the angular difference between the virtual aiming direction of the sight and the aiming line is within the permissible range.
优选的,上述诊断体内目标对象定位系统中,还包括:Preferably, in the above-mentioned diagnostic target object positioning system, the method further includes:
标注单元,用于获取虚拟三维模型中所述瞄准器的虚拟瞄准方向上的虚拟图像,记为虚拟位置图像,将所述虚拟位置图像与内窥设备采集到的真实图像进行融合,在所述真实图像中标注所述虚拟目标图像中的虚拟目标的位置;An annotation unit, configured to acquire a virtual image in a virtual aiming direction of the sight in the virtual three-dimensional model, recorded as a virtual location image, and fuse the virtual location image with a real image collected by the endoscopic device, where Marking the position of the virtual target in the virtual target image in the real image;
其中,所述虚拟图像为:以所述虚拟瞄准方向的中心轴为圆心,预设半径范围之内的虚拟图像,所述虚拟图像的中心位置对应的目标即为虚拟目标。The virtual image is: centered on a central axis of the virtual aiming direction, presetA virtual image within a radius range, and a target corresponding to a center position of the virtual image is a virtual target.
优选的,上述诊断体内目标对象定位系统中,还包括:Preferably, in the above-mentioned diagnostic target object positioning system, the method further includes:
图像分析单元,用于获取所述虚拟位置图像和真实图像,计算所述虚拟位置图像和真实图像的相似度,判断所述相似度是否大于预设值,如果否,对所述虚拟三维模型和电磁导航系统之间的坐标转换矩阵进行调整,直至使得所述虚拟位置图像和真实图像的相似度大于预设值。An image analyzing unit, configured to acquire the virtual location image and the real image, calculate a similarity between the virtual location image and the real image, determine whether the similarity is greater than a preset value, and if not, to the virtual three-dimensional model and The coordinate transformation matrix between the electromagnetic navigation systems is adjusted until the similarity between the virtual position image and the real image is made larger than a preset value.
优选的,上述诊断体内目标对象定位系统中,图像分析单元,包括:Preferably, in the above-mentioned diagnostic target object positioning system, the image analysis unit comprises:
相似度计算单元,用于获取所述虚拟位置图像和真实图像,计算所述虚拟位置图像和真实图像的相似度,判断所述相似度是否大于预设值,如果否,向所述坐标系统调整单元输出触发信号;a similarity calculation unit, configured to acquire the virtual location image and the real image, calculate a similarity between the virtual location image and the real image, determine whether the similarity is greater than a preset value, and if not, adjust to the coordinate system The unit outputs a trigger signal;
坐标系统调整单元,用于:获取内窥设备真实坐标、内窥设备虚拟坐标、内窥设备在电磁导航系统内的真实观察方向、内窥设备在虚拟三维模型中的虚拟观察方向;将所述真实坐标位置与虚拟坐标之间的差值记为坐标差值;将所述真实方向和虚拟方向之间的差值记为方向差值;依据所述坐标差值和方向差值,调整所述虚拟三维模型和电磁导航系统之间的坐标转换矩阵。a coordinate system adjustment unit, configured to: acquire real coordinates of the endoscopic device, virtual coordinates of the endoscopic device, a real observation direction of the endoscopic device in the electromagnetic navigation system, and a virtual observation direction of the endoscopic device in the virtual three-dimensional model; The difference between the real coordinate position and the virtual coordinate is recorded as a coordinate difference value; the difference between the real direction and the virtual direction is recorded as a direction difference value; and the adjustment is performed according to the coordinate difference value and the direction difference value A coordinate transformation matrix between a virtual three-dimensional model and an electromagnetic navigation system.
优选的,上述诊断体内目标对象定位系统中,还包括:Preferably, in the above-mentioned diagnostic target object positioning system, the method further includes:
方向匹配失败子模块,用于当所述瞄准器的虚拟瞄准方向与所述瞄准直线的角度差值在许可范围之外时,输出第一预设提示信号。The direction matching failure submodule is configured to output a first preset prompt signal when an angle difference between the virtual aiming direction of the sight and the aiming line is outside the allowable range.
优选的,上述诊断体内目标对象定位系统中,所述图像分析单元,还用于:Preferably, in the above-mentioned diagnostic target object positioning system, the image analyzing unit is further configured to:
当前判断所述虚拟位置图像和真实图像的相似度小于预设值时,输出第二预设提示信号。When it is determined that the similarity between the virtual location image and the real image is less than a preset value, the second preset prompt signal is output.
优选的,上述诊断体内目标对象定位系统中,所述许可范围为不大于10°。Preferably, in the above-mentioned diagnostic target object positioning system, the permission range is not more than 10°.
优选的,上述诊断体内目标对象定位系统中,所述预设值为0.5。Preferably, in the above-mentioned diagnostic target object positioning system, the preset value is 0.5.
一种医疗定位系统,包括:应用有上述任意一项公开的诊断体内目标对象定位系统的计算机,与所述计算机相连的内窥设备、瞄准器、电磁导航系统、CT设备、显示器和计算机;A medical positioning system comprising: a computer using the diagnostic target object positioning system disclosed in any one of the above, an endoscope device, a sight, an electromagnetic navigation system, a CT device, a display and a computer connected to the computer;
其中,所述CT设备,用于对诊断体进行扫描得到诊断体的虚拟三维模型;The CT device is configured to scan a diagnostic body to obtain a virtual three-dimensional model of the diagnostic body;
所述显示器用于显示所述内窥设备采集到的图像信息。The display is configured to display image information collected by the endoscopic device.
