US9271327B2 - Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling - Google Patents
Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware schedulingDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US9271327B2 US9271327B2US14/028,323US201314028323AUS9271327B2US 9271327 B2US9271327 B2US 9271327B2US 201314028323 AUS201314028323 AUS 201314028323AUS 9271327 B2US9271327 B2US 9271327B2
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- queue
- packet
- transmission
- determined
- weights
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W72/00—Local resource management
- H04W72/50—Allocation or scheduling criteria for wireless resources
- H04W72/56—Allocation or scheduling criteria for wireless resources based on priority criteria
- H04W72/566—Allocation or scheduling criteria for wireless resources based on priority criteria of the information or information source or recipient
- H04W72/569—Allocation or scheduling criteria for wireless resources based on priority criteria of the information or information source or recipient of the traffic information
- H04W72/1242—
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W80/00—Wireless network protocols or protocol adaptations to wireless operation
- H04W80/04—Network layer protocols, e.g. mobile IP [Internet Protocol]
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W88/00—Devices specially adapted for wireless communication networks, e.g. terminals, base stations or access point devices
- H04W88/02—Terminal devices
- H04W88/06—Terminal devices adapted for operation in multiple networks or having at least two operational modes, e.g. multi-mode terminals
- H04W72/1257—
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W72/00—Local resource management
- H04W72/50—Allocation or scheduling criteria for wireless resources
- H04W72/535—Allocation or scheduling criteria for wireless resources based on resource usage policies
Definitions
- the present inventiongenerally relates to communications networks. More particular, the present invention related to systems and method for increased data throughput in communications networks.
- a wireless channelis generally understood as a pathway between two communication endpoints. Through a wireless channel, the communication of any number of forms of data may take place. The efficient and effective communication of data is, however, subject to any number of characteristics of a particular wireless channel.
- a wireless channel with low throughputwould not be recommended for the communication of data related to a high-definition television program.
- the use of a wireless channel with a large amount of available bandwidthmay be better utilized in the context of time-sensitive data transfers (e.g., voice communications) rather than the exchange of low priority and low-bandwidth background data queries.
- Characteristics of a wireless channelmay vary over time. For example, a wireless channel that at one moment has available bandwidth may subsequently be subjected to bottlenecks and dropped data packets thus requiring retransmission of the same. These variances in network characteristics may be a result of, for example, terminal mobility, multipath fading, or interference.
- a terminalmay (while in motion) access wireless services from different locations.
- the mobility of the terminalrequires the network to expend resources related to identifying and locating that terminal.
- the accessing of the network at different locales over time in conjunction with the need of the network to identify and locate the terminalmay affect the quality of a wireless signal in that network.
- Multipath fadinginvolves the phenomenon of multipath propagation whereby a radio signal arrives at a receiving station (e.g., an antenna), at different times, via two or more paths.
- Multipath propagationmay be induced by the refracting and reflecting of a wireless signal by various objects in the wireless environment (e.g., walls and metal objects).
- the wireless signalis distorted thereby resulting in a deteriorated communications experience, which may include jitter or ghosting in the case of audio or video content.
- Interferencemay be mobile or static.
- a first mobile devicee.g., a wireless terminal
- Static interferenceis representative of the superposition of white noise (i.e., static) and other disturbing influences on a wireless signal. These influences are inclusive of thermal noise, electronic noise from receiver input circuits, and radiated electromagnetic noise that might be picked up by a receiving station's antenna.
- FIG. 1Aillustrates how characteristics of a wireless channel may vary over time in light of the aforementioned terminal mobility, multipath fading, and interference.
- FIG. 1Aillustrates a wireless channel 100 where signal quality 110 between an access point (AP) and station are illustrated as a function of time 120 .
- signal quality 110is less at T+1 than at T+2.
- the signal quality 110 for T+1 and T+2is less than the signal quality 110 illustrated at T+3, which is nearly equivalent to that of the signal quality 110 exhibited at T+4.
- Signal quality 110improves at T+5 while experiencing a significant decrease at T+6.
- FIG. 1Bis exemplary in this regard with respect to illustrating the signal quality 110 between the aforementioned AP and Station A ( 130 ) and the AP and Station B ( 140 ). As shown in FIG. 1B , there is no immediately recognizable correlation in signal quality vis-a-vis the AP and the differing stations ( 130 / 140 ).
- Schedulersmay be embodied in hardware and/or software components—the latter being executable from memory or a storage device by a corresponding processing device—with respect to providing scheduling policies, rules, procedure, or other criteria in making scheduling decisions.
- a schedulermay, in light of the aforementioned policies or criteria and a given set of packets, select particular packets for serial transmission over a particular wireless channel.
- policiesmay be used in an attempt to ensure a communications network's ability to provide different quality of service (QOS) guarantees.
- QOSquality of service
- Policiesmay include strict priority (SP) where a particular station queue is always allocated bandwidth and/or transmitted before other queues.
- An alternative policyincludes round robin (RR) scheduling, which assigns bandwidth and transmits packets in equal portion, in order, and without priority to a particular station queue.
- SPstrict priority
- RRround robin
- WRRWeighted round robin
- station queuescan be assigned a weight—an integer value that might indicate capacity or priority. Station queues with higher weights have their packets transmitted prior to those with lesser weights. All queues are eventually given regular transmission access to a channel albeit it those queues with higher weight will get more transmission access attempts than those with lesser weights.
- Fair queuingdiffers from first-in-first-out (FIFO) (i.e., what comes in first is handled first and what comes in next waits until the first is finished) in that an ill-behaved flow that consists of, for example, large data packets or a large number of packets will punish itself and not other packet flows.
- FIFOfirst-in-first-out
- the FQ algorithmestimates a virtual finishing time of all candidate packets (i.e., the packets at the head of all non-empty queues) based on, for example, the arrival time of the packet, the packet size, and the number of queues. The FQ scheduling algorithm or policy then compares the virtual finishing time and selects the minimum one. The packet with the minimum virtual finishing time is transmitted.
- WFQweighted fair queuing
- Typical wireless devicesimplement a simple class and/or priority scheduling mechanism with a FIFO queue per each traffic class.
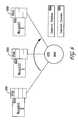
- An example of such a mechanism 200is illustrated in FIG. 2 .
- the scheduling mechanism 200 of FIG. 2illustrates four classes of traffic priority: voice ( 230 ), video ( 240 ), best-effort ( 250 ), and background ( 260 ). While the voice, video, best-effort, and background represent the typical four traffic priorities, the actual number of classes may vary in order to accommodate, for example, additional traffic classes and management traffic.
- packetsare introduced to the wireless device via a network/input interface 210 .
- a network/input interface 210It should be noted that certain hardware components (e.g. a processor or memory) are not illustrated in that one skilled in the art will appreciate and understand the requisite components to implement the various applications disclosed herein. Packets may be received from another wireless device, a network backbone, a router, or a primary source of content that has been converted into data packets for transmission.
- Packetsare then routed to the classifier 220 .
- the classifier 220may identify packets based on application layer data regardless of port.
- the classifier 220may alternatively identify packets based on Internet Protocol (IP) address, port numbers, and so on.
- IPInternet Protocol
- Packet classification based on multiple fieldsmay be implemented using basic search algorithms, geometric algorithms, heuristic algorithms, or hardware-specific search algorithms. A variety of methodologies for packet classification are generally known in the art.
- packetsare then routed to an appropriate queue: voice, video, best-effort, background ( 230 - 260 ).
- the priority scheduler 270then schedules the classified and queued packets.
- all packet traffic of a specific classe.g., voice ( 230 ) is subjected to FIFO queuing. Scheduling is done strictly by priority (SP).
- priority Ne.g., voice ( 230 )
- priority N+1e.g., video ( 240 )
- Packetsare then transmitted or further routed via the appropriate network/output interface 280 .
- Channel aware scheduling(as discussed in further detail below) may not be implemented in this context. For example, traffic to different stations is interleaved within each FIFO queue. Further, only one packet is available at any given time—the packet at the head of the highest priority queue.
- Typical prior art scheduler implementationsalso blindly retransmit the head end packet from the highest priority active queue until that packet is either successfully acknowledged by the recipient or some maximum number of retransmissions occurs. This blind retransmission causes head-of-line blocking. As a result, poor system performance results and, in many circumstances, clients may become completely impaired.
- An embodiment of the presently claimed inventionincludes a system for increasing wireless network throughput.
- the systemincludes a classifier configured to assign a packet to one of a plurality of transmission queues.
- the systemfurther includes a first scheduling module and a second scheduling module.
- the first scheduling moduleis stored in a computer-readable medium and executable by a processing device to select an assigned packet for transmission from one of the plurality of transmission queues in accordance with a strict priority schedule.
- the second scheduling moduleis likewise stored in a computer-readable medium and executable to select a priority scheduled packet for transmission, wherein the selection is made in accordance with a weighted scheduling technique.
- a method for increasing wireless throughputincludes the steps of assigning a packet to one of a plurality of transmission queues; selecting an assigned packet for transmission from one of the plurality of transmission queues in accordance with a priority schedule; selecting a priority scheduled packet for transmission in accordance with a weighted scheduling technique; and transmitting the packet.
- a third embodimentis for a computer-readable storage medium having embodied thereon a program.
- the programis executable by a processing device to perform a method for increasing wireless throughput, the method includes the steps of assigning a packet to one of a plurality of transmission queues; selecting an assigned packet for transmission from one of the plurality of transmission queues in accordance with a priority schedule; selecting a priority scheduled packet for transmission in accordance with a weighted scheduling technique; and transmitting the packet.
- FIG. 1Aillustrates a wireless channel where signal quality between an access point and station are sown as a function of time.
- FIG. 1Billustrates signal quality between an access point and two stations.
- FIG. 2illustrates a class/priority scheduling mechanism with a FIFO queue for each traffic class.
- FIG. 3illustrates the biasing of a scheduler in a channel aware scheduler network environment involving an AP and two stations.
- FIG. 4illustrates an embodiment of a channel aware scheduling mechanism utilizing hierarchical schedulers.
- FIG. 5illustrates a method for channel aware scheduling transmission including a channel aware scheduler mechanism utilizing a deferred retransmission module.
- FIG. 6illustrates queue weighting as may occur in the context of the channel aware scheduler mechanism of FIG. 4 and the corresponding method of FIG. 5 .
- the presently disclosed inventionutilizes channel aware scheduling.
- an optimized schedulera channel aware scheduler (CAS)—takes advantage of changing wireless channel conditions in order to maximize aggregated system throughput.
- CASchannel aware scheduler
- a CASis aware of the different channel conditions for one or more stations and adjusts its scheduling of packet transmissions in light of the same.
- the CAS algorithmmay take advantage of that knowledge in order to increase aggregated system throughput while concurrently addressing other potential fairness constraints.
- FIG. 3illustrates an example of how a CAS may be beneficial in a network environment 300 involving an AP and two stations (A and B).
- the scheduleris biased toward one station or the other (i.e., the scheduler is aware of the quality of both channels). For example, at time T+1, +2 and, +3, the scheduler is biased toward station B while at time T+4 and T+5, the scheduler is biased to station A.
- the CAS mechanism of the present inventionallows for finer queuing and scheduling granularity with respect to individual stations and packet flows.
- An embodiment of the present inventionutilizes hierarchical scheduling. In a first level of the hierarchy, an SP scheduling algorithm may be employed as is common to enterprise and service-provider class networking equipment. In a second level, the CAS mechanism may utilize WRR or WFQ scheduling algorithms as described above.
- FIG. 4illustrates an embodiment of a CAS mechanism 400 utilizing the aforementioned hierarchical schedulers. Packets are received at classifier 410 following initial receipt by a network/input interface. Classifier 410 may operate in a manner similar to classifier 220 as illustrated in FIG. 2 .
- the packetis routed to a first part of the scheduling hierarchy (i.e., a second level scheduler).
- this first portion of the scheduling hierarchyis represented by a queue with an associated priority.
- the CAS mechanism 400 of FIG. 4illustrates three priority queues, which may be representative of voice, video, and background ( 420 - 440 , respectively). Differing numbers of priority queues may be implemented subject to the particular type of packet flows being received at the CAS mechanism 400 . For example, if the wireless device implementing CAS mechanism 400 is dedicated to the delivery of Internet Packet Television (IPTV) content, the voice queue ( 420 ) may be omitted.
- IPTVInternet Packet Television
- each priority queue ( 420 - 440 ) in FIG. 4is one or more station queues ( 420 A- 420 C; 430 A- 430 C; and 440 A- 440 C).
- Each of the station queues 420 A- 420 C; 430 A- 430 C; and 440 A- 440 Coperates in conjunction with a WRR mechanism ( 450 - 470 ).
- a WRR mechanism450 - 470
- each station queue 420 A- 420 C; 430 A- 430 C; and 440 A- 440 Cis assigned a weight indicative of capacity or priority.
- Station queues 420 A- 420 C; 430 A- 430 C; and 440 A- 440 C with higher weightswill have their packets transmitted prior to those with lesser weights. Weighting of a station queue is discussed in greater detail with respect to FIG. 6 below.
- the priority scheduler 480 of the second portion of the hierarchy(i.e., the first level scheduler) assumes responsibility for scheduling the transmission of the classified, prioritized, weighted, and queued packets.
- the priority scheduler 480 of FIG. 4may operate in a fashion similar to that of the priority scheduler 270 in FIG. 2 . Packets are then transmitted or further routed via an appropriate network/output interface.
- the CAS mechanism 400 of FIG. 4may utilize additional scheduling techniques such as deferred retransmission and weighted feedback. Both of these techniques may be implemented in the context of the second level schedulers of FIG. 4 .
- an indication of a failed transmissionmay be used to temporarily defer transmission or retransmission to the failed station and instead service other active stations in a priority queue.
- a deferred retransmission modulemay make direct use of a standard retransmission request mechanism such as an 802.11 acknowledgment (ACK) that would indicates a retransmission is required when no ACK is received.
- ACK802.11 acknowledgment
- an Automated Repeat Requestwhich uses acknowledgments and timeouts to achieve reliable data transmission
- a Hybrid Automated Repeat Requestmay also be used.
- error-detection informationED
- CRCcyclic redundancy check
- FECforward error correction
- HARQperforms better than ordinary ARQ in poor signal conditions but may adversely affect the environment in good signal conditions.
- HARQmay have particular applicability to the IEEE 802.16-2005 standard for mobile broadband wireless access, also known as ‘mobile WiMAX.’ HARQ mechanisms also tend to be implemented in hardware.
- the absence of an ACK or the receipt of an ARQ or HARQ(i.e., a retransmission request) operates as an indication of packet corruption.
- Packet corruptionis an indication of potential channel fade or other adverse channel condition.
- the second level scheduler mechanismmay elect to defer retransmission and move on to the next queue station that has pending packets.
- FIG. 5illustrates a method for CAS transmission in accordance with the CAS mechanism 400 of FIG. 4 as well as a CAS mechanism utilizing a deferred retransmission module.
- a packetis received. Receipt of the packet may occur via a network/input interface. Packets may be received from another wireless device, a network backbone, a router, or a primary source of content that has been converted into data packets for transmission.
- received packetsare classified.
- the packetsmay be classified based on an application layer data regardless of port. Packets may also be identified and subsequently classified based on IP address, port numbers, and so on. Packet classification based on multiple fields may be implemented using basic search algorithms, geometric algorithms, heuristic algorithms, or hardware-specific search algorithms.
- step 530packets are routed to an appropriate priority queue. Packets are then assigned to a station queue in step 540 . Weighting of the station queues takes place in step 550 . It should be noted that station queue weighting may be dynamic or static and may take place prior to or concurrent with the transmission of any particular packet or packet flow. Weighting of a station queue is discussed further with respect to FIG. 6 . Packets are scheduled solely based on priority in 560 and transmitted in accordance with that priority in step 570 .
- a retransmission requestis received at optional step 580 .
- a particular station queueis deferred in optional step 590 .
- Scheduling of the remaining priority and channel queuestakes place in step 560 as would occur in an embodiment not utilizing a deferred retransmission module.
- Transmission of the scheduled packetstakes place in step 570 .
- FIG. 6illustrates queue weighting as may occur in the context of the CAS mechanism of FIG. 4 and the corresponding method of FIG. 5 .
- a weight( 640 - 660 ) is determined for each queue ( 610 - 630 ).
- the WRR scheduler 670e.g., WRR 450
- WRR scheduler 670then round robins between active queues (those that have pending packets) and transmits up to N packets from a queue where N is the weight associated with that queue.
- Weightingmay be implemented via credit register 690 that is loaded with a particular weight when a new station queue 680 is selected.
- the credit register 680is decremented with each transmission from that station queue 680 .
