USRE48546E1 - System and method for presenting content with time based metadata - Google Patents
System and method for presenting content with time based metadataDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- USRE48546E1 USRE48546E1US16/567,246US201916567246AUSRE48546EUS RE48546 E1USRE48546 E1US RE48546E1US 201916567246 AUS201916567246 AUS 201916567246AUS RE48546 EUSRE48546 EUS RE48546E
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- media content
- metadata
- content
- media
- playback
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/47—End-user applications
- H04N21/472—End-user interface for requesting content, additional data or services; End-user interface for interacting with content, e.g. for content reservation or setting reminders, for requesting event notification, for manipulating displayed content
- H04N21/4722—End-user interface for requesting content, additional data or services; End-user interface for interacting with content, e.g. for content reservation or setting reminders, for requesting event notification, for manipulating displayed content for requesting additional data associated with the content
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/40—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of multimedia data, e.g. slideshows comprising image and additional audio data
- G06F16/43—Querying
- G06F16/432—Query formulation
- G06F16/433—Query formulation using audio data
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/40—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of multimedia data, e.g. slideshows comprising image and additional audio data
- G06F16/48—Retrieval characterised by using metadata, e.g. metadata not derived from the content or metadata generated manually
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11B—INFORMATION STORAGE BASED ON RELATIVE MOVEMENT BETWEEN RECORD CARRIER AND TRANSDUCER
- G11B27/00—Editing; Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Monitoring; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/10—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/102—Programmed access in sequence to addressed parts of tracks of operating record carriers
- G11B27/105—Programmed access in sequence to addressed parts of tracks of operating record carriers of operating discs
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11B—INFORMATION STORAGE BASED ON RELATIVE MOVEMENT BETWEEN RECORD CARRIER AND TRANSDUCER
- G11B27/00—Editing; Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Monitoring; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/10—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/11—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel by using information not detectable on the record carrier
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/43—Processing of content or additional data, e.g. demultiplexing additional data from a digital video stream; Elementary client operations, e.g. monitoring of home network or synchronising decoder's clock; Client middleware
- H04N21/431—Generation of visual interfaces for content selection or interaction; Content or additional data rendering
- H04N21/4312—Generation of visual interfaces for content selection or interaction; Content or additional data rendering involving specific graphical features, e.g. screen layout, special fonts or colors, blinking icons, highlights or animations
- H04N21/4316—Generation of visual interfaces for content selection or interaction; Content or additional data rendering involving specific graphical features, e.g. screen layout, special fonts or colors, blinking icons, highlights or animations for displaying supplemental content in a region of the screen, e.g. an advertisement in a separate window
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/43—Processing of content or additional data, e.g. demultiplexing additional data from a digital video stream; Elementary client operations, e.g. monitoring of home network or synchronising decoder's clock; Client middleware
- H04N21/439—Processing of audio elementary streams
- H04N21/4394—Processing of audio elementary streams involving operations for analysing the audio stream, e.g. detecting features or characteristics in audio streams
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/43—Processing of content or additional data, e.g. demultiplexing additional data from a digital video stream; Elementary client operations, e.g. monitoring of home network or synchronising decoder's clock; Client middleware
- H04N21/44—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing a video clip retrieved from local storage with an incoming video stream or rendering scenes according to encoded video stream scene graphs
- H04N21/44008—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing a video clip retrieved from local storage with an incoming video stream or rendering scenes according to encoded video stream scene graphs involving operations for analysing video streams, e.g. detecting features or characteristics in the video stream
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/80—Generation or processing of content or additional data by content creator independently of the distribution process; Content per se
- H04N21/81—Monomedia components thereof
- H04N21/8126—Monomedia components thereof involving additional data, e.g. news, sports, stocks, weather forecasts
- H04N21/8133—Monomedia components thereof involving additional data, e.g. news, sports, stocks, weather forecasts specifically related to the content, e.g. biography of the actors in a movie, detailed information about an article seen in a video program
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/80—Generation or processing of content or additional data by content creator independently of the distribution process; Content per se
- H04N21/85—Assembly of content; Generation of multimedia applications
- H04N21/854—Content authoring
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11B—INFORMATION STORAGE BASED ON RELATIVE MOVEMENT BETWEEN RECORD CARRIER AND TRANSDUCER
- G11B20/00—Signal processing not specific to the method of recording or reproducing; Circuits therefor
- G11B20/10—Digital recording or reproducing
- G11B20/10527—Audio or video recording; Data buffering arrangements
- G11B2020/10537—Audio or video recording
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11B—INFORMATION STORAGE BASED ON RELATIVE MOVEMENT BETWEEN RECORD CARRIER AND TRANSDUCER
- G11B2220/00—Record carriers by type
- G11B2220/20—Disc-shaped record carriers
- G11B2220/25—Disc-shaped record carriers characterised in that the disc is based on a specific recording technology
- G11B2220/2537—Optical discs
- G11B2220/2541—Blu-ray discs; Blue laser DVR discs
Definitions
- Embodiments described hereinpertain generally to a system and method for presenting content, and more specifically, a system and method for presenting content with time based metadata.
- FIG. 1A-1Dillustrate systems for including time based metadata information as a form of supplemental content in connection with the presentation of media content, according to one or more embodiments.
- FIG. 2illustrates a method for generating time based metadata for a media content, according to embodiments.
- FIG. 3illustrates a method for providing media data that is packaged or integrated with time based metadata, according to an embodiment.
- FIG. 4illustrates a method for providing time based metadata to a media source, for transmission to a media playback device with media content, under an embodiment.
- FIG. 5illustrates a method for providing time based metadata to a playback device that receives the media content from a media source, according to another embodiment.
- FIG. 6A through FIG. 6Fillustrate examples of media content presentation that includes metadata content, according to some embodiments described herein.
- FIG. 7A through FIG. 7Fillustrate examples of media content presentations that include metadata content for playback and/or paired devices, according to some embodiments described herein.
- FIG. 8 through FIG. 9Cillustrate various interface tools for facilitating different metadata placement or selection operators in generating metadata for a media content, according to an embodiment.
- FIG. 10A-10Billustrate examples of media content interfaces generated using metadata content for a paired device, according to embodiments described herein.
- FIG. 11illustrates a method for providing media data to be shared or published, according to an embodiment.
- FIG. 12A-12Eillustrate example interfaces for providing media data to be shared or published, according to an embodiment.
- FIG. 13is a block diagram that illustrates a computer system upon which embodiments described herein may be implemented.
- Embodiments described hereininclude a service that enables devices to utilize various web services independent of the communication protocol and format utilized by the devices.
- devices that are capable of media playback and/or web browsingtypically use communication protocols such as XML, EBIF (set-top boxes), REST or JSON.
- communication protocolssuch as XML, EBIF (set-top boxes), REST or JSON.
- content publishersmake available various forms of content, often to supplement or augment the user's playback and/or web browsing experience.
- cinematic studiosoften publish movie previews and bonus clips on websites, which can be downloaded and viewed by a device that uses an XML communication format (e.g. ANDROID device), EBIF (set-top box) or JSON.
- the content publishersare required to address the various communication protocols and formats used by the various devices individually.
- embodiments described hereininclude a service that is capable of interfacing a device using any of multiple possible communication protocols with a web service that may or may not handle the particular communication protocol in question.
- the web service providersmay update functionality and content provided without having to address various possible communication protocols that are in use. Accordingly, otherwise incompatible devices that normally would not communicate with each other may be able to connect, communicate and/or share information.
- BDrefers to Blu-ray Disc®
- BD specificationrefers to the various documents that define the behavior and requirements of BD players, software and related systems, and, in particular, “System Description Blu-ray Disc Read-Only Format: Part 3. Audio Visual Basic Specifications”.
- the BD specificationincludes a section pertaining to virtual file system (“VFS”) updates.
- VFSvirtual file system
- a Blu-ray playergenerally supports a virtual file system (VFS) that utilizes files located on an optical disc itself, as well as files that reside in a local storage area of the playback device.
- VFSvirtual file system
- the Blu-ray environmentgenerally permits updates to the environment by way of new files and content.
- a Blu-ray playeris able to retrieve information and data from a network, under programmatic instructions that originate from logic or software operating on the player, as well as those executing with the disc.
- the Blu-ray playermay be configured to access and retrieve metadata for presentation in connection with media content that is provided at least in part from the optical disc.
- the original contents and functionality of the optical disccan be augmented through the addition of content, namely, audio and video files, application files, or data files, such as those downloaded from a network server.
- Information that updates the playback environment of the playeris received through the VFS of the playback device.
- the servicemay perform functions, such as dynamically generating a manifest for the data communicated to the player, as well as a digital signature that is sufficiently in compliance with Blu-ray Specifications (e.g. See System Description Blu-ray Disc Read-Only Format: Part Audio Visual Basic Specifications”).
- the manifestdefines modifications that are to be made to a file system in the playback device. More specifically, the manifest file maps files located on the Blu-ray disc and in local storage to their relative positions and names in the virtual file system.
- One or more embodiments described hereinprovide that methods, techniques and actions performed by a computing device are performed programmatically, or as a computer-implemented method. Programmatically means through the use of code, or computer-executable instructions. A programmatically performed step may or may not be automatic.
- a programmatic module or componentmay include a program, a subroutine, a portion of a program, or a software component or a hardware component capable of performing one or more stated tasks or functions.
- a module or componentcan exist on a hardware component independently of other modules or components. Alternatively, a module or component can be a shared element or process of other modules, programs or machines.
- one or more embodiments described hereinmay be implemented through the use of instructions that are executable by one or more processors. These instructions may be carried on a computer-readable medium.
- Machines shown or described with figures belowprovide examples of processing resources and computer-readable mediums on which instructions for implementing embodiments of the invention can be carried and/or executed.
- the numerous machines shown with embodiments of the inventioninclude processor(s) and various forms of memory for holding data and instructions.
- Examples of computer-readable mediumsinclude permanent memory storage devices, such as hard drives on personal computers or servers.
- Other examples of computer storage mediumsinclude portable storage units, such as CD or DVD units, flash memory (such as carried on many cell phones and personal digital assistants (PDAs)), and magnetic memory.
- Computers, terminals, network enabled devicese.g.
- mobile devicessuch as cell phones
- processorssuch as RAM
- memorysuch as RAM
- instructionsstored on computer-readable mediums
- embodimentsmay be implemented in the form of computer-programs, or a computer usable carrier medium capable of carrying such a program.
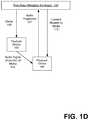
- FIGS. 1A-1Dillustrate a system for including time based metadata information as a form of supplemental content in connection with the presentation of media content, according to one or more embodiments.
- Each of the embodiments described with respect to FIG. 1A - FIG. 1Dincluding components and programmatic processes described with each embodiment, may be used individually or in combination with one another.
- embodiments described hereinenable the rendering of content, such as movies and/or television programs, to be enhanced with the display of relevant metadata information that pertains to events that are part of the content being watched. For example, the appearance of an actor in the movie or program may be supplemented with relevant metadata information that includes the name of the actor who is playing the character, as well as additional information about the actor or character.
- the presence of objects that appear in the contentmay be highlighted by metadata, particularly as to commercial products;
- the use of locations in the contentmay also be supplemented with information about such location; or
- music and/or a soundtrack playing in the audio background or as the primary audio trackmay be supplemented with metadata.
- metadataparticularly as to commercial products
- music and/or a soundtrack playing in the audio background or as the primary audio trackmay be supplemented with metadata.
- Numerous other examplesare provided herein for enhancing or supplementing the presentation of content, such as provided by movies and programs, with metadata information regarding the events that occur as part of the content being watched.
- metadatain the context of movies and programs, refers to information and content that is displayed to the user, but which is not part of the content itself. Rather, such metadata is delivered to the user watching the movie or program as an additional or independent layer.
- system 100is described in the context of multiple operational environments. According to embodiments, a system 100 may be operational in one or more of the operational environments described.
- System 100includes metadata generation subsystem 110 and time metadata service (or services) 120 .
- the metadata generation subsystem 110processes media files 102 corresponding to movies and/or programs.
- the output of the metadata generation 110includes a metadata file 111 , which includes a combination of time stamps 113 and associated information 115 .
- the metadata file 111includes the time stamps 113 by which the sync time triggers 131 can be programmatically or automatically activated by a playback device in order to cause the rendering of associated information or content items for a particular trigger.
- the time stamps 113are timed to coincide with the occurrence of a particular event in the media content.
- Each time stamp 113may signify the beginning of an event, and last for a duration that coincides with the ending of the event.
- the introduction of an actor into a scenemay signify the beginning of a particular time stamp 113
- the actor's exit from the scenemay signify the end of the event associated with the time stamp 113 .
- a time stamp 113may be associated when music or a particular song is played in the background of the media content, and a time stamp 113 may have the duration equivalent to the length of the song (e.g., the duration of time the music is playing).
- One frame or series of frames in the media contentcan be associated with multiple time stamps 113 . Furthermore, each time stamp 113 is associated with a corresponding item of information or content 115 . Such information or content 115 can be displayed over the movie/program content on a playback device, or on a separate, paired device, as a mechanism for providing the viewer with additional information.
- the information and content displayed to the usercan be interactive.
- the usermay select a link presented with the information or content item 115 as a mechanism for viewing additional information, or partaking in a supplemental activity (e.g. make online purchase).
- one or more embodimentsmay include a combination of manual and programmatic resources comprising the metadata generation system 110 .
- a programmatic/manual enhancement 112 componentmay be used to facilitate operators to identify time stamps 113 , and associated information or content 115 .
- the programmatic manual enhancement 112may include a user interface tool 800 that displays a general timeline 812 for a particular movie or program (e.g. the “Incredibles”).
- the user interface tool 800enables an operator to create events for scenes of the media content. The events may correspond to an actor, playing a role in the content, appearing in a scene of the media content.
- the user interface tool 800may also include one or more event columns 814 .
- the event columns 814may include a list of actors, as well as other events relating to the media content.
- the timeline 812extends horizontally relative to the event columns 814 .
- various time stamps 813are identified by the operator each of which corresponds to one or more events in the event column.
- Each time stamp 813is represented by brackets that can vary in dimension to represent a duration of the time stamp 813 over the course of the timeline 812 .
- an operatoris enabled to (i) view a given scene or frame; (ii) view the exact time within the timeline in which the scene takes place; and (iii) have the ability to add new events, as well as to associate a particular senior time stamp 813 within an existing event in the event column 814 .
- the metadata generation subsystem 110can also include programmatic resources to automate the generation of some or all of the metadata.
- programmatic automation 114may be used to identify some or all of the time stamps 113 , as well as to generate some or all of the information or content items associated with individual time stamps 113 .
- the programmatic automation 114uses a script for the media content in order to determine when events occur in the media content (e.g. the introduction of a character into a scene), what the event pertains to (e.g. the character involved), and what the associated information or content item 115 should include (e.g. the name of actor who plays the character of the event).
- closed-captioned text associated with the media contentcan be similarly used.
- some embodimentsmay use image analysis to identify persons or objects appearing in the content. For example, individual frames of the media content may be analyzed for faces, which are then compared to a facial recognition database of actors, in order to determine who the actor is that appears in the content.
- the interface tool 800can include information such as the cast and the soundtrack list.
- informationsuch as the cast and the soundtrack list.
- the operatorcan create a record that contains or references information about the particular event.
- the information or content itemscan be listed for the operator to edit (see list of records 818 ).
- the time based metadata service 120may utilize the metadata file 111 in one or more operational environments.
- the service 120may provide (i) media content that is packaged with time based metadata (as generated by the metadata generation subsystem 110 ); or (ii) time based metadata in connection with media that is to be played back or rendered from a media source independent of the service 120 .
- the service 120combines the time based data 113 and media content 121 for broadcast and/or distribution.
- An intermediate service or step 122may retransmit or deliver the combined time based data 113 and media content 123 to a playback device 118 .
- a combined transmission time based metadata and media content 121may be supplied to a cable head end, which in turn broadcasts (or retransmits) the combined time based data 113 and media content 123 to its user population.
- the time based data and media content 121may be stored onto media (e.g. Blu-ray disc) and distributed through Blu-ray disc distribution channels. Other forms of media may also be used to store the combined time based data and media content 121 .
- the combination of time based data and media content 121may be supplied as a download from a website.
- the playback device 118may correspond to a set-top box, and the intermediate service or step 122 may correspond to a cable head end that delivers the combined time based metadata and media 123 to the set-top box in the appropriate format (e.g. EBIF format).
- the service 120operates to supply the time based metadata 125 independent of the media content that pertains to the metadata. Accordingly, for a particular media content, the service 120 supplies a delivery node or trigger 126 with the time based metadata 125 and media content identifier.
- the delivery node 126may include a broadcast or distribution mechanism 127 , and an application or resource 129 to integrate or otherwise combine the metadata 125 with the underlying media content.
- the metadata 125may be structured to provide time stamps 113 and information or content items 115 all along a timeline that is based on the events that occur during the playback or rendering of the associated media content.
- the integration resource 129may synchronize the metadata 125 with the media content in retransmitting, or otherwise making available (e.g. download), in enhanced form, the media content 130 that includes metadata.
- the delivery node or trigger 126is able to deliver to a playback device 128 , a combination of integrated content or enhanced content 130 that includes the time based metadata and the associated content.
- Various mediums of playbackmay be encompassed by an operational mode such as described with delivery node 126 .
- the delivery node 126may correspond to a cable head end
- the playback device 128may correspond to (or be provided through) a set-top box.
- the integrated content 130may be delivered as an EBIF formatted content.
- the distribution node 126acquires the time based metadata for particular media content on a need to or real time basis.
- the playback device 128is provided as or through a set-top box
- one more embodimentsenable the set-top box or cable head end to request the time based metadata based on user input.
- the distribution node 126may supply the media content identifier to the service 120 , in order to receive the time based metadata 125 for the corresponding media content.
- the service 120supplies the time based metadata 143 to a playback device 138 that receives the media content from another source.
- a media source 132may correspond to, for example, a cable head end, or a website for downloading content, or a media that contains stored media. In the latter case, the media source 132 and media playback device 138 may be provided from the same device of the user.
- the usermay operate the playback device 138 to render media content 135 from the media source 132 .
- the end usercan elect to enhance the media playback with the time based metadata 143 provided through service 120 .
- the usermay make a request 141 for time based metadata information from the service 120 .
- the request 141may specify the media content the user is about to watch.
- the request 141may be generated from the media source 132 , which responds to programmatic conditions and/or user input.
- the service 120Upon receiving the request, the service 120 obtains synchronization timing information 131 from the media source.
- the service 120may query the media source 132 by specifying the media ID 133 for the media content that is to be rendered on the playback device 138 .
- the media sourcein turn may provide the service 120 with the synchronization timing information 131 .
- the synchronization timing information 131may include information that precisely indicates when a content item is to initiate, or where (e.g. which scene or frame) in the timeline of a particular content is being rendered at the time of the query.
- the service 120may query, for example, the user's playback device 138 , which can include media corresponding to the media source.
- the Blu-ray playermay communicate with service 120 over network in order to receive enhanced content in the form of time based metadata 143 .
- the playback devicemay be a television.
- the media source 132may supply the timing information 131 as a one-time event for the particular media content, thus initiating a clock or counter on the service 120 .
- the timing information 131may be provided repeatedly, or on an ongoing basis.
- the service 120supplies time based metadata 143 to the playback device 138 in a manner that synchronizes the timeline of the metadata 143 with that of the media content.
- the service 120supplies enhanced content in the form of time based metadata and the associated media content to a user end device for playback.
- the user and devicemay correspond to, for example, a tablet or personal computer that connects to the service 120 (or its affiliates or partners) via, for example, a website or web service.
- the playback device 148may correspond to, for example, a Blu-ray player or television which receives content and metadata from over a network.
- the user of the playback device 148makes a media request 147 from the service 120 .
- the media request 147may identify an underlying media content, such as a movie or program.
- the service 120supplies enhanced media 149 in that it includes both media and its associated time based metadata.
- the service 120may pre-synchronize the time based metadata with the underlying media content so as to transmit the content and metadata concurrently or at one time.
- the playback device 148may include programming resources that enable it to render both the media content and the information or content item included with the metadata.
- the service 120may be configured to supply the time based metadata 157 to a paired device 160 , in connection with corresponding media being rendered or played back on a user playback device 158 .
- the user playback device 158may correspond to a media source device, such as a Blu-ray player that plays back content from a disk, or tablet that plays back the content from the stored media file.
