WO2016202209A1 - Method and device for estimating user influence in social network using graph simplification technique - Google Patents
Method and device for estimating user influence in social network using graph simplification techniqueDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2016202209A1 WO2016202209A1PCT/CN2016/085242CN2016085242WWO2016202209A1WO 2016202209 A1WO2016202209 A1WO 2016202209A1CN 2016085242 WCN2016085242 WCN 2016085242WWO 2016202209 A1WO2016202209 A1WO 2016202209A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- influence
- graph
- edges
- layer
- social network
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/90—Details of database functions independent of the retrieved data types
- G06F16/95—Retrieval from the web
- G06F16/951—Indexing; Web crawling techniques
Definitions
- the present inventionrelates to the related art fields of impact propagation analysis, graph data management, and graph data mining of social networks, and more particularly to a method and apparatus for estimating user influence in a social network based on graph simplification technology.
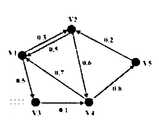
- the probability of interaction between each other, and the probability between edges and edgesis independent of each other. For example, in FIG. 1, the probability of influence of user v1 on user v2 is 0.3.
- the influence of a usercan be defined as the expected value of the number of nodes that the user can reach on the probability map.
- the existing literatureis based on Monte Carlo sampling algorithm [1, 2].
- the specific process of the Monte Carlo sampling algorithmis as follows: First, all the edges on the probability map are sampled according to their probability values, and the process is repeated N times independently, thereby generating N "possible graphs" (also called “possible graphs”). Produce N samples. Next, we calculate the number of nodes that the u-node can reach in these N "possible graphs”. Then, we take the mean to get an unbiased estimate of the influence of node u.
- Monte Carlo sampling-based algorithmsusually produce large variances, thus reducing the accuracy of the influence estimation.
- Li et al.proposed an estimation algorithm based on recursive stratified sampling. Li et al. proved that the algorithm can significantly reduce the variance of the basic sampling algorithm, thus improving the accuracy of the estimation.
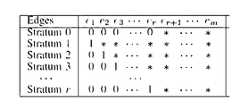
- the specific method of recursive stratified samplingis to randomly select r edges from the probability map, and then layer the entire possible graph sample space according to the state of the r edges.
- the 0th layercorresponds to all r edges and the state is 0; that is, in this layer, all possible graphs do not contain the r edges.
- the state of the first layer corresponding to the first sideis 1, and the state of the other r-1 edges is undefined; that is, in this layer, all possible maps include the first side.
- the state of the second layer corresponding to the first sideis 0, the state of the second side is 1, and the state of the other r-2 sides is uncertain; that is, in this layer, all possible figures include the second side, And does not include the first side.
- the third layercorresponds to the first and second edges, and the state of the third edge is 1, and the states of the remaining r-3 edges are uncertain; that is, in this layer, all possible maps contain the third edge.
- the basic Monte Carlo sampling algorithmhas a large variance. Therefore, in order to achieve a certain estimation accuracy, this algorithm usually needs to extract many possible graphs. Extracting a possible graph usually requires O(m) time complexity, where m represents the number of edges in the probability graph. Therefore, the algorithm is not efficient in practice.
- the recursive stratified sampling algorithmcan usually significantly reduce the large variance problem of the basic Monte Carlo algorithm, but this algorithm still needs to spend O(m) time to extract a possible graph, and the algorithm may select some computing nodes.
- the influence-independent edgesare layered to reduce the accuracy of the algorithm.
- An object of the present inventionis to provide a method and apparatus for estimating user influence in a social network based on a simplified graph technique, which overcomes the shortcomings of the conventional recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm which are more expensive to estimate and have lower estimation accuracy.
- a method for estimating user influence in a social network based on graph simplification technologycomprising:
- step (2)further comprises:
- the step (2)further includes: when determining that the number of edges in the probability map G is less than r or the number N of the extracted possible graphs is less than t, estimating the influence of the node u by using basic Monte Carlo sampling force.
- a device for estimating user influence in a social network based on graph simplification technologycomprising:
- a probability map obtaining unitconfigured to acquire a probability map G of the social network to which the user influence is to be estimated, preset a number of possible maps N, a node u, and parameters r and t;
- the influence estimating unitis configured to estimate the influence of the node u in the probability map G by using a recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm and a graph simplification technique.
- the present inventionhas the following advantages:
- the recursive hierarchical sampling method based on the simplified technology of the present inventioncan be used to estimate the influence of users in a social network.
- the methodintegrates the technology of graph simplification, and on the one hand, can quickly pruning those influences on estimated users. Force-independent nodes and edges, so that rapid impact estimation can be achieved; on the other hand, the simplified process of the graph can avoid stratification by selecting edges that are independent of the influence of the computational nodes in the recursive stratified sampling process, thereby improving the algorithm. Precision.
- the recursive stratified sampling method based on graph simplification technologyhas faster speed and higher precision than the existing recursive stratified sampling method.
- Figure 1is a probability map of a social network
- FIG. 2is an exemplary diagram of a basic recursive layering method
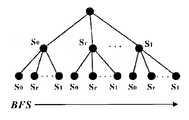
- FIG. 3is a diagram showing an example of a recursive layering method based on graph simplification provided by an embodiment of the present invention
- the technical solution adopted by the present inventionis to develop a recursive hierarchical sampling method based on the graph simplification technique.