- the WRR scheduler 670advances in a round robin fashion to the next queue with an associated load of credits.
- An embodiment of the CAS mechanism utilizing a deferred retransmission modulemay modify the WRR scheduler 670 as follows. Upon receipt of a retransmission requirement, it is determined from which station queue the failed packet originated. The failed packet is then re-queued at the head of that queue. If that particular queue is still active (i.e., the queue still has credits), the queue is penalized through the additional decrement of the credit register or decrementing the credit register to zero thereby forcing an activation of a queue associated with a different station. These penalization activities may take place in the context of optional step 590 of FIG. 5 .
- a further embodiment of the CAS mechanism disclosed hereinmay implement weighted feedback, which may be applicable to a hierarchical implementation utilizing WFQ or WRR.
- per-station channel conditionsare estimated. These estimates may utilize low-level metrics such as signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) or error-to-vector magnitude (EVM).
- SNRsignal-to-noise ratio
- EVMerror-to-vector magnitude
- Queue weightsare modified to reflect channel conditions such that the scheduler favors stations with the better channel. Generally, weights are proportional to each channel capacity in order to maximize throughput. Weights may be limited to some minimal value to prevent the starvation of poor stations.
- a still further embodiment of weight feedbackinvolves, for each associated station, the performance of throughput estimation. Estimation may occur using a throughput model and packet encoding rule (PER) statistics. Packet transmission time stamps may also be used. If the estimated throughput is below some minimum threshold, the estimated throughput is set to the minimum threshold in order to ensure that some minimal bandwidth allocation is made with respect to each station.
- the WRR or WFQ weightis scaled proportionally to the estimated throughput.
- Computer-executable instructions and associated data structuresrepresent examples of the programming means for executing steps of the methods and implementing particular system configurations disclosed herein. Such methodologies may be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. Such methodologies may be executed in the context of a corresponding processing device.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
An end-to-end delay bound can be guaranteed in WFQ scheduling. By dynamically regulating WFQ weights, this policy can be used to control QOS and achieve a guaranteed data rate.
Claims (17)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/028,323US9271327B2 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2013-09-16 | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling |
| US15/050,317US9674862B2 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2016-02-22 | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US95255707P | 2007-07-28 | 2007-07-28 | |
| US12/181,274US8547899B2 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2008-07-28 | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling |
| US14/028,323US9271327B2 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2013-09-16 | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/181,274ContinuationUS8547899B2 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2008-07-28 | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/050,317ContinuationUS9674862B2 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2016-02-22 | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US20140016563A1 US20140016563A1 (en) | 2014-01-16 |
| US9271327B2true US9271327B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 |
Family
ID=40295265
Family Applications (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/181,274Active2031-07-31US8547899B2 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2008-07-28 | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling |
| US14/028,323Expired - Fee RelatedUS9271327B2 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2013-09-16 | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling |
| US15/050,317Expired - Fee RelatedUS9674862B2 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2016-02-22 | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling |
Family Applications Before (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/181,274Active2031-07-31US8547899B2 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2008-07-28 | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/050,317Expired - Fee RelatedUS9674862B2 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2016-02-22 | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US8547899B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10250722B2 (en) | 2015-12-18 | 2019-04-02 | Sonicwall Inc. | TCP traffic priority bandwidth management control based on TCP window adjustment |
Families Citing this family (46)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7505447B2 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2009-03-17 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Systems and methods for improved data throughput in communications networks |
| US8619662B2 (en)* | 2004-11-05 | 2013-12-31 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Unicast to multicast conversion |
| US9240868B2 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2016-01-19 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Increasing reliable data throughput in a wireless network |
| US8638708B2 (en)* | 2004-11-05 | 2014-01-28 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | MAC based mapping in IP based communications |
| US8934416B2 (en)* | 2005-03-09 | 2015-01-13 | Xirrus, Inc. | System for allocating channels in a multi-radio wireless LAN array |
| US9088907B2 (en)* | 2007-06-18 | 2015-07-21 | Xirrus, Inc. | Node fault identification in wireless LAN access points |
| US8547899B2 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2013-10-01 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling |
| US8355343B2 (en) | 2008-01-11 | 2013-01-15 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Determining associations in a mesh network |
| US8482478B2 (en)* | 2008-11-12 | 2013-07-09 | Xirrus, Inc. | MIMO antenna system |
| WO2010101002A1 (en)* | 2009-03-02 | 2010-09-10 | 日本電気株式会社 | Wireless packet transmission apparatus, and packet priority control scheduling method |
| US8780762B2 (en)* | 2009-03-11 | 2014-07-15 | Sony Corporation | Node query in ad hoc home mesh network |
| US20100232400A1 (en)* | 2009-03-11 | 2010-09-16 | Sony Corporation | Virtualizing single radio for multiple wireless interfaces in home mesh network |
| US7974297B2 (en)* | 2009-03-11 | 2011-07-05 | Sony Corporation | Quality of service queue management in home mesh network |
| US8223786B2 (en)* | 2009-03-11 | 2012-07-17 | Sony Corporation | Quality of service scheduling for home mesh network |
| US8761174B2 (en)* | 2009-03-11 | 2014-06-24 | Sony Corporation | Quality of service traffic recognition and packet classification home mesh network |
| US8194593B2 (en)* | 2009-03-11 | 2012-06-05 | Sony Corporation | Quality of service architecture for home mesh network |
| US8861445B2 (en)* | 2009-03-11 | 2014-10-14 | Sony Cororation | Multi-channel single radio communication in home mesh network |
| US9979626B2 (en)* | 2009-11-16 | 2018-05-22 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Establishing a mesh network with wired and wireless links |
| WO2011060454A2 (en)* | 2009-11-16 | 2011-05-19 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Establishing a mesh network with wired and wireless links |
| CN101784082A (en)* | 2009-12-22 | 2010-07-21 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method and device for enhancing service quality in wireless local area network |
| US8462802B2 (en)* | 2010-09-13 | 2013-06-11 | Juniper Networks, Inc. | Hybrid weighted round robin (WRR) traffic scheduling |
| US20120195200A1 (en)* | 2011-01-31 | 2012-08-02 | Joe Regan | Method and apparatus for hierarchical policing |
| US8830854B2 (en) | 2011-07-28 | 2014-09-09 | Xirrus, Inc. | System and method for managing parallel processing of network packets in a wireless access device |
| US8868002B2 (en) | 2011-08-31 | 2014-10-21 | Xirrus, Inc. | System and method for conducting wireless site surveys |
| US9055450B2 (en) | 2011-09-23 | 2015-06-09 | Xirrus, Inc. | System and method for determining the location of a station in a wireless environment |
| JP5768624B2 (en)* | 2011-09-26 | 2015-08-26 | 富士通株式会社 | Relay device and relay method |
| US9584179B2 (en)* | 2012-02-23 | 2017-02-28 | Silver Spring Networks, Inc. | System and method for multi-channel frequency hopping spread spectrum communication |
| JP6098633B2 (en)* | 2012-03-02 | 2017-03-22 | 日本電気株式会社 | Packet transfer apparatus, packet transfer method, and computer program |
| US9997830B2 (en) | 2012-05-13 | 2018-06-12 | Amir Keyvan Khandani | Antenna system and method for full duplex wireless transmission with channel phase-based encryption |
| WO2013173250A1 (en) | 2012-05-13 | 2013-11-21 | Invention Mine Llc | Full duplex wireless transmission with self-interference cancellation |
| US9167466B2 (en) | 2012-09-06 | 2015-10-20 | Apple Inc. | Enhanced measurement reporting to improve throughput when using multicarrier cells |
| CN103067308A (en)* | 2012-12-26 | 2013-04-24 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method and system for bandwidth distribution |
| US9148817B1 (en)* | 2013-01-21 | 2015-09-29 | Sprint Spectrum L.P. | Methods and systems for routing signaling traffic |
| US10177896B2 (en) | 2013-05-13 | 2019-01-08 | Amir Keyvan Khandani | Methods for training of full-duplex wireless systems |
| US9236996B2 (en) | 2013-11-30 | 2016-01-12 | Amir Keyvan Khandani | Wireless full-duplex system and method using sideband test signals |
| US9820311B2 (en) | 2014-01-30 | 2017-11-14 | Amir Keyvan Khandani | Adapter and associated method for full-duplex wireless communication |
| US10075965B2 (en)* | 2016-04-06 | 2018-09-11 | P2 Solutions Limited | Apparatus and method for detecting and alleviating unfairness in wireless network |
| US10333593B2 (en) | 2016-05-02 | 2019-06-25 | Amir Keyvan Khandani | Systems and methods of antenna design for full-duplex line of sight transmission |
| US10700766B2 (en) | 2017-04-19 | 2020-06-30 | Amir Keyvan Khandani | Noise cancelling amplify-and-forward (in-band) relay with self-interference cancellation |
| CN107483363B (en)* | 2017-08-15 | 2020-04-14 | 无锡职业技术学院 | A hierarchical weighted round-robin scheduling device and method |
| US11057204B2 (en) | 2017-10-04 | 2021-07-06 | Amir Keyvan Khandani | Methods for encrypted data communications |
| US11012144B2 (en) | 2018-01-16 | 2021-05-18 | Amir Keyvan Khandani | System and methods for in-band relaying |
| US10911568B2 (en)* | 2018-10-03 | 2021-02-02 | Twitter, Inc. | Client software back off |
| US11121953B2 (en) | 2019-06-11 | 2021-09-14 | Arris Enterprises Llc | Access point performance monitoring and anomaly detection based on temporal and spatial anomalies |
| US11221883B2 (en)* | 2019-06-26 | 2022-01-11 | Twilio Inc. | Hierarchical scheduler |
| US12369148B2 (en)* | 2022-12-21 | 2025-07-22 | Aespula Technology Inc. | Sorting method of communication data and communication apparatus thereof |
Citations (277)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US1653664A (en) | 1927-12-27 | Lavatory | ||
| US4176356A (en) | 1977-06-27 | 1979-11-27 | Motorola, Inc. | Directional antenna system including pattern control |
| US4193077A (en) | 1977-10-11 | 1980-03-11 | Avnet, Inc. | Directional antenna system with end loaded crossed dipoles |
| US4253193A (en) | 1977-11-05 | 1981-02-24 | The Marconi Company Limited | Tropospheric scatter radio communication systems |
| US4305052A (en) | 1978-12-22 | 1981-12-08 | Thomson-Csf | Ultra-high-frequency diode phase shifter usable with electronically scanning antenna |
| US4513412A (en) | 1983-04-25 | 1985-04-23 | At&T Bell Laboratories | Time division adaptive retransmission technique for portable radio telephones |
| US4814777A (en) | 1987-07-31 | 1989-03-21 | Raytheon Company | Dual-polarization, omni-directional antenna system |
| US5097484A (en) | 1988-10-12 | 1992-03-17 | Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. | Diversity transmission and reception method and equipment |
| US5117430A (en) | 1991-02-08 | 1992-05-26 | International Business Machines Corporation | Apparatus and method for communicating between nodes in a network |
| US5173711A (en) | 1989-11-27 | 1992-12-22 | Kokusai Denshin Denwa Kabushiki Kaisha | Microstrip antenna for two-frequency separate-feeding type for circularly polarized waves |
| US5203010A (en) | 1990-11-13 | 1993-04-13 | Motorola, Inc. | Radio telephone system incorporating multiple time periods for communication transfer |
| US5220678A (en) | 1991-08-12 | 1993-06-15 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and apparatus for adjusting the power of a transmitter |
| US5220340A (en) | 1992-04-29 | 1993-06-15 | Lotfollah Shafai | Directional switched beam antenna |
| EP0534612A3 (en) | 1991-08-28 | 1993-11-24 | Motorola Inc | Cellular system sharing of logical channels |
| US5361256A (en) | 1992-11-27 | 1994-11-01 | International Business Machines Corporation | Inter-domain multicast routing |
| US5373548A (en) | 1991-01-04 | 1994-12-13 | Thomson Consumer Electronics, Inc. | Out-of-range warning system for cordless telephone |
| US5408465A (en) | 1993-06-21 | 1995-04-18 | Hewlett-Packard Company | Flexible scheme for admission control of multimedia streams on integrated networks |
| EP0352787B1 (en) | 1988-07-28 | 1995-05-10 | Motorola, Inc. | High bit rate communication system for overcoming multipath |
| US5507035A (en) | 1993-04-30 | 1996-04-09 | International Business Machines Corporation | Diversity transmission strategy in mobile/indoor cellula radio communications |
| US5559800A (en) | 1994-01-19 | 1996-09-24 | Research In Motion Limited | Remote control of gateway functions in a wireless data communication network |
| US5570366A (en) | 1994-12-08 | 1996-10-29 | International Business Machines Corporation | Broadcast/multicast filtering by the bridge-based access point |
| US5608726A (en) | 1995-04-25 | 1997-03-04 | Cabletron Systems, Inc. | Network bridge with multicast forwarding table |
| US5636213A (en) | 1994-12-28 | 1997-06-03 | Motorola | Method, transceiver, and system for providing wireless communication compatible with 10BASE-T Ethernet |
| US5754145A (en) | 1995-08-23 | 1998-05-19 | U.S. Philips Corporation | Printed antenna |
| US5767809A (en) | 1996-03-07 | 1998-06-16 | Industrial Technology Research Institute | OMNI-directional horizontally polarized Alford loop strip antenna |
| US5802312A (en) | 1994-09-27 | 1998-09-01 | Research In Motion Limited | System for transmitting data files between computers in a wireless environment utilizing a file transfer agent executing on host system |
| US5867109A (en) | 1995-06-06 | 1999-02-02 | Globalstar L.P. | Satellite repeater diversity resource management system |
| US5930259A (en) | 1995-08-25 | 1999-07-27 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Packet transmission node device realizing packet transfer scheme and control information transfer scheme using multiple virtual connections |
| US5940771A (en) | 1991-05-13 | 1999-08-17 | Norand Corporation | Network supporting roaming, sleeping terminals |
| US5960344A (en) | 1993-12-20 | 1999-09-28 | Norand Corporation | Local area network having multiple channel wireless access |
| US5964830A (en) | 1995-08-22 | 1999-10-12 | Durrett; Charles M. | User portal device for the world wide web to communicate with a website server |
| US5970410A (en) | 1996-02-27 | 1999-10-19 | Airnet Communications Corp. | Cellular system plan using in band-translators to enable efficient deployment of high capacity base transceiver systems |
| US5974034A (en) | 1997-01-16 | 1999-10-26 | Gwcom, Inc. | System and method for synchronized wide and local area communications utilizing a single frequency |
| GB2306278B (en) | 1995-10-14 | 1999-12-08 | Nec Corp | Radio transmission system |
| US6018659A (en) | 1996-10-17 | 2000-01-25 | The Boeing Company | Airborne broadband communication network |
| US6034638A (en) | 1993-05-27 | 2000-03-07 | Griffith University | Antennas for use in portable communications devices |
| US6044062A (en) | 1996-12-06 | 2000-03-28 | Communique, Llc | Wireless network system and method for providing same |
| US6088570A (en) | 1998-11-24 | 2000-07-11 | Airnet Communications Corporation | Method and apparatus employing delay elements in multiple diversity paths of a wireless system repeater translator to allow for selective diversity and automatic level control in a time-division multiple access system |
| US6094177A (en) | 1997-11-27 | 2000-07-25 | Yamamoto; Kiyoshi | Planar radiation antenna elements and omni directional antenna using such antenna elements |