- the playback device 158may receive the media 155 from the service 120 .
- the playback device 158may receive the media 155 from any media source, such as a cable head end or website.
- the media playback device 158receives the media from the service 120 .
- the metadata 157may be communicated to the paired device 160 .
- the paired device 160makes the request 161 for time based media data of an identified media content.
- the paired device 160may be configured to identify itself as being a paired device, rather than a playback (or primary playback) device.
- the service 120may be configured to identify from the request 161 that the paired device 160 is to receive the time based metadata 157 information for an identified media content, in which the media content is played back on a different device or medium.
- the service 120supplies a time based metadata 157 to the paired device 160 .
- the service 120controls transmission of both the media content and the metadata.
- the service 120is able to synchronize the delivery of metadata information to the paired device 160 , while transmitting media 155 to the playback device 158 .
- the service 120may receive synchronization timing information for media content being played back, so that the delivery of the time based metadata 157 to the paired device 160 is synchronized so that the timelines of the metadata and the media content are aligned.
- the synchronization timing informationmay be received by querying the media source (e.g. cable head end), as similarly described with other embodiments.
- the media playback device 158may provide the necessary synchronization timing information, by initiating playback of the media content upon the paired device 160 receiving the time based metadata 157 .
- the paired device 160may be operated to request the time based metadata 161 that is associated with the media content that is to be played back on the device 158 .
- the usermay operate the paired device 160 to identify the media content that is to be played back on the media playback device 158 .
- the two devices 158 , 160may communicate with one another across, for example, a local communication port (e.g. Bluetooth or WiFi).
- the playback device 158may be triggered to contact the service 120 in response to a playback request from a user (e.g. insertion or play command of a Blu-ray disc, play command for stored media file on a tablet etc.).
- service 120may query the media playback device 158 for synchronization timing information, in response to receiving the request 161 .
- a usermay be associated with an account on the service 120 . Once the user accesses the service 120 , the service 120 locates and communicates with both of the user devices, thus enabling identification of the paired device for receiving the time based metadata 157 .
- the time based metadata 157may be communicated to the paired device 160 from the playback device 158 .
- the playback device 158may synchronize both the time based metadata and the media content by receiving respective transmissions of one or both from an external source (e.g. content source or service 120 ), and then retransmitting the metadata to the paired device 160 .
- the transmission of the metadata 157 to the paired device 160can be done through a communication medium such as, for example, Bluetooth or other short radiofrequency wave communication channels.
- FIG. 1Bis a block diagram illustrating the architecture of the time based metadata service(s) 120 according to some embodiments described with FIG. 1A . More specifically, according to some embodiments, the services described in connection with the use of the time based metadata service (s) 120 may include one or more components, modules or services shown in FIG. 1B depending on the operating environment of the implementation.
- time based metadata service(s) 120may also be configured to map multiple media playback devices to each other thereby enabling the devices to share metadata and/or associated content, even if one or more of the playback devices are not capable of communicating directly with each other.
- the metadata generation subsystem 110processes media files 102 corresponding to movies and/or programs.
- the output of the metadata generation subsystem 110includes a metadata file 111 having a combination of time stamps 113 and associated information 115 or content ( FIG. 1A ).
- the metadata file 111may be sent from metadata generation subsystem 110 while the associated information 115 or content may be provided from a second source, such as, for example, content service(s) 195 .
- the time base metadata service 120can include a content service communication interface 173 to receive content (e.g. movies or programs) from different sources, either in real-time or asynchronously with re-transmission of such content in enhanced form.
- the content service communication interface 173includes a program interface to receive content as file uploads from content providers.
- content interface 173receives content in form of streaming or via broadcast medium (e.g. cable, satellite) or data communications only (e.g. questions for a quiz, consumer user's commentary and web posts, lists of friends related to the content).
- time metadata service(s) 120is configured to associate or map the content (e.g. as received from content service(s) 195 ) to the metadata file 111 and provide the newly associated content to one or more playback devices.
- the metadata file 111may be received via a metadata services(s) communication 170 of the time metadata service(s) 120 and provided to a metadata content mapping component 171 .
- the mapping component 171then associates or maps the metadata 111 with content (e.g., movie or programming content) received from the content service(s) 195 via content service(s) communication 173 .
- the metadata 111includes time stamps that correlate to scenes, frames and/or events in the content.
- the metadata to content mapping 171programmatically links the time stamps and the associated metadata to the run time of the corresponding content. For example, one file, or two linked files may be created that can be played simultaneously by a playback device in order to render the content (e.g. movie) and time based metadata at appropriate times (e.g. frame indicated by the time stamp).
- contente.g. movie
- time based metadatae.g. frame indicated by the time stamp
- the service 120communicates the mapped metadata/content to a playback device using, for example, a delivery node 126 such as described above with respect to FIG. 1A .
- a delivery node 126such as described above with respect to FIG. 1A .
- Other delivery nodessuch as described with FIG. 1A may alternatively be used.
- the service 120may also include a user accounts management service 175 .
- the service 120may associate individual users with accounts, which can incorporate pay for service functionality or other capabilities requiring the activation of an account. For example, functionality provided via the service 120 can be provided via a pay per view or monthly subscription basis.
- account informationcan carry device and user profile information of a particular user.
- Such informationmay include (i) contact information about the user; (ii) one or more identifiers as to a type or types of playback device(s) the user is utilizing; (iii) historical data indicating the interactions of the user with a particular media file; (iv) linked accounts for other web services which the user may have registered to; and/or (v) preferences of the user regarding the output and display of the supplemental content.
- service 120provides programmatic enhancements to enable third-parties (e.g. advertisers) to identify appropriate topics and information to supply with content.
- the service 120includes a programmatic service communication (PSC) 176 that provides an interface for third-parties (e.g. advertisers, content owners, movie studios or sponsors) to research content and time based metadata from a library or collection of media files (e.g. movie library of studio).
- PSCprogrammatic service communication
- the PSC 176can be used by the third-party (e.g. via service 190 ) in order to specify additional metadata content, such as, for example, promotional metadata content.
- the advertisermay use the PSC 176 to specify overlay ads or content that relate to a particular commercial product, or, conversely, a particular commercial product approved for display with a particular media asset.
- the advertisermay also specify the media content, or supply information to have the media content selected programmatically.
- the programmatic mapping component 177can use information provided from the advertiser to perform one or more of the following: (i) select the media content on which the advertiser content is to be displayed, (ii) select the scene(s) or events of the media content, and/or (iii) identify the particular time stamp within the media content that is to serve as the stamp for the supplied content.
- the programmatic mapping 177may include logic (algorithms) to scan media content, its associated metadata and/or time base metadata in order to identify one or more semantic categories corresponding to the media being viewed by the user. This information may be communicated to the programmatic service(s) 190 .
- the servicecan enable manual or programmatic selection of supplemental metadata content, in connection with time based metadata.
- mapping 177can communicate the information to the programmatic service(s) 190 .
- the service 190may then determine which supplemental content (e.g., advertisements regarding dog food, dog breeders, etc.) can be added to the media and provided to the user.
- service 120may also include a device identification service 178 configured to identify a type of playback device utilized by a user.
- the device identification service 178may determine that a user has access to, or is using, a particular device such as, for example, tablet computer, Blu-ray player, set-top box, etc., as well as the communication format for each device (such as determined by device communications 179 ).
- the informationmay be associated with a user and stored using the user accounts management 175 .
- Device identificationmay also trigger the service 120 to operate in one of multiple possible computing environments, as described with prior embodiments.
- Service 120may also include mapping tool 180 configured for associating content received from programmatic mapping service(s) 190 to metadata 111 .
- An exemplary mapping tool 180is shown in FIG. 9A .
- mapping tool 900includes a selector interface 910 to enable a manual operator to filter the time stamps and/or metadata based on scenes.
- the manual operatormay utilize the interface through, for example, the service 190 .
- the interface 910may be generated or provided with the mapping tool 180 .
- the operatorcan view the context of numerous scenes in a media content, view the time based metadata and its information, generate new time based metadata, verify the additional information and/or select other information, if any, that could be added. For example, if a particular song by an artist is playing in the given scene, additional content or advertisements corresponding to additional songs performed by that artist may be selected by the operator to later be provided to the user at the time of content playback.
- songs and/or artists from a particular genre of the identified song and/or artistmay be associated by the operator with the metadata which can be later presented to the user.
- the mapping tool 900may be used on any number of categories such as, for example, clothing, food, scene or shooting locations, scene mood, atmosphere or ambience, objects present in screen, etc.
- the mapping toolmay identify presence of commercial objects, or objects that are identifiable to a theme or topic (e.g. advertisement theme), or other factors, including user specified or user generated (“crowd-sourced”) factors.
- service 120may be configured to map one playback device to another playback device without each of the playback devices having capabilities of communicating directly with each other.
- a first playback devicemay deliver relevant information 115 through service 120 to a second playback device or paired device.
- device communications 179determines a communication protocol of one device and may convert the relevant information 115 from a first communication protocol utilized by the first playback device, to a second communication protocol, utilized by the second playback device.
- the imported metadata and related time stampsmay be imported in a first format (e.g., the format in which they were created) and transferred to a playback as is.
- the time stamps and metadataare programmatically processed to match the structure of the metadata file 111 and/or the playback device to which the information will be sent.
- FIG. 1C - FIG. 1Dillustrate variations or additions to embodiments described in FIG. 1A and/or FIG. 1B .
- FIG. 1Cillustrates an architecture in which the service 120 provides the media 149 to a playback device (e.g., playback device 148 ).
- the playback device 158communicates an audio fingerprint 151 to the service 120 .
- the audio fingerprintcan be used to determine information about the media content, such as which media content is being played back, or alternatively, which scene is being played back.
- the audio fingerprint 151can be communicated to the service and used to identify the media content, or the particular portion or scene of the media content.
- the media ID 133can be determined from the audio fingerprint 151 .
- This informationis provided to the service 120 which, under some embodiments, can map or associate the relevant time stamps 113 to the identified media ID 133 and provides the Information 115 back to the playback device 148 .
- an audio signal 153 associated with the media 149may be played on a first device (e.g., playback device 158 ) and listened to on a paired device (e.g., paired device 160 ) after which the paired device 160 provides the audio fingerprint 151 to the service 120 .
- a first devicee.g., playback device 158
- a paired devicee.g., paired device 160
- the audio fingerprint 151is identified and mapped to a media ID 133 and the information is provided to the service 120 .
- Service 120maps or associates the relevant time stamps 113 to the identified media ID 133 and provides the information 115 back to the paired device 160 .
- the relationship between the paired device 160 and playback device 158may be reversed such that the paired device 160 transmits the audio signal to the playback device 158 , which in turn, transmits the audio fingerprint to the service 120 .
- the paired devicemay be used to receive metadata, either from the service or from the playback device 158 , 160 .
- the paired devicecan alternatively display portions of the content.
- FIG. 2 through FIG. 5illustrate various embodiments for providing time based metadata in connection with the rendering of a media content.
- Methods, such as described by FIG. 2 through FIG. 5may be implemented using components such as described with a system of FIG. 1 . Accordingly, reference to elements of system 100 is intended to illustrate suitable components or subsystems for performing a step or sub step being described.
- FIG. 2illustrates a method for generating time based metadata for a media content, according to embodiments.
- the media contentmay correspond to, for example, a movie, a television program, a short film, an animation, a homemade video, or other audio/video work or creation.
- the media contentmay be processed or analyzed ( 210 ) using programmatic resources that facilitate manual operation and/or automation.
- embodimentsmay include a metadata generation sub-system 110 that includes a manual editor interface (e.g. See FIG. 8 ), and one or more programmatic resources that enable automated processing.
- the automated resourcescan include, for example, image analysis ( 214 ) which uses image recognition to identify persons and objects appearing in the content.
- the automated processcan include steps for analyzing script and/or closed-captioned analysis ( 216 ), which uses text content associated with the content in order to facilitate programmatic detection of events (e.g. the presence of a person in a scene, the use of a location, etc.).
- steps for analyzing script and/or closed-captioned analysis216
- uses text content associated with the contentin order to facilitate programmatic detection of events (e.g. the presence of a person in a scene, the use of a location, etc.).
- the media contentis processed in order to identify the occurrence of events for which supplemental information or content can be provided ( 220 ).
- Various kinds of eventsmay be detected in the media content. These include, for example, events pertaining to (i) an actor or character ( 222 ), (ii) the use of objects ( 224 ), such as commercial objects, (iii) the playing of songs or supplemental media (e.g. television show in background) as part of the media content, and/or (iv) depiction of locations ( 226 ) (e.g. landmarks, geographic regions etc.).
- the events of the media contentmay be individually associated with time stamps that are included as part of an associated metadata file ( 230 ).
- the metadata fileis structured to reflect a timeline of the media content.
- the occurrence of an event in the media contentmay be signified by a trigger, which is marked in the metadata file to coincide with the occurrence of the event at the playtime of the media content. In this way, individual triggers are associated with corresponding events of the media content.
- time stampsthat signify the presence of an actor or character in a scene of the media content may be linked to a data item that includes additional information about the actor, the character or the scene.
- Each time stampcan be linked to a data file that contains additional information pertaining to the event signified by the time stamp.
- the data filemay be created programmatically and/or manually. For example, if an actor is signified by a time stamp, programmatic resources may automatically identify a profile of the actor from a movie database and include information (or a link) to the movie profile as part of the data item that is associated with the time stamp.
- an operatormay manually edit or create content for the data item that is associated with the trigger.
- metadata generation subsystem 110processes a media content in order to detect events that occur as part of the media content.
- the metadata generation sub-system 110associates the detected events with time stamps, which are in turn associated with timing information that signifies when the events occur during the playback of the media content. Additionally, the detected events can be associated with information or content items that supplement the content during portions that coincide with the placement of a corresponding time stamps (signifying when the event is taking place as part of the content).
- the metadata generation sub-system 110includes a manual editor interface (e.g. see FIG.
- programmatic enhancementsfor facilitating an operator in (i) inserting time stamps along an appropriate timeline of the corresponding media content, (ii) associating time stamps with data items (e.g. information/content), or programmatic services 190 or content services 195 that pertain to (e.g. describe or supplement) the event identified by each of the time stamps.
- data itemse.g. information/content
- programmatic services 190 or content services 195that pertain to (e.g. describe or supplement) the event identified by each of the time stamps.
- the process of event detection and subsequent data item associationmay be performed programmatically and with automation.
- individual frames that comprise the video portion of the media contentare analyzed using image analysis. For example, individual frames are analyzed to detect faces, and to associate the faces with identities of persons (e.g. actors) from a database.
- frames of the media contentmay be analyzed to detect objects (e.g. commercial objects) and to recognize the objects by type of brand using image analysis. The objects can then be mapped to programmatic services 190 or content services 195 .
- the metadata fileis made available to manual operators.
- the manual operatorsmay utilize tools shown and described with respect to FIG. 9A through FIG. 9C to check the accuracy of the time stamps, and the associations of those time stamps with relevant information 115 and programmatic services 190 or content services 195 .
- toolsmay be used by third-party metadata providers.
- the time stamps and metadataare then communicated to playback devices and/or media sources for use with playback of the associated media file ( 250 ).
- the contents of the metadata filecan be transmitted in real-time, to coincide with playback of the associated media content on a playback device.
- the contents of the metadata filecan be transmitted and stored in a playback environment, for use when the associated media content is played back from a particular source or on a paired device 160 at a later time.
- the metadata file and/or its contentscan be transmitted to a media source (e.g. cable head-end, website) where it is re-transmitted to a user playback device (e.g. set-top box).
- the metadatamay be transmitted to the media source (e.g. cable broadcast, website).
- the receiving media sourcemay combine a media content transmission with the metadata, so as to transmit the media content and the metadata to the user for playback.
- the media sourcemay include programmatic resources for (i) requesting the metadata that is to accompany the media content transmission, and (ii) combining transmission of the metadata with the media content, including synchronizing the delivery of metadata with the transmission of the media content along a timeline that is reflected by the media content.
- the contents of the metadata filecan be communicated to the playback device while the playback device receives the media content from another media source (e.g. cable/set top box, website).
- the playback devicemay receive the metadata from time metadata service 120 , while receiving the coinciding media content from a media source (e.g. cable head end).
- the service 120may synchronize the transmission of the metadata using reference timing information for the playback of the media content (e.g. start time).
- the playback devicemay synchronize the receipt of metadata from one source with the receipt of media content from another source in creating an enhanced playback containing both the media content and the time based metadata.
- the contents of the metadata filemay be transmitted and stored by, for example, a user of a playback device.
- the stored filecan be accessed and used when the playback device renders the associated media content or file.
- the metadata filemay be transmitted to a paired device of a user, for use in conjunction with rendering of the associated media content on a playback device.
- the metadata filemay be transmitted over a network to a tablet device that the user can hold and view, while watching the associated media content on a set-top box or Blu-ray environment.
- FIG. 3illustrates a method for providing media content that is packaged or integrated with time based metadata, according to an embodiment.
- a metadata fileis generated for a particular media content ( 310 ).
- the metadata filemay be structured to include timing information that identifies the occurrence of events in the runtime of the corresponding media content.
- the metadata filemay be provided as a separate file from the media content, but the packaging of the metadata with the media content can inherently include programmatic resources that can trigger the metadata file and the media content to synchronously initiate their respective playback, so that the timeline for each of the metadata and the media content are aligned during the playback of the media content.
- the metadatais packed with the media file and then delivered ( 320 ).
- the combined media and metadataare transmitted to a media source, such as a broadcast source (e.g. cable head end in distribution) or website, where the data is retransmitted to a playback device of the user ( 322 ).
- the combined media and metadataare transmitted to the media playback device of a user without an intervening distribution of broadcast source ( 324 ).
- service 120may be provided through a website that can deliver the combined media and metadata package to an end user operating a computing device, such as a laptop, personal computer, game station, or Internet television.
- the combined metadata and mediamay be provided on a storage medium, such as on a Blu-ray disc, or flash memory device (e.g. accessory device, tablet) ( 326 ).
- FIG. 4illustrates a method for providing time based metadata to a media source, for transmission to a media playback device with media content, under an embodiment.
- a method such as described with FIG. 4may be implemented to enable a media source to deliver or otherwise provide media content in an enhanced form (as provided by time based metadata).
- a media sourcee.g. broadcaster
- the requestmay be initiated by the media playback device of the user, which may use a network connection to communicate with the service 120 separately from the media source.
- the service 120may respond to the request by delivering metadata associated with the media content identified in the request to the media source ( 420 ).
- the media sourcemay be provided with programmatic resources to synchronize the timing of the metadata with the playback of the media content ( 430 ).
- the media sourcemay include an application that synchronizes the metadata with the playback of the media content, so as to transmit both metadata and media content in synchronous fashion to the media playback device.
- the media playback devicemay request and receive the metadata independently from the media source.
- the media playback devicemay request the metadata from the service 120 .
- the service 120may acquire the synchronization timing information from the media source, and deliver metadata in real-time to the playback device.
- the playback devicemay receive the metadata in real-time or synchronously, and include programmatic resources for synchronizing the playback of the metadata with the associated media content. Numerous such variations are possible.
- FIG. 5illustrates a method for providing time based metadata to a playback device that receives the media content from a media source, according to another embodiment.
- a userrequests metadata for a media content that the user is to playback ( 510 ).
- the media contentmay, for example, reside on the user's device, or be provided from a separate media source (e.g. cable or website).
- the service 120may respond to the request in real-time, so as to transmit metadata concurrently and in-sync with playback of the media content on the playback device.
- service 120may acquire synchronization timing information in order to transmit the media content in sync ( 520 ).
- the synchronization timing informationmay correspond to, for example, the exact time that the media content was initiated, or the precise frame or portion of the media content that is rendered at a reference time.
- the service 120acquires the synchronization timing information from the media source ( 522 ).
- the service 120acquires the synchronization timing information from the media playback device ( 524 ).
- the media sourcemay reside on a user device.
- the media sourcemay correspond to a Blu-ray player.
- the synchronization timing informationmay be communicated from the Blu-ray player of the user.
- the service 120may then transmit the metadata information in real-time to the device of the user ( 530 ).
- the metadatais transmitted to the media playback device of the user ( 532 ).
- the metadatais transmitted to a paired device of the user ( 534 ).
- the paired devicemay correspond to, for example, a tablet, smart phone or laptop, while the media playback device may correspond to a set-top box and television, personal computer, Blu-ray player or Internet television.