- the basic idea of this methodis to introduce a technique of graph simplification based on the recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm. Specifically, in each layering process, since some of the selected r edges are ok, it is determined that they are not included in all possible maps corresponding to the layer. For example, according to the algorithm of recursive hierarchical sampling, in the rth layer, the state of the front r-1 side is 0, that is, the r-1 side does not appear in all possible maps corresponding to the layer.
- the present inventioncan delete the r-1 edges from the probability map and then sample the remaining maps. It is noted that when some edges are deleted, some of the edges in the remaining graph may not have an effect on the computational node, and the present invention refers to these edges as irrelevant edges. For irrelevant edges, the present invention can be deleted together to achieve the effect of simplifying the graph. Moreover, such a simplified technique can be applied recursively to each layering process of a basic recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm. The specific method flow is as follows:
- graph G(V, E, P), extract the number N of possible graphs, node u, and parameters r and t;
- Step 1If the number of sides of the graph G is less than r, or N is less than t, then the basic Monte Carlo pumping is invoked. Estimate the influence of node u;
- Step 2otherwise perform the following steps
- Step 2.1arbitrarily select r edges from G, and divide G into r+1 layers according to the state of r edges;
- Step 2.2From the 0th layer to the rth layer, perform the following steps in a loop:
- Step 2.2.1For the i-th layer, simplify the graph G according to the state of the r-edge corresponding to the i-th layer, and make the simplified graph G i ;
- Step 2.2.2Calculate the number N i of possible graphs to be extracted by the i-th layer according to the recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm
- Step 2.2.3recursively calling the algorithm with the parameters G i , N i , u, r, t;
- Step 2.2.4Accumulate the estimated value according to the recursive stratified sampling algorithm.
- the algorithm in the present inventionhas 2.2.1 more steps.
- the specific approachis as follows: First, a recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm based on graph simplification will generate a recursive tree. Each node in the recursive tree represents a layer, which is a subset of a possible graph. For example, the root node of the recursive tree represents the entire set of possible graphs, and the r+1 child nodes of the root node represent the r+1 layer in the first layering process.
- each internal node in the recursive treerepresents the 0th, r, ..., 1 layers obtained after layering the internal nodes from left to right.
- the specific schematiccan be seen in Figure 3.
- simplifying the layering of all r+1 internal nodes of layer 2 in the recursive treeWe simplify the r+1 layers in order from left to right.
- layer 0that is, the leftmost node in the second layer of the recursive tree
- BFSbreadth-first traversal
- the simplified diagramis the graph of nodes and edges that have been accessed by the BFS process.
- the pruned BFSto simplify the r-th layer. Specifically, we first delete the edge of the r-th layer corresponding to the state of 0, and then run the pruned BFS to traverse the entire graph. In this process, we will not traverse the edges that were accessed by the previous BFS, and we also mark the edges of the BFS that were pruned. Since the rth layer has a strip side with a state of 1 than the 0th layer (see Figure 2 for details).
- the BFS process of this pruningis equivalent to finding nodes that can only be reached by this edge with a state of 1.
- the simplified graphis a graph composed of nodes and edges accessed by the two BFS processes.
- the time complexity of the recursive stratified sampling algorithm based on graph simplification technologyis consistent with the ordinary recursive stratified sampling algorithm.
- the edges that are simplifiedcan be omitted, and thus the speed of the algorithm can be improved.
- the algorithmcan avoid the use of useless edges for stratification, and the process of graph simplification is to reduce the uncertainty of the probability map, the estimation accuracy of the algorithm can be improved.
- the simplified graph corresponding to layer 0is a zero graph, that is, a graph that does not contain any nodes and edges. Since the influence of the node u is obviously 0 in the zero graph, in the 0th layer, the influence of the node u can be calculated without sampling. Then, according to the simplified method of the present invention, the second layer is started to be simplified. In layer 2, it can be seen that the (v5, v2) edge is not accessed by the pruned BFS process, so this edge will be simplified during this process.
- the simplified diagram corresponding to the second layeris the subtracted edges (v4, v5) and (v5, v2) of FIG.
- the simplified graphis then sampled according to an algorithm of recursive stratified sampling.
- simplify the first layerIn Simplified Layer 1, the BFS that invokes pruning starts from v4 and traverses nodes and edges that have not been accessed by the previous BFS. It is easy to find that in this process, only the two edges (v4, v5) and (v5, v2) will be accessed by the BFS of this pruning. In the first layer, no side can be simplified, so the simplified picture is the original picture.
- Figure 1is then sampled according to an algorithm for recursive stratified sampling. In this process, it is not difficult to find that all BFS and pruning BFS processes only access the edges in Figure 1 at most, so the time complexity of the simplified process is O(m).
- the time complexity of the recursive stratified sampling estimation method based on the graph simplification techniqueis consistent with the ordinary recursive stratified sampling algorithm, but the map is integrated by the present invention.