优选的,上述医疗定位系统中,电磁导航系统至少包括:平铺的磁场发生器,与磁场发生器相连的磁场发生主机;Preferably, in the above medical positioning system, the electromagnetic navigation system comprises at least: a tiled magnetic field generator, and a magnetic field generating host connected to the magnetic field generator;
所述磁场发生器用于在磁场发生器主机的控制下产生磁场信号,通过感应所述内窥设备和瞄准器内置的导航传感器,计算得到所述内窥设备和瞄准器内置在所述电磁导航系统中的位置信息和瞄准方向信息。The magnetic field generator is configured to generate a magnetic field signal under the control of a magnetic field generator host, and the inner endoscope and the sight built in the sight are sensed to calculate that the endoscopic device and the sight are built in the electromagnetic navigation system Location information and aiming direction information.
优选的,上述医疗定位系统为电视辅助胸腔镜手术系统或穿刺活检系统。Preferably, the medical positioning system is a TV-assisted thoracoscopic surgery system or a needle biopsy system.
基于上述技术方案,本发明实施例提供的上述方案中,当内窥设备在诊断体内找到目标对象后,可通过所述内窥设备的位置信息确定目标对象的坐标信息,将体外的瞄准器瞄准所述目标对象的坐标后,该瞄准路径上位于诊断体体表的位置记为标定位置,可见,该标定位置可由设备自动定位完成,对工作人员的技能要求较低,且定位过程快速准确。Based on the foregoing technical solution, in the foregoing solution provided by the embodiment of the present invention, after the endoscopic device finds the target object in the diagnostic body, the coordinate information of the target object may be determined by using the position information of the endoscopic device, and the external scope sight is aimed After the coordinates of the target object, the position of the target body on the target path is recorded as a calibration position. It can be seen that the calibration position can be automatically positioned by the device, the skill requirement of the staff is low, and the positioning process is fast and accurate.
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例或现有技术中的技术方案,下面将对实施例或现有技术描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本发明的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the embodiments of the present invention or the technical solutions in the prior art, the drawings used in the embodiments or the description of the prior art will be briefly described below. Obviously, the drawings in the following description are only It is a certain embodiment of the present invention, and other drawings can be obtained from those skilled in the art without any creative work.
图1为本申请实施例公开的一种诊断体内目标对象定位系统的系统结构示意图;1 is a schematic structural diagram of a system for locating a target object positioning system in a body according to an embodiment of the present application;
图2为本申请实施例公开的一种所述瞄准器调整模块的系统结构示意图;2 is a schematic structural diagram of a system of the sight adjustment module disclosed in the embodiment of the present application;
图3为本申请另一实施例公开的一种诊断体内目标对象定位系统的系统结构示意图;3 is a schematic structural diagram of a system for locating a target object positioning system in a body according to another embodiment of the present application;
图4为本申请又一实施例公开的一种诊断体内目标对象定位系统的系统结构示意图;4 is a schematic structural diagram of a system for locating a target object positioning system in a body according to another embodiment of the present disclosure;
图5为本申请实施例公开的一种医疗定位系统的结构示意图。FIG. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of a medical positioning system disclosed in an embodiment of the present application.
下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例仅仅是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention are clearly and completely described in the following with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. It is obvious that the described embodiments are only a part of the embodiments of the present invention, but not all embodiments. All other embodiments obtained by those skilled in the art based on the embodiments of the present invention without creative efforts are within the scope of the present invention.
为了能够在诊断体表面精确定位目标对象的位置,本申请公开了一种诊断体内目标对象定位系统,该系统用于需要采用内窥设备定位目标对象的系统中,参见图1,本申请实施例公开的所述诊断体内目标对象定位系统,可以包括:In order to be able to accurately locate the position of the target object on the surface of the diagnostic body, the present application discloses a system for locating a target object in a system for locating a target object by using an endoscopic device. Referring to FIG. 1 , the embodiment of the present application The disclosed in vivo target object location system may include:
目标对象坐标计算单元100,用于当内窥设备达到诊断体的目标位置(目标对象所在的位置)后,计算目标对象的坐标信息;The target object
所述内窥设备可以为内窥镜设备,例如支气管内窥镜、肠胃内窥镜等,用户可以结合其他辅助系统控制所述内窥设备在所述诊断体内的运动路径,最终使得所述内窥设备达到目标对象所在的位置,通过定位系统,定位所述内窥设备的坐标位置信息;The endoscopic device may be an endoscopic device, such as a bronchial endoscope, a gastrointestinal endoscope, etc., and the user may control the movement path of the endoscopic device in the diagnostic body in combination with other auxiliary systems, ultimately causing the inner The device is located at a position where the target object is located, and the coordinate position information of the endoscopic device is located through the positioning system;
瞄准器调整模块200,依据所述目标对象的坐标信息调整位于诊断体外部的瞄准器的瞄准方向,使得所述瞄准器的瞄准方向穿过所述目标对象;The
当所述目标对象的坐标信息确定以后,只需要采用位于诊断体外的瞄准器瞄准所述目标对象,所述瞄准器正对的诊断体的体表位置作为目标对象在诊断体体外的标定位置,当诊断体为需要患者时,所述标定位置即为要进行手术的位置(例如开刀位置),当然,用户可以通过改变所述瞄准器的位置,调整位于诊断体体表的标定位置,最终由多个标定位置中选择一个合理的位置;After the coordinate information of the target object is determined, it is only necessary to aim the target object with a sight located outside the diagnostic body, and the body surface position of the diagnostic body facing the sight is used as the target position of the target object outside the diagnostic body. When the diagnostic body is a patient in need, the calibration position is the position to be operated on (for example, the operation position). Of course, the user can adjust the position of the sight to adjust the calibration position of the body chart, and finally Select a reasonable location among the multiple calibration locations;
瞄准器投射控制模块300,用于控制所述瞄准器在所述诊断体上进行光束投射,以在诊断体外确定标定位置。The sight
通过本申请上述实施例公开的技术方案可见,当内窥设备在诊断体内找到目标对象后,可通过所述内窥设备的位置信息确定目标对象的坐标信息,将体外的瞄准器瞄准所述目标对象的坐标后,该瞄准路径上位于诊断体体表的位置记为标定位置,可见,该标定位置可由设备自动定位完成,对工作人员的技能要求较低,且定位过程快速准确。According to the technical solution disclosed in the foregoing embodiment of the present application, after the endoscopic device finds the target object in the diagnostic body, the coordinate information of the target object may be determined by the position information of the endoscopic device, and the external scope sight is aimed at the target. After the coordinates of the object, the position of the diagnostic body surface on the aiming path is recorded as the calibration position. It can be seen that the calibration position can be automatically positioned by the device, the skill requirement of the staff is low, and the positioning process is fast and accurate.