- the service 120may maintain an account for the user from which it maintains information to identify and locate the media playback device and the paired device on a network.
- the service 120can broker a request.
- service 120may provide response actions to a user interacting with the media, either through the playback device or paired device and connect the user to programmatic services 190 or content services 195 .
- FIG. 6A through FIG. 6Fillustrate examples of media content presentation that includes metadata content, according to some embodiments described herein.
- the enhanced presentation of media contentmay be implemented using, for example, a system such as described with an embodiment of FIG. 1 . Accordingly, reference is made to elements of FIG. 1 for purpose of illustrating suitable components or elements for creating metadata presentations as shown.
- FIG. 6Aillustrates a media content presentation that is enhanced with presentation of time based metadata, in accordance with one or more embodiments.
- the media contentis a movie
- the metadata that is presented with the movieincludes actor names for characters that appear in individual scenes.
- a given sceneis marked by the presence of three actors.
- Eachare identified by metadata items 602 .
- the metadata items 602may also include additional information, such as the name of the character that the actor is playing in the given content item.
- a song or track that starts playing in a scenemay include an informational tag 604 .
- the metadata filemay be provided in form of a file that includes time based triggers that coincide with the timeline of the movie.
- the informational tagis presented as an overlay.
- FIG. 6Billustrates the information tag being interactive or able to include supplemental information, such as the filmography 606 of an individual actor.
- the useris able to interact with the information tags that appear over the media content.
- the user interactionmay, for example, be the user operating the playback or paired device requesting additional or supplemental metadata from the metadata source (which may be the media source or the service 120 ).
- the user interactionmay be a request to receive (e.g., video on demand, purchase a digital copy, or Blu-ray copy etc.) and/or view additional media content the selected actor(s) is in.
- FIG. 6Cillustrates additional examples of metadata content that can be overlaid with the media content.
- the metadata content 612can occupy a majority of the screen space, so as to present additional information about the actor (or event that is being described).
- FIG. 6Dillustrates an example in which metadata includes supplemental information or services, such as an interactive feature that enables the user to purchase a product associated with an event of media content (or the media content itself).
- the useris able to purchase a soundtrack by interacting with metadata content 622 .
- the metadata content 622can be displayed to the user at, for example, the occurrence of a relevant event, such as the playback of a song that appears on the soundtrack.
- FIG. 6E and FIG. 6Fillustrate the user of metadata content that coincide with product placement within a media content.
- the product placement eventcoincides with an actor of a television show riding in a sports car.
- the metadata content 624identifies, for example, the make and model of the car. Additional information, such as information about the character 626 or program, may also be displayed as an overlay of the content.
- FIG. 7A through FIG. 7Fillustrate examples of media content presentations that include metadata content for playback and/or paired devices, according to some embodiments described herein.
- a useris able to login to a service that is provided in connection with the playback of the media content.
- the usermay include an account with service 120 , and have the ability to login in order to receive metadata in connection with media content that is either received from the service, from a different media source (e.g. cable or website), or played back from a local source (e.g. Blu-ray player).
- FIG. 7Cillustrates an implementation in which the metadata presentation over the media content is personalized.
- the metadata content presentationmay also be configured or tailored for the particular user based on, for example, preferences of the user. For example, as shown in FIG. 7C , the user preference may be to have all spoken dialogue displayed in real time.
- FIG. 7D through FIG. 7Fillustrate presentations that supplement the media content independently of the media content presentations.
- Such supplemental presentationsmay be displayed on a playback device in lieu of, for example, the media content (e.g. the media content may be paused), or displayed on a paired device (e.g. tablet) while the user watches the media content on a media playback device (television).
- the supplemental metadata contentmay be provided independent of the occurrence of events or triggers.
- the supplemental content showing the website contentmay be accessible to the user throughout the playback of the media content.
- the presentationsinclude, for example, website content which can display various forms of content about individual characters of a program.
- the supplemental contentincludes online auction or e-commerce content from programmatic services 190 or content services 195 .
- programmatic services 190 or content services 195Various alternatives to the form of supplemental content that can be displayed are possible.
- an operator of the metadata generation sub-system 110may place metadata according to a default criteria (e.g. identify all actors, songs, bibliography etc.).
- Other operators, such as users of the service 190may place metadata by themes.
- the operatorsmay be provided an interface (e.g. See FIG. 9A and FIG. 9C ) where metadata is identified, and commercial or user-selected themes can be specified for scene(s). The operator can view the content, the product placement, see tags associated with placed content etc. to develop product placement, themes and other content.
- a usermay be able to check the relevant information in a particular scene such as items of clothing worn by the actors, information regarding the character played by the actor, and/or a story line associated with the scene.
- the user interface tool of FIG. 9Cmay present metadata information 115 as an overlay to the media file 102 .
- a manual operatormay verify the accuracy of the metadata mapping to the time stamps 113 .
- the manual operatormay also determine the relevance of the information to the content of the media.
- the user interface toolis dynamic, and the visual elements of the interface appear and disappear as the timeline of the media 115 is traversed.
- a web based toolmay be provided to enable the manual operator to selectively verify information in a particular scene.
- the manual operatormay be able to select one or more categories of the supplemental content to verify (e.g., products, portrayals etc.). As a result, only information corresponding to the selected categories will be displayed. Additionally, the manual operator may be able to add events and/or content using this tool.
- FIG. 10A-10Billustrate examples of media content interfaces generated using metadata content for a paired device, according to embodiments described herein.
- a paired device 160may receive time based metadata, such as from metadata service 120 , in connection with corresponding media being rendered or played back on a user playback device 158 .
- Embodimentsprovide for the programmatic services on the paired device 1000 (e.g. a phone, tablet or personal computer) receiving metadata corresponding to a media being rendered or played back on a main playback device, and providing selectable features to enable a user to access supplemental content related to the received metadata in an interface 1000 .
- the interfaces of FIGS. 10A and 10Bmay be in lieu of or in addition to any interfaces displayed on the main playback device.
- An indicator 1002may be provided to specify to a user that the features being displayed include content relating to the media playback, relative to the beginning and end of the media.
- the interfaces of FIG. 10A-10Binclude a plurality of selectable features 1004 that relate to persons or objects appearing in the media.
- the featuresinclude graphical and/or text content that describe persons or objects appearing in the media being rendered or played back on the user playback device, and further describe supplemental content which may be generated and displayed in response to a user selection of the feature.
- the graphical content of the featuremay include an image from the media being rendered or played back on the user playback device, and when selected may cause the interface to be removed and a supplemental content (e.g. graphic and/or text content) relating to the media and/or feature to be displayed on the paired device.
- generating the supplemental contentmay include, in response to a user selection of a selectable feature, causing a larger version of the image and a text caption to be displayed on the paired device.
- a series of features 1004 , 1006 and 1008are displayed on the interface 1000 .
- Embodimentsprovide for the features to be selectable by a user.
- the paired deviceis a mobile computing device that includes a touch screen display
- the interface 1000is provided on the touch screen display
- the usermay select a particular feature by touching the portion of the screen corresponding to the selectable feature.
- service 120can detect selection of the feature and provide supplemental content on the main playback device and/or on the paired device 1000 corresponding to the selected feature.
- the supplemental contentmay include, for example, information about actors or objects that relate to a description of the selected feature, and the information may be displayed on the paired device.
- the service 120may cause content to be displayed on the paired device relating to characters who appear in the scene and/or the graphic of the feature.
- FIG. 10Billustrates a media content interface in an embodiment of the invention.
- a series of selectable features 1010are displayed on the interface.
- the selectable features 1010may cause supplemental content to be displayed on the user playback device and/or the paired device.
- the example of solid-square features 1012which display solid squares without any graphical or text content, may be replaced with selectable features 1010 by programmatic services on the paired device including graphical and/or text content based on time based metadata such as supplied by metadata services 120 .
- the selectable features 1010may be replaced by solid-squares features 1012 (or other selectable features) based on the time based metadata.
- FIG. 11illustrates a method for providing media data to be shared or published, according to an embodiment.
- a method such as described by an embodiment of FIG. 11can be implemented using components such as described with other embodiments (e.g., a system of FIG. 1 ). Accordingly, reference may be made to elements of FIG. 1 for purpose of illustrating suitable components for performing a step or sub-step being described.
- a useridentifies a movie segment to share ( 1110 ).
- a usercan specify input that corresponds to the movie segment using user playback device 158 and/or on the paired device 160 ( 1112 ).
- the inputcan identify the start/finish times, in reference to a movie's runtime. In this way, the timing specification can designate a beginning time and an end time of the movie segment.
- the user inputcan identify a predefined segment ( 1114 ).
- the predefined segmentmay have a set of predefined features, for example a predefined start/finish time.
- the user playback device 158 and/or the paired device 160may respond to the user input, by, for example, communicating the identified segment to a service or set top box, etc. ( 1116 ).
- the paired device 1160can, for example, determine, from user input, the start/end times for a movie, and then communicate the start/end times (along with an identifier of the movie) to the service or set top box.
- a usercan operate the paired device 160 in order to provide input that identifies the desired segment ( 1118 ).
- a user's interaction with a second screene.g., touch screen
- a second screen interaction 1118may be provided to a user in response to determine, for example, a predefined segment.
- Various other input mechanisms and/or interfacescan be used to enable a user to specify an input corresponding to a segment of the movie.
- a linkis generated ( 1120 ).
- the linkmay be generated to include, for example, data elements that provide or correspond to one or more of the following: (i) data that identifies a location of source file for the movie or movie segment ( 1122 ), (ii) start and end times for the segment ( 1124 ), (iii) time-based metadata that is associated with the segment of the movie (persons and/or objects that appear or are referenced in the identified segment) ( 1126 ).
- an identifier for the movie segmentcan be identified by the link.
- the linkcan be a selectable hypertext link that, when triggered, causes the identified movie segment 1110 to be played or otherwise displayed.
- the generated linkcan be published ( 1130 ). This can include publishing the link on a social networking account ( 1132 ) (e.g. Facebook, or any social network known in the art) or sharing the link through messaging ( 1134 ). For example, the link can be shared by sending the link by e-mail, text message, or another direct form of communication.
- a social networking accounte.g. Facebook, or any social network known in the art
- messaging1134
- the linkcan be shared by sending the link by e-mail, text message, or another direct form of communication.
- FIG. 12A-12Eillustrate example interfaces for providing media data to be shared or published, according to an embodiment.
- the interfacescan be provided for use on, for example, a mobile computing device or tablet.
- the interface 1210can enable a user to provide inputs through interaction with, for example, a mobile computing device 1200 .
- the mobile computing deviceor tablet or other computing device
- the usertriggers a selectable feature 1210 .
- the feature 1210can programmed to, for example, identify a segment, or alternatively provide user input that identifies a start/finish for the movie segment.
- time-based metadatae.g., related shopping panel 1214
- the user inputcan also be used to enable the user to publish the clip 1215 of the segment.
- the usercan communicate the clip 1215 to the service, either with or without, for example, the time-based or rich metadata.
- FIG. 12Billustrates an interface where a user initiates sharing or publishing of the clip 1215 by preparing an email message.
- the usermay designate a recipient of the email message.
- a subject linecan optionally be automatically pre-populated based on, for example, metadata associated with the selected segment or movie.
- FIG. 12Cillustrates an interface where the user may view an image for inclusion in the email message.
- the imagemay, for example, correspond to a frame from the clip.
- the interfacecan enable the user to provide commentary, such as a text comment, with the link that is shared.
- the text commentarycan be provided with an email message.
- a usermay provide a comment (“This is my favorite moment in this show”) which will be included in the email message.
- the interfacecan enable the user to provide the commentary in connection with a link that is published on, for example, a social networking account.
- FIG. 12Eillustrates an interface where the user has shared the clip by sending the email message.
- the messageincluded an image corresponding to the clip, a text comment prepared by the user, and the published link.
- FIG. 13is a block diagram that illustrates a computer system upon which embodiments described herein may be implemented.
- system 100may be implemented using a computer system such as described by FIG. 13 .
- service 120(or portions thereof) may be implemented on a computer system such as shown and described with FIG. 13 .
- the computer service 120may communicate with playback devices, paired devices and/or distribution sources of media content and/or associated metadata using a network such as the Internet.
- a metadata generation sub-system 110may be implemented using a computing system such as shown and described by FIG. 13 .
- computer system 1300includes processor 1304 , main memory 1306 , ROM 1308 , storage device 1310 , and communication interface 1316 .
- Computer system 1300includes at least one processor 1304 for processing information.
- Computer system 1300also includes a main memory 1306 , such as a random access memory (RAM) or other dynamic storage device, for storing information and instructions to be executed by processor 1304 .
- Main memory 1306also may be used for storing temporary variables or other intermediate information during execution of instructions to be executed by processor 1304 .
- Computer system 1300may also include a read only memory (ROM) 1308 or other static storage device for storing static information and instructions for processor 1304 .
- a storage device 1310such as a magnetic disk or optical disk, is provided for storing information and instructions.
- the communication interface 1316may enable the computer system 1300 to communicate with one or more networks through use of the network link 1320 .
- Computer system 1300can include display 1312 , such as a cathode ray tube (CRT), a LCD monitor, and a television set, for displaying information to a user.
- An input device 1314is coupled to computer system 1300 for communicating information and command selections to processor 1304 .
- Other non-limiting, illustrative examples of input device 1314include a mouse, a trackball, or cursor direction keys for communicating direction information and command selections to processor 1304 and for controlling cursor movement on display 1312 . While only one input device 1314 is depicted in FIG. 13 , embodiments may include any number of input devices 1314 coupled to computer system 1300 .
- Embodiments described hereinare related to the use of computer system 1300 for implementing the techniques described herein. According to one embodiment, those techniques are performed by computer system 1300 in response to processor 1304 executing one or more sequences of one or more instructions contained in main memory 1306 . Such instructions may be read into main memory 1306 from another machine-readable medium, such as storage device 1310 . Execution of the sequences of instructions contained in main memory 1306 causes processor 1304 to perform the process steps described herein. In alternative embodiments, hard-wired circuitry may be used in place of or in combination with software instructions to implement embodiments described herein. Thus, embodiments described are not limited to any specific combination of hardware circuitry and software.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Library & Information Science (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Two-Way Televisions, Distribution Of Moving Picture Or The Like (AREA)
- Television Signal Processing For Recording (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims (20)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/567,246USRE48546E1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2019-09-11 | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201161497023P | 2011-06-14 | 2011-06-14 | |
| US13/523,829US9762967B2 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2012-06-14 | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
| US16/567,246USRE48546E1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2019-09-11 | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/523,829ReissueUS9762967B2 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2012-06-14 | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| USRE48546E1true USRE48546E1 (en) | 2021-05-04 |
Family
ID=47357474
Family Applications (4)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/523,829CeasedUS9762967B2 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2012-06-14 | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
| US15/670,883ActiveUS10306324B2 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2017-08-07 | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
| US16/281,229PendingUS20190394531A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2019-02-21 | System And Method For Presenting Content With Time Based Metadata |
| US16/567,246ActiveUSRE48546E1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2019-09-11 | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