- Simplified techniqueso in the calculation process of extracting possible graphs, those edges that are simplified can be omitted, so that the estimation speed can be improved; in addition, since the present invention can avoid the use of useless edges for stratification, the process of graph simplification itself is Reduce the uncertainty of the probability map, thus It also improves the estimation accuracy.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese本发明涉及社交网络的影响传播分析、图数据管理,以及图数据挖掘等相关技术领域,尤其涉及一种基于图简化技术的社交网络中用户影响力估算方法及装置。The present invention relates to the related art fields of impact propagation analysis, graph data management, and graph data mining of social networks, and more particularly to a method and apparatus for estimating user influence in a social network based on graph simplification technology.
近年来,在线社交网络的分析与挖掘引起了学术界和工业界的广泛兴趣。对于在线社交网络分析,其中的一个重要研究问题是分析和估计社交网络中用户的影响力(参考文献[1]:D.Kempe,J.Kleinberg,and E.Tardos.Maximizing the spread of influence through a social network.In KDD,2003)。通过估计用户的影响力,我们可以评估该用户对社交网络中的其它用户的影响程度,从而可以用于社交网络推荐等相关的应用。例如,假设我们知道用户A对用户B具有较大的影响力,那么我们可以推荐A买过的物品给用户B。In recent years, the analysis and mining of online social networks has aroused widespread interest in academia and industry. An important research issue for online social network analysis is the analysis and estimation of the influence of users in social networks (Reference [1]: D. Kempe, J. Kleinberg, and E. Tardos. Maximizing the spread of influence through a Social network.In KDD, 2003). By estimating the user's influence, we can assess the extent to which the user's influence on other users in the social network can be used for related applications such as social network recommendations. For example, suppose we know that User A has a greater influence on User B, then we can recommend A bought items to User B.
通常,我们可以用一个概率图的模型来对一个在线社交网络进行建模,其中图中的一个顶点对应一个用户,图中的一条边对应用户之间的朋友关系,边上的概率值对应朋友之间的相互影响的概率,并且边与边之间的概率是相互独立的。例如,在图1中,用户v1对用户v2的影响概率为0.3。Usually, we can model an online social network with a model of a probability graph, where one vertex corresponds to one user, one edge in the graph corresponds to the friend relationship between users, and the probability value on the edge corresponds to the friend. The probability of interaction between each other, and the probability between edges and edges is independent of each other. For example, in FIG. 1, the probability of influence of user v1 on user v2 is 0.3.
在一个社交网络中,一个用户的影响力可以定义为该用户在概率图上所能到达的节点个数的期望值。基于这一定义,社交网络中的用户影响力估计问题即为:给定一个用户u和一个概率图G=(V,E,P),估计u在G中所能到达的节点个数的期望。由于这一问题被证明是#P完全的(参考文献[2]:W.Chen,Y.Wang,and S.Yang.Efficient influence maximization in social networks.In KDD,2009),所以基本上不可能存在多项式时间的算法,除非P=#P。为了计算节点的影响力,现有的文献都是基于蒙特卡罗抽样算法[1,2]。蒙特卡罗抽样算法的具体流程如下:首先,对概率图上所有的边根据其概率值进行抽样,独立重复这一过程N次,从而生成N个“可能图”(possible graph),也称为生产N个样本。接着,我们分别在这N个“可能图”中计算u节点所能到达的节点的个数。然后,我们取均值,从而得到节点u的影响力的一个无偏估计。然而,这种基于蒙特卡罗抽样的算法通常都会产生较大的方差,因此会降低影响力估计的精度。为减少蒙特卡罗抽样算法的方差,在文献[3](R.-H.Li,J.X.Yu,R.Mao,and T.Jin.Efficient and accurate query evaluation on uncertain graphs via recursive stratified sampling.In ICDE,2014)中,Li等人提出了一种基于递归分层抽样的估计算法。Li等人证明该算法能够显著降低基本的抽样算法的方差,从而提高估计的精度。递归分层抽样的具体做法是,从概率图中任意选取r条边,然后根据这r条边的状态对整个可能图样本空间进行分层。第0层对应所有的r条边的状态都是0;也即在该层中,所有可能图都不包含这r条边。第1层对应第1条边的状态为1,其它r-1条边的状态不确定;也即在该层中,所有可能图都包含第1条边。第2层对应第1条边的状态为0,第2条边的状态为1,其它r-2条边的状态不确定;也即在该层中,所有可能图都包含第2条边,并且不包含第1条边。第3层对应第1,2条边状态为0,第3条边的状态为1,其余r-3条边的状态不确定;也即在该层中,所有可能图都包含第3条边,并且不包含第1,2条边。以此类推,第r层对应第1至r-1条的状态为0,第r条边的状态为1,其余边不确定;在该层中,所有可能图都包含第r条边,并且不包含第1至r-1条边。具体分层方法详见图2。这种选取r条边进行分层的策略可以递归地运用到每一层,从而得到递归的分层抽样算法。Li等人证明该算法较基本的蒙特卡罗抽样算法具有更小的方差,从而具有更高的精度。In a social network, the influence of a user can be defined as the expected value of the number of nodes that the user can reach on the probability map. Based on this definition, the user influence estimation problem in the social network is: given a user u and a probability map G = (V, E, P), estimate the expected number of nodes that u can reach in G . Since this problem has been proved to be #P complete (Reference [2]: W. Chen, Y.Wang, and S. Yang. Efficient influence maximization in social networks. In KDD, 2009), so it is basically impossible to have a polynomial time algorithm unless P = #P. In order to calculate the influence of nodes, the existing literature is based on Monte Carlo sampling algorithm [1, 2]. The specific process of the Monte Carlo sampling algorithm is as follows: First, all the edges on the probability map are sampled according to their probability values, and the process is repeated N times independently, thereby generating N "possible graphs" (also called "possible graphs"). Produce N samples. Next, we calculate the number of nodes that the u-node can reach in these N "possible graphs". Then, we take the mean to get an unbiased estimate of the influence of node u. However, such Monte Carlo sampling-based algorithms usually produce large variances, thus reducing the accuracy of the influence estimation. In order to reduce the variance of the Monte Carlo sampling algorithm, in the literature [3] (R.