| US6132306A (en) | 1995-09-06 | 2000-10-17 | Cisco Systems, Inc. | Cellular communication system with dedicated repeater channels |
| US6181697B1 (en) | 1998-03-31 | 2001-01-30 | At&T Corp. | Method for a unicast endpoint client to access a multicast internet protocol (IP) session and to serve as a redistributor of such session |
| JP2001057560A (en) | 1999-08-18 | 2001-02-27 | Hitachi Kokusai Electric Inc | Wireless LAN system |
| US6266528B1 (en) | 1998-12-23 | 2001-07-24 | Arraycomm, Inc. | Performance monitor for antenna arrays |
| US6266537B1 (en) | 1998-03-27 | 2001-07-24 | Nec Corporation | Radio communication system |
| US6292153B1 (en) | 1999-08-27 | 2001-09-18 | Fantasma Network, Inc. | Antenna comprising two wideband notch regions on one coplanar substrate |
| US6307524B1 (en) | 2000-01-18 | 2001-10-23 | Core Technology, Inc. | Yagi antenna having matching coaxial cable and driven element impedances |
| US6317599B1 (en) | 1999-05-26 | 2001-11-13 | Wireless Valley Communications, Inc. | Method and system for automated optimization of antenna positioning in 3-D |
| US20010047474A1 (en) | 2000-05-23 | 2001-11-29 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Communication control scheme using proxy device and security protocol in combination |
| US6326922B1 (en) | 2000-06-29 | 2001-12-04 | Worldspace Corporation | Yagi antenna coupled with a low noise amplifier on the same printed circuit board |
| US20010055312A1 (en) | 2000-04-07 | 2001-12-27 | Negus Kevin J. | Asymmetric data traffic throughput in CSMA/CA networks |
| US20020001310A1 (en) | 2000-06-29 | 2002-01-03 | Khanh Mai | Virtual multicasting |
| US6337668B1 (en) | 1999-03-05 | 2002-01-08 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Antenna apparatus |
| US6337628B2 (en) | 1995-02-22 | 2002-01-08 | Ntp, Incorporated | Omnidirectional and directional antenna assembly |
| US6339404B1 (en) | 1999-08-13 | 2002-01-15 | Rangestar Wirless, Inc. | Diversity antenna system for lan communication system |
| US6345043B1 (en) | 1998-07-06 | 2002-02-05 | National Datacomm Corporation | Access scheme for a wireless LAN station to connect an access point |
| US6356243B1 (en) | 2000-07-19 | 2002-03-12 | Logitech Europe S.A. | Three-dimensional geometric space loop antenna |
| US6356242B1 (en) | 2000-01-27 | 2002-03-12 | George Ploussios | Crossed bent monopole doublets |
| US6356553B1 (en) | 1996-07-11 | 2002-03-12 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Network node and method of packet transfer |
| US6356905B1 (en) | 1999-03-05 | 2002-03-12 | Accenture Llp | System, method and article of manufacture for mobile communication utilizing an interface support framework |
| US20020031130A1 (en) | 2000-05-30 | 2002-03-14 | Kazuaki Tsuchiya | Multicast routing method and an apparatus for routing a multicast packet |
| WO2002025967A1 (en) | 2000-09-22 | 2002-03-28 | Widcomm Inc. | Wireless network and method for providing improved handoff performance |
| US20020036996A1 (en) | 1995-06-30 | 2002-03-28 | Ozluturk Fatih M. | Initial power control for spread-spectrum communications |
| US20020045435A1 (en) | 2000-10-18 | 2002-04-18 | Steve Fantaske | Wireless communication system |
| US6377227B1 (en) | 1999-04-28 | 2002-04-23 | Superpass Company Inc. | High efficiency feed network for antennas |
| US20020047800A1 (en) | 1998-09-21 | 2002-04-25 | Tantivy Communications, Inc. | Adaptive antenna for use in same frequency networks |
| US6393261B1 (en) | 1998-05-05 | 2002-05-21 | Telxon Corporation | Multi-communication access point |
| US6392610B1 (en) | 1999-10-29 | 2002-05-21 | Allgon Ab | Antenna device for transmitting and/or receiving RF waves |
| US6404775B1 (en) | 1997-11-21 | 2002-06-11 | Allen Telecom Inc. | Band-changing repeater with protocol or format conversion |
| US6404386B1 (en) | 1998-09-21 | 2002-06-11 | Tantivy Communications, Inc. | Adaptive antenna for use in same frequency networks |
| US6407719B1 (en) | 1999-07-08 | 2002-06-18 | Atr Adaptive Communications Research Laboratories | Array antenna |
| WO2002049360A1 (en) | 2000-12-13 | 2002-06-20 | THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG A body corporate of Hong Kong SAR | Method and system for delivering media selections through a network |
| US20020080767A1 (en) | 2000-12-22 | 2002-06-27 | Ji-Woong Lee | Method of supporting small group multicast in mobile IP |
| US6414955B1 (en) | 1999-03-23 | 2002-07-02 | Innovative Technology Licensing, Llc | Distributed topology learning method and apparatus for wireless networks |
| US20020084942A1 (en) | 2001-01-03 | 2002-07-04 | Szu-Nan Tsai | Pcb dipole antenna |
| US6418138B1 (en) | 2000-03-02 | 2002-07-09 | Worldcom, Inc. | Internet radio communication system |
| US20020105471A1 (en) | 2000-05-24 | 2002-08-08 | Suguru Kojima | Directional switch antenna device |
| US20020112058A1 (en) | 2000-12-01 | 2002-08-15 | Microsoft Corporation | Peer networking host framework and hosting API |
| US6442507B1 (en) | 1998-12-29 | 2002-08-27 | Wireless Communications, Inc. | System for creating a computer model and measurement database of a wireless communication network |
| US6445688B1 (en) | 2000-08-31 | 2002-09-03 | Ricochet Networks, Inc. | Method and apparatus for selecting a directional antenna in a wireless communication system |
| US20020143951A1 (en) | 2001-03-30 | 2002-10-03 | Eyeball.Com Network Inc. | Method and system for multicast to unicast bridging |
| US20020158798A1 (en) | 2001-04-30 | 2002-10-31 | Bing Chiang | High gain planar scanned antenna array |
| US20020158801A1 (en) | 2001-04-27 | 2002-10-31 | Crilly William J. | Wireless packet switched communication systems and networks using adaptively steered antenna arrays |
| US20020164963A1 (en) | 2001-04-09 | 2002-11-07 | Tehrani Ardavan Maleki | Method and system for providing antenna diversity |
| US20020170064A1 (en) | 2001-05-11 | 2002-11-14 | Monroe David A. | Portable, wireless monitoring and control station for use in connection with a multi-media surveillance system having enhanced notification functions |
| US6493679B1 (en) | 1999-05-26 | 2002-12-10 | Wireless Valley Communications, Inc. | Method and system for managing a real time bill of materials |
| US20020194367A1 (en) | 2001-06-14 | 2002-12-19 | The Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd. | Data relay method, its apparatus, and data relay system using the apparatus |
| US6499006B1 (en) | 1999-07-14 | 2002-12-24 | Wireless Valley Communications, Inc. | System for the three-dimensional display of wireless communication system performance |
| US6498589B1 (en) | 1999-03-18 | 2002-12-24 | Dx Antenna Company, Limited | Antenna system |
| US20030003917A1 (en) | 2001-06-29 | 2003-01-02 | Copley Rich T. | Wireless communication system, apparatus and method for providing wireless communication within a building structure |
| US6505253B1 (en) | 1998-06-30 | 2003-01-07 | Sun Microsystems | Multiple ACK windows providing congestion control in reliable multicast protocol |
| US6507321B2 (en) | 2000-05-26 | 2003-01-14 | Sony International (Europe) Gmbh | V-slot antenna for circular polarization |
| US20030026268A1 (en) | 2000-11-28 | 2003-02-06 | Siemens Technology-To-Business Center, Llc | Characteristic routing |
| US20030026240A1 (en) | 2001-07-23 | 2003-02-06 | Eyuboglu M. Vedat | Broadcasting and multicasting in wireless communication |
| JP2003038933A (en) | 2001-07-26 | 2003-02-12 | Akira Mizuno | Discharge plasma generating apparatus |
| US20030030588A1 (en) | 2001-08-10 | 2003-02-13 | Music Sciences, Inc. | Antenna system |
| US20030043786A1 (en) | 2001-08-28 | 2003-03-06 | Jan Kall | Apparatus, and associated method, for multicasting data in a radio communications system |
| US20030063591A1 (en) | 2001-10-03 | 2003-04-03 | Leung Nikolai K.N. | Method and apparatus for data packet transport in a wireless communication system using an internet protocol |
| US6570883B1 (en)* | 1999-08-28 | 2003-05-27 | Hsiao-Tung Wong | Packet scheduling using dual weight single priority queue |
| US6584080B1 (en) | 1999-01-14 | 2003-06-24 | Aero-Vision Technologies, Inc. | Wireless burstable communications repeater |
| US20030122714A1 (en) | 2001-11-16 | 2003-07-03 | Galtronics Ltd. | Variable gain and variable beamwidth antenna (the hinged antenna) |
| US20030133458A1 (en) | 2002-01-17 | 2003-07-17 | Masaaki Sato | Unicast-to-multicast converting apparatus, method, and computer program product, and monitoring system comprising the same |
| US20030169330A1 (en) | 2001-10-24 | 2003-09-11 | Microsoft Corporation | Network conference recording system and method including post-conference processing |
| US6625454B1 (en) | 2000-08-04 | 2003-09-23 | Wireless Valley Communications, Inc. | Method and system for designing or deploying a communications network which considers frequency dependent effects |
| US20030184490A1 (en) | 2002-03-26 | 2003-10-02 | Raiman Clifford E. | Sectorized omnidirectional antenna |
| US20030189514A1 (en) | 2001-09-06 | 2003-10-09 | Kentaro Miyano | Array antenna apparatus |
| US20030189523A1 (en) | 2002-04-09 | 2003-10-09 | Filtronic Lk Oy | Antenna with variable directional pattern |
| US20030189521A1 (en) | 2002-04-05 | 2003-10-09 | Atsushi Yamamoto | Directivity controllable antenna and antenna unit using the same |
| US20030210207A1 (en) | 2002-02-08 | 2003-11-13 | Seong-Youp Suh | Planar wideband antennas |
| US20030227414A1 (en) | 2002-03-04 | 2003-12-11 | Saliga Stephen V. | Diversity antenna for UNII access point |
| US20030228857A1 (en) | 2002-06-06 | 2003-12-11 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Optimum scan for fixed-wireless smart antennas |
| US20030231593A1 (en) | 2002-06-04 | 2003-12-18 | James Bauman | Flexible multilevel output traffic control |
| US20040008663A1 (en) | 2000-12-29 | 2004-01-15 | Devabhaktuni Srikrishna | Selection of routing paths based upon path quality of a wireless mesh network |
| US20040014432A1 (en) | 2000-03-23 | 2004-01-22 | U.S. Philips Corporation | Antenna diversity arrangement |
| WO2003079484A3 (en) | 2002-03-15 | 2004-01-22 | Andrew Corp | Antenna interface protocol |
| US20040017310A1 (en) | 2002-07-24 | 2004-01-29 | Sarah Vargas-Hurlston | Position optimized wireless communication |
| US20040017860A1 (en) | 2002-07-29 | 2004-01-29 | Jung-Tao Liu | Multiple antenna system for varying transmission streams |
| US20040027304A1 (en) | 2001-04-30 | 2004-02-12 | Bing Chiang | High gain antenna for wireless applications |
| US20040028006A1 (en) | 2002-05-22 | 2004-02-12 | Ntt Docomo, Inc. | Random access method and radio station |
| US20040027291A1 (en) | 2002-05-24 | 2004-02-12 | Xin Zhang | Planar antenna and array antenna |
| US20040032378A1 (en) | 2001-10-31 | 2004-02-19 | Vladimir Volman | Broadband starfish antenna and array thereof |
| US20040036654A1 (en) | 2002-08-21 | 2004-02-26 | Steve Hsieh | Antenna assembly for circuit board |
| US20040036651A1 (en) | 2002-06-05 | 2004-02-26 | Takeshi Toda | Adaptive antenna unit and terminal equipment |
| US6701522B1 (en) | 2000-04-07 | 2004-03-02 | Danger, Inc. | Apparatus and method for portal device authentication |
| US20040041732A1 (en) | 2001-10-03 | 2004-03-04 | Masayoshi Aikawa | Multielement planar antenna |
| US6704301B2 (en) | 2000-12-29 | 2004-03-09 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Method and apparatus to provide a routing protocol for wireless devices |
| US20040048593A1 (en) | 2000-12-21 | 2004-03-11 | Hiroyasu Sano | Adaptive antenna receiver |
| US20040058690A1 (en) | 2000-11-20 | 2004-03-25 | Achim Ratzel | Antenna system |
| US6714551B1 (en) | 1997-10-14 | 2004-03-30 | Alvarion Israel (2003) Ltd. | Method and apparatus for maintaining a predefined transmission quality in a wireless network for a metropolitan area |
| US20040061653A1 (en) | 2002-09-26 | 2004-04-01 | Andrew Corporation | Dynamically variable beamwidth and variable azimuth scanning antenna |
| US20040070543A1 (en) | 2002-10-15 | 2004-04-15 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Antenna structure for electronic device with wireless communication unit |
| US6725281B1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2004-04-20 | Microsoft Corporation | Synchronization of controlled device state using state table and eventing in data-driven remote device control model |
| US6728514B2 (en) | 2000-09-08 | 2004-04-27 | Wi-Lan Inc. | Scalable wireless network topology systems and methods |
| US20040080455A1 (en) | 2002-10-23 | 2004-04-29 | Lee Choon Sae | Microstrip array antenna |
| US20040085993A1 (en) | 2002-11-05 | 2004-05-06 | Wentink Maarten Menzo | Shared-medium contention algorithm exhibiting fairness |
| US20040095278A1 (en) | 2001-12-28 | 2004-05-20 | Hideki Kanemoto | Multi-antenna apparatus multi-antenna reception method, and multi-antenna transmission method |
| US20040114535A1 (en) | 2002-09-30 | 2004-06-17 | Tantivy Communications, Inc. | Method and apparatus for antenna steering for WLAN |
| US6753814B2 (en) | 2002-06-27 | 2004-06-22 | Harris Corporation | Dipole arrangements using dielectric substrates of meta-materials |
| US20040125777A1 (en) | 2001-05-24 | 2004-07-01 | James Doyle | Method and apparatus for affiliating a wireless device with a wireless local area network |
| WO2004057817A2 (en) | 2002-12-19 | 2004-07-08 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Protecting real-time data in wireless networks |
| US6762723B2 (en) | 2002-11-08 | 2004-07-13 | Motorola, Inc. | Wireless communication device having multiband antenna |
| US6778517B1 (en) | 1999-10-14 | 2004-08-17 | Bellsouth Intellectual Property Corporation | Wireless broadband service |
| EP1450521A2 (en) | 2003-02-19 | 2004-08-25 | Nec Corporation | Wireless communication system and method which improves reliability and throughput of communication through retransmission timeout optimization |
| US20040190477A1 (en) | 2003-03-28 | 2004-09-30 | Olson Jonathan P. | Dynamic wireless network |
| US6819287B2 (en) | 2002-03-15 | 2004-11-16 | Centurion Wireless Technologies, Inc. | Planar inverted-F antenna including a matching network having transmission line stubs and capacitor/inductor tank circuits |
| US20040260800A1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2004-12-23 | Microsoft Corporation | Dynamic self-configuration for ad hoc peer networking |
| US6836481B1 (en) | 2000-02-17 | 2004-12-28 | Fujitsu Limited | Packet conversion device and packet conversion method |
| US20040264463A1 (en) | 2003-06-26 | 2004-12-30 | Hidehiro Fukushima | Method, apparatus and system for distributing multicast data |
| US20050002395A1 (en) | 2003-06-04 | 2005-01-06 | Nec Corporation | IP multicast distribution system, streaming data distribution system and program therefor |
| US20050009523A1 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2005-01-13 | Nokia Corporation | Protocol using forward error correction to improve handover |
| US20050032531A1 (en) | 2003-08-06 | 2005-02-10 | Hong Kong Applied Science And Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd. | Location positioning in wireless networks |
| US20050041739A1 (en) | 2001-04-28 | 2005-02-24 | Microsoft Corporation | System and process for broadcast and communication with very low bit-rate bi-level or sketch video |
| US20050042988A1 (en) | 2003-08-18 | 2005-02-24 | Alcatel | Combined open and closed loop transmission diversity system |
| WO2005008938A3 (en) | 2003-07-08 | 2005-03-24 | Kiwi Networks Inc | Implementing 'all wireless' network over wifi equipment using 'scheduled tdma' |
| US6873627B1 (en) | 1995-01-19 | 2005-03-29 | The Fantastic Corporation | System and method for sending packets over a computer network |
| US6876280B2 (en) | 2002-06-24 | 2005-04-05 | Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | High-frequency switch, and electronic device using the same |
| US20050074019A1 (en) | 2003-10-03 | 2005-04-07 | Nortel Networks Limited | Method and apparatus for providing mobile inter-mesh communication points in a multi-level wireless mesh network |
| US20050074018A1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2005-04-07 | Microsoft Corporation | XML-based template language for devices and services |
| US20050074108A1 (en) | 1995-04-21 | 2005-04-07 | Dezonno Anthony J. | Method and system for establishing voice communications using a computer network |
| US6888504B2 (en) | 2002-02-01 | 2005-05-03 | Ipr Licensing, Inc. | Aperiodic array antenna |
| US6888893B2 (en) | 2001-01-05 | 2005-05-03 | Microsoft Corporation | System and process for broadcast and communication with very low bit-rate bi-level or sketch video |
| US6906678B2 (en) | 2002-09-24 | 2005-06-14 | Gemtek Technology Co. Ltd. | Multi-frequency printed antenna |
| US20050138193A1 (en) | 2003-12-19 | 2005-06-23 | Microsoft Corporation | Routing of resource information in a network |
| US20050138137A1 (en) | 2003-12-19 | 2005-06-23 | Microsoft Corporation | Using parameterized URLs for retrieving resource content items |