Family Applications Before (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/523,829CeasedUS9762967B2 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2012-06-14 | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
| US15/670,883ActiveUS10306324B2 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2017-08-07 | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
| US16/281,229PendingUS20190394531A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2019-02-21 | System And Method For Presenting Content With Time Based Metadata |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (4) | US9762967B2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2012174301A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (193)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8413205B2 (en) | 2001-09-19 | 2013-04-02 | Tvworks, Llc | System and method for construction, delivery and display of iTV content |
| AU2002327677A1 (en) | 2001-09-19 | 2003-04-01 | Meta Tv, Inc. | Interactive user interface for television applications |
| US8042132B2 (en) | 2002-03-15 | 2011-10-18 | Tvworks, Llc | System and method for construction, delivery and display of iTV content |
| US11388451B2 (en) | 2001-11-27 | 2022-07-12 | Comcast Cable Communications Management, Llc | Method and system for enabling data-rich interactive television using broadcast database |
| US7703116B1 (en) | 2003-07-11 | 2010-04-20 | Tvworks, Llc | System and method for construction, delivery and display of iTV applications that blend programming information of on-demand and broadcast service offerings |
| US8220018B2 (en) | 2002-09-19 | 2012-07-10 | Tvworks, Llc | System and method for preferred placement programming of iTV content |
| US8578411B1 (en) | 2003-03-14 | 2013-11-05 | Tvworks, Llc | System and method for controlling iTV application behaviors through the use of application profile filters |
| US11381875B2 (en) | 2003-03-14 | 2022-07-05 | Comcast Cable Communications Management, Llc | Causing display of user-selectable content types |
| US10664138B2 (en) | 2003-03-14 | 2020-05-26 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Providing supplemental content for a second screen experience |
| US8819734B2 (en) | 2003-09-16 | 2014-08-26 | Tvworks, Llc | Contextual navigational control for digital television |
| US7818667B2 (en) | 2005-05-03 | 2010-10-19 | Tv Works Llc | Verification of semantic constraints in multimedia data and in its announcement, signaling and interchange |
| US20110191809A1 (en) | 2008-01-30 | 2011-08-04 | Cinsay, Llc | Viral Syndicated Interactive Product System and Method Therefor |
| US11227315B2 (en) | 2008-01-30 | 2022-01-18 | Aibuy, Inc. | Interactive product placement system and method therefor |
| US8312486B1 (en) | 2008-01-30 | 2012-11-13 | Cinsay, Inc. | Interactive product placement system and method therefor |
| US11832024B2 (en) | 2008-11-20 | 2023-11-28 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Method and apparatus for delivering video and video-related content at sub-asset level |
| US20130191745A1 (en)* | 2012-01-10 | 2013-07-25 | Zane Vella | Interface for displaying supplemental dynamic timeline content |
| US12212791B2 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2025-01-28 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Metadata delivery system for rendering supplementary content |
| WO2012174301A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2012-12-20 | Related Content Database, Inc. | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
| US9210208B2 (en)* | 2011-06-21 | 2015-12-08 | The Nielsen Company (Us), Llc | Monitoring streaming media content |
| KR101753547B1 (en)* | 2011-08-04 | 2017-07-03 | 이베이 인크. | Content display systems and methods |
| US8935719B2 (en) | 2011-08-25 | 2015-01-13 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Application triggering |
| IN2014CN02406A (en) | 2011-08-29 | 2015-06-19 | Cinsay Inc | |
| US8689255B1 (en) | 2011-09-07 | 2014-04-01 | Imdb.Com, Inc. | Synchronizing video content with extrinsic data |
| US9339691B2 (en) | 2012-01-05 | 2016-05-17 | Icon Health & Fitness, Inc. | System and method for controlling an exercise device |
| US9197911B2 (en)* | 2012-02-16 | 2015-11-24 | Gopop.tv | Method and apparatus for providing interaction packages to users based on metadata associated with content |
| US20130222418A1 (en)* | 2012-02-24 | 2013-08-29 | Ihigh.Com, Inc. | Providing a Graphic for Video Production |
| US9576334B2 (en) | 2012-03-26 | 2017-02-21 | Max Abecassis | Second screen recipes function |
| US9583147B2 (en) | 2012-03-26 | 2017-02-28 | Max Abecassis | Second screen shopping function |
| US9609395B2 (en) | 2012-03-26 | 2017-03-28 | Max Abecassis | Second screen subtitles function |
| US9578370B2 (en) | 2012-03-26 | 2017-02-21 | Max Abecassis | Second screen locations function |
| US20130276008A1 (en)* | 2012-04-12 | 2013-10-17 | Google Inc. | Content Based Advertising |
| US20130283143A1 (en)* | 2012-04-24 | 2013-10-24 | Eric David Petajan | System for Annotating Media Content for Automatic Content Understanding |
| US10277933B2 (en)* | 2012-04-27 | 2019-04-30 | Arris Enterprises Llc | Method and device for augmenting user-input information related to media content |
| US10389779B2 (en) | 2012-04-27 | 2019-08-20 | Arris Enterprises Llc | Information processing |
| US9607330B2 (en) | 2012-06-21 | 2017-03-28 | Cinsay, Inc. | Peer-assisted shopping |
| US10789631B2 (en) | 2012-06-21 | 2020-09-29 | Aibuy, Inc. | Apparatus and method for peer-assisted e-commerce shopping |
| US9800951B1 (en) | 2012-06-21 | 2017-10-24 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Unobtrusively enhancing video content with extrinsic data |
| JP5593352B2 (en)* | 2012-07-10 | 2014-09-24 | ヤフー株式会社 | Information providing apparatus, information providing method, and information providing program |
| US9113128B1 (en) | 2012-08-31 | 2015-08-18 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Timeline interface for video content |
| US8763041B2 (en)* | 2012-08-31 | 2014-06-24 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Enhancing video content with extrinsic data |
| US8955021B1 (en)* | 2012-08-31 | 2015-02-10 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Providing extrinsic data for video content |
| US8763042B2 (en) | 2012-10-05 | 2014-06-24 | Motorola Mobility Llc | Information provision |
| US11115722B2 (en) | 2012-11-08 | 2021-09-07 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Crowdsourcing supplemental content |
| US9544647B2 (en) | 2012-11-21 | 2017-01-10 | Google Technology Holdings LLC | Attention-based advertisement scheduling in time-shifted content |
| US9389745B1 (en) | 2012-12-10 | 2016-07-12 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Providing content via multiple display devices |
| US20140201778A1 (en)* | 2013-01-15 | 2014-07-17 | Sap Ag | Method and system of interactive advertisement |
| GB2510424A (en)* | 2013-02-05 | 2014-08-06 | British Broadcasting Corp | Processing audio-video (AV) metadata relating to general and individual user parameters |
| US10424009B1 (en) | 2013-02-27 | 2019-09-24 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Shopping experience using multiple computing devices |
| WO2014138305A1 (en)* | 2013-03-05 | 2014-09-12 | Grusd Brandon | Systems and methods for providing user interactions with media |
| US9414114B2 (en) | 2013-03-13 | 2016-08-09 | Comcast Cable Holdings, Llc | Selective interactivity |
| WO2014153158A1 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2014-09-25 | Icon Health & Fitness, Inc. | Strength training apparatus with flywheel and related methods |
| US10880609B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2020-12-29 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Content event messaging |
| US20140282683A1 (en)* | 2013-03-14 | 2014-09-18 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Computing system with device interaction mechanism and method of operation thereof |
| US9374411B1 (en) | 2013-03-21 | 2016-06-21 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Content recommendations using deep data |
| US9197926B2 (en)* | 2013-06-05 | 2015-11-24 | International Business Machines Corporation | Location based determination of related content |
| US11019300B1 (en) | 2013-06-26 | 2021-05-25 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Providing soundtrack information during playback of video content |
| US20150036016A1 (en)* | 2013-07-30 | 2015-02-05 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Methods and apparatus for determining the orientation of a mobile phone in an indoor environment |
| EP3044954A4 (en) | 2013-09-11 | 2017-02-08 | Cinsay, Inc. | Dynamic binding of content transactional items |
| US10194189B1 (en) | 2013-09-23 | 2019-01-29 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Playback of content using multiple devices |
| WO2015048377A1 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2015-04-02 | Cinsay, Inc. | Apparatus and method for supporting relationships associated with content provisioning |
| EP3049954A4 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2017-04-05 | Cinsay, Inc. | N-level replication of supplemental content |
| US11589127B2 (en)* | 2013-10-04 | 2023-02-21 | Disney Enterprises, Inc. | Interactive multimedia package methods and systems |
| CN105848733B (en) | 2013-12-26 | 2018-02-13 | 爱康保健健身有限公司 | Magnetic resistance mechanism in hawser apparatus |
| WO2015107424A1 (en)* | 2014-01-15 | 2015-07-23 | Disrupt Ck | System and method for product placement |
| US10945016B2 (en)* | 2014-02-27 | 2021-03-09 | Aibuy, Inc. | Apparatus and method for gathering analytics |
| US11076205B2 (en) | 2014-03-07 | 2021-07-27 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Retrieving supplemental content |
| US10433612B2 (en) | 2014-03-10 | 2019-10-08 | Icon Health & Fitness, Inc. | Pressure sensor to quantify work |
| US9747727B2 (en) | 2014-03-11 | 2017-08-29 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Object customization and accessorization in video content |
| WO2015138612A1 (en) | 2014-03-14 | 2015-09-17 | Cinsay, Inc. | Apparatus and method for automatic provisioning of merchandise |
| US9838740B1 (en) | 2014-03-18 | 2017-12-05 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Enhancing video content with personalized extrinsic data |
| GB2527734A (en)* | 2014-04-30 | 2016-01-06 | Piksel Inc | Device synchronization |
| US20150319506A1 (en)* | 2014-04-30 | 2015-11-05 | Netflix, Inc. | Displaying data associated with a program based on automatic recognition |
| JP5852171B2 (en)* | 2014-05-09 | 2016-02-03 | 株式会社Jストリーム | Content additional information provision system |
| WO2015191445A1 (en) | 2014-06-09 | 2015-12-17 | Icon Health & Fitness, Inc. | Cable system incorporated into a treadmill |
| WO2015195965A1 (en) | 2014-06-20 | 2015-12-23 | Icon Health & Fitness, Inc. | Post workout massage device |
| US10228751B2 (en) | 2014-08-06 | 2019-03-12 | Apple Inc. | Low power mode |
| US9647489B2 (en) | 2014-08-26 | 2017-05-09 | Apple Inc. | Brownout avoidance |
| US10231033B1 (en) | 2014-09-30 | 2019-03-12 | Apple Inc. | Synchronizing out-of-band content with a media stream |
| US10708391B1 (en) | 2014-09-30 | 2020-07-07 | Apple Inc. | Delivery of apps in a media stream |
| US11783382B2 (en) | 2014-10-22 | 2023-10-10 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Systems and methods for curating content metadata |
| US10885570B2 (en) | 2014-12-31 | 2021-01-05 | Aibuy, Inc. | System and method for managing a product exchange |
| US9521496B2 (en)* | 2015-02-12 | 2016-12-13 | Harman International Industries, Inc. | Media content playback system and method |
| US9794618B2 (en) | 2015-02-12 | 2017-10-17 | Harman International Industries, Incorporated | Media content playback system and method |
| US10391361B2 (en) | 2015-02-27 | 2019-08-27 | Icon Health & Fitness, Inc. | Simulating real-world terrain on an exercise device |
| US10970843B1 (en)* | 2015-06-24 | 2021-04-06 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Generating interactive content using a media universe database |
| US11513658B1 (en) | 2015-06-24 | 2022-11-29 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Custom query of a media universe database |
| JP6234408B2 (en)* | 2015-08-24 | 2017-11-22 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Content information providing device, content display device, data structure of object metadata, data structure of event metadata, content information providing method, content information providing program, and content information providing system |
| US10963925B2 (en)* | 2015-08-25 | 2021-03-30 | Seilas PHILLIPS | Product placement, purchase and information from within streaming or other content |
| US10271109B1 (en) | 2015-09-16 | 2019-04-23 | Amazon Technologies, LLC | Verbal queries relative to video content |
| DE102015225388A1 (en)* | 2015-12-16 | 2017-06-22 | Osram Gmbh | METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ANALYZING AN ENVIRONMENT OF A MOBILE TERMINAL |
| US9596502B1 (en) | 2015-12-21 | 2017-03-14 | Max Abecassis | Integration of multiple synchronization methodologies |
| US9516373B1 (en) | 2015-12-21 | 2016-12-06 | Max Abecassis | Presets of synchronized second screen functions |
| US10771508B2 (en)* | 2016-01-19 | 2020-09-08 | Nadejda Sarmova | Systems and methods for establishing a virtual shared experience for media playback |
| US9947316B2 (en) | 2016-02-22 | 2018-04-17 | Sonos, Inc. | Voice control of a media playback system |
| US10264030B2 (en) | 2016-02-22 | 2019-04-16 | Sonos, Inc. | Networked microphone device control |
| US9811314B2 (en) | 2016-02-22 | 2017-11-07 | Sonos, Inc. | Metadata exchange involving a networked playback system and a networked microphone system |
| US9965247B2 (en) | 2016-02-22 | 2018-05-08 | Sonos, Inc. | Voice controlled media playback system based on user profile |
| US9826306B2 (en) | 2016-02-22 | 2017-11-21 | Sonos, Inc. | Default playback device designation |
| US10142754B2 (en) | 2016-02-22 | 2018-11-27 | Sonos, Inc. | Sensor on moving component of transducer |
| US10095470B2 (en) | 2016-02-22 | 2018-10-09 | Sonos, Inc. | Audio response playback |
| US10272317B2 (en) | 2016-03-18 | 2019-04-30 | Icon Health & Fitness, Inc. | Lighted pace feature in a treadmill |
| US10493349B2 (en) | 2016-03-18 | 2019-12-03 | Icon Health & Fitness, Inc. | Display on exercise device |
| US10625137B2 (en) | 2016-03-18 | 2020-04-21 | Icon Health & Fitness, Inc. | Coordinated displays in an exercise device |
| US10951935B2 (en)* | 2016-04-08 | 2021-03-16 | Source Digital, Inc. | Media environment driven content distribution platform |
| US10397663B2 (en)* | 2016-04-08 | 2019-08-27 | Source Digital, Inc. | Synchronizing ancillary data to content including audio |
| US20170323342A1 (en)* | 2016-05-04 | 2017-11-09 | International Business Machines Corporation | Advertisement management based on mobile resource performance |
| US9978390B2 (en) | 2016-06-09 | 2018-05-22 | Sonos, Inc. | Dynamic player selection for audio signal processing |
| CA2973717A1 (en)* | 2016-07-14 | 2018-01-14 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | System and method for supplemental content selection and delivery |
| US10152969B2 (en) | 2016-07-15 | 2018-12-11 | Sonos, Inc. | Voice detection by multiple devices |
| US10134399B2 (en) | 2016-07-15 | 2018-11-20 | Sonos, Inc. | Contextualization of voice inputs |
| US10115400B2 (en) | 2016-08-05 | 2018-10-30 | Sonos, Inc. | Multiple voice services |
| US9942678B1 (en) | 2016-09-27 | 2018-04-10 | Sonos, Inc. | Audio playback settings for voice interaction |
| US10277816B2 (en)* | 2016-09-28 | 2019-04-30 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Systems and methods to reduce actuator power leakage |
| US10671705B2 (en) | 2016-09-28 | 2020-06-02 | Icon Health & Fitness, Inc. | Customizing recipe recommendations |
| US9743204B1 (en) | 2016-09-30 | 2017-08-22 | Sonos, Inc. | Multi-orientation playback device microphones |
| US10181323B2 (en) | 2016-10-19 | 2019-01-15 | Sonos, Inc. | Arbitration-based voice recognition |
| WO2018094201A1 (en)* | 2016-11-17 | 2018-05-24 | Painted Dog, Inc. | Machine-based object recognition of video content |
| US10482327B1 (en) | 2017-01-18 | 2019-11-19 | Snap Inc. | Media overlay selection system |
| US11183181B2 (en) | 2017-03-27 | 2021-11-23 | Sonos, Inc. | Systems and methods of multiple voice services |
| US10475449B2 (en) | 2017-08-07 | 2019-11-12 | Sonos, Inc. | Wake-word detection suppression |
| US10048930B1 (en) | 2017-09-08 | 2018-08-14 | Sonos, Inc. | Dynamic computation of system response volume |
| US10264297B1 (en)* | 2017-09-13 | 2019-04-16 | Perfect Sense, Inc. | Time-based content synchronization |
| US10446165B2 (en) | 2017-09-27 | 2019-10-15 | Sonos, Inc. | Robust short-time fourier transform acoustic echo cancellation during audio playback |
| US10051366B1 (en) | 2017-09-28 | 2018-08-14 | Sonos, Inc. | Three-dimensional beam forming with a microphone array |
| US10482868B2 (en) | 2017-09-28 | 2019-11-19 | Sonos, Inc. | Multi-channel acoustic echo cancellation |
| US10621981B2 (en) | 2017-09-28 | 2020-04-14 | Sonos, Inc. | Tone interference cancellation |
| US10466962B2 (en) | 2017-09-29 | 2019-11-05 | Sonos, Inc. | Media playback system with voice assistance |
| US20230111817A1 (en)* | 2021-01-13 | 2023-04-13 | Mack Craft | Fingerprinted media triggering virtual repository |
| US10880650B2 (en) | 2017-12-10 | 2020-12-29 | Sonos, Inc. | Network microphone devices with automatic do not disturb actuation capabilities |
| US10818290B2 (en) | 2017-12-11 | 2020-10-27 | Sonos, Inc. | Home graph |
| US10817307B1 (en) | 2017-12-20 | 2020-10-27 | Apple Inc. | API behavior modification based on power source health |
| US11363133B1 (en) | 2017-12-20 | 2022-06-14 | Apple Inc. | Battery health-based power management |
| US11343614B2 (en) | 2018-01-31 | 2022-05-24 | Sonos, Inc. | Device designation of playback and network microphone device arrangements |
| US11175880B2 (en) | 2018-05-10 | 2021-11-16 | Sonos, Inc. | Systems and methods for voice-assisted media content selection |
| US10847178B2 (en) | 2018-05-18 | 2020-11-24 | Sonos, Inc. | Linear filtering for noise-suppressed speech detection |
| US10959029B2 (en) | 2018-05-25 | 2021-03-23 | Sonos, Inc. | Determining and adapting to changes in microphone performance of playback devices |
| US10681460B2 (en) | 2018-06-28 | 2020-06-09 | Sonos, Inc. | Systems and methods for associating playback devices with voice assistant services |
| US10461710B1 (en) | 2018-08-28 | 2019-10-29 | Sonos, Inc. | Media playback system with maximum volume setting |
| US11076035B2 (en) | 2018-08-28 | 2021-07-27 | Sonos, Inc. | Do not disturb feature for audio notifications |
| US10587430B1 (en) | 2018-09-14 | 2020-03-10 | Sonos, Inc. | Networked devices, systems, and methods for associating playback devices based on sound codes |
| US10878811B2 (en) | 2018-09-14 | 2020-12-29 | Sonos, Inc. | Networked devices, systems, and methods for intelligently deactivating wake-word engines |
| US11024331B2 (en) | 2018-09-21 | 2021-06-01 | Sonos, Inc. | Voice detection optimization using sound metadata |
| US10811015B2 (en) | 2018-09-25 | 2020-10-20 | Sonos, Inc. | Voice detection optimization based on selected voice assistant service |
| US11100923B2 (en) | 2018-09-28 | 2021-08-24 | Sonos, Inc. | Systems and methods for selective wake word detection using neural network models |
| US10692518B2 (en) | 2018-09-29 | 2020-06-23 | Sonos, Inc. | Linear filtering for noise-suppressed speech detection via multiple network microphone devices |
| US11899519B2 (en) | 2018-10-23 | 2024-02-13 | Sonos, Inc. | Multiple stage network microphone device with reduced power consumption and processing load |
| EP3654249A1 (en) | 2018-11-15 | 2020-05-20 | Snips | Dilated convolutions and gating for efficient keyword spotting |
| US11183183B2 (en) | 2018-12-07 | 2021-11-23 | Sonos, Inc. | Systems and methods of operating media playback systems having multiple voice assistant services |
| US11132989B2 (en) | 2018-12-13 | 2021-09-28 | Sonos, Inc. | Networked microphone devices, systems, and methods of localized arbitration |
| US10880515B2 (en)* | 2018-12-14 | 2020-12-29 | Sony Corporation | Audio-video reproduction for closed caption display control based on multi-media content |
| US10602268B1 (en) | 2018-12-20 | 2020-03-24 | Sonos, Inc. | Optimization of network microphone devices using noise classification |
| US11770579B2 (en) | 2018-12-21 | 2023-09-26 | Streamlayer, Inc. | Method and system for providing interactive content delivery and audience engagement |
| USD947233S1 (en) | 2018-12-21 | 2022-03-29 | Streamlayer, Inc. | Display screen or portion thereof with transitional graphical user interface |
| US12350587B2 (en) | 2018-12-21 | 2025-07-08 | Streamlayer Inc. | Method and system for providing interactive content delivery and audience engagement |