-H.Li, JXYu, R.Mao, and T.Jin.Efficient and accurate query evaluation on uncertain graphs via recursive stratified sampling.In ICDE In 2014), Li et al. proposed an estimation algorithm based on recursive stratified sampling. Li et al. proved that the algorithm can significantly reduce the variance of the basic sampling algorithm, thus improving the accuracy of the estimation. The specific method of recursive stratified sampling is to randomly select r edges from the probability map, and then layer the entire possible graph sample space according to the state of the r edges. The 0th layer corresponds to all r edges and the state is 0; that is, in this layer, all possible graphs do not contain the r edges. The state of the first layer corresponding to the first side is 1, and the state of the other r-1 edges is undefined; that is, in this layer, all possible maps include the first side. The state of the second layer corresponding to the first side is 0, the state of the second side is 1, and the state of the other r-2 sides is uncertain; that is, in this layer, all possible figures include the second side, And does not include the first side. The third layer corresponds to the first and second edges, and the state of the third edge is 1, and the states of the remaining r-3 edges are uncertain; that is, in this layer, all possible maps contain the third edge. And does not contain the 1st and 2nd sides. By analogy, the state of the rth layer corresponding to the first to r-1 is 0, the state of the rth side is 1, and the remaining edges are undefined; in this layer, all possible maps include the rth side, and Does not include the 1st to r-1 sides. The specific layering method is shown in Figure 2. This strategy of selecting r edges for stratification can be applied recursively to each layer, thereby obtainingRecursive stratified sampling algorithm. Li et al. proved that the algorithm has a smaller variance than the basic Monte Carlo sampling algorithm, and thus has higher precision.
在上述算法中,基本的蒙特卡罗抽样算法具有较大的方差。因此为了达到一定的估计精度,这一算法通常需要抽取很多可能图。抽取一个可能图通常需要O(m)的时间复杂度,这里的m表示概率图中边的条数。因此,该算法在实践中并不高效。递归分层抽样算法通常能够显著地减少基本蒙特卡罗算法的大方差问题,但是这一算法仍然需要花费O(m)的时间抽取一个可能图,并且该算法有可能会选到一些与计算节点影响力无关的边进行分层,从而降低算法的精度。In the above algorithm, the basic Monte Carlo sampling algorithm has a large variance. Therefore, in order to achieve a certain estimation accuracy, this algorithm usually needs to extract many possible graphs. Extracting a possible graph usually requires O(m) time complexity, where m represents the number of edges in the probability graph. Therefore, the algorithm is not efficient in practice. The recursive stratified sampling algorithm can usually significantly reduce the large variance problem of the basic Monte Carlo algorithm, but this algorithm still needs to spend O(m) time to extract a possible graph, and the algorithm may select some computing nodes. The influence-independent edges are layered to reduce the accuracy of the algorithm.
发明内容Summary of the invention
本发明的目的在于提供一种基于图简化技术的社交网络中用户影响力估算方法及装置,克服传统的递归分层抽样算法中存在的耗费较多估算时间以及估算精度低的缺陷。An object of the present invention is to provide a method and apparatus for estimating user influence in a social network based on a simplified graph technique, which overcomes the shortcomings of the conventional recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm which are more expensive to estimate and have lower estimation accuracy.
本发明的目的是通过以下技术方案实现的。The object of the present invention is achieved by the following technical solutions.
一种基于图简化技术的社交网络中用户影响力估算方法,包括:A method for estimating user influence in a social network based on graph simplification technology, comprising:
(一)获取待估算用户影响力的社交网络的概率图G,预设抽取可能图的个数N、节点u,以及参数r和t;(1) obtaining a probability map G of the social network to which the user influence is to be estimated, and preset the number of possible maps N, the node u, and the parameters r and t;
(二)利用递归分层抽样算法和图简化技术估算概率图G中节点u的影响力。(2) Using the recursive stratified sampling algorithm and the graph simplification technique to estimate the influence of the node u in the probability map G.