在本申请实施例公开的技术方案中,可以通过电磁导航系统确定本申请上述方案中各个设备的真实坐标,所述真实坐标即为各个设备在电磁导航系统中的坐标,其中,所述电磁导航系统至少包括:磁场发生器,与磁场发生器相连的磁场发生主机,所述磁场发生器平铺在水平面上,所述诊断体放置于磁场发生器上,所述磁场发生器在磁场发生器主机的控制下产生磁场信号,通过所述磁场信号定位所述瞄准器、内窥设备等的坐标信息。In the technical solution disclosed in the embodiment of the present application, the real coordinates of each device in the foregoing solution of the present application may be determined by an electromagnetic navigation system, where the real coordinates are coordinates of each device in the electromagnetic navigation system, wherein the electromagnetic navigation The system includes at least: a magnetic field generator, a magnetic field generating host coupled to the magnetic field generator, the magnetic field generator being tiled on a horizontal surface, the diagnostic body being placed on a magnetic field generator, the magnetic field generator being in a magnetic field generator host A magnetic field signal is generated under control, and coordinate information of the sight, endoscopic device, etc. is located by the magnetic field signal.
在医疗设备中,为了方便确定目标对象的位置信息,还预先建立所述诊断体的虚拟三维模型,将所述电磁导航系统与虚拟三维模型相结合,将由电磁导航系统定位得到的内窥设备的坐标信息通过坐标转换矩阵,将内窥设备的坐标映射到虚拟三维模型中,以在虚拟三维模型中标定所述内窥设备在诊断体内的位置信息。In the medical device, in order to conveniently determine the position information of the target object, a virtual three-dimensional model of the diagnostic body is also established in advance, and the electromagnetic navigation system is combined with the virtual three-dimensional model to locate the endoscopic device obtained by the electromagnetic navigation system. The coordinate information maps the coordinates of the endoscopic device into the virtual three-dimensional model through the coordinate transformation matrix to calibrate the position information of the endoscopic device in the diagnostic body in the virtual three-dimensional model.
为了精确调整所述瞄准器的瞄准方向,在本申请上述实施例公开的技术方案中,参见图2,所述瞄准器调整模块200,可以包括:In order to accurately adjust the aiming direction of the sight, in the technical solution disclosed in the above embodiments of the present application, referring to FIG. 2, the
坐标计算单元210,用于计算内窥设备在电磁导航系统中的内窥设备真实坐标;依据内窥设备真实坐标和内窥设备的瞄准方向,计算得到目标对象在电磁导航系统中的对象真实坐标;计算瞄准器在电磁导航系统中的瞄准器真实坐标和真实瞄准方向;The coordinate
具体的,为了方便所述坐标计算单元210计算所述内窥设备和瞄准器的坐标信息,所述内窥设备和瞄准器内各配置有一导航传感器,所述电磁导航系统用于通过感应所述内窥设备和瞄准器内置的导航传感器,感应所述内窥设备和瞄准器在所述电磁导航系统中的坐标位置信息和所述内窥设备和瞄准器的瞄准方向信息,通过电磁导航系统和虚拟三维模型之间的坐标转换矩阵,可将所述内窥设备和瞄准器的位置信息和瞄准方向映射到所述虚拟三维模型中;Specifically, in order to facilitate the coordinate
瞄准方向调整单元220,用于调整所述瞄准器的瞄准方向,使得所述电磁导航系统中,所述瞄准器的瞄准方向穿过所述对象虚拟坐标。The aiming
当然,为了将瞄准情况更加直观的展示给用户,本系统还可以采用所述虚拟三维模型向用户展现当前瞄准情况,即,坐标计算单元210,具体用于将电磁导航系统和虚拟三维模型相结合,计算内窥设备在电磁导航系统中的内窥设备真实坐标和内窥设备的瞄准方向;依据电磁导航系统和虚拟三维模型之间的转换矩阵对所述内窥设备真实坐标和瞄准方向进行转换,得到所述内窥设备在虚拟三维模型中的内窥设备虚拟坐标和其在虚拟三维模型中的瞄准方向;依据内窥设备虚拟坐标和内窥设备在虚拟三维模型中的瞄准方向,计算得到所述诊断体内的目标对象在虚拟三维模型中的对象虚拟坐标(当然,在计算对象虚拟坐标时,也可以由内窥设备真实坐标和内窥设备在电磁导航系统中的瞄准方向,计算得到所述目标对象在电磁导航系统中的对象真实坐标,然后再依据电磁导航系统和虚拟三维模型之间的转换矩阵得到所述目标对象在虚拟三维模型中的对象虚拟坐标);计算瞄准器在电磁导航系统中的瞄准器真实坐标和真实瞄准方向;依据电磁导航系统和虚拟三维模型之间的转换矩阵对所述瞄准器真实坐标和真实瞄准方向进行转换,得到所述瞄准器在虚拟三维模型中的瞄准器虚拟坐标和虚拟瞄准方向;Of course, in order to display the aiming situation more intuitively to the user, the system can also use the virtual three-dimensional model to present the current aiming situation to the user, that is, the coordinate calculating
瞄准方向调整单元220,具体用于调整所述瞄准器的瞄准方向,使得所述虚拟三维模型中的虚拟瞄准方向穿过所述对象虚拟坐标。The aiming