| USD997952S1 (en) | 2018-12-21 | 2023-09-05 | Streamlayer, Inc. | Display screen with transitional graphical user interface |
| US11315556B2 (en) | 2019-02-08 | 2022-04-26 | Sonos, Inc. | Devices, systems, and methods for distributed voice processing by transmitting sound data associated with a wake word to an appropriate device for identification |
| US10867604B2 (en) | 2019-02-08 | 2020-12-15 | Sonos, Inc. | Devices, systems, and methods for distributed voice processing |
| EP3926967A4 (en)* | 2019-02-14 | 2022-09-14 | LG Electronics Inc. | DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD OF OPERATION |
| JP7186120B2 (en)* | 2019-03-27 | 2022-12-08 | オリンパス株式会社 | image file generator |
| USD951267S1 (en) | 2019-04-09 | 2022-05-10 | Streamlayer, Inc. | Display screen with a transitional graphical user interface for an interactive content overlay |
| US11120794B2 (en) | 2019-05-03 | 2021-09-14 | Sonos, Inc. | Voice assistant persistence across multiple network microphone devices |
| US11335343B2 (en) | 2019-05-30 | 2022-05-17 | Adam Tom | Adding audio and video context to smart speaker and voice assistant interaction |
| US11200894B2 (en) | 2019-06-12 | 2021-12-14 | Sonos, Inc. | Network microphone device with command keyword eventing |
| US10586540B1 (en) | 2019-06-12 | 2020-03-10 | Sonos, Inc. | Network microphone device with command keyword conditioning |
| US11361756B2 (en) | 2019-06-12 | 2022-06-14 | Sonos, Inc. | Conditional wake word eventing based on environment |
| US11494824B2 (en)* | 2019-06-21 | 2022-11-08 | NBTV Channels, LLC | Systems and methods for user personalization and recommendations |
| US11138975B2 (en) | 2019-07-31 | 2021-10-05 | Sonos, Inc. | Locally distributed keyword detection |
| US10871943B1 (en) | 2019-07-31 | 2020-12-22 | Sonos, Inc. | Noise classification for event detection |
| US11138969B2 (en) | 2019-07-31 | 2021-10-05 | Sonos, Inc. | Locally distributed keyword detection |
| US11189286B2 (en) | 2019-10-22 | 2021-11-30 | Sonos, Inc. | VAS toggle based on device orientation |
| US11200900B2 (en) | 2019-12-20 | 2021-12-14 | Sonos, Inc. | Offline voice control |
| US11562740B2 (en) | 2020-01-07 | 2023-01-24 | Sonos, Inc. | Voice verification for media playback |
| KR102686864B1 (en)* | 2020-01-28 | 2024-07-22 | 라인플러스 주식회사 | Method, apparatus, and computer program for providing additional information on contents |
| US11556307B2 (en) | 2020-01-31 | 2023-01-17 | Sonos, Inc. | Local voice data processing |
| US11308958B2 (en) | 2020-02-07 | 2022-04-19 | Sonos, Inc. | Localized wakeword verification |
| US11727919B2 (en) | 2020-05-20 | 2023-08-15 | Sonos, Inc. | Memory allocation for keyword spotting engines |
| US11308962B2 (en) | 2020-05-20 | 2022-04-19 | Sonos, Inc. | Input detection windowing |
| US11482224B2 (en) | 2020-05-20 | 2022-10-25 | Sonos, Inc. | Command keywords with input detection windowing |
| US12387716B2 (en) | 2020-06-08 | 2025-08-12 | Sonos, Inc. | Wakewordless voice quickstarts |
| JP2023138873A (en)* | 2020-08-21 | 2023-10-03 | ソニーグループ株式会社 | Information processing device, information processing system, information processing method and program |
| US11698771B2 (en) | 2020-08-25 | 2023-07-11 | Sonos, Inc. | Vocal guidance engines for playback devices |
| US11625928B1 (en)* | 2020-09-01 | 2023-04-11 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Language agnostic drift correction |
| USD1028999S1 (en) | 2020-09-17 | 2024-05-28 | Streamlayer, Inc. | Display screen with transitional graphical user interface |
| US12283269B2 (en) | 2020-10-16 | 2025-04-22 | Sonos, Inc. | Intent inference in audiovisual communication sessions |
| US11984123B2 (en) | 2020-11-12 | 2024-05-14 | Sonos, Inc. | Network device interaction by range |
| US11551700B2 (en) | 2021-01-25 | 2023-01-10 | Sonos, Inc. | Systems and methods for power-efficient keyword detection |
| US11516539B2 (en) | 2021-03-01 | 2022-11-29 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Systems and methods for providing contextually relevant information |
| EP4409933A1 (en) | 2021-09-30 | 2024-08-07 | Sonos, Inc. | Enabling and disabling microphones and voice assistants |
| US12295081B2 (en) | 2022-01-06 | 2025-05-06 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Video display environmental lighting |
| US12327549B2 (en) | 2022-02-09 | 2025-06-10 | Sonos, Inc. | Gatekeeping for voice intent processing |
| US12093328B2 (en)* | 2022-05-19 | 2024-09-17 | Apple Inc. | Playback engine |
| US12375749B2 (en)* | 2022-07-18 | 2025-07-29 | Atmosphere.tv | Synchronization of independent services |
| US12328473B2 (en)* | 2023-10-30 | 2025-06-10 | Dish Network L.L.C. | Token merging for legacy content receiving devices |
Citations (230)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6188398B1 (en) | 1999-06-02 | 2001-02-13 | Mark Collins-Rector | Targeting advertising using web pages with video |
| US20010001160A1 (en) | 1996-03-29 | 2001-05-10 | Microsoft Corporation | Interactive entertainment system for presenting supplemental interactive content together with continuous video programs |
| US6317784B1 (en) | 1998-09-29 | 2001-11-13 | Radiowave.Com, Inc. | Presenting supplemental information for material currently and previously broadcast by a radio station |
| US6357042B2 (en)* | 1998-09-16 | 2002-03-12 | Anand Srinivasan | Method and apparatus for multiplexing separately-authored metadata for insertion into a video data stream |
| US20020042920A1 (en)* | 2000-10-11 | 2002-04-11 | United Video Properties, Inc. | Systems and methods for supplementing on-demand media |
| US20020053078A1 (en) | 2000-01-14 | 2002-05-02 | Alex Holtz | Method, system and computer program product for producing and distributing enhanced media downstreams |
| US20020064149A1 (en) | 1996-11-18 | 2002-05-30 | Elliott Isaac K. | System and method for providing requested quality of service in a hybrid network |
| US20020073424A1 (en) | 1996-12-19 | 2002-06-13 | Eguide, Inc. | System and method for modifying advertisement responsive to EPG information |
| US6415326B1 (en) | 1998-09-15 | 2002-07-02 | Microsoft Corporation | Timeline correlation between multiple timeline-altered media streams |
| US20020104101A1 (en)* | 2001-01-31 | 2002-08-01 | Yamato Jun-Ichi | Information providing system and information providing method |
| US20020112249A1 (en)* | 1992-12-09 | 2002-08-15 | Hendricks John S. | Method and apparatus for targeting of interactive virtual objects |
| US20020120933A1 (en) | 1998-04-30 | 2002-08-29 | United Video Properties, Inc | Program guide system with flip and browse advertisements |
| US20020120925A1 (en) | 2000-03-28 | 2002-08-29 | Logan James D. | Audio and video program recording, editing and playback systems using metadata |
| US20020131511A1 (en) | 2000-08-25 | 2002-09-19 | Ian Zenoni | Video tags and markers |
| US20020162117A1 (en)* | 2001-04-26 | 2002-10-31 | Martin Pearson | System and method for broadcast-synchronized interactive content interrelated to broadcast content |
| US20020188628A1 (en) | 2001-04-20 | 2002-12-12 | Brian Cooper | Editing interactive content with time-based media |
| US20030001880A1 (en) | 2001-04-18 | 2003-01-02 | Parkervision, Inc. | Method, system, and computer program product for producing and distributing enhanced media |
| US20030012548A1 (en)* | 2000-12-21 | 2003-01-16 | Levy Kenneth L. | Watermark systems for media |
| US20030033157A1 (en) | 2001-08-08 | 2003-02-13 | Accenture Global Services Gmbh | Enhanced custom content television |
| US20030067554A1 (en) | 2000-09-25 | 2003-04-10 | Klarfeld Kenneth A. | System and method for personalized TV |
| US20030093790A1 (en) | 2000-03-28 | 2003-05-15 | Logan James D. | Audio and video program recording, editing and playback systems using metadata |
| US20030093792A1 (en) | 2000-06-30 | 2003-05-15 | Labeeb Ismail K. | Method and apparatus for delivery of television programs and targeted de-coupled advertising |
| US20030101454A1 (en) | 2001-11-21 | 2003-05-29 | Stuart Ozer | Methods and systems for planning advertising campaigns |
| US20030126200A1 (en) | 1996-08-02 | 2003-07-03 | Wolff James J. | Dynamic load balancing of a network of client and server computer |
| US20030229900A1 (en)* | 2002-05-10 | 2003-12-11 | Richard Reisman | Method and apparatus for browsing using multiple coordinated device sets |
| US20040003400A1 (en) | 2002-03-15 | 2004-01-01 | John Carney | System and method for construction, delivery and display of iTV content |
| US6741977B1 (en) | 1999-01-29 | 2004-05-25 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Image recording/reproducing apparatus in monitor system |
| US20040226051A1 (en) | 2001-09-19 | 2004-11-11 | John Carney | System and method for construction, delivery and display of iTV content |
| US20040260682A1 (en) | 2003-06-19 | 2004-12-23 | Microsoft Corporation | System and method for identifying content and managing information corresponding to objects in a signal |
| US20050038794A1 (en)* | 2003-08-14 | 2005-02-17 | Ricoh Company, Ltd. | Transmission of event markers to data stream recorder |
| US20050050218A1 (en) | 2003-09-02 | 2005-03-03 | Microsoft Corporation | Video delivery workflow |
| US20050060741A1 (en) | 2002-12-10 | 2005-03-17 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Media data audio-visual device and metadata sharing system |
| US6874126B1 (en) | 2001-11-30 | 2005-03-29 | View Space Technologies | Method and apparatus for controlling content display by the cursor motion |
| US20050125428A1 (en) | 2003-10-04 | 2005-06-09 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Storage medium storing search information and reproducing apparatus and method |
| US20050188402A1 (en) | 2002-09-19 | 2005-08-25 | De Andrade David | System and method for preferred placement programming of iTV content |
| US20050235318A1 (en) | 1997-01-06 | 2005-10-20 | Grauch Edward R | Method and system for tracking network use |
| US20060015908A1 (en) | 2004-06-30 | 2006-01-19 | Nokia Corporation | Multiple services within a channel-identification in a device |
| US20060174310A1 (en) | 2003-03-13 | 2006-08-03 | Hee-Kyung Lee | Extended metadata and adaptive program service providing system and method for providing digital broadcast program service |
| US7096271B1 (en) | 1998-09-15 | 2006-08-22 | Microsoft Corporation | Managing timeline modification and synchronization of multiple media streams in networked client/server systems |
| US20060190336A1 (en) | 2001-12-28 | 2006-08-24 | Pisaris-Henderson Craig A | System and method for pay for performance advertising in general media |
| US7136871B2 (en) | 2001-11-21 | 2006-11-14 | Microsoft Corporation | Methods and systems for selectively displaying advertisements |
| US20070011050A1 (en) | 2005-05-20 | 2007-01-11 | Steven Klopf | Digital advertising system |
| US20070061838A1 (en) | 2005-09-12 | 2007-03-15 | I7 Corp | Methods and systems for displaying audience targeted information |
| US20070088609A1 (en) | 2002-10-25 | 2007-04-19 | Medio Systems, Inc. | Optimizer For Selecting Supplemental Content Based on Content Productivity of a Document |
| US20070124789A1 (en) | 2005-10-26 | 2007-05-31 | Sachson Thomas I | Wireless interactive communication system |
| US20070124756A1 (en)* | 2005-11-29 | 2007-05-31 | Google Inc. | Detecting Repeating Content in Broadcast Media |
| US20070127720A1 (en) | 2004-01-26 | 2007-06-07 | David White | Timeline protection |
| US20070250761A1 (en) | 2004-06-04 | 2007-10-25 | Bob Bradley | System and method for synchronizing media presentation at multiple recipients |
| US7302490B1 (en) | 2000-05-03 | 2007-11-27 | Microsoft Corporation | Media file format to support switching between multiple timeline-altered media streams |
| US20070274676A1 (en) | 2004-09-10 | 2007-11-29 | Giuseppe Diomelli | Method and Apparatus For Unified Management Of Different Type Of Communications Over Lanwan And Internet Networks, Using A Web Browser |
| US20080017722A1 (en) | 2000-01-03 | 2008-01-24 | Tripletail Ventures, Inc. | Method for data interchange |
| US20080036917A1 (en)* | 2006-04-07 | 2008-02-14 | Mark Pascarella | Methods and systems for generating and delivering navigatable composite videos |
| US20080066110A1 (en) | 2006-09-11 | 2008-03-13 | Rainer Brodersen | Media preview user interface |
| US20080066100A1 (en) | 2006-09-11 | 2008-03-13 | Apple Computer, Inc. | Enhancing media system metadata |
| US20080068500A1 (en) | 2006-09-18 | 2008-03-20 | Rgb Networks, Inc. | Methods, apparatus, and systems for insertion of overlay content into a video signal with transrating capabilities |
| US20080113789A1 (en) | 2006-11-15 | 2008-05-15 | Microsoft Corporation | Console integrated downloadable game service |
| US7379661B2 (en) | 1999-04-21 | 2008-05-27 | Sonic Solutions, A California Corporation | Presentation of media content |
| US20080168133A1 (en) | 2007-01-05 | 2008-07-10 | Roland Osborne | Video distribution system including progressive playback |
| US20080195746A1 (en) | 2007-02-13 | 2008-08-14 | Microsoft Corporation | Live content streaming using file-centric media protocols |
| US7415529B2 (en) | 2002-08-20 | 2008-08-19 | Microsoft Corporation | Media streaming of web content data |
| US20080209485A1 (en) | 1999-07-14 | 2008-08-28 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Information provision apparatus, information receiving apparatus, and storage medium |
| US7428696B2 (en) | 2003-06-30 | 2008-09-23 | Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. | System and method for time synchronization between multimedia content and segment metadata |
| US20080249853A1 (en) | 2007-04-05 | 2008-10-09 | Elan Dekel | Advertising campaign template |
| US20080255904A1 (en) | 2007-04-13 | 2008-10-16 | Google Inc. | Estimating Off-Line Advertising Impressions |
| US20080267588A1 (en) | 2005-08-25 | 2008-10-30 | Ayako Iwase | Reproduction Device, Reproduction Method, Program, Program Storage Medium, Data Structure, and Recording Medium Fabrication Method |
| US20080301727A1 (en) | 2007-02-01 | 2008-12-04 | Cristofalo Michael | Intelligent targeting of tags in a broadcast network |
| US20080307454A1 (en) | 2007-06-11 | 2008-12-11 | Gulrukh Ahanger | Systems and methods for inserting ads during playback of video media |
| US20080313229A1 (en) | 2007-06-17 | 2008-12-18 | Global Telegenetics, Inc. | PORTALS and DOORS for the Semantic Web and Grid |
| US20090006191A1 (en) | 2007-06-27 | 2009-01-01 | Google Inc. | Targeting in-video advertising |
| US20090044246A1 (en) | 2007-02-01 | 2009-02-12 | Patrick Sheehan | Targeting content based on location |
| US20090041418A1 (en)* | 2007-08-08 | 2009-02-12 | Brant Candelore | System and Method for Audio Identification and Metadata Retrieval |
| US20090113468A1 (en) | 2007-10-31 | 2009-04-30 | Ryan Steelberg | System and method for creation and management of advertising inventory using metadata |
| US20090125812A1 (en) | 2007-10-17 | 2009-05-14 | Yahoo! Inc. | System and method for an extensible media player |
| US20090132371A1 (en) | 2007-11-20 | 2009-05-21 | Big Stage Entertainment, Inc. | Systems and methods for interactive advertising using personalized head models |
| US20090150947A1 (en)* | 2007-10-05 | 2009-06-11 | Soderstrom Robert W | Online search, storage, manipulation, and delivery of video content |
| US20090150215A1 (en) | 2007-12-10 | 2009-06-11 | Kalb Kenneth J | System and method for real-time management and optimization of off-line advertising campaigns |
| US20090171948A1 (en) | 2007-12-31 | 2009-07-02 | Peer 39 Inc. | Method and a system for selecting advertising spots |
| US20090204481A1 (en)* | 2008-02-12 | 2009-08-13 | Murgesh Navar | Discovery and Analytics for Episodic Downloaded Media |
| US20090216745A1 (en) | 2008-02-26 | 2009-08-27 | Microsoft Corporation | Techniques to Consume Content and Metadata |
| US20090226152A1 (en) | 2008-03-10 | 2009-09-10 | Hanes Brett E | Method for media playback optimization |
| US20090235298A1 (en) | 2008-03-13 | 2009-09-17 | United Video Properties, Inc. | Systems and methods for synchronizing time-shifted media content and related communications |
| US20090234815A1 (en) | 2006-12-12 | 2009-09-17 | Marco Boerries | Open framework for integrating, associating, and interacting with content objects including automatic feed creation |
| US20090240734A1 (en) | 2008-01-24 | 2009-09-24 | Geoffrey Wayne Lloyd-Jones | System and methods for the creation, review and synchronization of digital media to digital audio data |
| US20090240564A1 (en) | 2006-12-12 | 2009-09-24 | Marco Boerries | Open framework for integrating, associating, and interacting with content objects including advertisement and content personalization |
| US20090245058A1 (en) | 2008-03-28 | 2009-10-01 | Sony Corporation | Information processing apparatus and method, program, recording medium, and information processing system |
| US20090276821A1 (en) | 2008-04-30 | 2009-11-05 | At&T Knowledge Ventures, L.P. | Dynamic synchronization of media streams within a social network |
| US20090285550A1 (en) | 2008-05-14 | 2009-11-19 | Eiju Yamada | Electronic Apparatus, Content Reproduction Method, Record Medium, and Server Apparatus |
| US20090295993A1 (en) | 2008-01-07 | 2009-12-03 | Toshiba America Consumer Products, Llc | Control systems and methods using markers in image portion of audiovisual content |
| US20090307227A1 (en) | 2008-06-06 | 2009-12-10 | Disney Enterprises, Inc. | Methods and apparatuses for combining and distributing user enhanced video/audio content |
| US20100011392A1 (en) | 2007-07-16 | 2010-01-14 | Novafora, Inc. | Methods and Systems For Media Content Control |
| US20100031299A1 (en) | 2008-08-04 | 2010-02-04 | Opanga Networks, Llc | Systems and methods for device dependent media content delivery in a local area network |
| US20100064311A1 (en)* | 2008-09-08 | 2010-03-11 | Robin Ross Cooper | BD-Live Interface to the Distribution Supply Chain |
| US20100070643A1 (en) | 2008-09-11 | 2010-03-18 | Yahoo! Inc. | Delivery of synchronized metadata using multiple transactions |
| US20100088716A1 (en) | 2008-10-02 | 2010-04-08 | Softhills Corporation | Content slots for digital media |
| US20100106798A1 (en) | 2008-05-16 | 2010-04-29 | Wyse Technology Inc. | Multimedia redirection |
| US20100118206A1 (en) | 2007-06-21 | 2010-05-13 | Wen Gao | Apparatus and method for use in mobile/handheld communications system |
| US20100135637A1 (en) | 2008-06-06 | 2010-06-03 | Deluxe Digital Studios, Inc. | Methods and systems for use in providing playback of variable length content in a fixed length framework |
| US20100142915A1 (en) | 2008-06-06 | 2010-06-10 | Deluxe Digital Studios, Inc. | Methods and systems for use in providing playback of variable length content in a fixed length framework |
| US20100146542A1 (en) | 2008-12-04 | 2010-06-10 | Joseph Weihs | System and method of scheduling advertising content for dynamic insertion during playback of video on demand assets |
| US20100161825A1 (en) | 2008-12-22 | 2010-06-24 | David Randall Ronca | On-device multiplexing of streaming media content |
| US20100162286A1 (en) | 2008-11-24 | 2010-06-24 | Digitalsmiths Corporation | Systems and methods for analyzing trends in video consumption based on embedded video metadata |
| US20100158099A1 (en)* | 2008-09-16 | 2010-06-24 | Realnetworks, Inc. | Systems and methods for video/multimedia rendering, composition, and user interactivity |
| US20100169460A1 (en) | 2007-03-30 | 2010-07-01 | Robert Charles Angell | Methods and Apparatus for Distributing Electronic Media Content for the Purpose of Enhancing Existing Media |
| US20100169303A1 (en) | 2008-12-31 | 2010-07-01 | David Biderman | Playlists for real-time or near real-time streaming |
| US20100169910A1 (en) | 2006-01-06 | 2010-07-01 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Apparatus and methods of selective collection and selective presentation of content |
| US20100180289A1 (en) | 2009-01-12 | 2010-07-15 | Jonathan Barsook | System and/or method for distributing media content and providing an option to maintain an advertising experience |
| US20100205049A1 (en) | 2009-02-12 | 2010-08-12 | Long Dustin W | Advertisement management for live internet multimedia content |
| US7788262B1 (en) | 2006-08-04 | 2010-08-31 | Sanika Shirwadkar | Method and system for creating context based summary |
| US20100228693A1 (en) | 2009-03-06 | 2010-09-09 | phiScape AG | Method and system for generating a document representation |
| US20100235472A1 (en) | 2009-03-16 | 2010-09-16 | Microsoft Corporation | Smooth, stateless client media streaming |
| US20100241961A1 (en) | 2009-03-23 | 2010-09-23 | Peterson Troy A | Content presentation control and progression indicator |
| US20100246666A1 (en) | 2008-12-30 | 2010-09-30 | Mozaik Multimedia, Inc. | Bluflex: flexible, true, live video streaming on blu-ray platforms |
| US20100274667A1 (en) | 2009-04-24 | 2010-10-28 | Nexidia Inc. | Multimedia access |