其中,所述步骤(二)进一步包括:Wherein, the step (2) further comprises:
判断所述概率图G中的边数是否小于r或者所述抽取可能图的个数N是否小于t,若否,则循环执行以下步骤:It is determined whether the number of edges in the probability map G is less than r or whether the number N of the extracted possible graphs is less than t. If not, the loop performs the following steps:
(S1)从G中任意选取r条边,并对G按照r条边的状态分为r+1层;(S1) arbitrarily selecting r edges from G, and dividing G into r+1 layers according to the state of r edges;
(S2)从第0层至第r层,循环执行以下步骤:(S2) From the 0th layer to the rth layer, perform the following steps in a loop:
(S21)对于第i层,根据第i层所对应的r条边的状态简化图G,并令简化后的图为Gi;(S21) For the i-th layer, the graph G is simplified according to the state of the r-edge corresponding to the i-th layer, and the simplified graph is Gi ;
(S22)根据递归分层抽样算法计算第i层需要抽取的可能图的个数Ni;(S22) calculating, according to the recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm, the number Ni of possible graphs to be extracted by the i-th layer;
(S23)以参数Gi,Ni,u,r,t递归调用这一算法;(S23) recursively calling the algorithm with the parameters Gi , Ni , u, r, t;
(S24)根据递归分层抽样算法累计估计值。(S24) Accumulating the estimated values according to the recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm.
其中,所述步骤(二)还包括:在判断所述概率图G中的边数小于r或者所述抽取可能图的个数N小于t时,利用基本的蒙特卡罗抽样估算节点u的影响力。The step (2) further includes: when determining that the number of edges in the probability map G is less than r or the number N of the extracted possible graphs is less than t, estimating the influence of the node u by using basic Monte Carlo sampling force.
一种基于图简化技术的社交网络中用户影响力估算装置,包括:A device for estimating user influence in a social network based on graph simplification technology, comprising:
概率图获取单元,用于获取待估算用户影响力的社交网络的概率图G,预设抽取可能图的个数N、节点u,以及参数r和t;a probability map obtaining unit, configured to acquire a probability map G of the social network to which the user influence is to be estimated, preset a number of possible maps N, a node u, and parameters r and t;
影响力估算单元,用于利用递归分层抽样算法和图简化技术估算概率图G中节点u的影响力。The influence estimating unit is configured to estimate the influence of the node u in the probability map G by using a recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm and a graph simplification technique.
本发明实施例与现有技术相比,本发明具有以下优点:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following advantages:
本发明实施例基于图简化技术的递归分层抽样方法可以用于估计社交网络中的用户的影响力,该方法集成了图简化的技术,一方面可以较快地剪枝掉那些对估计用户影响力无关的节点和边,从而可以实现快速的影响力估计;另一方面,图简化的过程可以避免在递归分层抽样过程中选取与计算节点影响力无关的边进行分层,从而可以提高算法的精度。总体上讲,基于图简化技术的递归分层抽样方法较现有的递归分层抽样方法具有更快的速度和更高的精度。The recursive hierarchical sampling method based on the simplified technology of the present invention can be used to estimate the influence of users in a social network. The method integrates the technology of graph simplification, and on the one hand, can quickly pruning those influences on estimated users. Force-independent nodes and edges, so that rapid impact estimation can be achieved; on the other hand, the simplified process of the graph can avoid stratification by selecting edges that are independent of the influence of the computational nodes in the recursive stratified sampling process, thereby improving the algorithm. Precision. In general, the recursive stratified sampling method based on graph simplification technology has faster speed and higher precision than the existing recursive stratified sampling method.
图1是一个社交网络的概率图;Figure 1 is a probability map of a social network;
图2是基本的递归分层方法示例图;2 is an exemplary diagram of a basic recursive layering method;
图3是本发明实施例提供的基于图简化的递归分层方法示例图;3 is a diagram showing an example of a recursive layering method based on graph simplification provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
为了使本发明的目的、技术方案及优点更加清楚明白,以下结合附图及实施例,对本发明进行进一步详细说明。应当理解,此处所描述的具体实施例仅仅用以解释本发明,并不用于限定本发明。The present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It is understood that the specific embodiments described herein are merely illustrative of the invention and are not intended to limit the invention.