具体的,所述瞄准方向调整单元220,用于依据所述瞄准器在虚拟三维模型中的瞄准器虚拟坐标和虚拟瞄准方向判断所述瞄准器的是否瞄准所述对象虚拟坐标,如果否,对所述瞄准器的瞄准方向和/或坐标位置进行调整,最终使得所述虚拟三维模型中的对象虚拟坐标位于所述瞄准器的虚拟瞄准方向上。Specifically, the aiming
在本申请上述实施例公开的技术方案中,通过所述瞄准方向调整单元220对瞄准器的瞄准方向进行调整,以使得所述瞄准器的瞄准方向穿过目标对象,在调整瞄准器的瞄准方向时,可采用闭环调整的方式对瞄准器的瞄准方向进行调整,具体的,当瞄准过程是基于目标对象在电磁导航系统中的对象真实坐标进行的时,所述瞄准方向调整单元220具体用于:将所述瞄准器在电磁导航系统中的瞄准器真实坐标和对象真实坐标作为瞄准直线,获取并调整所述瞄准器在电磁导航系统中的瞄准方向,使其与所述瞄准直线的方向相一致。当瞄准过程是基于目标对象在虚拟三维模型的对象虚拟坐标进行的时,所述瞄准方向调整单元220具体用于:将穿过所述瞄准器虚拟坐标和对象虚拟坐标的直线作为瞄准直线;判断所述瞄准器的虚拟瞄准方向与所述瞄准直线的角度差值是否在许可范围之内,如果否,调整所述瞄准器的真实瞄准方向,直至使得所述瞄准器的虚拟瞄准方向与所述瞄准直线的角度差值位于许可范围之内。In the technical solution disclosed in the above embodiment of the present application, the aiming
在本申请上述实施例公开的技术方案中,在具体实施过程中为了方便用户观察内窥设备采集到的真实图像,以使得所述内窥设备能够准确的采集到目标对象的真实图像,在本申请上述实施例公开的技术方案中还需通过显示设备实时显示所述内窥设备采集到的图像信息,为了更近一步的向用户展示所述瞄准器当前所瞄准的诊断体的体内位置,上述系统中还可以包括:In the technical solution disclosed in the foregoing embodiment of the present application, in order to facilitate the user to observe the real image collected by the endoscopic device, the endoscopic device can accurately collect the real image of the target object in the specific implementation process. In the technical solution disclosed in the above application, the image information collected by the endoscopic device needs to be displayed in real time through the display device, in order to further display to the user the in-vivo position of the diagnostic body currently aimed by the sight, The system can also include:
标注单元,用于获取虚拟三维模型中所述瞄准器的虚拟瞄准方向上的虚拟图像,记为虚拟位置图像,在获取所述虚拟位置图像时,将所述内窥设备采集到的图像信息与所述虚拟三维模型进行图像匹配,在所述虚拟三维模型中标出所述内窥设备当前采集到的图像在所述虚拟三维模型中的区域信息,即为虚拟拍摄区域,当所述瞄准器瞄准所述目标对象后,瞄准器的瞄准方向必然穿过所述虚拟拍摄区域,将所述瞄准器的瞄准方向上正对的虚拟拍摄区域记为虚拟位置图像,在所述显示设备中,将所述虚拟位置图像与内窥设备采集到的真实图像进行融合,在所述真实图像中标注所述虚拟目标图像中的虚拟目标的位置,并通过显示设备进行显示,从而能够使得用户更加快捷的判定所述瞄准器的瞄准对象;An annotation unit, configured to acquire a virtual image in a virtual aiming direction of the sight in the virtual three-dimensional model, recorded as a virtual location image, and when acquiring the virtual location image, the image information collected by the endoscopic device and Performing image matching on the virtual three-dimensional model, and marking, in the virtual three-dimensional model, area information of the image currently acquired by the endoscopic device in the virtual three-dimensional model, that is, a virtual shooting area, when the sight is aimed After the target object, the aiming direction of the sight necessarily passes through the virtual shooting area, and the virtual shooting area facing the aiming direction of the sight is recorded as a virtual position image, and in the display device, The virtual position image is merged with the real image collected by the endoscopic device, and the position of the virtual target in the virtual target image is marked in the real image, and displayed by the display device, thereby enabling the user to make a quicker determination The aiming object of the sight;
其中,所述虚拟图像为:以所述虚拟瞄准方向的中心轴为圆心,预设半径范围之内的虚拟拍摄区域,所述虚拟拍摄区域的中心位置对应的目标即为虚拟三维模型中与所述目标对象对应的虚拟目标。The virtual image is: a virtual shooting area within a predetermined radius within a center axis of the virtual aiming direction, and a target corresponding to a center position of the virtual shooting area is a virtual three-dimensional model The virtual target corresponding to the target object.