| US20050153720A1 (en) | 2003-12-15 | 2005-07-14 | White Graeme E. | Apparatus, system, and method for managing distribution and coverage channels in a cellular communication system having a wireless backhaul |
| US6924768B2 (en) | 2002-05-23 | 2005-08-02 | Realtek Semiconductor Corp. | Printed antenna structure |
| US6931429B2 (en) | 2001-04-27 | 2005-08-16 | Left Gate Holdings, Inc. | Adaptable wireless proximity networking |
| US20050180381A1 (en) | 2004-02-12 | 2005-08-18 | Retzer Michael H. | Method and apparatus for improving throughput in a wireless local area network |
| US20050188193A1 (en) | 2004-02-20 | 2005-08-25 | Microsoft Corporation | Secure network channel |
| US20050185666A1 (en) | 2004-02-23 | 2005-08-25 | Maxim Raya | Misbehaving detection method for contention-based wireless communications |
| US6941143B2 (en) | 2002-08-29 | 2005-09-06 | Thomson Licensing, S.A. | Automatic channel selection in a radio access network |
| US6950019B2 (en) | 2000-12-07 | 2005-09-27 | Raymond Bellone | Multiple-triggering alarm system by transmitters and portable receiver-buzzer |
| US20050226239A1 (en) | 2004-03-30 | 2005-10-13 | Sony Corporation And Sony Electronics, Inc. | Optimizing IEEE 802.11 for TCP/IP data transfer |
| US6957277B2 (en) | 2000-02-28 | 2005-10-18 | Nec Corporation | Multicast packet transferring apparatus, multicast packet transferring system and storage medium used in same |
| US6957042B2 (en) | 2000-01-10 | 2005-10-18 | Airnet Communications Corporation | Packet based backhaul channel configuration for a wireless repeater |
| US20050232179A1 (en) | 2003-05-08 | 2005-10-20 | Dacosta Francis | Multiple-radio mission critical wireless mesh networks |
| US6961028B2 (en) | 2003-01-17 | 2005-11-01 | Lockheed Martin Corporation | Low profile dual frequency dipole antenna structure |
| US20050250544A1 (en) | 2004-05-07 | 2005-11-10 | Stephen Grant | Base station, mobile terminal device and method for implementing a selective-per-antenna-rate-control (S-PARC) technique in a wireless communications network |
| US20050267935A1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2005-12-01 | Microsoft Corporation | Data driven remote device control model with general programming interface-to-network messaging adaptor |
| US6973622B1 (en) | 2000-09-25 | 2005-12-06 | Wireless Valley Communications, Inc. | System and method for design, tracking, measurement, prediction and optimization of data communication networks |
| US20050271070A1 (en) | 2004-05-20 | 2005-12-08 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Radio module |
| US6975834B1 (en) | 2000-10-03 | 2005-12-13 | Mineral Lassen Llc | Multi-band wireless communication device and method |
| JP2005354249A (en) | 2004-06-09 | 2005-12-22 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Network communication terminal |
| US20060018335A1 (en) | 2004-07-26 | 2006-01-26 | Koch Christopher D | Multicast to unicast traffic conversion in a network |
| US6996086B2 (en) | 2001-04-26 | 2006-02-07 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Radio access network with meshed radio base stations |
| JP2006060408A (en) | 2004-08-18 | 2006-03-02 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Radio packet communication method and radio station |
| US20060045089A1 (en) | 2004-08-27 | 2006-03-02 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method and apparatus for providing network virtualization |
| US7034770B2 (en) | 2002-04-23 | 2006-04-25 | Broadcom Corporation | Printed dipole antenna |
| US20060094371A1 (en) | 2004-10-29 | 2006-05-04 | Colubris Networks, Inc. | Wireless access point (AP) automatic channel selection |
| US7043277B1 (en) | 2004-05-27 | 2006-05-09 | Autocell Laboratories, Inc. | Automatically populated display regions for discovered access points and stations in a user interface representing a wireless communication network deployed in a physical environment |
| US20060098607A1 (en) | 2004-10-28 | 2006-05-11 | Meshnetworks, Inc. | System and method to support multicast routing in large scale wireless mesh networks |
| US20060098613A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2006-05-11 | Video54 Technologies, Inc. | Systems and methods for improved data throughput in communications networks |
| US20060098605A1 (en) | 2003-04-07 | 2006-05-11 | Shaolin Li | Method of secure communications in a wireless distribution system |
| US20060098616A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2006-05-11 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Throughput enhancement by acknowledgement suppression |
| US7050809B2 (en) | 2001-12-27 | 2006-05-23 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | System and method for providing concurrent data transmissions in a wireless communication network |
| US7053853B2 (en) | 2003-06-26 | 2006-05-30 | Skypilot Network, Inc. | Planar antenna for a wireless mesh network |
| US20060114881A1 (en) | 2000-12-29 | 2006-06-01 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Mesh network that includes fixed and mobile access nodes |
| US20060123455A1 (en) | 2004-12-02 | 2006-06-08 | Microsoft Corporation | Personal media channel |
| US7064717B2 (en) | 2003-12-30 | 2006-06-20 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | High performance low cost monopole antenna for wireless applications |
| US20060133341A1 (en) | 2003-06-24 | 2006-06-22 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Client roaming from a first access node to a second access node within a wireless network |
| US7076274B2 (en) | 2001-05-02 | 2006-07-11 | Strix Systems, Inc. | Method and system for indicating link quality among neighboring wireless base station |
| US20060184660A1 (en) | 2005-02-15 | 2006-08-17 | Microsoft Corporation | Scaling UPnP v1.0 device eventing using peer groups |
| US20060184693A1 (en) | 2005-02-15 | 2006-08-17 | Microsoft Corporation | Scaling and extending UPnP v1.0 device discovery using peer groups |
| US7113519B2 (en) | 2001-04-18 | 2006-09-26 | Skypilot Networks, Inc. | Network channel access protocol—slot scheduling |
| US20060225107A1 (en) | 2005-04-01 | 2006-10-05 | Microsoft Corporation | System for running applications in a resource-constrained set-top box environment |
| US20060224690A1 (en) | 2005-04-01 | 2006-10-05 | Microsoft Corporation | Strategies for transforming markup content to code-bearing content for consumption by a receiving device |
| US20060227761A1 (en) | 2005-04-07 | 2006-10-12 | Microsoft Corporation | Phone-based remote media system interaction |
| US20060239369A1 (en) | 2005-04-25 | 2006-10-26 | Benq Corporation | Methods and systems for transmission channel drlrction in wireless communication |
| US7136655B2 (en) | 2002-11-21 | 2006-11-14 | Bandspeed, Inc. | Method and apparatus for coverage and throughput enhancement in a wireless communication system |
| EP1315311B1 (en) | 2000-08-10 | 2006-11-15 | Fujitsu Limited | Transmission diversity communication device |
| US20060268881A1 (en) | 2003-09-22 | 2006-11-30 | Moreton Michael John V | Method of data handling in a wlan |
| US7149197B2 (en) | 2001-08-15 | 2006-12-12 | Meshnetworks, Inc. | Movable access points and repeaters for minimizing coverage and capacity constraints in a wireless communications network and a method for using the same |
| US20060280131A1 (en) | 2005-05-31 | 2006-12-14 | Rahman Shahriar I | Spanning tree protocol for wireless networks |
| US7157757B2 (en) | 2004-08-27 | 2007-01-02 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Semiconductor constructions |
| US20070002750A1 (en)* | 2005-07-01 | 2007-01-04 | Nec Laboratories America, Inc. | Generic Real Time Scheduler for Wireless Packet Data Systems |
| US7161934B2 (en) | 2001-03-21 | 2007-01-09 | Intelsat | Satellite based content distribution system using IP multicast technology |
| US20070010271A1 (en) | 2005-06-14 | 2007-01-11 | Interdigital Technology Corporation | Method and system for conveying backhaul link information for intelligent selection of a mesh access point |
| US7164667B2 (en) | 2002-06-28 | 2007-01-16 | Belair Networks Inc. | Integrated wireless distribution and mesh backhaul networks |
| US7171223B2 (en) | 2003-01-10 | 2007-01-30 | Belair Networks, Inc. | Automatic antenna selection for mesh backhaul network nodes |
| US20070027622A1 (en) | 2005-07-01 | 2007-02-01 | Microsoft Corporation | State-sensitive navigation aid |
| WO2007016326A1 (en) | 2005-08-02 | 2007-02-08 | Skypilot Networks, Inc. | Method and apparatus for maximizing data transmission capacity of a mesh network |
| US7187925B2 (en) | 2003-02-28 | 2007-03-06 | Microsoft Corporation | Access point to access point range extension |
| US20070072612A1 (en)* | 2005-09-29 | 2007-03-29 | Fujitsu Limited | HSDPA wireless communication system |
| US7203508B2 (en) | 2001-06-13 | 2007-04-10 | Ntt Docomo, Inc. | Mobile communication systems, mobile communication methods, base stations, mobile stations, and signal transmission methods in the mobile communication systems |
| EP1608108B1 (en) | 2004-06-17 | 2007-04-25 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Improving channel ulilization efficiency in a wireless communication system comprising high-throughput terminals and legacy terminals |
| US20070101020A1 (en) | 2005-10-28 | 2007-05-03 | Tzu-Ming Lin | Packet transmitting method of wireless network |
| CN1965598A (en) | 2004-04-02 | 2007-05-16 | 特鲁波斯网络公司 | Multi-channel mesh network |
| US20070109961A1 (en) | 2005-11-16 | 2007-05-17 | Tropos Networks Inc. | Determining throughput between hosts |
| US20070135167A1 (en) | 2005-12-08 | 2007-06-14 | Accton Technology Corporation | Method and system for steering antenna beam |
| US20070189283A1 (en) | 2002-03-06 | 2007-08-16 | Agere Systems Inc. | Characterizing transmission of data segments within a switch fabric using multiple counters for each destination node |
| US20070223451A1 (en) | 2006-03-21 | 2007-09-27 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Mobile access node routing selections through a mesh network |
| US20070242602A1 (en) | 2006-04-18 | 2007-10-18 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Blocked redundant link-aware spanning tree protocol enhancement |
| US7289505B2 (en) | 2002-06-04 | 2007-10-30 | Lucent Technologies Inc. | Efficient reverse path forwarding check mechanism |
| US7292617B2 (en) | 2001-05-02 | 2007-11-06 | Strix Systems, Inc. | Reducing mutual channel interference in frequency-hopping spread spectrum wireless communication systems |
| US20070280168A1 (en)* | 2006-06-02 | 2007-12-06 | Nec Corporation | Radio base station apparatus and scheduling method |
| US7321571B2 (en) | 2002-09-27 | 2008-01-22 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | In-band wireless communication network backhaul |
| US20080043638A1 (en) | 2006-08-17 | 2008-02-21 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Content throughput on wireless mesh networks |
| US7336642B2 (en) | 2003-08-07 | 2008-02-26 | Skypilot Networks, Inc. | Communication protocol for a wireless mesh architecture |
| US20080069068A1 (en) | 2006-09-18 | 2008-03-20 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Providing a client with wireless link quality, and network information |
| US7355997B2 (en) | 2004-05-07 | 2008-04-08 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Data rate shifting methods and techniques |
| JP2008088633A (en) | 2006-09-29 | 2008-04-17 | Taiheiyo Cement Corp | Burying type form made of polymer cement mortar |
| US7362737B2 (en) | 2004-04-08 | 2008-04-22 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Minimization of channel filters within wireless access nodes |
| US7369510B1 (en) | 2002-05-06 | 2008-05-06 | Atheros Communications, Inc. | Wireless LAN using RSSI and BER parameters for transmission rate adaptation |
| US20080159207A1 (en) | 2006-12-28 | 2008-07-03 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and apparatus for cognitive spectrum assignment for mesh networks |
| US20080225804A1 (en) | 2007-03-14 | 2008-09-18 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Real-Time Sessions for Wireless Mesh Networks |
| US20080247327A1 (en) | 2007-04-03 | 2008-10-09 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Identifying correlations within wireless networks |
| US20080267116A1 (en) | 2007-04-27 | 2008-10-30 | Yong Kang | Routing method and system for a wireless network |
| US20090019314A1 (en) | 2007-07-13 | 2009-01-15 | Purenetworks, Inc. | Network advisor |
| US20090028095A1 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2009-01-29 | Kish William S | Wireless Network Throughput Enhancement Through Channel Aware Scheduling |
| US7489932B2 (en) | 2004-06-03 | 2009-02-10 | Tropos Networks | Channel assignments within a mesh network |
| US20090040989A1 (en) | 2002-10-28 | 2009-02-12 | Mesh Dynamics, Inc. | High performance wireless networks using distributed control |
| US7496680B2 (en) | 2002-11-13 | 2009-02-24 | Telenor Asa | Method for routing messages from a source node to a destination node in a dynamic network |
| US20090067369A1 (en) | 2007-09-06 | 2009-03-12 | Anastasios Stamoulis | Routing in a mesh network |
| US20090073921A1 (en) | 2007-09-19 | 2009-03-19 | At&T Services Inc. | Data forwarding in hybrid mesh networks |
| US20090080333A1 (en) | 2007-09-20 | 2009-03-26 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and device for providing an alternative backhaul portal in a mesh network |
| US7522731B2 (en) | 2003-04-28 | 2009-04-21 | Firetide, Inc. | Wireless service points having unique identifiers for secure communication |
| US7546126B2 (en) | 2001-05-02 | 2009-06-09 | Strix Systems, Inc. | Wireless base station neighbor discovery in a communication system, such as a system employing a short-range frequency hopping scheme |
| US20090154359A1 (en) | 2007-12-12 | 2009-06-18 | Motorola, Inc. | Method for calculating service redundancy of a wireless network |
| US7551562B2 (en) | 2000-12-29 | 2009-06-23 | Tropos Networks | Determining bidirectional path quality within a wireless mesh network |
| WO2009088488A1 (en) | 2008-01-11 | 2009-07-16 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Determining associations in a mesh network |
| US20090207730A1 (en) | 2008-02-14 | 2009-08-20 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Scheduling policy-based traffic management |
| US20090213730A1 (en) | 2008-02-21 | 2009-08-27 | Jianlin Zeng | Backhaul failover method and system for a wireless network |
| US20090225676A1 (en) | 2008-03-09 | 2009-09-10 | Fluke Corporation | Method and apparatus of duplicate packet detection and discard |
| US20090262677A1 (en) | 2008-04-18 | 2009-10-22 | Raja Banerjea | Multicast to unicast conversion system |
| US20100040056A1 (en) | 2003-02-06 | 2010-02-18 | Fujitsu Limited | Data generating device |
| US7672274B2 (en) | 2002-01-11 | 2010-03-02 | Broadcom Corporation | Mobility support via routing |
| US20100085916A1 (en) | 2007-01-31 | 2010-04-08 | Noosphere Communications, Inc. | Systems and Methods for Hybrid Wired and Wireless Universal Access Networks |
| US7715395B2 (en) | 2004-11-24 | 2010-05-11 | Microsoft Corporation | System and method for expanding the range of a mesh network |
| US7733833B2 (en) | 2003-03-24 | 2010-06-08 | Strix Systems, Inc. | Self-configuring, self-optimizing wireless local area network system |
| US7916684B2 (en) | 2004-11-11 | 2011-03-29 | Pine Valley Investments, Inc. | Wireless communication network providing communication between mobile devices and access points |
| US20110096712A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2011-04-28 | William Kish | Unicast to Multicast Conversion |
| US20110119401A1 (en) | 2009-11-16 | 2011-05-19 | Kish William S | Determining Role Assignment in a Hybrid Mesh Network |
| US20110119360A1 (en) | 2009-11-16 | 2011-05-19 | Kish William S | Establishing a Mesh Network with Wired and Wireless Links |
| US20110158233A1 (en) | 2007-12-20 | 2011-06-30 | Hwan-Sik NAMGUNG | Group communication system using media server having distributed structure and method thereof |
| US7974223B2 (en) | 2004-11-19 | 2011-07-05 | Corrigent Systems Ltd. | Virtual private LAN service over ring networks |
| US20110216685A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2011-09-08 | Kish William S | Mac based mapping in ip based communications |
| EP1653664B1 (en) | 2004-10-29 | 2013-03-13 | Research In Motion Limited | Wireless/wired mobile communication device, method and computer program medium with option to automatically block wireless communication when connected for wired communication |
| US8688834B2 (en) | 2004-07-09 | 2014-04-01 | Toshiba America Research, Inc. | Dynamic host configuration and network access authentication |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0338933A (en) | 1989-07-06 | 1991-02-20 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | Space diversity system |
| JP3038933B2 (en) | 1991-01-31 | 2000-05-08 | ソニー株式会社 | System controller for video signal processor |
| US5541927A (en) | 1994-08-24 | 1996-07-30 | At&T Corp. | Method of multicasting |