为了解决上述背景技术的缺陷,本发明采用的技术方案是开发一种基于图简化技术的递归分层抽样方法。该方法的基本思路是基于递归分层抽样算法之上引入一种图简化的技术。具体地,在每次分层的过程中,由于选中的r条边中有些边是可以确定知道它们不会包含在该层所对应的所有可能图中。例如根据递归分层抽样的算法,在第r层中,前r-1条边的状态为0,也即这r-1条边不会出现在该层所对应的所有可能图中。基于这一观察,本发明可以从概率图中删除这r-1条边,然后再来对剩余的图进行抽样。注意到,当删除一些边后,剩余图中的某些边可能对计算节点的影响力不起作用,本发明称这些边为无关边。对于无关边,本发明可以一并删除,从而达到简化图的效果。而且,这种图简化的技术可以递归地应用于基本的递归分层抽样算法的每次分层过程中。具体的方法流程如下:In order to solve the above drawbacks of the background art, the technical solution adopted by the present invention is to develop a recursive hierarchical sampling method based on the graph simplification technique. The basic idea of this method is to introduce a technique of graph simplification based on the recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm. Specifically, in each layering process, since some of the selected r edges are ok, it is determined that they are not included in all possible maps corresponding to the layer. For example, according to the algorithm of recursive hierarchical sampling, in the rth layer, the state of the front r-1 side is 0, that is, the r-1 side does not appear in all possible maps corresponding to the layer. Based on this observation, the present invention can delete the r-1 edges from the probability map and then sample the remaining maps. It is noted that when some edges are deleted, some of the edges in the remaining graph may not have an effect on the computational node, and the present invention refers to these edges as irrelevant edges. For irrelevant edges, the present invention can be deleted together to achieve the effect of simplifying the graph. Moreover, such a simplified technique can be applied recursively to each layering process of a basic recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm. The specific method flow is as follows:
输入:图G=(V,E,P),抽取可能图的个数N,节点u,以及参数r和t;Input: graph G = (V, E, P), extract the number N of possible graphs, node u, and parameters r and t;
输出:节点u的影响力的一个无偏估计Output: an unbiased estimate of the influence of node u
步骤1、如果图G的边数小于r,或者N小于t,则调用基本的蒙特卡罗抽样估计节点u的影响力;
步骤2、否则执行以下步骤;
步骤2.1、从G中任意选取r条边,并对G按照r条边的状态分为r+1层;Step 2.1: arbitrarily select r edges from G, and divide G into r+1 layers according to the state of r edges;
步骤2.2、从第0层至第r层,循环执行以下步骤:Step 2.2: From the 0th layer to the rth layer, perform the following steps in a loop:
步骤2.2.1对于第i层,根据第i层所对应的r条边的状态简化图G,并令简化后的图为Gi;Step 2.2.1 For the i-th layer, simplify the graph G according to the state of the r-edge corresponding to the i-th layer, and make the simplified graph Gi ;
步骤2.2.2、根据递归分层抽样算法计算第i层需要抽取的可能图的个数Ni;Step 2.2.2. Calculate the number Ni of possible graphs to be extracted by the i-th layer according to the recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm;
步骤2.2.3、以参数Gi,Ni,u,r,t递归调用这一算法;Step 2.2.3, recursively calling the algorithm with the parameters Gi , Ni , u, r, t;
步骤2.2.4、根据递归分层抽样算法累计估计值。Step 2.2.4. Accumulate the estimated value according to the recursive stratified sampling algorithm.
相对于递归分层抽样算法,本发明中的算法多了2.2.1这一步骤。在整个算法中,我们可以在O(m)的时间复杂度内实现所有的图简化步骤。具体做法如下:首先,基于图简化的递归分层抽样算法将产生一个递归树。在递归树中的每一个节点都代表了一个分层,也即代表一个可能图的子集。例如,递归树的根节点代表了整个可能图的集合,根节点的r+1个孩子节点代表了第一次分层过程中的r+1层。我们约定递归树中的每个内部节点的孩子节点从左至右分别代表了在该内部节点分层后所得到的第0,r,…,1层。具体示意图可以详见图3。然后,考虑简化递归树中的第2层的所有r+1个内部节点所对应的分层。我们按照从左至右的顺序简化这r+1个层。在简化第0层(也即递归树第2层中最左边的节点)时,我们将第0层所对应的状态为0的边删除,然后从u节点出发执行广度优先遍历(BFS)整个图。那些没有被BFS遍历到的节点以及其相连的边都是无用边,可以一并删除。这是因为这些节点在第0层所对应的所有可能图中,对估计节点u的影响力无关。我们将该BFS所遍历到的边进行标记。在第0层中,简化后的图即为被BFS过程访问过的节点和边组成的图。接着,我们采用剪枝的BFS来简化第r层。具体地,我们首先删除第r层所对应的状态为0的边,然后运行剪枝的BFS来遍历整个图。在这个过程中,被之前的BFS访问过的边我们将不再遍历,并且我们同样标记被剪枝的BFS访问过的边。由于第r层比第0层多了一条状态为1的条边(详见图2)。因此,这一剪枝的BFS过程等价于找到那些只能通过这条状态为1的边到达的节点。在第r层中,简化后的图为被这2个BFS过程访问过的节点和边组成的图。依次类推,在简化第r-1至第1层时,我们采用类似的剪枝的BFS过程。不难验证,由于我们采用了剪枝的BFS来简化所有的r+1层,所以在整个过程中,算法最多访问图中的每条边一次。因此,在简化递归树的第二层的所有节点所对应的r+1个分层的时间复杂度为O(m)。同样,在简化递归树的第三层以及其它层时,我们采用类似的从左至右调用剪枝BFS算法来简化所有的内部节点所对应的分层。容易验证,在每一层中,算法所需的时间复杂度为O(m)。由于在实践过程中,r通常为一个相对不小的常数,例如r=50,而样本大小N通常为10000左右,那样递归树的高度d最多为log50(10000)<3。因此,整个算法的时间复杂度为O(dm)=O(m)。Compared to the recursive stratified sampling algorithm, the algorithm in the present invention has 2.2.1 more steps. Throughout the algorithm, we can implement all the graph simplification steps within the time complexity of O(m). The specific approach is as follows: First, a recursive hierarchical sampling algorithm based on graph simplification will generate a recursive tree. Each node in the recursive tree represents a layer, which is a subset of a possible graph. For example, the root node of the recursive tree represents the entire set of possible graphs, and the r+1 child nodes of the root node represent the r+1 layer in the first layering process. We stipulate that the child nodes of each internal node in the recursive tree represent the 0th, r, ..., 1 layers obtained after layering the internal nodes from left to right. The specific schematic can be seen in Figure 3. Then, consider simplifying the layering of all r+1 internal nodes of
由于图简化的过程与图的大小呈线性关系,所以整个基于图简化技术的递归分层抽样算法的时间复杂度与普通的递归分层抽样算法一致。但是由于我们集成了图简化的技术,因此在抽取可能图的计算过程中,可以省略那些被简化掉的边,因而可以提高算法的速度。此外,由于该算法能够避免选取无用边做分层,而且图简化的过程本身就是在降低概率图的不确定性,因而可以提高算法的估计精度。Since the process of graph simplification is linear with the size of the graph, the time complexity of the recursive stratified sampling algorithm based on graph simplification technology is consistent with the ordinary recursive stratified sampling algorithm. However, since we integrate the technique of graph simplification, in the calculation process of extracting possible graphs, the edges that are simplified can be omitted, and thus the speed of the algorithm can be improved. In addition, because the algorithm can avoid the use of useless edges for stratification, and the process of graph simplification is to reduce the uncertainty of the probability map, the estimation accuracy of the algorithm can be improved.