在本申请上述实施例公开的技术方案中,所述电磁导航系统和虚拟三维模型之间的转换矩阵为用户依据经验计算得到的转换矩阵,在实际使用时,其必然存在一定误差,针对于此,在上述系统工作过程中,还需要对得到的虚拟位置图像和真实图像进行对比,判断两者的相似度,如果两者的相似度高于预设值,则表明两个图像对应的时同一目标对象,此时,说明该转换矩阵能够精确地实现电磁导航系统与虚拟三维模型之间的坐标转换。In the technical solution disclosed in the above embodiment of the present application, the electromagnetic navigation system and the virtual threeThe transformation matrix between the dimensional models is the transformation matrix calculated by the user based on experience. In actual use, there must be certain errors. For this, in the above system work process, the obtained virtual position image and real image are also needed. Compare and judge the similarity between the two. If the similarity between the two is higher than the preset value, it indicates that the two images correspond to the same target object. At this time, the transformation matrix can accurately realize the electromagnetic navigation system and virtual Coordinate transformation between 3D models.
针对于此,在本申请上述实施例公开的技术方案中,还包括:In this regard, in the technical solution disclosed in the foregoing embodiment of the present application, the method further includes:
图像分析单元400,用于获取所述虚拟位置图像和真实图像,计算所述虚拟位置图像和真实图像的相似度,判断所述相似度是否大于预设值,如果否,对所述虚拟三维模型和电磁导航系统之间的坐标转换矩阵进行调整,直至使得所述虚拟位置图像和真实图像的相似度大于预设值。The
具体的,所述图像分析单元400,可以包括相似度计算单元410和坐标系统调整单元420:Specifically, the
相似度计算单元410,用于获取所述虚拟位置图像和真实图像,计算所述虚拟位置图像和真实图像的相似度,判断所述相似度是否大于预设值,如果否,向所述坐标系统调整单元输出触发信号;The
坐标系统调整单元420,用于:在获取到触发信号后,获取内窥设备真实坐标、内窥设备虚拟坐标、内窥设备在电磁导航系统内的真实观察方向、内窥设备在虚拟三维模型中的虚拟观察方向;将所述真实坐标位置与虚拟坐标之间的差值记为坐标差值;将所述真实方向和虚拟方向之间的差值记为方向差值;依据所述坐标差值和方向差值,调整所述虚拟三维模型和电磁导航系统之间的坐标转换矩阵,以使得所述真实坐标位置与虚拟坐标之间的坐标差值、真实方向和虚拟方向之间的方向差值在许可范围之内。The coordinate
在本申请上述实施例公开的技术方案中,在调整所述瞄准器的瞄准方向时,可以采用手动调整的方式,当然也可以采用自动瞄准的方式,其中,为了方便用户直观判断所述瞄准器的瞄准方向是否与所述瞄准直线相一致,本申请上述实施例公开的技术方案中,还可以包括方向匹配失败子模块,其用于当所述瞄准器的虚拟瞄准方向与所述瞄准直线的角度差值在许可范围之外时,输出用于表征方向不匹配的第一预设提示信号,以提示用户所述瞄准器的瞄准方向还需继续调整。In the technical solution disclosed in the above embodiment of the present application, when the aiming direction of the sight is adjusted, a manual adjustment mode may be adopted, and of course, an automatic aiming mode may also be adopted, wherein the sight is intuitively judged for the convenience of the user. The aiming direction of the aiming line is consistent with the aiming line. In the technical solution disclosed in the above embodiment, the direction matching failure sub-module may be further included, when the virtual aiming direction of the sight and the aiming line are When the angle difference is outside the permitted range, the first preset prompt signal for characterizing the direction mismatch is output to prompt the user that the aiming direction of the sight needs to be further adjusted.
其中,所述虚拟瞄准方向与所述瞄准直线(在虚拟三维模型中的瞄准直线)的角度差值的许可范围的大小,可以依据用户对精确度的要求自定确定,如果用户对瞄准的精确度要求较高,可以将所述许可范围设定的适当较小,例如,在本申请上述实施例公开的技术方案中,所述许可范围为[0°,10°],即只要两者的角度差值不大于10°,就可认为所述瞄准器的虚拟瞄准方向与所述瞄准直线的方向相一致。Wherein, the size of the allowable range of the angular difference between the virtual aiming direction and the aiming line (the aiming line in the virtual three-dimensional model) may be determined according to the user's requirement for accuracy, if the user is precise to aiming The permission requirement is relatively high, and the permission range may be set to be appropriately small. For example, in the technical solution disclosed in the above embodiment of the present application, the permission range is [0°, 10°], that is, as long as the two If the angle difference is not more than 10°, the virtual aiming direction of the sight can be considered to coincide with the direction of the aiming line.
与所述图像分析单元相对应,本申请上述系统中,所述图像分析单元还用于:当前判断所述虚拟位置图像和真实图像的相似度小于预设值时,输出用于提示用户或系统需继续对所述电磁导航系统和虚拟坐标系统之间的坐标转换矩阵继续调整的第二预设提示信号。其中,用户可以依据自身对精度的需求设定所述用于判定相似度时的预设值的大小,例如,在本申请上述实施例公开的技术方案中,所述预设值可以设定为0.5,即,只要认为两者的相似度大于0.5,即可认为两个图像一致。Corresponding to the image analysis unit, in the above system of the present application, the image analysis unit is further configured to: when it is determined that the similarity between the virtual location image and the real image is less than a preset value, outputting to prompt the user or the system A second preset prompt signal for continuing adjustment of the coordinate transformation matrix between the electromagnetic navigation system and the virtual coordinate system is continued. The user can set the size of the preset value for determining the similarity according to the requirement of the accuracy of the user. For example, in the technical solution disclosed in the foregoing embodiment of the present application, the preset value may be set to 0.5, that is, as long as the similarity between the two is considered to be greater than 0.5, the two images are considered to be identical.