| US20100287580A1 (en) | 2009-05-08 | 2010-11-11 | Harding John M | Content syndication in web-based media via ad tagging |
| US20100299687A1 (en) | 2009-05-23 | 2010-11-25 | Adrian Bertino-Clarke | Peer-to-peer video content distribution |
| US20100333152A1 (en) | 2007-03-29 | 2010-12-30 | William Gibbens Redmann | Method and apparatus for content distribution to and playout with a digital cinema system |
| US20110044601A1 (en) | 2009-08-24 | 2011-02-24 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method for play synchronization and device using the same |
| US20110058675A1 (en) | 2009-09-04 | 2011-03-10 | Brueck David F | Controlling access to copies of media content by a client device |
| US20110061001A1 (en) | 2009-09-04 | 2011-03-10 | Yahoo! Inc. | Synchronization of advertisment display updates with user revisitation rates |
| US7913157B1 (en) | 2006-04-18 | 2011-03-22 | Overcast Media Incorporated | Method and system for the authoring and playback of independent, synchronized media through the use of a relative virtual time code |
| US20110078623A1 (en) | 2009-09-30 | 2011-03-31 | Microsoft Corporation | Video content-aware advertisement placement |
| US20110134321A1 (en) | 2009-09-11 | 2011-06-09 | Digitalsmiths Corporation | Timeline Alignment for Closed-Caption Text Using Speech Recognition Transcripts |
| US20110178854A1 (en) | 2008-09-04 | 2011-07-21 | Somertech Ltd. | Method and system for enhancing and/or monitoring visual content and method and/or system for adding a dynamic layer to visual content |
| US20110196747A1 (en) | 2010-02-11 | 2011-08-11 | Microsoft Corporation | Facilitating advertisement selection using advancement bids |
| US20110218851A1 (en) | 2010-03-06 | 2011-09-08 | O'hanlon David Joseph | Search engine optimization purchasing economic method |
| US20110246622A1 (en) | 2010-04-01 | 2011-10-06 | Roger Pantos | Real-Time or Near Real-Time Streaming |
| US20110246885A1 (en) | 2008-12-31 | 2011-10-06 | Roger Pantos | Real-time or near real-time streaming |
| US20110258529A1 (en) | 2010-04-16 | 2011-10-20 | Toby Doig | Systems and methods for excluding serving an advertisement campaign to undesired web pages |
| US20110258545A1 (en) | 2010-04-20 | 2011-10-20 | Witstreams | Service for Sharing User Created Comments that Overlay and are Synchronized with Video |
| US20110273455A1 (en)* | 2010-05-04 | 2011-11-10 | Shazam Entertainment Ltd. | Systems and Methods of Rendering a Textual Animation |
| US20110276372A1 (en) | 2010-05-04 | 2011-11-10 | Live Matrix, Inc. | Temporal indices of the web that associate index elements with metadata |
| US20110321096A1 (en) | 2010-06-29 | 2011-12-29 | Echostar Technologies L.L.C. | Apparatus, systems and methods for accessing and synchronizing presentation of media content and supplemental media rich content in response to selection of a presented object |
| US20110319160A1 (en) | 2010-06-25 | 2011-12-29 | Idevcor Media, Inc. | Systems and Methods for Creating and Delivering Skill-Enhancing Computer Applications |
| US20120102042A1 (en) | 2010-10-20 | 2012-04-26 | Flick christopher | Temporal metadata track |
| US20120110627A1 (en) | 2010-10-29 | 2012-05-03 | Nbc Universal, Inc. | Time-adapted content delivery system and method |
| US20120116883A1 (en) | 2010-11-08 | 2012-05-10 | Sony Corporation | Methods and systems for use in incorporating targeted advertising into multimedia content streams |
| US20120144417A1 (en) | 2010-12-01 | 2012-06-07 | Ensequence, Inc. | Method and system for controlling content in a multimedia display |
| US20120158472A1 (en) | 2010-12-21 | 2012-06-21 | Research In Motion Limited | Contextual customization of content display on a communication device |
| US20120167146A1 (en)* | 2010-12-28 | 2012-06-28 | White Square Media Llc | Method and apparatus for providing or utilizing interactive video with tagged objects |
| WO2012094539A2 (en) | 2011-01-05 | 2012-07-12 | Related Content Databases, Inc. | System and method for streaming content to blu-ray devices |
| WO2012094432A1 (en) | 2011-01-04 | 2012-07-12 | Related Content Databases, Inc. | System and method for interfacing content playback devices with network sites to supplement content playback |
| US20120179536A1 (en) | 2008-01-17 | 2012-07-12 | Kalb Kenneth J | System and method for management and optimization of off-line advertising campaigns with a consumer call to action |
| US20120192227A1 (en) | 2011-01-21 | 2012-07-26 | Bluefin Labs, Inc. | Cross Media Targeted Message Synchronization |
| US20120192220A1 (en) | 2011-01-25 | 2012-07-26 | Youtoo Technologies, LLC | User-generated social television content |
| US20120192225A1 (en) | 2011-01-25 | 2012-07-26 | Youtoo Technologies, LLC | Administration of Content Creation and Distribution System |
| US20120197419A1 (en) | 2011-01-31 | 2012-08-02 | Cbs Interactive, Inc. | Media Playback Control |
| US20120203589A1 (en) | 2009-07-27 | 2012-08-09 | Nextgen Healthcare Information Systems, Inc. | Systematic Rule-Based Workflow Tasking and Event Scheduling |
| US20120233646A1 (en) | 2011-03-11 | 2012-09-13 | Coniglio Straker J | Synchronous multi-platform content consumption |
| US20120256762A1 (en) | 2006-07-24 | 2012-10-11 | Upmc | Emergency management system |
| US20120290644A1 (en) | 2010-01-18 | 2012-11-15 | Frederic Gabin | Methods and Arrangements for HTTP Media Stream Distribution |
| US20120310750A1 (en) | 2011-06-01 | 2012-12-06 | Intercast Networks, Inc. | Interface and module for real-time advertising presentation |
| WO2012174301A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2012-12-20 | Related Content Database, Inc. | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
| US20130011120A1 (en) | 2010-04-09 | 2013-01-10 | Kazumasa Tanaka | Content processing apparatus and method, and program |
| US8359399B2 (en) | 2008-10-16 | 2013-01-22 | Echostar Technologies L.L.C. | Method and device for delivering supplemental content associated with audio/visual content to a user |
| US20130036007A1 (en) | 2011-05-06 | 2013-02-07 | Lau Emil O | Cross-platform collection of advertising metrics |
| US8381259B1 (en) | 2012-01-05 | 2013-02-19 | Vinod Khosla | Authentication and synchronous interaction between a secondary device and a multi-perspective audiovisual data stream broadcast on a primary device |
| US8385633B2 (en) | 2006-03-12 | 2013-02-26 | Google Inc. | Techniques for enabling or establishing the use of face recognition algorithms |
| US20130071090A1 (en) | 2011-09-16 | 2013-03-21 | Nbcuniversal Media Llc | Automatic content recongition system and method for providing supplementary content |
| US20130070152A1 (en) | 2011-09-16 | 2013-03-21 | Nbcuniversal Media Llc | Sampled digital content based syncronization of supplementary digital content |
| US20130074141A1 (en) | 2011-09-21 | 2013-03-21 | University Of Seoul Industry Cooperation Foundation | Method and apparatus for synchronizing media data of multimedia broadcast service |
| US20130077876A1 (en) | 2010-04-09 | 2013-03-28 | Kazumasa Tanaka | Apparatus and method for identifying a still image contained in moving image contents |
| US20130091518A1 (en) | 2011-10-07 | 2013-04-11 | Accenture Global Services Limited | Synchronizing Digital Media Content |
| US20130097190A1 (en) | 2009-05-27 | 2013-04-18 | Ajay Shah | Supplementing synchronization with programming metadata |
| US20130095864A1 (en) | 2010-11-16 | 2013-04-18 | Jack L. Marovets | System, method, and apparatus for storing, transmitting, receiving, and using structured data using un-structured text message bodies |
| US8448208B2 (en) | 2003-03-14 | 2013-05-21 | Tvworks, Llc | System and method for construction, delivery and display of iTV applications that blend programming information of on-demand and broadcast service offerings |
| US20130132854A1 (en) | 2009-01-28 | 2013-05-23 | Headwater Partners I Llc | Service Plan Design, User Interfaces, Application Programming Interfaces, and Device Management |
| US20130132818A1 (en) | 2011-06-03 | 2013-05-23 | Mark Anders | Controlling The Structure Of Animated Documents |
| US20130170753A1 (en) | 2010-04-09 | 2013-07-04 | Sony Corporation | Apparatus and method of content retrieval and program |
| US20130170813A1 (en) | 2011-12-30 | 2013-07-04 | United Video Properties, Inc. | Methods and systems for providing relevant supplemental content to a user device |
| US20130183021A1 (en) | 2010-07-13 | 2013-07-18 | Sony Computer Entertainment Inc. | Supplemental content on a mobile device |
| US20130191745A1 (en) | 2012-01-10 | 2013-07-25 | Zane Vella | Interface for displaying supplemental dynamic timeline content |
| US20130198642A1 (en) | 2003-03-14 | 2013-08-01 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Providing Supplemental Content |
| US20130204698A1 (en) | 2004-03-12 | 2013-08-08 | Ttn Holdings, Llc | Systems and methods for automated mass media commerce |
| US20130254340A1 (en) | 2009-01-30 | 2013-09-26 | Jonathan Lang | Advertising in a digital media playback system |
| US20130262997A1 (en) | 2012-03-27 | 2013-10-03 | Roku, Inc. | Method and Apparatus for Displaying Information on a Secondary Screen |
| US20130293677A1 (en) | 2011-01-19 | 2013-11-07 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Reception device for receiving a plurality of real-time transfer streams, transmission device for transmitting same, and method for playing multimedia content |
| US8595781B2 (en) | 2009-05-29 | 2013-11-26 | Cognitive Media Networks, Inc. | Methods for identifying video segments and displaying contextual targeted content on a connected television |
| US20130332839A1 (en) | 2012-06-11 | 2013-12-12 | Cellco Partnership D/B/A Verizon Wireless | Cross-platform schedule management interface |
| US20130347018A1 (en) | 2012-06-21 | 2013-12-26 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Providing supplemental content with active media |
| US20140009680A1 (en) | 2010-11-24 | 2014-01-09 | Lg Electhonics Inc. | Video display device and method for controlling same |
| US20140046775A1 (en) | 2009-02-23 | 2014-02-13 | Joseph Harb | Method, system and apparatus for synchronizing radio content and external content |
| US20140089967A1 (en) | 2012-09-27 | 2014-03-27 | General Instrument Corporation | Providing secondary content to accompany a primary content item |
| US8701005B2 (en) | 2006-04-26 | 2014-04-15 | At&T Intellectual Property I, Lp | Methods, systems, and computer program products for managing video information |
| US8699862B1 (en) | 2013-02-06 | 2014-04-15 | Google Inc. | Synchronized content playback related to content recognition |
| US8719869B2 (en) | 2010-08-04 | 2014-05-06 | Nagravision S.A. | Method for sharing data and synchronizing broadcast data with additional information |
| US20140149918A1 (en) | 2010-12-20 | 2014-05-29 | Ashwini Asokan | Techniques for management and presentation of content |
| US20140157307A1 (en) | 2011-07-21 | 2014-06-05 | Stuart Anderson Cox | Method and apparatus for delivery of programs and metadata to provide user alerts to tune to corresponding program channels before high interest events occur during playback of programs |
| US8763060B2 (en) | 2010-07-11 | 2014-06-24 | Apple Inc. | System and method for delivering companion content |
| US20140181868A1 (en) | 2012-12-21 | 2014-06-26 | Verizon Patent And Licensing Inc. | Systems, methods, and user interfaces for facilitating user access to media content |
| US20140180829A1 (en) | 2011-09-09 | 2014-06-26 | Dennoo Inc. | Advertising Platform |
| US8793256B2 (en) | 2008-03-26 | 2014-07-29 | Tout Industries, Inc. | Method and apparatus for selecting related content for display in conjunction with a media |
| US8850495B2 (en) | 2010-08-14 | 2014-09-30 | Yang Pan | Advertisement delivering system based on digital television system and mobile communication device |
| US20140310243A1 (en) | 2010-08-16 | 2014-10-16 | Mr. Steven James McGee | Heart beacon cycle |
| US20140327677A1 (en) | 2012-01-06 | 2014-11-06 | Thomson Licensing | Method and system for providing a graphical representation on a second screen of social messages related to content on a first screen |
| US20140337127A1 (en) | 2013-04-23 | 2014-11-13 | Brightcove, Inc. | Client bridge |
| US20150135206A1 (en) | 2002-05-10 | 2015-05-14 | Convergent Media Solutions Llc | Method and apparatus for browsing using alternative linkbases |
| US20150135214A1 (en) | 2002-05-10 | 2015-05-14 | Convergent Media Solutions Llc | Method and apparatus for browsing using alternative linkbases |
| US20150134673A1 (en) | 2013-10-03 | 2015-05-14 | Minute Spoteam Ltd. | System and method for creating synopsis for multimedia content |
| US20150199968A1 (en) | 2014-01-16 | 2015-07-16 | CloudCar Inc. | Audio stream manipulation for an in-vehicle infotainment system |
| US20150237389A1 (en) | 2014-02-14 | 2015-08-20 | Pluto Inc. | Methods and systems for generating and providing program guides and content |
| US20150245111A1 (en) | 2007-09-07 | 2015-08-27 | Tivo Inc. | Systems and methods for using video metadata to associate advertisements therewith |
| US20150281763A1 (en) | 2014-03-25 | 2015-10-01 | Cisco Technology Inc. | System and Method for Synchronized Presentation of Video Timeline Metadata |
| US9154852B2 (en) | 2003-12-23 | 2015-10-06 | Opentv, Inc. | Advertising methods for advertising time slots and embedded objects |
| US20150289030A1 (en) | 2009-12-04 | 2015-10-08 | At&T Intellectual Property I, Lp | Apparatus and method for tagging media content and managing marketing |
| US9191722B2 (en) | 1997-07-21 | 2015-11-17 | Rovi Guides, Inc. | System and method for modifying advertisement responsive to EPG information |
| US20160127776A1 (en) | 2014-11-05 | 2016-05-05 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Increased user efficiency and interaction performance through dynamic adjustment of auxiliary content duration |
| US20160182923A1 (en) | 2014-12-19 | 2016-06-23 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (Publ) | End user-based personalized ad insertion in broadcast-broadband hybrid terminals |
| US20160191957A1 (en) | 2014-12-31 | 2016-06-30 | Opentv, Inc. | Lull management for content delivery |
| US20160234295A1 (en) | 2015-02-05 | 2016-08-11 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Correlation of Actionable Events To An Actionable Instruction |
| US20170013314A1 (en)* | 2010-04-01 | 2017-01-12 | Sony Interactive Entertainment Inc. | Media fingerprinting for content determination and retrieval |
| US9554093B2 (en) | 2006-02-27 | 2017-01-24 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Automatically inserting advertisements into source video content playback streams |
| US20170041648A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2017-02-09 | Watchwith, Inc. | System and method for supplemental content selection and delivery |
| US20170041644A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2017-02-09 | Watchwith, Inc. | Metadata delivery system for rendering supplementary content |
| US20170041649A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2017-02-09 | Watchwith, Inc. | Supplemental content playback system |
| US9674562B1 (en)* | 2008-12-18 | 2017-06-06 | Vmware, Inc. | Quality evaluation of multimedia delivery in cloud environments |
| US20170201850A1 (en) | 2009-01-28 | 2017-07-13 | Headwater Research Llc | Method for Child Wireless Device Activation to Subscriber Account of a Master Wireless Device |
| US20170295386A1 (en) | 2016-04-12 | 2017-10-12 | Verizon Patent And Licensing Inc. | Stream boundary marking for dynamic content replacement |
| US9814977B2 (en) | 2010-07-13 | 2017-11-14 | Sony Interactive Entertainment Inc. | Supplemental video content on a mobile device |
| US9832532B1 (en) | 2008-02-20 | 2017-11-28 | CSC Holdings, LLC | Interactive save and purchase of content and products |
| US20170344439A1 (en) | 2016-05-27 | 2017-11-30 | Raytheon Company | System and method for input data fault recovery in a massively parallel real time computing system |
| US20180014077A1 (en) | 2016-07-05 | 2018-01-11 | Pluto Inc. | Methods and systems for generating and providing program guides and content |
| CA2973717A1 (en) | 2016-07-14 | 2018-01-14 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | System and method for supplemental content selection and delivery |
| US9911126B2 (en) | 2007-04-10 | 2018-03-06 | Google Llc | Refreshing advertisements in offline or virally distributed content |
| US9922334B1 (en) | 2012-04-06 | 2018-03-20 | Google Llc | Providing an advertisement based on a minimum number of exposures |
| US20190107906A1 (en) | 2010-10-15 | 2019-04-11 | Tivo Solutions Inc. | Time-based metadata management system for digital media |
| US20190349619A1 (en) | 2018-05-09 | 2019-11-14 | Pluto Inc. | Methods and systems for generating and providing program guides and content |
| US10528631B1 (en) | 2007-08-23 | 2020-01-07 | Sony Interactive Entertainment Inc. | Media data presented with time-based metadata |
| US20200068256A1 (en) | 2010-11-01 | 2020-02-27 | Gracenote, Inc. | Method and system for presenting additional content at a media system |
| US10579215B2 (en) | 2012-12-10 | 2020-03-03 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Providing content via multiple display devices |
| US10708336B2 (en) | 2016-12-04 | 2020-07-07 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | System and method for announcing media changes |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5659350A (en)* | 1992-12-09 | 1997-08-19 | Discovery Communications, Inc. | Operations center for a television program packaging and delivery system |
| US6411949B1 (en)* | 1999-08-12 | 2002-06-25 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V., | Customizing database information for presentation with media selections |
| US20040220926A1 (en)* | 2000-01-03 | 2004-11-04 | Interactual Technologies, Inc., A California Cpr[P | Personalization services for entities from multiple sources |
| AUPQ867700A0 (en)* | 2000-07-10 | 2000-08-03 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Delivering multimedia descriptions |
| US7367043B2 (en)* | 2000-11-16 | 2008-04-29 | Meevee, Inc. | System and method for generating metadata for programming events |
| US7930624B2 (en)* | 2001-04-20 | 2011-04-19 | Avid Technology, Inc. | Editing time-based media with enhanced content |
| GB2418506A (en)* | 2003-06-02 | 2006-03-29 | Disney Entpr Inc | System and method of video player commerce |
| WO2007115224A2 (en)* | 2006-03-30 | 2007-10-11 | Sri International | Method and apparatus for annotating media streams |
| US20080092047A1 (en)* | 2006-10-12 | 2008-04-17 | Rideo, Inc. | Interactive multimedia system and method for audio dubbing of video |
| KR20090000647A (en)* | 2007-03-15 | 2009-01-08 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method and apparatus for outputting additional data in real time in real time streaming service |
| US20100023968A1 (en)* | 2008-07-23 | 2010-01-28 | Tvworks, Llc, C/O Comcast Cable | Community-Based Enhanced Television |
| US8782724B2 (en)* | 2009-12-15 | 2014-07-15 | Verizon Patent And Licensing Inc. | User editable metadata for interactive television programs |
- 2012
- 2012-06-14WOPCT/US2012/042541patent/WO2012174301A1/enactiveApplication Filing
- 2012-06-14USUS13/523,829patent/US9762967B2/ennot_activeCeased
- 2017
- 2017-08-07USUS15/670,883patent/US10306324B2/enactiveActive
- 2019
- 2019-02-21USUS16/281,229patent/US20190394531A1/enactivePending
- 2019-09-11USUS16/567,246patent/USRE48546E1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (266)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20020112249A1 (en)* | 1992-12-09 | 2002-08-15 | Hendricks John S. | Method and apparatus for targeting of interactive virtual objects |
| US20010001160A1 (en) | 1996-03-29 | 2001-05-10 | Microsoft Corporation | Interactive entertainment system for presenting supplemental interactive content together with continuous video programs |
| US7757254B2 (en) | 1996-03-29 | 2010-07-13 | Microsoft Corporation | Interactive entertainment system for presenting supplemental interactive content together with continuous video programs |
| US20050015815A1 (en) | 1996-03-29 | 2005-01-20 | Microsoft Corporation | Interactive entertainment system for presenting supplemental interactive content together with continuous video programs |
| US20030126200A1 (en) | 1996-08-02 | 2003-07-03 | Wolff James J. | Dynamic load balancing of a network of client and server computer |
| US20020064149A1 (en) | 1996-11-18 | 2002-05-30 | Elliott Isaac K. | System and method for providing requested quality of service in a hybrid network |
| US8635649B2 (en) | 1996-12-19 | 2014-01-21 | Gemstar Development Corporation | System and method for modifying advertisement responsive to EPG information |
| US20020073424A1 (en) | 1996-12-19 | 2002-06-13 | Eguide, Inc. | System and method for modifying advertisement responsive to EPG information |
| US20050235318A1 (en) | 1997-01-06 | 2005-10-20 | Grauch Edward R | Method and system for tracking network use |