下面,以图1为例来说明整个算法的运行过程。假设目前需要要估计图1中节点v4的影响力。另外,假设r=2。下面将考虑一次分层算法的运行过程,多次分层的算法过程与一次分层算法的过程非常类似,因此不再赘述。假设选取(v4,v5),(v4,v1)两条边来分层。其中第0层的所有可能图都不包含这两条边,第1层的所有可能图包含(v4,v5)这条边,以及第2层的所有可能图包含边(v4,v1),但不包含边(v4,v5)。在第0层中,本实施例可以简化所有的节点。这是因为删除边(v4,v5)和边(v4,v1)后v4不能到达任何其它节点。所以,第0层所对应的简化后的图为一个零图,即不包含任何节点和边的图。由于在零图中,节点u的影响力显然为0,因此在第0层中,无需抽样即可计算节点u的影响力。然后,根据本发明的图简化方法,开始简化第2层。在第2层中,可以发现(v5,v2)这条边不会被剪枝的BFS过程访问,因此在这一过程中,这条边将会被简化。因此第2层所对应的简化后的图为图1减去边(v4,v5)和(v5,v2)。然后,根据递归分层抽样的算法对简化后的图进行抽样。接着,简化第1层。在简化第1层中,调用剪枝的BFS从v4出发,遍历那些未被之前的BFS访问过的节点和边。容易发现,在此过程中,仅有(v4,v5)和(v5,v2)这2条边才会被本次剪枝的BFS访问。在第1层中,不能简化任何边,因此简化后的图即为原图。然后再根据递归分层抽样的算法对图1进行抽样。在这个过程中,不难发现,所有的BFS和剪枝BFS过程最多只会对图1中的边访问1次,因此整个图简化的过程的时间复杂度为O(m)。Next, the operation of the entire algorithm will be described by taking FIG. 1 as an example. Suppose now that you need to estimate Figure 1.The influence of the middle node v4. Also, assume that r = 2. The operation process of a hierarchical algorithm will be considered below. The algorithm process of multiple layers is very similar to the process of a layered algorithm, and therefore will not be described again. Suppose you select (v4, v5), (v4, v1) two edges to layer. Where all possible maps of
综上,由于图简化的过程与图的大小呈线性关系,所以整个基于图简化技术的递归分层抽样估算方法的时间复杂度与普通的递归分层抽样算法一致,但是由于本发明集成了图简化的技术,因此在抽取可能图的计算过程中,可以省略那些被简化掉的边,因而可以提高估算速度;此外,由于本发明能够避免选取无用边做分层,而且图简化的过程本身就是在降低概率图的不确定性,因而还可以提高估计精度。In summary, since the process of graph simplification is linear with the size of the graph, the time complexity of the recursive stratified sampling estimation method based on the graph simplification technique is consistent with the ordinary recursive stratified sampling algorithm, but the map is integrated by the present invention. Simplified technique, so in the calculation process of extracting possible graphs, those edges that are simplified can be omitted, so that the estimation speed can be improved; in addition, since the present invention can avoid the use of useless edges for stratification, the process of graph simplification itself is Reduce the uncertainty of the probability map, thusIt also improves the estimation accuracy.
以上所述仅为本发明的较佳实施例而已,并不用以限制本发明,凡在本发明的精神和原则之内所作的任何修改、等同替换和改进等,均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。The above is only the preferred embodiment of the present invention, and is not intended to limit the present invention. Any modifications, equivalent substitutions and improvements made within the spirit and principles of the present invention should be included in the protection of the present invention. Within the scope.