针对于上述诊断体内目标对象定位系统,参见图5,在本申请另一实施例中,还公开了一种医疗定位系统,其包括内窥设备X1、瞄准器X2、电磁导航系统X3、CT设备X4、显示器X5和计算机X6,该医疗定位系统可以为电视辅助胸腔镜手术系统或穿刺活检系统;For the above-mentioned diagnostic target object positioning system, referring to FIG. 5, in another embodiment of the present application, a medical positioning system including an endoscopic device X1, a sight X2, an electromagnetic navigation system X3, and a CT device is also disclosed. X4, display X5 and computer X6, the medical positioning system may be a television assisted thoracoscopic surgery system or a needle biopsy system;
其中,所述CT设备用于对诊断体进行扫描,得到诊断体的虚拟三维模型,所述内窥设备、瞄准器内设置有导航传感器,所述电磁导航系统用于建立电磁导航坐标系,通过所述电磁导航坐标系可感应所述内窥设备、瞄准器内的导航传感器,从而确定所述内窥设备、瞄准器的位置信息以及瞄准方向,所述计算机中应用有本申请上述任意一项实施例公开的诊断体内目标对象定位系统,所述计算机用于获取并显示所述CT设备采集到的虚拟三维模型,依据电磁导航系统和虚拟三维模型之间的转换矩阵,确定所述内窥设备在所述虚拟三维模型中的位置信息,所述显示器用于显示所述内窥设备采集到的图像信息。The CT device is configured to scan a diagnostic body to obtain a virtual three-dimensional model of the diagnostic body. The endoscopic device and the sight are provided with a navigation sensor, and the electromagnetic navigation system is used to establish an electromagnetic navigation coordinate system. The electromagnetic navigation coordinate system may sense the navigation sensor in the endoscopic device and the sight to determine the position information of the endoscopic device, the sight, and the aiming direction, and the computer has any of the above-mentioned applications of the present application. The diagnostic in vivo target object positioning system disclosed in the embodiment, the computer is configured to acquire and display a virtual three-dimensional model acquired by the CT device, and determine the endoscopic device according to a conversion matrix between the electromagnetic navigation system and the virtual three-dimensional model The position information in the virtual three-dimensional model, the display is used to display image information collected by the endoscopic device.
可选的,在本申请实施例公开的技术方案中,所述瞄准器能够发射出三束激光,这三束激光呈三角式分布,该三角的中心位置即为所述瞄准器的瞄准位置。Optionally, in the technical solution disclosed in the embodiment of the present application, the sight can emit three laser beams, and the three laser beams are distributed in a triangle shape, and the center position of the triangle is the aiming position of the sight.
当应用本申请上述实施例公开的医疗定位系统在诊断体体外进行目标定位时,首先,采用CT设备对诊断体进行扫描,得到诊断体的虚拟三维模型,通过计算机显示该虚拟三维模型。将诊断体安置在所述磁场发生器上,通过所述磁场发生器主机控制所述磁场发生器工作,医护人员将内窥设备植入至诊断体体内,通过所述磁场发生器通过内窥设备和瞄准器内置的导航传感器感应所述内窥设备和瞄准器的位置信息以及瞄准方向信息,并将这些信息发送给计算机,依据所述电磁导航系统和虚拟三维模型之间的坐标转换矩阵,在所述虚拟三维模型中标定所述内窥设备的位置信息,同时通过显示器实时显示所述内窥设备采集到的图像信息,医护人员通过所述显示器显示的图像信息查找所述诊断体内的目标对象,当所述内窥设备采集到所述目标对象的图像信息后,所述计算机控制内置的诊断体内目标对象定位系统动作。When the medical positioning system disclosed in the above embodiment of the present application is used for target positioning outside the diagnostic body, first, the CT device is used to scan the diagnostic body to obtain a virtual three-dimensional model of the diagnostic body, and the virtual three-dimensional model is displayed by a computer. Positioning the diagnostic body on the magnetic field generator, controlling the magnetic field generator by the magnetic field generator main body, and the medical staff implanting the endoscopic device into the diagnostic body, and passing the magnetic field generator through the endoscopic device And a navigation sensor built in the sight sensing the position information of the endoscopic device and the sight and the aiming direction information, and transmitting the information to the computer, according to a coordinate transformation matrix between the electromagnetic navigation system and the virtual three-dimensional model, Locating the location information of the endoscopic device in the virtual three-dimensional model, and displaying the image information collected by the endoscopic device in real time through the display, and the medical staff searching for the target object in the diagnostic body through the image information displayed by the display After the endoscopic device collects the image information of the target object, the computer controls the built-in diagnostic in vivo target object positioning system action.
为了描述的方便,描述以上系统时以功能分为各种模块分别描述。当然,在实施本申请时可以把各模块的功能在同一个或多个软件和/或硬件中实现。For the convenience of description, the above system is described as being divided into various modules by function. Of course, the functions of each module can be implemented in the same software or software and/or hardware when implementing the present application.
本说明书中的各个实施例均采用递进的方式描述,各个实施例之间相同相似的部分互相参见即可,每个实施例重点说明的都是与其他实施例的不同之处。尤其,对于系统或系统实施例而言,由于其基本相似于方法实施例,所以描述得比较简单,相关之处参见方法实施例的部分说明即可。以上所描述的系统及系统实施例仅仅是示意性的,其中所述作为分离部件说明的单元可以是或者也可以不是物理上分开的,作为单元显示的部件可以是或者也可以不是物理单元,即可以位于一个地方,或者也可以分布到多个网络单元上。可以根据实际的需要选择其中的部分或者全部模块来实现本实施例方案的目的。本领域普通技术人员在不付出创造性劳动的情况下,即可以理解并实施。The various embodiments in the specification are described in a progressive manner, and the same or similar parts between the various embodiments may be referred to each other, and each embodiment focuses on the differences from the other embodiments. In particular, for a system or system embodiment, since it is substantially similar to the method embodiment, the description is relatively simple, and the relevant parts can be referred to the description of the method embodiment. The system and system embodiments described above are merely illustrative, wherein the units described as separate components may or may not be physically separate, and the components displayed as units may or may not be physical units, ie It can be located in one place or it can be distributed to multiple network units. Some or all of the modules may be selected according to actual needs to achieve the purpose of the solution of the embodiment. Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand and implement without any creative effort.