| US9191722B2 (en) | 1997-07-21 | 2015-11-17 | Rovi Guides, Inc. | System and method for modifying advertisement responsive to EPG information |
| US20020120933A1 (en) | 1998-04-30 | 2002-08-29 | United Video Properties, Inc | Program guide system with flip and browse advertisements |
| US6415326B1 (en) | 1998-09-15 | 2002-07-02 | Microsoft Corporation | Timeline correlation between multiple timeline-altered media streams |
| US7096271B1 (en) | 1998-09-15 | 2006-08-22 | Microsoft Corporation | Managing timeline modification and synchronization of multiple media streams in networked client/server systems |
| US6357042B2 (en)* | 1998-09-16 | 2002-03-12 | Anand Srinivasan | Method and apparatus for multiplexing separately-authored metadata for insertion into a video data stream |
| US6317784B1 (en) | 1998-09-29 | 2001-11-13 | Radiowave.Com, Inc. | Presenting supplemental information for material currently and previously broadcast by a radio station |
| US6741977B1 (en) | 1999-01-29 | 2004-05-25 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Image recording/reproducing apparatus in monitor system |
| US8230343B2 (en) | 1999-03-29 | 2012-07-24 | Digitalsmiths, Inc. | Audio and video program recording, editing and playback systems using metadata |
| US7379661B2 (en) | 1999-04-21 | 2008-05-27 | Sonic Solutions, A California Corporation | Presentation of media content |
| US6188398B1 (en) | 1999-06-02 | 2001-02-13 | Mark Collins-Rector | Targeting advertising using web pages with video |
| US20080209485A1 (en) | 1999-07-14 | 2008-08-28 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Information provision apparatus, information receiving apparatus, and storage medium |
| US20080017722A1 (en) | 2000-01-03 | 2008-01-24 | Tripletail Ventures, Inc. | Method for data interchange |
| US20020053078A1 (en) | 2000-01-14 | 2002-05-02 | Alex Holtz | Method, system and computer program product for producing and distributing enhanced media downstreams |
| US20020120925A1 (en) | 2000-03-28 | 2002-08-29 | Logan James D. | Audio and video program recording, editing and playback systems using metadata |
| US20030093790A1 (en) | 2000-03-28 | 2003-05-15 | Logan James D. | Audio and video program recording, editing and playback systems using metadata |
| US7302490B1 (en) | 2000-05-03 | 2007-11-27 | Microsoft Corporation | Media file format to support switching between multiple timeline-altered media streams |
| US7472198B2 (en) | 2000-05-03 | 2008-12-30 | Microsoft Corporation | Media file format to support switching between multiple timeline-altered media streams |
| US20030093792A1 (en) | 2000-06-30 | 2003-05-15 | Labeeb Ismail K. | Method and apparatus for delivery of television programs and targeted de-coupled advertising |
| US7421729B2 (en) | 2000-08-25 | 2008-09-02 | Intellocity Usa Inc. | Generation and insertion of indicators using an address signal applied to a database |
| US20020131511A1 (en) | 2000-08-25 | 2002-09-19 | Ian Zenoni | Video tags and markers |
| US20030067554A1 (en) | 2000-09-25 | 2003-04-10 | Klarfeld Kenneth A. | System and method for personalized TV |
| US20020042920A1 (en)* | 2000-10-11 | 2002-04-11 | United Video Properties, Inc. | Systems and methods for supplementing on-demand media |
| US20030012548A1 (en)* | 2000-12-21 | 2003-01-16 | Levy Kenneth L. | Watermark systems for media |
| US20020104101A1 (en)* | 2001-01-31 | 2002-08-01 | Yamato Jun-Ichi | Information providing system and information providing method |
| US20030001880A1 (en) | 2001-04-18 | 2003-01-02 | Parkervision, Inc. | Method, system, and computer program product for producing and distributing enhanced media |
| US20020188628A1 (en) | 2001-04-20 | 2002-12-12 | Brian Cooper | Editing interactive content with time-based media |
| US20020162117A1 (en)* | 2001-04-26 | 2002-10-31 | Martin Pearson | System and method for broadcast-synchronized interactive content interrelated to broadcast content |
| US20030033157A1 (en) | 2001-08-08 | 2003-02-13 | Accenture Global Services Gmbh | Enhanced custom content television |
| US20100083306A1 (en) | 2001-08-08 | 2010-04-01 | Accenture Global Services Gmbh | Enhanced custom content television |
| US20130024906A9 (en) | 2001-09-19 | 2013-01-24 | John Carney | System and method for construction, delivery and display of itv content |
| US8413205B2 (en) | 2001-09-19 | 2013-04-02 | Tvworks, Llc | System and method for construction, delivery and display of iTV content |
| US20040226051A1 (en) | 2001-09-19 | 2004-11-11 | John Carney | System and method for construction, delivery and display of iTV content |
| US7136871B2 (en) | 2001-11-21 | 2006-11-14 | Microsoft Corporation | Methods and systems for selectively displaying advertisements |
| US20030101454A1 (en) | 2001-11-21 | 2003-05-29 | Stuart Ozer | Methods and systems for planning advertising campaigns |
| US6874126B1 (en) | 2001-11-30 | 2005-03-29 | View Space Technologies | Method and apparatus for controlling content display by the cursor motion |
| US20060190336A1 (en) | 2001-12-28 | 2006-08-24 | Pisaris-Henderson Craig A | System and method for pay for performance advertising in general media |
| US20040003400A1 (en) | 2002-03-15 | 2004-01-01 | John Carney | System and method for construction, delivery and display of iTV content |
| US8042132B2 (en) | 2002-03-15 | 2011-10-18 | Tvworks, Llc | System and method for construction, delivery and display of iTV content |
| US20040031058A1 (en) | 2002-05-10 | 2004-02-12 | Richard Reisman | Method and apparatus for browsing using alternative linkbases |
| US20150135206A1 (en) | 2002-05-10 | 2015-05-14 | Convergent Media Solutions Llc | Method and apparatus for browsing using alternative linkbases |
| US20150135214A1 (en) | 2002-05-10 | 2015-05-14 | Convergent Media Solutions Llc | Method and apparatus for browsing using alternative linkbases |
| US20030229900A1 (en)* | 2002-05-10 | 2003-12-11 | Richard Reisman | Method and apparatus for browsing using multiple coordinated device sets |
| US7415529B2 (en) | 2002-08-20 | 2008-08-19 | Microsoft Corporation | Media streaming of web content data |
| US8220018B2 (en) | 2002-09-19 | 2012-07-10 | Tvworks, Llc | System and method for preferred placement programming of iTV content |
| US20050188402A1 (en) | 2002-09-19 | 2005-08-25 | De Andrade David | System and method for preferred placement programming of iTV content |
| US8943533B2 (en) | 2002-09-19 | 2015-01-27 | Tvworks, Llc | System and method for preferred placement programming of iTV content |
| US20070088609A1 (en) | 2002-10-25 | 2007-04-19 | Medio Systems, Inc. | Optimizer For Selecting Supplemental Content Based on Content Productivity of a Document |
| US20050060741A1 (en) | 2002-12-10 | 2005-03-17 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Media data audio-visual device and metadata sharing system |
| US20060174310A1 (en) | 2003-03-13 | 2006-08-03 | Hee-Kyung Lee | Extended metadata and adaptive program service providing system and method for providing digital broadcast program service |
| US20130198642A1 (en) | 2003-03-14 | 2013-08-01 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Providing Supplemental Content |
| US8448208B2 (en) | 2003-03-14 | 2013-05-21 | Tvworks, Llc | System and method for construction, delivery and display of iTV applications that blend programming information of on-demand and broadcast service offerings |
| US20040260682A1 (en) | 2003-06-19 | 2004-12-23 | Microsoft Corporation | System and method for identifying content and managing information corresponding to objects in a signal |
| US7428696B2 (en) | 2003-06-30 | 2008-09-23 | Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. | System and method for time synchronization between multimedia content and segment metadata |
| US20050038794A1 (en)* | 2003-08-14 | 2005-02-17 | Ricoh Company, Ltd. | Transmission of event markers to data stream recorder |
| US20050050218A1 (en) | 2003-09-02 | 2005-03-03 | Microsoft Corporation | Video delivery workflow |
| US20050125428A1 (en) | 2003-10-04 | 2005-06-09 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Storage medium storing search information and reproducing apparatus and method |
| US9154852B2 (en) | 2003-12-23 | 2015-10-06 | Opentv, Inc. | Advertising methods for advertising time slots and embedded objects |
| US20070127720A1 (en) | 2004-01-26 | 2007-06-07 | David White | Timeline protection |
| US20130204698A1 (en) | 2004-03-12 | 2013-08-08 | Ttn Holdings, Llc | Systems and methods for automated mass media commerce |
| US20070250761A1 (en) | 2004-06-04 | 2007-10-25 | Bob Bradley | System and method for synchronizing media presentation at multiple recipients |
| US8681822B2 (en) | 2004-06-04 | 2014-03-25 | Apple Inc. | System and method for synchronizing media presentation at multiple recipients |
| US20060015908A1 (en) | 2004-06-30 | 2006-01-19 | Nokia Corporation | Multiple services within a channel-identification in a device |
| US20070274676A1 (en) | 2004-09-10 | 2007-11-29 | Giuseppe Diomelli | Method and Apparatus For Unified Management Of Different Type Of Communications Over Lanwan And Internet Networks, Using A Web Browser |
| US20070011050A1 (en) | 2005-05-20 | 2007-01-11 | Steven Klopf | Digital advertising system |
| US20080267588A1 (en) | 2005-08-25 | 2008-10-30 | Ayako Iwase | Reproduction Device, Reproduction Method, Program, Program Storage Medium, Data Structure, and Recording Medium Fabrication Method |
| US20070061838A1 (en) | 2005-09-12 | 2007-03-15 | I7 Corp | Methods and systems for displaying audience targeted information |
| US20070124789A1 (en) | 2005-10-26 | 2007-05-31 | Sachson Thomas I | Wireless interactive communication system |
| US20070124756A1 (en)* | 2005-11-29 | 2007-05-31 | Google Inc. | Detecting Repeating Content in Broadcast Media |
| US20100169910A1 (en) | 2006-01-06 | 2010-07-01 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Apparatus and methods of selective collection and selective presentation of content |
| US9554093B2 (en) | 2006-02-27 | 2017-01-24 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Automatically inserting advertisements into source video content playback streams |
| US8385633B2 (en) | 2006-03-12 | 2013-02-26 | Google Inc. | Techniques for enabling or establishing the use of face recognition algorithms |
| US20080036917A1 (en)* | 2006-04-07 | 2008-02-14 | Mark Pascarella | Methods and systems for generating and delivering navigatable composite videos |
| US7913157B1 (en) | 2006-04-18 | 2011-03-22 | Overcast Media Incorporated | Method and system for the authoring and playback of independent, synchronized media through the use of a relative virtual time code |
| US8701005B2 (en) | 2006-04-26 | 2014-04-15 | At&T Intellectual Property I, Lp | Methods, systems, and computer program products for managing video information |
| US20120256762A1 (en) | 2006-07-24 | 2012-10-11 | Upmc | Emergency management system |
| US7788262B1 (en) | 2006-08-04 | 2010-08-31 | Sanika Shirwadkar | Method and system for creating context based summary |
| US20080066110A1 (en) | 2006-09-11 | 2008-03-13 | Rainer Brodersen | Media preview user interface |
| US20080066100A1 (en) | 2006-09-11 | 2008-03-13 | Apple Computer, Inc. | Enhancing media system metadata |
| US20080068500A1 (en) | 2006-09-18 | 2008-03-20 | Rgb Networks, Inc. | Methods, apparatus, and systems for insertion of overlay content into a video signal with transrating capabilities |
| US20080113789A1 (en) | 2006-11-15 | 2008-05-15 | Microsoft Corporation | Console integrated downloadable game service |
| US20090234815A1 (en) | 2006-12-12 | 2009-09-17 | Marco Boerries | Open framework for integrating, associating, and interacting with content objects including automatic feed creation |
| US20090240564A1 (en) | 2006-12-12 | 2009-09-24 | Marco Boerries | Open framework for integrating, associating, and interacting with content objects including advertisement and content personalization |
| US20080168133A1 (en) | 2007-01-05 | 2008-07-10 | Roland Osborne | Video distribution system including progressive playback |
| US20110099225A1 (en) | 2007-01-05 | 2011-04-28 | Divx, Llc | Video distribution system including progressive playback |
| US20090044246A1 (en) | 2007-02-01 | 2009-02-12 | Patrick Sheehan | Targeting content based on location |
| US20080301727A1 (en) | 2007-02-01 | 2008-12-04 | Cristofalo Michael | Intelligent targeting of tags in a broadcast network |
| US20150237386A1 (en) | 2007-02-01 | 2015-08-20 | Invidi Technologies Corporation | Targeting content based on location |
| US20080195746A1 (en) | 2007-02-13 | 2008-08-14 | Microsoft Corporation | Live content streaming using file-centric media protocols |
| US20100333152A1 (en) | 2007-03-29 | 2010-12-30 | William Gibbens Redmann | Method and apparatus for content distribution to and playout with a digital cinema system |
| US20100169460A1 (en) | 2007-03-30 | 2010-07-01 | Robert Charles Angell | Methods and Apparatus for Distributing Electronic Media Content for the Purpose of Enhancing Existing Media |
| US20080249853A1 (en) | 2007-04-05 | 2008-10-09 | Elan Dekel | Advertising campaign template |
| US9911126B2 (en) | 2007-04-10 | 2018-03-06 | Google Llc | Refreshing advertisements in offline or virally distributed content |
| US20080255904A1 (en) | 2007-04-13 | 2008-10-16 | Google Inc. | Estimating Off-Line Advertising Impressions |
| US20080307454A1 (en) | 2007-06-11 | 2008-12-11 | Gulrukh Ahanger | Systems and methods for inserting ads during playback of video media |
| US20080313229A1 (en) | 2007-06-17 | 2008-12-18 | Global Telegenetics, Inc. | PORTALS and DOORS for the Semantic Web and Grid |
| US20100118206A1 (en) | 2007-06-21 | 2010-05-13 | Wen Gao | Apparatus and method for use in mobile/handheld communications system |
| US20090006191A1 (en) | 2007-06-27 | 2009-01-01 | Google Inc. | Targeting in-video advertising |
| US20100011392A1 (en) | 2007-07-16 | 2010-01-14 | Novafora, Inc. | Methods and Systems For Media Content Control |
| US20090041418A1 (en)* | 2007-08-08 | 2009-02-12 | Brant Candelore | System and Method for Audio Identification and Metadata Retrieval |
| US10528631B1 (en) | 2007-08-23 | 2020-01-07 | Sony Interactive Entertainment Inc. | Media data presented with time-based metadata |
| US20150245111A1 (en) | 2007-09-07 | 2015-08-27 | Tivo Inc. | Systems and methods for using video metadata to associate advertisements therewith |
| US20090150947A1 (en)* | 2007-10-05 | 2009-06-11 | Soderstrom Robert W | Online search, storage, manipulation, and delivery of video content |
| US20090125812A1 (en) | 2007-10-17 | 2009-05-14 | Yahoo! Inc. | System and method for an extensible media player |
| US20090113468A1 (en) | 2007-10-31 | 2009-04-30 | Ryan Steelberg | System and method for creation and management of advertising inventory using metadata |
| US9294727B2 (en) | 2007-10-31 | 2016-03-22 | Veritone, Inc. | System and method for creation and management of advertising inventory using metadata |
| US20090132371A1 (en) | 2007-11-20 | 2009-05-21 | Big Stage Entertainment, Inc. | Systems and methods for interactive advertising using personalized head models |
| US20090150215A1 (en) | 2007-12-10 | 2009-06-11 | Kalb Kenneth J | System and method for real-time management and optimization of off-line advertising campaigns |
| US20090171948A1 (en) | 2007-12-31 | 2009-07-02 | Peer 39 Inc. | Method and a system for selecting advertising spots |
| US20090295993A1 (en) | 2008-01-07 | 2009-12-03 | Toshiba America Consumer Products, Llc | Control systems and methods using markers in image portion of audiovisual content |
| US20120179536A1 (en) | 2008-01-17 | 2012-07-12 | Kalb Kenneth J | System and method for management and optimization of off-line advertising campaigns with a consumer call to action |
| US20090240734A1 (en) | 2008-01-24 | 2009-09-24 | Geoffrey Wayne Lloyd-Jones | System and methods for the creation, review and synchronization of digital media to digital audio data |
| US20090204481A1 (en)* | 2008-02-12 | 2009-08-13 | Murgesh Navar | Discovery and Analytics for Episodic Downloaded Media |
| US9832532B1 (en) | 2008-02-20 | 2017-11-28 | CSC Holdings, LLC | Interactive save and purchase of content and products |
| US20090216745A1 (en) | 2008-02-26 | 2009-08-27 | Microsoft Corporation | Techniques to Consume Content and Metadata |
| US20090226152A1 (en) | 2008-03-10 | 2009-09-10 | Hanes Brett E | Method for media playback optimization |
| US20090235298A1 (en) | 2008-03-13 | 2009-09-17 | United Video Properties, Inc. | Systems and methods for synchronizing time-shifted media content and related communications |
| US8793256B2 (en) | 2008-03-26 | 2014-07-29 | Tout Industries, Inc. | Method and apparatus for selecting related content for display in conjunction with a media |
| US20090245058A1 (en) | 2008-03-28 | 2009-10-01 | Sony Corporation | Information processing apparatus and method, program, recording medium, and information processing system |
| US8549575B2 (en) | 2008-04-30 | 2013-10-01 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | Dynamic synchronization of media streams within a social network |
| US20090276821A1 (en) | 2008-04-30 | 2009-11-05 | At&T Knowledge Ventures, L.P. | Dynamic synchronization of media streams within a social network |
| US20090285550A1 (en) | 2008-05-14 | 2009-11-19 | Eiju Yamada | Electronic Apparatus, Content Reproduction Method, Record Medium, and Server Apparatus |
| US20100106798A1 (en) | 2008-05-16 | 2010-04-29 | Wyse Technology Inc. | Multimedia redirection |
| US20100142915A1 (en) | 2008-06-06 | 2010-06-10 | Deluxe Digital Studios, Inc. | Methods and systems for use in providing playback of variable length content in a fixed length framework |
| US20090307227A1 (en) | 2008-06-06 | 2009-12-10 | Disney Enterprises, Inc. | Methods and apparatuses for combining and distributing user enhanced video/audio content |
| US20100135637A1 (en) | 2008-06-06 | 2010-06-03 | Deluxe Digital Studios, Inc. | Methods and systems for use in providing playback of variable length content in a fixed length framework |
| US20100031299A1 (en) | 2008-08-04 | 2010-02-04 | Opanga Networks, Llc | Systems and methods for device dependent media content delivery in a local area network |
| US20110178854A1 (en) | 2008-09-04 | 2011-07-21 | Somertech Ltd. | Method and system for enhancing and/or monitoring visual content and method and/or system for adding a dynamic layer to visual content |
| US20100064311A1 (en)* | 2008-09-08 | 2010-03-11 | Robin Ross Cooper | BD-Live Interface to the Distribution Supply Chain |
| US20100070643A1 (en) | 2008-09-11 | 2010-03-18 | Yahoo! Inc. | Delivery of synchronized metadata using multiple transactions |
| US20100158099A1 (en)* | 2008-09-16 | 2010-06-24 | Realnetworks, Inc. | Systems and methods for video/multimedia rendering, composition, and user interactivity |
| US20100088716A1 (en) | 2008-10-02 | 2010-04-08 | Softhills Corporation | Content slots for digital media |
| US8359399B2 (en) | 2008-10-16 | 2013-01-22 | Echostar Technologies L.L.C. | Method and device for delivering supplemental content associated with audio/visual content to a user |
| US20100162286A1 (en) | 2008-11-24 | 2010-06-24 | Digitalsmiths Corporation | Systems and methods for analyzing trends in video consumption based on embedded video metadata |
| US20100146542A1 (en) | 2008-12-04 | 2010-06-10 | Joseph Weihs | System and method of scheduling advertising content for dynamic insertion during playback of video on demand assets |
| US9674562B1 (en)* | 2008-12-18 | 2017-06-06 | Vmware, Inc. | Quality evaluation of multimedia delivery in cloud environments |
| US20100161825A1 (en) | 2008-12-22 | 2010-06-24 | David Randall Ronca | On-device multiplexing of streaming media content |
| US20100246666A1 (en) | 2008-12-30 | 2010-09-30 | Mozaik Multimedia, Inc. | Bluflex: flexible, true, live video streaming on blu-ray platforms |
| US20100169303A1 (en) | 2008-12-31 | 2010-07-01 | David Biderman | Playlists for real-time or near real-time streaming |
| US20110246885A1 (en) | 2008-12-31 | 2011-10-06 | Roger Pantos | Real-time or near real-time streaming |
| US8776108B2 (en) | 2009-01-12 | 2014-07-08 | Disney Enterprises, Inc. | System and/or method for distributing media content and providing an option to maintain an advertising experience |
| US20100180289A1 (en) | 2009-01-12 | 2010-07-15 | Jonathan Barsook | System and/or method for distributing media content and providing an option to maintain an advertising experience |
| US20170201850A1 (en) | 2009-01-28 | 2017-07-13 | Headwater Research Llc | Method for Child Wireless Device Activation to Subscriber Account of a Master Wireless Device |
| US20130132854A1 (en) | 2009-01-28 | 2013-05-23 | Headwater Partners I Llc | Service Plan Design, User Interfaces, Application Programming Interfaces, and Device Management |
| US10061742B2 (en) | 2009-01-30 | 2018-08-28 | Sonos, Inc. | Advertising in a digital media playback system |