Claims (4)
Translated fromChineseApplications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201510336864.5ACN104951531B (en) | 2015-06-17 | 2015-06-17 | Simplify the user influence in social network evaluation method and device of technology based on figure |
| CN2015103368645 | 2015-06-17 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2016202209A1true WO2016202209A1 (en) | 2016-12-22 |
Family
ID=54166189
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2016/085242CeasedWO2016202209A1 (en) | 2015-06-17 | 2016-06-08 | Method and device for estimating user influence in social network using graph simplification technique |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN104951531B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2016202209A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN117573990A (en)* | 2023-11-22 | 2024-02-20 | 深圳福恋智能信息科技有限公司 | Virtual social network user influence evaluation method and system |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104951531B (en)* | 2015-06-17 | 2018-10-19 | 深圳大学 | Simplify the user influence in social network evaluation method and device of technology based on figure |
| CN108009933B (en)* | 2016-10-27 | 2021-06-11 | 中国科学技术大学先进技术研究院 | Graph centrality calculation method and device |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101551789A (en)* | 2009-05-14 | 2009-10-07 | 天津大学 | Interval propagation reasoning method of Ising graphical model |
| CN102722566A (en)* | 2012-06-04 | 2012-10-10 | 上海电力学院 | Method for inquiring potential friends in social network |
| CN102799625A (en)* | 2012-06-25 | 2012-11-28 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and system for excavating topic core circle in social networking service |
| CN104598605A (en)* | 2015-01-30 | 2015-05-06 | 福州大学 | Method for user influence evaluation in social network |
| CN104951531A (en)* | 2015-06-17 | 2015-09-30 | 深圳大学 | Method and device for estimating user influences in social networking services based on graph simplification technology |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110320250A1 (en)* | 2010-06-25 | 2011-12-29 | Microsoft Corporation | Advertising products to groups within social networks |
| CN102156706A (en)* | 2011-01-28 | 2011-08-17 | 清华大学 | Mentor recommendation system and method |
- 2015
- 2015-06-17CNCN201510336864.5Apatent/CN104951531B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
- 2016
- 2016-06-08WOPCT/CN2016/085242patent/WO2016202209A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101551789A (en)* | 2009-05-14 | 2009-10-07 | 天津大学 | Interval propagation reasoning method of Ising graphical model |
| CN102722566A (en)* | 2012-06-04 | 2012-10-10 | 上海电力学院 | Method for inquiring potential friends in social network |
| CN102799625A (en)* | 2012-06-25 | 2012-11-28 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and system for excavating topic core circle in social networking service |
| CN104598605A (en)* | 2015-01-30 | 2015-05-06 | 福州大学 | Method for user influence evaluation in social network |
| CN104951531A (en)* | 2015-06-17 | 2015-09-30 | 深圳大学 | Method and device for estimating user influences in social networking services based on graph simplification technology |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| LI, RONGHUA ET AL.: "Efficient and Accurate Query Evaluation on Uncertain Graphs via Recursive Stratified Sampling", 2014 ICDE, 31 December 2014 (2014-12-31), pages 892 - 894, XP032595840* |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN117573990A (en)* | 2023-11-22 | 2024-02-20 | 深圳福恋智能信息科技有限公司 | Virtual social network user influence evaluation method and system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN104951531A (en) | 2015-09-30 |
| CN104951531B (en) | 2018-10-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Lofgren et al. | Personalized pagerank estimation and search: A bidirectional approach | |
| CN104102745B (en) | Complex network community method for digging based on Local Minimum side | |
| Kapralov et al. | Spectral sparsification via random spanners | |
| CN104537025B (en) | Frequent episodes method for digging | |
| CN102810113B (en) | A kind of mixed type clustering method for complex network | |
| CN107145526B (en) | An anti-nearest neighbor query processing method for geo-social keywords under road network | |
| CN107766406A (en) | A kind of track similarity join querying method searched for using time priority | |
| CN110968802B (en) | Analysis method and analysis device for user characteristics and readable storage medium | |
| CN113554115B (en) | Three-dimensional model sketch retrieval method based on uncertain learning | |
| Xu et al. | A general framework of hybrid graph sampling for complex network analysis | |
| WO2015094315A1 (en) | Discarding data points in a time series | |
| WO2016202209A1 (en) | Method and device for estimating user influence in social network using graph simplification technique | |
| CN110858805A (en) | Method and device for predicting network traffic of cell | |
| Zhou et al. | Leveraging history for faster sampling of online social networks | |
| Katsis et al. | Combining Databases and Signal Processing in Plato. | |
| CN113779385A (en) | Friend attention degree measurement sequencing method and system based on complex network graph embedding | |
| CN110727836A (en) | Social network analysis system based on Spark GraphX and implementation method thereof | |
| CN102523286A (en) | Method and device for obtaining credit degree of service | |
| Zhang et al. | An improved label propagation algorithm based on the similarity matrix using random walk | |
| Chen et al. | Scaling up Markov logic probabilistic inference for social graphs | |
| Sun et al. | Fast computation for the forest matrix of an evolving graph | |
| CN105426764A (en) | Submodel optimization based parallel abnormal sub-graph detection method and system | |
| CN107229621B (en) | Method and device for cleaning difference data | |
| CN112579831B (en) | Network community discovery method, device and storage medium based on SimRank global matrix smooth convergence | |
| CN104699599B (en) | Interprocedual static slicing extracting method based on five meta structures of idUCf |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | Ref document number:16810950 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 | |
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase | Ref country code:DE | |
| 32PN | Ep: public notification in the ep bulletin as address of the adressee cannot be established | Free format text:NOTING OF LOSS OF RIGHTS PURSUANT TO RULE 112(1) EPC (EPO FORM 1205A DATED 01.06.2018) | |
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase | Ref document number:16810950 Country of ref document:EP Kind code of ref document:A1 |