专业人员还可以进一步意识到,结合本文中所公开的实施例描述的各示例的单元及算法步骤,能够以电子硬件、计算机软件或者二者的结合来实现,为了清楚地说明硬件和软件的可互换性,在上述说明中已经按照功能一般性地描述了各示例的组成及步骤。这些功能究竟以硬件还是软件方式来执行,取决于技术方案的特定应用和设计约束条件。专业技术人员可以对每个特定的应用来使用不同方法来实现所描述的功能,但是这种实现不应认为超出本发明的范围。A person skilled in the art will further appreciate that the elements and algorithm steps of the various examples described in connection with the embodiments disclosed herein can be implemented in electronic hardware, computer software or a combination of both, in order to clearly illustrate the hardware and software. Interchangeability, the composition and steps of the various examples have been generally described in terms of function in the above description. Whether these functions are hardware or softwareExecution depends on the specific application and design constraints of the technical solution. A person skilled in the art can use different methods for implementing the described functions for each particular application, but such implementation should not be considered to be beyond the scope of the present invention.
结合本文中所公开的实施例描述的方法或算法的步骤可以直接用硬件、处理器执行的软件模块,或者二者的结合来实施。软件模块可以置于随机存储器(RAM)、内存、只读存储器(ROM)、电可编程ROM、电可擦除可编程ROM、寄存器、硬盘、可移动磁盘、CD-ROM、或技术领域内所公知的任意其它形式的存储介质中。The steps of a method or algorithm described in connection with the embodiments disclosed herein can be implemented directly in hardware, a software module executed by a processor, or a combination of both. The software module can be placed in random access memory (RAM), memory, read only memory (ROM), electrically programmable ROM, electrically erasable programmable ROM, registers, hard disk, removable disk, CD-ROM, or technical field. Any other form of storage medium known.
还需要说明的是,在本文中,诸如第一和第二等之类的关系术语仅仅用来将一个实体或者操作与另一个实体或操作区分开来,而不一定要求或者暗示这些实体或操作之间存在任何这种实际的关系或者顺序。而且,术语“包括”、“包含”或者其任何其他变体意在涵盖非排他性的包含,从而使得包括一系列要素的过程、方法、物品或者设备不仅包括那些要素,而且还包括没有明确列出的其他要素,或者是还包括为这种过程、方法、物品或者设备所固有的要素。在没有更多限制的情况下,由语句“包括一个……”限定的要素,并不排除在包括所述要素的过程、方法、物品或者设备中还存在另外的相同要素。It should also be noted that, in this context, relational terms such as first and second, etc. are used merely to distinguish one entity or operation from another entity or operation, without necessarily requiring or implying such entities or operations. There is any such actual relationship or order between them. Furthermore, the term "comprises" or "comprises" or "comprises" or any other variations thereof is intended to encompass a non-exclusive inclusion, such that a process, method, article, or device that comprises a plurality of elements includes not only those elements but also Other elements, or elements that are inherent to such a process, method, item, or device. An element that is defined by the phrase "comprising a ..." does not exclude the presence of additional equivalent elements in the process, method, item, or device that comprises the element.
对所公开的实施例的上述说明,使本领域专业技术人员能够实现或使用本发明。对这些实施例的多种修改对本领域的专业技术人员来说将是显而易见的,本文中所定义的一般原理可以在不脱离本发明的精神或范围的情况下,在其它实施例中实现。因此,本发明将不会被限制于本文所示的这些实施例,而是要符合与本文所公开的原理和新颖特点相一致的最宽的范围。The above description of the disclosed embodiments enables those skilled in the art to make or use the invention. Various modifications to these embodiments are obvious to those skilled in the art, and the general principles defined herein may be implemented in other embodiments without departing from the spirit or scope of the invention. Therefore, the present invention is not to be limited to the embodiments shown herein, but the scope of the invention is to be accorded
Claims (11)
Translated fromChineseApplications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610971071.5 | 2016-10-28 | ||
| CN201610971071.5ACN106491216B (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2016-10-28 | It is a kind of to diagnose internal target object positioning system and medical treatment alignment system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2018076503A1true WO2018076503A1 (en) | 2018-05-03 |
Family
ID=58320979
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2016/110725CeasedWO2018076503A1 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2016-12-19 | Positioning system and medical positioning system for diagnosing of target object in body |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN106491216B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2018076503A1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109674536A (en)* | 2019-01-25 | 2019-04-26 | 上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院 | Operation guiding system and its equipment, method and storage medium based on laser |
| CN113729941A (en)* | 2021-09-23 | 2021-12-03 | 上海卓昕医疗科技有限公司 | VR-based surgery auxiliary positioning system and control method thereof |
| CN114159158A (en)* | 2020-09-10 | 2022-03-11 | 杭州三坛医疗科技有限公司 | Surgical navigation system |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107560616B (en)* | 2017-08-17 | 2020-11-13 | 深圳市元智慧科技有限公司 | Magnetic navigation method and magnetic navigator thereof |
| CN108761237A (en)* | 2018-05-29 | 2018-11-06 | 福州大学 | Unmanned plane electric inspection process image vital electrical component diagnoses automatically and labeling system |
| CN109934798A (en)* | 2019-01-24 | 2019-06-25 | 深圳安泰创新科技股份有限公司 | Internal object information labeling method and device, electronic equipment, storage medium |
| CN114376727B (en)* | 2020-10-16 | 2025-03-07 | 常州朗合医疗器械有限公司 | Medical system |
| CN112244737A (en)* | 2020-10-19 | 2021-01-22 | 重庆金山医疗器械有限公司 | Capsule positioning method, device and system |
| CN113017857B (en)* | 2021-02-25 | 2022-12-20 | 上海联影医疗科技股份有限公司 | Positioning method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110054304A1 (en)* | 2009-08-31 | 2011-03-03 | Medtronic, Inc. | Combination Localization System |