| US20130254340A1 (en) | 2009-01-30 | 2013-09-26 | Jonathan Lang | Advertising in a digital media playback system |
| US20100205049A1 (en) | 2009-02-12 | 2010-08-12 | Long Dustin W | Advertisement management for live internet multimedia content |
| US20140046775A1 (en) | 2009-02-23 | 2014-02-13 | Joseph Harb | Method, system and apparatus for synchronizing radio content and external content |
| US20100228693A1 (en) | 2009-03-06 | 2010-09-09 | phiScape AG | Method and system for generating a document representation |
| US20100235472A1 (en) | 2009-03-16 | 2010-09-16 | Microsoft Corporation | Smooth, stateless client media streaming |
| US20100241961A1 (en) | 2009-03-23 | 2010-09-23 | Peterson Troy A | Content presentation control and progression indicator |
| US20100241962A1 (en) | 2009-03-23 | 2010-09-23 | Peterson Troy A | Multiple content delivery environment |
| US20100274667A1 (en) | 2009-04-24 | 2010-10-28 | Nexidia Inc. | Multimedia access |
| US20100287580A1 (en) | 2009-05-08 | 2010-11-11 | Harding John M | Content syndication in web-based media via ad tagging |
| US20100299687A1 (en) | 2009-05-23 | 2010-11-25 | Adrian Bertino-Clarke | Peer-to-peer video content distribution |
| US20130097190A1 (en) | 2009-05-27 | 2013-04-18 | Ajay Shah | Supplementing synchronization with programming metadata |
| US20130104179A1 (en) | 2009-05-27 | 2013-04-25 | Ajay Shah | Supplemental synchronization to time-based media |
| US8595781B2 (en) | 2009-05-29 | 2013-11-26 | Cognitive Media Networks, Inc. | Methods for identifying video segments and displaying contextual targeted content on a connected television |
| US20120203589A1 (en) | 2009-07-27 | 2012-08-09 | Nextgen Healthcare Information Systems, Inc. | Systematic Rule-Based Workflow Tasking and Event Scheduling |
| US20110044601A1 (en) | 2009-08-24 | 2011-02-24 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method for play synchronization and device using the same |
| US20110061001A1 (en) | 2009-09-04 | 2011-03-10 | Yahoo! Inc. | Synchronization of advertisment display updates with user revisitation rates |
| US20110058675A1 (en) | 2009-09-04 | 2011-03-10 | Brueck David F | Controlling access to copies of media content by a client device |
| US8775945B2 (en) | 2009-09-04 | 2014-07-08 | Yahoo! Inc. | Synchronization of advertisment display updates with user revisitation rates |
| US20110134321A1 (en) | 2009-09-11 | 2011-06-09 | Digitalsmiths Corporation | Timeline Alignment for Closed-Caption Text Using Speech Recognition Transcripts |
| US20110078623A1 (en) | 2009-09-30 | 2011-03-31 | Microsoft Corporation | Video content-aware advertisement placement |
| US20150289030A1 (en) | 2009-12-04 | 2015-10-08 | At&T Intellectual Property I, Lp | Apparatus and method for tagging media content and managing marketing |
| US20120290644A1 (en) | 2010-01-18 | 2012-11-15 | Frederic Gabin | Methods and Arrangements for HTTP Media Stream Distribution |
| US20110196747A1 (en) | 2010-02-11 | 2011-08-11 | Microsoft Corporation | Facilitating advertisement selection using advancement bids |
| US20110218851A1 (en) | 2010-03-06 | 2011-09-08 | O'hanlon David Joseph | Search engine optimization purchasing economic method |
| US20170013314A1 (en)* | 2010-04-01 | 2017-01-12 | Sony Interactive Entertainment Inc. | Media fingerprinting for content determination and retrieval |
| US20110246622A1 (en) | 2010-04-01 | 2011-10-06 | Roger Pantos | Real-Time or Near Real-Time Streaming |
| US20130011120A1 (en) | 2010-04-09 | 2013-01-10 | Kazumasa Tanaka | Content processing apparatus and method, and program |
| US20130170753A1 (en) | 2010-04-09 | 2013-07-04 | Sony Corporation | Apparatus and method of content retrieval and program |
| US9594957B2 (en) | 2010-04-09 | 2017-03-14 | Sony Corporation | Apparatus and method for identifying a still image contained in moving image contents |
| US20130077876A1 (en) | 2010-04-09 | 2013-03-28 | Kazumasa Tanaka | Apparatus and method for identifying a still image contained in moving image contents |
| US20110258529A1 (en) | 2010-04-16 | 2011-10-20 | Toby Doig | Systems and methods for excluding serving an advertisement campaign to undesired web pages |
| US20110258545A1 (en) | 2010-04-20 | 2011-10-20 | Witstreams | Service for Sharing User Created Comments that Overlay and are Synchronized with Video |
| US20110273455A1 (en)* | 2010-05-04 | 2011-11-10 | Shazam Entertainment Ltd. | Systems and Methods of Rendering a Textual Animation |
| US20110276372A1 (en) | 2010-05-04 | 2011-11-10 | Live Matrix, Inc. | Temporal indices of the web that associate index elements with metadata |
| US20110319160A1 (en) | 2010-06-25 | 2011-12-29 | Idevcor Media, Inc. | Systems and Methods for Creating and Delivering Skill-Enhancing Computer Applications |
| US20110321096A1 (en) | 2010-06-29 | 2011-12-29 | Echostar Technologies L.L.C. | Apparatus, systems and methods for accessing and synchronizing presentation of media content and supplemental media rich content in response to selection of a presented object |
| US8763060B2 (en) | 2010-07-11 | 2014-06-24 | Apple Inc. | System and method for delivering companion content |
| US9814977B2 (en) | 2010-07-13 | 2017-11-14 | Sony Interactive Entertainment Inc. | Supplemental video content on a mobile device |
| US20130183021A1 (en) | 2010-07-13 | 2013-07-18 | Sony Computer Entertainment Inc. | Supplemental content on a mobile device |
| US8719869B2 (en) | 2010-08-04 | 2014-05-06 | Nagravision S.A. | Method for sharing data and synchronizing broadcast data with additional information |
| US8850495B2 (en) | 2010-08-14 | 2014-09-30 | Yang Pan | Advertisement delivering system based on digital television system and mobile communication device |
| US20140310243A1 (en) | 2010-08-16 | 2014-10-16 | Mr. Steven James McGee | Heart beacon cycle |
| US20190107906A1 (en) | 2010-10-15 | 2019-04-11 | Tivo Solutions Inc. | Time-based metadata management system for digital media |
| US20120102042A1 (en) | 2010-10-20 | 2012-04-26 | Flick christopher | Temporal metadata track |
| US20120110627A1 (en) | 2010-10-29 | 2012-05-03 | Nbc Universal, Inc. | Time-adapted content delivery system and method |
| US20200068256A1 (en) | 2010-11-01 | 2020-02-27 | Gracenote, Inc. | Method and system for presenting additional content at a media system |
| US20120116883A1 (en) | 2010-11-08 | 2012-05-10 | Sony Corporation | Methods and systems for use in incorporating targeted advertising into multimedia content streams |
| US20130095864A1 (en) | 2010-11-16 | 2013-04-18 | Jack L. Marovets | System, method, and apparatus for storing, transmitting, receiving, and using structured data using un-structured text message bodies |
| US20140009680A1 (en) | 2010-11-24 | 2014-01-09 | Lg Electhonics Inc. | Video display device and method for controlling same |
| US20120144417A1 (en) | 2010-12-01 | 2012-06-07 | Ensequence, Inc. | Method and system for controlling content in a multimedia display |
| US20140149918A1 (en) | 2010-12-20 | 2014-05-29 | Ashwini Asokan | Techniques for management and presentation of content |
| US20120158472A1 (en) | 2010-12-21 | 2012-06-21 | Research In Motion Limited | Contextual customization of content display on a communication device |
| US20120167146A1 (en)* | 2010-12-28 | 2012-06-28 | White Square Media Llc | Method and apparatus for providing or utilizing interactive video with tagged objects |
| WO2012094432A1 (en) | 2011-01-04 | 2012-07-12 | Related Content Databases, Inc. | System and method for interfacing content playback devices with network sites to supplement content playback |
| WO2012094539A2 (en) | 2011-01-05 | 2012-07-12 | Related Content Databases, Inc. | System and method for streaming content to blu-ray devices |
| US20130293677A1 (en) | 2011-01-19 | 2013-11-07 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Reception device for receiving a plurality of real-time transfer streams, transmission device for transmitting same, and method for playing multimedia content |
| US9432721B2 (en) | 2011-01-21 | 2016-08-30 | Bluefin Labs, Inc. | Cross media targeted message synchronization |
| US20120192227A1 (en) | 2011-01-21 | 2012-07-26 | Bluefin Labs, Inc. | Cross Media Targeted Message Synchronization |
| US8898698B2 (en) | 2011-01-21 | 2014-11-25 | Bluefin Labs, Inc. | Cross media targeted message synchronization |
| US20120192225A1 (en) | 2011-01-25 | 2012-07-26 | Youtoo Technologies, LLC | Administration of Content Creation and Distribution System |
| US20120192220A1 (en) | 2011-01-25 | 2012-07-26 | Youtoo Technologies, LLC | User-generated social television content |
| US20120197419A1 (en) | 2011-01-31 | 2012-08-02 | Cbs Interactive, Inc. | Media Playback Control |
| US20120233646A1 (en) | 2011-03-11 | 2012-09-13 | Coniglio Straker J | Synchronous multi-platform content consumption |
| US20130036007A1 (en) | 2011-05-06 | 2013-02-07 | Lau Emil O | Cross-platform collection of advertising metrics |
| US20120310750A1 (en) | 2011-06-01 | 2012-12-06 | Intercast Networks, Inc. | Interface and module for real-time advertising presentation |
| US20130132818A1 (en) | 2011-06-03 | 2013-05-23 | Mark Anders | Controlling The Structure Of Animated Documents |
| US20170041648A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2017-02-09 | Watchwith, Inc. | System and method for supplemental content selection and delivery |
| WO2012174301A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2012-12-20 | Related Content Database, Inc. | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
| US20170041644A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2017-02-09 | Watchwith, Inc. | Metadata delivery system for rendering supplementary content |
| US20170041649A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2017-02-09 | Watchwith, Inc. | Supplemental content playback system |
| US20170339462A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2017-11-23 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | System And Method For Presenting Content With Time Based Metadata |
| US9762967B2 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2017-09-12 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
| US20130014155A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2013-01-10 | Douglas Clarke | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata |
| US20140157307A1 (en) | 2011-07-21 | 2014-06-05 | Stuart Anderson Cox | Method and apparatus for delivery of programs and metadata to provide user alerts to tune to corresponding program channels before high interest events occur during playback of programs |
| US20140180829A1 (en) | 2011-09-09 | 2014-06-26 | Dennoo Inc. | Advertising Platform |
| US8737813B2 (en) | 2011-09-16 | 2014-05-27 | Nbcuniversal Media, Llc | Automatic content recognition system and method for providing supplementary content |
| US20130071090A1 (en) | 2011-09-16 | 2013-03-21 | Nbcuniversal Media Llc | Automatic content recongition system and method for providing supplementary content |
| US20130070152A1 (en) | 2011-09-16 | 2013-03-21 | Nbcuniversal Media Llc | Sampled digital content based syncronization of supplementary digital content |
| US20130074141A1 (en) | 2011-09-21 | 2013-03-21 | University Of Seoul Industry Cooperation Foundation | Method and apparatus for synchronizing media data of multimedia broadcast service |
| US20130091518A1 (en) | 2011-10-07 | 2013-04-11 | Accenture Global Services Limited | Synchronizing Digital Media Content |
| US20130170813A1 (en) | 2011-12-30 | 2013-07-04 | United Video Properties, Inc. | Methods and systems for providing relevant supplemental content to a user device |
| US8381259B1 (en) | 2012-01-05 | 2013-02-19 | Vinod Khosla | Authentication and synchronous interaction between a secondary device and a multi-perspective audiovisual data stream broadcast on a primary device |
| US20130176493A1 (en) | 2012-01-05 | 2013-07-11 | Vinod Khosla | Authentication and synchronous interaction between a secondary device and a multi-perspective audiovisual data stream broadcast on a primary device geospatially proximate to the secondary device |
| US20150019644A1 (en) | 2012-01-06 | 2015-01-15 | Thomsom Licensing | Method and system for providing a display of socialmessages on a second screen which is synched to content on a first screen |
| US20150020096A1 (en) | 2012-01-06 | 2015-01-15 | Thomson Licensing | Method and system for synchronising social messages with a content timeline |
| US20140327677A1 (en) | 2012-01-06 | 2014-11-06 | Thomson Licensing | Method and system for providing a graphical representation on a second screen of social messages related to content on a first screen |
| US20150003798A1 (en) | 2012-01-06 | 2015-01-01 | Thomson Licensing | Alternate view video playback on a second screen |
| US20140365302A1 (en) | 2012-01-06 | 2014-12-11 | Thomson Licensing | Method and system for providing dynamic advertising on a second screen based on social messages |
| US20130191745A1 (en) | 2012-01-10 | 2013-07-25 | Zane Vella | Interface for displaying supplemental dynamic timeline content |
| US20130262997A1 (en) | 2012-03-27 | 2013-10-03 | Roku, Inc. | Method and Apparatus for Displaying Information on a Secondary Screen |
| US9922334B1 (en) | 2012-04-06 | 2018-03-20 | Google Llc | Providing an advertisement based on a minimum number of exposures |
| US20130332839A1 (en) | 2012-06-11 | 2013-12-12 | Cellco Partnership D/B/A Verizon Wireless | Cross-platform schedule management interface |
| US20130347018A1 (en) | 2012-06-21 | 2013-12-26 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Providing supplemental content with active media |
| US20140089967A1 (en) | 2012-09-27 | 2014-03-27 | General Instrument Corporation | Providing secondary content to accompany a primary content item |
| US10579215B2 (en) | 2012-12-10 | 2020-03-03 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Providing content via multiple display devices |
| US20140181868A1 (en) | 2012-12-21 | 2014-06-26 | Verizon Patent And Licensing Inc. | Systems, methods, and user interfaces for facilitating user access to media content |
| US8699862B1 (en) | 2013-02-06 | 2014-04-15 | Google Inc. | Synchronized content playback related to content recognition |
| US20140337127A1 (en) | 2013-04-23 | 2014-11-13 | Brightcove, Inc. | Client bridge |
| US20150134673A1 (en) | 2013-10-03 | 2015-05-14 | Minute Spoteam Ltd. | System and method for creating synopsis for multimedia content |
| US20150199968A1 (en) | 2014-01-16 | 2015-07-16 | CloudCar Inc. | Audio stream manipulation for an in-vehicle infotainment system |
| US20150237389A1 (en) | 2014-02-14 | 2015-08-20 | Pluto Inc. | Methods and systems for generating and providing program guides and content |
| US20150281763A1 (en) | 2014-03-25 | 2015-10-01 | Cisco Technology Inc. | System and Method for Synchronized Presentation of Video Timeline Metadata |
| US20160127776A1 (en) | 2014-11-05 | 2016-05-05 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Increased user efficiency and interaction performance through dynamic adjustment of auxiliary content duration |
| US20160182923A1 (en) | 2014-12-19 | 2016-06-23 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (Publ) | End user-based personalized ad insertion in broadcast-broadband hybrid terminals |
| US20160191957A1 (en) | 2014-12-31 | 2016-06-30 | Opentv, Inc. | Lull management for content delivery |
| US20160234295A1 (en) | 2015-02-05 | 2016-08-11 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | Correlation of Actionable Events To An Actionable Instruction |
| US20170295386A1 (en) | 2016-04-12 | 2017-10-12 | Verizon Patent And Licensing Inc. | Stream boundary marking for dynamic content replacement |
| US20170344439A1 (en) | 2016-05-27 | 2017-11-30 | Raytheon Company | System and method for input data fault recovery in a massively parallel real time computing system |
| US20180014077A1 (en) | 2016-07-05 | 2018-01-11 | Pluto Inc. | Methods and systems for generating and providing program guides and content |
| EP3270600A1 (en) | 2016-07-14 | 2018-01-17 | Comcast Cable Communications LLC | System and method for supplemental content selection and delivery |
| CA2973717A1 (en) | 2016-07-14 | 2018-01-14 | Comcast Cable Communications, Llc | System and method for supplemental content selection and delivery |
| US10708336B2 (en) | 2016-12-04 | 2020-07-07 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | System and method for announcing media changes |
| US20190349619A1 (en) | 2018-05-09 | 2019-11-14 | Pluto Inc. | Methods and systems for generating and providing program guides and content |
Non-Patent Citations (11)
| Title |
|---|
| International Search Report and Written Opinion, International Application No. PCT/US2012/020239, dated Apr. 24, 2012, 9 Pages. |
| International Search Report and Written Opinion, International Application No. PCT/US2012/020387, dated Jul. 10, 2012, 11 Pages. |
| International Search Report and Written Opinion, International Application No. PCT/US2012/042541, dated Aug. 31, 2012, 9 Pages. |
| Non-Office Action dated Jul. 18, 2013, for related U.S. Appl. No. 13/343,683, filed Jan. 4, 2012, 15 pages. |
| Non-Office Action dated Jun. 5, 2013, for related U.S. Appl. No. 13/344,579, filed Jan. 5, 2012, 25 pages. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 15/331,815, filed Oct. 22, 2016, entitled "Supplemental Content Playback System". |
| U.S. Appl. No. 15/929,300, filed Apr. 23, 2020, entitled "Interface for Displaying Supplemental Dynamic Timeline Content". |
| U.S. Appl. No. 61/497,023, filed Jun. 14, 2011, entitled "System and Method for Presenting Content with Time Based Metadata". |
| U.S. Appl. No. 61/631,814, filed Jan. 10, 2012, entitled "Interface for Displaying Supplemental Dynamic Timeline Content". |
| U.S. Appl. No. 62/362,587, filed Jul. 14, 2016, entitled "Metadata Delivery System for Rendering Supplementary Content". |
| U.S. Appl. No. 62/366,540, filed Jul. 25, 2016, entitled "System to Select Supplemental Content for Playback Devices". |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20130014155A1 (en) | 2013-01-10 |
| US20190394531A1 (en) | 2019-12-26 |
| US9762967B2 (en) | 2017-09-12 |
| US10306324B2 (en) | 2019-05-28 |
| WO2012174301A1 (en) | 2012-12-20 |
| US20170339462A1 (en) | 2017-11-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| USRE48546E1 (en) | System and method for presenting content with time based metadata | |
| US11659244B2 (en) | Methods and systems for generating and providing program guides and content | |
| US9912994B2 (en) | Interactive distributed multimedia system | |
| US20250142146A1 (en) | Metadata delivery system for rendering supplementary content | |
| US20180167698A1 (en) | Instant clip creation based on media content recognition | |
| US20170041648A1 (en) | System and method for supplemental content selection and delivery | |
| US20130312049A1 (en) | Authoring, archiving, and delivering time-based interactive tv content | |
| US20170041649A1 (en) | Supplemental content playback system | |
| KR101328270B1 (en) | Annotation method and augmenting video process in video stream for smart tv contents and system thereof | |
| EP3270600A1 (en) | System and method for supplemental content selection and delivery | |
| US20120143661A1 (en) | Interactive E-Poster Methods and Systems | |
| KR20180041879A (en) | Method for editing and apparatus thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| FEPP | Fee payment procedure | Free format text:ENTITY STATUS SET TO UNDISCOUNTED (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: BIG.); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: LARGE ENTITY | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:RELATED CONTENT DATABASE, INC., CALIFORNIA Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:CLARKE, DOUGLAS;DALRYMPLE, MICHAEL;ELLIOTT, EDWARD LEE;AND OTHERS;REEL/FRAME:054851/0215 Effective date:20120614 Owner name:COMCAST CABLE COMMUNICATIONS, LLC, PENNSYLVANIA Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:WATCHWITH, INC.;REEL/FRAME:054851/0297 Effective date:20161207 Owner name:COMCAST CABLE COMMUNICATIONS, LLC, PENNSYLVANIA Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:LUTJENS, OLE;VELLA, ZANE;SIGNING DATES FROM 20180110 TO 20190523;REEL/FRAME:054851/0165 Owner name:WATCHWITH, INC., DELAWARE Free format text:CHANGE OF NAME;ASSIGNOR:RELATED CONTENT DATABASE, INC.;REEL/FRAME:054927/0461 Effective date:20130503 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:COMCAST CABLE COMMUNICATIONS, LLC, PENNSYLVANIA Free format text:CORRECTIVE ASSIGNMENT TO CORRECT THE RECEIVING PARTY DATA CITY PREVIOUSLY RECORDED AT REEL: 054851 FRAME: 0297. ASSIGNOR(S) HEREBY CONFIRMS THE ASSIGNMENT;ASSIGNOR:WATCHWITH, INC.;REEL/FRAME:055760/0627 Effective date:20161207 | |
| MAFP | Maintenance fee payment | Free format text:PAYMENT OF MAINTENANCE FEE, 8TH YEAR, LARGE ENTITY (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: M1552); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: LARGE ENTITY Year of fee payment:8 |