| US20050259682A1 (en) | 2000-02-03 | 2005-11-24 | Yuval Yosef | Broadcast system |
| US7133361B2 (en) | 2001-09-26 | 2006-11-07 | Hughes Network Systems, Inc. | Method and system for improvement of network performance over asymmetic links |
| JP4075461B2 (en) | 2001-11-27 | 2008-04-16 | ソニー株式会社 | Communication system, communication terminal, and communication method |
| JP4428934B2 (en) | 2003-03-24 | 2010-03-10 | 富士通株式会社 | Video selection server, video distribution system, and video selection method |
| CN1864366B (en) | 2003-10-07 | 2011-06-01 | 汤姆森特许公司 | Method and device for multicast over unicast in network |
| US7852837B1 (en) | 2003-12-24 | 2010-12-14 | At&T Intellectual Property Ii, L.P. | Wi-Fi/BPL dual mode repeaters for power line networks |
| US7684342B2 (en) | 2004-11-03 | 2010-03-23 | Intel Corporation | Media independent trigger model for multiple network types |
| WO2006066396A1 (en) | 2004-12-22 | 2006-06-29 | Dragonwave, Inc. | Wireless communication path management methods and systems |
| WO2008031361A1 (en) | 2006-09-11 | 2008-03-20 | 3Dsp Corporation | A multi-gateway system and methods for same |
| WO2009113798A2 (en) | 2008-03-14 | 2009-09-17 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Scanning method in wireless system |
| US8506395B2 (en) | 2008-07-18 | 2013-08-13 | Wms Gaming, Inc. | Communicating wagering game information using mesh networks |
- 2008
- 2008-07-28USUS12/181,274patent/US8547899B2/enactiveActive
- 2013
- 2013-09-16USUS14/028,323patent/US9271327B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
- 2016
- 2016-02-22USUS15/050,317patent/US9674862B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (336)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US1653664A (en) | 1927-12-27 | Lavatory | ||
| US4176356A (en) | 1977-06-27 | 1979-11-27 | Motorola, Inc. | Directional antenna system including pattern control |
| US4193077A (en) | 1977-10-11 | 1980-03-11 | Avnet, Inc. | Directional antenna system with end loaded crossed dipoles |
| US4253193A (en) | 1977-11-05 | 1981-02-24 | The Marconi Company Limited | Tropospheric scatter radio communication systems |
| US4305052A (en) | 1978-12-22 | 1981-12-08 | Thomson-Csf | Ultra-high-frequency diode phase shifter usable with electronically scanning antenna |
| US4513412A (en) | 1983-04-25 | 1985-04-23 | At&T Bell Laboratories | Time division adaptive retransmission technique for portable radio telephones |
| US4814777A (en) | 1987-07-31 | 1989-03-21 | Raytheon Company | Dual-polarization, omni-directional antenna system |
| EP0352787B1 (en) | 1988-07-28 | 1995-05-10 | Motorola, Inc. | High bit rate communication system for overcoming multipath |
| US5097484A (en) | 1988-10-12 | 1992-03-17 | Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. | Diversity transmission and reception method and equipment |
| US5173711A (en) | 1989-11-27 | 1992-12-22 | Kokusai Denshin Denwa Kabushiki Kaisha | Microstrip antenna for two-frequency separate-feeding type for circularly polarized waves |
| US5203010A (en) | 1990-11-13 | 1993-04-13 | Motorola, Inc. | Radio telephone system incorporating multiple time periods for communication transfer |
| US5373548A (en) | 1991-01-04 | 1994-12-13 | Thomson Consumer Electronics, Inc. | Out-of-range warning system for cordless telephone |
| US5117430A (en) | 1991-02-08 | 1992-05-26 | International Business Machines Corporation | Apparatus and method for communicating between nodes in a network |
| US5940771A (en) | 1991-05-13 | 1999-08-17 | Norand Corporation | Network supporting roaming, sleeping terminals |
| US5220678A (en) | 1991-08-12 | 1993-06-15 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and apparatus for adjusting the power of a transmitter |
| EP0534612A3 (en) | 1991-08-28 | 1993-11-24 | Motorola Inc | Cellular system sharing of logical channels |
| US5220340A (en) | 1992-04-29 | 1993-06-15 | Lotfollah Shafai | Directional switched beam antenna |
| US5361256A (en) | 1992-11-27 | 1994-11-01 | International Business Machines Corporation | Inter-domain multicast routing |
| US5507035A (en) | 1993-04-30 | 1996-04-09 | International Business Machines Corporation | Diversity transmission strategy in mobile/indoor cellula radio communications |
| US6034638A (en) | 1993-05-27 | 2000-03-07 | Griffith University | Antennas for use in portable communications devices |
| US5408465A (en) | 1993-06-21 | 1995-04-18 | Hewlett-Packard Company | Flexible scheme for admission control of multimedia streams on integrated networks |
| US5960344A (en) | 1993-12-20 | 1999-09-28 | Norand Corporation | Local area network having multiple channel wireless access |
| US5559800A (en) | 1994-01-19 | 1996-09-24 | Research In Motion Limited | Remote control of gateway functions in a wireless data communication network |
| US5802312A (en) | 1994-09-27 | 1998-09-01 | Research In Motion Limited | System for transmitting data files between computers in a wireless environment utilizing a file transfer agent executing on host system |
| US5570366A (en) | 1994-12-08 | 1996-10-29 | International Business Machines Corporation | Broadcast/multicast filtering by the bridge-based access point |
| US5636213A (en) | 1994-12-28 | 1997-06-03 | Motorola | Method, transceiver, and system for providing wireless communication compatible with 10BASE-T Ethernet |
| US6873627B1 (en) | 1995-01-19 | 2005-03-29 | The Fantastic Corporation | System and method for sending packets over a computer network |
| US6337628B2 (en) | 1995-02-22 | 2002-01-08 | Ntp, Incorporated | Omnidirectional and directional antenna assembly |
| US20050074108A1 (en) | 1995-04-21 | 2005-04-07 | Dezonno Anthony J. | Method and system for establishing voice communications using a computer network |
| US5608726A (en) | 1995-04-25 | 1997-03-04 | Cabletron Systems, Inc. | Network bridge with multicast forwarding table |
| US5867109A (en) | 1995-06-06 | 1999-02-02 | Globalstar L.P. | Satellite repeater diversity resource management system |
| US20020036996A1 (en) | 1995-06-30 | 2002-03-28 | Ozluturk Fatih M. | Initial power control for spread-spectrum communications |
| US5964830A (en) | 1995-08-22 | 1999-10-12 | Durrett; Charles M. | User portal device for the world wide web to communicate with a website server |
| US5754145A (en) | 1995-08-23 | 1998-05-19 | U.S. Philips Corporation | Printed antenna |
| US5930259A (en) | 1995-08-25 | 1999-07-27 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Packet transmission node device realizing packet transfer scheme and control information transfer scheme using multiple virtual connections |
| US6132306A (en) | 1995-09-06 | 2000-10-17 | Cisco Systems, Inc. | Cellular communication system with dedicated repeater channels |
| GB2306278B (en) | 1995-10-14 | 1999-12-08 | Nec Corp | Radio transmission system |
| US5970410A (en) | 1996-02-27 | 1999-10-19 | Airnet Communications Corp. | Cellular system plan using in band-translators to enable efficient deployment of high capacity base transceiver systems |
| US5767809A (en) | 1996-03-07 | 1998-06-16 | Industrial Technology Research Institute | OMNI-directional horizontally polarized Alford loop strip antenna |
| US6356553B1 (en) | 1996-07-11 | 2002-03-12 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Network node and method of packet transfer |
| US6018659A (en) | 1996-10-17 | 2000-01-25 | The Boeing Company | Airborne broadband communication network |
| US6044062A (en) | 1996-12-06 | 2000-03-28 | Communique, Llc | Wireless network system and method for providing same |
| US6249516B1 (en) | 1996-12-06 | 2001-06-19 | Edwin B. Brownrigg | Wireless network gateway and method for providing same |
| US5974034A (en) | 1997-01-16 | 1999-10-26 | Gwcom, Inc. | System and method for synchronized wide and local area communications utilizing a single frequency |
| US6714551B1 (en) | 1997-10-14 | 2004-03-30 | Alvarion Israel (2003) Ltd. | Method and apparatus for maintaining a predefined transmission quality in a wireless network for a metropolitan area |
| US6404775B1 (en) | 1997-11-21 | 2002-06-11 | Allen Telecom Inc. | Band-changing repeater with protocol or format conversion |
| US6094177A (en) | 1997-11-27 | 2000-07-25 | Yamamoto; Kiyoshi | Planar radiation antenna elements and omni directional antenna using such antenna elements |
| US6266537B1 (en) | 1998-03-27 | 2001-07-24 | Nec Corporation | Radio communication system |
| US6181697B1 (en) | 1998-03-31 | 2001-01-30 | At&T Corp. | Method for a unicast endpoint client to access a multicast internet protocol (IP) session and to serve as a redistributor of such session |
| US6393261B1 (en) | 1998-05-05 | 2002-05-21 | Telxon Corporation | Multi-communication access point |
| US6505253B1 (en) | 1998-06-30 | 2003-01-07 | Sun Microsystems | Multiple ACK windows providing congestion control in reliable multicast protocol |
| US6345043B1 (en) | 1998-07-06 | 2002-02-05 | National Datacomm Corporation | Access scheme for a wireless LAN station to connect an access point |
| US6404386B1 (en) | 1998-09-21 | 2002-06-11 | Tantivy Communications, Inc. | Adaptive antenna for use in same frequency networks |
| US20020047800A1 (en) | 1998-09-21 | 2002-04-25 | Tantivy Communications, Inc. | Adaptive antenna for use in same frequency networks |
| US6088570A (en) | 1998-11-24 | 2000-07-11 | Airnet Communications Corporation | Method and apparatus employing delay elements in multiple diversity paths of a wireless system repeater translator to allow for selective diversity and automatic level control in a time-division multiple access system |
| US6266528B1 (en) | 1998-12-23 | 2001-07-24 | Arraycomm, Inc. | Performance monitor for antenna arrays |
| US6442507B1 (en) | 1998-12-29 | 2002-08-27 | Wireless Communications, Inc. | System for creating a computer model and measurement database of a wireless communication network |
| US6584080B1 (en) | 1999-01-14 | 2003-06-24 | Aero-Vision Technologies, Inc. | Wireless burstable communications repeater |
| US6337668B1 (en) | 1999-03-05 | 2002-01-08 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Antenna apparatus |
| US6356905B1 (en) | 1999-03-05 | 2002-03-12 | Accenture Llp | System, method and article of manufacture for mobile communication utilizing an interface support framework |
| US6498589B1 (en) | 1999-03-18 | 2002-12-24 | Dx Antenna Company, Limited | Antenna system |
| US6414955B1 (en) | 1999-03-23 | 2002-07-02 | Innovative Technology Licensing, Llc | Distributed topology learning method and apparatus for wireless networks |
| US6377227B1 (en) | 1999-04-28 | 2002-04-23 | Superpass Company Inc. | High efficiency feed network for antennas |
| US6493679B1 (en) | 1999-05-26 | 2002-12-10 | Wireless Valley Communications, Inc. | Method and system for managing a real time bill of materials |
| US6317599B1 (en) | 1999-05-26 | 2001-11-13 | Wireless Valley Communications, Inc. | Method and system for automated optimization of antenna positioning in 3-D |
| US20050074018A1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2005-04-07 | Microsoft Corporation | XML-based template language for devices and services |
| US6779004B1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2004-08-17 | Microsoft Corporation | Auto-configuring of peripheral on host/peripheral computing platform with peer networking-to-host/peripheral adapter for peer networking connectivity |
| US6725281B1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2004-04-20 | Microsoft Corporation | Synchronization of controlled device state using state table and eventing in data-driven remote device control model |
| US7130895B2 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2006-10-31 | Microsoft Corporation | XML-based language description for controlled devices |
| US20050240665A1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2005-10-27 | Microsoft Corporation | Dynamic self-configuration for ad hoc peer networking |
| US7085814B1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2006-08-01 | Microsoft Corporation | Data driven remote device control model with general programming interface-to-network messaging adapter |
| US6910068B2 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2005-06-21 | Microsoft Corporation | XML-based template language for devices and services |
| US20040260800A1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2004-12-23 | Microsoft Corporation | Dynamic self-configuration for ad hoc peer networking |
| US20050267935A1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2005-12-01 | Microsoft Corporation | Data driven remote device control model with general programming interface-to-network messaging adaptor |
| US6892230B1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2005-05-10 | Microsoft Corporation | Dynamic self-configuration for ad hoc peer networking using mark-up language formated description messages |
| US20050022210A1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2005-01-27 | Microsoft Corporation | Synchronization of controlled device state using state table and eventing in data-driven remote device control model |
| US20050097503A1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2005-05-05 | Microsoft Corporation | XML-based template language for devices and services |
| US20060291434A1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2006-12-28 | Microsoft Corporation | Dynamic self-configuration for ad hoc peer networking |
| US7089307B2 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2006-08-08 | Microsoft Corporation | Synchronization of controlled device state using state table and eventing in data-driven remote device control model |
| US6407719B1 (en) | 1999-07-08 | 2002-06-18 | Atr Adaptive Communications Research Laboratories | Array antenna |
| US6499006B1 (en) | 1999-07-14 | 2002-12-24 | Wireless Valley Communications, Inc. | System for the three-dimensional display of wireless communication system performance |
| US6339404B1 (en) | 1999-08-13 | 2002-01-15 | Rangestar Wirless, Inc. | Diversity antenna system for lan communication system |
| JP2001057560A (en) | 1999-08-18 | 2001-02-27 | Hitachi Kokusai Electric Inc | Wireless LAN system |
| US6292153B1 (en) | 1999-08-27 | 2001-09-18 | Fantasma Network, Inc. | Antenna comprising two wideband notch regions on one coplanar substrate |
| US6570883B1 (en)* | 1999-08-28 | 2003-05-27 | Hsiao-Tung Wong | Packet scheduling using dual weight single priority queue |
| US6778517B1 (en) | 1999-10-14 | 2004-08-17 | Bellsouth Intellectual Property Corporation | Wireless broadband service |
| US6392610B1 (en) | 1999-10-29 | 2002-05-21 | Allgon Ab | Antenna device for transmitting and/or receiving RF waves |
| US6957042B2 (en) | 2000-01-10 | 2005-10-18 | Airnet Communications Corporation | Packet based backhaul channel configuration for a wireless repeater |
| US6307524B1 (en) | 2000-01-18 | 2001-10-23 | Core Technology, Inc. | Yagi antenna having matching coaxial cable and driven element impedances |
| US6356242B1 (en) | 2000-01-27 | 2002-03-12 | George Ploussios | Crossed bent monopole doublets |
| US6836481B1 (en) | 2000-02-17 | 2004-12-28 | Fujitsu Limited | Packet conversion device and packet conversion method |
| US6957277B2 (en) | 2000-02-28 | 2005-10-18 | Nec Corporation | Multicast packet transferring apparatus, multicast packet transferring system and storage medium used in same |
| US6418138B1 (en) | 2000-03-02 | 2002-07-09 | Worldcom, Inc. | Internet radio communication system |
| US20040014432A1 (en) | 2000-03-23 | 2004-01-22 | U.S. Philips Corporation | Antenna diversity arrangement |
| US6701522B1 (en) | 2000-04-07 | 2004-03-02 | Danger, Inc. | Apparatus and method for portal device authentication |
| US20010055312A1 (en) | 2000-04-07 | 2001-12-27 | Negus Kevin J. | Asymmetric data traffic throughput in CSMA/CA networks |
| US20010047474A1 (en) | 2000-05-23 | 2001-11-29 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Communication control scheme using proxy device and security protocol in combination |
| US20020105471A1 (en) | 2000-05-24 | 2002-08-08 | Suguru Kojima | Directional switch antenna device |
| US6507321B2 (en) | 2000-05-26 | 2003-01-14 | Sony International (Europe) Gmbh | V-slot antenna for circular polarization |
| US20020031130A1 (en) | 2000-05-30 | 2002-03-14 | Kazuaki Tsuchiya | Multicast routing method and an apparatus for routing a multicast packet |
| US6326922B1 (en) | 2000-06-29 | 2001-12-04 | Worldspace Corporation | Yagi antenna coupled with a low noise amplifier on the same printed circuit board |
| US20020001310A1 (en) | 2000-06-29 | 2002-01-03 | Khanh Mai | Virtual multicasting |
| US6356243B1 (en) | 2000-07-19 | 2002-03-12 | Logitech Europe S.A. | Three-dimensional geometric space loop antenna |
| US6625454B1 (en) | 2000-08-04 | 2003-09-23 | Wireless Valley Communications, Inc. | Method and system for designing or deploying a communications network which considers frequency dependent effects |
| EP1315311B1 (en) | 2000-08-10 | 2006-11-15 | Fujitsu Limited | Transmission diversity communication device |