| CN102999902A (en)* | 2012-11-13 | 2013-03-27 | 上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院 | Optical navigation positioning system based on CT (computed tomography) registration result and navigation method thereof |
| CN103169445A (en)* | 2013-04-16 | 2013-06-26 | 苏州朗开医疗技术有限公司 | Navigation method and system for endoscope |
| US20140357986A1 (en)* | 2013-06-03 | 2014-12-04 | Faculty Physicians And Surgeons Of Loma Linda University School Of Medicine | Methods and apparatuses for fluoro-less or near fluoro-less percutaneous surgery access |
| CN105943161A (en)* | 2016-06-04 | 2016-09-21 | 深圳市前海康启源科技有限公司 | Surgical navigation system and method based on medical robot |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6041249A (en)* | 1997-03-13 | 2000-03-21 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Device for making a guide path for an instrument on a patient |
| US7603163B2 (en)* | 2003-10-31 | 2009-10-13 | Minrad Inc. | Targeting system and method of targeting |
| WO2010144402A2 (en)* | 2009-06-08 | 2010-12-16 | Surgivision, Inc. | Mri-guided surgical systems with preset scan planes |
| CN202365910U (en)* | 2011-11-23 | 2012-08-08 | 北京集翔多维信息技术有限公司 | Intramedullary nail remote end locking sighting device |
| CN205378133U (en)* | 2015-12-25 | 2016-07-06 | 深圳超多维光电子有限公司 | Stereo display system |
- 2016
- 2016-10-28CNCN201610971071.5Apatent/CN106491216B/enactiveActive
- 2016-12-19WOPCT/CN2016/110725patent/WO2018076503A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110054304A1 (en)* | 2009-08-31 | 2011-03-03 | Medtronic, Inc. | Combination Localization System |
| CN102999902A (en)* | 2012-11-13 | 2013-03-27 | 上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院 | Optical navigation positioning system based on CT (computed tomography) registration result and navigation method thereof |
| CN103169445A (en)* | 2013-04-16 | 2013-06-26 | 苏州朗开医疗技术有限公司 | Navigation method and system for endoscope |
| US20140357986A1 (en)* | 2013-06-03 | 2014-12-04 | Faculty Physicians And Surgeons Of Loma Linda University School Of Medicine | Methods and apparatuses for fluoro-less or near fluoro-less percutaneous surgery access |
| CN105943161A (en)* | 2016-06-04 | 2016-09-21 | 深圳市前海康启源科技有限公司 | Surgical navigation system and method based on medical robot |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109674536A (en)* | 2019-01-25 | 2019-04-26 | 上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院 | Operation guiding system and its equipment, method and storage medium based on laser |
| CN114159158A (en)* | 2020-09-10 | 2022-03-11 | 杭州三坛医疗科技有限公司 | Surgical navigation system |
| CN113729941A (en)* | 2021-09-23 | 2021-12-03 | 上海卓昕医疗科技有限公司 | VR-based surgery auxiliary positioning system and control method thereof |
| CN113729941B (en)* | 2021-09-23 | 2024-01-30 | 上海卓昕医疗科技有限公司 | VR-based operation auxiliary positioning system and control method thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN106491216A (en) | 2017-03-15 |
| CN106491216B (en) | 2019-06-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2018076503A1 (en) | Positioning system and medical positioning system for diagnosing of target object in body | |
| US11730562B2 (en) | Systems and methods for imaging a patient | |
| US11596475B2 (en) | Systems and methods for ultrasound image-guided ablation antenna placement | |
| US11622815B2 (en) | Systems and methods for providing proximity awareness to pleural boundaries, vascular structures, and other critical intra-thoracic structures during electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy | |
| US20210145387A1 (en) | System and method for pose estimation of an imaging device and for determining the location of a medical device with respect to a target | |
| CN111568544B (en) | Systems and methods for visualizing navigation of a medical device relative to a target | |
| ES2901703T3 (en) | Integration of multiple data sources for location and navigation | |
| EP3164050B1 (en) | Dynamic 3d lung map view for tool navigation inside the lung | |
| US9782198B2 (en) | Localization of robotic remote center of motion point using custom trocar | |
| JP6404713B2 (en) | System and method for guided injection in endoscopic surgery | |
| US20190290247A1 (en) | Image-based fusion of endoscopic image and ultrasound images | |
| CA2986168C (en) | Electromagnetic navigation registration using ultrasound | |
| CN106572887B (en) | Image integration and robotic endoscope control in an X-ray suite | |
| JP6952740B2 (en) | How to assist users, computer program products, data storage media, and imaging systems | |
| US10799146B2 (en) | Interactive systems and methods for real-time laparoscopic navigation | |
| CN116829091B (en) | Surgical assistance system and presentation method | |
| WO2017006708A1 (en) | Medical device, medical image generating method, and medical image generating program | |
| US20240225735A9 (en) | Dynamic tissue imagery updating | |
| CN118891018A (en) | MRI-based navigation | |
| EP3782529A1 (en) | Systems and methods for selectively varying resolutions | |
| CN116831728A (en) | Bulls-eye plane display method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | Ref document number:16920321 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 | |
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase | Ref country code:DE | |
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase | Ref document number:16920321 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 |