| US6445688B1 (en) | 2000-08-31 | 2002-09-03 | Ricochet Networks, Inc. | Method and apparatus for selecting a directional antenna in a wireless communication system |
| US6728514B2 (en) | 2000-09-08 | 2004-04-27 | Wi-Lan Inc. | Scalable wireless network topology systems and methods |
| WO2002025967A1 (en) | 2000-09-22 | 2002-03-28 | Widcomm Inc. | Wireless network and method for providing improved handoff performance |
| US6973622B1 (en) | 2000-09-25 | 2005-12-06 | Wireless Valley Communications, Inc. | System and method for design, tracking, measurement, prediction and optimization of data communication networks |
| US6975834B1 (en) | 2000-10-03 | 2005-12-13 | Mineral Lassen Llc | Multi-band wireless communication device and method |
| US20020045435A1 (en) | 2000-10-18 | 2002-04-18 | Steve Fantaske | Wireless communication system |
| US20040058690A1 (en) | 2000-11-20 | 2004-03-25 | Achim Ratzel | Antenna system |
| US20030026268A1 (en) | 2000-11-28 | 2003-02-06 | Siemens Technology-To-Business Center, Llc | Characteristic routing |
| US20020112058A1 (en) | 2000-12-01 | 2002-08-15 | Microsoft Corporation | Peer networking host framework and hosting API |
| US20060168159A1 (en) | 2000-12-01 | 2006-07-27 | Microsoft Corporation | Peer networking host framework and hosting API |
| US7171475B2 (en) | 2000-12-01 | 2007-01-30 | Microsoft Corporation | Peer networking host framework and hosting API |
| US20060184661A1 (en) | 2000-12-01 | 2006-08-17 | Microsoft Corporation | Peer networking host framework and hosting API |
| US20060123125A1 (en) | 2000-12-01 | 2006-06-08 | Microsoft Corporation | Peer networking host framework and hosting API |
| US20060123124A1 (en) | 2000-12-01 | 2006-06-08 | Microsoft Corporation | Peer networking host framework and hosting API |
| US6950019B2 (en) | 2000-12-07 | 2005-09-27 | Raymond Bellone | Multiple-triggering alarm system by transmitters and portable receiver-buzzer |
| US20020114330A1 (en) | 2000-12-13 | 2002-08-22 | Cheung Kwok Wai | Method and system for delivering media selections through a network |
| WO2002049360A1 (en) | 2000-12-13 | 2002-06-20 | THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG A body corporate of Hong Kong SAR | Method and system for delivering media selections through a network |
| US20040048593A1 (en) | 2000-12-21 | 2004-03-11 | Hiroyasu Sano | Adaptive antenna receiver |
| US20020080767A1 (en) | 2000-12-22 | 2002-06-27 | Ji-Woong Lee | Method of supporting small group multicast in mobile IP |
| US7697504B2 (en) | 2000-12-29 | 2010-04-13 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Mesh network that includes fixed and mobile access nodes |
| US20060114881A1 (en) | 2000-12-29 | 2006-06-01 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Mesh network that includes fixed and mobile access nodes |
| US7551562B2 (en) | 2000-12-29 | 2009-06-23 | Tropos Networks | Determining bidirectional path quality within a wireless mesh network |
| US6704301B2 (en) | 2000-12-29 | 2004-03-09 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Method and apparatus to provide a routing protocol for wireless devices |
| US20040008663A1 (en) | 2000-12-29 | 2004-01-15 | Devabhaktuni Srikrishna | Selection of routing paths based upon path quality of a wireless mesh network |
| US7505426B2 (en) | 2000-12-29 | 2009-03-17 | Tropos Networks | Multi-channel mesh network |
| US20020084942A1 (en) | 2001-01-03 | 2002-07-04 | Szu-Nan Tsai | Pcb dipole antenna |
| US20050135480A1 (en) | 2001-01-05 | 2005-06-23 | Microsoft Corporation | System and process for broadcast and communication with very low bit-rate bi-level or sketch video |
| US6888893B2 (en) | 2001-01-05 | 2005-05-03 | Microsoft Corporation | System and process for broadcast and communication with very low bit-rate bi-level or sketch video |
| US7161934B2 (en) | 2001-03-21 | 2007-01-09 | Intelsat | Satellite based content distribution system using IP multicast technology |
| US20020143951A1 (en) | 2001-03-30 | 2002-10-03 | Eyeball.Com Network Inc. | Method and system for multicast to unicast bridging |
| US20020164963A1 (en) | 2001-04-09 | 2002-11-07 | Tehrani Ardavan Maleki | Method and system for providing antenna diversity |
| US7113519B2 (en) | 2001-04-18 | 2006-09-26 | Skypilot Networks, Inc. | Network channel access protocol—slot scheduling |
| US7283494B2 (en) | 2001-04-18 | 2007-10-16 | Skypilot Networks, Inc. | Network channel access protocol-interference and load adaptive |
| US6996086B2 (en) | 2001-04-26 | 2006-02-07 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Radio access network with meshed radio base stations |
| US6931429B2 (en) | 2001-04-27 | 2005-08-16 | Left Gate Holdings, Inc. | Adaptable wireless proximity networking |
| US20020158801A1 (en) | 2001-04-27 | 2002-10-31 | Crilly William J. | Wireless packet switched communication systems and networks using adaptively steered antenna arrays |
| US20050041739A1 (en) | 2001-04-28 | 2005-02-24 | Microsoft Corporation | System and process for broadcast and communication with very low bit-rate bi-level or sketch video |
| US20040027304A1 (en) | 2001-04-30 | 2004-02-12 | Bing Chiang | High gain antenna for wireless applications |
| US20020158798A1 (en) | 2001-04-30 | 2002-10-31 | Bing Chiang | High gain planar scanned antenna array |
| US7546126B2 (en) | 2001-05-02 | 2009-06-09 | Strix Systems, Inc. | Wireless base station neighbor discovery in a communication system, such as a system employing a short-range frequency hopping scheme |
| US7292617B2 (en) | 2001-05-02 | 2007-11-06 | Strix Systems, Inc. | Reducing mutual channel interference in frequency-hopping spread spectrum wireless communication systems |
| US7076274B2 (en) | 2001-05-02 | 2006-07-11 | Strix Systems, Inc. | Method and system for indicating link quality among neighboring wireless base station |
| US20020170064A1 (en) | 2001-05-11 | 2002-11-14 | Monroe David A. | Portable, wireless monitoring and control station for use in connection with a multi-media surveillance system having enhanced notification functions |
| US20040125777A1 (en) | 2001-05-24 | 2004-07-01 | James Doyle | Method and apparatus for affiliating a wireless device with a wireless local area network |
| US7203508B2 (en) | 2001-06-13 | 2007-04-10 | Ntt Docomo, Inc. | Mobile communication systems, mobile communication methods, base stations, mobile stations, and signal transmission methods in the mobile communication systems |
| US20020194367A1 (en) | 2001-06-14 | 2002-12-19 | The Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd. | Data relay method, its apparatus, and data relay system using the apparatus |
| US20030003917A1 (en) | 2001-06-29 | 2003-01-02 | Copley Rich T. | Wireless communication system, apparatus and method for providing wireless communication within a building structure |
| US20030026240A1 (en) | 2001-07-23 | 2003-02-06 | Eyuboglu M. Vedat | Broadcasting and multicasting in wireless communication |
| JP2003038933A (en) | 2001-07-26 | 2003-02-12 | Akira Mizuno | Discharge plasma generating apparatus |
| US20030030588A1 (en) | 2001-08-10 | 2003-02-13 | Music Sciences, Inc. | Antenna system |
| US7149197B2 (en) | 2001-08-15 | 2006-12-12 | Meshnetworks, Inc. | Movable access points and repeaters for minimizing coverage and capacity constraints in a wireless communications network and a method for using the same |
| US20030043786A1 (en) | 2001-08-28 | 2003-03-06 | Jan Kall | Apparatus, and associated method, for multicasting data in a radio communications system |
| US20030189514A1 (en) | 2001-09-06 | 2003-10-09 | Kentaro Miyano | Array antenna apparatus |
| US20030063591A1 (en) | 2001-10-03 | 2003-04-03 | Leung Nikolai K.N. | Method and apparatus for data packet transport in a wireless communication system using an internet protocol |
| US20040041732A1 (en) | 2001-10-03 | 2004-03-04 | Masayoshi Aikawa | Multielement planar antenna |
| US6674459B2 (en) | 2001-10-24 | 2004-01-06 | Microsoft Corporation | Network conference recording system and method including post-conference processing |
| US20030169330A1 (en) | 2001-10-24 | 2003-09-11 | Microsoft Corporation | Network conference recording system and method including post-conference processing |
| US20040032378A1 (en) | 2001-10-31 | 2004-02-19 | Vladimir Volman | Broadband starfish antenna and array thereof |
| US20030122714A1 (en) | 2001-11-16 | 2003-07-03 | Galtronics Ltd. | Variable gain and variable beamwidth antenna (the hinged antenna) |
| US7050809B2 (en) | 2001-12-27 | 2006-05-23 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | System and method for providing concurrent data transmissions in a wireless communication network |
| US20040095278A1 (en) | 2001-12-28 | 2004-05-20 | Hideki Kanemoto | Multi-antenna apparatus multi-antenna reception method, and multi-antenna transmission method |
| US7672274B2 (en) | 2002-01-11 | 2010-03-02 | Broadcom Corporation | Mobility support via routing |
| US20030133458A1 (en) | 2002-01-17 | 2003-07-17 | Masaaki Sato | Unicast-to-multicast converting apparatus, method, and computer program product, and monitoring system comprising the same |
| US6888504B2 (en) | 2002-02-01 | 2005-05-03 | Ipr Licensing, Inc. | Aperiodic array antenna |
| US20030210207A1 (en) | 2002-02-08 | 2003-11-13 | Seong-Youp Suh | Planar wideband antennas |
| US20030227414A1 (en) | 2002-03-04 | 2003-12-11 | Saliga Stephen V. | Diversity antenna for UNII access point |
| US20070189283A1 (en) | 2002-03-06 | 2007-08-16 | Agere Systems Inc. | Characterizing transmission of data segments within a switch fabric using multiple counters for each destination node |
| WO2003079484A3 (en) | 2002-03-15 | 2004-01-22 | Andrew Corp | Antenna interface protocol |
| US6819287B2 (en) | 2002-03-15 | 2004-11-16 | Centurion Wireless Technologies, Inc. | Planar inverted-F antenna including a matching network having transmission line stubs and capacitor/inductor tank circuits |
| US20030184490A1 (en) | 2002-03-26 | 2003-10-02 | Raiman Clifford E. | Sectorized omnidirectional antenna |
| US20030189521A1 (en) | 2002-04-05 | 2003-10-09 | Atsushi Yamamoto | Directivity controllable antenna and antenna unit using the same |
| US20030189523A1 (en) | 2002-04-09 | 2003-10-09 | Filtronic Lk Oy | Antenna with variable directional pattern |
| US7034770B2 (en) | 2002-04-23 | 2006-04-25 | Broadcom Corporation | Printed dipole antenna |
| US7369510B1 (en) | 2002-05-06 | 2008-05-06 | Atheros Communications, Inc. | Wireless LAN using RSSI and BER parameters for transmission rate adaptation |
| US20040028006A1 (en) | 2002-05-22 | 2004-02-12 | Ntt Docomo, Inc. | Random access method and radio station |
| US6924768B2 (en) | 2002-05-23 | 2005-08-02 | Realtek Semiconductor Corp. | Printed antenna structure |
| US20040027291A1 (en) | 2002-05-24 | 2004-02-12 | Xin Zhang | Planar antenna and array antenna |
| US7289505B2 (en) | 2002-06-04 | 2007-10-30 | Lucent Technologies Inc. | Efficient reverse path forwarding check mechanism |
| US20030231593A1 (en) | 2002-06-04 | 2003-12-18 | James Bauman | Flexible multilevel output traffic control |
| US20040036651A1 (en) | 2002-06-05 | 2004-02-26 | Takeshi Toda | Adaptive antenna unit and terminal equipment |
| US20030228857A1 (en) | 2002-06-06 | 2003-12-11 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Optimum scan for fixed-wireless smart antennas |
| US6876280B2 (en) | 2002-06-24 | 2005-04-05 | Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | High-frequency switch, and electronic device using the same |
| US6753814B2 (en) | 2002-06-27 | 2004-06-22 | Harris Corporation | Dipole arrangements using dielectric substrates of meta-materials |
| US7164667B2 (en) | 2002-06-28 | 2007-01-16 | Belair Networks Inc. | Integrated wireless distribution and mesh backhaul networks |
| US20040017310A1 (en) | 2002-07-24 | 2004-01-29 | Sarah Vargas-Hurlston | Position optimized wireless communication |
| US20040017860A1 (en) | 2002-07-29 | 2004-01-29 | Jung-Tao Liu | Multiple antenna system for varying transmission streams |
| US20040036654A1 (en) | 2002-08-21 | 2004-02-26 | Steve Hsieh | Antenna assembly for circuit board |
| US6941143B2 (en) | 2002-08-29 | 2005-09-06 | Thomson Licensing, S.A. | Automatic channel selection in a radio access network |
| US6906678B2 (en) | 2002-09-24 | 2005-06-14 | Gemtek Technology Co. Ltd. | Multi-frequency printed antenna |
| US20040061653A1 (en) | 2002-09-26 | 2004-04-01 | Andrew Corporation | Dynamically variable beamwidth and variable azimuth scanning antenna |
| US7321571B2 (en) | 2002-09-27 | 2008-01-22 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | In-band wireless communication network backhaul |
| US20040114535A1 (en) | 2002-09-30 | 2004-06-17 | Tantivy Communications, Inc. | Method and apparatus for antenna steering for WLAN |
| US20040070543A1 (en) | 2002-10-15 | 2004-04-15 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Antenna structure for electronic device with wireless communication unit |
| US20040080455A1 (en) | 2002-10-23 | 2004-04-29 | Lee Choon Sae | Microstrip array antenna |
| US20090040989A1 (en) | 2002-10-28 | 2009-02-12 | Mesh Dynamics, Inc. | High performance wireless networks using distributed control |
| US20040085993A1 (en) | 2002-11-05 | 2004-05-06 | Wentink Maarten Menzo | Shared-medium contention algorithm exhibiting fairness |
| US6762723B2 (en) | 2002-11-08 | 2004-07-13 | Motorola, Inc. | Wireless communication device having multiband antenna |
| US7496680B2 (en) | 2002-11-13 | 2009-02-24 | Telenor Asa | Method for routing messages from a source node to a destination node in a dynamic network |
| US7136655B2 (en) | 2002-11-21 | 2006-11-14 | Bandspeed, Inc. | Method and apparatus for coverage and throughput enhancement in a wireless communication system |
| WO2004057817A2 (en) | 2002-12-19 | 2004-07-08 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Protecting real-time data in wireless networks |
| US20060165029A1 (en) | 2002-12-19 | 2006-07-27 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Protecting real-time data in wireless networks |
| US7171223B2 (en) | 2003-01-10 | 2007-01-30 | Belair Networks, Inc. | Automatic antenna selection for mesh backhaul network nodes |
| US6961028B2 (en) | 2003-01-17 | 2005-11-01 | Lockheed Martin Corporation | Low profile dual frequency dipole antenna structure |
| US20100040056A1 (en) | 2003-02-06 | 2010-02-18 | Fujitsu Limited | Data generating device |
| EP1450521A2 (en) | 2003-02-19 | 2004-08-25 | Nec Corporation | Wireless communication system and method which improves reliability and throughput of communication through retransmission timeout optimization |
| US7187925B2 (en) | 2003-02-28 | 2007-03-06 | Microsoft Corporation | Access point to access point range extension |
| US7733833B2 (en) | 2003-03-24 | 2010-06-08 | Strix Systems, Inc. | Self-configuring, self-optimizing wireless local area network system |
| US7269174B2 (en) | 2003-03-28 | 2007-09-11 | Modular Mining Systems, Inc. | Dynamic wireless network |
| US20040190477A1 (en) | 2003-03-28 | 2004-09-30 | Olson Jonathan P. | Dynamic wireless network |
| US20060098605A1 (en) | 2003-04-07 | 2006-05-11 | Shaolin Li | Method of secure communications in a wireless distribution system |
| US7522731B2 (en) | 2003-04-28 | 2009-04-21 | Firetide, Inc. | Wireless service points having unique identifiers for secure communication |
| US20050232179A1 (en) | 2003-05-08 | 2005-10-20 | Dacosta Francis | Multiple-radio mission critical wireless mesh networks |
| US20050002395A1 (en) | 2003-06-04 | 2005-01-06 | Nec Corporation | IP multicast distribution system, streaming data distribution system and program therefor |
| US7586879B2 (en) | 2003-06-24 | 2009-09-08 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Client roaming from a first access node to a second access node within a wireless network |
| US20060133341A1 (en) | 2003-06-24 | 2006-06-22 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Client roaming from a first access node to a second access node within a wireless network |
| US20040264463A1 (en) | 2003-06-26 | 2004-12-30 | Hidehiro Fukushima | Method, apparatus and system for distributing multicast data |
| US7053853B2 (en) | 2003-06-26 | 2006-05-30 | Skypilot Network, Inc. | Planar antenna for a wireless mesh network |
| US20050009523A1 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2005-01-13 | Nokia Corporation | Protocol using forward error correction to improve handover |
| WO2005008938A3 (en) | 2003-07-08 | 2005-03-24 | Kiwi Networks Inc | Implementing 'all wireless' network over wifi equipment using 'scheduled tdma' |
| US20050032531A1 (en) | 2003-08-06 | 2005-02-10 | Hong Kong Applied Science And Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd. | Location positioning in wireless networks |
| US7336642B2 (en) | 2003-08-07 | 2008-02-26 | Skypilot Networks, Inc. | Communication protocol for a wireless mesh architecture |
| US20050042988A1 (en) | 2003-08-18 | 2005-02-24 | Alcatel | Combined open and closed loop transmission diversity system |
| US20060268881A1 (en) | 2003-09-22 | 2006-11-30 | Moreton Michael John V | Method of data handling in a wlan |
| US20050074019A1 (en) | 2003-10-03 | 2005-04-07 | Nortel Networks Limited | Method and apparatus for providing mobile inter-mesh communication points in a multi-level wireless mesh network |
| US20050153720A1 (en) | 2003-12-15 | 2005-07-14 | White Graeme E. | Apparatus, system, and method for managing distribution and coverage channels in a cellular communication system having a wireless backhaul |
| US20050138193A1 (en) | 2003-12-19 | 2005-06-23 | Microsoft Corporation | Routing of resource information in a network |
| US20050138137A1 (en) | 2003-12-19 | 2005-06-23 | Microsoft Corporation | Using parameterized URLs for retrieving resource content items |
| US7064717B2 (en) | 2003-12-30 | 2006-06-20 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | High performance low cost monopole antenna for wireless applications |
| US20050180381A1 (en) | 2004-02-12 | 2005-08-18 | Retzer Michael H. | Method and apparatus for improving throughput in a wireless local area network |
| US20050188193A1 (en) | 2004-02-20 | 2005-08-25 | Microsoft Corporation | Secure network channel |
| US20050185666A1 (en) | 2004-02-23 | 2005-08-25 | Maxim Raya | Misbehaving detection method for contention-based wireless communications |
| US20050226239A1 (en) | 2004-03-30 | 2005-10-13 | Sony Corporation And Sony Electronics, Inc. | Optimizing IEEE 802.11 for TCP/IP data transfer |
| CN1965598A (en) | 2004-04-02 | 2007-05-16 | 特鲁波斯网络公司 | Multi-channel mesh network |
| US7362737B2 (en) | 2004-04-08 | 2008-04-22 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Minimization of channel filters within wireless access nodes |
| US20050250544A1 (en) | 2004-05-07 | 2005-11-10 | Stephen Grant | Base station, mobile terminal device and method for implementing a selective-per-antenna-rate-control (S-PARC) technique in a wireless communications network |
| US7355997B2 (en) | 2004-05-07 | 2008-04-08 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Data rate shifting methods and techniques |
| US20050271070A1 (en) | 2004-05-20 | 2005-12-08 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Radio module |
| US7043277B1 (en) | 2004-05-27 | 2006-05-09 | Autocell Laboratories, Inc. | Automatically populated display regions for discovered access points and stations in a user interface representing a wireless communication network deployed in a physical environment |
| US7489932B2 (en) | 2004-06-03 | 2009-02-10 | Tropos Networks | Channel assignments within a mesh network |
| JP2005354249A (en) | 2004-06-09 | 2005-12-22 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Network communication terminal |
| EP1608108B1 (en) | 2004-06-17 | 2007-04-25 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Improving channel ulilization efficiency in a wireless communication system comprising high-throughput terminals and legacy terminals |
| US8688834B2 (en) | 2004-07-09 | 2014-04-01 | Toshiba America Research, Inc. | Dynamic host configuration and network access authentication |
| US20060018335A1 (en) | 2004-07-26 | 2006-01-26 | Koch Christopher D | Multicast to unicast traffic conversion in a network |
| JP2006060408A (en) | 2004-08-18 | 2006-03-02 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Radio packet communication method and radio station |
| US7157757B2 (en) | 2004-08-27 | 2007-01-02 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Semiconductor constructions |
| US7515589B2 (en) | 2004-08-27 | 2009-04-07 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method and apparatus for providing network virtualization |
| US20060045089A1 (en) | 2004-08-27 | 2006-03-02 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method and apparatus for providing network virtualization |
| US20060098607A1 (en) | 2004-10-28 | 2006-05-11 | Meshnetworks, Inc. | System and method to support multicast routing in large scale wireless mesh networks |
| US20060094371A1 (en) | 2004-10-29 | 2006-05-04 | Colubris Networks, Inc. | Wireless access point (AP) automatic channel selection |
| EP1653664B1 (en) | 2004-10-29 | 2013-03-13 | Research In Motion Limited | Wireless/wired mobile communication device, method and computer program medium with option to automatically block wireless communication when connected for wired communication |
| US8089949B2 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2012-01-03 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Distributed access point for IP based communications |
| US8619662B2 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2013-12-31 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Unicast to multicast conversion |
| US20150312727A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2015-10-29 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Distributed access point for ip based communications |
| US20060098613A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2006-05-11 | Video54 Technologies, Inc. | Systems and methods for improved data throughput in communications networks |
| US9071942B2 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2015-06-30 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | MAC based mapping in IP based communications |
| US20100182944A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2010-07-22 | Kish William S | Distributed access point for ip based communications |
| US9066152B2 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2015-06-23 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Distributed access point for IP based communications |
| US20060098616A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2006-05-11 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Throughput enhancement by acknowledgement suppression |
| US8824357B2 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2014-09-02 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Throughput enhancement by acknowledgment suppression |
| US20140177511A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2014-06-26 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Unicast to multicast conversion |
| US7787436B2 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2010-08-31 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Communications throughput with multiple physical data rate transmission determinations |
| US20080137681A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2008-06-12 | Kish William S | Communications throughput with unicast packet transmission alternative |
| US20080137682A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2008-06-12 | Kish William S | Communications throughput with multiple physical data rate transmission determinations |
| US20140133385A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2014-05-15 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Distributed access point for ip based communications |
| US20140071879A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2014-03-13 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Mac based mapping in ip based communications |
| US8638708B2 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2014-01-28 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | MAC based mapping in IP based communications |
| US8634402B2 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2014-01-21 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Distributed access point for IP based communications |
| WO2006052639A3 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2006-12-21 | Ruckus Wireless Inc | Systems and methods for improved data throughput in communications networks |
| US20130010775A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2013-01-10 | Kish William S | Throughput enhancement by acknowledgment suppression |
| US20120063379A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2012-03-15 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Distributed access point for ip based communications |
| US20110096712A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2011-04-28 | William Kish | Unicast to Multicast Conversion |
| US8125975B2 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2012-02-28 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Communications throughput with unicast packet transmission alternative |
| US7505447B2 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2009-03-17 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Systems and methods for improved data throughput in communications networks |
| US20110216685A1 (en) | 2004-11-05 | 2011-09-08 | Kish William S | Mac based mapping in ip based communications |
| US7916684B2 (en) | 2004-11-11 | 2011-03-29 | Pine Valley Investments, Inc. | Wireless communication network providing communication between mobile devices and access points |
| US7974223B2 (en) | 2004-11-19 | 2011-07-05 | Corrigent Systems Ltd. | Virtual private LAN service over ring networks |
| US7715395B2 (en) | 2004-11-24 | 2010-05-11 | Microsoft Corporation | System and method for expanding the range of a mesh network |
| US20060123455A1 (en) | 2004-12-02 | 2006-06-08 | Microsoft Corporation | Personal media channel |
| US20060184660A1 (en) | 2005-02-15 | 2006-08-17 | Microsoft Corporation | Scaling UPnP v1.0 device eventing using peer groups |
| US20060184693A1 (en) | 2005-02-15 | 2006-08-17 | Microsoft Corporation | Scaling and extending UPnP v1.0 device discovery using peer groups |
| US20060224690A1 (en) | 2005-04-01 | 2006-10-05 | Microsoft Corporation | Strategies for transforming markup content to code-bearing content for consumption by a receiving device |
| US20060225107A1 (en) | 2005-04-01 | 2006-10-05 | Microsoft Corporation | System for running applications in a resource-constrained set-top box environment |
| US20060227761A1 (en) | 2005-04-07 | 2006-10-12 | Microsoft Corporation | Phone-based remote media system interaction |
| US20060239369A1 (en) | 2005-04-25 | 2006-10-26 | Benq Corporation | Methods and systems for transmission channel drlrction in wireless communication |
| US20060280131A1 (en) | 2005-05-31 | 2006-12-14 | Rahman Shahriar I | Spanning tree protocol for wireless networks |
| US20070010271A1 (en) | 2005-06-14 | 2007-01-11 | Interdigital Technology Corporation | Method and system for conveying backhaul link information for intelligent selection of a mesh access point |
| US20070002750A1 (en)* | 2005-07-01 | 2007-01-04 | Nec Laboratories America, Inc. | Generic Real Time Scheduler for Wireless Packet Data Systems |
| US20070027622A1 (en) | 2005-07-01 | 2007-02-01 | Microsoft Corporation | State-sensitive navigation aid |
| WO2007016326A1 (en) | 2005-08-02 | 2007-02-08 | Skypilot Networks, Inc. | Method and apparatus for maximizing data transmission capacity of a mesh network |
| US20070030811A1 (en) | 2005-08-02 | 2007-02-08 | Skypilot Networks, Inc. | Method and apparatus for maximizing data transmission capacity of a mesh network |
| US20070072612A1 (en)* | 2005-09-29 | 2007-03-29 | Fujitsu Limited | HSDPA wireless communication system |
| US20070101020A1 (en) | 2005-10-28 | 2007-05-03 | Tzu-Ming Lin | Packet transmitting method of wireless network |
| US20070109961A1 (en) | 2005-11-16 | 2007-05-17 | Tropos Networks Inc. | Determining throughput between hosts |
| US20070135167A1 (en) | 2005-12-08 | 2007-06-14 | Accton Technology Corporation | Method and system for steering antenna beam |
| US20070223451A1 (en) | 2006-03-21 | 2007-09-27 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Mobile access node routing selections through a mesh network |
| US20070242602A1 (en) | 2006-04-18 | 2007-10-18 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Blocked redundant link-aware spanning tree protocol enhancement |
| US20070280168A1 (en)* | 2006-06-02 | 2007-12-06 | Nec Corporation | Radio base station apparatus and scheduling method |
| US20080043638A1 (en) | 2006-08-17 | 2008-02-21 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Content throughput on wireless mesh networks |
| US20080069068A1 (en) | 2006-09-18 | 2008-03-20 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Providing a client with wireless link quality, and network information |
| JP2008088633A (en) | 2006-09-29 | 2008-04-17 | Taiheiyo Cement Corp | Burying type form made of polymer cement mortar |
| US20080159207A1 (en) | 2006-12-28 | 2008-07-03 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and apparatus for cognitive spectrum assignment for mesh networks |
| US20100085916A1 (en) | 2007-01-31 | 2010-04-08 | Noosphere Communications, Inc. | Systems and Methods for Hybrid Wired and Wireless Universal Access Networks |
| US20080225804A1 (en) | 2007-03-14 | 2008-09-18 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Real-Time Sessions for Wireless Mesh Networks |
| US20080247327A1 (en) | 2007-04-03 | 2008-10-09 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Identifying correlations within wireless networks |
| US20080247317A1 (en) | 2007-04-03 | 2008-10-09 | Tropos Networks, Inc. | Monitoring network conditions of a wireless network |
| US20080267116A1 (en) | 2007-04-27 | 2008-10-30 | Yong Kang | Routing method and system for a wireless network |
| US7853829B2 (en) | 2007-07-13 | 2010-12-14 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Network advisor |
| US20090019314A1 (en) | 2007-07-13 | 2009-01-15 | Purenetworks, Inc. | Network advisor |
| US8547899B2 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2013-10-01 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling |
| US20090028095A1 (en) | 2007-07-28 | 2009-01-29 | Kish William S | Wireless Network Throughput Enhancement Through Channel Aware Scheduling |
| US20090067369A1 (en) | 2007-09-06 | 2009-03-12 | Anastasios Stamoulis | Routing in a mesh network |
| US20090073921A1 (en) | 2007-09-19 | 2009-03-19 | At&T Services Inc. | Data forwarding in hybrid mesh networks |
| US20090080333A1 (en) | 2007-09-20 | 2009-03-26 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and device for providing an alternative backhaul portal in a mesh network |
| US20090154359A1 (en) | 2007-12-12 | 2009-06-18 | Motorola, Inc. | Method for calculating service redundancy of a wireless network |
| US20110158233A1 (en) | 2007-12-20 | 2011-06-30 | Hwan-Sik NAMGUNG | Group communication system using media server having distributed structure and method thereof |
| US8780760B2 (en) | 2008-01-11 | 2014-07-15 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Determining associations in a mesh network |
| US20090180396A1 (en) | 2008-01-11 | 2009-07-16 | Kish William S | Determining associations in a mesh network |
| US20130194969A1 (en) | 2008-01-11 | 2013-08-01 | William S. Kish | Determining associations in a mesh network |
| US8355343B2 (en) | 2008-01-11 | 2013-01-15 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Determining associations in a mesh network |
| WO2009088488A1 (en) | 2008-01-11 | 2009-07-16 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Determining associations in a mesh network |
| US20090207730A1 (en) | 2008-02-14 | 2009-08-20 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Scheduling policy-based traffic management |
| US20090213730A1 (en) | 2008-02-21 | 2009-08-27 | Jianlin Zeng | Backhaul failover method and system for a wireless network |
| US20090225676A1 (en) | 2008-03-09 | 2009-09-10 | Fluke Corporation | Method and apparatus of duplicate packet detection and discard |
| US8089869B2 (en) | 2008-03-09 | 2012-01-03 | Fluke Corporation | Method and apparatus of duplicate packet detection and discard |
| US20090262677A1 (en) | 2008-04-18 | 2009-10-22 | Raja Banerjea | Multicast to unicast conversion system |
| WO2011060454A2 (en) | 2009-11-16 | 2011-05-19 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Establishing a mesh network with wired and wireless links |
| US20110119360A1 (en) | 2009-11-16 | 2011-05-19 | Kish William S | Establishing a Mesh Network with Wired and Wireless Links |
| EP2350863B1 (en) | 2009-11-16 | 2015-08-26 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Establishing a mesh network with wired and wireless links |
| CN102763378B (en) | 2009-11-16 | 2015-09-23 | 鲁库斯无线公司 | Set up and there is wired and mesh network that is wireless link |
| US20110119401A1 (en) | 2009-11-16 | 2011-05-19 | Kish William S | Determining Role Assignment in a Hybrid Mesh Network |
| WO2012061531A1 (en) | 2010-11-02 | 2012-05-10 | Ruckus Wireless, Inc. | Unicast to multicast conversion |
Non-Patent Citations (79)
| Title |
|---|
| Akyildiz et al., "Wireless mesh networks: a survey," Computer Networks, 2005. |
| Areg Alimian et al., "Analysis of Roaming Techniques," doc.:IEEE 802.11-04/0377r1, Submission, Mar. 2004. |
| Cato et al., "Method for Easier, Better, and Faster Site Surveys for Wireless Networks," IBM Technical Disclosure Bulletin, vol. 40, No. 1, 1997. |
| Chang, Nicholas B. et al., "Optimal Channel Probing and Transmission Scheduling for Opportunistics Spectrum Access," Sep. 2007. |
| Chawla, "Design of a Wireless Backhaul Network for Microcells," 1999. |
| Chinese Application No. 20058001629.7, Office Action dated Aug. 6, 2014. |
| Chinese Application No. 20058001629.7, Office Action dated Jan. 21, 2014. |
| Chinese Application No. 201080002467.X, Office Action dated Jul. 3, 2014. |
| Chinese Application No. 201080002467.X, Second Office Action dated Jan. 26, 2015. |
| Cisco Systems, "Cisco Aironet Access Point Software Configuration Guide: Configuring Filters and Quality of Service," Aug. 2003. |
| CN Application No. 20058001629.7, Office Action dated Feb. 21, 2012. |
| Dell Inc., "How Much Broadcast and Multicast Traffic Should I Allow in My Network," PowerConnect Application Note #5, Nov. 2003. |
| Dunkels, Adam et al., "Connecting Wireless Sensornets with TCP/IP Networks," Proc. of the 2d Int'l Conf. on Wired Networks, Frankfurt, Feb. 2004. |
| Dunkels, Adam et al., "Making TCP/IP Viable for Wireless Sensor Networks," Proc. of the 1st Euro. Workshop on Wireless Sensor Networks, Berlin, Jan. 2004. |
| Dutta, Ashutosh et al., "MarconiNet Supporting Streaming Media Over Localized Wireless Multicast," Proc. of the 2d Int'l Workshop on Mobile Commerce, 2002. |
| EP Application No. 10813061.8. Extended European Search Report dated Oct. 21, 2011. |
| EP Application No. 10813061.8. Supplementary European Search Report dated Jul. 23, 2012. |
| Fair queuing, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/fair-queuing. Aug. 11, 2008. |
| Festag, Andreas, "What is MOMBASA?" Telecommunication Networks Group (TKN), Technical University of Berlin, Mar. 7, 2002. |
| Gillham, Burce et al. JUNOSe Internet Software for E-Series Routing Platforms Policy and QoS Configuration Guide, Release 7.0x, Sep. 7, 2005. |
| Golmie, Nada, "Coexistence in Wireless Networks: Challenges and System-Level Solutions in the Unlicensed Bands," Cambridge University Press, 2006. |
| Hewlett Packard, "HP ProCurve Networking: Enterprise Wireless LAN Networking and Mobility Solutions," 2003. |
| Hirayama, Koji et al., "Next-Generation Mobile-Access IP Network," Hitachi Review vol. 49, No. 4, 2000. |
| Hjalmtysson et al., Overcoming Last-Hop/First-Hop Problems in IP Multicast, Reykjavik University, Dept. of Computer Science, Ofanleiti 2, 103 Reykjavik, Iceland, (The Icelandic Center for Research under grant No. 020500002.). Sep. 16-19, 2003. |
| Ian R. Akyildiz, et al., "A Virtual Topology Based Routing Protocol for Multihop Dynamic Wireless Networks," Broadband and Wireless Networking Lab, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Jul. 1, 2001. |
| Information Society Technologies Ultrawaves, "System Concept / Architecture Design and Communication Stack Requirement Document," Feb. 23, 2004. |
| Johansson et al., "Relaying Access Points and Related Business Models for Low Cost Mobile Systems," 2004. |
| Ken Tang, et al., "MAC Layer Broadcast Support in 802.11 Wireless Networks," Computer Science Department, University of California, Los Angeles, 2000 IEEE, pp. 544-548. |
| Ken Tang, et al., "MAC Reliable Broadcast in Ad Hoc Networks," Computer Science Department, University of California, Los Angeles, 2001 IEEE, pp. 1008-1013. |
| Mawa, Rakesh, "Power Control in 3G Systems," Hughes Systique Corporation, Jun. 28, 2006. |
| Microsoft Corporation, "IEEE 802.11 Networks and Windows XP," Windows Hardware Developer Central, Dec. 4, 2001. |
| Pat Calhoun et al., "802.11r strengthens wireless voice," Technology Update, Network World, Aug. 22, 2005, http://www.networkworld.com/news/tech/2005/082208techupdate.html. |
| PCT Search Report and Written Opinion for PCT/US05/039760 mailed Sep. 14, 2006. |
| PCT Search Report and Written Opinion for PCT/US08/014148 mailed Mar. 30, 2009. |
| PCT Search Report and Written Opinion for PCT/US10/56908 mailed May 3, 2011. |
| PCT Search Report and Written Opinion for PCT/US11/059019 mailed Feb. 21, 2012. |
| Steger, Christopher et al., "Performance of IEEE 802.11b Wireless LAN in an Emulated Mobile Channel," 2003. |
| Taiwan Application No. 103106913, Office Action dated May 28, 2015. |
| Toskala, Antti, "Enhancement of Broadcast and Introduction of Multicast Capabilities in RAN," Nokia Networks, Palm Springs, California, Mar. 13-16, 2001. |
| Tsunekawa, Kouichi "Diversity Antennas for Portable Telephones," 39th IEEE Vehicular Technology, May 1-3, 1989, San Francisco, CA. |
| TW Application No. 094138837, Office Action dated Apr. 25, 2013. |
| TW Application No. 094138837, Office Action dated Nov. 28, 2011. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 11/232,196, Final Office Action mailed Dec. 26, 2007. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 11/232,196, Office Action mailed Apr. 5, 2007. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 11/232,196, Office Action mailed May 15, 2008. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 11/267,477, Decision on Appeal mailed Nov. 14, 2014. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 11/267,477, Final Office Action mailed Jun. 10, 2009. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 11/267,477, Final Office Action mailed Oct. 6, 2010. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 11/267,477, Office Action mailed Jun. 16, 2010. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 11/267,477, Office Action mailed Sep. 25, 2008. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 11/985,865, Office Action mailed Dec. 20, 2010. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 11/985,866, Office Action mailed Dec. 16, 2009. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 11/985,866, Office Action mailed May 29, 2009. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 12/008,715, Final Office Action mailed Nov. 23, 2010. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 12/008,715, Office Action mailed Jun. 7, 2010. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 12/008,715, Office Action mailed Oct. 16, 2009. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 12/008,715, Office Action mailed Sep. 2, 2011. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 12/181,274, Final Office Action mailed Jan. 18, 2012. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 12/181,274, Final Office Action mailed Jun. 19, 2013. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 12/181,274, Office Action mailed Jun. 10, 2011. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 12/181,274, Office Action mailed Nov. 15, 2012. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 12/938,316, Office Action mailed Nov. 20, 2012. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 12/947,800, Final Office Action mailed Jul. 17, 2013. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 12/947,800, Office Action mailed Sep. 26, 2012. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 12/947,803, Final Office Action mailed Jul. 17, 2013. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 12/947,803, Office Action mailed Aug. 27, 2012. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 13/736,017 Office Action mailed Nov. 21, 2013. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 14/080,488, Office Action mailed Oct. 21, 2014. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 14/080,488, William S.Kish, Mac Based Mapping in IP Based Communications, Nov. 14, 2013. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 14/106,514, Office Action mailed Sep. 22, 2014. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 14/106,514, William S.Kish, Unicast to Multicast Conversion, Dec. 13, 2013. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 14/160,402 Office Action mailed Oct. 22, 2014. |
| U.S. Appl. No. 14/748,141, William S. Kish, Distributed Access Point for IP Based Communications, Jun. 23, 2015. |
| Vincent D. Park, et al., "A Performance Comparison of the Temporally-Ordered Routing Algorithm and Ideal Link-State Routing," IEEE, Jul. 1998, pp. 592-598. |
| Visoottiviseth et al., Sender-Initiated Mulitcast Forwarding Scheme, Telecommunications, 2003, ICT 2003 10th International Conference, pp. 334-339, downloaded on Mar. 26, 2009 from IEEE Xplore, 0-7803-7661 (c) 2003 IEEE. |
| Weighted Fair Queuing, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Weighted-fair-queuing. Aug. 11, 2008. |
| Weighted Round Robin, http:en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Weighted-round-robin Aug. 8, 2008. |
| Wennstrom, Mattias et al., "Transmit Antenna Diversity in Ricean Fading MIMO Channels with Co-Channel Interference," 2001. |
| Yanikomeroglu, "Cellular Multihop Communications: Infrastructure-Based Relay Network Architecture for 4G Wireless Systems," 2004. |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10250722B2 (en) | 2015-12-18 | 2019-04-02 | Sonicwall Inc. | TCP traffic priority bandwidth management control based on TCP window adjustment |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US9674862B2 (en) | 2017-06-06 |
| US20090028095A1 (en) | 2009-01-29 |
| US20160249376A1 (en) | 2016-08-25 |
| US8547899B2 (en) | 2013-10-01 |
| US20140016563A1 (en) | 2014-01-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9674862B2 (en) | Wireless network throughput enhancement through channel aware scheduling | |
| US7734805B2 (en) | Method for scheduling transmissions in communication systems | |
| US7274676B2 (en) | Burst-mode weighted sender scheduling for ad-hoc wireless medium access control protocols | |
| JP4624816B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for dynamically allocating resources in a wireless network | |
| US7283814B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for scheduling transmissions in wireless data networks | |
| US7697561B2 (en) | Communication apparatus, communication method, and communication system | |
| US7349338B2 (en) | Scheduler and method for scheduling transmissions in a communication network | |
| US7633863B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for scheduling data in a communication system | |
| US9525519B2 (en) | Method and system of transferring data in a carrier aggregation environment | |
| CN101346971B (en) | Method and device for solving data grouping service congestion | |
| US7668201B2 (en) | Bandwidth management in wireless networks | |
| US7724750B2 (en) | Expedited data transmission in packet based network | |
| US7032153B1 (en) | Dynamic automatic retransmission request in wireless access networks | |
| EP1443719A1 (en) | Packet transmission scheduling method and base station device | |
| JP2008502238A (en) | Shared physical channel mapping according to quality of service class | |
| US20060291395A1 (en) | Packet transmission control method and apparatus | |
| US20100218065A1 (en) | Method and apparatus of HARQ process selection | |
| US6728257B1 (en) | Fluid flow fair scheduling emulation in wireless shared channel packet communication network | |
| JP4907545B2 (en) | Provisions for fair transmission of communication time without using clear traffic specifications for wireless networks | |
| Mukhtar et al. | Efficient Internet traffic delivery over wireless networks | |
| Gomez et al. | Havana: Supporting application and channel dependent QoS in wireless packet networks | |
| Morawski et al. | A Game-Based Scheduler for Reducing Protocol Delay in Multipath Communication | |
| Fukui et al. | Packet transfer scheduling scheme with throughput compensated considering wireless conditions | |
| Feller et al. | Comparison of opportunistic scheduling algorithms for HSDPA networks | |
| Chen | Dynamic Flow-Based Scheduling for Low-Latency Elephant VR Flows in Home WiFi Networks |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:RUCKUS WIRELESS, INC., CALIFORNIA Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:KISH, WILLIAM S.;REEL/FRAME:034254/0077 Effective date:20080825 | |
| ZAAA | Notice of allowance and fees due | Free format text:ORIGINAL CODE: NOA | |
| ZAAB | Notice of allowance mailed | Free format text:ORIGINAL CODE: MN/=. | |
| STCF | Information on status: patent grant | Free format text:PATENTED CASE | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:BANK OF AMERICA, N.A., AS ADMINISTRATIVE AGENT, NORTH CAROLINA Free format text:GRANT OF SECURITY INTEREST IN PATENT RIGHTS;ASSIGNOR:RUCKUS WIRELESS, INC.;REEL/FRAME:046379/0431 Effective date:20180330 Owner name:BANK OF AMERICA, N.A., AS ADMINISTRATIVE AGENT, NO Free format text:GRANT OF SECURITY INTEREST IN PATENT RIGHTS;ASSIGNOR:RUCKUS WIRELESS, INC.;REEL/FRAME:046379/0431 Effective date:20180330 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC, PENNSYLVANIA Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:RUCKUS WIRELESS, INC.;REEL/FRAME:046730/0854 Effective date:20180401 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:RUCKUS WIRELESS, INC., CALIFORNIA Free format text:TERMINATION AND RELEASE OF SECURITY INTEREST IN PATENTS;ASSIGNOR:BANK OF AMERICA, N.A., AS ADMINISTRATIVE AGENT;REEL/FRAME:048817/0832 Effective date:20190404 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:WILMINGTON TRUST, NATIONAL ASSOCIATION, AS COLLATE Free format text:PATENT SECURITY AGREEMENT;ASSIGNOR:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC;REEL/FRAME:049820/0495 Effective date:20190404 Owner name:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK, N.A., NEW YORK Free format text:TERM LOAN SECURITY AGREEMENT;ASSIGNORS:COMMSCOPE, INC. OF NORTH CAROLINA;COMMSCOPE TECHNOLOGIES LLC;ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC;AND OTHERS;REEL/FRAME:049905/0504 Effective date:20190404 Owner name:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK, N.A., NEW YORK Free format text:ABL SECURITY AGREEMENT;ASSIGNORS:COMMSCOPE, INC. OF NORTH CAROLINA;COMMSCOPE TECHNOLOGIES LLC;ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC;AND OTHERS;REEL/FRAME:049892/0396 Effective date:20190404 Owner name:WILMINGTON TRUST, NATIONAL ASSOCIATION, AS COLLATERAL AGENT, CONNECTICUT Free format text:PATENT SECURITY AGREEMENT;ASSIGNOR:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC;REEL/FRAME:049820/0495 Effective date:20190404 | |
| MAFP | Maintenance fee payment | Free format text:PAYMENT OF MAINTENANCE FEE, 4TH YEAR, LARGE ENTITY (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: M1551); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: LARGE ENTITY Year of fee payment:4 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:WILMINGTON TRUST, DELAWARE Free format text:SECURITY INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:ARRIS SOLUTIONS, INC.;ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC;COMMSCOPE TECHNOLOGIES LLC;AND OTHERS;REEL/FRAME:060752/0001 Effective date:20211115 | |
| FEPP | Fee payment procedure | Free format text:MAINTENANCE FEE REMINDER MAILED (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: REM.); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: LARGE ENTITY | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:RUCKUS IP HOLDINGS LLC, NORTH CAROLINA Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC;REEL/FRAME:066399/0561 Effective date:20240103 | |
| LAPS | Lapse for failure to pay maintenance fees | Free format text:PATENT EXPIRED FOR FAILURE TO PAY MAINTENANCE FEES (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: EXP.); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: LARGE ENTITY | |
| STCH | Information on status: patent discontinuation | Free format text:PATENT EXPIRED DUE TO NONPAYMENT OF MAINTENANCE FEES UNDER 37 CFR 1.362 | |
| FP | Lapsed due to failure to pay maintenance fee | Effective date:20240223 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:RUCKUS WIRELESS, LLC (F/K/A RUCKUS WIRELESS, INC.), NORTH CAROLINA Free format text:RELEASE OF SECURITY INTEREST AT REEL/FRAME 049905/0504;ASSIGNOR:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK, N.A., AS COLLATERAL AGENT;REEL/FRAME:071477/0255 Effective date:20241217 Owner name:COMMSCOPE TECHNOLOGIES LLC, NORTH CAROLINA Free format text:RELEASE OF SECURITY INTEREST AT REEL/FRAME 049905/0504;ASSIGNOR:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK, N.A., AS COLLATERAL AGENT;REEL/FRAME:071477/0255 Effective date:20241217 Owner name:COMMSCOPE, INC. OF NORTH CAROLINA, NORTH CAROLINA Free format text:RELEASE OF SECURITY INTEREST AT REEL/FRAME 049905/0504;ASSIGNOR:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK, N.A., AS COLLATERAL AGENT;REEL/FRAME:071477/0255 Effective date:20241217 Owner name:ARRIS SOLUTIONS, INC., NORTH CAROLINA Free format text:RELEASE OF SECURITY INTEREST AT REEL/FRAME 049905/0504;ASSIGNOR:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK, N.A., AS COLLATERAL AGENT;REEL/FRAME:071477/0255 Effective date:20241217 Owner name:ARRIS TECHNOLOGY, INC., NORTH CAROLINA Free format text:RELEASE OF SECURITY INTEREST AT REEL/FRAME 049905/0504;ASSIGNOR:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK, N.A., AS COLLATERAL AGENT;REEL/FRAME:071477/0255 Effective date:20241217 Owner name:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC (F/K/A ARRIS ENTERPRISES, INC.), NORTH CAROLINA Free format text:RELEASE OF SECURITY INTEREST AT REEL/FRAME 049905/0504;ASSIGNOR:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK, N.A., AS COLLATERAL AGENT;REEL/FRAME:071477/0255 Effective date:20241217 |